Royal Gallery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the
 The site of the Palace of Westminster was strategically important during the
The site of the Palace of Westminster was strategically important during the  Being originally a royal residence, the Palace included no purpose-built chambers for the two Houses. Important state ceremonies took place in the Painted Chamber – originally built in the 13th century as the main bedchamber for King Henry III (). In 1801 the Upper House moved into the larger White Chamber (also known as the Lesser Hall), which had housed the
Being originally a royal residence, the Palace included no purpose-built chambers for the two Houses. Important state ceremonies took place in the Painted Chamber – originally built in the 13th century as the main bedchamber for King Henry III (). In 1801 the Upper House moved into the larger White Chamber (also known as the Lesser Hall), which had housed the
 The Lords Chamber was completed in 1847, and the Commons Chamber in 1852 (at which point architect
The Lords Chamber was completed in 1847, and the Commons Chamber in 1852 (at which point architect
 The worst raid took place in the night of 10–11 May 1941, when the Palace took at least twelve hits and three people (two policemen and Resident Superintendent of the House of Lords Edward Elliott) were killed. Fell and Mackenzie (1994), p. 27. An incendiary bomb hit the chamber of the House of Commons and set it on fire; another set the roof of Westminster Hall alight. The firefighters could not save both, and a decision was taken to try to rescue the Hall. In this they were successful; the abandoned Commons Chamber, on the other hand, was destroyed, as was the Members' Lobby. A bomb also struck the Lords Chamber, but went through the floor without exploding. The Clock Tower took a hit by a small bomb or anti-aircraft shell at the eaves of the roof, suffering much damage there. All the glass on the south dial was blown out, but the hands and bells were not affected, and the Great Clock continued to keep time accurately.
Following the destruction of the Commons Chamber, the Lords offered their own
The worst raid took place in the night of 10–11 May 1941, when the Palace took at least twelve hits and three people (two policemen and Resident Superintendent of the House of Lords Edward Elliott) were killed. Fell and Mackenzie (1994), p. 27. An incendiary bomb hit the chamber of the House of Commons and set it on fire; another set the roof of Westminster Hall alight. The firefighters could not save both, and a decision was taken to try to rescue the Hall. In this they were successful; the abandoned Commons Chamber, on the other hand, was destroyed, as was the Members' Lobby. A bomb also struck the Lords Chamber, but went through the floor without exploding. The Clock Tower took a hit by a small bomb or anti-aircraft shell at the eaves of the roof, suffering much damage there. All the glass on the south dial was blown out, but the hands and bells were not affected, and the Great Clock continued to keep time accurately.
Following the destruction of the Commons Chamber, the Lords offered their own
 The Palace of Westminster, which is a Grade 1 listed building, is in urgent need of extensive restoration to its fabric. A 2012 pre-feasibility report set out several options, including the possibility of Parliament moving to other premises while work is carried out. At the same time, the option of moving Parliament to a new location was discounted, with staying at the Westminster site preferred. An Independent Options Appraisal Report released in June 2015 found that the cost to restore the Palace of Westminster could be as much as £7.1 billion if MPs were to remain at the Palace whilst works take place. MPs decided in 2016 to vacate the building for six years starting in 2022. In January 2018, the House of Commons voted for both houses to vacate the Palace of Westminster to allow for a complete refurbishment of the building which may take up to six years starting in 2025. It is expected that the House of Commons will be temporarily housed in a replica chamber to be located in Richmond House in Whitehall and the House of Lords will be housed at the Queen Elizabeth II Conference Centre in Parliament Square.
The Palace of Westminster, which is a Grade 1 listed building, is in urgent need of extensive restoration to its fabric. A 2012 pre-feasibility report set out several options, including the possibility of Parliament moving to other premises while work is carried out. At the same time, the option of moving Parliament to a new location was discounted, with staying at the Westminster site preferred. An Independent Options Appraisal Report released in June 2015 found that the cost to restore the Palace of Westminster could be as much as £7.1 billion if MPs were to remain at the Palace whilst works take place. MPs decided in 2016 to vacate the building for six years starting in 2022. In January 2018, the House of Commons voted for both houses to vacate the Palace of Westminster to allow for a complete refurbishment of the building which may take up to six years starting in 2025. It is expected that the House of Commons will be temporarily housed in a replica chamber to be located in Richmond House in Whitehall and the House of Lords will be housed at the Queen Elizabeth II Conference Centre in Parliament Square.
Accessed 4 January 2014. They selected Anston, a sand-coloured magnesian
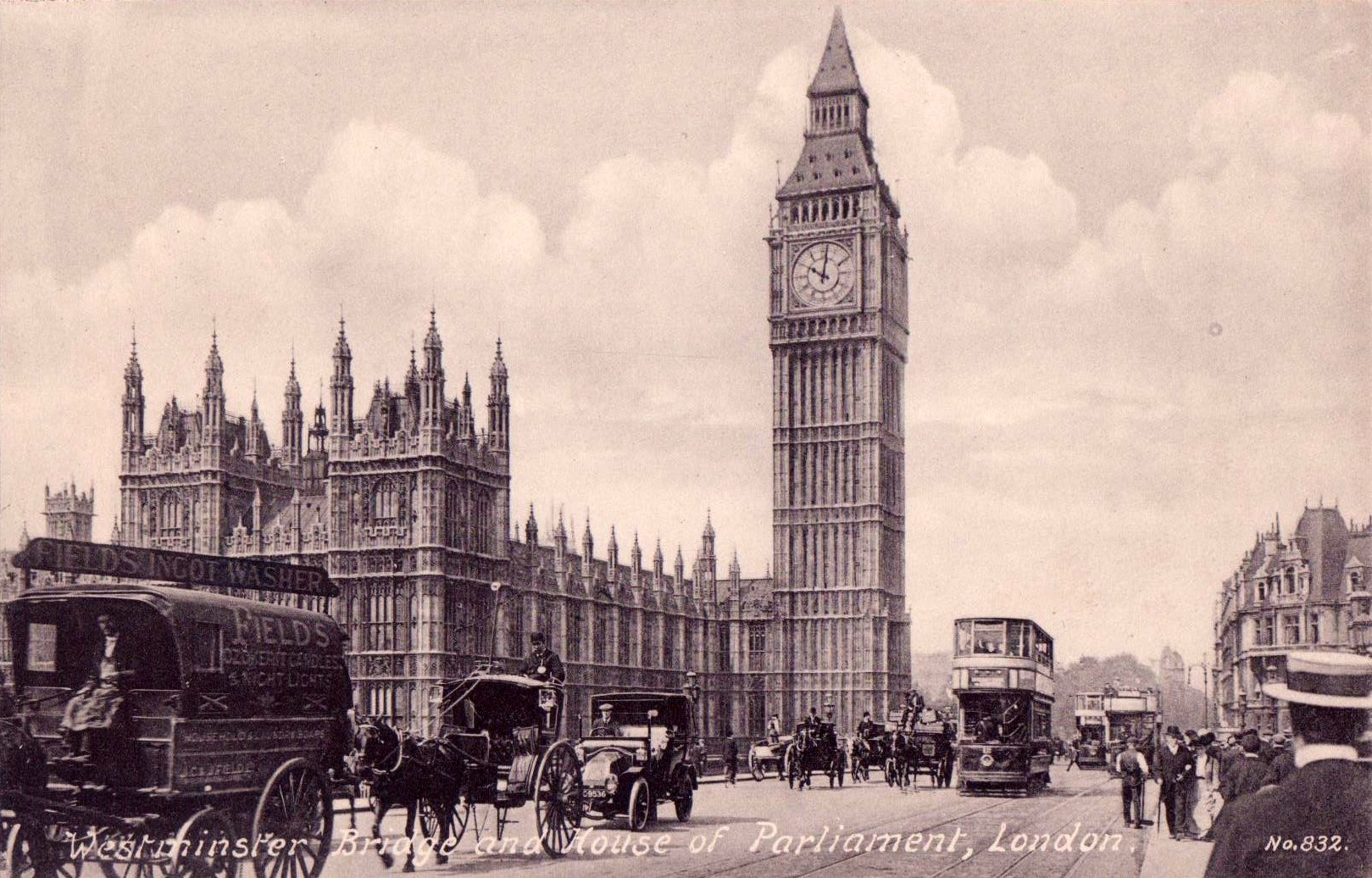
 The Palace of Westminster has three main towers. Of these, the largest and tallest is the
The Palace of Westminster has three main towers. Of these, the largest and tallest is the  At the north end of the Palace rises the most famous of the towers, the Elizabeth Tower, commonly known as
At the north end of the Palace rises the most famous of the towers, the Elizabeth Tower, commonly known as  The shortest of the Palace's three principal towers (at ), the octagonal Central Tower stands over the middle of the building, immediately above the Central Lobby. It was added to the plans on the insistence of Dr.
The shortest of the Palace's three principal towers (at ), the octagonal Central Tower stands over the middle of the building, immediately above the Central Lobby. It was added to the plans on the insistence of Dr.
 There are a number of small gardens surrounding the Palace of Westminster. Victoria Tower Gardens is open as a public park along the side of the river south of the palace. Black Rod's Garden (named after the office of
There are a number of small gardens surrounding the Palace of Westminster. Victoria Tower Gardens is open as a public park along the side of the river south of the palace. Black Rod's Garden (named after the office of
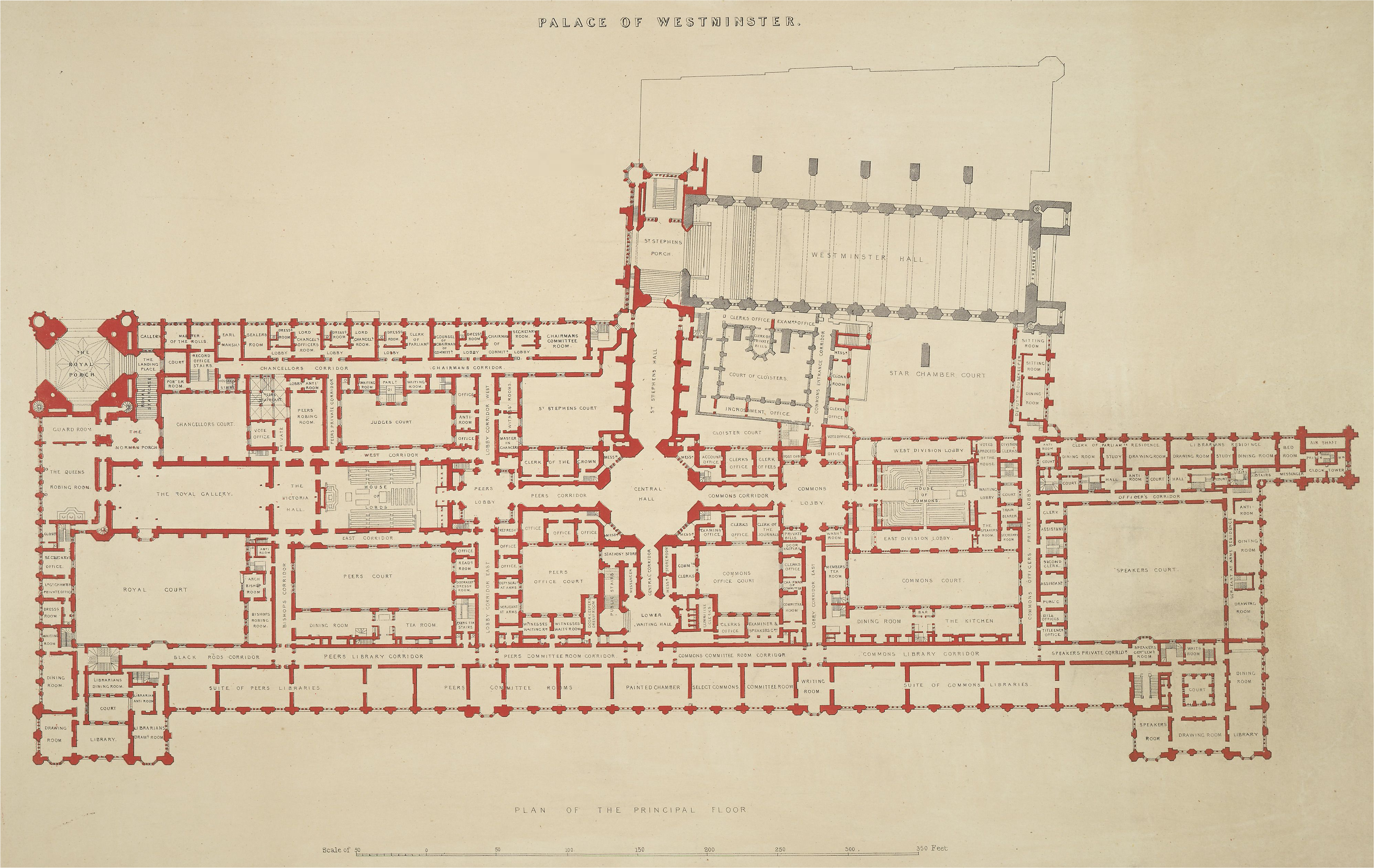 Instead of one main entrance, the Palace features separate entrances for the different user groups of the building. The Sovereign's Entrance, at the base of the Victoria Tower, is located in the south-west corner of the Palace and is the starting point of the royal procession route, the suite of ceremonial rooms used by the monarch at State Openings of Parliament. This consists of the Royal Staircase, the Norman Porch, the Robing Room, the Royal Gallery and the Prince's Chamber, and culminates in the Lords Chamber, where the ceremony takes place. Members of the House of Lords use the Peers' Entrance in the middle of the Old Palace Yard front, which is covered by a stone
Instead of one main entrance, the Palace features separate entrances for the different user groups of the building. The Sovereign's Entrance, at the base of the Victoria Tower, is located in the south-west corner of the Palace and is the starting point of the royal procession route, the suite of ceremonial rooms used by the monarch at State Openings of Parliament. This consists of the Royal Staircase, the Norman Porch, the Robing Room, the Royal Gallery and the Prince's Chamber, and culminates in the Lords Chamber, where the ceremony takes place. Members of the House of Lords use the Peers' Entrance in the middle of the Old Palace Yard front, which is covered by a stone
 The Prince's Chamber is a small wiktionary:anteroom, anteroom between the Royal Gallery and the Lords Chamber, named after the room adjoining the Parliament Chamber in the Old Palace of Westminster. Thanks to its location, it is a place where members of the Lords meet to discuss business of the House. Several doors lead out of the room, to the Division of the assembly, division lobbies of the House of Lords and to a number of important offices.
The theme of the Prince's Chamber is Tudor history, and 28 oil portraits painted on panels around the room depict members of the Tudor dynasty. They are the work of Richard Burchett and his pupils, and their creation entailed extensive research, which contributed to the founding of the National Portrait Gallery, London, National Portrait Gallery in 1856. 12 bronze bas-reliefs are set into the wall below the portraits, executed by William Theed in 1855–1857. Scenes included are ''The Field of the Cloth of Gold'', ''The Escape of Mary, Queen of Scots'' and ''Walter Raleigh, Raleigh Spreading His Cloak As a Carpet for the Queen''. Above the portraits, at window level, there are compartments intended for copies of six of the ten Armada tapestries, which hung in the chamber of the House of Lords until their destruction in the 1834 fire and depicted the defeat of the Spanish Armada in 1588. The project was put on hold in 1861 (by which time only one painting had been completed), and was not revived until 2007; , all six paintings have been finished and are on display in the Royal Gallery. They are scheduled to be fixed in the Prince's Chamber in the following months.
The room also contains a statue of Queen Victoria, seated on a throne (itself placed on a pedestal) and holding a sceptre and a laurel crown, which show that she both governs and rules. This figure is flanked by allegorical statues of Justice and Clemency—the former with a bare sword and an inflexible expression and the latter showing sympathy and offering an olive branch. The sculptural ensemble, made of white marble and carved by John Gibson (sculptor), John Gibson in 1855, reaches in height; its size has long been considered out of proportion with the fittings of the Prince's Chamber, and the flanking statues ended up in storage between 1955 and 1976. However, the size and location of the group, in the archway opposite the doors to the Royal Gallery (which are removed before State Openings of Parliament to facilitate the royal procession), indicate that it was meant to be seen from a distance, and to symbolically remind the monarch of their royal duties as they would walk down the Royal Gallery on their way to deliver their speech.
The Prince's Chamber is a small wiktionary:anteroom, anteroom between the Royal Gallery and the Lords Chamber, named after the room adjoining the Parliament Chamber in the Old Palace of Westminster. Thanks to its location, it is a place where members of the Lords meet to discuss business of the House. Several doors lead out of the room, to the Division of the assembly, division lobbies of the House of Lords and to a number of important offices.
The theme of the Prince's Chamber is Tudor history, and 28 oil portraits painted on panels around the room depict members of the Tudor dynasty. They are the work of Richard Burchett and his pupils, and their creation entailed extensive research, which contributed to the founding of the National Portrait Gallery, London, National Portrait Gallery in 1856. 12 bronze bas-reliefs are set into the wall below the portraits, executed by William Theed in 1855–1857. Scenes included are ''The Field of the Cloth of Gold'', ''The Escape of Mary, Queen of Scots'' and ''Walter Raleigh, Raleigh Spreading His Cloak As a Carpet for the Queen''. Above the portraits, at window level, there are compartments intended for copies of six of the ten Armada tapestries, which hung in the chamber of the House of Lords until their destruction in the 1834 fire and depicted the defeat of the Spanish Armada in 1588. The project was put on hold in 1861 (by which time only one painting had been completed), and was not revived until 2007; , all six paintings have been finished and are on display in the Royal Gallery. They are scheduled to be fixed in the Prince's Chamber in the following months.
The room also contains a statue of Queen Victoria, seated on a throne (itself placed on a pedestal) and holding a sceptre and a laurel crown, which show that she both governs and rules. This figure is flanked by allegorical statues of Justice and Clemency—the former with a bare sword and an inflexible expression and the latter showing sympathy and offering an olive branch. The sculptural ensemble, made of white marble and carved by John Gibson (sculptor), John Gibson in 1855, reaches in height; its size has long been considered out of proportion with the fittings of the Prince's Chamber, and the flanking statues ended up in storage between 1955 and 1976. However, the size and location of the group, in the archway opposite the doors to the Royal Gallery (which are removed before State Openings of Parliament to facilitate the royal procession), indicate that it was meant to be seen from a distance, and to symbolically remind the monarch of their royal duties as they would walk down the Royal Gallery on their way to deliver their speech.
 The Chamber of the
The Chamber of the
 Originally named "Octagon Hall" because of its shape, the Central Lobby is the heart of the Palace of Westminster. It lies directly below the Central Tower and forms a busy crossroads between the House of Lords to the south, the House of Commons to the north, St Stephen's Hall and the public entrance to the west, and the Lower Waiting Hall and the libraries to the east. Its location halfway between the two debating chambers has led constitutional theorist Erskine May, 1st Baron Farnborough, Erskine May to describe the Lobby as "the political centre of the British Empire", and allows a person standing under the great chandelier to see both the Royal Throne and the Speaker's Chair, provided that all the intervening doors are open. Constituents may meet their Members of Parliament here, even without an appointment, and this practice is the origin of the term ''lobbying''. The hall is also the theatre of the Speaker's Procession, which passes from here on its way to the Commons Chamber before every sitting of the House.
The Central Lobby measures across and from the floor to the centre of the vaulted ceiling. The panels between the vault's ribs are covered with Venetian glass mosaic displaying floral emblems and heraldic badges, and the bosses in the intersections of the ribs are also carved into heraldic symbols. Each wall of the Lobby is contained in an arch ornamented with statues of English and Scottish monarchs; on four sides there are doorways, and the Tympanum (architecture), tympana above them are adorned with mosaics representing the patron saints of the United Kingdom's constituent nations:
Originally named "Octagon Hall" because of its shape, the Central Lobby is the heart of the Palace of Westminster. It lies directly below the Central Tower and forms a busy crossroads between the House of Lords to the south, the House of Commons to the north, St Stephen's Hall and the public entrance to the west, and the Lower Waiting Hall and the libraries to the east. Its location halfway between the two debating chambers has led constitutional theorist Erskine May, 1st Baron Farnborough, Erskine May to describe the Lobby as "the political centre of the British Empire", and allows a person standing under the great chandelier to see both the Royal Throne and the Speaker's Chair, provided that all the intervening doors are open. Constituents may meet their Members of Parliament here, even without an appointment, and this practice is the origin of the term ''lobbying''. The hall is also the theatre of the Speaker's Procession, which passes from here on its way to the Commons Chamber before every sitting of the House.
The Central Lobby measures across and from the floor to the centre of the vaulted ceiling. The panels between the vault's ribs are covered with Venetian glass mosaic displaying floral emblems and heraldic badges, and the bosses in the intersections of the ribs are also carved into heraldic symbols. Each wall of the Lobby is contained in an arch ornamented with statues of English and Scottish monarchs; on four sides there are doorways, and the Tympanum (architecture), tympana above them are adorned with mosaics representing the patron saints of the United Kingdom's constituent nations:
 Continuing north from the Central Lobby is the Commons' Corridor. It is of almost identical design to its southern counterpart and is decorated with scenes of 17th-century political history between the Civil War and the Glorious Revolution, Revolution of 1688. They were painted by Edward Matthew Ward and include subjects like ''George Monck, 1st Duke of Albemarle, Monk Declaring for a Free Parliament'' and ''The Lords and Commons Presenting the Crown to William III of England, William III and Mary II of England, Mary II in the Banqueting Hall''. Then, mirroring the arrangement at the Lords part of the Palace, is another antechamber, the Members' Lobby. In this room, Members of Parliament hold discussions or negotiations, and are often interviewed by accredited journalists, collectively known as "The Lobby".
The room is similar to the Peers' Lobby but plainer in design and slightly larger, forming a cube on all sides. After the heavy damage it sustained in the 1941 bombing, it was rebuilt in a simplified style, something most evident in the floor, which is almost completely unadorned. The archway of the door leading into the Commons Chamber has been left unrepaired as a reminder of the evils of war, and is now known as the Rubble Arch or Churchill Arch. It is flanked by bronze statues of Winston Churchill and David Lloyd George, the prime ministers who led Britain through the Second and First World War respectively; a foot of each is conspicuously shiny, a result of a long tradition of MPs rubbing them for good luck on their way in before their maiden speech. The Lobby contains the busts and statues of most 20th-century prime ministers, as well as two large boards where MPs can receive letters and telephone messages, designed for the use of the House and installed in the early 1960s.
Continuing north from the Central Lobby is the Commons' Corridor. It is of almost identical design to its southern counterpart and is decorated with scenes of 17th-century political history between the Civil War and the Glorious Revolution, Revolution of 1688. They were painted by Edward Matthew Ward and include subjects like ''George Monck, 1st Duke of Albemarle, Monk Declaring for a Free Parliament'' and ''The Lords and Commons Presenting the Crown to William III of England, William III and Mary II of England, Mary II in the Banqueting Hall''. Then, mirroring the arrangement at the Lords part of the Palace, is another antechamber, the Members' Lobby. In this room, Members of Parliament hold discussions or negotiations, and are often interviewed by accredited journalists, collectively known as "The Lobby".
The room is similar to the Peers' Lobby but plainer in design and slightly larger, forming a cube on all sides. After the heavy damage it sustained in the 1941 bombing, it was rebuilt in a simplified style, something most evident in the floor, which is almost completely unadorned. The archway of the door leading into the Commons Chamber has been left unrepaired as a reminder of the evils of war, and is now known as the Rubble Arch or Churchill Arch. It is flanked by bronze statues of Winston Churchill and David Lloyd George, the prime ministers who led Britain through the Second and First World War respectively; a foot of each is conspicuously shiny, a result of a long tradition of MPs rubbing them for good luck on their way in before their maiden speech. The Lobby contains the busts and statues of most 20th-century prime ministers, as well as two large boards where MPs can receive letters and telephone messages, designed for the use of the House and installed in the early 1960s.
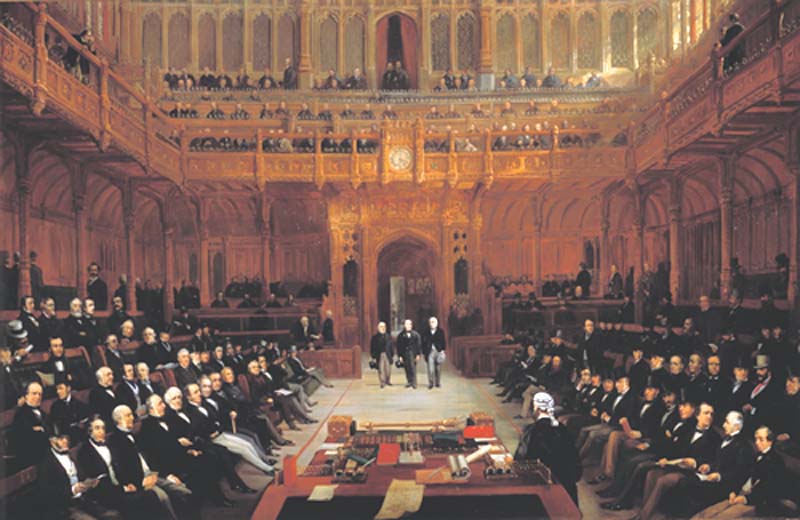
 The debating chamber, Chamber of the
The debating chamber, Chamber of the  At the north end of the Chamber is the Speaker of the House of Commons (United Kingdom), Speaker's Chair, a present to Parliament from the Commonwealth of Australia. The current British Speaker's Chair is an exact copy of the Speaker's Chair given to Australia, by the House of Commons, to celebrate the opening of Old Parliament House, Canberra. In front of the Speaker's Chair is the Table of the House, at which the clerks sit, and on which is placed the Commons' ceremonial mace. The Table was a gift from Canada. The dispatch boxes, which front-bench Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Members of Parliament (MPs) often lean on or rest notes on during Questions and speeches, are a gift from New Zealand. There are green benches on either side of the House; members of the Government party occupy benches on the Speaker's right, while those of the Opposition occupy benches on the Speaker's left. There are no cross-benches as in the House of Lords. The Chamber is relatively small, and can accommodate only 427 of the 650 Members of Parliament—during Prime Minister's Questions and in major debates MPs stand at either end of the House.
By tradition, the British Sovereign does not enter the Chamber of the House of Commons. The last monarch to do so was King Charles I, in 1642. The King sought to arrest five Members of Parliament on charges of high treason, but when he asked the Speaker, William Lenthall, if he had any knowledge of the whereabouts of these individuals, Lenthall famously replied: "May it please your Majesty, I have neither eyes to see nor tongue to speak in this place but as the House is pleased to direct me, whose servant I am here." Since then, in the
At the north end of the Chamber is the Speaker of the House of Commons (United Kingdom), Speaker's Chair, a present to Parliament from the Commonwealth of Australia. The current British Speaker's Chair is an exact copy of the Speaker's Chair given to Australia, by the House of Commons, to celebrate the opening of Old Parliament House, Canberra. In front of the Speaker's Chair is the Table of the House, at which the clerks sit, and on which is placed the Commons' ceremonial mace. The Table was a gift from Canada. The dispatch boxes, which front-bench Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Members of Parliament (MPs) often lean on or rest notes on during Questions and speeches, are a gift from New Zealand. There are green benches on either side of the House; members of the Government party occupy benches on the Speaker's right, while those of the Opposition occupy benches on the Speaker's left. There are no cross-benches as in the House of Lords. The Chamber is relatively small, and can accommodate only 427 of the 650 Members of Parliament—during Prime Minister's Questions and in major debates MPs stand at either end of the House.
By tradition, the British Sovereign does not enter the Chamber of the House of Commons. The last monarch to do so was King Charles I, in 1642. The King sought to arrest five Members of Parliament on charges of high treason, but when he asked the Speaker, William Lenthall, if he had any knowledge of the whereabouts of these individuals, Lenthall famously replied: "May it please your Majesty, I have neither eyes to see nor tongue to speak in this place but as the House is pleased to direct me, whose servant I am here." Since then, in the
 Westminster Hall, the oldest existing part of the Palace of Westminster, was erected in 1097 by William II of England, King William II ('William Rufus'), at which point it was the largest hall in Europe. The roof was probably originally supported by pillars, giving three aisles, but during the reign of Richard II of England, King Richard II, this was replaced by a hammerbeam roof by the royal carpenter Hugh Herland, "the greatest creation of medieval timber architecture", which allowed the original three aisles to be replaced with a single huge open space, with a dais at the end. The new roof was commissioned in 1393. Richard's master builder Henry Yevele retained the original dimensions, refacing the walls, with fifteen life-size statues of kings placed in niches. The rebuilding had been begun by King Henry III in 1245, but by Richard's time had been dormant for over a century. In Westminster Hall, the favourite heraldic badge of Richard II – a white hart, chained, and in an attitude of rest – is repeated eighty-three times, without any of them being an exact copy of another.
The largest clearspan medieval roof in England, Westminster Hall's roof measures . Oak timbers for the roof came from royal woods in Hampshire and from parks in Hertfordshire and from that of William Crozier of Stoke d'Abernon, who supplied over 600 oaks in Surrey, among other sources; they were assembled near Farnham, Surrey, away. Accounts record the large number of wagons and barges which delivered the Timber framing, jointed timbers to Westminster for assembly.
Westminster Hall, the oldest existing part of the Palace of Westminster, was erected in 1097 by William II of England, King William II ('William Rufus'), at which point it was the largest hall in Europe. The roof was probably originally supported by pillars, giving three aisles, but during the reign of Richard II of England, King Richard II, this was replaced by a hammerbeam roof by the royal carpenter Hugh Herland, "the greatest creation of medieval timber architecture", which allowed the original three aisles to be replaced with a single huge open space, with a dais at the end. The new roof was commissioned in 1393. Richard's master builder Henry Yevele retained the original dimensions, refacing the walls, with fifteen life-size statues of kings placed in niches. The rebuilding had been begun by King Henry III in 1245, but by Richard's time had been dormant for over a century. In Westminster Hall, the favourite heraldic badge of Richard II – a white hart, chained, and in an attitude of rest – is repeated eighty-three times, without any of them being an exact copy of another.
The largest clearspan medieval roof in England, Westminster Hall's roof measures . Oak timbers for the roof came from royal woods in Hampshire and from parks in Hertfordshire and from that of William Crozier of Stoke d'Abernon, who supplied over 600 oaks in Surrey, among other sources; they were assembled near Farnham, Surrey, away. Accounts record the large number of wagons and barges which delivered the Timber framing, jointed timbers to Westminster for assembly.
 Westminster Hall has served numerous functions. Until the 19th century, it was regularly used for judicial purposes, housing three of the most important courts in the land: the Court of King's Bench (England), Court of King's Bench, the Court of Common Pleas (England), Court of Common Pleas and the Court of Chancery. In the reign of Henry II of England, Henry II (1154–89) a royal decree established a fixed sitting of judges in the Hall. In 1215, Magna Carta stipulated that these courts would sit regularly in the Hall for the convenience of litigants. In 1875, the courts were amalgamated into the High Court of Justice, which continued to have chambers adjacent to Westminster Hall until moved to the then new Royal Courts of Justice building in 1882. In addition to regular courts, Westminster Hall also housed important state trials, including impeachment trials and the state trials of King Charles I at the end of the English Civil War, William Wallace, Thomas More, Cardinal John Fisher, Guy Fawkes, the Thomas Wentworth, 1st Earl of Strafford, Earl of Strafford, the rebel Scottish lords of the 1715 and 1745 uprisings, and Impeachment of Warren Hastings, Warren Hastings. The St Stephen's Porch end of the Hall displays under the stained glass window the Parliamentary War Memorial listing on eight panels the names of Members and staff of both Houses of Parliament and their sons killed serving in the First World War; the window itself, installed in 1952, commemorates members and staff of both Houses who died in the Second World War. In 2012, a new stained glass window commemorating Queen Elizabeth II's diamond jubilee was installed opposite this window, at the other end of the hall.
Westminster Hall has served numerous functions. Until the 19th century, it was regularly used for judicial purposes, housing three of the most important courts in the land: the Court of King's Bench (England), Court of King's Bench, the Court of Common Pleas (England), Court of Common Pleas and the Court of Chancery. In the reign of Henry II of England, Henry II (1154–89) a royal decree established a fixed sitting of judges in the Hall. In 1215, Magna Carta stipulated that these courts would sit regularly in the Hall for the convenience of litigants. In 1875, the courts were amalgamated into the High Court of Justice, which continued to have chambers adjacent to Westminster Hall until moved to the then new Royal Courts of Justice building in 1882. In addition to regular courts, Westminster Hall also housed important state trials, including impeachment trials and the state trials of King Charles I at the end of the English Civil War, William Wallace, Thomas More, Cardinal John Fisher, Guy Fawkes, the Thomas Wentworth, 1st Earl of Strafford, Earl of Strafford, the rebel Scottish lords of the 1715 and 1745 uprisings, and Impeachment of Warren Hastings, Warren Hastings. The St Stephen's Porch end of the Hall displays under the stained glass window the Parliamentary War Memorial listing on eight panels the names of Members and staff of both Houses of Parliament and their sons killed serving in the First World War; the window itself, installed in 1952, commemorates members and staff of both Houses who died in the Second World War. In 2012, a new stained glass window commemorating Queen Elizabeth II's diamond jubilee was installed opposite this window, at the other end of the hall.
 Westminster Hall has also served ceremonial functions. From the twelfth century to the nineteenth, coronation banquets honouring new monarchs were held here. The last coronation banquet was that of King George IV, held in 1821; his successor, William IV of the United Kingdom, William IV, abandoned the idea because he deemed it too expensive. The Hall has been used as a place for lying in state during State funeral, state and ceremonial funerals. Such an honour is usually reserved for the Sovereign and for their consorts; the only non-royals to receive it in the twentieth century were Frederick Sleigh Roberts, 1st Earl Roberts (1914), the 48 victims of the crash of the airship R101 (1930) and Winston Churchill (1965). In 2002 the hall was used for the lying in state of Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother, and in 2022, the hall was used for the lying in state of Elizabeth II, Queen Elizabeth II. Around 250,000 mourners filed past the coffin, which resulted in the delamination of the Yorkstone floor.
The two Houses have presented ceremonial Addresses to the Crown in Westminster Hall on important public occasions. For example, Addresses were presented at Elizabeth II's Silver Jubilee of Elizabeth II, Silver Jubilee (1977), Golden Jubilee of Elizabeth II, Golden Jubilee (2002) and Diamond Jubilee of Elizabeth II, Diamond Jubilee (2012), the Accession of Charles III (2022), the 300th anniversary of the Glorious Revolution (1988), and the fiftieth anniversary of the end of the Second World War (1995).
It is considered a rare privilege for a foreign leader to be invited to address both Houses of Parliament in Westminster Hall. Since the Second World War, the only leaders to have done so have been French president Charles de Gaulle in 1960, South African president Nelson Mandela in 1996, Pope Benedict XVI in 2010, U.S. president Barack Obama in 2011 and Burma, Burmese opposition leader Aung San Suu Kyi in 2012. President Obama was the first US president to be invited to use the Hall for an address to Parliament and Aung San Suu Kyi was the first non-head of state to be given the accolade of addressing MPs and peers in Westminster Hall.
Following reforms in 1999, the House of Commons now uses the Grand Committee Room next to Westminster Hall as an additional debating chamber. (Although it is not part of the main hall, these are usually spoken of as Westminster Hall debates.) In contrast with the two main Chambers, in which the government and opposition benches directly face each other, the seating in the Grand Committee Room is laid out in a U-shape, a pattern meant to reflect the non-partisan nature of the debates there.
Westminster Hall has also served ceremonial functions. From the twelfth century to the nineteenth, coronation banquets honouring new monarchs were held here. The last coronation banquet was that of King George IV, held in 1821; his successor, William IV of the United Kingdom, William IV, abandoned the idea because he deemed it too expensive. The Hall has been used as a place for lying in state during State funeral, state and ceremonial funerals. Such an honour is usually reserved for the Sovereign and for their consorts; the only non-royals to receive it in the twentieth century were Frederick Sleigh Roberts, 1st Earl Roberts (1914), the 48 victims of the crash of the airship R101 (1930) and Winston Churchill (1965). In 2002 the hall was used for the lying in state of Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother, and in 2022, the hall was used for the lying in state of Elizabeth II, Queen Elizabeth II. Around 250,000 mourners filed past the coffin, which resulted in the delamination of the Yorkstone floor.
The two Houses have presented ceremonial Addresses to the Crown in Westminster Hall on important public occasions. For example, Addresses were presented at Elizabeth II's Silver Jubilee of Elizabeth II, Silver Jubilee (1977), Golden Jubilee of Elizabeth II, Golden Jubilee (2002) and Diamond Jubilee of Elizabeth II, Diamond Jubilee (2012), the Accession of Charles III (2022), the 300th anniversary of the Glorious Revolution (1988), and the fiftieth anniversary of the end of the Second World War (1995).
It is considered a rare privilege for a foreign leader to be invited to address both Houses of Parliament in Westminster Hall. Since the Second World War, the only leaders to have done so have been French president Charles de Gaulle in 1960, South African president Nelson Mandela in 1996, Pope Benedict XVI in 2010, U.S. president Barack Obama in 2011 and Burma, Burmese opposition leader Aung San Suu Kyi in 2012. President Obama was the first US president to be invited to use the Hall for an address to Parliament and Aung San Suu Kyi was the first non-head of state to be given the accolade of addressing MPs and peers in Westminster Hall.
Following reforms in 1999, the House of Commons now uses the Grand Committee Room next to Westminster Hall as an additional debating chamber. (Although it is not part of the main hall, these are usually spoken of as Westminster Hall debates.) In contrast with the two main Chambers, in which the government and opposition benches directly face each other, the seating in the Grand Committee Room is laid out in a U-shape, a pattern meant to reflect the non-partisan nature of the debates there.
 The Lady Usher of the Black Rod oversees security for the House of Lords, and the Serjeant at Arms of the British House of Commons, Serjeant at Arms does the same for the House of Commons. These officers, however, have primarily ceremonial roles outside the actual chambers of their respective Houses. Security is the responsibility of the Parliamentary Security Director. Parliament has its own professional security force. Tradition still dictates that only the Serjeant at Arms may enter the Commons chamber armed.
With rising concern about the possibility that a vehicle full of explosives could be driven into the building, a series of concrete blocks were placed in the roadway in 2003. On the river, an exclusion zone extending from the bank exists, which no unauthorised vessels are allowed to enter.
The Serious Organised Crime and Police Act 2005 formerly made it illegal to hold a protest near the Palace, or anywhere else within a designated area extending up to from Parliament Square, without authorisation from the Metropolitan Police. The Act also restricted the operation of loudspeakers in the designated area. These provisions were repealed by the Police Reform and Social Responsibility Act 2011, which replaced them with a total ban on tents and sleeping bags in Parliament Square, as well as a prohibition on the use of loudspeakers in the Square without permission from the relevant local authority.
Members of the public continue to have access to the Strangers' Gallery in the House of Commons. Visitors pass through metal detectors and their possessions are scanned. Police from the Palace of Westminster Division of the Metropolitan Police, supported by some armed police from the Diplomatic Protection Group, are always on duty in and around the Palace.
The Lady Usher of the Black Rod oversees security for the House of Lords, and the Serjeant at Arms of the British House of Commons, Serjeant at Arms does the same for the House of Commons. These officers, however, have primarily ceremonial roles outside the actual chambers of their respective Houses. Security is the responsibility of the Parliamentary Security Director. Parliament has its own professional security force. Tradition still dictates that only the Serjeant at Arms may enter the Commons chamber armed.
With rising concern about the possibility that a vehicle full of explosives could be driven into the building, a series of concrete blocks were placed in the roadway in 2003. On the river, an exclusion zone extending from the bank exists, which no unauthorised vessels are allowed to enter.
The Serious Organised Crime and Police Act 2005 formerly made it illegal to hold a protest near the Palace, or anywhere else within a designated area extending up to from Parliament Square, without authorisation from the Metropolitan Police. The Act also restricted the operation of loudspeakers in the designated area. These provisions were repealed by the Police Reform and Social Responsibility Act 2011, which replaced them with a total ban on tents and sleeping bags in Parliament Square, as well as a prohibition on the use of loudspeakers in the Square without permission from the relevant local authority.
Members of the public continue to have access to the Strangers' Gallery in the House of Commons. Visitors pass through metal detectors and their possessions are scanned. Police from the Palace of Westminster Division of the Metropolitan Police, supported by some armed police from the Diplomatic Protection Group, are always on duty in and around the Palace.
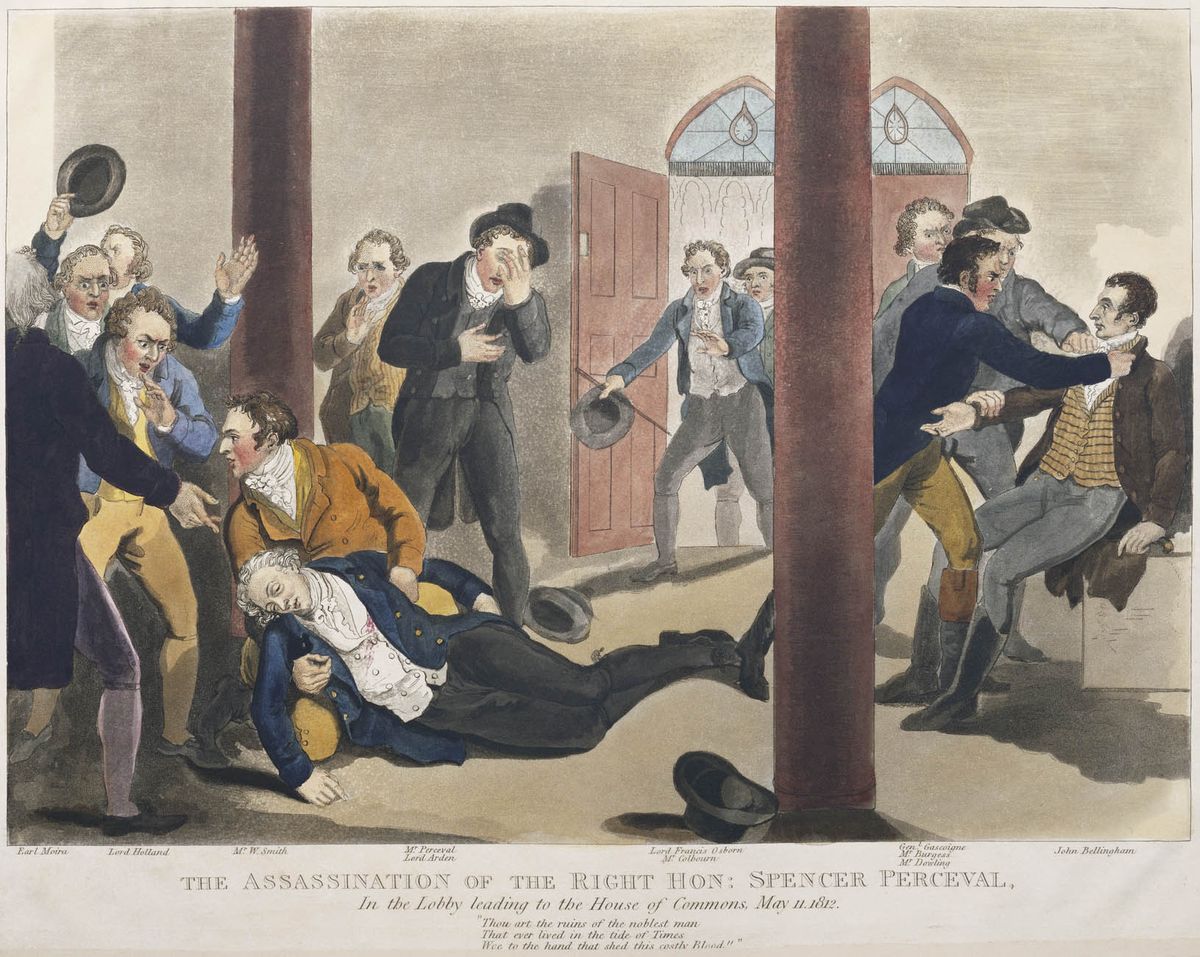 The previous Palace of Westminster was also the site of a prime-ministerial assassination on 11 May 1812. While in the lobby of the House of Commons, on his way to a parliamentary inquiry, Spencer Perceval was Assassination of Spencer Perceval, shot and killed by a Liverpool merchant adventurer, John Bellingham. Perceval remains the only Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister to have been assassinated.
The New Palace became the target of Fenian bombs on 24 January 1885, along with the Tower of London. The first bomb, a black bag containing dynamite, was discovered by a visitor on the steps towards the Chapel of St Mary Undercroft. Police Constable (PC) William Cole attempted to carry it to New Palace Yard, but the bag became so hot that Cole dropped it and it exploded. The blast opened a crater in the floor in diameter, damaged the roof of the chapel and shattered all the windows in the Hall, including the stained-glass South Window at St Stephen's Porch. Both Cole and PC Cox, a colleague who had joined him to offer assistance, were seriously injured. A second explosion followed almost immediately in the Commons Chamber, causing great damage—especially to its south end—but no injuries, as it was empty at the time. The incident resulted in the closure of Westminster Hall to visitors for several years; when visitors were re-admitted in 1889, it was under certain restrictions and never while the two Houses were sitting.
On 17 June 1974, a bomb planted by the Provisional Irish Republican Army, Provisional IRA exploded in Westminster Hall. The explosion and the resulting fire, which was fed by a ruptured gas main, injured 11 people and caused extensive damage. Five years later, a car bomb claimed the life of Airey Neave, a prominent Conservative politician, while he was driving out of the Commons car park in New Palace Yard. The attack occurred on 30 March 1979, one day after the announcement of 1979 United Kingdom general election, that year's general election; both the Irish National Liberation Army and the Provisional IRA claimed responsibility for Neave's assassination, but it is now accepted that the former were responsible.
The previous Palace of Westminster was also the site of a prime-ministerial assassination on 11 May 1812. While in the lobby of the House of Commons, on his way to a parliamentary inquiry, Spencer Perceval was Assassination of Spencer Perceval, shot and killed by a Liverpool merchant adventurer, John Bellingham. Perceval remains the only Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister to have been assassinated.
The New Palace became the target of Fenian bombs on 24 January 1885, along with the Tower of London. The first bomb, a black bag containing dynamite, was discovered by a visitor on the steps towards the Chapel of St Mary Undercroft. Police Constable (PC) William Cole attempted to carry it to New Palace Yard, but the bag became so hot that Cole dropped it and it exploded. The blast opened a crater in the floor in diameter, damaged the roof of the chapel and shattered all the windows in the Hall, including the stained-glass South Window at St Stephen's Porch. Both Cole and PC Cox, a colleague who had joined him to offer assistance, were seriously injured. A second explosion followed almost immediately in the Commons Chamber, causing great damage—especially to its south end—but no injuries, as it was empty at the time. The incident resulted in the closure of Westminster Hall to visitors for several years; when visitors were re-admitted in 1889, it was under certain restrictions and never while the two Houses were sitting.
On 17 June 1974, a bomb planted by the Provisional Irish Republican Army, Provisional IRA exploded in Westminster Hall. The explosion and the resulting fire, which was fed by a ruptured gas main, injured 11 people and caused extensive damage. Five years later, a car bomb claimed the life of Airey Neave, a prominent Conservative politician, while he was driving out of the Commons car park in New Palace Yard. The attack occurred on 30 March 1979, one day after the announcement of 1979 United Kingdom general election, that year's general election; both the Irish National Liberation Army and the Provisional IRA claimed responsibility for Neave's assassination, but it is now accepted that the former were responsible.
 The Palace has also been the scene of numerous acts of politically motivated "direct action", which often took place in the Chamber of the House of Commons. In July 1970, a man in the Strangers' Gallery threw two canisters of CS gas, tear gas into the Chamber to protest against the use of such gas in Northern Ireland; an MP and two members of the House's staff were taken to hospital and the sitting was suspended for almost two hours. In 1978, activist Yana Mintoff and another dissident threw bags of horse manure, and in June 1996 demonstrators dropped leaflets. Concern about such attacks and a possible chemical or biological attack led to the installation of a glass screen across the Strangers' Gallery in early 2004.
The new barrier does not cover the gallery in front of the Strangers' Gallery, which is reserved for ambassadors, members of the House of Lords, guests of MPs and other dignitaries, and in May 2004 protesters from Fathers 4 Justice attacked Prime Minister Tony Blair with flour bombs from this part, after obtaining admission by bidding for a place in the visitors' gallery in a charity auction. Subsequently, rules on admission to the visitors' galleries were changed, and now individuals wishing to sit in the galleries must first obtain a written pass from a Member certifying that that individual is personally known to them. In September of the same year, five protesters opposed to the proposed ban on fox hunting disrupted the proceedings of the House of Commons by running into the Chamber, the first such occurrence since Charles I of England, King Charles I's unauthorised entry in 1642, which triggered the English Civil War.
The House of Lords has also been targeted by protesters. On 2 February 1988, the House debated the Local Government Act 1988, Local Government Bill's controversial Section 28, Clause 28, a measure to prohibit the promotion of homosexuality in schools. Following the Division of the assembly, division, in which the clause passed, a number of lesbian demonstrators in the public gallery started chanting slogans, and three of them tied ropes to the railing and climbed down onto the floor of the Chamber. Gerard Collier, 5th Baron Monkswell, Lord Monkswell, who had provided the women with passes to attend the debate, later apologised to the House for the incident but did not criticise the protest.
Similar actions have been carried out outside the Palace of Westminster. Early in the morning of 20 March 2004, two Greenpeace members scaled the Clock Tower to demonstrate against the Iraq War, raising questions about the security around such a likely target of terrorist attacks. In March 2007, another four members of Greenpeace made their way to the Palace's roof by means of a nearby crane, which was being used for repairs to Westminster Bridge. Once up, they unfurled a banner protesting against the British government's plans to update the Trident nuclear programme.
In February 2008, five campaigners from the Plane Stupid group gained admittance to the building as visitors and then moved up to the roof to demonstrate against the proposed expansion of Heathrow Airport; from there they hung two banners they had smuggled past security. MPs and security experts found it worrying that the protesters made it to the roof in spite of the heightened security measures, and the prosecution at the activists' trial argued that they may have received help from a House of Lords employee. In October 2009, at least forty Greenpeace activists climbed to the roof of Westminster Hall to call for the adoption of policies climate change mitigation, combating climate change. Some of them climbed down after nearly five hours, while the rest spent the night on the roof.
On 22 March 2017 an Islamic terrorism, Islamist-related terror attack happened in which 2017 Westminster attack, a man stabbed a police officer after ploughing into pedestrians on Westminster Bridge. Five people were killed, including the attacker and the police officer. In August 2018 there was 2018 Westminster car incident, another attack, treated by prosecutors as terrorism.
On 1 April 2019, a group of environmental protestors from the group Extinction Rebellion stripped semi-naked in the public gallery during a Brexit debate and glued themselves to the handrail and glass screen with their buttocks facing the Commons Chamber. MPs attempted to continue the debate, some of them incorporating puns and references to nakedness into their speeches, to much hilarity.
There have been four fires on the Palace of Westminster site during 2019, and eight in 2018.
In 2022, the body of the late Queen Elizabeth was left inside the hall for people to pay their respects. A man decided to jump the barriers and pull the flag off coffin. He was detained and taken away by police and officials.
The Palace has also been the scene of numerous acts of politically motivated "direct action", which often took place in the Chamber of the House of Commons. In July 1970, a man in the Strangers' Gallery threw two canisters of CS gas, tear gas into the Chamber to protest against the use of such gas in Northern Ireland; an MP and two members of the House's staff were taken to hospital and the sitting was suspended for almost two hours. In 1978, activist Yana Mintoff and another dissident threw bags of horse manure, and in June 1996 demonstrators dropped leaflets. Concern about such attacks and a possible chemical or biological attack led to the installation of a glass screen across the Strangers' Gallery in early 2004.
The new barrier does not cover the gallery in front of the Strangers' Gallery, which is reserved for ambassadors, members of the House of Lords, guests of MPs and other dignitaries, and in May 2004 protesters from Fathers 4 Justice attacked Prime Minister Tony Blair with flour bombs from this part, after obtaining admission by bidding for a place in the visitors' gallery in a charity auction. Subsequently, rules on admission to the visitors' galleries were changed, and now individuals wishing to sit in the galleries must first obtain a written pass from a Member certifying that that individual is personally known to them. In September of the same year, five protesters opposed to the proposed ban on fox hunting disrupted the proceedings of the House of Commons by running into the Chamber, the first such occurrence since Charles I of England, King Charles I's unauthorised entry in 1642, which triggered the English Civil War.
The House of Lords has also been targeted by protesters. On 2 February 1988, the House debated the Local Government Act 1988, Local Government Bill's controversial Section 28, Clause 28, a measure to prohibit the promotion of homosexuality in schools. Following the Division of the assembly, division, in which the clause passed, a number of lesbian demonstrators in the public gallery started chanting slogans, and three of them tied ropes to the railing and climbed down onto the floor of the Chamber. Gerard Collier, 5th Baron Monkswell, Lord Monkswell, who had provided the women with passes to attend the debate, later apologised to the House for the incident but did not criticise the protest.
Similar actions have been carried out outside the Palace of Westminster. Early in the morning of 20 March 2004, two Greenpeace members scaled the Clock Tower to demonstrate against the Iraq War, raising questions about the security around such a likely target of terrorist attacks. In March 2007, another four members of Greenpeace made their way to the Palace's roof by means of a nearby crane, which was being used for repairs to Westminster Bridge. Once up, they unfurled a banner protesting against the British government's plans to update the Trident nuclear programme.
In February 2008, five campaigners from the Plane Stupid group gained admittance to the building as visitors and then moved up to the roof to demonstrate against the proposed expansion of Heathrow Airport; from there they hung two banners they had smuggled past security. MPs and security experts found it worrying that the protesters made it to the roof in spite of the heightened security measures, and the prosecution at the activists' trial argued that they may have received help from a House of Lords employee. In October 2009, at least forty Greenpeace activists climbed to the roof of Westminster Hall to call for the adoption of policies climate change mitigation, combating climate change. Some of them climbed down after nearly five hours, while the rest spent the night on the roof.
On 22 March 2017 an Islamic terrorism, Islamist-related terror attack happened in which 2017 Westminster attack, a man stabbed a police officer after ploughing into pedestrians on Westminster Bridge. Five people were killed, including the attacker and the police officer. In August 2018 there was 2018 Westminster car incident, another attack, treated by prosecutors as terrorism.
On 1 April 2019, a group of environmental protestors from the group Extinction Rebellion stripped semi-naked in the public gallery during a Brexit debate and glued themselves to the handrail and glass screen with their buttocks facing the Commons Chamber. MPs attempted to continue the debate, some of them incorporating puns and references to nakedness into their speeches, to much hilarity.
There have been four fires on the Palace of Westminster site during 2019, and eight in 2018.
In 2022, the body of the late Queen Elizabeth was left inside the hall for people to pay their respects. A man decided to jump the barriers and pull the flag off coffin. He was detained and taken away by police and officials.
 Men are expected to wear formal attire, women are expected to dress in business-like clothing and the wearing of T-shirts with slogans is not allowed. Hats must not be worn (although they used to be worn when a point of order was being raised), and Members may not wear military decorations or insignia. Members are not allowed to have their hands in their pocketsAndrew Robathan was heckled by opposing MPs for doing this on 19 December 1994.
Men are expected to wear formal attire, women are expected to dress in business-like clothing and the wearing of T-shirts with slogans is not allowed. Hats must not be worn (although they used to be worn when a point of order was being raised), and Members may not wear military decorations or insignia. Members are not allowed to have their hands in their pocketsAndrew Robathan was heckled by opposing MPs for doing this on 19 December 1994.
Westminster Hall – A Virtual Experience
Winston Churchill State Funeral – Westminster Hall – UK Parliament Living Heritage
"A Victorian Novel in Stone"
Rosemary Hill, ''The Wall Street Journal'', 20 March 2009
Parliamentary Archives, Designs and working drawings for the rebuilding of the Houses of Parliament
{{Authority control Palace of Westminster, 1870 establishments in England Augustus Pugin buildings Buildings and structures completed in 1097 Buildings and structures on the River Thames Burned buildings and structures in the United Kingdom Gothic Revival architecture in London Government buildings completed in 1870 Grade I listed buildings in the City of Westminster Grade I listed government buildings Grade I listed palaces, Westminster, Palace Of History of the City of Westminster Legislative buildings in the United Kingdom Limestone buildings in the United Kingdom National government buildings in London Official residences in the United Kingdom Parliament of the United Kingdom Parliamentary Estate Rebuilt buildings and structures in the United Kingdom Royal residences in the City of Westminster, Westminster, Palace Of Legislative buildings in Europe, Westminster, Palace Of Seats of national legislatures Tourist attractions in the City of Westminster World Heritage Sites in London
House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
and the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative suprem ...
. Informally known as the Houses of Parliament, the Palace lies on the north bank of the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
in the City of Westminster
The City of Westminster is a city and borough in Inner London. It is the site of the United Kingdom's Houses of Parliament and much of the British government. It occupies a large area of central Greater London, including most of the West En ...
, in central London
Central London is the innermost part of London, in England, spanning several boroughs. Over time, a number of definitions have been used to define the scope of Central London for statistics, urban planning and local government. Its characteris ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
.
Its name, which derives from the neighbouring Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
, may refer to several historic structures but most often: the ''Old Palace'', a medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
building-complex largely destroyed by fire in 1834, or its replacement, the ''New Palace'' that stands today. The palace is owned by the Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has differ ...
. Committees appointed by both houses manage the building and report to the Speaker of the House of Commons and to the Lord Speaker
The Lord Speaker is the presiding officer, chairman and highest authority of the House of Lords in the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The office is analogous to the Speaker of the House of Commons: the Lord Speaker is elected by the membe ...
.
The first royal palace constructed on the site dated from the 11th century, and Westminster became the primary residence of the Kings of England until fire destroyed the royal apartments in 1512 (after which, the nearby Palace of Whitehall
The Palace of Whitehall (also spelt White Hall) at Westminster was the main residence of the English monarchs from 1530 until 1698, when most of its structures, except notably Inigo Jones's Banqueting House of 1622, were destroyed by fire. ...
was established). The remainder of Westminster continued to serve as the home of the Parliament of England
The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England from the 13th century until 1707 when it was replaced by the Parliament of Great Britain. Parliament evolved from the great council of bishops and peers that advise ...
, which had met there since the 13th century, and also as the seat of the Royal Courts of Justice, based in and around Westminster Hall
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parli ...
. In 1834 an even greater fire ravaged the heavily rebuilt Houses of Parliament, and the only significant medieval structures to survive were Westminster Hall, the Cloisters of St Stephen's, the Chapel of St Mary Undercroft
The Chapel of St Mary Undercroft is a Church of England chapel located in the Palace of Westminster, London, England. The chapel is accessed via a flight of stairs in the south east corner of Westminster Hall.
It had been a crypt below St S ...
, and the Jewel Tower
The Jewel Tower is a 14th-century surviving element of the Palace of Westminster, in London, England. It was built between 1365 and 1366, under the direction of William of Sleaford and Henry de Yevele, to house the personal treasure of King ...
.
In the subsequent competition for the reconstruction of the Palace, the architect Charles Barry
Sir Charles Barry (23 May 1795 – 12 May 1860) was a British architect, best known for his role in the rebuilding of the Palace of Westminster (also known as the Houses of Parliament) in London during the mid-19th century, but also respon ...
won with a design for new buildings in the Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
style, specifically inspired by the English Perpendicular Gothic
Perpendicular Gothic (also Perpendicular, Rectilinear, or Third Pointed) architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-c ...
style of the 14th–16th centuries. The remains of the Old Palace (except the detached Jewel Tower) were incorporated into its much larger replacement, which contains over 1,100 rooms organised symmetrically around two series of courtyards and which has a floor area of . Part of the New Palace's area of was reclaimed from the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
, which is the setting of its nearly façade, called the River Front. Augustus Pugin
Augustus Welby Northmore Pugin ( ; 1 March 181214 September 1852) was an English architect, designer, artist and critic with French and, ultimately, Swiss origins. He is principally remembered for his pioneering role in the Gothic Revival st ...
, a leading authority on Gothic architecture and style, assisted Barry and designed the interior of the Palace. Construction started in 1840 and lasted for 30 years, suffering great delays and cost overruns, as well as the death of both leading architects; works for the interior decoration continued intermittently well into the 20th century. Major conservation work has taken place since then to reverse the effects of London's air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different type ...
, and extensive repairs followed the Second World War, including the simplified reconstruction of the Commons Chamber following its bombing in 1941.
The Palace is one of the centres of political life in the United Kingdom; "Westminster" has become a metonym
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something closely associated with that thing or concept.
Etymology
The words ''metonymy'' and ''metonym'' come from grc, μετωνυμία, 'a change of name' ...
for the UK Parliament and the British Government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_est ...
, and the Westminster system of government commemorates the name of the palace. The Elizabeth Tower, in particular, often referred to by the name of its main bell, Big Ben
Big Ben is the nickname for the Great Bell of the Great Clock of Westminster, at the north end of the Palace of Westminster in London, England, and the name is frequently extended to refer also to the clock and the clock tower. The officia ...
, has become an iconic landmark of London and of the United Kingdom in general, one of the most popular tourist attractions in the city, and an emblem of parliamentary democracy. Tsar Nicholas I of Russia
, house = Romanov-Holstein-Gottorp
, father = Paul I of Russia
, mother = Maria Feodorovna (Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg)
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Gatchina Palace, Gatchina, Russian Empire
, death_date ...
called the new palace "a dream in stone". The Palace of Westminster has been a Grade I listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern I ...
since 1970 and part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
since 1987.
History
Old Palace
 The site of the Palace of Westminster was strategically important during the
The site of the Palace of Westminster was strategically important during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, as it was located on the banks of the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
. Known in medieval times as Thorney Island, the site may have been first-used for a royal residence by Canute the Great
Cnut (; ang, Cnut cyning; non, Knútr inn ríki ; or , no, Knut den mektige, sv, Knut den Store. died 12 November 1035), also known as Cnut the Great and Canute, was King of England from 1016, King of Denmark from 1018, and King of Norwa ...
during his reign from 1016 to 1035. St Edward the Confessor
Edward the Confessor ; la, Eduardus Confessor , ; ( 1003 – 5 January 1066) was one of the last Anglo-Saxon English kings. Usually considered the last king of the House of Wessex, he ruled from 1042 to 1066.
Edward was the son of Æth ...
, the penultimate Anglo-Saxon monarch of England, built a royal palace on Thorney Island just west of the City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London f ...
at about the same time as he built (1045–1050) Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
. Thorney Island and the surrounding area soon became known as Westminster (from the words ''west'' and ''minster''). Neither the buildings used by the Anglo-Saxons nor those used by William I () survive. The oldest existing part of the Palace (Westminster Hall) dates from the reign of William I's successor, King William II ().
The Palace of Westminster functioned as the English monarchs' principal residence in the late Medieval period. The predecessors of Parliament, the Witenagemot
The Witan () was the king's council in Anglo-Saxon England from before the seventh century until the 11th century. It was composed of the leading magnates, both ecclesiastic and secular, and meetings of the council were sometimes called the Wi ...
and the Curia Regis, met in Westminster Hall (although they followed the King when he moved to other palaces). Simon de Montfort's Parliament
Simon de Montfort's Parliament was an English parliament held from 20 January 1265 until mid-March of the same year, called by Simon de Montfort, a baronial rebel leader.
Montfort had seized power in England following his victory over Henry I ...
, the first to include representatives of the major towns, met at the Palace in 1265. The " Model Parliament", the first official Parliament of England, met there in 1295, and almost all subsequent English Parliaments and then, after 1707, all British Parliaments have met at the Palace.
In 1512, during the early years of the reign of King Henry VIII, fire destroyed the royal residential ("privy") area of the palace. In 1534 Henry VIII acquired York Place from Cardinal Thomas Wolsey
Thomas Wolsey ( – 29 November 1530) was an English statesman and Catholic bishop. When Henry VIII became King of England in 1509, Wolsey became the king's Lord High Almoner, almoner. Wolsey's affairs prospered and by 1514 he had become the ...
, a powerful minister who had lost the King's favour. Renaming it the Palace of Whitehall
The Palace of Whitehall (also spelt White Hall) at Westminster was the main residence of the English monarchs from 1530 until 1698, when most of its structures, except notably Inigo Jones's Banqueting House of 1622, were destroyed by fire. ...
, Henry used it as his principal residence. Although Westminster officially remained a royal palace, it was used by the two Houses of Parliament and by the various royal law courts.
 Being originally a royal residence, the Palace included no purpose-built chambers for the two Houses. Important state ceremonies took place in the Painted Chamber – originally built in the 13th century as the main bedchamber for King Henry III (). In 1801 the Upper House moved into the larger White Chamber (also known as the Lesser Hall), which had housed the
Being originally a royal residence, the Palace included no purpose-built chambers for the two Houses. Important state ceremonies took place in the Painted Chamber – originally built in the 13th century as the main bedchamber for King Henry III (). In 1801 the Upper House moved into the larger White Chamber (also known as the Lesser Hall), which had housed the Court of Requests
The Court of Requests was a minor equity court in England and Wales. It was instituted by King Richard III in his 1484 parliament. It first became a formal tribunal with some Privy Council elements under Henry VII, hearing cases from the poor a ...
; the expansion of the peerage by King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great B ...
during the first ministry (1783–1801) of William Pitt the Younger
William Pitt the Younger (28 May 175923 January 1806) was a British statesman, the youngest and last prime minister of Great Britain (before the Acts of Union 1800) and then first prime minister of the United Kingdom (of Great Britain and Ir ...
, along with the imminent Act of Union with Ireland, necessitated the move, as the original chamber could not accommodate the increased number of peers.
The House of Commons, which did not have a chamber of its own, sometimes held its debates in the Chapter House of Westminster Abbey. The Commons acquired a permanent home at the Palace in St Stephen's Chapel, the former chapel of the royal palace, during the reign of Edward VI
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. Edward was the son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour and the first E ...
(). In 1547 the building became available for the Commons' use following the disbanding of St Stephen's College. Alterations were made to St Stephen's Chapel over the following three centuries for the convenience of the lower House, gradually destroying, or covering up, its original mediaeval appearance. A major renovation project undertaken by Christopher Wren
Sir Christopher Wren PRS FRS (; – ) was one of the most highly acclaimed English architects in history, as well as an anatomist, astronomer, geometer, and mathematician-physicist. He was accorded responsibility for rebuilding 52 church ...
in the late-17th century completely redesigned the building's interior.
The Palace of Westminster as a whole underwent significant alterations from the 18th century onwards, as Parliament struggled to carry out its business in the limited available space of ageing buildings. Calls for an entirely new palace went unheeded – instead more buildings of varying quality and style were added. A new west façade, known as the Stone Building, facing onto St Margaret's Street, was designed by John Vardy and built in the Palladian style between 1755 and 1770, providing more space for document storage and for committee rooms. The House of Commons and House of Lords Engrossing Office of Henry (Robert) Gunnell (1724–1794) and Edward Barwell was on the lower floor beside the corner tower at the west side of Vardy's western façade. It was here where the Tax Laws for the American Colonies were put together. A new official residence for the Speaker of the House of Commons was built adjoining St Stephen's Chapel and completed in 1795. The neo-Gothic
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
architect James Wyatt
James Wyatt (3 August 1746 – 4 September 1813) was an English architect, a rival of Robert Adam in the neoclassical and neo-Gothic styles. He was elected to the Royal Academy in 1785 and was its president from 1805 to 1806.
Early life
W ...
carried out works both on the House of Lords and on the House of Commons between 1799 and 1801, including alterations to the exterior of St Stephen's Chapel and a much-derided new neo-Gothic building (referred to by Wyatt's critics as "The Cotton Mill") adjoining the House of Lords and facing onto Old Palace Yard.
Sir John Soane substantially remodelled the palace complex between 1824 and 1827. The medieval House of Lords chamber, which had been the target of the failed Gunpowder Plot
The Gunpowder Plot of 1605, in earlier centuries often called the Gunpowder Treason Plot or the Jesuit Treason, was a failed assassination attempt against King James I by a group of provincial English Catholics led by Robert Catesby who sough ...
of 1605, was demolished as part of this work in order to build a new Royal Gallery and a ceremonial entrance at the southern end of the palace. Soane's work at the palace also included new library facilities for both Houses of Parliament and new law courts for the Chancery and King's Bench. Soane's alterations caused controversy owing to his use of neo-classical architectural styles, seen as conflicting with the Gothic style of the original buildings.
Fire and reconstruction
On 16 October 1834, a fire broke out in the Palace after an overheated stove used to destroy theExchequer
In the civil service of the United Kingdom, His Majesty’s Exchequer, or just the Exchequer, is the accounting process of central government and the government's '' current account'' (i.e., money held from taxation and other government revenu ...
's stockpile of tally stick
A tally stick (or simply tally) was an ancient memory aid device used to record and document numbers, quantities and messages. Tally sticks first appear as animal bones carved with notches during the Upper Palaeolithic; a notable example is the ...
s set fire to the House of Lords Chamber. In the resulting conflagration both Houses of Parliament were destroyed, along with most of the other buildings in the palace complex. Westminster Hall was saved thanks to fire-fighting efforts and a change in the direction of the wind. The Jewel Tower
The Jewel Tower is a 14th-century surviving element of the Palace of Westminster, in London, England. It was built between 1365 and 1366, under the direction of William of Sleaford and Henry de Yevele, to house the personal treasure of King ...
, the Undercroft Chapel and the Cloister
A cloister (from Latin ''claustrum'', "enclosure") is a covered walk, open gallery, or open arcade running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle or garth. The attachment of a cloister to a cathedral or church, commonly against ...
s and Chapter House of St Stephen's were the only other parts of the Palace to survive.
Immediately after the fire, King William IV offered the almost-completed Buckingham Palace
Buckingham Palace () is a London royal residence and the administrative headquarters of the monarch of the United Kingdom. Located in the City of Westminster, the palace is often at the centre of state occasions and royal hospitality. It ...
to Parliament, hoping to dispose of a residence he disliked. The building was considered unsuitable for parliamentary use, however, and the gift was rejected. Proposals to move to Charing Cross or St James's Park had a similar fate; the allure of tradition and the historical and political associations of Westminster proved too strong for relocation, despite the deficiencies of that site. In the meantime, the immediate priority was to provide accommodation for the next Parliament, and so the Painted Chamber and White Chamber were hastily repaired for temporary use.
In 1835, following that year's General Election, the King permitted Parliament to make "plans for tspermanent accommodation". Each house created a committee and a public debate over the proposed styles ensued.
 The Lords Chamber was completed in 1847, and the Commons Chamber in 1852 (at which point architect
The Lords Chamber was completed in 1847, and the Commons Chamber in 1852 (at which point architect Charles Barry
Sir Charles Barry (23 May 1795 – 12 May 1860) was a British architect, best known for his role in the rebuilding of the Palace of Westminster (also known as the Houses of Parliament) in London during the mid-19th century, but also respon ...
received a knighthood
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the ...
). Although most of the work had been carried out by 1860, construction was not finished until a decade afterwards.
World War II damage and restoration
During the Second World War (see ''The Blitz
The Blitz was a German bombing campaign against the United Kingdom in 1940 and 1941, during the Second World War. The term was first used by the British press and originated from the term , the German word meaning 'lightning war'.
The Germa ...
''), the Palace of Westminster was hit by bombs on fourteen separate occasions. One bomb fell into Old Palace Yard on 26 September 1940 and severely damaged the south wall of St Stephen's Porch and the west front. The statue of Richard the Lionheart was lifted from its pedestal by the force of the blast, and its upheld sword bent, an image that was used as a symbol of the strength of democracy, "which would bend but not break under attack".
 The worst raid took place in the night of 10–11 May 1941, when the Palace took at least twelve hits and three people (two policemen and Resident Superintendent of the House of Lords Edward Elliott) were killed. Fell and Mackenzie (1994), p. 27. An incendiary bomb hit the chamber of the House of Commons and set it on fire; another set the roof of Westminster Hall alight. The firefighters could not save both, and a decision was taken to try to rescue the Hall. In this they were successful; the abandoned Commons Chamber, on the other hand, was destroyed, as was the Members' Lobby. A bomb also struck the Lords Chamber, but went through the floor without exploding. The Clock Tower took a hit by a small bomb or anti-aircraft shell at the eaves of the roof, suffering much damage there. All the glass on the south dial was blown out, but the hands and bells were not affected, and the Great Clock continued to keep time accurately.
Following the destruction of the Commons Chamber, the Lords offered their own
The worst raid took place in the night of 10–11 May 1941, when the Palace took at least twelve hits and three people (two policemen and Resident Superintendent of the House of Lords Edward Elliott) were killed. Fell and Mackenzie (1994), p. 27. An incendiary bomb hit the chamber of the House of Commons and set it on fire; another set the roof of Westminster Hall alight. The firefighters could not save both, and a decision was taken to try to rescue the Hall. In this they were successful; the abandoned Commons Chamber, on the other hand, was destroyed, as was the Members' Lobby. A bomb also struck the Lords Chamber, but went through the floor without exploding. The Clock Tower took a hit by a small bomb or anti-aircraft shell at the eaves of the roof, suffering much damage there. All the glass on the south dial was blown out, but the hands and bells were not affected, and the Great Clock continued to keep time accurately.
Following the destruction of the Commons Chamber, the Lords offered their own debating chamber
A debate chamber is a room for people to discuss and debate. Debate chambers are used in governmental and educational bodies, such as a parliament, congress, city council, or a university, either for formal proceedings or for informal discourse ...
for the use of the Commons; for their own sittings, the Queen's Robing Room was converted into a makeshift chamber. The Commons Chamber was rebuilt after the war under the architect Sir Giles Gilbert Scott
Sir Giles Gilbert Scott (9 November 1880 – 8 February 1960) was a British architect known for his work on the New Bodleian Library, Cambridge University Library, Lady Margaret Hall, Oxford, Battersea Power Station, Liverpool Cathedral, and ...
, in a simplified version of the old chamber's style. The work was undertaken by John Mowlem & Co., and construction lasted until 1950. The Lords Chamber was then renovated over the ensuing months; the Lords re-occupied it in May 1951.
Recent history
As the need for office space in the Palace increased, Parliament acquired office space in the nearbyNorman Shaw Building
The Norman Shaw Buildings (formerly known as New Scotland Yard) are a pair of buildings in Westminster, London, overlooking the River Thames. The buildings were designed by the architects Richard Norman Shaw and John Dixon Butler, between 18 ...
in 1975, and in the custom-built Portcullis House, completed in 2000. This increase has enabled all Members of Parliament (MP) to have their own office facilities.
 The Palace of Westminster, which is a Grade 1 listed building, is in urgent need of extensive restoration to its fabric. A 2012 pre-feasibility report set out several options, including the possibility of Parliament moving to other premises while work is carried out. At the same time, the option of moving Parliament to a new location was discounted, with staying at the Westminster site preferred. An Independent Options Appraisal Report released in June 2015 found that the cost to restore the Palace of Westminster could be as much as £7.1 billion if MPs were to remain at the Palace whilst works take place. MPs decided in 2016 to vacate the building for six years starting in 2022. In January 2018, the House of Commons voted for both houses to vacate the Palace of Westminster to allow for a complete refurbishment of the building which may take up to six years starting in 2025. It is expected that the House of Commons will be temporarily housed in a replica chamber to be located in Richmond House in Whitehall and the House of Lords will be housed at the Queen Elizabeth II Conference Centre in Parliament Square.
The Palace of Westminster, which is a Grade 1 listed building, is in urgent need of extensive restoration to its fabric. A 2012 pre-feasibility report set out several options, including the possibility of Parliament moving to other premises while work is carried out. At the same time, the option of moving Parliament to a new location was discounted, with staying at the Westminster site preferred. An Independent Options Appraisal Report released in June 2015 found that the cost to restore the Palace of Westminster could be as much as £7.1 billion if MPs were to remain at the Palace whilst works take place. MPs decided in 2016 to vacate the building for six years starting in 2022. In January 2018, the House of Commons voted for both houses to vacate the Palace of Westminster to allow for a complete refurbishment of the building which may take up to six years starting in 2025. It is expected that the House of Commons will be temporarily housed in a replica chamber to be located in Richmond House in Whitehall and the House of Lords will be housed at the Queen Elizabeth II Conference Centre in Parliament Square.
Restoration and Renewal Client Board
In September 2022, the formation of a new joint committee of the House of Lords and the House of Commons was announced to oversee the necessary works: called the Restoration and Renewal Client Board, its Parliamentarian members are: * The Speaker of the House of Commons (Sir Lindsay Hoyle
Sir Lindsay Harvey Hoyle (born 10 June 1957)'HOYLE, Hon. Lindsay (Harvey)', Who's Who 2013, A & C Black, an imprint of Bloomsbury Publishing plc, 2013; online edn, Oxford University Press, Dec 2012 ; online edn, Nov 201 Retrieved 31 December 20 ...
)
* The Lord Speaker
The Lord Speaker is the presiding officer, chairman and highest authority of the House of Lords in the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The office is analogous to the Speaker of the House of Commons: the Lord Speaker is elected by the membe ...
(Lord McFall of Alcluith
John Francis McFall, Baron McFall of Alcluith, (born 4 October 1944) is a Scottish politician, now the Lord Speaker having previously been Senior Deputy Speaker of the House of Lords from 1 September 2016 to 30 April 2021. He was previously a ...
)
* Nickie Aiken,
* Deidre Brock,
* Nick Brown,
*Thangam Debbonaire
Thangam Elizabeth Rachel Debbonaire (' Singh; born 3 August 1966) is a British Labour Party politician, serving as Shadow Leader of the House of Commons since May 2021. She was previously the Shadow Secretary of State for Housing from 2020 t ...
,
*Lord Gardiner of Kimble
:''See also Gerald Gardiner, Baron Gardiner''
John Gardiner, Baron Gardiner of Kimble (born 17 March 1956) is a British politician. He is a life peer, and has served as Senior Deputy Speaker of the House of Lords since May 2021.
Early life, edu ...
,
*Lord German
Michael James German, Baron German, OBE (born 8 May 1945) is a British politician, serving currently as a member of the House of Lords and formerly as a member of the National Assembly for Wales for the South Wales East region. He was leader ...
,
*Lord Hill of Oareford
Jonathan Hopkin Hill, Baron Hill of Oareford, (born 24 July 1960) is a British Conservative politician and former European Commissioner for Financial Stability, Financial Services and Capital Markets Union. Hill was Leader of the House of Lor ...
,
* Lord Judge,
* Penny Mordaunt,
*Lord Newby
Richard Mark Newby, Baron Newby (born 14 February 1953), known popularly as Dick Newby, is a British politician, who has been the Leader of the Liberal Democrats in the House of Lords since September 2016. He served as the Deputy Government C ...
,
*Baroness Smith of Basildon
Baron is a rank of nobility or title of honour, often hereditary, in various European countries, either current or historical. The female equivalent is baroness. Typically, the title denotes an aristocrat who ranks higher than a lord or knigh ...
,
* Lord Touhig,
*Lord True
Nicholas Edward True, Baron True (born 31 July 1951) is a British Conservative politician serving as Leader of the House of Lords and Lord Keeper of the Privy Seal since September 2022.
Early life and education
True was born on 31 July 1951 ...
,
* Lord Vaux of Harrowden,
*Sir Charles Walker
Sir Charles Ashley Rupert Walker (born 11 September 1967) is a British politician who served as chair of the House of Commons Procedure Committee from 2012 to 2019. A member of the Conservative Party, he has been Member of Parliament (MP) ...
.
They are joined by lay members:
* Dr John Benger, Clerk of the House of Commons,
* Simon Burton, Clerk of the Parliaments,
*Marianne Cwynarski
Marianne () has been the national personification of the French Republic since the French Revolution, as a personification of liberty, equality, fraternity and reason, as well as a portrayal of the Goddess of Liberty.
Marianne is displayed in ...
, Director General of the House of Commons,
*Mathew Duncan
Mathew is a masculine given name and a variant of Matthew. It is also used as a surname.
As a given name
Notable people with the given name include:
* Mat Erpelding (born 1975), American politician
* Mat Kearney (born 1978), American singer-s ...
, external member of the House of Lords Commission,
*Andy Helliwell
Andy may refer to:
People
*Andy (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
* Horace Andy (born 1951), Jamaican roots reggae songwriter and singer born Horace Hinds
* Katja Andy (1907–2013), German-American pianist and pia ...
, Chief Operating Officer of the House of Lords,
* Shrinivas Honap, external member of the House of Commons Commission,
*Nora Senior
Nora Margaret Senior CBE is a Scottish businesswoman. She has received awards including the First Women UK Media Award (2013), and the global ‘Stevie’ for Best Woman in Business (in Europe, Middle East and Asia), In 2013 she was appointed pres ...
, external member of the House of Lords Commission,
*Louise Wilson
Louise Janet Wilson (23 February 1962 – 16 May 2014) was a British professor of fashion design. Louise Wilson was based at the Central Saint Martins College of Arts and Design in London, where she was the course director of their MA in Fash ...
, external member of the House of Commons Commission.
Exterior
Sir Charles Barry
Sir Charles Barry (23 May 1795 – 12 May 1860) was a British architect, best known for his role in the rebuilding of the Palace of Westminster (also known as the Houses of Parliament) in London during the mid-19th century, but also respon ...
's collaborative design for the Palace of Westminster uses the Perpendicular Gothic
Perpendicular Gothic (also Perpendicular, Rectilinear, or Third Pointed) architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-c ...
style, which was popular during the 15th century and returned during the Gothic revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
of the 19th century. Barry was a classical architect, but he was aided by the Gothic architect Augustus Pugin
Augustus Welby Northmore Pugin ( ; 1 March 181214 September 1852) was an English architect, designer, artist and critic with French and, ultimately, Swiss origins. He is principally remembered for his pioneering role in the Gothic Revival st ...
. Westminster Hall, which was built in the 11th century and survived the fire of 1834, was incorporated in Barry's design. Pugin was displeased with the result of the work, especially with the symmetrical layout designed by Barry; he famously remarked, "All Grecian, sir; Tudor details on a classic body".
Stonework
In 1839 Charles Barry toured Britain, looking at quarries and buildings, with a committee which included two leading geologists and a stonecarver.UK Parliament website "stonework" pageAccessed 4 January 2014. They selected Anston, a sand-coloured magnesian
limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
quarried in the villages of Anston
Anston is a civil parish in South Yorkshire, England, formally known as North and South Anston. The parish of Anston consists of the settlements of North Anston and South Anston, divided by the Anston Brook.
History
Anston, first recorded as ...
, South Yorkshire
South Yorkshire is a ceremonial and metropolitan county in the Yorkshire and Humber Region of England. The county has four council areas which are the cities of Doncaster and Sheffield as well as the boroughs of Barnsley and Rotherham.
...
, and Mansfield Woodhouse, Nottinghamshire
Nottinghamshire (; abbreviated Notts.) is a landlocked county in the East Midlands region of England, bordering South Yorkshire to the north-west, Lincolnshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south, and Derbyshire to the west. The trad ...
. Two quarries were chosen from a list of 102, with the majority of the stone coming from the former. A crucial consideration was transportation, achieved on water via the Chesterfield Canal, the North Sea, and the rivers Trent and Thames. Furthermore, Anston was cheaper, and "could be supplied in blocks up to four feet thick and lent itself to elaborate carving".
Barry's New Palace of Westminster was rebuilt using the sandy-coloured Anston limestone. However, the stone soon began to decay due to pollution and the poor quality of some of the stone used. Although such defects were clear as early as 1849, nothing was done for the remainder of the 19th century even after much studying. During the 1910s, however, it became clear that some of the stonework had to be replaced. In 1928 it was deemed necessary to use Clipsham stone
Clipsham is a small village in the county of Rutland in the East Midlands of England. It is in the northeast of Rutland, close to the county boundary with Lincolnshire. The population of the civil parish was 120 at the 2001 census increasing ...
, a honey-coloured limestone from Rutland
Rutland () is a ceremonial county and unitary authority in the East Midlands, England. The county is bounded to the west and north by Leicestershire, to the northeast by Lincolnshire and the southeast by Northamptonshire.
Its greatest len ...
, to replace the decayed Anston. The project began in the 1930s but was halted by the outbreak of the Second World War, and completed only during the 1950s. By the 1960s pollution had again begun to take its toll. A stone conservation and restoration programme to the external elevations and towers began in 1981, and ended in 1994.
Towers
 The Palace of Westminster has three main towers. Of these, the largest and tallest is the
The Palace of Westminster has three main towers. Of these, the largest and tallest is the Victoria Tower
The Victoria Tower is a square tower at the south-west end of the Palace of Westminster in London, adjacent to Black Rod's Garden on the west and Old Palace Yard on the east. At , it is slightly taller than the Elizabeth Tower (formerly known ...
, which occupies the south-western corner of the Palace. Originally named "The King's Tower" because the fire of 1834 which destroyed the old Palace of Westminster occurred during the reign of King William IV, the tower was an integral part of Barry's original design, of which he intended it to be the most memorable element. The architect conceived the great square tower as the keep
A keep (from the Middle English ''kype'') is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in c ...
of a legislative "castle" (echoing his selection of the portcullis
A portcullis (from Old French ''porte coleice'', "sliding gate") is a heavy vertically-closing gate typically found in medieval fortifications, consisting of a latticed grille made of wood, metal, or a combination of the two, which slides down ...
as his identifying mark in the planning competition), and used it as the royal entrance to the Palace and as a fireproof repository for the archives of Parliament. The Victoria Tower was re-designed several times, and its height increased progressively; upon its completion in 1858, it was the tallest secular building in the world.
At the base of the tower is the Sovereign's Entrance, used by the monarch whenever entering the Palace to open Parliament or for other state occasions. The high archway is richly decorated with sculptures, including statues of Saints George, Andrew
Andrew is the English form of a given name common in many countries. In the 1990s, it was among the top ten most popular names given to boys in English-speaking countries. "Andrew" is frequently shortened to "Andy" or "Drew". The word is derive ...
and Patrick, as well as of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previ ...
herself. The main body of the Victoria Tower houses the three million documents of the Parliamentary Archives
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of t ...
in of steel shelves spread over 12 floors; these include the master copies of all Acts of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of parliament be ...
since 1497, and important manuscripts such as the original Bill of Rights
A bill of rights, sometimes called a declaration of rights or a charter of rights, is a list of the most important rights to the citizens of a country. The purpose is to protect those rights against infringement from public officials and pr ...
and the death warrant of King Charles I. At the top of the cast-iron pyramidal roof is a flagstaff, from which flies the Royal Standard (the monarch's personal flag) when the Sovereign is present in the Palace. On all other days the Union Flag
The Union Jack, or Union Flag, is the ''de facto'' national flag of the United Kingdom. Although no law has been passed making the Union Flag the official national flag of the United Kingdom, it has effectively become such through precedent. ...
flies from the mast.
 At the north end of the Palace rises the most famous of the towers, the Elizabeth Tower, commonly known as
At the north end of the Palace rises the most famous of the towers, the Elizabeth Tower, commonly known as Big Ben
Big Ben is the nickname for the Great Bell of the Great Clock of Westminster, at the north end of the Palace of Westminster in London, England, and the name is frequently extended to refer also to the clock and the clock tower. The officia ...
. At , it is only slightly shorter than the Victoria Tower but much slimmer. Originally known simply as the Clock Tower (the name Elizabeth Tower was conferred on it in 2012 to celebrate the Diamond Jubilee of Elizabeth II
The year 2012 marked the Diamond Jubilee of Elizabeth II being the 60th anniversary of the accession of Queen Elizabeth II on 6 February 1952. The only diamond jubilee celebration for any of Elizabeth's predecessors was in 1897, for the 60th a ...
), it houses the Great Clock of Westminster, built by Edward John Dent
Edward John Dent (1790–1853) was a famous English watchmaker noted for his highly accurate clocks and marine chronometers.
He founded the Dent company.
Early years
Edward John Dent, son of John and Elizabeth Dent, was born in London on 1 ...
on designs by amateur horologist Edmund Beckett Denison. Striking the hour to within a second of the time, the Great Clock achieved standards of accuracy considered impossible by 19th-century clockmakers, and it has remained consistently reliable since it entered service in 1859. The time is shown on four dials in diameter, which are made of milk glass and are lit from behind at night; the hour hand is long and the minute hand . The Clock Tower was designed by Augustus Pugin
Augustus Welby Northmore Pugin ( ; 1 March 181214 September 1852) was an English architect, designer, artist and critic with French and, ultimately, Swiss origins. He is principally remembered for his pioneering role in the Gothic Revival st ...
and built after his death. Charles Barry asked Pugin to design the clock tower because Pugin had previously helped Barry design the Palace.
In a 2012 BBC Four
BBC Four is a British free-to-air public broadcast television channel owned and operated by the BBC. It was launched on 2 March 2002
documentary, Richard Taylor gives a description of Pugin's Clock Tower:
It rises up from the ground in this stately rhythm, higher and higher, before you reach the clock face, picked out as a giant rose, its petals fringed with gold. There's some medieval windows above that and then you hits the grey ast ironroof, its greyness relieved by these delicate little windows, again picked out in gold leaf. And then it rises up again in this great jet of gold to the higher roof that curves gracefully upwards to a spire with a crown and flowers and a cross. It's elegant, it's grand, it's pretty and has this fairy-tale quality and it makes you proud to be British.Five bells hang in the belfry above the clock. The four quarter bells strike the Westminster Chimes every quarter-hour. The largest bell strikes the hours; officially called ''The Great Bell of Westminster'', it is generally referred to as ''Big Ben'', a nickname of uncertain origins which, over time, has been colloquially applied to the whole tower. The first bell to bear this name cracked during testing and was recast; the present bell later developed a crack of its own, which gives it a distinctive sound. It is the third-heaviest bell in Britain, weighing 13.8 tonnes. In the lantern at the top of Elizabeth Tower is the Ayrton Light, which is lit when either House of Parliament is sitting after dark. It was installed in 1885 at the request of Queen Victoria—so that she could see from
Buckingham Palace
Buckingham Palace () is a London royal residence and the administrative headquarters of the monarch of the United Kingdom. Located in the City of Westminster, the palace is often at the centre of state occasions and royal hospitality. It ...
whether the members were "at work"—and named after Acton Smee Ayrton
Acton Smee Ayrton (5 August 1816 – 30 November 1886) was a British barrister and Liberal Party politician. Considered a radical and champion of the working classes, he served as First Commissioner of Works under William Ewart Gladstone between ...
, who was First Commissioner of Works
The First Commissioner of Works and Public Buildings was a position within the government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and subsequent to 1922, within the government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ir ...
in the 1870s.
 The shortest of the Palace's three principal towers (at ), the octagonal Central Tower stands over the middle of the building, immediately above the Central Lobby. It was added to the plans on the insistence of Dr.
The shortest of the Palace's three principal towers (at ), the octagonal Central Tower stands over the middle of the building, immediately above the Central Lobby. It was added to the plans on the insistence of Dr. David Boswell Reid
Prof David Boswell Reid MD FRSE FRCPE (1805 – 5 April 1863) was a British physician, chemist and inventor. Through reports on public hygiene and ventilation projects in public buildings, he made a reputation in the field of sanitation. He has ...
, who was in charge of the ventilation of the new Houses of Parliament: his plan called for a great central chimney through which what he called "vitiated air" would be drawn out of the building with the heat and smoke of about four hundred fires around the Palace. To accommodate the tower, Barry was forced to lower the lofty ceiling he had planned for the Central Lobby and reduce the height of its windows; however, the tower itself proved to be an opportunity to improve the Palace's exterior design, Riding and Riding (2000), p. 120. and Barry chose for it the form of a spire
A spire is a tall, slender, pointed structure on top of a roof of a building or tower, especially at the summit of church steeples. A spire may have a square, circular, or polygonal plan, with a roughly conical or pyramidal shape. Spires a ...
in order to balance the effect of the more massive lateral towers. In the end, the Central Tower failed completely to fulfill its stated purpose, but it is notable as "the first occasion when mechanical services had a real influence on architectural design".
Apart from the pinnacles which rise from between the window bays along the fronts of the Palace, numerous turret
Turret may refer to:
* Turret (architecture), a small tower that projects above the wall of a building
* Gun turret, a mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon
* Objective turret, an indexable holder of multiple lenses in an optical microscope
* M ...
s enliven the building's skyline. Like the Central Tower, these have been added for practical reasons, and mask ventilation shafts.
There are some other features of the Palace of Westminster which are also known as towers. St Stephen's Tower is positioned in the middle of the west front of the Palace, between Westminster Hall and Old Palace Yard, and houses the public entrance to the Houses of Parliament, known as ''St Stephen's Entrance''. The pavilions at the northern and southern ends of the river front are called Speaker's Tower and Chancellor's Tower respectively, after the presiding officers of the two Houses at the time of the Palace's reconstruction—the Speaker of the House of Commons and the Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
. Speaker's Tower contains Speaker's House, the official residence of the Speaker of the Commons.
Grounds
 There are a number of small gardens surrounding the Palace of Westminster. Victoria Tower Gardens is open as a public park along the side of the river south of the palace. Black Rod's Garden (named after the office of
There are a number of small gardens surrounding the Palace of Westminster. Victoria Tower Gardens is open as a public park along the side of the river south of the palace. Black Rod's Garden (named after the office of Gentleman Usher of the Black Rod
Black Rod (officially known as the Lady Usher of the Black Rod or, if male, the Gentleman Usher of the Black Rod) is an official in the parliaments of several Commonwealth countries. The position originates in the House of Lords of the Parliam ...
) is closed to the public and is used as a private entrance. Old Palace Yard
Old Palace Yard is a paved open space in the City of Westminster in Central London, England. It lies between the Palace of Westminster to its north and east and Westminster Abbey to its west. It is known as the site of executions, including those ...
, in front of the Palace, is paved over and covered in concrete security blocks (''see security" \n\n\nsecurity.txt is a proposed standard for websites' security information that is meant to allow security researchers to easily report security vulnerabilities. The standard prescribes a text file called \"security.txt\" in the well known locat ...
below''). Cromwell Green (also on the frontage, and in 2006 enclosed by hoardings for the construction of a new visitor centre), New Palace Yard
New Palace Yard is a yard (area of grounds) northwest of the Palace of Westminster in Westminster, London, England. It is part of the grounds not open to the public. However, it can be viewed from the two adjoining streets, as a result of Edwa ...
(on the north side) and Speaker's Green (directly north of the Palace) are all private and closed to the public. College Green, opposite the House of Lords, is a small triangular green commonly used for television interviews with politicians.
Interior
The Palace of Westminster contains over 1,100 rooms, 100 staircases and of passageways, which are spread over four floors. The ground floor is occupied by offices, dining rooms and bars; the first floor (known as the ''principal floor'') houses the main rooms of the Palace, including the debating chambers, the lobbies and the libraries. The top-two floors are used as committee rooms and offices. Some of the interiors were designed and painted byJ. G. Crace
John Gregory Crace (26 May 1809 – 13 August 1889) was a British interior decorator and author.
Early life and education
The Crace family had been prominent London interior decorators since Edward Crace (1725–1799), later keeper of the roya ...
, working in collaboration with Pugin and others. For example, Crace decorated and gilded the ceiling of the Chapel of St. Mary Undercroft.
Layout
 Instead of one main entrance, the Palace features separate entrances for the different user groups of the building. The Sovereign's Entrance, at the base of the Victoria Tower, is located in the south-west corner of the Palace and is the starting point of the royal procession route, the suite of ceremonial rooms used by the monarch at State Openings of Parliament. This consists of the Royal Staircase, the Norman Porch, the Robing Room, the Royal Gallery and the Prince's Chamber, and culminates in the Lords Chamber, where the ceremony takes place. Members of the House of Lords use the Peers' Entrance in the middle of the Old Palace Yard front, which is covered by a stone
Instead of one main entrance, the Palace features separate entrances for the different user groups of the building. The Sovereign's Entrance, at the base of the Victoria Tower, is located in the south-west corner of the Palace and is the starting point of the royal procession route, the suite of ceremonial rooms used by the monarch at State Openings of Parliament. This consists of the Royal Staircase, the Norman Porch, the Robing Room, the Royal Gallery and the Prince's Chamber, and culminates in the Lords Chamber, where the ceremony takes place. Members of the House of Lords use the Peers' Entrance in the middle of the Old Palace Yard front, which is covered by a stone carriage porch
A carriage is a private four-wheeled vehicle for people and is most commonly horse-drawn. Second-hand private carriages were common public transport, the equivalent of modern cars used as taxis. Carriage suspensions are by leather strapping an ...
and opens to an entrance hall. A staircase from there leads, through a corridor, to the Prince's Chamber. ''Guide to the Palace of Westminster'', p. 28.
Members of Parliament enter their part of the building from the Members' Entrance in the south side of New Palace Yard. Their route passes through a cloakroom in the lower level of the Cloisters and eventually reaches the Members' Lobby directly south of the Commons Chamber. From New Palace Yard, access can also be gained to the Speaker's Court and the main entrance of the Speaker's House, located in the pavilion at the north-east corner of the Palace
St Stephen's Entrance, roughly in the middle of the building's western front, is the entrance for members of the public. From there, visitors walk through a flight of stairs to St Stephen's Hall, location of a collection of marbles, which includes Somers Mansfield
Mansfield is a market town and the administrative centre of Mansfield District in Nottinghamshire, England. It is the largest town in the wider Mansfield Urban Area (followed by Sutton-in-Ashfield). It gained the Royal Charter of a market to ...
,The Illustrated London News, illustration accompanying "The New Houses of Parliament", 2 February 1856, p.121 Hampden, Walpole, Pitt and Fox. Traversal of this hallway brings them to the octagonal Central Lobby, the hub of the Palace. This hall is flanked by symmetrical corridors decorated with fresco paintings, which lead to the ante-rooms and debating chambers of the two Houses: the Members' Lobby and Commons Chamber to the north, and the Peers' Lobby and Lords Chamber to the south. Another mural-lined corridor leads east to the Lower Waiting Hall and the staircase to the first floor, where the river front is occupied by a row of 16 committee rooms. Directly below them, the libraries of the two Houses overlook the Thames from the principal floor.
Norman Porch
The grandest entrance to the Palace of Westminster is the Sovereign's Entrance beneath the Victoria Tower. It was designed for the use of the monarch, who travels fromBuckingham Palace
Buckingham Palace () is a London royal residence and the administrative headquarters of the monarch of the United Kingdom. Located in the City of Westminster, the palace is often at the centre of state occasions and royal hospitality. It ...
by carriage every year for the State Opening of Parliament
The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremonial event which formally marks the beginning of a session of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It includes a speech from the throne known as the King's (or Queen's) Speech. The event takes plac ...
. The Imperial State Crown, which is worn by the sovereign for the ceremony, as well as the Cap of Maintenance and the Sword of State, which are symbols of royal authority and are borne before the monarch during the procession, also travel to the Palace by coach, accompanied by members of the Royal Household; the regalia, as they are collectively known, arrive some time before the monarch and are exhibited in the Royal Gallery until they are needed. The Sovereign's Entrance is also the formal entrance used by visiting dignitaries, as well as the starting point of public tours of the Palace.
From there, the Royal Staircase leads up to the principal floor with a broad, unbroken flight of 26 steps made of grey granite. The staircase is followed by the Norman Porch, a square landing distinguished by its central clustered column and the intricate ceiling it supports, which is made up of four groin vaults with lierne ribs and carved bosses. The Porch was named for its proposed decorative scheme, based on Norman history. In the event, neither the planned statues of Norman kings nor the frescoes were executed, and only the stained-glass window portraying Edward the Confessor
Edward the Confessor ; la, Eduardus Confessor , ; ( 1003 – 5 January 1066) was one of the last Anglo-Saxon English kings. Usually considered the last king of the House of Wessex, he ruled from 1042 to 1066.
Edward was the son of Æt ...
hints at this theme. Queen Victoria is depicted twice in the room: as a young woman in the other stained-glass window, and near the end of her life, sitting on the throne of the House of Lords, in a copy of a 1900 painting by Jean-Joseph Benjamin-Constant
Jean-Joseph Benjamin-Constant (also known as Benjamin-Constant), born Jean-Joseph Constant (10 June 1845 – 26 May 1902), was a French painter and etcher best known for his Oriental subjects and portraits.
Biography
Benjamin-Constant was bor ...
which hangs on the eastern wall. The sixteen plinths intended for the statues now house busts of prime ministers who have sat in the House of Lords, such as the Earl Grey and the Marquess of Salisbury. A double door opposite the stairs leads to the Royal Gallery, and another to the right opens to the Robing Room.
King's Robing Room
The King's Robing Room (usually referred to simply as "the Robing Room") lies at the southern end of the ceremonial axis of the Palace and occupies the centre of the building's south front, overlooking the Victoria Tower Gardens. Wilson (2005), pp. 8–9. As its name indicates, it is where the Sovereign prepares for the State Opening of Parliament by donning official robes and wearing the Imperial State Crown. The focus of this richly decorated room is the Chair of State; it sits on a dais of three steps, under a canopy adorned with the arms and floral emblems of England, Scotland and Ireland. A panel of purple velvet forms the backdrop to the chair, embroidered by theRoyal School of Needlework
The Royal School of Needlework (RSN) is a hand embroidery school in the United Kingdom, founded in 1872 and based at Hampton Court Palace since 1987.
History
The RSN began as the School of Art Needlework in 1872, founded by Lady Victoria Welb ...
with the royal arms, surrounded by stars and ''VR'' monograms. Edward Barry designed both the chair—the cushion and back of which are also embroidered—and the ornate marble fireplace across the room, which features gilded statuettes of Saint George
Saint George ( Greek: Γεώργιος (Geórgios), Latin: Georgius, Arabic: القديس جرجس; died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was a Christian who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition he was a soldie ...
and Saint Michael
Michael (; he, מִיכָאֵל, lit=Who is like El od, translit=Mīḵāʾēl; el, Μιχαήλ, translit=Mikhaḗl; la, Michahel; ar, ميخائيل ، مِيكَالَ ، ميكائيل, translit=Mīkāʾīl, Mīkāl, Mīkhāʾīl), also ...
.
The decorative theme of the room is the legend of King Arthur, considered by many Victorians the source of their nationhood.#Field, Field (2002), p. 192. Five frescos painted by William Dyce between 1848 and 1864 cover the walls, depicting allegorical scenes from the legend. Each scene represents a chivalric virtue; the largest, between the two doors, is titled ''Admission of Sir Tristram to the Round Table'' and illustrates the virtue of Hospitality. Seven were originally commissioned but the remaining two paintings were not carried out due to the artist's death, and on the wallpapered panels flanking the Chair of State hang oil portraits of Queen Victoria and Prince Albert by Franz Xaver Winterhalter. Other decorations in the room are also inspired by the Arthurian legend, namely a series of 18 bas-reliefs beneath the paintings, carved in oak by Henry Hugh Armstead, and the frieze running below the ceiling, which displays the attributed coats of arms of the Knights of the Round Table. The ceiling itself is decorated with heraldic badges, as is the border of the wooden floor—which, as can be seen in the adjacent image, is left exposed by the carpeting.
The Robing Room was also briefly used as the House of Lords' meeting chamber while the House of Lords Chamber was occupied by the House of Commons, whose chamber had been destroyed by the Blitz in 1941.
Royal Gallery
Immediately north of the Robing Room is the Royal Gallery. At , it is one of the largest rooms in the Palace. Its main purpose is to serve as the stage of the State Procession at the UK Opening of Parliament, royal procession at State Openings of Parliament, which the audience watch from temporary tiered seating on both sides of the route. It has also been used on occasion by visiting statesmen from abroad when List of people who have addressed both Houses of the United Kingdom Parliament, addressing both Houses of Parliament, as well as for receptions in honour of foreign dignitaries, and more regularly for the Lord Chancellor's Breakfast; in the past it was the theatre of several trials of peers by the House of Lords. Documents from the Parliamentary Archives are on display in the Royal Gallery (including a facsimile of Charles I of England, Charles I's death warrant), and the tables and seating offer a workspace for members of the Lords that is conveniently close to their debating chamber. The decorative scheme of the Royal Gallery was meant to display important moments in British military history, and the walls are decorated by two large paintings by Daniel Maclise, each measuring : ''The Death of Nelson (Maclise painting), The Death of Nelson'' (depicting Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, Lord Nelson's demise at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805) and ''The Meeting of Wellington and Blücher after the Battle of Waterloo'' (showing the Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Duke of Wellington meeting Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher at the Battle of Waterloo in 1815). The murals deteriorated rapidly after their completion due to a range of factors, most importantly atmospheric pollution, and today they are almost monochrome, although a finished study of ''The Death of Nelson'' in better condition hangs in the Walker Art Gallery, Liverpool. The rest of the planned frescos were cancelled, and the walls are filled with portraits of kings and queens from George I of Great Britain, George I onwards. Another decorative element with military undertones are the eight statues of gilded Caen stone that flank the three doorways and the bay window of the Gallery, sculpted by John Birnie Philip. Each depicts a monarch during whose reign a key battle or war took place. They are: Alfred the Great and William the Conqueror; Richard I of England, Richard I and Edward III of England, Edward III; Henry V of England, Henry V and Elizabeth I of England, Elizabeth I; William III of England, William III and Anne, Queen of Great Britain, Anne. The panelled ceiling, above the floor, features Tudor roses and lions, and the stained-glass windows show the coats of arms of the Kings of England and Scotland.Prince's Chamber
 The Prince's Chamber is a small wiktionary:anteroom, anteroom between the Royal Gallery and the Lords Chamber, named after the room adjoining the Parliament Chamber in the Old Palace of Westminster. Thanks to its location, it is a place where members of the Lords meet to discuss business of the House. Several doors lead out of the room, to the Division of the assembly, division lobbies of the House of Lords and to a number of important offices.
The theme of the Prince's Chamber is Tudor history, and 28 oil portraits painted on panels around the room depict members of the Tudor dynasty. They are the work of Richard Burchett and his pupils, and their creation entailed extensive research, which contributed to the founding of the National Portrait Gallery, London, National Portrait Gallery in 1856. 12 bronze bas-reliefs are set into the wall below the portraits, executed by William Theed in 1855–1857. Scenes included are ''The Field of the Cloth of Gold'', ''The Escape of Mary, Queen of Scots'' and ''Walter Raleigh, Raleigh Spreading His Cloak As a Carpet for the Queen''. Above the portraits, at window level, there are compartments intended for copies of six of the ten Armada tapestries, which hung in the chamber of the House of Lords until their destruction in the 1834 fire and depicted the defeat of the Spanish Armada in 1588. The project was put on hold in 1861 (by which time only one painting had been completed), and was not revived until 2007; , all six paintings have been finished and are on display in the Royal Gallery. They are scheduled to be fixed in the Prince's Chamber in the following months.
The room also contains a statue of Queen Victoria, seated on a throne (itself placed on a pedestal) and holding a sceptre and a laurel crown, which show that she both governs and rules. This figure is flanked by allegorical statues of Justice and Clemency—the former with a bare sword and an inflexible expression and the latter showing sympathy and offering an olive branch. The sculptural ensemble, made of white marble and carved by John Gibson (sculptor), John Gibson in 1855, reaches in height; its size has long been considered out of proportion with the fittings of the Prince's Chamber, and the flanking statues ended up in storage between 1955 and 1976. However, the size and location of the group, in the archway opposite the doors to the Royal Gallery (which are removed before State Openings of Parliament to facilitate the royal procession), indicate that it was meant to be seen from a distance, and to symbolically remind the monarch of their royal duties as they would walk down the Royal Gallery on their way to deliver their speech.
The Prince's Chamber is a small wiktionary:anteroom, anteroom between the Royal Gallery and the Lords Chamber, named after the room adjoining the Parliament Chamber in the Old Palace of Westminster. Thanks to its location, it is a place where members of the Lords meet to discuss business of the House. Several doors lead out of the room, to the Division of the assembly, division lobbies of the House of Lords and to a number of important offices.
The theme of the Prince's Chamber is Tudor history, and 28 oil portraits painted on panels around the room depict members of the Tudor dynasty. They are the work of Richard Burchett and his pupils, and their creation entailed extensive research, which contributed to the founding of the National Portrait Gallery, London, National Portrait Gallery in 1856. 12 bronze bas-reliefs are set into the wall below the portraits, executed by William Theed in 1855–1857. Scenes included are ''The Field of the Cloth of Gold'', ''The Escape of Mary, Queen of Scots'' and ''Walter Raleigh, Raleigh Spreading His Cloak As a Carpet for the Queen''. Above the portraits, at window level, there are compartments intended for copies of six of the ten Armada tapestries, which hung in the chamber of the House of Lords until their destruction in the 1834 fire and depicted the defeat of the Spanish Armada in 1588. The project was put on hold in 1861 (by which time only one painting had been completed), and was not revived until 2007; , all six paintings have been finished and are on display in the Royal Gallery. They are scheduled to be fixed in the Prince's Chamber in the following months.
The room also contains a statue of Queen Victoria, seated on a throne (itself placed on a pedestal) and holding a sceptre and a laurel crown, which show that she both governs and rules. This figure is flanked by allegorical statues of Justice and Clemency—the former with a bare sword and an inflexible expression and the latter showing sympathy and offering an olive branch. The sculptural ensemble, made of white marble and carved by John Gibson (sculptor), John Gibson in 1855, reaches in height; its size has long been considered out of proportion with the fittings of the Prince's Chamber, and the flanking statues ended up in storage between 1955 and 1976. However, the size and location of the group, in the archway opposite the doors to the Royal Gallery (which are removed before State Openings of Parliament to facilitate the royal procession), indicate that it was meant to be seen from a distance, and to symbolically remind the monarch of their royal duties as they would walk down the Royal Gallery on their way to deliver their speech.
Lords Chamber
 The Chamber of the
The Chamber of the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
is located in the southern part of the Palace of Westminster. The lavishly decorated room measures . The benches in the Chamber, as well as other furnishings in the Lords' side of the Palace, are coloured red. The upper part of the Chamber is decorated by stained glass windows and by six allegorical frescoes representing religion, chivalry and law.
At the south end of the Chamber are the ornate gold Canopy and Throne; although the Sovereign may theoretically occupy the Throne during any sitting, he or she attends only the State Opening of Parliament. Other members of the Royal Family who attend the State Opening use Chairs of State next to the Throne, and peers' sons are always entitled to sit on the steps of the Throne. In front of the Throne is the Woolsack, an armless red cushion stuffed with wool, representing the historical importance of the wool trade, and used by the officer presiding over the House (the Lord Speaker
The Lord Speaker is the presiding officer, chairman and highest authority of the House of Lords in the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The office is analogous to the Speaker of the House of Commons: the Lord Speaker is elected by the membe ...
since 2006, but historically the Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
or a deputy). The House's Ceremonial mace, mace, which represents royal authority, is placed on the back of the Woolsack. In front of the Woolsack is the Judges' Woolsack, a larger red cushion that used to be occupied during the State Opening by the Lords of Appeal in Ordinary, Law Lords (who were members of the House of Lords), and prospectively by the Supreme Court Justices and other Judges (whether or not members), to represent the Judicial Branch of Government. The Table of the House, at which the clerks sit, is in front.
Members of the House occupy red benches on three sides of the Chamber. The benches on the Lord Speaker's right form the Spiritual Side and those to his left form the Temporal Side. The Lords Spiritual (archbishops and bishops of the established Church of England) all occupy the Spiritual Side. The Lords Temporal (Peerage, nobles) sit according to party affiliation: members of the Government party sit on the Spiritual Side, while those of the Opposition sit on the Temporal Side. Some peers, who have no party affiliation, sit on the benches in the middle of the House opposite the Woolsack; they are accordingly known as crossbenchers.
The Lords Chamber is the site of nationally televised ceremonies, the most important of which is the State Opening of Parliament
The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremonial event which formally marks the beginning of a session of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It includes a speech from the throne known as the King's (or Queen's) Speech. The event takes plac ...
, which is held formally to open each annual parliamentary session, either after a General Election or in the autumn. At this occasion every constitutional element of the government is represented: the Crown (both literally, and figuratively in the person of the Sovereign), The Lords Spiritual and Temporal, and The Commons, (who together form the Legislature), the Judiciary (although no judges are members of either House of Parliament), and the Executive (both Minister of the Crown, Government Ministers, and ceremonial military units in attendance on the Sovereign); and a large number of guests are invited to attend in the large Royal Gallery immediately outside the Chamber. The Sovereign, seated on the Throne, delivers the Speech from the Throne, outlining the Government's programme for the year and legislative agenda for the forthcoming parliamentary session. The Commons may not enter the Lords' debating floor; instead, they watch the proceedings from beyond the Bar of the House, just inside the door. A small purely formal ceremony is held to end each parliamentary session, when the Sovereign is merely represented by a group of Lords Commissioners.
Following the Blitz, which destroyed the chamber of the House of Commons, the Lords' chamber was occupied by the Commons. The Lords temporarily used the Robing Room during the reconstruction. The State Opening Of Parliament was carried out as normal, with the new rooms being used. Evidence can still be seen of this today, with damage clearly visible on one of the doors where they were struck by Black Rod.
Peers' Lobby
Directly north of the Lords Chamber lies the Peers' Lobby, an antechamber where Lords can informally discuss or negotiate matters during sittings of the House, as well as collect messages from the Doorkeeper (Houses of Parliament), doorkeepers, who control access to the Chamber. The Lobby is a square room measuring on each side and in height, and one of its main features is the floor centrepiece, a radiant Tudor rose made of Derbyshire marbles and set within an octagon of engraved brass plates. The rest of the floor is paved with encaustic tiles featuring heraldic designs and Latin mottoes. The walls are faced with white stone and each is pierced by a doorway; above the arches are displayed arms representing the six royal dynasties which ruled England until Queen Victoria's reign (House of Wessex, Saxon, Norman dynasty, Norman, House of Plantagenet, Plantagenet, Tudor dynasty, Tudor, House of Stuart, Stuart and House of Hanover, Hanoverian), and between them there are windows stained with the arms of the early aristocratic families of England. Of the doorways, the one to the south—which leads into the Lords Chamber—is the most magnificent, and sports much gilding and decoration, including the full royal arms. It is enclosed by the Brass Gates, a pair of elaborately pierced and studded doors together weighing 1.5 tonnes. The side doors, which feature clocks, open into corridors: to the east extends the Law Lords Corridor, which leads to the libraries, and nearby to the west lies the Moses Room, used for Grand Committees. To the north is the vaulted Peers' Corridor, which is decorated with eight murals by Charles West Cope depicting historical scenes from the period around the English Civil War. The frescoes were executed between 1856 and 1866, and each scene was "specifically chosen to depict the struggles through which national liberties were won". Examples include ''Speaker William Lenthall, Lenthall Asserting the Privileges of the Commons Against Charles I when the Attempt was Made to Seize the Five Members'', representing resistance against absolute rule, and ''The Embarkation of the Pilgrim Fathers for New England'', which illustrates the principle of freedom of worship.Central Lobby
 Originally named "Octagon Hall" because of its shape, the Central Lobby is the heart of the Palace of Westminster. It lies directly below the Central Tower and forms a busy crossroads between the House of Lords to the south, the House of Commons to the north, St Stephen's Hall and the public entrance to the west, and the Lower Waiting Hall and the libraries to the east. Its location halfway between the two debating chambers has led constitutional theorist Erskine May, 1st Baron Farnborough, Erskine May to describe the Lobby as "the political centre of the British Empire", and allows a person standing under the great chandelier to see both the Royal Throne and the Speaker's Chair, provided that all the intervening doors are open. Constituents may meet their Members of Parliament here, even without an appointment, and this practice is the origin of the term ''lobbying''. The hall is also the theatre of the Speaker's Procession, which passes from here on its way to the Commons Chamber before every sitting of the House.
The Central Lobby measures across and from the floor to the centre of the vaulted ceiling. The panels between the vault's ribs are covered with Venetian glass mosaic displaying floral emblems and heraldic badges, and the bosses in the intersections of the ribs are also carved into heraldic symbols. Each wall of the Lobby is contained in an arch ornamented with statues of English and Scottish monarchs; on four sides there are doorways, and the Tympanum (architecture), tympana above them are adorned with mosaics representing the patron saints of the United Kingdom's constituent nations:
Originally named "Octagon Hall" because of its shape, the Central Lobby is the heart of the Palace of Westminster. It lies directly below the Central Tower and forms a busy crossroads between the House of Lords to the south, the House of Commons to the north, St Stephen's Hall and the public entrance to the west, and the Lower Waiting Hall and the libraries to the east. Its location halfway between the two debating chambers has led constitutional theorist Erskine May, 1st Baron Farnborough, Erskine May to describe the Lobby as "the political centre of the British Empire", and allows a person standing under the great chandelier to see both the Royal Throne and the Speaker's Chair, provided that all the intervening doors are open. Constituents may meet their Members of Parliament here, even without an appointment, and this practice is the origin of the term ''lobbying''. The hall is also the theatre of the Speaker's Procession, which passes from here on its way to the Commons Chamber before every sitting of the House.
The Central Lobby measures across and from the floor to the centre of the vaulted ceiling. The panels between the vault's ribs are covered with Venetian glass mosaic displaying floral emblems and heraldic badges, and the bosses in the intersections of the ribs are also carved into heraldic symbols. Each wall of the Lobby is contained in an arch ornamented with statues of English and Scottish monarchs; on four sides there are doorways, and the Tympanum (architecture), tympana above them are adorned with mosaics representing the patron saints of the United Kingdom's constituent nations: Saint George
Saint George ( Greek: Γεώργιος (Geórgios), Latin: Georgius, Arabic: القديس جرجس; died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was a Christian who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition he was a soldie ...
for England, Saint Andrew for Scotland, Saint David for Wales and Saint Patrick for Ireland. The other four arches are occupied by high windows, under which there are stone screens—the hall's post office, one of two in the Palace, is located behind one of these screens. In front of them stand four bigger-than-life statues of 19th-century statesmen, including one of four-time prime minister William Ewart Gladstone, William Gladstone. The floor on which they stand is tiled with Minton encaustic tiles in intricate patterns and includes a passage from wikisource:Bible, King James, Psalms#Psalm 127, Psalm 127 written in Latin, which translates as follows: "Except the Lord build the House their labour is but lost that build it".
The East Corridor leads from the Central Lobby to the Lower Waiting Hall, and its six panels remained blank until 1910, when they were filled with scenes from Tudor history. They were all paid for by Liberal Party (UK), Liberal peers and each was the work of a different artist, but uniformity was achieved between the frescoes thanks to a common colour palette of red, black and gold and a uniform height for the depicted characters. One of the scenes is probably not historical: ''Plucking the Red Rose of Lancaster, Red and White Rose of York, White Roses in the Old Temple Gardens'', depicting the origin of these flowers as emblems of the House of Lancaster, Houses of Lancaster and House of York, York respectively, was taken from Shakespeare's play ''Henry VI, Part 1''.
Members' Lobby
 Continuing north from the Central Lobby is the Commons' Corridor. It is of almost identical design to its southern counterpart and is decorated with scenes of 17th-century political history between the Civil War and the Glorious Revolution, Revolution of 1688. They were painted by Edward Matthew Ward and include subjects like ''George Monck, 1st Duke of Albemarle, Monk Declaring for a Free Parliament'' and ''The Lords and Commons Presenting the Crown to William III of England, William III and Mary II of England, Mary II in the Banqueting Hall''. Then, mirroring the arrangement at the Lords part of the Palace, is another antechamber, the Members' Lobby. In this room, Members of Parliament hold discussions or negotiations, and are often interviewed by accredited journalists, collectively known as "The Lobby".
The room is similar to the Peers' Lobby but plainer in design and slightly larger, forming a cube on all sides. After the heavy damage it sustained in the 1941 bombing, it was rebuilt in a simplified style, something most evident in the floor, which is almost completely unadorned. The archway of the door leading into the Commons Chamber has been left unrepaired as a reminder of the evils of war, and is now known as the Rubble Arch or Churchill Arch. It is flanked by bronze statues of Winston Churchill and David Lloyd George, the prime ministers who led Britain through the Second and First World War respectively; a foot of each is conspicuously shiny, a result of a long tradition of MPs rubbing them for good luck on their way in before their maiden speech. The Lobby contains the busts and statues of most 20th-century prime ministers, as well as two large boards where MPs can receive letters and telephone messages, designed for the use of the House and installed in the early 1960s.
Continuing north from the Central Lobby is the Commons' Corridor. It is of almost identical design to its southern counterpart and is decorated with scenes of 17th-century political history between the Civil War and the Glorious Revolution, Revolution of 1688. They were painted by Edward Matthew Ward and include subjects like ''George Monck, 1st Duke of Albemarle, Monk Declaring for a Free Parliament'' and ''The Lords and Commons Presenting the Crown to William III of England, William III and Mary II of England, Mary II in the Banqueting Hall''. Then, mirroring the arrangement at the Lords part of the Palace, is another antechamber, the Members' Lobby. In this room, Members of Parliament hold discussions or negotiations, and are often interviewed by accredited journalists, collectively known as "The Lobby".
The room is similar to the Peers' Lobby but plainer in design and slightly larger, forming a cube on all sides. After the heavy damage it sustained in the 1941 bombing, it was rebuilt in a simplified style, something most evident in the floor, which is almost completely unadorned. The archway of the door leading into the Commons Chamber has been left unrepaired as a reminder of the evils of war, and is now known as the Rubble Arch or Churchill Arch. It is flanked by bronze statues of Winston Churchill and David Lloyd George, the prime ministers who led Britain through the Second and First World War respectively; a foot of each is conspicuously shiny, a result of a long tradition of MPs rubbing them for good luck on their way in before their maiden speech. The Lobby contains the busts and statues of most 20th-century prime ministers, as well as two large boards where MPs can receive letters and telephone messages, designed for the use of the House and installed in the early 1960s.
Commons Chamber
 The debating chamber, Chamber of the
The debating chamber, Chamber of the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
is at the northern end of the Palace of Westminster; it was opened in 1950 after the Victorian chamber had been destroyed in 1941 and re-built under the architect Giles Gilbert Scott. The Chamber measures and is plainer in style than the Lords Chamber; the benches, as well as other furnishings in the Commons side of the Palace, are coloured green. Members of the public are forbidden to sit on the benches. Other parliaments in Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth nations, including those of Parliament of India, India, Parliament of Canada, Canada, Parliament of Australia, Australia and Parliament of New Zealand, New Zealand, have copied the colour scheme under which the Lower House is associated with green, and the Upper House with red.
 At the north end of the Chamber is the Speaker of the House of Commons (United Kingdom), Speaker's Chair, a present to Parliament from the Commonwealth of Australia. The current British Speaker's Chair is an exact copy of the Speaker's Chair given to Australia, by the House of Commons, to celebrate the opening of Old Parliament House, Canberra. In front of the Speaker's Chair is the Table of the House, at which the clerks sit, and on which is placed the Commons' ceremonial mace. The Table was a gift from Canada. The dispatch boxes, which front-bench Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Members of Parliament (MPs) often lean on or rest notes on during Questions and speeches, are a gift from New Zealand. There are green benches on either side of the House; members of the Government party occupy benches on the Speaker's right, while those of the Opposition occupy benches on the Speaker's left. There are no cross-benches as in the House of Lords. The Chamber is relatively small, and can accommodate only 427 of the 650 Members of Parliament—during Prime Minister's Questions and in major debates MPs stand at either end of the House.
By tradition, the British Sovereign does not enter the Chamber of the House of Commons. The last monarch to do so was King Charles I, in 1642. The King sought to arrest five Members of Parliament on charges of high treason, but when he asked the Speaker, William Lenthall, if he had any knowledge of the whereabouts of these individuals, Lenthall famously replied: "May it please your Majesty, I have neither eyes to see nor tongue to speak in this place but as the House is pleased to direct me, whose servant I am here." Since then, in the
At the north end of the Chamber is the Speaker of the House of Commons (United Kingdom), Speaker's Chair, a present to Parliament from the Commonwealth of Australia. The current British Speaker's Chair is an exact copy of the Speaker's Chair given to Australia, by the House of Commons, to celebrate the opening of Old Parliament House, Canberra. In front of the Speaker's Chair is the Table of the House, at which the clerks sit, and on which is placed the Commons' ceremonial mace. The Table was a gift from Canada. The dispatch boxes, which front-bench Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Members of Parliament (MPs) often lean on or rest notes on during Questions and speeches, are a gift from New Zealand. There are green benches on either side of the House; members of the Government party occupy benches on the Speaker's right, while those of the Opposition occupy benches on the Speaker's left. There are no cross-benches as in the House of Lords. The Chamber is relatively small, and can accommodate only 427 of the 650 Members of Parliament—during Prime Minister's Questions and in major debates MPs stand at either end of the House.
By tradition, the British Sovereign does not enter the Chamber of the House of Commons. The last monarch to do so was King Charles I, in 1642. The King sought to arrest five Members of Parliament on charges of high treason, but when he asked the Speaker, William Lenthall, if he had any knowledge of the whereabouts of these individuals, Lenthall famously replied: "May it please your Majesty, I have neither eyes to see nor tongue to speak in this place but as the House is pleased to direct me, whose servant I am here." Since then, in the State Opening of Parliament
The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremonial event which formally marks the beginning of a session of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It includes a speech from the throne known as the King's (or Queen's) Speech. The event takes plac ...
, when Black Rod representing the monarch approaches the doors to the chamber of the House of Commons to make the summons, the doors are pointedly slammed in his or her face. Black Rod has to strike the door three times with a staff, to be admitted and issue the summons from the monarch to the MPs to attend. When repairs after the World War II bombing were completed, the rebuilt chamber was opened by King George VI on 26 October 1950 who was invited to an "unofficial" tour of the new structure by Commons leaders.
The two red lines on the floor of the House of Commons are apart, which, by apocryphal tradition, is intended to be just over two sword-lengths. It is said that the original purpose of this was to prevent disputes in the House from degenerating into duels. However, there is no record of a time when Members of Parliament were allowed to bring swords into the Chamber; historically only the Serjeant at Arms of the British House of Commons, Serjeant at Arms has been allowed to carry a sword as a symbol of their role in Parliament, plus Black Rod when summoning the Commons to the Lords, and there are loops of pink ribbon in the Members' cloakroom for MPs to hang up their swords before entering the Chamber. In the days when gentlemen carried swords, there were no lines in the Chamber. Protocol dictates that MPs may not cross these lines when speaking; a Member of Parliament who violates this convention will be lambasted by opposition Members.
Westminster Hall
 Westminster Hall, the oldest existing part of the Palace of Westminster, was erected in 1097 by William II of England, King William II ('William Rufus'), at which point it was the largest hall in Europe. The roof was probably originally supported by pillars, giving three aisles, but during the reign of Richard II of England, King Richard II, this was replaced by a hammerbeam roof by the royal carpenter Hugh Herland, "the greatest creation of medieval timber architecture", which allowed the original three aisles to be replaced with a single huge open space, with a dais at the end. The new roof was commissioned in 1393. Richard's master builder Henry Yevele retained the original dimensions, refacing the walls, with fifteen life-size statues of kings placed in niches. The rebuilding had been begun by King Henry III in 1245, but by Richard's time had been dormant for over a century. In Westminster Hall, the favourite heraldic badge of Richard II – a white hart, chained, and in an attitude of rest – is repeated eighty-three times, without any of them being an exact copy of another.
The largest clearspan medieval roof in England, Westminster Hall's roof measures . Oak timbers for the roof came from royal woods in Hampshire and from parks in Hertfordshire and from that of William Crozier of Stoke d'Abernon, who supplied over 600 oaks in Surrey, among other sources; they were assembled near Farnham, Surrey, away. Accounts record the large number of wagons and barges which delivered the Timber framing, jointed timbers to Westminster for assembly.
Westminster Hall, the oldest existing part of the Palace of Westminster, was erected in 1097 by William II of England, King William II ('William Rufus'), at which point it was the largest hall in Europe. The roof was probably originally supported by pillars, giving three aisles, but during the reign of Richard II of England, King Richard II, this was replaced by a hammerbeam roof by the royal carpenter Hugh Herland, "the greatest creation of medieval timber architecture", which allowed the original three aisles to be replaced with a single huge open space, with a dais at the end. The new roof was commissioned in 1393. Richard's master builder Henry Yevele retained the original dimensions, refacing the walls, with fifteen life-size statues of kings placed in niches. The rebuilding had been begun by King Henry III in 1245, but by Richard's time had been dormant for over a century. In Westminster Hall, the favourite heraldic badge of Richard II – a white hart, chained, and in an attitude of rest – is repeated eighty-three times, without any of them being an exact copy of another.
The largest clearspan medieval roof in England, Westminster Hall's roof measures . Oak timbers for the roof came from royal woods in Hampshire and from parks in Hertfordshire and from that of William Crozier of Stoke d'Abernon, who supplied over 600 oaks in Surrey, among other sources; they were assembled near Farnham, Surrey, away. Accounts record the large number of wagons and barges which delivered the Timber framing, jointed timbers to Westminster for assembly.
 Westminster Hall has served numerous functions. Until the 19th century, it was regularly used for judicial purposes, housing three of the most important courts in the land: the Court of King's Bench (England), Court of King's Bench, the Court of Common Pleas (England), Court of Common Pleas and the Court of Chancery. In the reign of Henry II of England, Henry II (1154–89) a royal decree established a fixed sitting of judges in the Hall. In 1215, Magna Carta stipulated that these courts would sit regularly in the Hall for the convenience of litigants. In 1875, the courts were amalgamated into the High Court of Justice, which continued to have chambers adjacent to Westminster Hall until moved to the then new Royal Courts of Justice building in 1882. In addition to regular courts, Westminster Hall also housed important state trials, including impeachment trials and the state trials of King Charles I at the end of the English Civil War, William Wallace, Thomas More, Cardinal John Fisher, Guy Fawkes, the Thomas Wentworth, 1st Earl of Strafford, Earl of Strafford, the rebel Scottish lords of the 1715 and 1745 uprisings, and Impeachment of Warren Hastings, Warren Hastings. The St Stephen's Porch end of the Hall displays under the stained glass window the Parliamentary War Memorial listing on eight panels the names of Members and staff of both Houses of Parliament and their sons killed serving in the First World War; the window itself, installed in 1952, commemorates members and staff of both Houses who died in the Second World War. In 2012, a new stained glass window commemorating Queen Elizabeth II's diamond jubilee was installed opposite this window, at the other end of the hall.
Westminster Hall has served numerous functions. Until the 19th century, it was regularly used for judicial purposes, housing three of the most important courts in the land: the Court of King's Bench (England), Court of King's Bench, the Court of Common Pleas (England), Court of Common Pleas and the Court of Chancery. In the reign of Henry II of England, Henry II (1154–89) a royal decree established a fixed sitting of judges in the Hall. In 1215, Magna Carta stipulated that these courts would sit regularly in the Hall for the convenience of litigants. In 1875, the courts were amalgamated into the High Court of Justice, which continued to have chambers adjacent to Westminster Hall until moved to the then new Royal Courts of Justice building in 1882. In addition to regular courts, Westminster Hall also housed important state trials, including impeachment trials and the state trials of King Charles I at the end of the English Civil War, William Wallace, Thomas More, Cardinal John Fisher, Guy Fawkes, the Thomas Wentworth, 1st Earl of Strafford, Earl of Strafford, the rebel Scottish lords of the 1715 and 1745 uprisings, and Impeachment of Warren Hastings, Warren Hastings. The St Stephen's Porch end of the Hall displays under the stained glass window the Parliamentary War Memorial listing on eight panels the names of Members and staff of both Houses of Parliament and their sons killed serving in the First World War; the window itself, installed in 1952, commemorates members and staff of both Houses who died in the Second World War. In 2012, a new stained glass window commemorating Queen Elizabeth II's diamond jubilee was installed opposite this window, at the other end of the hall.
 Westminster Hall has also served ceremonial functions. From the twelfth century to the nineteenth, coronation banquets honouring new monarchs were held here. The last coronation banquet was that of King George IV, held in 1821; his successor, William IV of the United Kingdom, William IV, abandoned the idea because he deemed it too expensive. The Hall has been used as a place for lying in state during State funeral, state and ceremonial funerals. Such an honour is usually reserved for the Sovereign and for their consorts; the only non-royals to receive it in the twentieth century were Frederick Sleigh Roberts, 1st Earl Roberts (1914), the 48 victims of the crash of the airship R101 (1930) and Winston Churchill (1965). In 2002 the hall was used for the lying in state of Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother, and in 2022, the hall was used for the lying in state of Elizabeth II, Queen Elizabeth II. Around 250,000 mourners filed past the coffin, which resulted in the delamination of the Yorkstone floor.
The two Houses have presented ceremonial Addresses to the Crown in Westminster Hall on important public occasions. For example, Addresses were presented at Elizabeth II's Silver Jubilee of Elizabeth II, Silver Jubilee (1977), Golden Jubilee of Elizabeth II, Golden Jubilee (2002) and Diamond Jubilee of Elizabeth II, Diamond Jubilee (2012), the Accession of Charles III (2022), the 300th anniversary of the Glorious Revolution (1988), and the fiftieth anniversary of the end of the Second World War (1995).
It is considered a rare privilege for a foreign leader to be invited to address both Houses of Parliament in Westminster Hall. Since the Second World War, the only leaders to have done so have been French president Charles de Gaulle in 1960, South African president Nelson Mandela in 1996, Pope Benedict XVI in 2010, U.S. president Barack Obama in 2011 and Burma, Burmese opposition leader Aung San Suu Kyi in 2012. President Obama was the first US president to be invited to use the Hall for an address to Parliament and Aung San Suu Kyi was the first non-head of state to be given the accolade of addressing MPs and peers in Westminster Hall.
Following reforms in 1999, the House of Commons now uses the Grand Committee Room next to Westminster Hall as an additional debating chamber. (Although it is not part of the main hall, these are usually spoken of as Westminster Hall debates.) In contrast with the two main Chambers, in which the government and opposition benches directly face each other, the seating in the Grand Committee Room is laid out in a U-shape, a pattern meant to reflect the non-partisan nature of the debates there.
Westminster Hall has also served ceremonial functions. From the twelfth century to the nineteenth, coronation banquets honouring new monarchs were held here. The last coronation banquet was that of King George IV, held in 1821; his successor, William IV of the United Kingdom, William IV, abandoned the idea because he deemed it too expensive. The Hall has been used as a place for lying in state during State funeral, state and ceremonial funerals. Such an honour is usually reserved for the Sovereign and for their consorts; the only non-royals to receive it in the twentieth century were Frederick Sleigh Roberts, 1st Earl Roberts (1914), the 48 victims of the crash of the airship R101 (1930) and Winston Churchill (1965). In 2002 the hall was used for the lying in state of Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother, and in 2022, the hall was used for the lying in state of Elizabeth II, Queen Elizabeth II. Around 250,000 mourners filed past the coffin, which resulted in the delamination of the Yorkstone floor.
The two Houses have presented ceremonial Addresses to the Crown in Westminster Hall on important public occasions. For example, Addresses were presented at Elizabeth II's Silver Jubilee of Elizabeth II, Silver Jubilee (1977), Golden Jubilee of Elizabeth II, Golden Jubilee (2002) and Diamond Jubilee of Elizabeth II, Diamond Jubilee (2012), the Accession of Charles III (2022), the 300th anniversary of the Glorious Revolution (1988), and the fiftieth anniversary of the end of the Second World War (1995).
It is considered a rare privilege for a foreign leader to be invited to address both Houses of Parliament in Westminster Hall. Since the Second World War, the only leaders to have done so have been French president Charles de Gaulle in 1960, South African president Nelson Mandela in 1996, Pope Benedict XVI in 2010, U.S. president Barack Obama in 2011 and Burma, Burmese opposition leader Aung San Suu Kyi in 2012. President Obama was the first US president to be invited to use the Hall for an address to Parliament and Aung San Suu Kyi was the first non-head of state to be given the accolade of addressing MPs and peers in Westminster Hall.
Following reforms in 1999, the House of Commons now uses the Grand Committee Room next to Westminster Hall as an additional debating chamber. (Although it is not part of the main hall, these are usually spoken of as Westminster Hall debates.) In contrast with the two main Chambers, in which the government and opposition benches directly face each other, the seating in the Grand Committee Room is laid out in a U-shape, a pattern meant to reflect the non-partisan nature of the debates there.
Other rooms
There are two suites of libraries on the Principal Floor, overlooking the river, for the House of Lords Library and House of Commons Library. The Palace of Westminster also includes state apartments for the presiding officers of the two Houses. The official residence of the Speaker stands at the northern end of the Palace; the Lord Chancellor's apartments are at the southern end. Each day, the Speaker and Lord Speaker take part in formal processions from their apartments to their respective Chambers. The Strangers' Bar is one of the numerous bars, cafeterias and restaurants in the Palace of Westminster, with differing rules regarding who is allowed to use their facilities; many of them never close while the House is sitting. There is also a gymnasium, a hair salon; and a rifle range. Parliament also has two souvenir shops, where items on sale range from House of Commons key-rings and china to House of Commons Champagne.Security
 The Lady Usher of the Black Rod oversees security for the House of Lords, and the Serjeant at Arms of the British House of Commons, Serjeant at Arms does the same for the House of Commons. These officers, however, have primarily ceremonial roles outside the actual chambers of their respective Houses. Security is the responsibility of the Parliamentary Security Director. Parliament has its own professional security force. Tradition still dictates that only the Serjeant at Arms may enter the Commons chamber armed.
With rising concern about the possibility that a vehicle full of explosives could be driven into the building, a series of concrete blocks were placed in the roadway in 2003. On the river, an exclusion zone extending from the bank exists, which no unauthorised vessels are allowed to enter.
The Serious Organised Crime and Police Act 2005 formerly made it illegal to hold a protest near the Palace, or anywhere else within a designated area extending up to from Parliament Square, without authorisation from the Metropolitan Police. The Act also restricted the operation of loudspeakers in the designated area. These provisions were repealed by the Police Reform and Social Responsibility Act 2011, which replaced them with a total ban on tents and sleeping bags in Parliament Square, as well as a prohibition on the use of loudspeakers in the Square without permission from the relevant local authority.
Members of the public continue to have access to the Strangers' Gallery in the House of Commons. Visitors pass through metal detectors and their possessions are scanned. Police from the Palace of Westminster Division of the Metropolitan Police, supported by some armed police from the Diplomatic Protection Group, are always on duty in and around the Palace.
The Lady Usher of the Black Rod oversees security for the House of Lords, and the Serjeant at Arms of the British House of Commons, Serjeant at Arms does the same for the House of Commons. These officers, however, have primarily ceremonial roles outside the actual chambers of their respective Houses. Security is the responsibility of the Parliamentary Security Director. Parliament has its own professional security force. Tradition still dictates that only the Serjeant at Arms may enter the Commons chamber armed.
With rising concern about the possibility that a vehicle full of explosives could be driven into the building, a series of concrete blocks were placed in the roadway in 2003. On the river, an exclusion zone extending from the bank exists, which no unauthorised vessels are allowed to enter.
The Serious Organised Crime and Police Act 2005 formerly made it illegal to hold a protest near the Palace, or anywhere else within a designated area extending up to from Parliament Square, without authorisation from the Metropolitan Police. The Act also restricted the operation of loudspeakers in the designated area. These provisions were repealed by the Police Reform and Social Responsibility Act 2011, which replaced them with a total ban on tents and sleeping bags in Parliament Square, as well as a prohibition on the use of loudspeakers in the Square without permission from the relevant local authority.
Members of the public continue to have access to the Strangers' Gallery in the House of Commons. Visitors pass through metal detectors and their possessions are scanned. Police from the Palace of Westminster Division of the Metropolitan Police, supported by some armed police from the Diplomatic Protection Group, are always on duty in and around the Palace.
Incidents
The failedGunpowder Plot
The Gunpowder Plot of 1605, in earlier centuries often called the Gunpowder Treason Plot or the Jesuit Treason, was a failed assassination attempt against King James I by a group of provincial English Catholics led by Robert Catesby who sough ...
of 1605 was a conspiracy among a group of Roman Catholic gentry to re-establish Roman Catholicism in England and Wales, Catholicism in England by assassinating the Protestant James I of England, King James I and replacing him with a Catholic monarch. To this end, they placed large quantities of gunpowder beneath the House of Lords, which one of the conspirators, Guy Fawkes, would detonate during the State Opening of Parliament on 5 November 1605. If successful, the explosion would have destroyed the Palace, killing the King, his family and most of the aristocracy. However, the plot was discovered and most of the conspirators were either arrested or killed while trying to evade capture. The survivors were tortured in the Tower of London, tried for high treason in Westminster Hall, convicted and gruesomely executed by hanging, drawing and quartering. Since then, the cellars of the Palace have been searched by the Yeomen of the Guard before every State Opening of Parliament, a traditional precaution against any similar attempts against the Sovereign.
Sir Walter Raleigh Sir Walter Raleigh#Execution and aftermath, was executed at the Palace of Westminster on 29 October 1618.
 The previous Palace of Westminster was also the site of a prime-ministerial assassination on 11 May 1812. While in the lobby of the House of Commons, on his way to a parliamentary inquiry, Spencer Perceval was Assassination of Spencer Perceval, shot and killed by a Liverpool merchant adventurer, John Bellingham. Perceval remains the only Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister to have been assassinated.
The New Palace became the target of Fenian bombs on 24 January 1885, along with the Tower of London. The first bomb, a black bag containing dynamite, was discovered by a visitor on the steps towards the Chapel of St Mary Undercroft. Police Constable (PC) William Cole attempted to carry it to New Palace Yard, but the bag became so hot that Cole dropped it and it exploded. The blast opened a crater in the floor in diameter, damaged the roof of the chapel and shattered all the windows in the Hall, including the stained-glass South Window at St Stephen's Porch. Both Cole and PC Cox, a colleague who had joined him to offer assistance, were seriously injured. A second explosion followed almost immediately in the Commons Chamber, causing great damage—especially to its south end—but no injuries, as it was empty at the time. The incident resulted in the closure of Westminster Hall to visitors for several years; when visitors were re-admitted in 1889, it was under certain restrictions and never while the two Houses were sitting.
On 17 June 1974, a bomb planted by the Provisional Irish Republican Army, Provisional IRA exploded in Westminster Hall. The explosion and the resulting fire, which was fed by a ruptured gas main, injured 11 people and caused extensive damage. Five years later, a car bomb claimed the life of Airey Neave, a prominent Conservative politician, while he was driving out of the Commons car park in New Palace Yard. The attack occurred on 30 March 1979, one day after the announcement of 1979 United Kingdom general election, that year's general election; both the Irish National Liberation Army and the Provisional IRA claimed responsibility for Neave's assassination, but it is now accepted that the former were responsible.
The previous Palace of Westminster was also the site of a prime-ministerial assassination on 11 May 1812. While in the lobby of the House of Commons, on his way to a parliamentary inquiry, Spencer Perceval was Assassination of Spencer Perceval, shot and killed by a Liverpool merchant adventurer, John Bellingham. Perceval remains the only Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister to have been assassinated.
The New Palace became the target of Fenian bombs on 24 January 1885, along with the Tower of London. The first bomb, a black bag containing dynamite, was discovered by a visitor on the steps towards the Chapel of St Mary Undercroft. Police Constable (PC) William Cole attempted to carry it to New Palace Yard, but the bag became so hot that Cole dropped it and it exploded. The blast opened a crater in the floor in diameter, damaged the roof of the chapel and shattered all the windows in the Hall, including the stained-glass South Window at St Stephen's Porch. Both Cole and PC Cox, a colleague who had joined him to offer assistance, were seriously injured. A second explosion followed almost immediately in the Commons Chamber, causing great damage—especially to its south end—but no injuries, as it was empty at the time. The incident resulted in the closure of Westminster Hall to visitors for several years; when visitors were re-admitted in 1889, it was under certain restrictions and never while the two Houses were sitting.
On 17 June 1974, a bomb planted by the Provisional Irish Republican Army, Provisional IRA exploded in Westminster Hall. The explosion and the resulting fire, which was fed by a ruptured gas main, injured 11 people and caused extensive damage. Five years later, a car bomb claimed the life of Airey Neave, a prominent Conservative politician, while he was driving out of the Commons car park in New Palace Yard. The attack occurred on 30 March 1979, one day after the announcement of 1979 United Kingdom general election, that year's general election; both the Irish National Liberation Army and the Provisional IRA claimed responsibility for Neave's assassination, but it is now accepted that the former were responsible.
 The Palace has also been the scene of numerous acts of politically motivated "direct action", which often took place in the Chamber of the House of Commons. In July 1970, a man in the Strangers' Gallery threw two canisters of CS gas, tear gas into the Chamber to protest against the use of such gas in Northern Ireland; an MP and two members of the House's staff were taken to hospital and the sitting was suspended for almost two hours. In 1978, activist Yana Mintoff and another dissident threw bags of horse manure, and in June 1996 demonstrators dropped leaflets. Concern about such attacks and a possible chemical or biological attack led to the installation of a glass screen across the Strangers' Gallery in early 2004.
The new barrier does not cover the gallery in front of the Strangers' Gallery, which is reserved for ambassadors, members of the House of Lords, guests of MPs and other dignitaries, and in May 2004 protesters from Fathers 4 Justice attacked Prime Minister Tony Blair with flour bombs from this part, after obtaining admission by bidding for a place in the visitors' gallery in a charity auction. Subsequently, rules on admission to the visitors' galleries were changed, and now individuals wishing to sit in the galleries must first obtain a written pass from a Member certifying that that individual is personally known to them. In September of the same year, five protesters opposed to the proposed ban on fox hunting disrupted the proceedings of the House of Commons by running into the Chamber, the first such occurrence since Charles I of England, King Charles I's unauthorised entry in 1642, which triggered the English Civil War.
The House of Lords has also been targeted by protesters. On 2 February 1988, the House debated the Local Government Act 1988, Local Government Bill's controversial Section 28, Clause 28, a measure to prohibit the promotion of homosexuality in schools. Following the Division of the assembly, division, in which the clause passed, a number of lesbian demonstrators in the public gallery started chanting slogans, and three of them tied ropes to the railing and climbed down onto the floor of the Chamber. Gerard Collier, 5th Baron Monkswell, Lord Monkswell, who had provided the women with passes to attend the debate, later apologised to the House for the incident but did not criticise the protest.
Similar actions have been carried out outside the Palace of Westminster. Early in the morning of 20 March 2004, two Greenpeace members scaled the Clock Tower to demonstrate against the Iraq War, raising questions about the security around such a likely target of terrorist attacks. In March 2007, another four members of Greenpeace made their way to the Palace's roof by means of a nearby crane, which was being used for repairs to Westminster Bridge. Once up, they unfurled a banner protesting against the British government's plans to update the Trident nuclear programme.
In February 2008, five campaigners from the Plane Stupid group gained admittance to the building as visitors and then moved up to the roof to demonstrate against the proposed expansion of Heathrow Airport; from there they hung two banners they had smuggled past security. MPs and security experts found it worrying that the protesters made it to the roof in spite of the heightened security measures, and the prosecution at the activists' trial argued that they may have received help from a House of Lords employee. In October 2009, at least forty Greenpeace activists climbed to the roof of Westminster Hall to call for the adoption of policies climate change mitigation, combating climate change. Some of them climbed down after nearly five hours, while the rest spent the night on the roof.
On 22 March 2017 an Islamic terrorism, Islamist-related terror attack happened in which 2017 Westminster attack, a man stabbed a police officer after ploughing into pedestrians on Westminster Bridge. Five people were killed, including the attacker and the police officer. In August 2018 there was 2018 Westminster car incident, another attack, treated by prosecutors as terrorism.
On 1 April 2019, a group of environmental protestors from the group Extinction Rebellion stripped semi-naked in the public gallery during a Brexit debate and glued themselves to the handrail and glass screen with their buttocks facing the Commons Chamber. MPs attempted to continue the debate, some of them incorporating puns and references to nakedness into their speeches, to much hilarity.
There have been four fires on the Palace of Westminster site during 2019, and eight in 2018.
In 2022, the body of the late Queen Elizabeth was left inside the hall for people to pay their respects. A man decided to jump the barriers and pull the flag off coffin. He was detained and taken away by police and officials.
The Palace has also been the scene of numerous acts of politically motivated "direct action", which often took place in the Chamber of the House of Commons. In July 1970, a man in the Strangers' Gallery threw two canisters of CS gas, tear gas into the Chamber to protest against the use of such gas in Northern Ireland; an MP and two members of the House's staff were taken to hospital and the sitting was suspended for almost two hours. In 1978, activist Yana Mintoff and another dissident threw bags of horse manure, and in June 1996 demonstrators dropped leaflets. Concern about such attacks and a possible chemical or biological attack led to the installation of a glass screen across the Strangers' Gallery in early 2004.
The new barrier does not cover the gallery in front of the Strangers' Gallery, which is reserved for ambassadors, members of the House of Lords, guests of MPs and other dignitaries, and in May 2004 protesters from Fathers 4 Justice attacked Prime Minister Tony Blair with flour bombs from this part, after obtaining admission by bidding for a place in the visitors' gallery in a charity auction. Subsequently, rules on admission to the visitors' galleries were changed, and now individuals wishing to sit in the galleries must first obtain a written pass from a Member certifying that that individual is personally known to them. In September of the same year, five protesters opposed to the proposed ban on fox hunting disrupted the proceedings of the House of Commons by running into the Chamber, the first such occurrence since Charles I of England, King Charles I's unauthorised entry in 1642, which triggered the English Civil War.
The House of Lords has also been targeted by protesters. On 2 February 1988, the House debated the Local Government Act 1988, Local Government Bill's controversial Section 28, Clause 28, a measure to prohibit the promotion of homosexuality in schools. Following the Division of the assembly, division, in which the clause passed, a number of lesbian demonstrators in the public gallery started chanting slogans, and three of them tied ropes to the railing and climbed down onto the floor of the Chamber. Gerard Collier, 5th Baron Monkswell, Lord Monkswell, who had provided the women with passes to attend the debate, later apologised to the House for the incident but did not criticise the protest.
Similar actions have been carried out outside the Palace of Westminster. Early in the morning of 20 March 2004, two Greenpeace members scaled the Clock Tower to demonstrate against the Iraq War, raising questions about the security around such a likely target of terrorist attacks. In March 2007, another four members of Greenpeace made their way to the Palace's roof by means of a nearby crane, which was being used for repairs to Westminster Bridge. Once up, they unfurled a banner protesting against the British government's plans to update the Trident nuclear programme.
In February 2008, five campaigners from the Plane Stupid group gained admittance to the building as visitors and then moved up to the roof to demonstrate against the proposed expansion of Heathrow Airport; from there they hung two banners they had smuggled past security. MPs and security experts found it worrying that the protesters made it to the roof in spite of the heightened security measures, and the prosecution at the activists' trial argued that they may have received help from a House of Lords employee. In October 2009, at least forty Greenpeace activists climbed to the roof of Westminster Hall to call for the adoption of policies climate change mitigation, combating climate change. Some of them climbed down after nearly five hours, while the rest spent the night on the roof.
On 22 March 2017 an Islamic terrorism, Islamist-related terror attack happened in which 2017 Westminster attack, a man stabbed a police officer after ploughing into pedestrians on Westminster Bridge. Five people were killed, including the attacker and the police officer. In August 2018 there was 2018 Westminster car incident, another attack, treated by prosecutors as terrorism.
On 1 April 2019, a group of environmental protestors from the group Extinction Rebellion stripped semi-naked in the public gallery during a Brexit debate and glued themselves to the handrail and glass screen with their buttocks facing the Commons Chamber. MPs attempted to continue the debate, some of them incorporating puns and references to nakedness into their speeches, to much hilarity.
There have been four fires on the Palace of Westminster site during 2019, and eight in 2018.
In 2022, the body of the late Queen Elizabeth was left inside the hall for people to pay their respects. A man decided to jump the barriers and pull the flag off coffin. He was detained and taken away by police and officials.
Rules and traditions
The Palace has accumulated many rules and traditions over the centuries.Eating, drinking and smoking
Smoking has not been allowed in the chamber of the House of Commons since the 17th century. As a result, Members may take snuff (tobacco), snuff instead and the doorkeepers still keep a Parliamentary snuff box, snuff-box for this purpose. Despite persistent media rumours, it has not been permitted to smoke anywhere inside the Palace since 2005. Members may not eat or drink in the chamber; the exception to this rule is the Chancellor of the Exchequer, who may have a beverage of the Chancellors' choice while delivering the United Kingdom budget, Budget statement. Traditionally this is an alcoholic beverage, often whisky or a similar spirit, but in recent times, some Chancellors have opted for mineral water.Dress code
 Men are expected to wear formal attire, women are expected to dress in business-like clothing and the wearing of T-shirts with slogans is not allowed. Hats must not be worn (although they used to be worn when a point of order was being raised), and Members may not wear military decorations or insignia. Members are not allowed to have their hands in their pocketsAndrew Robathan was heckled by opposing MPs for doing this on 19 December 1994.
Men are expected to wear formal attire, women are expected to dress in business-like clothing and the wearing of T-shirts with slogans is not allowed. Hats must not be worn (although they used to be worn when a point of order was being raised), and Members may not wear military decorations or insignia. Members are not allowed to have their hands in their pocketsAndrew Robathan was heckled by opposing MPs for doing this on 19 December 1994.
Other traditions
The only animals allowed in the Palace of Westminster are guide dogs. Police dog, Sniffer dogs and Mounted police, police horses are also allowed on the grounds. Speeches may not be read out during debate in the House of Commons, although notes may be referred to. Similarly, the reading of newspapers is not allowed. Visual aids are discouraged in the chamber. Applause is also not normally allowed in the Commons, but it has since been tolerated in certain cases. Some notable exceptions to this were when Robin Cook gave his resignation speech in 2003; when Prime Minister Tony Blair appeared for the last time at Prime Minister's Questions; when Speaker Michael Martin, Baron Martin of Springburn, Michael Martin gave his leaving speech on 17 June 2009; and after the resignation statement of Robert Rogers, Baron Lisvane, Sir Robert Rogers, Clerk of the House. At the start of the new parliament in May 2015, the large influx of new Scottish National Party MPs flouted the convention and repeatedly applauded their party leader, to the displeasure of the Speaker of the House of Commons (United Kingdom), Speaker. The status of the Palace as a royal palace raises legal questionsaccording to Halsbury's Laws of England, it is not possible to arrest a person within the "verges" of the Palace (the Palace itself and its immediate surroundings). However, according to a memorandum by the Clerk of the House of Commons, there is no prohibition on arrest within the Palace and such arrests have been effected in the past.Culture and tourism
The exterior of the Palace of Westminsterespecially the Elizabeth Tower which houses the bell known asBig Ben
Big Ben is the nickname for the Great Bell of the Great Clock of Westminster, at the north end of the Palace of Westminster in London, England, and the name is frequently extended to refer also to the clock and the clock tower. The officia ...
, and its setting on the bank of the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
—is recognised worldwide, and is one of the most visited tourist attractions in London. Tsar Nicholas I called it "a dream in stone". The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) classifies the Palace of Westminster, along with neighbouring Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
and St Margaret's, Westminster, St Margaret's, as a World Heritage Site. It is also a Grade I listed building.
Although there is no casual access to the interior of the Palace, there are several ways to gain admittance. UK residents may obtain tickets from an MP for a place in the viewing ("strangers") gallery of the House of Commons, or from a Lord for a seat in the gallery of the House of Lords. It is also possible for both UK residents and overseas visitors to queue for admission to them at any time of the day or night when either House is in session, but capacity is limited and there is no guarantee of admission. Either House may exclude "strangers" if it desires to sit in private. Members of the public can also queue for a seat in a committee session, where admission is free and places cannot be booked, or they may visit the Parliamentary Archives for research purposes. Booking an appointment is necessary in the latter case, along with a proof of identity.
Free guided tours of the Palace are held throughout the parliamentary session for UK residents, who can apply through their MP or a member of the House of Lords. The tours last about 75 minutes and include the state rooms, the chambers of the two Houses and Westminster Hall. Paid-for tours are available to both UK and overseas visitors during the summer recess and Saturdays throughout the year. Tours of the Elizabeth Tower have been suspended until 2021 while the tower undergoes refurbishment.
Architectural historian Dan Cruickshank selected the Palace as one of his five choices for the 2006 BBC television documentary series ''Britain's Best Buildings''.
The nearest London Underground station is Westminster tube station, Westminster, on the District line, District, Circle line (London Underground), Circle and Jubilee lines.
In 2015, Parliament organised a year-long programme of events called "Parliament in the Making" to celebrate the 800th anniversary of the sealing of Magna Carta on 15 June, and the 750th anniversary of the Montfort's Parliament, first representative parliament on 20 January. Events were coordinated with Parliament Week. The BBC held events throughout the year including a "Democracy Day" on 20 January consisting of live discussions and debate in partnership with the Speaker of the House of Commons (United Kingdom), Speaker's Office of the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
, including broadcasts from inside the Palace of Westminster.
See also
* Parliament of the United Kingdom relocation * List of palaces#England, Official royal residences in London: **Buckingham Palace
Buckingham Palace () is a London royal residence and the administrative headquarters of the monarch of the United Kingdom. Located in the City of Westminster, the palace is often at the centre of state occasions and royal hospitality. It ...
– The principal royal residence since 1837
** Kensington Palace – The principal residence of English and later British monarchs between 1689 and 1760
** Palace of Whitehall
The Palace of Whitehall (also spelt White Hall) at Westminster was the main residence of the English monarchs from 1530 until 1698, when most of its structures, except notably Inigo Jones's Banqueting House of 1622, were destroyed by fire. ...
– The principal residence of the English kings from 1530 until 1689
** St James's Palace – The principal royal residence from 1702 until 1837, which continues today as the formal palace of the monarchy as the Court of St James's
*** Bushy House – future William IV took up residence here in 1797 when appointed Ranger of Bushy Park, and remained through his reign as king (1830–1837)
Notes
References
Footnotes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*External links
*Westminster Hall – A Virtual Experience
Winston Churchill State Funeral – Westminster Hall – UK Parliament Living Heritage
"A Victorian Novel in Stone"
Rosemary Hill, ''The Wall Street Journal'', 20 March 2009
Parliamentary Archives, Designs and working drawings for the rebuilding of the Houses of Parliament
{{Authority control Palace of Westminster, 1870 establishments in England Augustus Pugin buildings Buildings and structures completed in 1097 Buildings and structures on the River Thames Burned buildings and structures in the United Kingdom Gothic Revival architecture in London Government buildings completed in 1870 Grade I listed buildings in the City of Westminster Grade I listed government buildings Grade I listed palaces, Westminster, Palace Of History of the City of Westminster Legislative buildings in the United Kingdom Limestone buildings in the United Kingdom National government buildings in London Official residences in the United Kingdom Parliament of the United Kingdom Parliamentary Estate Rebuilt buildings and structures in the United Kingdom Royal residences in the City of Westminster, Westminster, Palace Of Legislative buildings in Europe, Westminster, Palace Of Seats of national legislatures Tourist attractions in the City of Westminster World Heritage Sites in London