Royal Yugoslavia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Srba, Hrvata i Slovenaca, Краљевина Срба, Хрвата и Словенаца; sl, Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev), but the term " Yugoslavia" (literally "Land of South Slavs") was its colloquial name due to its origins."Kraljevina Jugoslavija! Novi naziv naše države. No, mi smo itak med seboj vedno dejali Jugoslavija, četudi je bilo na vseh uradnih listih Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev. In tudi drugi narodi, kakor Nemci in Francozi, so pisali že prej v svojih listih mnogo o Jugoslaviji. 3. oktobra, ko je kralj Aleksander podpisal "Zakon o nazivu in razdelitvi kraljevine na upravna območja", pa je bil naslov kraljevine Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev za vedno izbrisan." (Naš rod ("Our Generation", a monthly Slovene language periodical), Ljubljana 1929/30, št. 1, str. 22, letnik I.) The official name of the state was changed to "Kingdom of Yugoslavia" by King Alexander I on 3 October 1929.
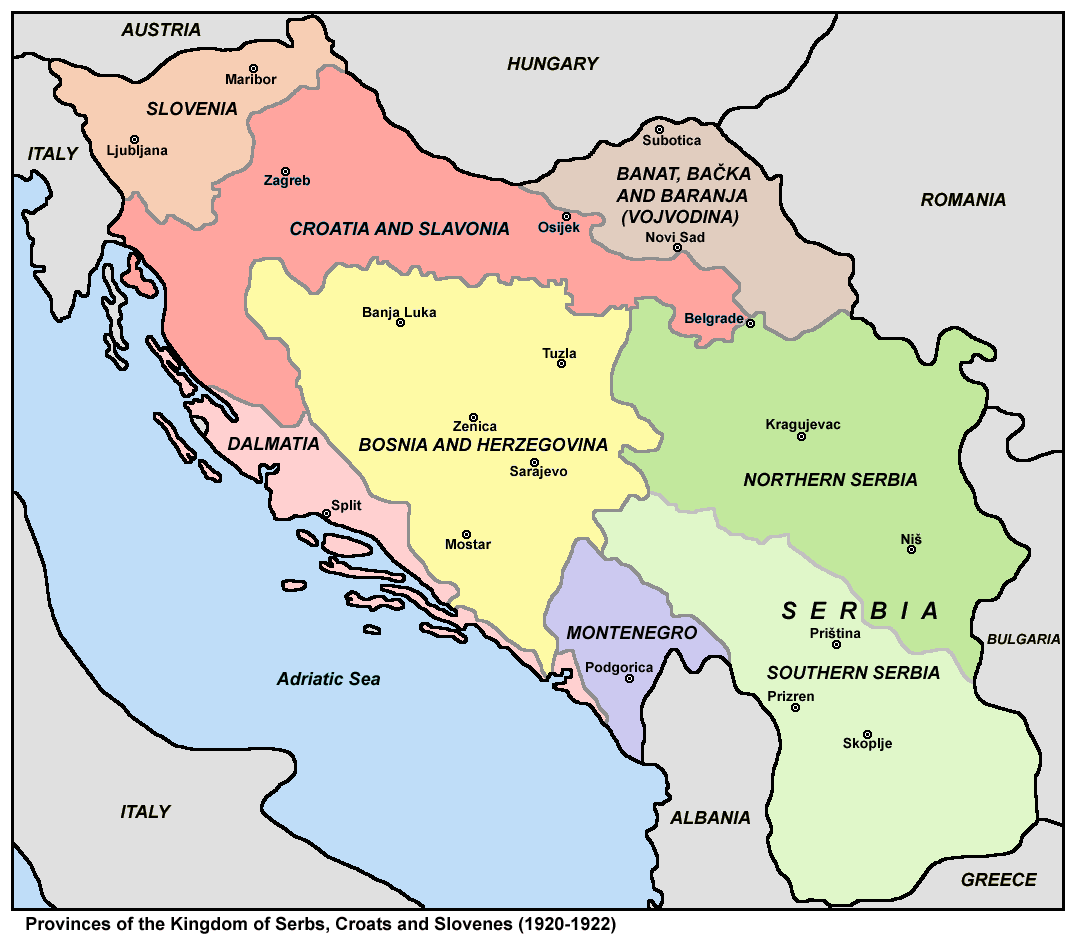
The preliminary kingdom was formed in 1918 by the merger of the provisional State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs (itself formed from territories of the former Austria-Hungary, encompassing today's Bosnia and Herzegovina and most of today's Croatia and Slovenia) and Banat, Bačka and Baranja (that had been part of the Kingdom of Hungary within Austria-Hungary) with the formerly independent
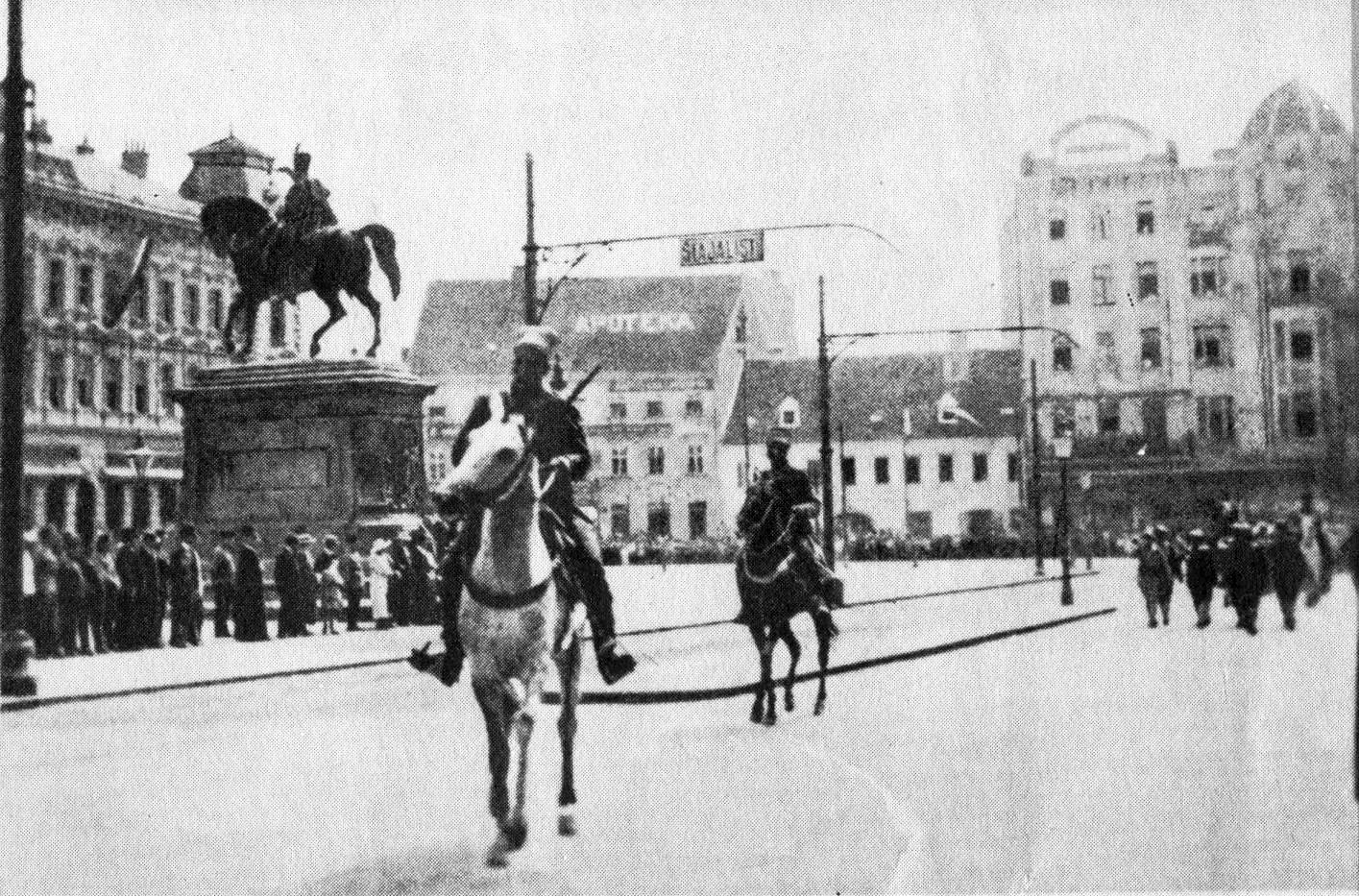


 Following the
Following the
from Corfu city hall Quote: "The Municipal Theatre was not only an Art-monument but also a historical one. On its premises the exiled Serbian parliament, held meetings in 1916, which decided the creation of the new Unified Kingdom of Yugoslavia." In November 1918, the National Council of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs appointed 28 members to start negotiation with the representatives of the government of the Kingdom of Serbia and Montenegro on creation of a new Yugoslav state, the delegation negotiated directly with regent Alexander Karađorđević. The negotiations would end, with the delegation of the National Council of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs led by Ante Pavelić reading the address in front of regent Alexander, who represented his father, King Peter I of Serbia, by which acceptance the kingdom was established. The name of the new Yugoslav state was Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Srba, Hrvata i Slovenaca, Краљевина Срба, Хрвата и Словенаца; sl, Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev) or its abbreviated form Kingdom of SCS ( / ). The new kingdom was made up of the formerly independent kingdoms of Serbia and Montenegro ( Montenegro having been absorbed into Serbia the previous month), and of a substantial amount of territory that was formerly part of Austria-Hungary, the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs. The main states which formed the new Kingdom were the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs; Vojvodina; and the Kingdom of Serbia with the Kingdom of Montenegro. The creation of the state was supported by
A Low Dishonest Decade: Italy, the Powers and Eastern Europe, 1918–1939.
, Chapter 2, ''Mussolini, Prisoner of the Mediterranean'' mostly Slovenes, were subjected to forced The Yugoslav kingdom bordered Italy and Austria to the northwest at the Rapallo border, Hungary and Romania to the north, Bulgaria to the east, Greece and Albania to the south, and the Adriatic Sea to the west. Almost immediately, it ran into disputes with most of its neighbours. Slovenia was difficult to determine, since it had been an integral part of Austria for 400 years. The Vojvodina region was disputed with Hungary,
The Yugoslav kingdom bordered Italy and Austria to the northwest at the Rapallo border, Hungary and Romania to the north, Bulgaria to the east, Greece and Albania to the south, and the Adriatic Sea to the west. Almost immediately, it ran into disputes with most of its neighbours. Slovenia was difficult to determine, since it had been an integral part of Austria for 400 years. The Vojvodina region was disputed with Hungary,
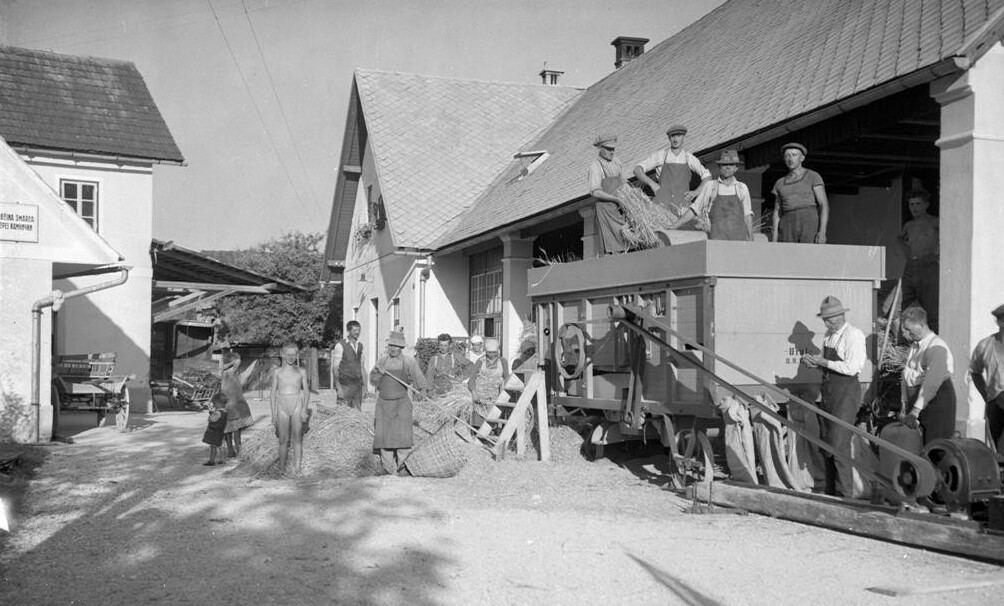 Three-quarters of the Yugoslav workforce was engaged in agriculture. A few commercial farmers existed, but most were subsistence peasants. Those in the south were especially poor, living in a hilly, infertile region. No large estates existed except in the north, and all of those were owned by foreigners. Indeed, one of the first actions undertaken by the new Yugoslav state in 1919 was to break up the estates and dispose of foreign, and in particular Hungarian landowners. Nearly 40% of the rural population was surplus (i.e., excess people not needed to maintain current production levels), and despite a warm climate, Yugoslavia was also relatively dry. Internal communications were poor, damage from World War I had been extensive, and with few exceptions agriculture was devoid of machinery or other modern farming technologies.
Three-quarters of the Yugoslav workforce was engaged in agriculture. A few commercial farmers existed, but most were subsistence peasants. Those in the south were especially poor, living in a hilly, infertile region. No large estates existed except in the north, and all of those were owned by foreigners. Indeed, one of the first actions undertaken by the new Yugoslav state in 1919 was to break up the estates and dispose of foreign, and in particular Hungarian landowners. Nearly 40% of the rural population was surplus (i.e., excess people not needed to maintain current production levels), and despite a warm climate, Yugoslavia was also relatively dry. Internal communications were poor, damage from World War I had been extensive, and with few exceptions agriculture was devoid of machinery or other modern farming technologies.
 Yugoslavia was typical of Eastern European nations in that it borrowed large sums of money from the West during the 1920s. When the
Yugoslavia was typical of Eastern European nations in that it borrowed large sums of money from the West during the 1920s. When the
 Immediately after 1 December proclamation, negotiations between the
Immediately after 1 December proclamation, negotiations between the
 One of the few laws successfully passed by the Provisional Representation was the electoral law for the constituent assembly. During the negotiations that preceded the foundation of the new state, it had been agreed that voting would be secret and based on universal suffrage. It had not occurred to them that universal might include women until the beginning of a movement for women's suffrage appeared with the creation of the new state. The Social Democrats and the Slovenian People's Party supported women's suffrage but the Radicals opposed it. The Democratic Party was open to the idea but not committed enough to make an issue of it so the proposal fell. Proportional Representation was accepted in principle but the system chosen ( d'Hondt with very small constituencies) favored large parties and parties with strong regional support.
The election was held on 28 November 1920. When the votes were counted the Democratic Party had won the most seats, more than the Radicals – but only just. For a party that had been so dominant in the Provisional Representation, that amounted to a defeat. Further it had done rather badly in all former Austria-Hungarian areas. That undercut the party's belief that its centralization policy represented the will of the Yugoslavian people as a whole. The Radicals had done no better in that region but this presented them far less of a problem because they had campaigned openly as a Serbian party. The most dramatic gains had been made by the two anti-system parties. The Croatian Republican Peasant Party's leadership had been released from prison only as the election campaign began to get underway. According to Gligorijević, this had helped them more than active campaigning. The Croatian community (that had in a timid way tried to express the discontent that Croatian Republican Peasant Party mobilized) had been too tainted by their participation in government and was all but eliminated. The other gainers were the communists who had done especially well in the wider
One of the few laws successfully passed by the Provisional Representation was the electoral law for the constituent assembly. During the negotiations that preceded the foundation of the new state, it had been agreed that voting would be secret and based on universal suffrage. It had not occurred to them that universal might include women until the beginning of a movement for women's suffrage appeared with the creation of the new state. The Social Democrats and the Slovenian People's Party supported women's suffrage but the Radicals opposed it. The Democratic Party was open to the idea but not committed enough to make an issue of it so the proposal fell. Proportional Representation was accepted in principle but the system chosen ( d'Hondt with very small constituencies) favored large parties and parties with strong regional support.
The election was held on 28 November 1920. When the votes were counted the Democratic Party had won the most seats, more than the Radicals – but only just. For a party that had been so dominant in the Provisional Representation, that amounted to a defeat. Further it had done rather badly in all former Austria-Hungarian areas. That undercut the party's belief that its centralization policy represented the will of the Yugoslavian people as a whole. The Radicals had done no better in that region but this presented them far less of a problem because they had campaigned openly as a Serbian party. The most dramatic gains had been made by the two anti-system parties. The Croatian Republican Peasant Party's leadership had been released from prison only as the election campaign began to get underway. According to Gligorijević, this had helped them more than active campaigning. The Croatian community (that had in a timid way tried to express the discontent that Croatian Republican Peasant Party mobilized) had been too tainted by their participation in government and was all but eliminated. The other gainers were the communists who had done especially well in the wider  On 28 June 1921, the Vidovdan Constitution was passed, establishing a
On 28 June 1921, the Vidovdan Constitution was passed, establishing a
 On 6 January 1929, using as a pretext the political crisis triggered by the shooting, King Alexander abolished the Constitution, prorogued the Parliament and introduced a personal dictatorship (known as the "January 6 Dictatorship", ''Šestosiječanjska diktatura'', ''Šestojanuarska diktatura'') with the aim of establishing the Yugoslav ideology and single Yugoslav nation. He changed the name of the country to "Kingdom of Yugoslavia", and changed the internal divisions from the 33 oblasts to nine new '' banovinas'' on 3 October. This decision was made following a proposal by the British ambassador to better decentralize the country, modeled on Czechoslovakia. A Court for the Protection of the State was soon established to act as the new regime's tool for putting down any dissent. Opposition politicians
On 6 January 1929, using as a pretext the political crisis triggered by the shooting, King Alexander abolished the Constitution, prorogued the Parliament and introduced a personal dictatorship (known as the "January 6 Dictatorship", ''Šestosiječanjska diktatura'', ''Šestojanuarska diktatura'') with the aim of establishing the Yugoslav ideology and single Yugoslav nation. He changed the name of the country to "Kingdom of Yugoslavia", and changed the internal divisions from the 33 oblasts to nine new '' banovinas'' on 3 October. This decision was made following a proposal by the British ambassador to better decentralize the country, modeled on Czechoslovakia. A Court for the Protection of the State was soon established to act as the new regime's tool for putting down any dissent. Opposition politicians
Einstein accuses Yugoslavian rulers in savant's murder
'', New York Times. 6 May 1931
mirror
In their letter Einstein and Mann held the Yugoslav king Aleksandar explicitly responsible for these circumstances.mirror
Croat opposition to the new régime was strong and, in late 1932, the Croatian Peasant Party issued the ''Zagreb Manifesto'' which sought an end to Serb hegemony and dictatorship. The government reacted by imprisoning many political opponents including the new Croatian Peasant Party leader Vladko Maček. Despite these measures, opposition to the dictatorship continued, with Croats calling for a solution to what was called the "Croatian question". In late 1934, the King planned to release Maček from prison, introduce democratic reforms, and attempt find common ground between Serbs and Croats. However, on 9 October 1934, the king was assassinated in Marseille, France, by Bulgarian Veličko Kerin (also known by his revolutionary pseudonym Vlado Chernozemski), an activist of IMRO, in a conspiracy with Yugoslav exiles and radical members of banned political parties in cooperation with the Croatian extreme nationalist Ustaše organisation.
 Officially, the last words of King Aleksandar had been "Save Yugoslavia, and the friendship with France". His successors were well aware of the need to try and do the first, but the second, maintaining close ties with France, was increasingly difficult. There were several reasons for this. By the mid-1930s, France, internally divided, was increasingly unable to play an important role in Eastern Europe and support its allies, many of whom had suffered badly from the economic crisis of that period. By contrast, Germany was increasingly willing to get into barter agreements with the countries of south east Europe. In the process those countries felt it was against their interests to closely follow France. An additional motive to improve relations with Italy and Germany was Italy's support of the Ustase movement. As Maček intimated Italy would support Croatian secession from Yugoslavia, First Regent Prince Paul judged closer relations with Italy were inevitable. In an effort to rob the HSS from potential Italian support, a treaty of friendship was signed between the two countries in 1937. This diminished the Ustasa threat somewhat since Mussolini imprisoned some of their leaders and temporarily withdrew financial support. In 1938, Germany, annexing Austria, became a neighbour of Yugoslavia. The feeble reaction of France and Britain, later that year, during the Sudeten Crisis convinced Belgrade that a European war was inevitable and that it would be unwise to support France and Britain. Instead, Yugoslavia tried to stay aloof, this in spite of Paul's personal sympathies for Britain and Serbia's establishment's predilections for France. In the meantime, Germany and Italy tried to exploit Yugoslavia's domestic problems, and so did Maček. In the end, the regency agreed to the formation of the
Officially, the last words of King Aleksandar had been "Save Yugoslavia, and the friendship with France". His successors were well aware of the need to try and do the first, but the second, maintaining close ties with France, was increasingly difficult. There were several reasons for this. By the mid-1930s, France, internally divided, was increasingly unable to play an important role in Eastern Europe and support its allies, many of whom had suffered badly from the economic crisis of that period. By contrast, Germany was increasingly willing to get into barter agreements with the countries of south east Europe. In the process those countries felt it was against their interests to closely follow France. An additional motive to improve relations with Italy and Germany was Italy's support of the Ustase movement. As Maček intimated Italy would support Croatian secession from Yugoslavia, First Regent Prince Paul judged closer relations with Italy were inevitable. In an effort to rob the HSS from potential Italian support, a treaty of friendship was signed between the two countries in 1937. This diminished the Ustasa threat somewhat since Mussolini imprisoned some of their leaders and temporarily withdrew financial support. In 1938, Germany, annexing Austria, became a neighbour of Yugoslavia. The feeble reaction of France and Britain, later that year, during the Sudeten Crisis convinced Belgrade that a European war was inevitable and that it would be unwise to support France and Britain. Instead, Yugoslavia tried to stay aloof, this in spite of Paul's personal sympathies for Britain and Serbia's establishment's predilections for France. In the meantime, Germany and Italy tried to exploit Yugoslavia's domestic problems, and so did Maček. In the end, the regency agreed to the formation of the
 The small middle class occupied the major population centers and almost everyone else were peasants engaged in subsistence agriculture. The largest ethnic group were Serbs followed by Croats and Slovenes, as three constitutive peoples of the Kingdom, while Montenegrins, Bosnian Muslims and Macedonians were not recognized as distinctive ethnic groups; further historical minority groups included Germans, Italians, Hungarians,
The small middle class occupied the major population centers and almost everyone else were peasants engaged in subsistence agriculture. The largest ethnic group were Serbs followed by Croats and Slovenes, as three constitutive peoples of the Kingdom, while Montenegrins, Bosnian Muslims and Macedonians were not recognized as distinctive ethnic groups; further historical minority groups included Germans, Italians, Hungarians,
Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Princi ...
. In the same year, the Kingdom of Montenegro also proclaimed its unification with Serbia, whereas the regions of Kosovo and Vardar Macedonia had become parts of Serbia prior to the unification.
The state was ruled by the Serbian dynasty of Karađorđević, which previously ruled the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Princi ...
under Peter I from 1903 (after the May Coup) onward. Peter I became the first king of Yugoslavia until his death in 1921. He was succeeded by his son Alexander I, who had been regent for his father. He was known as "Alexander the Unifier" and he renamed the kingdom "Yugoslavia" in 1929. He was assassinated in Marseille by Vlado Chernozemski, a member of the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO), during his visit to France in 1934. The crown passed to his 11-year-old son Peter. Alexander's cousin Paul ruled as Prince regent until 1941, when Peter II came of age. The royal family flew to London the same year, prior to the country being invaded
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing con ...
by the Axis powers.
In April 1941, the country was occupied and partitioned by the Axis powers. A royal government-in-exile, recognized by the United Kingdom and, later, by all the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
, was established in London. In 1944, after pressure from the British Prime Minister Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
, the King recognized the government of Democratic Federal Yugoslavia as the legitimate government. This was established on 2 November following the signing of the Treaty of Vis
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal perso ...
by Ivan Šubašić (on behalf of the Kingdom) and Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito (; sh-Cyrl, Тито, links=no, ), was a Yugoslav communist revolutionary and statesman, serving in various positions from 1943 until his deat ...
(on behalf of the Yugoslav Partisans).
Formation


 Following the
Following the assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
of Austrian
Austrian may refer to:
* Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent
** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law
* Austrian German dialect
* Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ...
Archduke
Archduke (feminine: Archduchess; German: ''Erzherzog'', feminine form: ''Erzherzogin'') was the title borne from 1358 by the Habsburg rulers of the Archduchy of Austria, and later by all senior members of that dynasty. It denotes a rank within ...
Francis Ferdinand
Archduke Franz Ferdinand Carl Ludwig Joseph Maria of Austria, (18 December 1863 – 28 June 1914) was the heir presumptive to the throne of Austria-Hungary. His assassination in Sarajevo was the most immediate cause of World War I.
F ...
by the Bosnian Serb Gavrilo Princip and the outbreak of World War I, Serbia was invaded and occupied by a combined Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
, Austrian and German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
force on 6 October 1915. This saw the escalation of South Slavic nationalism and calls by Slavic nationalists for the independence and unification of the South Slavic nationalities of Austria-Hungary along with Serbia and Montenegro into a single State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs.
The Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
n Croat politician Ante Trumbić became a prominent South Slavic leader during the war and led the Yugoslav Committee that lobbied the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
to support the creation of an independent Yugoslavia.Spencer Tucker. ''Encyclopedia of World War I: A Political, Social, and Military History''. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO, 2005. p. 1189. Trumbić faced initial hostility from Serbian Prime Minister Nikola Pašić, who preferred an enlarged Serbia over a unified Yugoslav state. However, both Pašić and Trumbić agreed to a compromise, which was delivered at the Corfu Declaration on 20 July 1917 that advocated the creation of a united state of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes to be led by the Serbian House of Karađorđević.
In 1916, the Yugoslav Committee started negotiations with the Serbian Government
The Government of Serbia ( sr, Влада Србије, Vlada Srbije), formally the Government of the Republic of Serbia ( sr, Влада Републике Србије, Vlada Republike Srbije), commonly abbreviated to Serbian Government ( sr, � ...
in exile
Exile is primarily penal expulsion from one's native country, and secondarily expatriation or prolonged absence from one's homeland under either the compulsion of circumstance or the rigors of some high purpose. Usually persons and peoples suf ...
, on which they decided on the creation of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, declaring the joint Corfu Declaration in 1917, the meetings were held at the Municipal Theatre of Corfu
The Municipal Theatre of Corfu ( el, Δημοτικό Θέατρο Κέρκυρας) was the main theatre and opera house in Corfu
Corfu (, ) or Kerkyra ( el, Κέρκυρα, Kérkyra, , ; ; la, Corcyra.) is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea, ...
.History of the municipal theatrefrom Corfu city hall Quote: "The Municipal Theatre was not only an Art-monument but also a historical one. On its premises the exiled Serbian parliament, held meetings in 1916, which decided the creation of the new Unified Kingdom of Yugoslavia." In November 1918, the National Council of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs appointed 28 members to start negotiation with the representatives of the government of the Kingdom of Serbia and Montenegro on creation of a new Yugoslav state, the delegation negotiated directly with regent Alexander Karađorđević. The negotiations would end, with the delegation of the National Council of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs led by Ante Pavelić reading the address in front of regent Alexander, who represented his father, King Peter I of Serbia, by which acceptance the kingdom was established. The name of the new Yugoslav state was Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Srba, Hrvata i Slovenaca, Краљевина Срба, Хрвата и Словенаца; sl, Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev) or its abbreviated form Kingdom of SCS ( / ). The new kingdom was made up of the formerly independent kingdoms of Serbia and Montenegro ( Montenegro having been absorbed into Serbia the previous month), and of a substantial amount of territory that was formerly part of Austria-Hungary, the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs. The main states which formed the new Kingdom were the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs; Vojvodina; and the Kingdom of Serbia with the Kingdom of Montenegro. The creation of the state was supported by
pan-Slavists
Pan-Slavism, a movement which crystallized in the mid-19th century, is the political ideology concerned with the advancement of integrity and unity for the Slavic people. Its main impact occurred in the Balkans, where non-Slavic empires had ruled ...
and Yugoslav nationalists. For the pan-Slavic movement, all of the South Slav (Yugoslav) people had united into a single state. The creation was also supported by the Allies, who sought to break up the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
The newly established Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes participated in the Paris Peace Conference with Trumbić as the country's representative. Since the Allies had lured the Italians into the war with a promise of substantial territorial gains in exchange, which cut off a quarter of Slovene ethnic territory from the remaining three-quarters of Slovenes living in the Kingdom of SCS, Trumbić successfully vouched for the inclusion of most Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
living in the former Austria-Hungary to be included within the borders of the new Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. Nevertheless, with the Treaty of Rapallo Following World War I there were two Treaties of Rapallo, both named after Rapallo, a resort on the Ligurian coast of Italy:
* Treaty of Rapallo, 1920, an agreement between Italy and the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (the later Yugoslav ...
a population of half a million South Slavs,Hehn, Paul N. (2005A Low Dishonest Decade: Italy, the Powers and Eastern Europe, 1918–1939.
, Chapter 2, ''Mussolini, Prisoner of the Mediterranean'' mostly Slovenes, were subjected to forced
Italianization
Italianization ( it, italianizzazione; hr, talijanizacija; french: italianisation; sl, poitaljančevanje; german: Italianisierung; el, Ιταλοποίηση) is the spread of Italian culture, language and identity by way of integration or a ...
until the fall of Fascism in Italy. At the time when Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
was willing to modify the Rapallo borders in order to annex the independent state of Rijeka
Rijeka ( , , ; also known as Fiume hu, Fiume, it, Fiume ; local Chakavian: ''Reka''; german: Sankt Veit am Flaum; sl, Reka) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia (after Zagreb and Split). It is located in Primor ...
to Italy, Pašić's attempts to correct the borders at Postojna
Postojna (; german: Adelsberg, it, Postumia) is a town in the traditional region of Inner Carniola, from Trieste, in southwestern Slovenia. It is the seat of the Municipality of Postojna.
and Idrija were effectively undermined by the regent Alexander who preferred "good relations
Relation or relations may refer to:
General uses
*International relations, the study of interconnection of politics, economics, and law on a global level
*Interpersonal relationship, association or acquaintance between two or more people
*Public ...
" with Italy.
 The Yugoslav kingdom bordered Italy and Austria to the northwest at the Rapallo border, Hungary and Romania to the north, Bulgaria to the east, Greece and Albania to the south, and the Adriatic Sea to the west. Almost immediately, it ran into disputes with most of its neighbours. Slovenia was difficult to determine, since it had been an integral part of Austria for 400 years. The Vojvodina region was disputed with Hungary,
The Yugoslav kingdom bordered Italy and Austria to the northwest at the Rapallo border, Hungary and Romania to the north, Bulgaria to the east, Greece and Albania to the south, and the Adriatic Sea to the west. Almost immediately, it ran into disputes with most of its neighbours. Slovenia was difficult to determine, since it had been an integral part of Austria for 400 years. The Vojvodina region was disputed with Hungary, Macedonia
Macedonia most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a traditional geographic reg ...
with Bulgaria, Rijeka with Italy.
A plebiscite was also held in the Province of Carinthia, which opted to remain in Austria. Austrians had formed a majority in this region although numbers reflected that some Slovenes did vote for Carinthia to become part of Austria. The Dalmatian port city of Zadar and a few of the Dalmatian islands were given to Italy. The city of Rijeka was declared to be the Free State of Fiume
The Free State of Fiume () was an independent free state that existed between 1920 and 1924. Its territory of comprised the city of Fiume (today Rijeka, Croatia) and rural areas to its north, with a corridor to its west connecting it to the K ...
, but it was soon occupied, and in 1924 annexed
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
, by Italy, which had also been promised the Dalmatian coast during World War I, and Yugoslavia claiming Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; ist, Eîstria; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the larges ...
, a part of the former Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (german: Österreichisches Küstenland, it, Litorale Austriaco, hr, Austrijsko primorje, sl, Avstrijsko primorje, hu, Osztrák Tengermellék) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. ...
which had been annexed to Italy, but which contained a considerable population of Croats and Slovenes.
The formation of the Vidovdan Constitution in 1921 sparked tensions between the different Yugoslav nationalities. Trumbić opposed the 1921 constitution and over time grew increasingly hostile towards the Yugoslav government that he saw as being centralized in the favor of Serb hegemony over Yugoslavia.
Economy
Farming
 Three-quarters of the Yugoslav workforce was engaged in agriculture. A few commercial farmers existed, but most were subsistence peasants. Those in the south were especially poor, living in a hilly, infertile region. No large estates existed except in the north, and all of those were owned by foreigners. Indeed, one of the first actions undertaken by the new Yugoslav state in 1919 was to break up the estates and dispose of foreign, and in particular Hungarian landowners. Nearly 40% of the rural population was surplus (i.e., excess people not needed to maintain current production levels), and despite a warm climate, Yugoslavia was also relatively dry. Internal communications were poor, damage from World War I had been extensive, and with few exceptions agriculture was devoid of machinery or other modern farming technologies.
Three-quarters of the Yugoslav workforce was engaged in agriculture. A few commercial farmers existed, but most were subsistence peasants. Those in the south were especially poor, living in a hilly, infertile region. No large estates existed except in the north, and all of those were owned by foreigners. Indeed, one of the first actions undertaken by the new Yugoslav state in 1919 was to break up the estates and dispose of foreign, and in particular Hungarian landowners. Nearly 40% of the rural population was surplus (i.e., excess people not needed to maintain current production levels), and despite a warm climate, Yugoslavia was also relatively dry. Internal communications were poor, damage from World War I had been extensive, and with few exceptions agriculture was devoid of machinery or other modern farming technologies.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing was limited toBelgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
and the other major population centers, and consisted mainly of small, comparatively primitive facilities that produced strictly for the domestic market. The commercial potential of Yugoslavia's Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) ...
ports went to waste because the nation lacked the capital or technical knowledge to operate a shipping industry. On the other hand, the mining industry was well developed due to the nation's abundance of mineral resources, but since it was primarily owned and operated by foreigners, most production was exported. Yugoslavia was the third least industrialized nation in Eastern Europe after Bulgaria and Albania.
Debt
Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
began in 1929, the Western lenders called in their debts, which could not be paid back. Some of the money was lost to graft, although most was used by farmers to improve production and export potential. Agricultural exports, however, were always an unstable prospect as their export earnings were heavily reliant on volatile world market prices. The Great Depression caused the market for them to collapse as global demand contracted heavily and the situation for export-oriented farmers further deteriorated when nations everywhere started to erect trade barriers. Italy was a major trading partner of Yugoslavia in the initial years after World War I, but ties fell off after Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
came to power in 1922. In the grim economic situation of the 1930s, Yugoslavia followed the lead of its neighbors in allowing itself to become a dependent of Nazi Germany.
Education
Although Yugoslavia had enacted a compulsory public education policy, it was inaccessible to many peasants in the countryside. Official literacy figures for the population stood at 50%, but it varied widely throughout the country. Less than 10% of Slovenes were illiterate, whereas over 80% of Macedonians and Bosnians could not read or write. Approximately 10% of initial elementary school students went on to attend higher forms of education, at one of the country's three universities inBelgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
, Ljubljana, and Zagreb.
Political history
Early politics
 Immediately after 1 December proclamation, negotiations between the
Immediately after 1 December proclamation, negotiations between the National Council of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
The State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs ( sh, Država Slovenaca, Hrvata i Srba / ; sl, Država Slovencev, Hrvatov in Srbov) was a political entity that was constituted in October 1918, at the end of World War I, by Slovenes, Croats and Serbs (P ...
and the Serbian government resulted in agreement over the new government which was to be headed by Nikola Pašić. However, when this agreement was submitted to the approval of the regent, Alexander Karađorđević, it was rejected, producing the new state's first governmental crisis. Many regarded this rejection as a violation of parliamentary principles, but the matter was resolved when the regent suggested replacing Pašić with Stojan Protić, a leading member of Pašić's Radical Party. The National Council and the Serbian government agreed and the new government came into existence on 20 December 1918.
In this period before the election of the Constituent Assembly, a Provisional Representation served as a parliament which was formed by delegates from the various elected bodies that had existed before the creation of the state. A realignment of parties combining several members of the Serbian opposition with political parties from the former Austria-Hungary led to the creation of a new party, The Democratic Party, that dominated the Provisional Representation and the government.
Because the Democratic Party led by Ljubomir Davidović pushed a highly centralized agenda a number of Croatian delegates moved into opposition. However, the radicals themselves were not happy that they had only three ministers to the Democratic Party's 11 and, on 16 August 1919, Protić handed in his resignation. Davidović then formed a coalition with the Social Democrats. This government had a majority, but the quorum of the Provisional Representation was half plus one vote. The opposition then began to boycott the parliament. As the government could never guarantee that all of its supporters would turn up, it became impossible to hold a quorate meeting of the parliament. Davidović soon resigned, but as no one else could form a government he again became prime minister. As the opposition continued their boycott, the government decided it had no alternative but to rule by decree. This was denounced by the opposition who began to style themselves as the Parliamentary Community. Davidović realized that the situation was untenable and asked the King to hold immediate elections for the Constituent Assembly. When the King refused, he felt he had no alternative but to resign.
The Parliamentary Community now formed a government led by Stojan Protić committed to the restoration of parliamentary norms and mitigating the centralization of the previous government. Their opposition to the former governments program of radical land reform also united them. As several small groups and individuals switched sides, Protić now even had a small majority. However, the Democratic Party and the Social Democrats now boycotted parliament and Protić was unable to muster a quorum. Hence the Parliamentary Community, now in government, was forced to rule by decree.
For the Parliamentary Community to thus violate the basic principle around which they had formed put them in an extremely difficult position. In April 1920, widespread worker unrest and a railway strike broke out. According to Gligorijević, this put pressure on the two main parties to settle their differences. After successful negotiations, Protić resigned to make way for a new government led by the neutral figure of Milenko Vesnić. The Social Democrats did not follow the Democratic Party, their former allies, into government because they were opposed to the anti-communist measures to which the new government was committed.
The controversies that had divided the parties earlier were still very much live issues. The Democratic Party continued to push its agenda of centralization and still insisted on the need for radical land reform. A disagreement over electoral law finally led the Democratic Party to vote against the government in Parliament and the government was defeated. Though this meeting had not been quorate, Vesnić used this as a pretext to resign. His resignation had the intended effect: the Radical Party agreed to accept the need for centralization, and the Democratic Party agreed to drop its insistence on land reform. Vesnić again headed the new government. The Croatian Community and the Slovenian People's Party were however not happy with the Radicals' acceptance of centralization. Neither was Stojan Protić, and he withdrew from the government on this issue.
In September 1920 a peasant revolt broke out in Croatia, the immediate cause of which was the branding of the peasants' cattle. The Croatian community blamed the centralizing policies of the government and of minister Svetozar Pribićević
Svetozar Pribićević ( sr-cyr, Светозар Прибићевић}, ; 26 October 1875 – 15 September 1936) was a Croatian Serb politician in Austria-Hungary and later Kingdom of Yugoslavia. He was one of the main proponents of Yugoslavism a ...
in particular.
Constituent assembly to dictatorship

 One of the few laws successfully passed by the Provisional Representation was the electoral law for the constituent assembly. During the negotiations that preceded the foundation of the new state, it had been agreed that voting would be secret and based on universal suffrage. It had not occurred to them that universal might include women until the beginning of a movement for women's suffrage appeared with the creation of the new state. The Social Democrats and the Slovenian People's Party supported women's suffrage but the Radicals opposed it. The Democratic Party was open to the idea but not committed enough to make an issue of it so the proposal fell. Proportional Representation was accepted in principle but the system chosen ( d'Hondt with very small constituencies) favored large parties and parties with strong regional support.
The election was held on 28 November 1920. When the votes were counted the Democratic Party had won the most seats, more than the Radicals – but only just. For a party that had been so dominant in the Provisional Representation, that amounted to a defeat. Further it had done rather badly in all former Austria-Hungarian areas. That undercut the party's belief that its centralization policy represented the will of the Yugoslavian people as a whole. The Radicals had done no better in that region but this presented them far less of a problem because they had campaigned openly as a Serbian party. The most dramatic gains had been made by the two anti-system parties. The Croatian Republican Peasant Party's leadership had been released from prison only as the election campaign began to get underway. According to Gligorijević, this had helped them more than active campaigning. The Croatian community (that had in a timid way tried to express the discontent that Croatian Republican Peasant Party mobilized) had been too tainted by their participation in government and was all but eliminated. The other gainers were the communists who had done especially well in the wider
One of the few laws successfully passed by the Provisional Representation was the electoral law for the constituent assembly. During the negotiations that preceded the foundation of the new state, it had been agreed that voting would be secret and based on universal suffrage. It had not occurred to them that universal might include women until the beginning of a movement for women's suffrage appeared with the creation of the new state. The Social Democrats and the Slovenian People's Party supported women's suffrage but the Radicals opposed it. The Democratic Party was open to the idea but not committed enough to make an issue of it so the proposal fell. Proportional Representation was accepted in principle but the system chosen ( d'Hondt with very small constituencies) favored large parties and parties with strong regional support.
The election was held on 28 November 1920. When the votes were counted the Democratic Party had won the most seats, more than the Radicals – but only just. For a party that had been so dominant in the Provisional Representation, that amounted to a defeat. Further it had done rather badly in all former Austria-Hungarian areas. That undercut the party's belief that its centralization policy represented the will of the Yugoslavian people as a whole. The Radicals had done no better in that region but this presented them far less of a problem because they had campaigned openly as a Serbian party. The most dramatic gains had been made by the two anti-system parties. The Croatian Republican Peasant Party's leadership had been released from prison only as the election campaign began to get underway. According to Gligorijević, this had helped them more than active campaigning. The Croatian community (that had in a timid way tried to express the discontent that Croatian Republican Peasant Party mobilized) had been too tainted by their participation in government and was all but eliminated. The other gainers were the communists who had done especially well in the wider Macedonia
Macedonia most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a traditional geographic reg ...
region. The remainder of the seats were taken up by smaller parties that were at best skeptical of the centralizing platform of the Democratic Party.
The results left Nikola Pašić in a very strong position as the Democrats had no choice but to ally with the Radicals if they wanted to get their concept of a centralized Yugoslavia through. Pašić was always careful to keep open the option of a deal with the Croatian opposition. The Democrats and the Radicals were not quite strong enough to get the constitution through on their own and they made an alliance with the Yugoslav Muslim Organization (JMO). The Muslim party sought and got concessions over the preservation of Bosnia in its borders and how the land reform would affect Muslim landowners in Bosnia.
The Croatian Republican Peasant Party refused to swear allegiance to the King on the grounds that this presumed that Yugoslavia would be a monarchy, something that it contended only the Constituent Assembly could decide. The party was unable to take its seats. Most of the opposition though initially taking their seats declared boycotts as time went so that there were few votes against. However, the constitution decided against 1918 agreement between the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs and the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Princi ...
, which stated that a 66% majority that 50% plus one vote would be needed to pass, irrespective of how many voted against. Only last minute concessions to Džemijet, a group of Muslims from Macedonia
Macedonia most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a traditional geographic reg ...
and Kosovo, saved it.
 On 28 June 1921, the Vidovdan Constitution was passed, establishing a
On 28 June 1921, the Vidovdan Constitution was passed, establishing a unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigroup ...
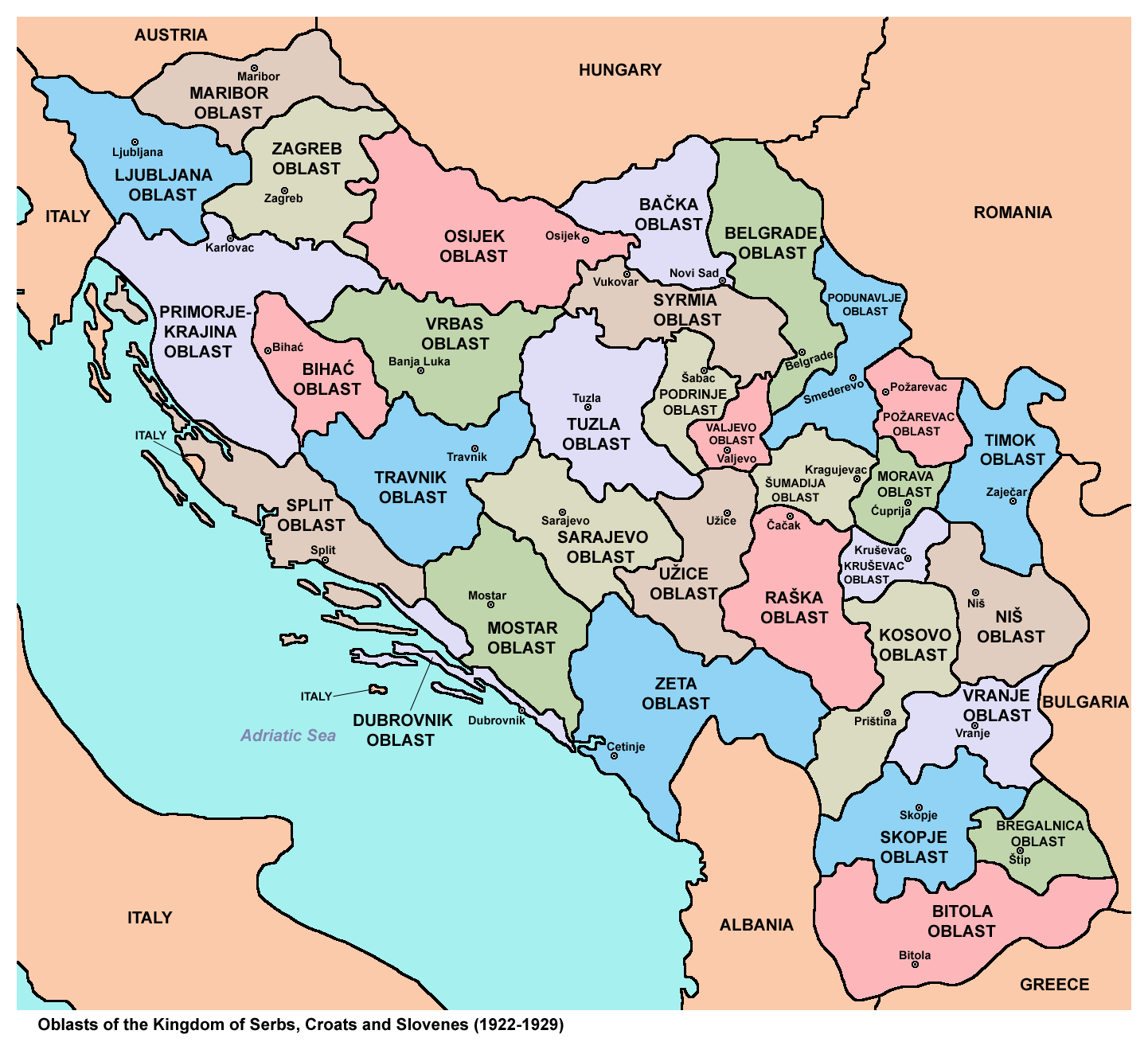
monarchy. The pre–World War I traditional regions were abolished and 33 new administrative '' oblasts'' (provinces) ruled from the center were instituted. During this time, King Peter I died (16 August 1921), and the prince-regent succeeded to the throne as King Alexander I.
Ljubomir Davidović of the Democrats began to have doubts about the wisdom of his party's commitment to centralization and opened up negotiations with the opposition. This threatened to provoke a split in his party as his action was opposed by Svetozar Pribićević. It also gave Pašić a pretext to end the coalition. At first the King gave Pašić a mandate to form a coalition with Pribićević's Democrats. However, Pašić offered Pribićević too little for there to be much chance that Pribićević would agree. A purely Radical government was formed with a mandate to hold elections. The Radicals made gains at the expense of the Democrats but elsewhere there were gains by Radić's Peasant's Party.
Serb politicians around Radic regarded Serbia as the standard bearer of Yugoslav unity, as the state of Piedmont had been for Italy, or Prussia for the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
; a kind of " Greater Serbia". Over the following years, Croatian resistance against a Serbo-centric policy increased.
In the early 1920s, the Yugoslav government of prime minister Nikola Pašić used police pressure over voters and ethnic minorities, confiscation of opposition pamphlets and other measure to rig elections. This was ineffective against the Croatian Peasant Party (formerly the Croatian Republican Peasant Party), whose members continued to win election to the Yugoslav parliament in large numbers, but did harm the Radicals' main Serbian rivals, the Democrats.
Stjepan Radić
Stjepan Radić (11 June 1871 – 8 August 1928) was a Croat politician and founder of the Croatian People's Peasant Party (HPSS), active in Austria-Hungary and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes.
He is credited with galvanizing Cro ...
, the head of the Croatian Peasant Party, was imprisoned many times for political reasons. He was released in 1925 and returned to parliament.
In the spring of 1928, Radić and Svetozar Pribićević
Svetozar Pribićević ( sr-cyr, Светозар Прибићевић}, ; 26 October 1875 – 15 September 1936) was a Croatian Serb politician in Austria-Hungary and later Kingdom of Yugoslavia. He was one of the main proponents of Yugoslavism a ...
waged a bitter parliamentary battle against the ratification of the Nettuno Convention
The Treaty of Nettuno was an agreement made between the governments of the Kingdom of Italy and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes on July 20, 1925, which permitted Italians to freely immigrate into Yugoslavia's coastal region of Dalmatia. ...
with Italy. In this they mobilised nationalist opposition in Serbia but provoked a violent reaction from the governing majority including death threats. On 20 June 1928, a member of the government majority, the Serb deputy Puniša Račić
Puniša Račić ( sr-cyr, Пуниша Рачић; 12 July 1886 – 16 October 1944) was a Montenegrin Serb leader and People's Radical Party (NRS) politician. He assassinated Croatian Peasant Party (HSS) representatives Pavle Radić and Đuro B ...
, shot five members of the Croatian Peasant Party, including their leader Stjepan Radić, after Radić refused to apologize for earlier offense in which he accused Račić of stealing from civilian population. Two died on the floor of the Assembly while the life of Radić hung in the balance.
The opposition now completely withdrew from parliament, declaring that they would not return to a parliament in which several of their representatives had been killed, and insisting on new elections. On 1 August, at a meeting in Zagreb, they renounced 1 December Declaration of 1920. They demanded that the negotiations for unification should begin from scratch. On 8 August Stjepan Radić died.
6 January dictatorship
 On 6 January 1929, using as a pretext the political crisis triggered by the shooting, King Alexander abolished the Constitution, prorogued the Parliament and introduced a personal dictatorship (known as the "January 6 Dictatorship", ''Šestosiječanjska diktatura'', ''Šestojanuarska diktatura'') with the aim of establishing the Yugoslav ideology and single Yugoslav nation. He changed the name of the country to "Kingdom of Yugoslavia", and changed the internal divisions from the 33 oblasts to nine new '' banovinas'' on 3 October. This decision was made following a proposal by the British ambassador to better decentralize the country, modeled on Czechoslovakia. A Court for the Protection of the State was soon established to act as the new regime's tool for putting down any dissent. Opposition politicians
On 6 January 1929, using as a pretext the political crisis triggered by the shooting, King Alexander abolished the Constitution, prorogued the Parliament and introduced a personal dictatorship (known as the "January 6 Dictatorship", ''Šestosiječanjska diktatura'', ''Šestojanuarska diktatura'') with the aim of establishing the Yugoslav ideology and single Yugoslav nation. He changed the name of the country to "Kingdom of Yugoslavia", and changed the internal divisions from the 33 oblasts to nine new '' banovinas'' on 3 October. This decision was made following a proposal by the British ambassador to better decentralize the country, modeled on Czechoslovakia. A Court for the Protection of the State was soon established to act as the new regime's tool for putting down any dissent. Opposition politicians Vladko Maček
Vladimir Maček (20 June 1879 – 15 May 1964) was a politician in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. As a leader of the Croatian Peasant Party (HSS) following the 1928 assassination of Stjepan Radić, Maček had been a leading Croatian political fig ...
and Svetozar Pribićević
Svetozar Pribićević ( sr-cyr, Светозар Прибићевић}, ; 26 October 1875 – 15 September 1936) was a Croatian Serb politician in Austria-Hungary and later Kingdom of Yugoslavia. He was one of the main proponents of Yugoslavism a ...
were arrested under charges by the court. Pribićević later went into exile, whereas over the course of the 1930s Maček would become the leader of the entire opposition bloc.
Immediately after the dictatorship was proclaimed, Croatian deputy Ante Pavelić left for exile from the country. The following years Pavelić worked to establish a revolutionary organization, the Ustaše, allied with the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO) against the state.
In 1931, Alexander decreed a new Constitution which made executive power the gift of the King. Elections were to be by universal male suffrage. The provision for a secret ballot was dropped, and pressure on public employees to vote for the governing party was to be a feature of all elections held under Alexander's constitution. Further, half the upper house was directly appointed by the King, and legislation could become law with the approval of one of the houses alone if also approved by the King.
That same year, Croatian historian and anti-Yugoslavist intellectual Milan Šufflay was assassinated in Zagreb. As a response, Albert Einstein and Heinrich Mann sent an appeal to the International League of Human Rights in Paris condemning the murder, accusing the Yugoslav government. The letter states of a "horrible brutality which is being practiced upon the Croatian People". The appeal was addressed to the Paris-based '' Ligue des droits de l'homme'' (Human Rights League).Einstein accuses Yugoslavian rulers in savant's murder
'', New York Times. 6 May 1931
mirror
In their letter Einstein and Mann held the Yugoslav king Aleksandar explicitly responsible for these circumstances.mirror
Croat opposition to the new régime was strong and, in late 1932, the Croatian Peasant Party issued the ''Zagreb Manifesto'' which sought an end to Serb hegemony and dictatorship. The government reacted by imprisoning many political opponents including the new Croatian Peasant Party leader Vladko Maček. Despite these measures, opposition to the dictatorship continued, with Croats calling for a solution to what was called the "Croatian question". In late 1934, the King planned to release Maček from prison, introduce democratic reforms, and attempt find common ground between Serbs and Croats. However, on 9 October 1934, the king was assassinated in Marseille, France, by Bulgarian Veličko Kerin (also known by his revolutionary pseudonym Vlado Chernozemski), an activist of IMRO, in a conspiracy with Yugoslav exiles and radical members of banned political parties in cooperation with the Croatian extreme nationalist Ustaše organisation.
Yugoslav regency
Because Alexander's eldest son, Peter II, was a minor, a regency council of three, specified in Alexander's will, took over the new king's royal powers and duties. The council was dominated by the 11-year-old king's first cousin once removed Prince Paul. In the late 1930s, internal tensions continued to increase with Serbs and Croats seeking to establish ethnic federal subdivisions. Serbs wantedVardar Banovina
The Vardar Banovina, or Vardar Banate ( mk, Вардарска бановина, Vardarska banovina; sr, Вардарска бановина, translit=Vardarska Banovina; al, Banovina e Vardarit, italics=no), was a province (banate) of the King ...
(later known within Yugoslavia as Vardar Macedonia), Vojvodina, Montenegro united with the Serb lands, and Croatia wanted Dalmatia and some of Vojvodina. Both sides claimed territory in present-day Bosnia and Herzegovina populated also by Bosnian Muslims. The expansion of Nazi Germany in 1938 gave new momentum to efforts to solve these problems and, in 1939, Prince Paul appointed Dragiša Cvetković as prime minister, with the goal of reaching an agreement with the Croatian opposition. Accordingly, on 26 August 1939, Vladko Maček became vice premier of Yugoslavia and an autonomous Banovina of Croatia
The Banovina of Croatia or Banate of Croatia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Banovina Hrvatska, Бановина Хрватска) was an autonomous province ( banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1939 and 1941. It was formed by a merg ...
was established with its own parliament.
These changes satisfied neither Serbs who were concerned with the status of the Serb minority in the new Banovina of Croatia and who wanted more of Bosnia and Herzegovina as Serbian territory, nor the Croatian nationalist Ustaše who were also angered by any settlement short of full independence for a Greater Croatia
Greater Croatia ( hr, Velika Hrvatska) is a term applied to certain currents within Croatian nationalism. In one sense, it refers to the territorial scope of the Croatian people, emphasising the ethnicity of those Croats living outside Croatia. I ...
including all of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Downfall
Fearing an invasion by the Axis powers, Yugoslavia signed the Tripartite Pact on 25 March 1941, pledging cooperation with the Axis. Massive anti-Axis demonstrations followed inBelgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
.
On 27 March, the regime of Prince Paul was overthrown by a military coup d'état
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
with British support. The 17-year-old Peter II was declared to be of age and placed in power. General Dušan Simović became his Prime Minister. The Kingdom of Yugoslavia withdrew its support for the Axis ''de facto'' without formally renouncing the Tripartite Pact. Although the new rulers opposed Nazi Germany, they also feared that if German dictator Adolf Hitler attacked Yugoslavia, the United Kingdom was not in any real position to help. Regardless of this, on 6 April 1941, the Axis powers launched the invasion of Yugoslavia
The invasion of Yugoslavia, also known as the April War or Operation 25, or ''Projekt 25'' was a German-led attack on the Kingdom of Yugoslavia by the Axis powers which began on 6 April 1941 during World War II. The order for the invasion was p ...
and quickly conquered it. The royal family, including Prince Paul, escaped abroad and were kept under house arrest
In justice and law, house arrest (also called home confinement, home detention, or, in modern times, electronic monitoring) is a measure by which a person is confined by the authorities to their residence. Travel is usually restricted, if all ...
in British Kenya.
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was soon divided by the Axis into several entities. Germany, Italy, Hungary, and Bulgaria annexed some border areas outright. A Greater Germany was expanded to include most of Slovenia. Italy added the Governorship of Dalmatia
The Governorate of Dalmatia ( it, Governatorato di Dalmazia) was a territory divided into three provinces of Italy during the Italian Kingdom and Italian Empire epoch. It was created later as an entity in April 1941 at the start of World War I ...
, part of Macedonia and Kosovo, Montenegro, southerly part of Croatia, and more than a third of western Slovenia
Western Slovenia (''Zahodna Slovenija'') is one of the two NUTS-2 Regions of Slovenia. The region forms the western part of the country and includes the cities of Ljubljana, Koper, Kranj and Nova Gorica. It is the wealthier of the two regions o ...
to the Italian Empire. An expanded Croatia was recognized by the Axis as the Independent State of Croatia ('' Nezavisna Država Hrvatska'', NDH). On paper, the NDH was a kingdom and the 4th Duke of Aosta was crowned as King Tomislav II of Croatia, but in reality the King was merely a figurehead and the real power was held by ''Poglavnik
() was the title used by Ante Pavelić, leader of the World War II Croatian movement Ustaše and of the Independent State of Croatia between 1941 and 1945.
Etymology and usage
The word was first recorded in a 16th-century dictionary compiled ...
'' Ante Pavelić. The rump
Rump may refer to:
* Rump (animal)
** Buttocks
* Rump steak, slightly different cuts of meat in Britain and America
* Rump kernel, software run in userspace that offers kernel functionality in NetBSD
Politics
*Rump cabinet
* Rump legislature
* Ru ...
Serbian territory became a military administration of Germany run by military governors and a Serb civil government led by Milan Nedić. Nedić attempted to gain German recognition of Serbia as a successor state to Yugoslavia and claimed King Peter II as Serbia's monarch. Hungary occupied several northern regions.
Following the fall of the Fascist regime in Italy
The fall of the Fascist regime in Italy, also known in Italy as 25 Luglio ( it, Venticinque Luglio, ; "25 July"), came as a result of parallel plots led respectively by Count Dino Grandi and King Victor Emmanuel III during the spring and sum ...
, Tomislav II abdicated from his Croatian throne and Pavelić assumed direct control over the NDH, annexing the Italian Governorate of Dalmatia in the process. After the invasion of Italy by the Axis powers in September 1943, the Italian governorates in Montenegro, Kosovo, Macedonia and Slovenia were occupied by the Germans and placed under direct Reich control.
Exile of the king
King Peter II, who had escaped into exile, was still recognized as King of the whole state of Yugoslavia by theAllies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
. From 13 May 1941, the largely Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguat ...
" Yugoslav Army of the Fatherland" (''Jugoslovenska vojska u otadžbini'', or JVUO, or Chetniks
The Chetniks ( sh-Cyrl-Latn, Четници, Četnici, ; sl, Četniki), formally the Chetnik Detachments of the Yugoslav Army, and also the Yugoslav Army in the Homeland and the Ravna Gora Movement, was a Yugoslav royalist and Serbian nationa ...
) resisted the Axis occupation of Yugoslavia. This resistance movement, which was both anti-German and anti-communist, was commanded by Royalist General Draža Mihailović
Dragoljub "Draža" Mihailović ( sr-Cyrl, Драгољуб Дража Михаиловић; 27 April 1893 – 17 July 1946) was a Yugoslavs, Yugoslav Serb general during World War II. He was the leader of the Chetniks, Chetnik Detachments ...
. For a long time, the Chetniks were supported by the British, the United States, and the Yugoslavian royal government in exile of King Peter II.
However, over the course of the war, effective power changed to the hands of Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito (; sh-Cyrl, Тито, links=no, ), was a Yugoslav communist revolutionary and statesman, serving in various positions from 1943 until his deat ...
's Communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a s ...
Partisans. In 1943, Tito proclaimed the creation of the Democratic Federative Yugoslavia (''Demokratska federativna Jugoslavija''). The Allies gradually recognized Tito's forces as the stronger opposition forces to the German occupation. They began to send most of their aid to Tito's Partisans, rather than to the Royalist Chetniks. On 16 June 1944, the Tito–Šubašić agreement was signed which merged the ''de facto'' and the ''de jure'' government of Yugoslavia.
In early 1945, after the Germans had been driven out, the Kingdom of Yugoslavia was formally restored, however real political power was held by Tito's Communist Partisans. On 29 November, King Peter II was deposed (and the monarchy abolished) by Yugoslavia's Communist Constituent Assembly while he was still in exile. On 2 December, the Communist authorities claimed the entire territory as part of the Democratic Federal Yugoslavia. The new Yugoslavia covered roughly the same territory as the Kingdom had, now a federal republic ruled by the Communist Party rather than a unitary monarchy.
Foreign policy
Pro-Allied government
The Kingdom nourished a close relationship with the Allies of World War I. This was especially the case between 1920 and 1934 with Yugoslavia's traditional supporters of Britain and France.Little Entente
From 1920, the Kingdom of Yugoslavia had formed the ''Little Entente
The Little Entente was an alliance formed in 1920 and 1921 by Czechoslovakia, Romania and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (since 1929 Yugoslavia) with the purpose of common defense against Hungarian revanchism and the prospect of a Hab ...
'' with Czechoslovakia and Romania, with the support of France. The primary aim of the alliance was to prevent Hungary from regaining the territories it had lost after the First World War. The alliance lost its significance in 1937 when Yugoslavia and Romania refused to support Czechoslovakia, then threatened by Germany, in the event of military aggression.
Balkan alliances
In 1924, the Kingdom of Yugoslavia formed a ''Balkan Bloc
The Balkan Pact, or Balkan Entente, was a treaty signed by Greece, Romania, Turkey and Yugoslavia on 9 February 1934
'' with Greece, Romania, and Turkey that was intent on keeping balance on the Balkan peninsula
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. The alliance was formalized and entrenched on 9 February 1934 when it became the "Balkan Entente
The Balkan Pact, or Balkan Entente, was a treaty signed by Greece, Romania, Turkey and Yugoslavia on 9 February 1934
". In 1934, with the assassination of King Alexander I by Vlado Chernozemski in Marseille and the shifting of Yugoslav foreign policy, the alliance crumbled.
Italian coalition
The Kingdom of Italy had territorial ambitions against the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. Relations between Italy and the kingdom's predecessors, theKingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Princi ...
and the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs became sour and hostile during World War I, as Italian and Yugoslav politicians were in dispute over the region of Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
which Italy demanded as part of Italy. These hostile relations were demonstrated on 1 November 1918, when Italian forces sunk the recently captured Austro-Hungarian battleship SMS Viribus Unitis being used by the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs. Italy formed a coalition against it with states with similar state designs, heavily influenced by Italy and/or fascism: Albania, Hungary, Romania and Bulgaria which lasted from 1924 to 1927.
The 1927 cooperation with Britain and France made Italy withdraw from its anti-Yugoslav alliance. Italian Fascist dictator Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
accepted the extreme Croatian nationalist Ustase movement of Ante Pavelić to reside in Italy and use training grounds in Italy to prepare for war with Yugoslavia. Hungary also permitted such Ustase training camps as well. Mussolini allowed Pavelić to reside in Rome.
=Friendship agreement
= In 1927, in response to the growing Italian expansionism, the royal government of Yugoslavia signed an agreement of friendship and cooperation with the United Kingdom and France.1935–1941
 Officially, the last words of King Aleksandar had been "Save Yugoslavia, and the friendship with France". His successors were well aware of the need to try and do the first, but the second, maintaining close ties with France, was increasingly difficult. There were several reasons for this. By the mid-1930s, France, internally divided, was increasingly unable to play an important role in Eastern Europe and support its allies, many of whom had suffered badly from the economic crisis of that period. By contrast, Germany was increasingly willing to get into barter agreements with the countries of south east Europe. In the process those countries felt it was against their interests to closely follow France. An additional motive to improve relations with Italy and Germany was Italy's support of the Ustase movement. As Maček intimated Italy would support Croatian secession from Yugoslavia, First Regent Prince Paul judged closer relations with Italy were inevitable. In an effort to rob the HSS from potential Italian support, a treaty of friendship was signed between the two countries in 1937. This diminished the Ustasa threat somewhat since Mussolini imprisoned some of their leaders and temporarily withdrew financial support. In 1938, Germany, annexing Austria, became a neighbour of Yugoslavia. The feeble reaction of France and Britain, later that year, during the Sudeten Crisis convinced Belgrade that a European war was inevitable and that it would be unwise to support France and Britain. Instead, Yugoslavia tried to stay aloof, this in spite of Paul's personal sympathies for Britain and Serbia's establishment's predilections for France. In the meantime, Germany and Italy tried to exploit Yugoslavia's domestic problems, and so did Maček. In the end, the regency agreed to the formation of the
Officially, the last words of King Aleksandar had been "Save Yugoslavia, and the friendship with France". His successors were well aware of the need to try and do the first, but the second, maintaining close ties with France, was increasingly difficult. There were several reasons for this. By the mid-1930s, France, internally divided, was increasingly unable to play an important role in Eastern Europe and support its allies, many of whom had suffered badly from the economic crisis of that period. By contrast, Germany was increasingly willing to get into barter agreements with the countries of south east Europe. In the process those countries felt it was against their interests to closely follow France. An additional motive to improve relations with Italy and Germany was Italy's support of the Ustase movement. As Maček intimated Italy would support Croatian secession from Yugoslavia, First Regent Prince Paul judged closer relations with Italy were inevitable. In an effort to rob the HSS from potential Italian support, a treaty of friendship was signed between the two countries in 1937. This diminished the Ustasa threat somewhat since Mussolini imprisoned some of their leaders and temporarily withdrew financial support. In 1938, Germany, annexing Austria, became a neighbour of Yugoslavia. The feeble reaction of France and Britain, later that year, during the Sudeten Crisis convinced Belgrade that a European war was inevitable and that it would be unwise to support France and Britain. Instead, Yugoslavia tried to stay aloof, this in spite of Paul's personal sympathies for Britain and Serbia's establishment's predilections for France. In the meantime, Germany and Italy tried to exploit Yugoslavia's domestic problems, and so did Maček. In the end, the regency agreed to the formation of the Banovina of Croatia
The Banovina of Croatia or Banate of Croatia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Banovina Hrvatska, Бановина Хрватска) was an autonomous province ( banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1939 and 1941. It was formed by a merg ...
in August 1939. This did not put an end to the pressures from Germany and Italy, and Yugoslavia's strategic position deteriorated by the day. It was increasingly dependent on the German market, about 90% of its exports went to Germany, and in April 1939 Italy invaded and annexed Albania. In October 1940 it attacked Greece, by when France had already been eliminated from the scene, leaving Britain as Yugoslavia's only potential ally – given that Belgrade had not recognized the Soviet Union. London however wanted to involve Yugoslavia in the war, which it rejected.
From late 1940, Hitler wanted Belgrade to unequivocally choose sides. Pressure intensified, culminating in the signing of the Tripartite Pact on 25 March 1941. Two days later, Prince Paul was deposed in a coup d'état and his nephew Peter II was proclaimed of age, but the new government, headed by General Simović, assured Germany it would adhere to the Pact. Hitler nonetheless ordered the invasion of Yugoslavia
The invasion of Yugoslavia, also known as the April War or Operation 25, or ''Projekt 25'' was a German-led attack on the Kingdom of Yugoslavia by the Axis powers which began on 6 April 1941 during World War II. The order for the invasion was p ...
. On 6 April 1941, Belgrade was bombed; on 10 April, the Independent State of Croatia was proclaimed; and on 17 April, the weak Yugoslav Army capitulated.
1941–1945
After the invasion, the Yugoslav royal government went into exile and local Yugoslav forces rose up in resistance to the occupying Axis powers. Initially the monarchy preferredDraža Mihailović
Dragoljub "Draža" Mihailović ( sr-Cyrl, Драгољуб Дража Михаиловић; 27 April 1893 – 17 July 1946) was a Yugoslavs, Yugoslav Serb general during World War II. He was the leader of the Chetniks, Chetnik Detachments ...
and his Serb-dominated Četnik
The Chetniks ( sh-Cyrl-Latn, Четници, Četnici, ; sl, Četniki), formally the Chetnik Detachments of the Yugoslav Army, and also the Yugoslav Army in the Homeland and the Ravna Gora Movement, was a Yugoslav royalist and Serbian nationa ...
resistance. However, in 1944, the Tito–Šubašić agreement recognised the Democratic Federal Yugoslavia as a provisional government, with the status of the monarchy to be decided at a later date. Three regents Srđan Budisavljević, a Serb; Ante Mandić, a Croat; and Dušan Sernec
Dušan ( sr-Cyrl, Душан) is a Slavic given name primarily used in countries of Yugoslavia; and among Slovaks and Czechs. The name is derived from the Slavic noun ''duša'' "soul".
Occurrence
In Serbia, it was the 29th most popular name ...
, a Slovenewere sworn in at Belgrade on 3 March 1945. They appointed the new government, to be headed by Tito as prime minister and minister of war, with Šubašić as foreign minister, on 7 March.
On 29 November 1945, while still in exile, King Peter II was deposed by the constituent assembly. The Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia was internationally recognized as Yugoslavia and Peter II became a pretender.
Demographics
Ethnic groups
 The small middle class occupied the major population centers and almost everyone else were peasants engaged in subsistence agriculture. The largest ethnic group were Serbs followed by Croats and Slovenes, as three constitutive peoples of the Kingdom, while Montenegrins, Bosnian Muslims and Macedonians were not recognized as distinctive ethnic groups; further historical minority groups included Germans, Italians, Hungarians,
The small middle class occupied the major population centers and almost everyone else were peasants engaged in subsistence agriculture. The largest ethnic group were Serbs followed by Croats and Slovenes, as three constitutive peoples of the Kingdom, while Montenegrins, Bosnian Muslims and Macedonians were not recognized as distinctive ethnic groups; further historical minority groups included Germans, Italians, Hungarians, Slovaks
The Slovaks ( sk, Slováci, singular: ''Slovák'', feminine: ''Slovenka'', plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.
In Slovakia, 4.4 mi ...
, Jews and Rusyns. Religion followed the same pattern with half the population following Orthodox Christianity, around 40% Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
and most the rest Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ...
. Beside "Serbo-Croato-Slovene
Serbo-Croatian () – also called Serbo-Croat (), Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) – is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and ...
", the most widely spoken languages by number of speakers were Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North M ...
, Albanian
Albanian may refer to:
*Pertaining to Albania in Southeast Europe; in particular:
**Albanians, an ethnic group native to the Balkans
**Albanian language
**Albanian culture
**Demographics of Albania, includes other ethnic groups within the country ...
, Italian, Hungarian, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
, Slovak and Rusyn
Rusyn may refer to:
* Rusyns, Rusyn people, an East Slavic people
** Pannonian Rusyns, Pannonian Rusyn people, a branch of Rusyn people
** Lemkos, a branch of Rusyn (or Ukrainian) people
** Boykos, a branch of Rusyn (or Ukrainian) people
* Rusyn l ...
.
In a multiethnic, multireligious and multilinguistic society, ethnic tensions and regional interests commonly surfaced in both politics and daily life, especially between the two largest and most influential groups who monopolized all political power in the country, the Serbs and Croats. Other quarrels were those between Serbs and Macedonians, as the Yugoslav government had as its official position that the latter were ethnic Serbs from "Old Serbia
Old Serbia ( sr, Стара Србија, Stara Srbija) is a Serbian historiographical term that is used to describe the territory that according to the dominant school of Serbian historiography in the late 19th century formed the core of the S ...
" ( sh, Stara Srbija). In the early 20th century the international community viewed the Macedonians predominantly as regional variety of Bulgarians on the basis on linguistics and cultural similarities, but during the Paris Peace Conference of 1919
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, the Allies sanctioned the Serbian control of Vardar Macedonia and its view, that Macedonian Slavs were in fact Southern Serbs. Bulgarian politicians later interpreted the decision as punishment for it being a Central Power
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in W ...
during World War I and as sanctioned Serbian irredentism
The term Greater Serbia or Great Serbia ( sr, Велика Србија, Velika Srbija) describes the Serbian nationalism, Serbian nationalist and irredentism, irredentist ideology of the creation of a Serb State (polity), state which would incorp ...
.
Rights of the Muslim minority were never enshrined in law but concessions were made to accommodate for religious relativism. Some regions of the country were allowed to exist as enclaves of Islamic law.
Aside from Vlachs, the Yugoslav government awarded no special treatment to non-Slavic ethnic minorities in terms of respect for their language, culture, or political autonomy.
With the language of the country being institutionalized and mandatory, ethnic minorities were expected to gradually assimilate into the Yugoslav panethnic
Panethnicity is a political neologism used to group various ethnic groups together based on their related cultural origins; geographic, linguistic, religious, or 'racial' (i.e. phenotypic) similarities are often used alone or in combination to dr ...
identity.
Until 1929, Serbs, Croats and Slovenes were the constitutional nations, when they were merged into a single "Yugoslav" nationality.
Languages
The following data, grouped by first language, is from the 1921 population census: * Serbo-Croatian: 8,911,509 (74.4%) ** Serbs and Montenegrins: 44.6% ** Croats: 23.5% ** Muslims of Yugoslavia: 6.3% * Slovene: 1,019,997 (8.5%) *German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
: 505,790 (4.2%)
* Hungarian: 467,658 (3.9%)
* Albanian
Albanian may refer to:
*Pertaining to Albania in Southeast Europe; in particular:
**Albanians, an ethnic group native to the Balkans
**Albanian language
**Albanian culture
**Demographics of Albania, includes other ethnic groups within the country ...
: 439,657 (3.7%)
* Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
***Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
**Romanian cuisine, traditional ...
: 231,068 (1.9%)
* Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
: 150,322 (1.3%)
* Czech and Slovak: 115,532 (1.0%)
* Ruthenian: 25,615 (0.2%)
* Russian: 20,568 (0.2%)
* Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
: 14,764 (0.1%)
* Italian: 12,553 (0.1%)
* ''Others'': 69,878 (''0.6%'')Group of Authors (1997). ''Istorijski atlas'' (1st ed.). Zavod za udžbenike i nastavna sredstva & Geokarta, Belgrade. p. 91. .
Based on language, the Yugoslavs (collectively Serbs, Croats, Slovenes and other South-Slavic groups in the kingdom) constituted 82.9% of the country's population.
Religious groups
*Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
: 10,571,569 (88.2%)
** Eastern Orthodox: 5,593,057 (46.7%)
** Roman Catholic: 4,708,657 (39.3%)
** Protestant: 229,517 (1.9%)
** Greek Catholic: 40,338 (0.3%)
* Sunni Muslim
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagree ...
: 1,345,271 (11.2%)
* Jewish: 64,746 (0.5%)
* others: 1,944 (nil%)
* atheists: 1,381 (nil%)
Class and occupation
* Agriculture, forestry and fishing – 78.9% * Industry and handicrafts – 9.9% * Banking, trade and traffic – 4.4% * Public service, free profession and military – 3.8% * Other professions – 3.1%Group of Authors (1997). ''Istorijski atlas'' (1st ed.). Zavod za udžbenike i nastavna sredstva & Geokarta, Belgrade. p. 86. .Education
The Kingdom had three universities: the University of Belgrade, University of Zagreb and the University of Ljubljana, located in what were then the most developed cities in the country.Vital statistics (1919–1940)
Marriages and divorces (1919–1940)
Rulers
Kings
* Peter I (1 December 1918 – 16 August 1921; Prince regent Alexander ruled in the name of the King) * Alexander I (16 August 1921 – 9 October 1934) * Peter II (9 October 1934 – 29 November 1945; in exile from 13/14 April 1941) ** Regency headed by Prince Paul (9 October 1934 – 27 March 1941)Prime Ministers 1918–1941
* 1918–1919 – Stojan Protić * 1919–1920 – Ljubomir Davidović * 1920 – Stojan Protić * 1920–1921 –Milenko Vesnić Milenko (Cyrillic script: Миленко) is a name of Slavic origin, primarily used as a masculine given name. Notable people named Milenko include:
People named Milenko
As a given name
* Milenko Ačimovič (born 1977), Slovenian football pla ...
* 1921–1924 – Nikola Pašić
* 1924 – Ljubomir Davidović
* 1924–1926 – Nikola Pašić
* 1926–1927 – Nikola Uzunović
* 1927–1928 – Velimir Vukićević
* 1928–1929 – Anton Korošec
* 1929–1932 – Petar Živković
* 1932 – Vojislav Marinković
Vojislav Marinković ( sr-cyr, Војислав Маринковић; 13 May 1876 Ministry, p. 1 – 18 September 1935) Yugoslav Archive (2008), p. 1 was a Serbian and Yugoslav diplomat and politician, serving two times as Minister of Foreign ...
* 1932–1934 – Milan Srškić
Milan Srškić (3 March 1880 – 12 April 1937) was a Yugoslav politician and lawyer, Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia during the dictatorship of King Alexander I.
Even before the establishment of the 6 January Dictatorship, Srškić ...
* 1934 – Nikola Uzunović
* 1934–1935 – Bogoljub Jevtić
Bogoljub Jevtić (Serbian Cyrillic: Богољуб Јевтић; 24 December 1886 – 7 June 1960) was a Serbian diplomat and politician in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia.
He was plenipotentiary minister of Yugoslavia in Albania, Austria and Hungary. ...
* 1935–1939 – Milan Stojadinović
* 1939–1941 – Dragiša Cvetković
* 1941 – Dušan Simović
Prime Ministers-in-exile 1941–1945
* 1941–1942 – Dušan Simović * 1942–1943 – Slobodan Jovanović * 1943 – Miloš Trifunović * 1943–1944 –Božidar Purić
Božidar Purić ( sr-Cyrl, Божидар Пурић; 19 February 1891 – 28 October 1977) was a Serbian and Yugoslav politician and diplomat. Between 1928 and 1934 he was a chargé d'affaires in the Embassy of Kingdom of Yugoslavia in the United ...
* 1944–1945 – Ivan Šubašić
* 1945 – Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito (; sh-Cyrl, Тито, links=no, ), was a Yugoslav communist revolutionary and statesman, serving in various positions from 1943 until his deat ...
Subdivisions
The subdivisions of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia existed successively in three different forms. From 1918 to 1922, the kingdom maintained the pre–World War I subdivisions of Yugoslavia's predecessor states. In 1922, the state was divided into thirty-three ''oblasts'' (provinces). In 1929, after the establishment of theJanuary 6 Dictatorship
The 6 January Dictatorship ( sr-cyr, Шестојануарска диктатура, Šestojanuarska diktatura; hr, Šestosiječanjska diktatura; sl, Šestojanuarska diktatura) was a royal dictatorship established in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croa ...
, a new system of nine ''banovinas'' (regions) was implemented by royal decree. In 1939, as an accommodation to Yugoslav Croats in the Cvetković-Maček Agreement, a single Banovina of Croatia
The Banovina of Croatia or Banate of Croatia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Banovina Hrvatska, Бановина Хрватска) was an autonomous province ( banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1939 and 1941. It was formed by a merg ...
was formed from two of these ''banovinas'' (and from sections of others).
Sport
The most popular sport in the Kingdom was association football. TheYugoslav Football Association
The Football Association of Yugoslavia (FSJ) ( sr, Фудбалски савез Југославије, Fudbalski savez Jugoslavije, hr, Nogometni savez Jugoslavije; bs, Fudbalski savez Jugoslavije; sl, Nogometna zveza Jugoslavije; mk, Фуд ...
was founded in Zagreb in 1919. It was based in Zagreb until the 6 January Dictatorship, when the association was moved to Belgrade. From 1923, a national championship was held annually. The national team played its first match at the 1920 Summer Olympics
The 1920 Summer Olympics (french: Jeux olympiques d'été de 1920; nl, Olympische Zomerspelen van 1920; german: Olympische Sommerspiele 1920), officially known as the Games of the VII Olympiad (french: Jeux de la VIIe olympiade; nl, Spelen van ...
. It also participated in the inaugural FIFA World Cup, finishing fourth.
Other popular sports included water polo, which was dominated nationally by the Croatian side VK Jug.
The Kingdom participated at the Olympic Games from 1920 until 1936. During this time, the country won eight medals, all in gymnastics and six of these were won by Leon Štukelj
Leon Štukelj (; 12 November 1898 – 8 November 1999) was a Slovene professional gymnast. He was an Olympic gold medalist and athlete who represented Yugoslavia at the Olympics.
He is a noted figure in Slovenian sporting history. Štukelj is o ...
, a Slovene who was the most nominated gymnast of that time.
See also
* List of Finance Ministers of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia *1923 Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes parliamentary election
Parliamentary elections were held in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes on 18 March 1923.Dieter Nohlen, Dolf Sternberger, Bernhard Vogel, Klaus Landfried (1969) ''Die Wahl der Parlamente und andere Staatsorgane'', Walter de Gruyter, p783 Th ...
* Republic of Prekmurje
* Slovene March (Kingdom of Hungary)
References
Sources
* * * * * * * Hadži-Jovančić, Perica. "Losing the Periphery: The British Foreign Office and Policy Towards Yugoslavia, 1935–1938." ''Diplomacy & Statecraft'' 31.1 (2020): 65–90. * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Kingdom of Yugoslavia States and territories established in 1918 States and territories disestablished in 1941 Yugoslavia, Kingdom of Yugoslavia 1918 establishments in Yugoslavia 1941 disestablishments in Yugoslavia 1918 establishments in Europe 1941 disestablishments in Europe 1945 establishments in Yugoslavia 1945 disestablishments in Yugoslavia 1945 establishments in Europe 1945 disestablishments in Europe 20th century in Kosovo 20th century in Montenegro Yugoslav Serbia 20th century in Slovenia Yugoslav Bosnia and Herzegovina Yugoslav Croatia Yugoslavia, Kingdom of Yugoslavia, Kingdom of