Router On A Stick on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In computing, a router on a stick, also known as a one-armed router, is a router that has a single physical or logical connection to a network. It is a method of inter-VLAN (virtual local area networks) routing where one router is connected to a switch via a single cable. The router has physical connections to the broadcast domains where one or more VLANs require the need for routing between them.
Devices on separate VLANs or in a typical LAN (local area network) are unable to communicate with each other. Therefore, it is often used to forward traffic between locally attached hosts on separate logical
In computing, a router on a stick, also known as a one-armed router, is a router that has a single physical or logical connection to a network. It is a method of inter-VLAN (virtual local area networks) routing where one router is connected to a switch via a single cable. The router has physical connections to the broadcast domains where one or more VLANs require the need for routing between them.
Devices on separate VLANs or in a typical LAN (local area network) are unable to communicate with each other. Therefore, it is often used to forward traffic between locally attached hosts on separate logical
 One-armed routers that perform traffic forwarding are often implemented on virtual local area networks (
One-armed routers that perform traffic forwarding are often implemented on virtual local area networks (
one-armed router
Computer networking
 In computing, a router on a stick, also known as a one-armed router, is a router that has a single physical or logical connection to a network. It is a method of inter-VLAN (virtual local area networks) routing where one router is connected to a switch via a single cable. The router has physical connections to the broadcast domains where one or more VLANs require the need for routing between them.
Devices on separate VLANs or in a typical LAN (local area network) are unable to communicate with each other. Therefore, it is often used to forward traffic between locally attached hosts on separate logical
In computing, a router on a stick, also known as a one-armed router, is a router that has a single physical or logical connection to a network. It is a method of inter-VLAN (virtual local area networks) routing where one router is connected to a switch via a single cable. The router has physical connections to the broadcast domains where one or more VLANs require the need for routing between them.
Devices on separate VLANs or in a typical LAN (local area network) are unable to communicate with each other. Therefore, it is often used to forward traffic between locally attached hosts on separate logical routing domain {{short description, Computer networking concept
In computer networking, a routing domain is a collection of networked systems that operate common routing protocol
A routing protocol specifies how routers communicate with each other to distribut ...
s or to facilitate routing table
In computer networking, a routing table, or routing information base (RIB), is a data table stored in a router or a network host that lists the routes to particular network destinations, and in some cases, metrics (distances) associated with tho ...
administration, distribution and relay.
Details
 One-armed routers that perform traffic forwarding are often implemented on virtual local area networks (
One-armed routers that perform traffic forwarding are often implemented on virtual local area networks (VLAN
A virtual local area network (VLAN) is any broadcast domain that is partitioned and isolated in a computer network at the data link layer (OSI layer 2).IEEE 802.1Q-2011, ''1.4 VLAN aims and benefits'' In this context, virtual, refers to a physi ...
s). They use a single Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 198 ...
network interface port that is part of two or more Virtual LANs, enabling them to be joined. A VLAN allows multiple virtual LANs
Lans or LANS may refer to:
Places
* Lans, Tyrol, a municipality in Tyrol, Austria
* Lake Lans, a lake near Lans, Tyrol
France
* Lans, Saône-et-Loire
* Lans-en-Vercors, a community near Grenoble in the Vercors
* Villard-de-Lans, a community and s ...
to coexist on the same physical LAN. This means that two machines attached to the same switch
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of ...
cannot send Ethernet frame
In computer networking, an Ethernet frame is a data link layer protocol data unit and uses the underlying Ethernet physical layer transport mechanisms. In other words, a data unit on an Ethernet link transports an Ethernet frame as its payload.
...
s to each other even though they pass over the same wires. If they need to communicate, then a router must be placed between the two VLANs to forward packets, just as if the two LANs
Lans or LANS may refer to:
Places
* Lans, Tyrol, a municipality in Tyrol, Austria
* Lake Lans, a lake near Lans, Tyrol
France
* Lans, Saône-et-Loire
* Lans-en-Vercors, a community near Grenoble in the Vercors
* Villard-de-Lans, a community and s ...
were physically isolated. The only difference is that the router in question may contain only a single Ethernet network interface controller
A network interface controller (NIC, also known as a network interface card, network adapter, LAN adapter or physical network interface, and by similar terms) is a computer hardware component that connects a computer to a computer network.
Ear ...
(NIC) that is part of both VLANs. Hence, "one-armed". While uncommon, hosts on the same physical medium may be assigned with addresses and to different networks. A one-armed router could be assigned addresses for each network and be used to forward traffic between locally distinct networks and to remote networks through another gateway.
One-armed routers are also used for administration purposes such as route collection, multi hop relay and looking glass servers.
All traffic goes over the trunk twice, so the theoretical maximum sum of up and download speed is the line rate. For a two-armed configuration, uploading does not need to impact download performance significantly. Furthermore, performance may be worse than these limits, such as in the case of half-duplexing and other system limitations.
Applications
Cases where this setup is used can be found in servers dedicated for prints, files or for segmenting different departments. An example of router on a stick usage is found in Call Manager Express installation, when theVoice over IP
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), also called IP telephony, is a method and group of technologies for the delivery of speech, voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as the Internet. The terms In ...
network and Cisco IP phone devices have a need to split. Enterprise networks implement this method of separating servers to prevent all users from ‘having equal access privilege to resources’.
Naming
As the network is separated virtually, the router does not need to be placed adjacent to the devices, rather is it placed to the side in thenetwork topology
Network topology is the arrangement of the elements ( links, nodes, etc.) of a communication network. Network topology can be used to define or describe the arrangement of various types of telecommunication networks, including command and contro ...
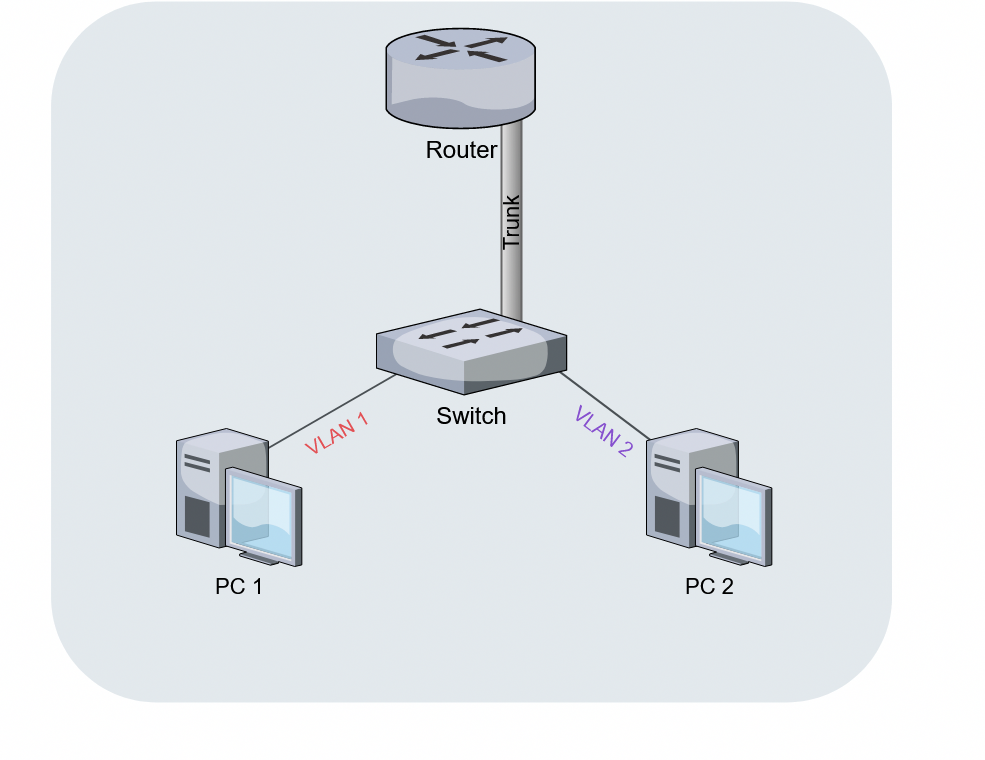
. The router is connected to the switch by a single cable. Therefore, giving the eponymous ‘stick’ formation. In some institutions, the abbreviation ''RoaS'' or ''ROAS'' is used instead of ''router on a stick''.
Protocol and design
Router on a stick relies on one ethernet link that is configured asIEEE 802.1Q
IEEE 802.1Q, often referred to as Dot1q, is the networking standard that supports virtual local area networking (VLANs) on an IEEE 802.3 Ethernet network. The standard defines a system of VLAN tagging for Ethernet frames and the accompanying proce ...
trunk link. The trunk is where data flows for the VLANs.
Advantages
Networks that utilise router on a stick benefit from only requiring one LAN connection to be used for multiple VLANs, i.e. the number of VLANs are not limited by the number of LAN ports available. Separation of network connections do not respond to the physical location of the ports on the router. Thus, this removes the need for multiple cable and wiring management. As VLANs are segmented, it reduces the amount of traffic flow through a connection. By separating VLANs, it provides enhanced network security. Network administrators have direct control over multiple broadcast domains. In the event of a malicious user attempting to access any switch port, they will have limited access to the network. The segmentation assists in restricting sensitive traffic that flows within an enterprise. Certain cases where workgroups are to be created. Users requiring high level of security can be isolated from other networks. Those outside of the VLANs cannot communicate, therefore departments are made independent from each other. Also third party users cannot access the network easily. Networks via router on a stick are independent from their physical locations, therefore sensitive data can be handled without compromise and with ease. Changes to networks like adding or removing abroadcast domain
A broadcast domain is a logical division of a computer network, in which all nodes can reach each other by broadcast at the data link layer. A broadcast domain can be within the same LAN segment or it can be bridged to other LAN segments.
In t ...
is achievable by assigning hosts to the appropriate VLANs.
Broadcasts of networks can be managed by multiple hosts, controlled by implementing as many VLANs as required. Therefore, this increases the number of networks while simultaneously decreasing their size.
Implementation of this setup only requires one router.
Disadvantages
Compared to the alternative of using L3 ( Layer 3 switching), the trunk may become a source of congestion as traffic from all VLANs must flow through the trunk link. Modern networks utilise L3 switch which provides greater bandwidth output and functionality. As all network traffic travel over the trunk twice, the trunk can become a major source of congestion, as there is only one trunk connection. Bottleneck can be mitigated if the single interface is combined with other interfaces vialink aggregation
In computer networking, link aggregation is the combining ( aggregating) of multiple network connections in parallel by any of several methods, in order to increase throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, to provide redundan ...
.
If the router fails, there is no backup and that may become the bottleneck in the network. Since all VLANs must traverse one router, there is a great potential in insufficient bandwidth provided for all network connections.
Before implementing inter-VLAN routing into the network, it requires additional configuration and virtual implementation. Additional latency may be induced when connecting the switch to the router.
Layer 3 switches can route traffic to other switches without the need for a router. It processes data packets faster than routers since the data traverses wire speed. Modern switches have bandwidth ports with greater limits that can improve the overall performance of the network.
See also
*Route server
A route server is a computer server that was originally developed by the Routing Arbiter project, with funding from the National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States governme ...
* Network switch
A network switch (also called switching hub, bridging hub, and, by the IEEE, MAC bridge) is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device.
A netw ...
References
{{reflistExternal links
one-armed router
Computer networking