Royal Opera House, London on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Royal Opera House (ROH) is an opera house and major performing arts venue in
 In 1817, bare flame gaslight had replaced the former candles and oil lamps that lighted the Covent Garden stage. This was an improvement, but in 1837 Macready employed
In 1817, bare flame gaslight had replaced the former candles and oil lamps that lighted the Covent Garden stage. This was an improvement, but in 1837 Macready employed  Costa and his successors presented all operas in Italian, even those originally written in French, German or English, until 1892, when
Costa and his successors presented all operas in Italian, even those originally written in French, German or English, until 1892, when
 Several renovations had taken place to parts of the house in the 1960s, including improvements to the amphitheatre but the theatre clearly needed a major overhaul. In 1975 the Labour government gave land adjacent to the Royal Opera House for a long-overdue modernisation, refurbishment, and extension. In the early 1980s the first part of a major renovation included an extension to the rear of the theatre on the James Street corner. The development added two new ballet studios, offices, a Chorus Rehearsal Room and the Opera Rehearsal room. Dressing rooms were also added.
Several renovations had taken place to parts of the house in the 1960s, including improvements to the amphitheatre but the theatre clearly needed a major overhaul. In 1975 the Labour government gave land adjacent to the Royal Opera House for a long-overdue modernisation, refurbishment, and extension. In the early 1980s the first part of a major renovation included an extension to the rear of the theatre on the James Street corner. The development added two new ballet studios, offices, a Chorus Rehearsal Room and the Opera Rehearsal room. Dressing rooms were also added.

 By 1995, sufficient funds from the Arts Lottery through
By 1995, sufficient funds from the Arts Lottery through  The new building has the same traditional horseshoe-shaped auditorium as before, but with greatly improved technical, rehearsal, office, and educational facilities. Additionally, a new studio theatre, the Linbury, as well as more public space was created. The inclusion of the adjacent old Floral Hall, which had fallen into disrepair and was used as a scenery store before redevelopment, created a new and extensive public gathering place. The venue is now claimed by the ROH to be the most modern theatre facility in Europe.
Surtitles, projected onto a screen above the proscenium, have been used for all opera performances since they were introduced for school matinees in 1983/4 season. Since the reopening of the theatre in 1999 an electronic libretto system provides translations onto small video screens for some seats, and additional monitors and screens are to be introduced to other parts of the house.
In 2014 design work, known as the Open Up Project, began with the aim of improving the entrances, lobby areas and the Linbury Theatre. As part of the Open Up Project, IQ Projects were tasked with the renovation of the upper floor bar area and restaurant utilising various elements of bespoke glazing.
In October 2020, the BBC reported that the Royal Opera House has lost 60% of its income as a result of restrictions implemented in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. As a consequence, the 1971 ''"
The new building has the same traditional horseshoe-shaped auditorium as before, but with greatly improved technical, rehearsal, office, and educational facilities. Additionally, a new studio theatre, the Linbury, as well as more public space was created. The inclusion of the adjacent old Floral Hall, which had fallen into disrepair and was used as a scenery store before redevelopment, created a new and extensive public gathering place. The venue is now claimed by the ROH to be the most modern theatre facility in Europe.
Surtitles, projected onto a screen above the proscenium, have been used for all opera performances since they were introduced for school matinees in 1983/4 season. Since the reopening of the theatre in 1999 an electronic libretto system provides translations onto small video screens for some seats, and additional monitors and screens are to be introduced to other parts of the house.
In 2014 design work, known as the Open Up Project, began with the aim of improving the entrances, lobby areas and the Linbury Theatre. As part of the Open Up Project, IQ Projects were tasked with the renovation of the upper floor bar area and restaurant utilising various elements of bespoke glazing.
In October 2020, the BBC reported that the Royal Opera House has lost 60% of its income as a result of restrictions implemented in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. As a consequence, the 1971 ''"
 The Paul Hamlyn Hall is a large iron and glass structure adjacent to, and with direct access to, the main opera house building. The hall now acts as the atrium and main public area of the opera house, with a champagne bar, restaurant and other hospitality services, and also providing access to the main auditorium at all levels.
The building was formerly known as Floral Hall. It was originally built by the Opera House to house a flower market (also selling fruits and vegetables), hence the name. It was designed by Edward Middleton Barry and opened in 1860. After being used as a concert hall, it became part of the Covent Garden Market in 1887. A fire broke out in the building in 1956, after which it sat derelict. It was acquired by the Opera House in 1977 and used as storage space.
The redevelopment of the Floral Hall as part of the 1990s redevelopment project involved lifting up the cast iron structure to accommodate new public areas for the opera house underneath. The southern side of the hall now connected with another building, so the cast iron south portico was dismantled and rebuilt in Borough Market, where it is separately Grate II heritage listed.
The redevelopment had gone ahead on the strength of a pledge of £10m from the philanthropist Alberto Vilar and for a number of years, it was known as the Vilar Floral Hall; however Vilar failed to make good his pledge. As a result, the name was changed in September 2005 to the Paul Hamlyn Hall, after the opera house received a donation of £10m from the estate of
The Paul Hamlyn Hall is a large iron and glass structure adjacent to, and with direct access to, the main opera house building. The hall now acts as the atrium and main public area of the opera house, with a champagne bar, restaurant and other hospitality services, and also providing access to the main auditorium at all levels.
The building was formerly known as Floral Hall. It was originally built by the Opera House to house a flower market (also selling fruits and vegetables), hence the name. It was designed by Edward Middleton Barry and opened in 1860. After being used as a concert hall, it became part of the Covent Garden Market in 1887. A fire broke out in the building in 1956, after which it sat derelict. It was acquired by the Opera House in 1977 and used as storage space.
The redevelopment of the Floral Hall as part of the 1990s redevelopment project involved lifting up the cast iron structure to accommodate new public areas for the opera house underneath. The southern side of the hall now connected with another building, so the cast iron south portico was dismantled and rebuilt in Borough Market, where it is separately Grate II heritage listed.
The redevelopment had gone ahead on the strength of a pledge of £10m from the philanthropist Alberto Vilar and for a number of years, it was known as the Vilar Floral Hall; however Vilar failed to make good his pledge. As a result, the name was changed in September 2005 to the Paul Hamlyn Hall, after the opera house received a donation of £10m from the estate of
 The Royal Opera House opened a scenery-making facility for their operas and ballets at
The Royal Opera House opened a scenery-making facility for their operas and ballets at
Retrieved 9 January 2011 The East of England Development Agency, which partly funded developments on the park, notes that "the first phase includes the Royal Opera House's Bob and Tamar Manoukian Production Workshop and Community areas". The Bob and Tamar Manoukian Costume Centre, also designed by Nicholas Hare Associates, opened in September 2015, and provides a costume-making facility for the Royal Opera House and a training centre for students of costume-making from South Essex College. The building also houses the Royal Opera House's collection of historically important costumes. Other elements at High House, Purfleet, include The Backstage Centre, a new technical theatre and music training centre which is currently run by the National College for Creative Industries and was formally opened byInformation (with illustration) about the Production Park from blog.roh.org.uk
Retrieved 25 November 2010
National Theatre in Transition: The London Patent Theatre Fires of 1808–1809 and the Old Price Riots.
''BRANCH: Britain, Representation, and Nineteenth-Century History.'' Web. 29 March 2016. * Tooley, John, ''In House: Covent Garden, Fifty Years of Opera and Ballet'', Faber and Faber, London, 1999. * Thubron, Colin (text) and Boursnell, Clive (photos), ''The Royal Opera House Covent Garden'', Hamish Hamilton, London, 1982.
Royal Opera House Collections Online (Archive Collections Catalogue and Performance Database)
The Royal Ballet School official website
* ttp://www.arthurlloyd.co.uk/RoyalOperaHouseCoventGarden.htm Theatre HistoryArticles, Images, and Archive Material {{Authority control West End theatres The Royal Ballet Opera houses in England Opera in London Grade I listed buildings in the City of Westminster Grade I listed theatres Theatres in the City of Westminster 1660 establishments in England Music venues completed in 1858 Ballet venues in the United Kingdom Covent Garden Theatres completed in 1732 Theatres completed in 1809 Theatres that have burned down Burned buildings and structures in the United Kingdom Edward Middleton Barry buildings
Covent Garden
Covent Garden is a district in London, on the eastern fringes of the West End, between St Martin's Lane and Drury Lane. It is associated with the former fruit-and-vegetable market in the central square, now a popular shopping and tourist si ...
, central London
Central London is the innermost part of London, in England, spanning several boroughs. Over time, a number of definitions have been used to define the scope of Central London for statistics, urban planning and local government. Its characteris ...
. The large building is often referred to as simply Covent Garden, after a previous use of the site. It is the home of The Royal Opera, The Royal Ballet, and the Orchestra of the Royal Opera House. The first theatre on the site, the Theatre Royal (1732), served primarily as a playhouse for the first hundred years of its history. In 1734, the first ballet was presented. A year later, the first season of operas, by George Frideric Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel (; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque music, Baroque composer well known for his opera#Baroque era, operas, oratorios, anthems, concerto grosso, concerti grossi, ...
, began. Many of his operas and oratorios were specifically written for Covent Garden and had their premieres there.
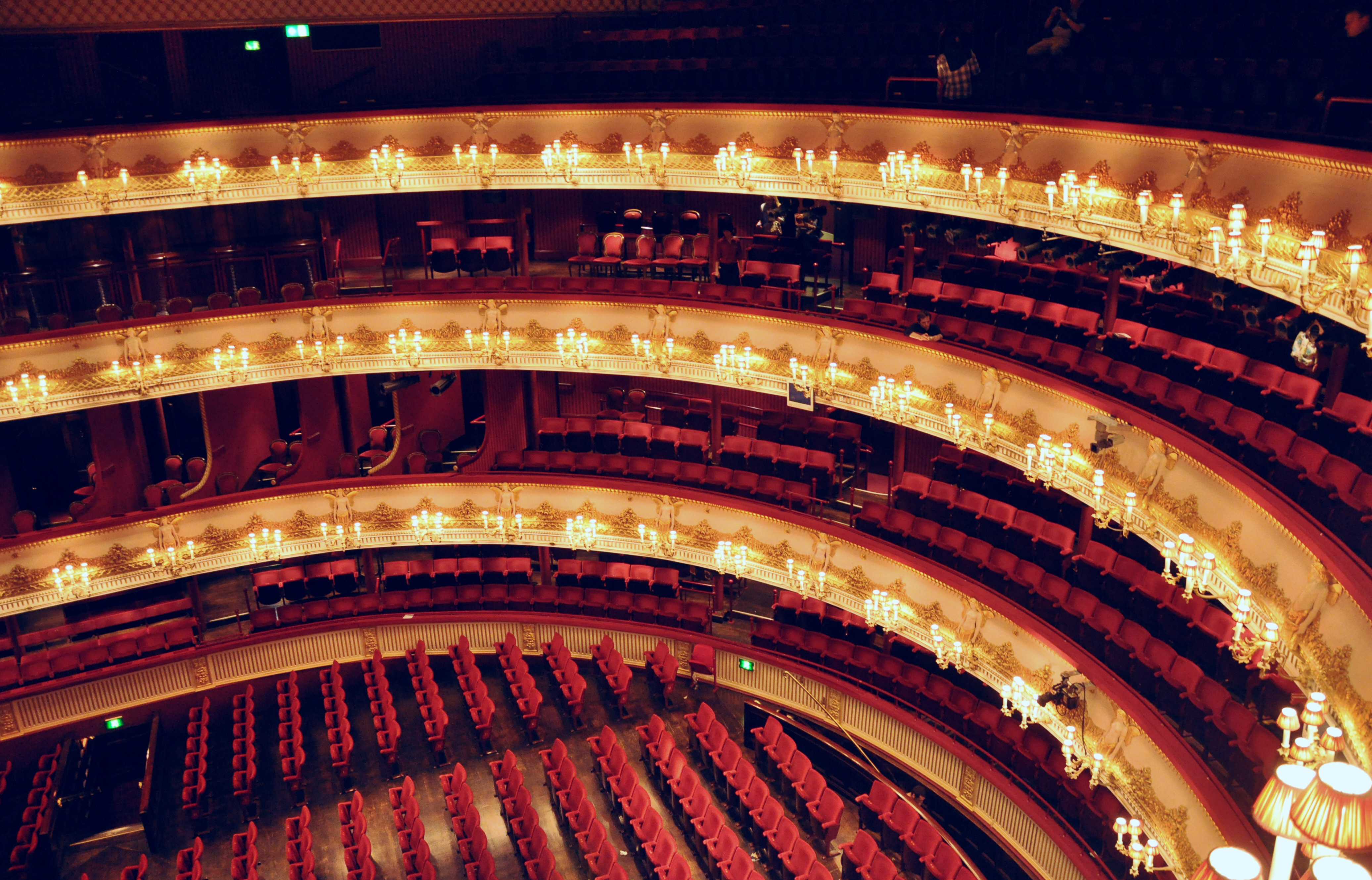
The current building is the third theatre on the site, following disastrous fires in 1808 and 1856 to previous buildings. The façade, foyer, and auditorium date from 1858, but almost every other element of the present complex dates from an extensive reconstruction in the 1990s. The main auditorium seats 2,256 people, making it the third largest in London, and consists of four tiers of box
A box (plural: boxes) is a container used for the storage or transportation of its contents. Most boxes have flat, parallel, rectangular sides. Boxes can be very small (like a matchbox) or very large (like a shipping box for furniture), and can ...
es and balconies and the amphitheatre gallery. The proscenium
A proscenium ( grc-gre, προσκήνιον, ) is the metaphorical vertical plane of space in a theatre, usually surrounded on the top and sides by a physical proscenium arch (whether or not truly "arched") and on the bottom by the stage floor ...
is wide, with the stage of the same depth and high. The main auditorium is a Grade I listed building.
History
Davenant patent
The foundation of the Theatre Royal, Covent Garden lies in theletters patent
Letters patent ( la, litterae patentes) ( always in the plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, president or other head of state, generally granting an office, right, monopoly, titl ...
awarded by Charles II to Sir William Davenant in 1662, allowing Davenant to operate one of only two patent theatre
The patent theatres were the theatres that were licensed to perform "spoken drama" after the Restoration of Charles II as King of England, Scotland and Ireland in 1660. Other theatres were prohibited from performing such "serious" drama, but w ...
companies (''The Duke's Company
The Duke's Company was a theatre company chartered by King Charles II at the start of the Restoration era, 1660. Sir William Davenant was manager of the company under the patronage of Prince James, Duke of York. During hats period, theatres b ...
'') in London. The letters patent remained in the possession of the patentees' heirs until the 19th century. Their whereabouts were unknown for some time, but as of 2019 they are held in the Rosenbach Museum & Library, Philadelphia.
First theatre
In 1728,John Rich
John Rich (born January 7, 1974) is an American country music singer-songwriter. From 1992 to 1998, he was a member of the country music band Lonestar, in which he played bass guitar and alternated with Richie McDonald as lead vocalist. After d ...
, actor-manager of the Duke's Company at Lincoln's Inn Fields Theatre
Lisle's Tennis Court was a building off Portugal Street in Lincoln's Inn Fields in London. Originally built as a real tennis court, it was used as a playhouse during two periods, 1661–1674 and 1695–1705. During the early period, ...
, commissioned '' The Beggar's Opera'' from John Gay
John Gay (30 June 1685 – 4 December 1732) was an English poet and dramatist and member of the Scriblerus Club. He is best remembered for ''The Beggar's Opera'' (1728), a ballad opera. The characters, including Captain Macheath and Polly Peac ...
. The success of this venture provided him with the capital to build the Theatre Royal (designed by Edward Shepherd
Edward Shepherd (died 1747) was a prominent London-based English architect and developer in the Georgian period.
Architectural work
Shepherd worked on the following projects, among others:
* Cannons, a house for James Brydges, 1st Duke of ...
) at the site of an ancient convent garden. Inigo Jones
Inigo Jones (; 15 July 1573 – 21 June 1652) was the first significant architect in England and Wales in the early modern period, and the first to employ Vitruvian rules of proportion and symmetry in his buildings.
As the most notable archit ...
had developed part of this property in the 1630s with a piazza and St Paul's church (now known colloquially as the actors' church). In addition, a Royal Charter had created a fruit and vegetable market in the area, a market which survived in that location until 1974.
At the opening of the theatre on 7 December 1732, Rich was carried by his actors in procession into the building for its inaugural production of William Congreve's '' The Way of the World''.
During its first century, the theatre was operated primarily as a playhouse, with the Letters Patent granted by Charles II giving the Theatre Royal, Covent Garden and Theatre Royal, Drury Lane exclusive rights to present spoken drama in London. Despite the frequent interchangeability between the two companies, competition was intense, and the companies often presented the same plays at the same time. Rich introduced pantomime to the repertoire, performing himself, under the stage name ''John Lun'', as Harlequin. A tradition of seasonal pantomime continued at the modern theatre until 1939.
In 1734, the theatre presented its first ballet, ''Pygmalion''. Marie Sallé
Marie Sallé (1707–1756) was a French dancer and choreographer in the 18th century known for her expressive, dramatic performances rather than a series of "leaps and frolics" typical of ballet of her time.
Biography
Marie Sallé was a promine ...
discarded tradition and her corset and danced in diaphanous robes. George Frideric Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel (; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque music, Baroque composer well known for his opera#Baroque era, operas, oratorios, anthems, concerto grosso, concerti grossi, ...
was named musical director of the company at Lincoln's Inn Fields in 1719, but his first season of opera for the theatre was not presented until 1734. His first opera was ''Il pastor fido
''Il pastor fido'' (''The Faithfull Shepherd'' in Richard Fanshawe's 1647 English translation) is a pastoral tragicomedy set in Arcadia by Giovanni Battista Guarini, first published in 1590 in Venice.
Plot summary
To redress an ancient wrong ...
,'' followed by '' Ariodante'' (1735), and the première of '' Alcina'', and '' Atalanta'' the following year. In 1743 there was a royal performance of '' Messiah''; its success resulted in a tradition of Lent
Lent ( la, Quadragesima, 'Fortieth') is a solemn religious observance in the liturgical calendar commemorating the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring temptation by Satan, according to the Gospels of Matthew, Mark and Luke ...
en oratorio performances. From 1735 until his death in 1759, Handel gave regular seasons at the theatre; many of his operas and oratorios were written for that venue or had their first London performances there. He bequeathed his organ to John Rich, and it was placed in a prominent position on the stage. It was among many valuable items lost in a fire that destroyed the theatre on 20 September 1808. In 1792 the architect Henry Holland rebuilt the auditorium; he expanded its capacity within the existing shell of the building.
Second theatre
Rebuilding began in December 1808, and the second Theatre Royal, Covent Garden (designed by Robert Smirke) opened on 18 September 1809 with a performance of ''Macbeth
''Macbeth'' (, full title ''The Tragedie of Macbeth'') is a tragedy by William Shakespeare. It is thought to have been first performed in 1606. It dramatises the damaging physical and psychological effects of political ambition on those w ...
'' followed by a musical entertainment called ''The Quaker''. The actor-manager John Philip Kemble, raised seat prices to help recoup the cost of rebuilding and the cost of an increased ground rent introduced by the landowner, the Duke of Bedford, but the move was so unpopular that audiences disrupted performances by beating sticks, hissing, booing and dancing. The ''Old Price Riots
The Old Price Riots of 1809 (also sometimes referred to as the O.P. or OP riots) were caused by rising prices at the new Theatre at Covent Garden, London, after the previous one had been destroyed by fire. Covent Garden was one of two "patent" t ...
'' lasted over two months, and the management was finally forced to accede to the audience's demands.
During this time, entertainments were varied; opera and ballet were presented, but not exclusively. Kemble engaged a variety of acts, including the child performer '' Master Betty''; the great clown
A clown is a person who performs comedy and arts in a state of open-mindedness using physical comedy, typically while wearing distinct makeup or costuming and reversing folkway-norms.
History
The most ancient clowns have been found in ...
Joseph Grimaldi
Joseph Grimaldi (18 December 1778 – 31 May 1837) was an English actor, comedian and dancer, who became the most popular English entertainer of the Regency era.Byrne, Eugene"The patient" Historyextra.com, 13 April 2012 In the early 1800s, ...
made his name at Covent Garden. Many famous actors of the day appeared at the theatre, including the tragediennes Sarah Siddons and Eliza O'Neill
Elizabeth O'Neill (179129 October 1872), also Eliza, was an Irish actress.
Biography
Born in Drogheda, she was the daughter of an actor and stage manager. Her first appearance on the stage was made at the Crow Street Theatre in 1811 as the Wido ...
, the Shakespearean actors William Macready, Edmund Kean and his son Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ...
. On 25 March 1833 Edmund Kean collapsed on stage while playing Othello
''Othello'' (full title: ''The Tragedy of Othello, the Moor of Venice'') is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare, probably in 1603, set in the contemporary Ottoman–Venetian War (1570–1573) fought for the control of the Island of Cypru ...
, and died two months later.
In 1806, the pantomime clown Joseph Grimaldi (''The Garrick of Clowns'') had performed his greatest success in '' Harlequin and Mother Goose; or the Golden Egg'' at Covent Garden, and this was subsequently revived, at the new theatre. Grimaldi was an innovator: his performance as ''Joey'' introduced the clown to the world, building on the existing role of Harlequin derived from the ''Commedia dell'arte
(; ; ) was an early form of professional theatre, originating from Italian theatre, that was popular throughout Europe between the 16th and 18th centuries. It was formerly called Italian comedy in English and is also known as , , and . Charact ...
''. His father had been ballet-master at Drury Lane, and his physical comedy, his ability to invent visual tricks and buffoon
A jester, court jester, fool or joker was a member of the household of a nobleman or a monarch employed to entertain guests during the medieval and Renaissance eras. Jesters were also itinerant performers who entertained common folk at fairs and ...
ery, and his ability to poke fun at the audience were extraordinary.
Early pantomimes were performed as mimes accompanied by music, but as Music hall
Music hall is a type of British theatrical entertainment that was popular from the early Victorian era, beginning around 1850. It faded away after 1918 as the halls rebranded their entertainment as variety. Perceptions of a distinction in Bri ...
became popular, Grimaldi introduced the pantomime dame to the theatre and was responsible for the tradition of audience singing. By 1821 dance and clowning had taken such a physical toll on Grimaldi that he could barely walk, and he retired from the theatre. By 1828, he was penniless; Drury Lane held a benefit concert for him after Covent Garden refused.
 In 1817, bare flame gaslight had replaced the former candles and oil lamps that lighted the Covent Garden stage. This was an improvement, but in 1837 Macready employed
In 1817, bare flame gaslight had replaced the former candles and oil lamps that lighted the Covent Garden stage. This was an improvement, but in 1837 Macready employed limelight
Limelight (also known as Drummond light or calcium light)James R. Smith (2004). ''San Francisco's Lost Landmarks'', Quill Driver Books. is a type of stage lighting once used in theatres and music halls. An intense illumination is created when ...
in the theatre for the first time, during a performance of a pantomime, ''Peeping Tom of Coventry''. Limelight used a block of quicklime
Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term "''lime''" connotes calcium-containing inorganic ma ...
heated by an oxygen and hydrogen flame. This allowed the use of spotlights to highlight performers on the stage.
The Theatres Act 1843 broke the patent theatres' monopoly of drama. At that time Her Majesty's Theatre in the Haymarket was the main centre of ballet and opera but after a dispute with the management in 1846 Michael Costa, conductor at Her Majesty's, transferred his allegiance to Covent Garden, bringing most of the company with him. The auditorium was completely remodeled after an 1846 fire, during the following 1846–47 seasons, the company performed at the Lyceum Theatre. The theatre reopened as the Royal Italian Opera on 6 April 1847 with a performance of Rossini
Gioachino Antonio Rossini (29 February 1792 – 13 November 1868) was an Italian composer who gained fame for his 39 operas, although he also wrote many songs, some chamber music and piano pieces, and some sacred music. He set new standards f ...
's ''Semiramide
''Semiramide'' () is an opera in two acts by Gioachino Rossini.
The libretto by Gaetano Rossi is based on Voltaire's tragedy ''Semiramis'', which in turn was based on the legend of Semiramis of Assyria. The opera was first performed at La Fenice ...
''.
In 1852, Louis Antoine Jullien the French eccentric composer of light music and conductor presented an opera of his own composition, ''Pietro il Grande''. Five performances were given of the 'spectacular', including live horses on the stage and very loud music. Critics considered it a complete failure and Jullien was ruined and fled to America.
 Costa and his successors presented all operas in Italian, even those originally written in French, German or English, until 1892, when
Costa and his successors presented all operas in Italian, even those originally written in French, German or English, until 1892, when Gustav Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 – 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism ...
presented the debut of Wagner's Ring cycle
(''The Ring of the Nibelung''), WWV 86, is a cycle of four German-language epic music dramas composed by Richard Wagner. The works are based loosely on characters from Germanic heroic legend, namely Norse legendary sagas and the ''Nibelung ...
at Covent Garden. The word "Italian" was then quietly dropped from the name of the opera house.Gordon-Powell, Robin. ''Ivanhoe'', full score, Introduction, vol. I, p. VIII, 2008, The Amber Ring
On 5 March 1856, the theatre was again destroyed by fire.
Third theatre
Work on a third theatre, designed by Edward Middleton Barry, started in 1857, and the new building, which still remains as the nucleus of the present theatre, was built by Lucas Brothers and opened on 15 May 1858 with a performance of Meyerbeer's ''Les Huguenots
() is an opera by Giacomo Meyerbeer and is one of the most popular and spectacular examples of grand opera. In five acts, to a libretto
A libretto (Italian for "booklet") is the text used in, or intended for, an extended musical work suc ...
''.
The Royal English Opera company under the management of Louisa Pyne
Louisa Bodda-Pyne (30 April 1828 – 20 March 1904) was an England, English soprano and opera company manager.
Biography
Life and career
Born into a theatrical family as Louisa Fanny Pyne, she was the youngest daughter of the alto George Griggs ...
and William Harrison, made their last performance at Theatre Royal, Drury Lane on 11 December 1858 and took up residence at Covent Garden on 20 December 1858 with the premiere of Michael Balfe's '' Satanella'' – the first opera to have its world premiere at the new theatre – and continued there until 1865.
The theatre became the Royal Opera House (ROH) in 1892, and the number of French and German works offered increased. Winter and summer seasons of opera and ballet were given, and the building was also used for pantomime, recitals and political meetings.
During the First World War, the theatre was requisitioned by the Ministry of Works for use as a furniture repository.
From 1934 to 1936, Geoffrey Toye
Edward Geoffrey Toye (17 February 1889 – 11 June 1942), known as Geoffrey Toye, was an English conductor, composer and opera producer.
He is best remembered as a musical director of the D'Oyly Carte Opera Company and for his association wit ...
was managing director, working alongside the Artistic Director, Sir Thomas Beecham. Despite early successes, Toye and Beecham eventually fell out, and Toye resigned.
During the Second World War the ROH became a dance hall. There was a possibility that it would remain so after the war but, following lengthy negotiations, the music publishers Boosey & Hawkes
Boosey & Hawkes is a British music publisher purported to be the largest specialist classical music publisher in the world. Until 2003, it was also a major manufacturer of brass, string and woodwind musical instruments.
Formed in 1930 throu ...
acquired the lease of the building. David Webster was appointed General Administrator, and Sadler's Wells Ballet was invited to become the resident ballet company. The Covent Garden Opera Trust was created and laid out plans "to establish Covent Garden as the national centre of opera and ballet, employing British artists in all departments, wherever that is consistent with the maintenance of the best possible standards ..."
The Royal Opera House reopened on 20 February 1946 with a performance of '' The Sleeping Beauty'' in an extravagant new production designed by Oliver Messel. Webster, with his music director Karl Rankl, immediately began to build a resident company. In December 1946, they shared their first production, Purcell's '' The Fairy-Queen'', with the ballet company. On 14 January 1947, the Covent Garden Opera Company gave its first performance of Bizet
Georges Bizet (; 25 October 18383 June 1875) was a French composer of the Romantic era. Best known for his operas in a career cut short by his early death, Bizet achieved few successes before his final work, ''Carmen'', which has become on ...
's ''Carmen
''Carmen'' () is an opera in four acts by the French composer Georges Bizet. The libretto was written by Henri Meilhac and Ludovic Halévy, based on the Carmen (novella), novella of the same title by Prosper Mérimée. The opera was first perfo ...
''.
Before the grand opening, the Royal Opera House presented one of the Robert Mayer Children's concerts on Saturday, 9 February 1946.
Opera at the Royal Opera House after 1945
Ballet at the Royal Opera House after 1945
Reconstruction from the 1980s forward
 Several renovations had taken place to parts of the house in the 1960s, including improvements to the amphitheatre but the theatre clearly needed a major overhaul. In 1975 the Labour government gave land adjacent to the Royal Opera House for a long-overdue modernisation, refurbishment, and extension. In the early 1980s the first part of a major renovation included an extension to the rear of the theatre on the James Street corner. The development added two new ballet studios, offices, a Chorus Rehearsal Room and the Opera Rehearsal room. Dressing rooms were also added.
Several renovations had taken place to parts of the house in the 1960s, including improvements to the amphitheatre but the theatre clearly needed a major overhaul. In 1975 the Labour government gave land adjacent to the Royal Opera House for a long-overdue modernisation, refurbishment, and extension. In the early 1980s the first part of a major renovation included an extension to the rear of the theatre on the James Street corner. The development added two new ballet studios, offices, a Chorus Rehearsal Room and the Opera Rehearsal room. Dressing rooms were also added.

 By 1995, sufficient funds from the Arts Lottery through
By 1995, sufficient funds from the Arts Lottery through Arts Council England
Arts Council England is an arm's length non-departmental public body of the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport. It is also a registered charity. It was formed in 1994 when the Arts Council of Great Britain was divided into three s ...
and private fundraising had been raised to enable the company to embark upon a major £213 million reconstruction of the building by Carillion
Carillion plc was a British multinational construction and facilities management services company headquartered in Wolverhampton in the United Kingdom, prior to its liquidation in January 2018.
Carillion was created in July 1999, following a ...
, which took place between 1997 and 1999, under the chairmanship of Sir Angus Stirling. This involved the demolition of almost the whole site including several adjacent buildings to make room for a major increase in the size of the complex. The auditorium itself remained, but well over half of the complex is new.
The design team was led by Jeremy Dixon and Edward Jones of Dixon Jones BDP as architects. The acoustic designers were Rob Harris and Jeremy Newton of Arup Acoustics. The building engineer was Arup with Stanhope as developer.
 The new building has the same traditional horseshoe-shaped auditorium as before, but with greatly improved technical, rehearsal, office, and educational facilities. Additionally, a new studio theatre, the Linbury, as well as more public space was created. The inclusion of the adjacent old Floral Hall, which had fallen into disrepair and was used as a scenery store before redevelopment, created a new and extensive public gathering place. The venue is now claimed by the ROH to be the most modern theatre facility in Europe.
Surtitles, projected onto a screen above the proscenium, have been used for all opera performances since they were introduced for school matinees in 1983/4 season. Since the reopening of the theatre in 1999 an electronic libretto system provides translations onto small video screens for some seats, and additional monitors and screens are to be introduced to other parts of the house.
In 2014 design work, known as the Open Up Project, began with the aim of improving the entrances, lobby areas and the Linbury Theatre. As part of the Open Up Project, IQ Projects were tasked with the renovation of the upper floor bar area and restaurant utilising various elements of bespoke glazing.
In October 2020, the BBC reported that the Royal Opera House has lost 60% of its income as a result of restrictions implemented in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. As a consequence, the 1971 ''"
The new building has the same traditional horseshoe-shaped auditorium as before, but with greatly improved technical, rehearsal, office, and educational facilities. Additionally, a new studio theatre, the Linbury, as well as more public space was created. The inclusion of the adjacent old Floral Hall, which had fallen into disrepair and was used as a scenery store before redevelopment, created a new and extensive public gathering place. The venue is now claimed by the ROH to be the most modern theatre facility in Europe.
Surtitles, projected onto a screen above the proscenium, have been used for all opera performances since they were introduced for school matinees in 1983/4 season. Since the reopening of the theatre in 1999 an electronic libretto system provides translations onto small video screens for some seats, and additional monitors and screens are to be introduced to other parts of the house.
In 2014 design work, known as the Open Up Project, began with the aim of improving the entrances, lobby areas and the Linbury Theatre. As part of the Open Up Project, IQ Projects were tasked with the renovation of the upper floor bar area and restaurant utilising various elements of bespoke glazing.
In October 2020, the BBC reported that the Royal Opera House has lost 60% of its income as a result of restrictions implemented in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. As a consequence, the 1971 ''"Portrait of Sir David Webster
The ''Portrait of Sir David Webster'' is a 1971 portrait by the artist David Hockney of the arts administrator David Webster. It was commissioned to mark Webster's retirement as the General Administrator of the Royal Opera House in London. The p ...
"'' by David Hockney, which had hung in the opera house for several decades, was put up for auction at Christie's
Christie's is a British auction house founded in 1766 by James Christie (auctioneer), James Christie. Its main premises are on King Street, St James's in London, at Rockefeller Center in New York City and at Alexandra House in Hong Kong. It is ...
. It eventually sold for £12.8 million. The funds raised from the sale were needed to ensure the survival of the institution. "Significant redundancies" and an appeal for public donations have also been made. In addition, the opera house has applied for a loan to the Culture Recovery Fund.
Facilities
Paul Hamlyn Hall
 The Paul Hamlyn Hall is a large iron and glass structure adjacent to, and with direct access to, the main opera house building. The hall now acts as the atrium and main public area of the opera house, with a champagne bar, restaurant and other hospitality services, and also providing access to the main auditorium at all levels.
The building was formerly known as Floral Hall. It was originally built by the Opera House to house a flower market (also selling fruits and vegetables), hence the name. It was designed by Edward Middleton Barry and opened in 1860. After being used as a concert hall, it became part of the Covent Garden Market in 1887. A fire broke out in the building in 1956, after which it sat derelict. It was acquired by the Opera House in 1977 and used as storage space.
The redevelopment of the Floral Hall as part of the 1990s redevelopment project involved lifting up the cast iron structure to accommodate new public areas for the opera house underneath. The southern side of the hall now connected with another building, so the cast iron south portico was dismantled and rebuilt in Borough Market, where it is separately Grate II heritage listed.
The redevelopment had gone ahead on the strength of a pledge of £10m from the philanthropist Alberto Vilar and for a number of years, it was known as the Vilar Floral Hall; however Vilar failed to make good his pledge. As a result, the name was changed in September 2005 to the Paul Hamlyn Hall, after the opera house received a donation of £10m from the estate of
The Paul Hamlyn Hall is a large iron and glass structure adjacent to, and with direct access to, the main opera house building. The hall now acts as the atrium and main public area of the opera house, with a champagne bar, restaurant and other hospitality services, and also providing access to the main auditorium at all levels.
The building was formerly known as Floral Hall. It was originally built by the Opera House to house a flower market (also selling fruits and vegetables), hence the name. It was designed by Edward Middleton Barry and opened in 1860. After being used as a concert hall, it became part of the Covent Garden Market in 1887. A fire broke out in the building in 1956, after which it sat derelict. It was acquired by the Opera House in 1977 and used as storage space.
The redevelopment of the Floral Hall as part of the 1990s redevelopment project involved lifting up the cast iron structure to accommodate new public areas for the opera house underneath. The southern side of the hall now connected with another building, so the cast iron south portico was dismantled and rebuilt in Borough Market, where it is separately Grate II heritage listed.
The redevelopment had gone ahead on the strength of a pledge of £10m from the philanthropist Alberto Vilar and for a number of years, it was known as the Vilar Floral Hall; however Vilar failed to make good his pledge. As a result, the name was changed in September 2005 to the Paul Hamlyn Hall, after the opera house received a donation of £10m from the estate of Paul Hamlyn
Paul Hamlyn, Baron Hamlyn, (12 February 1926 – 31 August 2001) was a German-born British publisher and philanthropist, who established the Paul Hamlyn Foundation in 1987.
Early life
He was born Paul Bertrand Wolfgang Hamburger in Berlin, Ger ...
, towards its education and development programmes.
As well as acting as a main public area for performances in the main auditorium, the Paul Hamlyn Hall is also used for hosting a number of events, including private functions, dances, exhibitions, concerts, and workshops.
Linbury Studio Theatre
The Linbury Studio Theatre is a flexible, secondary performance space, constructed below ground level within the Royal Opera House. It has retractable raked seating and a floor which can be raised or lowered to form a studio floor, a raised stage, or a stage with orchestra pit. The theatre can accommodate up to 400 patrons and host a variety of different events. It has been used for private functions, traditional theatre shows, and concerts, as well as community and educational events, product launches, dinners and exhibitions, etc., and is one of the most technologically advanced performance venues in London with its own public areas, including a bar and cloakroom. The Linbury is most notable for hosting performances of experimental and independent dance and music, by independent companies and as part of the ROH2, the contemporary producing arm of the Royal Opera House. The Linbury Studio Theatre regularly stages performances by the Royal Ballet School and also hosts theYoung British Dancer of the Year
The Young British Dancer of the Year Competition began in 2000. It is held annually at the Royal Ballet School, London and the Linbury Studio Theatre, Covent Garden. The competition is open to young British and British-trained classical dancers. Th ...
competition.
The venue was constructed as part of the 90s redevelopment of the Royal Opera House. It is named in recognition of donations made by the Linbury Trust towards the redevelopment. The Trust is operated by Lord Sainsbury of Preston Candover and his wife Anya Linden
Anya Linden, Baroness Sainsbury of Preston Candover (''née'' Eltenton; 3 January 1933) is an English retired ballerina and patron of the arts.
Born in Manchester, she spent her childhood in California, where she received her early training wi ...
, a former dancer with the Royal Ballet. The name Linbury is derived from the names Linden and Sainsbury. It was opened in 1999 with a collaboration from three Croydon secondary schools (including Coloma Convent Girls' School and Edenham High School) in an original performance called ''About Face''.
Royal Opera House, Manchester
In 2008 the Royal Opera House andManchester City Council
Manchester City Council is the local authority for Manchester, a city and metropolitan borough in Greater Manchester, England. Manchester is the sixth largest city in England by population. Its city council is composed of 96 councillors, three ...
began planning stages a new development known as Royal Opera House, Manchester. The proposal would have seen the Palace Theatre Palace Theatre, or Palace Theater, is the name of many theatres in different countries, including:
Australia
*Palace Theatre, Melbourne, Victoria
*Palace Theatre, Sydney, New South Wales
Canada
*Palace Theatre, housed in the Robillard Block, Mo ...
in Manchester refurbished, to create a theatre capable of staging productions by both the Royal Ballet and the Royal Opera. It was intended that the Royal Opera House would take residence of the theatre for an annual 18-week season, staging 16 performances by the Royal Opera, 28 performances by the Royal Ballet and other small-scale productions. A year later The Lowry sent an open letter to the then Secretary of State for Culture, Olympics, Media and Sport
The secretary of state for digital, culture, media and sport, also referred to as the culture secretary, is a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, with overall responsibility for strategy and policy across the Department f ...
, Ben Bradshaw
Benjamin Peter James Bradshaw (born 30 August 1960) is a British politician who served as Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport from 2009 to 2010. A member of the Labour Party, he has been Member of Parliament (MP) for Exeter since 1 ...
, Arts Council England, Manchester City Council and the ROH, calling for the scheme, in its current form, to be scrapped. In 2010 it was announced that the project was being shelved as part of larger arts-funding cuts.Alternative link.High House Production Park (High House, Purfleet)
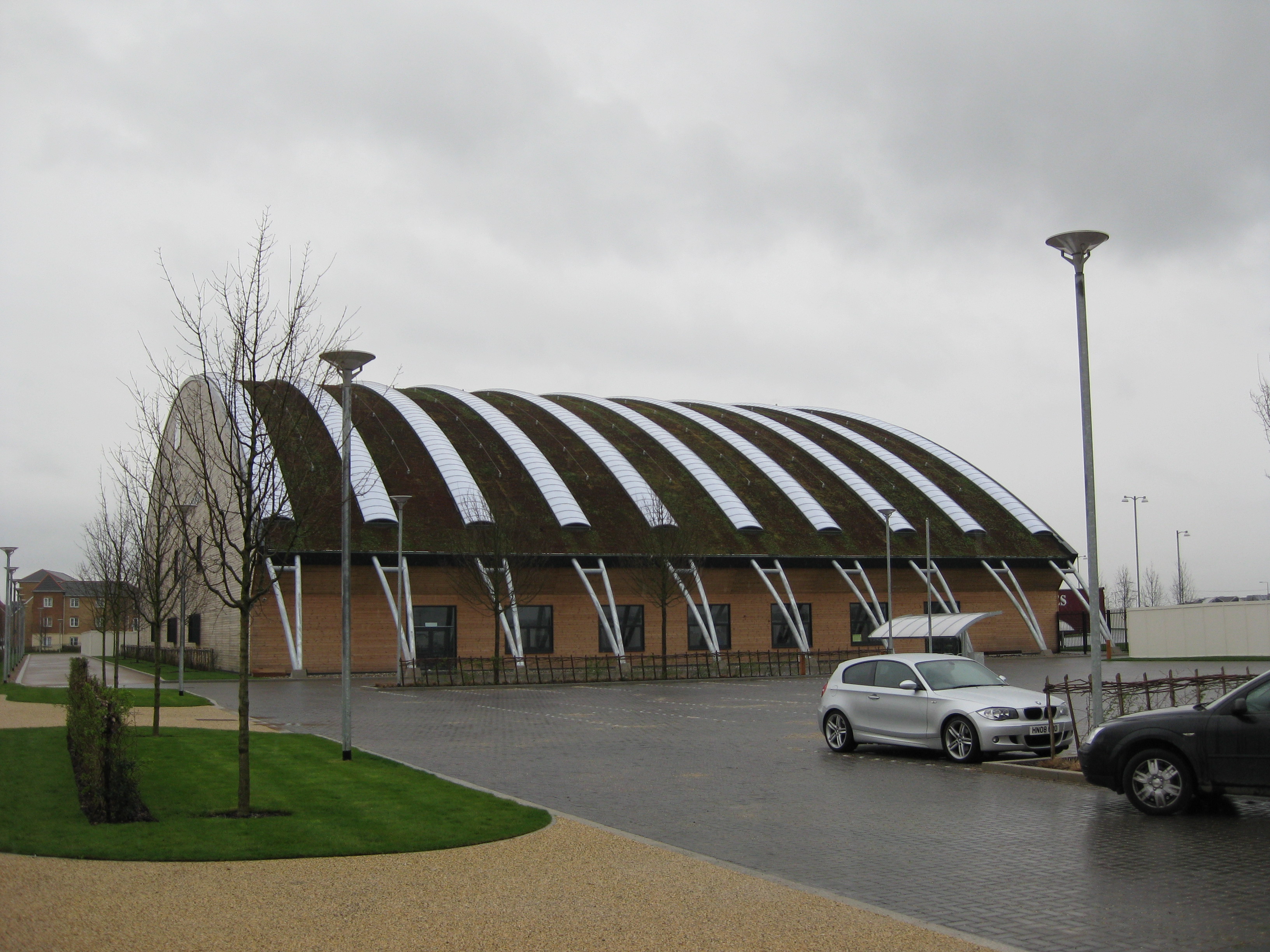
High House, Purfleet
High House is the collective name for a group of historic buildings in Purfleet, Thurrock, Essex, which was used as a farm for hundreds of years, with a Grade II listed house and barn, but with the addition of one of the best dovecotes (dove hous ...
, Essex, on 6 December 2010. The building was designed by Nicholas Hare Architects. "Thurrock launches new creative and cultural hub", 13 December 2010, East of England Development Agency press release on its website eeda.org.ukRetrieved 9 January 2011 The East of England Development Agency, which partly funded developments on the park, notes that "the first phase includes the Royal Opera House's Bob and Tamar Manoukian Production Workshop and Community areas". The Bob and Tamar Manoukian Costume Centre, also designed by Nicholas Hare Associates, opened in September 2015, and provides a costume-making facility for the Royal Opera House and a training centre for students of costume-making from South Essex College. The building also houses the Royal Opera House's collection of historically important costumes. Other elements at High House, Purfleet, include The Backstage Centre, a new technical theatre and music training centre which is currently run by the National College for Creative Industries and was formally opened by
Creative & Cultural Skills
Creative & Cultural Skills is one of the Sector Skills Councils established by the UK Government in 2005 to foster the development of a skilled workforce.
Function
It covers crafts, cultural heritage, jewelry, design, music, performing, literary ...
in March 2013, alongside renovated farm buildings. Acme studios opened a complex of 43 artist studios in Summer 2013.Retrieved 25 November 2010
Other uses
In addition to opera and ballet performances, the Royal Opera House has hosted a number of other events including: *British Academy Film Awards
The British Academy Film Awards, more commonly known as the BAFTA Film Awards is an annual award show hosted by the British Academy of Film and Television Arts (BAFTA) to honour the best British and international contributions to film. The cere ...
– 2008 to 2016
*Laurence Olivier Award
The Laurence Olivier Awards, or simply the Olivier Awards, are presented annually by the Society of London Theatre to recognise excellence in professional theatre in London at an annual ceremony in the capital. The awards were originally known as ...
s – 2012 to 2016
See also
* Owners, lessees and managers of the Royal Opera House, Covent Garden * European Route of Historic TheatresReferences
Notes
Cited sources
* * * * *Further reading
* Allen, Mary, ''A House Divided'', Simon & Schuster, 1998. * Beauvert, Thierry, ''Opera Houses of the World'', The Vendome Press, New York, 1995. * Donaldson, Frances, ''The Royal Opera House in the Twentieth Century'', Weidenfeld & Nicolson, London, 1988. * Earl, John and Sell, Michael ''Guide to British Theatres 1750–1950'', pp. 136–8 (Theatres Trust, 2000) . * Haltrecht, Montague, ''The Quiet Showman: Sir David Webster and the Royal Opera House'', Collins, London, 1975. * Isaacs, Jeremy, ''Never Mind the Moon'', Bantam Press, 1999. *Lebrecht, Norman
Norman Lebrecht (born 11 July 1948) is a British music journalist and author who specializes in classical music. He is best known as the owner of the classical music blog, ''Slipped Disc'', where he frequently publishes articles. Unlike other w ...
, ''Covent Garden: The Untold Story: Dispatches from the English Culture War, 1945–2000'', Northeastern University Press, 2001.
* Lord Drogheda, et al., ''The Covent Garden Album'', Routledge & Kegan Paul, London, 1981.
* Mosse, Kate, ''The House: Inside the Royal Opera House Covent Garden'', BBC Books, London, 1995.
*Robinson, Terry FNational Theatre in Transition: The London Patent Theatre Fires of 1808–1809 and the Old Price Riots.
''BRANCH: Britain, Representation, and Nineteenth-Century History.'' Web. 29 March 2016. * Tooley, John, ''In House: Covent Garden, Fifty Years of Opera and Ballet'', Faber and Faber, London, 1999. * Thubron, Colin (text) and Boursnell, Clive (photos), ''The Royal Opera House Covent Garden'', Hamish Hamilton, London, 1982.
External links
*Royal Opera House Collections Online (Archive Collections Catalogue and Performance Database)
The Royal Ballet School official website
* ttp://www.arthurlloyd.co.uk/RoyalOperaHouseCoventGarden.htm Theatre HistoryArticles, Images, and Archive Material {{Authority control West End theatres The Royal Ballet Opera houses in England Opera in London Grade I listed buildings in the City of Westminster Grade I listed theatres Theatres in the City of Westminster 1660 establishments in England Music venues completed in 1858 Ballet venues in the United Kingdom Covent Garden Theatres completed in 1732 Theatres completed in 1809 Theatres that have burned down Burned buildings and structures in the United Kingdom Edward Middleton Barry buildings