Round City Of Al-Mansur on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Round City of Baghdad is the original core of Baghdad, built by the Abbasid Caliph al-Mansur in 762–766 CE as the official residence of the Abbasid court. Its official name in Abbasid times was City of Peace ( ar, مدينة السلام, Madīnat as-Salām). The famous library known as the
 According to Ya'qubi, the plans for the city were drawn up, but it was not until 2 August 762 that construction began, under the supervision of four architects. Huge resources were amassed for the project: the Arab chroniclers report 100,000 workers and craftsmen, and sums of 18 million gold dinars or 100 million silver
According to Ya'qubi, the plans for the city were drawn up, but it was not until 2 August 762 that construction began, under the supervision of four architects. Huge resources were amassed for the project: the Arab chroniclers report 100,000 workers and craftsmen, and sums of 18 million gold dinars or 100 million silver
Al-Mansur's Round City of Baghdad
in "archnet" website
Baghdad (Madinat al-Salam)
in "islamic art" website {{authority control Buildings and structures completed in 766 Baghdad under the Abbasid Caliphate Buildings and structures in Baghdad Iraqi culture Abbasid architecture Planned capitals Sasanian architecture
House of Wisdom
The House of Wisdom ( ar, بيت الحكمة, Bayt al-Ḥikmah), also known as the Grand Library of Baghdad, refers to either a major Abbasid public academy and intellectual center in Baghdad or to a large private library belonging to the Abba ...
was located within its grounds.
Description
 According to Ya'qubi, the plans for the city were drawn up, but it was not until 2 August 762 that construction began, under the supervision of four architects. Huge resources were amassed for the project: the Arab chroniclers report 100,000 workers and craftsmen, and sums of 18 million gold dinars or 100 million silver
According to Ya'qubi, the plans for the city were drawn up, but it was not until 2 August 762 that construction began, under the supervision of four architects. Huge resources were amassed for the project: the Arab chroniclers report 100,000 workers and craftsmen, and sums of 18 million gold dinars or 100 million silver dirham
The dirham, dirhem or dirhm ( ar, درهم) is a silver unit of currency historically and currently used by several Arab and Arab influenced states. The term has also been used as a related unit of mass.
Unit of mass
The dirham was a un ...
s. The caliphal Palace of the Golden Gate
The Palace of the Golden Gate ( ar, باب الذهب, Bāb al-Dhahab) or Palace of the Green Dome ( ar, القبة الخضراء , al-Qubbat al-Khaḍrāʾ) was the official caliphal residence in Baghdad during the early Abbasid Caliphate.
Bagh ...
and the main mosque, as well as some of the administration offices, were apparently completed by 763, allowing al-Mansur to move his residence into the city, and the rest of the Round City was completed by 766.
Mansur believed that Baghdad was the perfect city to be the capital of the Islamic empire under the Abbasids
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
. Mansur loved the site so much he is quoted saying, "This is indeed the city that I am to found, where I am to live, and where my descendants will reign afterward". The goal was to replace Harran as the seat of the caliphal government; however, a city of Baghdad is mentioned in pre-Islamic texts, including the Talmud, and the Abbasid city was likely built on the site of this earlier settlement.
Baghdad eclipsed Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; Middle Persian: 𐭲𐭩𐭮𐭯𐭥𐭭 ''tyspwn'' or ''tysfwn''; fa, تیسفون; grc-gre, Κτησιφῶν, ; syr, ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢThomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modi ...
, the capital of the Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
, which was located some to the southeast, which had been under Muslim control since 637, and which became quickly deserted after the foundation of Baghdad. The site of Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
, which had been deserted since the 2nd century, lies some to the south.
The old Baghdad was a small village, and despite its name, which is of Iranian origin (''bag'' "god" + ''dād'' "gifted"), the original inhabitants were probably Aramaic-speaking Nabateans. The new city, however, was mainly Arabic-speaking, with considerable Persian elements in the population and urban environment, although there have not been any major Persian settlement in the village of Baghdad or its surrounding communities, all of which were absorbed into the new city of Baghdad. The Persian elements rather appeared after the foundation of the new city, and included Persian architectural influence, Persian military settlement in the early years, the continuing settlement of Persian scholars, and the late rulers of Persian origin (such as the Buyids).
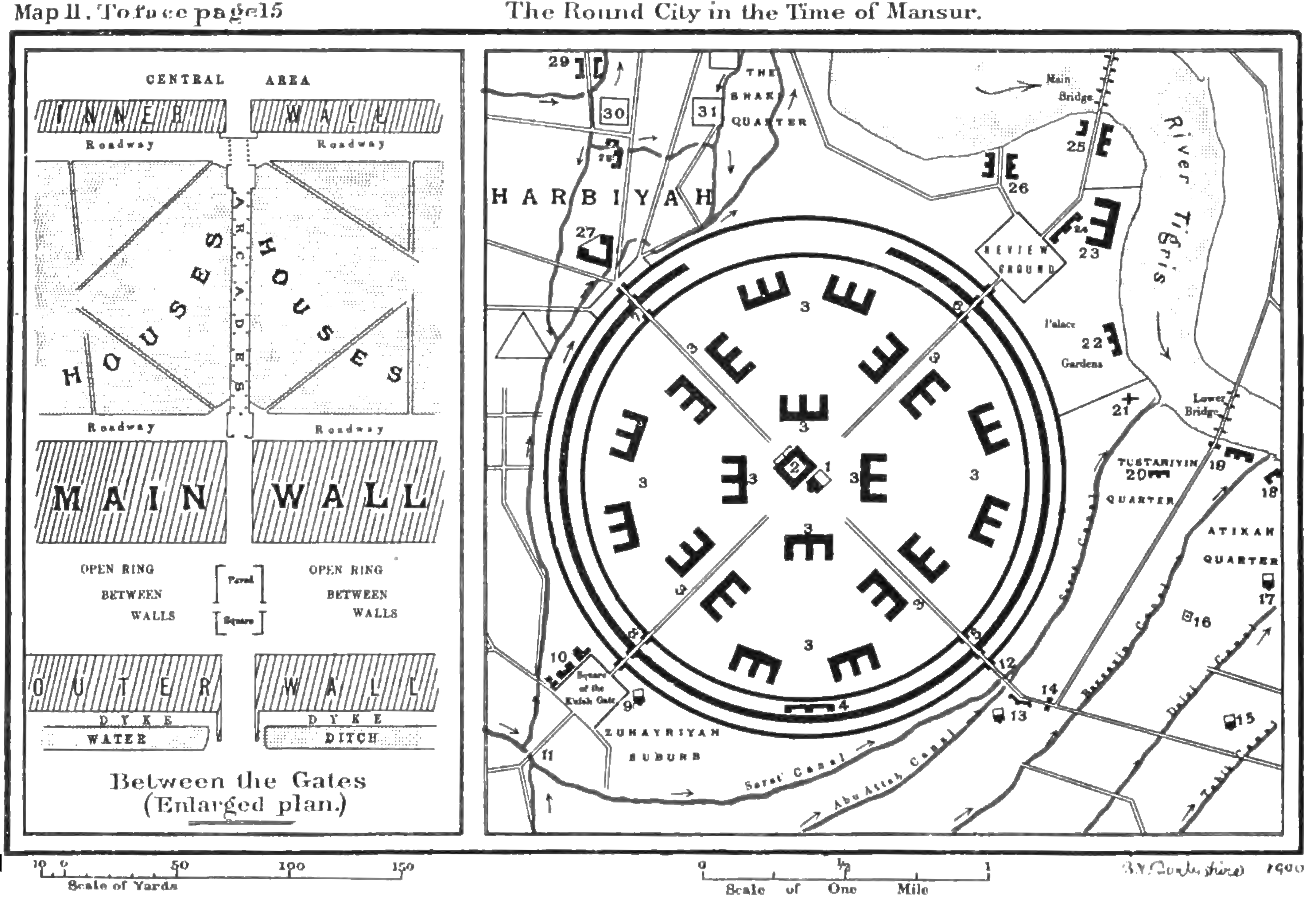
The city was designed as a circle about in radius, leading it to be known as the "Round City". Given this figure, it may be estimated that the original area of the city, shortly after its construction, was around . The original design shows a ring of residential and commercial structures along the inside of the city walls, but the final construction added another ring, inside the first. In the center of the city lay the mosque, as well as headquarters for guards. The purpose or use of the remaining space in the center is unknown. The circular design of the city was a direct reflection of the traditional Persian Sasanian urban design. The ancient Sasanian city of Gur/Firouzabad
Firuzabad ( fa, فيروزآباد or Piruzabad, also Romanized as Fīrūzābād; Middle Persian: Gōr or Ardashir-Khwarrah, literally "The Glory of Ardashir"; also Shahr-e Gūr ) is a city and capital of Firuzabad County, Fars Province, Iran. At ...
is nearly identical in its general circular design, radiating avenues, and the government buildings and temples at the center of the city. This points to the fact that it was based on Persian precedents. The two designers who were hired by al-Mansur to plan the city's design were Naubakht, a former Zoroastrian, and Mashallah ibn Athari
''Mashallah'' ( ar, مَا شَاءَ ٱللَّٰهُ, '), also written Masha'Allah, Maşallah (Turkey and Azerbaijan), Masya Allah (Malaysia and Indonesia), Maschallah (Germany), and Mašallah (Bosnia), is an Arabic phrase that is used to expres ...
, a Persian Jewish astrologer/astronomer.
The city had four gates: Bab al-Kufa ("gate of Kufa"), Bab al-Sham ("gate of al-Sham or Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
"), Bab al-Khorasan ("gate of Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
"), and Bab al-Basra ("gate of Basra"). This too is similar to the round cities of Darabgard and Gor, which had four gates. The Khuld Palace, the main palace of Baghdad built by al-Mansur, was located near the Bab al-Khorasan. The Khorasan Gate marked the beginning of the Great Khorasan Road The (Great) Khurasan Road was the great trunk road connecting Mesopotamia to the Iranian Plateau and thence to Central Asia, China, and the Indus Valley.
It is very well-documented in the Abbasid period, when it connected the core of the capital c ...
.
None of the structures of the city has survived, and information are based on literary sources. The caliphal Palace of the Golden Gate
The Palace of the Golden Gate ( ar, باب الذهب, Bāb al-Dhahab) or Palace of the Green Dome ( ar, القبة الخضراء , al-Qubbat al-Khaḍrāʾ) was the official caliphal residence in Baghdad during the early Abbasid Caliphate.
Bagh ...
and the main mosque were located at the centre of the circle. Influenced by the '' apadana'' design of ancient Iranian architecture, the mosque was built with a hypostyle
In architecture, a hypostyle () hall has a roof which is supported by columns.
Etymology
The term ''hypostyle'' comes from the ancient Greek ὑπόστυλος ''hypóstȳlos'' meaning "under columns" (where ὑπό ''hypó'' means below or un ...
prayer-hall with wooden columns supporting its flat roof. The caliphal palace featured an iwan
An iwan ( fa, ایوان , ar, إيوان , also spelled ivan) is a rectangular hall or space, usually vaulted, walled on three sides, with one end entirely open. The formal gateway to the iwan is called , a Persian term for a portal projecting ...
and a dome-chamber immediately behind it, resembling Sasanian palace design (such as that of Gor and Sarvestan
Sarvestan ( fa, سروستان ''Sarvestân'', "land of cedars"; ''sarv'' "cedar" (cypress) + '' estan''; also Romanized as Sarvestān and Sarvistān) is a city and capital of Sarvestan County, Fars Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its popul ...
). Building materials was mostly brick (sometimes strengthened by reeds), reflecting Mesopotamian architecture.
The residents were of two types: military people who were settled by the caliph, and a large number ordinary people who later settled in the city for economic opportunities. The second group were mostly Arabs and local Nabateans. The first group were mostly Persians from Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
and Transoxania, who were settled in the northwestern district known as ''Harbiyya'' (). The ''Harbiyya'' included ''Marwrūdiyya'' division (, for those from Marw al-Rudh i.e. modern-day Murghab, Afghanistan), a suburb of the ''Furus'' (" Persians", or possibly people from Fars), a suburb for the Khwarezmians, and a mosque dedicated to the people of Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
. As the future caliph Al-Mahdi moved from al-Rayy to Baghdad in 768, a second wave of Persian military people settled there. There were also noble Iranian families Barmakids
The Barmakids ( fa, برمکیان ''Barmakiyân''; ar, البرامكة ''al-Barāmikah''Harold Bailey, 1943. "Iranica" BSOAS 11: p. 2. India - Department of Archaeology, and V. S. Mirashi (ed.), ''Inscriptions of the Kalachuri-Chedi Era'' vol ...
(from Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan ...
) and the Sulids (from Gurgan). The descendants of these Iranians took the title ''abnāʾ'' (), short for ''abnāʾ al-dawla
The ''abnāʾ al-dawla'' ( ar, أبناء الدولة, meaning "sons of the regime/dynasty"), often simply " the ''Abnāʾ''", is a term for the Khorasani Arabs who had participated in the Abbasid Revolution of 749–750 and their descendants, wh ...
'' (, literally "sons of the state"), but also said to be echoing the title of the ''abna'
''Al-Abnāʾ'' () was a term that was used in pre-Islamic and early Islamic Yemen to refer to the descendants of Iranian soldiers who had intermarried with local Arab women in southern Arabia after its conquest by the Sasanian Iranian Empire. S ...
'' of Yemen, also of Persian origin. The Persians of Baghdad were gradually acculturated by the early 9th century.
Modern references to the "discovery" of the Round City
As the host of one of the major intellectual centers in the Abbasid Caliphs, the Grand Library of Baghdad, also known as The House of Wisdom, was likely to have attracted scholars of several disciplines. Among them, geographers, historians, or simple chroniclers provided extensive descriptions of the Madinat al-Mansur even years after the city's fading. All the information we have today related to the physical characteristics, structural functions, and social life in Abbasid Baghdad comes from these literary sources which were revisited in the 20th century. Some of the most important surviving literary sources from the late 10th and 11th centuries in Baghdad are "Description of Mesopotamia and Baghdad," written by Ibn Serapion; "Tarikh Baghdad (A History of Baghdad)", by the scholar and historianAl-Khatib al-Baghdadi
Abū Bakr Aḥmad ibn ʿAlī ibn Thābit ibn Aḥmad ibn Māhdī al-Shāfiʿī, commonly known as al-Khaṭīb al-Baghdādī ( ar, الخطيب البغدادي) or "the lecturer from Baghdad" (10 May 1002 – 5 September 1071; 392 AH-463 AH), wa ...
, and the "Geographical Dictionary" by the geographer and historian Ya'qubi. These three books have constituted the foundation and required reading for modern research on the matter.
The definite revelation for the academic community of the existence of the Round City of Baghdad was recorded by Guy Le Strange
Guy Le Strange (24 July 1854 – 24 December 1933) was a British Orientalist noted especially for his work in the field of the historical geography of the pre-modern Middle Eastern and Eastern Islamic lands, and his editing of Persian geographic ...
, a British Orientalist prominent in the field of historical geography. His work "Baghdad during the Abbasid Caliphate: from contemporary Arabic and Persian sources," (1900) revisited, among other scholars, the work of Serapion and Ya'qubi to reconstruct a plan of the old city. Le Strange himself wrote in the preface of his book:
"(...) the real basis of the present reconstruction of the medieval plan is the description of the Canals of Baghdad written by Ibn Serapion in about the year a.d. 900. By combining the network of the water system, as described by this writer, with the radiating high-roads, as described by his contemporary Yakubi, it has been possible to plot out the various quarters of older Baghdad, filling in details from the accounts of other authorities, which, taken alone, would have proved too fragmentary to serve for any systematic reconstruction of the plan."The book is illustrative of the kind of Orientalist studies such as this one, which enjoyed great popularity in Europe at the time, fostered interest in conducting surveys in situ. A few years after Le Strange's first publication of the Round City's plan, a wave of German and British excavations was commissioned by emerging museums and universities. Two scholars re-re-visited the topic while working in Iraq, conducting excavations in neighboring cities like Samarra. The first one to improve Le Strange's initial plan was Ernst Herzfeld, a German archeologist who produced between 1905–1913 a large body of work including translations, drawings, field notes, photographs, and objects inventories from his excavations at Samarra and elsewhere in Iraq and Iran. Concerned with the critical problems found in the original descriptive texts, Herzfeld, an architect by profession, offered new interpretations and developed new plans of the Round City of Baghdad. His study was more related to the description, arrangement, and function of the city's main buildings, contrasting with the more urbanistic approach of Le Strange. His reconstructions were celebrated as the first "major architectural work on this subject," accepted by subsequent scholars. One of them was British art historian Sir K. A. C. Creswell, whose 1932 publication of the first volume of his monumental survey "Early Muslim Architecture" remains widely acknowledged as an essential reference for early Islamic architecture. The lack of archeological excavations at the Round City's suspected site has left the task of reconstructing the Medinat al-Mansur as a mere theoretical and hypothetical exercise. The topic was again revisited in the second half of the 20th century in new contexts. One of the more recent scholars who has undertaken the subject again is
Jacob Lassner
Jacob Lassner is an American writer and Jewish studies academic. He is the Philip M. & Ethel Klutznick Professor of Jewish civilization Emeritus at Northwestern University and former Director of the Crown Family Center for Jewish Studies. Lassner ...
, who presented a new critical interpretation based on the original texts "Tarikh Baghdad, (A History of Baghdad)," the "Geographical Dictionary" by al-Baghdadi and Ya'qubi, and the assessments made by Herzfeld and Creswell in the beginnings of the 20th century. Lassner's "The Topography of Baghdad in the Early Middle Ages" (1970) and "The Shaping of Abbasid Rule" (1980) presented a new concept of the city plan and a contrasting view of its architectural function and historical development in the earliest period, improving our current understanding of the city's design. In Lassner's studies, at least four previously held ideas about the al-Mansur's city were revised.
First, Lassner rejected the idea that al-Mansûr himself, "who had no known experience in architectural design (or with round structures) could have personally created ex nihilo such a sophisticated and unusual design." Second, he argues against the view that Baghdad's building was a sign of the Abbasid assumption of Iranian rulership, being more a visible manifestation of the Abbasid inheritance of Persian Sassanian urban design royal tradition. Third, he rejects the claims that the palace-city had symbolic cosmological significance "simply because there are no explicit statements in the sources connecting the caliph with such symbolism." Finally, he affirms that "The Round City was, in fact, an administrative center, and not at all a city in the conventional sense of the term."
See also
*Gates of Baghdad
The gates of Baghdad ( ar, أبواب بغداد) refers to the several bab, meaning gate in Arabic, connected by walls surrounding the city of Baghdad. The gates and the walls were designed to protect the city from foreign incursions. Some of the ...
* List of circular cities
Several ancient cities of Mesopotamia and Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia ...
References
Sources
* *External links
Al-Mansur's Round City of Baghdad
in "archnet" website
Baghdad (Madinat al-Salam)
in "islamic art" website {{authority control Buildings and structures completed in 766 Baghdad under the Abbasid Caliphate Buildings and structures in Baghdad Iraqi culture Abbasid architecture Planned capitals Sasanian architecture