

A robot is a
machine
A machine is a physical system using Power (physics), power to apply Force, forces and control Motion, movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to na ...
—especially one
program
Program, programme, programmer, or programming may refer to:
Business and management
* Program management, the process of managing several related projects
* Time management
* Program, a part of planning
Arts and entertainment Audio
* Progra ...
mable by a
computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as C ...
—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the
control
Control may refer to:
Basic meanings Economics and business
* Control (management), an element of management
* Control, an element of management accounting
* Comptroller (or controller), a senior financial officer in an organization
* Controlling ...
may be embedded within. Robots may be constructed to evoke
human form, but most robots are task-performing machines, designed with an emphasis on stark functionality, rather than expressive aesthetics.
Robots can be
autonomous or semi-autonomous and range from humanoids such as
Honda's ''Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility'' (
ASIMO) and
TOSY's ''TOSY Ping Pong Playing Robot'' (
TOPIO) to
industrial robots,
medical operating robots, patient assist robots, dog therapy robots, collectively programmed
''swarm'' robots,
UAV drones
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controlle ...
such as
General Atomics MQ-1 Predator
The General Atomics MQ-1 Predator (often referred to as the predator drone) is an American remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) built by General Atomics that was used primarily by the United States Air Force (USAF) and Central Intelligence Agency ( ...
, and even microscopic
nano robots. By mimicking a lifelike appearance or automating movements, a robot may convey a sense of intelligence or
thought
In their most common sense, the terms thought and thinking refer to conscious cognitive processes that can happen independently of sensory stimulation. Their most paradigmatic forms are judging, reasoning, concept formation, problem solving, a ...
of its own.
Autonomous things are expected to proliferate in the future, with home robotics and the
autonomous car as some of the main drivers.
The branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, and application of robots,
as well as computer systems for their control, sensory feedback, and
information processing
Information processing is the change (processing) of information in any manner detectable by an observer. As such, it is a process that ''describes'' everything that happens (changes) in the universe, from the falling of a rock (a change in posit ...
is
robotics. These technologies deal with automated machines that can take the place of humans in dangerous environments or
manufacturing processes, or resemble humans in appearance, behavior, or cognition. Many of today's robots are inspired by nature contributing to the field of
bio-inspired robotics. These robots have also created a newer branch of robotics:
soft robotics.
From the time of
ancient civilization, there have been many accounts of user-configurable automated devices and even
automata resembling humans and other animals, such as
animatronics
Animatronics refers to mechatronic puppets. They are a modern variant of the automaton and are often used for the portrayal of characters in films and in theme park attractions.
It is a multidisciplinary field integrating puppetry, anatomy a ...
, designed primarily as entertainment. As mechanical techniques developed through the
Industrial age, there appeared more practical applications such as automated machines, remote-control and wireless
remote-control.
The term comes from a Slavic root, ''robot-'', with meanings associated with labor. The word 'robot' was first used to denote a fictional humanoid in a 1920
Czech-language play ''
R.U.R.
''R.U.R.'' is a 1920 science-fiction play by the Czech writer Karel Čapek. "R.U.R." stands for (Rossum's Universal Robots, a phrase that has been used as a subtitle in English versions). The play had its world premiere on 2 January 1921 in ...
'' ''(Rossumovi Univerzální Roboti – Rossum's Universal Robots)'' by
Karel Čapek, though it was Karel's brother
Josef Čapek who was the word's true inventor.
Electronics evolved into the driving force of development with the advent of the first electronic autonomous robots created by
William Grey Walter in Bristol, England in 1948, as well as
Computer Numerical Control
Numerical control (also computer numerical control, and commonly called CNC) is the automated control of machining tools (such as drills, lathes, mills, grinders, routers and 3D printers) by means of a computer. A CNC machine processes a pie ...
(CNC) machine tools in the late 1940s by
John T. Parsons
John T. Parsons (October 11, 1913April 18, 2007) pioneered numerical control (NC) for machine tools in the 1940s.
These developments were done in collaboration with his Chief Engineer and Vice President of Engineering, Frank L. Stulen, who Pars ...
and
Frank L. Stulen
Frank Lem Stulen (January 22, 1921 – June 25, 2010) graduated from Carnegie Mellon University (then Carnegie Tech) in 1942 with a degree in aeronautical engineering. After graduation, Stulen served in the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and in the ...
.
The first modern digital and
programmable robot was invented by
George Devol in 1954 and spawned his seminal robotics company,
Unimation. The first
Unimate was sold to
General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
in 1961 where it lifted pieces of hot metal from
die casting machines at the
Inland Fisher Guide Plant in the
West Trenton section of
Ewing Township, New Jersey.
Robots have replaced humans in performing repetitive and dangerous tasks which humans prefer not to do, or are unable to do because of size limitations, or which take place in extreme environments such as outer space or the bottom of the sea. There are concerns about the increasing use of robots and their role in society. Robots are blamed for rising
technological unemployment as they replace workers in increasing numbers of functions.
The use of robots in military combat raises ethical concerns. The possibilities of robot autonomy and potential repercussions have been addressed in fiction and may be a realistic concern in the future.
Summary
The word ''robot'' can refer to both physical robots and
virtual software agents, but the latter are usually referred to as
bots
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remnants of the former Bri ...
. There is no consensus on which machines qualify as robots but there is general agreement among experts, and the public, that robots tend to possess some or all of the following abilities and functions: accept electronic programming, process data or
physical perceptions electronically, operate autonomously to some degree, move around, operate physical parts of itself or physical processes, sense and manipulate their environment, and exhibit intelligent behavior, especially behavior which mimics humans or other animals. Related to the concept of a ''robot'' is the field of
synthetic biology, which studies entities whose nature is more comparable to
living things than to machines.
History
The idea of automata originates in the mythologies of many cultures around the world. Engineers and inventors from ancient civilizations, including
Ancient China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapte ...
,
, and
Ptolemaic Egypt,
attempted to build self-operating machines, some resembling animals and humans. Early descriptions of automata include the artificial doves of
Archytas
Archytas (; el, Ἀρχύτας; 435/410–360/350 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosopher, mathematician, music theorist, astronomer, statesman, and strategist. He was a scientist of the Pythagorean school and famous for being the reputed founder ...
, the artificial birds of
Mozi
Mozi (; ; Latinized as Micius ; – ), original name Mo Di (), was a Chinese philosopher who founded the school of Mohism during the Hundred Schools of Thought period (the early portion of the Warring States period, –221 BCE). The ancie ...
and
Lu Ban
Lu Ban (–444BC). was a Chinese architect or master carpenter, structural engineer, and inventor, during the Zhou Dynasty. He is revered as the Chinese Deity (Patron) of builders and contractors.
Life
Lu Ban was born in the state of Lu; a few ...
,
[Needham, Volume 2, 54.] a "speaking" automaton by
Hero of Alexandria, a washstand automaton by
Philo of Byzantium
Philo of Byzantium ( el, , ''Phílōn ho Byzántios'', ca. 280 BC – ca. 220 BC), also known as Philo Mechanicus, was a Greek engineer, physicist and writer on mechanics, who lived during the latter half of the 3rd century BC. Although he was f ...
, and a human automaton described in the ''
Lie Zi
The ''Liezi'' () is a Taoist text attributed to Lie Yukou, a c. 5th century BC Hundred Schools of Thought philosopher. Although there were references to Lie's ''Liezi'' from the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, a number of Chinese and Western scholar ...
''.
Early beginnings
Many ancient mythologies, and most modern religions include artificial people, such as the mechanical servants built by the Greek god
Hephaestus (
Vulcan to the Romans), the clay
golems of Jewish legend and clay giants of Norse legend, and
Galatea, the mythical statue of
Pygmalion
Pygmalion or Pigmalion may refer to:
Mythology
* Pygmalion (mythology), a sculptor who fell in love with his statue
Stage
* ''Pigmalion'' (opera), a 1745 opera by Jean-Philippe Rameau
* ''Pygmalion'' (Rousseau), a 1762 melodrama by Jean-Jacques ...
that came to life. Since circa 400 BC, myths of
Crete include
Talos, a man of bronze who guarded the island from pirates.
In ancient Greece, the Greek engineer
Ctesibius (c. 270 BC) "applied a knowledge of pneumatics and hydraulics to produce the first organ and water clocks with moving figures."
In the 4th century BC, the
Greek mathematician
Archytas
Archytas (; el, Ἀρχύτας; 435/410–360/350 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosopher, mathematician, music theorist, astronomer, statesman, and strategist. He was a scientist of the Pythagorean school and famous for being the reputed founder ...
of Tarentum postulated a mechanical steam-operated bird he called "The Pigeon".
Hero of Alexandria , a Greek mathematician and inventor, created numerous user-configurable automated devices, and described machines powered by air pressure, steam and water.
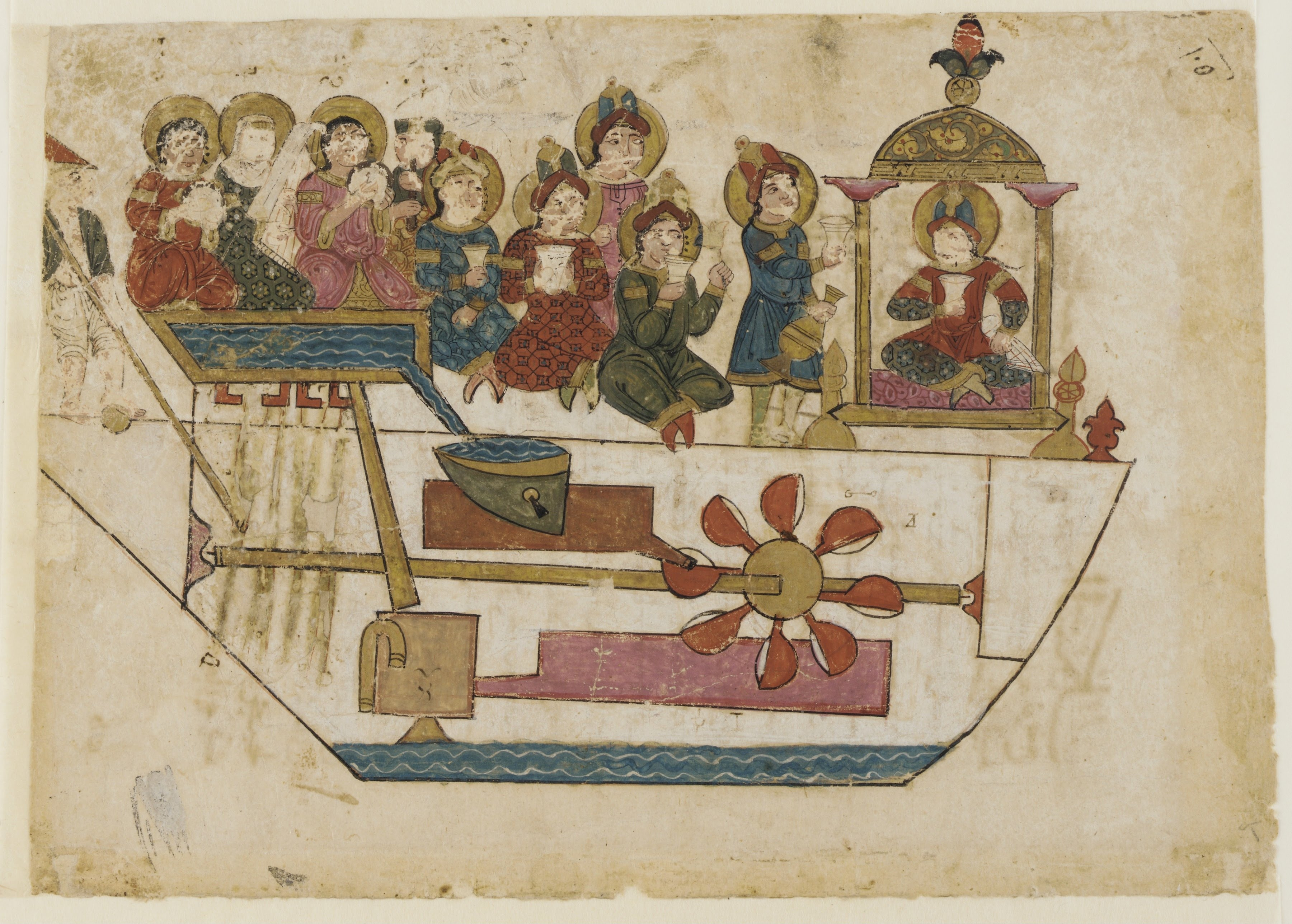

The 11th century Lokapannatti tells of how the Buddha's relics were protected by mechanical robots (bhuta vahana yanta), from the kingdom of Roma visaya (Rome); until they were disarmed by King
Ashoka.
In ancient China, the 3rd-century text of the ''Lie Zi'' describes an account of humanoid automata, involving a much earlier encounter between Chinese emperor
King Mu of Zhou
King Mu of Zhou (), personal name Ji Man, was the fifth king of the Zhou dynasty of China. The dates of his reign are 976–922 BC or 956–918 BC.
Life
King Mu came to the throne after his father King Zhao’s death during his tour to the Sout ...
and a mechanical engineer known as Yan Shi, an 'artificer'. Yan Shi proudly presented the king with a life-size, human-shaped figure of his mechanical 'handiwork' made of leather, wood, and artificial organs.
There are also accounts of flying automata in the ''Han Fei Zi'' and other texts, which attributes the 5th century BC
Mohist philosopher
Mozi
Mozi (; ; Latinized as Micius ; – ), original name Mo Di (), was a Chinese philosopher who founded the school of Mohism during the Hundred Schools of Thought period (the early portion of the Warring States period, –221 BCE). The ancie ...
and his contemporary
Lu Ban
Lu Ban (–444BC). was a Chinese architect or master carpenter, structural engineer, and inventor, during the Zhou Dynasty. He is revered as the Chinese Deity (Patron) of builders and contractors.
Life
Lu Ban was born in the state of Lu; a few ...
with the invention of artificial wooden birds (''ma yuan'') that could successfully fly.
In 1066, the Chinese inventor
Su Song
Su Song (, 1020–1101), courtesy name Zirong (), was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman. Excelling in a variety of fields, he was accomplished in mathematics, Chinese astronomy, astronomy, History of cartography#China, cartography, ...
built a
water clock in the form of a tower which featured mechanical figurines which chimed the hours.
His mechanism had a programmable drum machine with pegs (
cams) that bumped into little
levers that operated percussion instruments. The drummer could be made to play different rhythms and different drum patterns by moving the pegs to different locations.
''
Samarangana Sutradhara
''Samarangana Sutradhara'', sometimes referred to as ''Samarāṅgaṇasūtradhāra'', is an 11th-century poetic treatise on classical Indian architecture (Vastu Shastra) written in Sanskrit language attributed to Paramara King Bhoja of Dhar. T ...
'', a
Sanskrit treatise by
Bhoja (11th century), includes a chapter about the construction of mechanical contrivances (
automata), including mechanical bees and birds, fountains shaped like humans and animals, and male and female dolls that refilled oil lamps, danced, played instruments, and re-enacted scenes from Hindu mythology.
13th century
Muslim Scientist
This is a list of Muslim scientists who have contributed significantly to science and civilization in the Islamic Golden Age (i.e. from the 8th century to the 14th century).
Astronomers and astrologers
* Ibrahim al-Fazari (d. 777)
* Muhammad al ...
Ismail al-Jazari created several automated devices. He built automated moving peacocks driven by hydropower.
He also invented the earliest known automatic gates, which were driven by hydropower,
created automatic doors as part of one of his elaborate
water clocks.
[ ( cf. )] One of al-Jazari's
humanoid automata was a waitress that could serve water, tea or drinks. The drink was stored in a tank with a reservoir from where the drink drips into a bucket and, after seven minutes, into a cup, after which the waitress appears out of an automatic door serving the drink. Al-Jazari invented a hand washing
automaton incorporating a flush mechanism now used in modern
flush toilets. It features a female
humanoid automaton standing by a basin filled with water. When the user pulls the lever, the water drains and the female automaton refills the basin.
Mark E. Rosheim summarizes the advances in
robotics made by Muslim engineers, especially al-Jazari, as follows:
Unlike the Greek designs, these Arab examples reveal an interest, not only in dramatic illusion, but in manipulating the environment for human comfort. Thus, the greatest contribution the Arabs made, besides preserving, disseminating and building on the work of the Greeks, was the concept of practical application. This was the key element that was missing in Greek robotic science.

In
Renaissance Italy,
Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519) sketched plans for a humanoid robot around 1495. Da Vinci's notebooks, rediscovered in the 1950s, contained detailed drawings of a mechanical knight now known as
Leonardo's robot, able to sit up, wave its arms and move its head and jaw. The design was probably based on anatomical research recorded in his ''
Vitruvian Man''. It is not known whether he attempted to build it. According to ''
Encyclopædia Britannica'',
Leonardo da Vinci may have been influenced by the classic automata of al-Jazari.
In Japan, complex animal and human automata were built between the 17th to 19th centuries, with many described in the 18th century ''Karakuri zui'' (''Illustrated Machinery'', 1796). One such automaton was the
karakuri ningyō
are traditional Japanese mechanized puppets or automata, made from the 17th century to the 19th century. The dolls' gestures provided a form of entertainment. The word has also come to mean "mechanisms" or "trick" in Japanese language, Japan ...
, a mechanized
puppet
A puppet is an object, often resembling a human, animal or Legendary creature, mythical figure, that is animated or manipulated by a person called a puppeteer. The puppeteer uses movements of their hands, arms, or control devices such as rods ...
. Different variations of the karakuri existed: the ''Butai karakuri'', which were used in theatre, the ''Zashiki karakuri'', which were small and used in homes, and the ''Dashi karakuri'' which were used in religious festivals, where the puppets were used to perform reenactments of traditional
myths and
legends.
In France, between 1738 and 1739,
Jacques de Vaucanson
Jacques de Vaucanson (; February 24, 1709 – November 21, 1782) was a French inventor and artist who built the first all-metal lathe which was very important to the Industrial Revolution. The lathe is known as the mother of machine tools, as it ...
exhibited several life-sized automatons: a flute player, a pipe player and a duck. The mechanical duck could flap its wings, crane its neck, and swallow food from the exhibitor's hand, and it gave the illusion of digesting its food by excreting matter stored in a hidden compartment. About 30 years later in Switzerland the clockmaker
Pierre Jaquet-Droz made several complex mechanical figures that could write and play music. Several of these devices still exist and work.
Remote-controlled systems
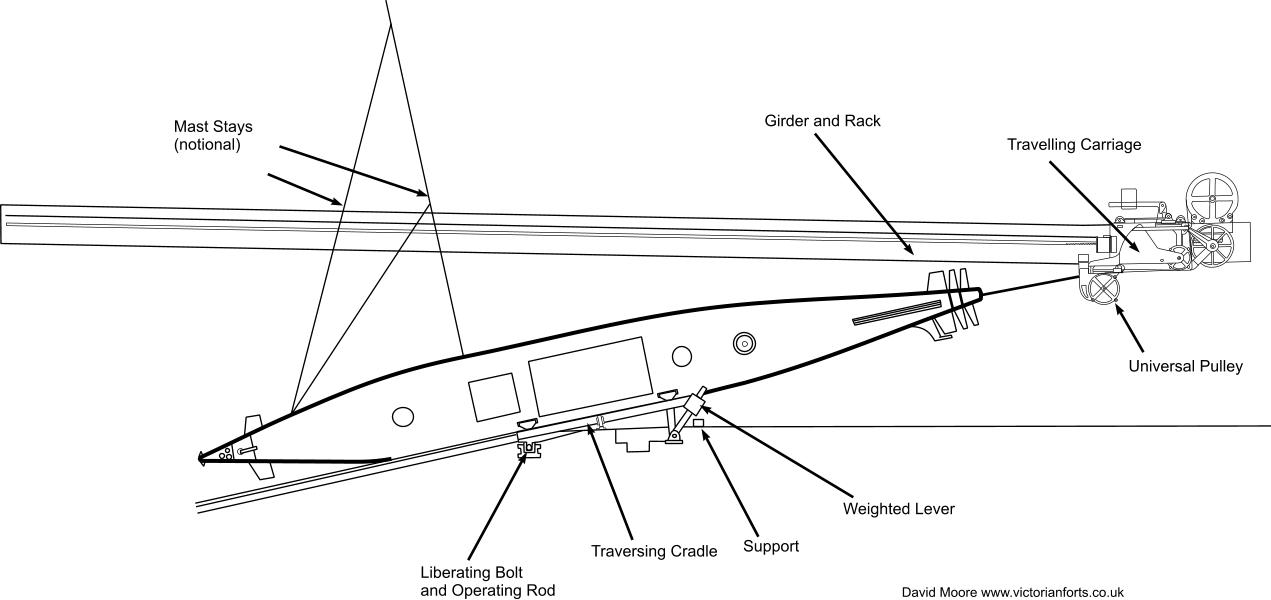
Remotely operated vehicles were demonstrated in the late 19th century in the form of several types of remotely controlled
torpedoes. The early 1870s saw remotely controlled
torpedoes by
John Ericsson
John Ericsson (born Johan Ericsson; July 31, 1803 – March 8, 1889) was a Swedish-American inventor. He was active in England and the United States.
Ericsson collaborated on the design of the railroad steam locomotive ''Novelty'', which com ...
(
pneumatic
Pneumatics (from Greek ‘wind, breath’) is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air.
Pneumatic systems used in Industrial sector, industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A central ...
),
John Louis Lay (electric wire guided), and
Victor von Scheliha
The name Victor or Viktor may refer to:
* Victor (name), including a list of people with the given name, mononym, or surname
Arts and entertainment
Film
* ''Victor'' (1951 film), a French drama film
* ''Victor'' (1993 film), a French shor ...
(electric wire guided).
[Edwyn Gray, Nineteenth-century torpedoes and their inventors, page 18]
The
Brennan torpedo, invented by
Louis Brennan
Louis Brennan (28 January 1852 – 17 January 1932) was an Irish-Australian mechanical engineer and inventor.
Biography
Brennan was born in Castlebar, Ireland, and moved to Melbourne, Australia in 1861 with his parents. He started his caree ...
in 1877, was powered by two contra-rotating propellers that were spun by rapidly pulling out wires from drums wound inside the
torpedo. Differential speed on the wires connected to the shore station allowed the torpedo to be guided to its target, making it "the world's first ''practical''
guided missile
In military terminology, a missile is a guided airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight usually by a jet engine or rocket motor. Missiles are thus also called guided missiles or guided rockets (when a previously unguided rocket ...
".
In 1897 the British inventor Ernest Wilson was granted a patent for a torpedo remotely controlled by "Hertzian" (radio) waves and in 1898
Nikola Tesla publicly demonstrated a wireless-controlled
torpedo that he hoped to sell to the
US Navy.
In 1903, the Spanish engineer
Leonardo Torres y Quevedo demonstrated a radio control system called "''Telekino''", which he wanted to use to control an
airship of his own design. Unlike the previous systems, which carried out actions of the 'on/off' type, Torres device was able to memorize the signals received to execute the operations on its own and could carry out to 19 different orders.
Archibald Low
Archibald Montgomery Low (17 October 1888 – 13 September 1956) developed the first powered drone aircraft. He was an English consulting engineer, research physicist and inventor, and author of more than 40 books.
Low has been called the "fa ...
, known as the "father of radio guidance systems" for his pioneering work on guided rockets and planes during the
First World War. In 1917, he demonstrated a remote controlled aircraft to the
Royal Flying Corps
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colors =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries =
, decorations ...
and in the same year built the first wire-guided rocket.
Early robots

In 1928, one of the first humanoid robots,
Eric, was exhibited at the annual exhibition of the Model Engineers Society in London, where it delivered a speech. Invented by W. H. Richards, the robot's frame consisted of an aluminium
body of armour with eleven
electromagnets and one motor powered by a twelve-volt power source. The robot could move its hands and head and could be controlled through remote control or voice control. Both Eric and his "brother" George toured the world.
Westinghouse Electric Corporation built Televox in 1926; it was a cardboard cutout connected to various devices which users could turn on and off. In 1939, the humanoid robot known as
Elektro was debuted at the
1939 New York World's Fair
The 1939–40 New York World's Fair was a world's fair held at Flushing Meadows–Corona Park in Queens, New York, United States. It was the second-most expensive American world's fair of all time, exceeded only by St. Louis's Louisiana Purchas ...
. Seven feet tall (2.1 m) and weighing 265 pounds (120.2 kg), it could walk by voice command, speak about 700 words (using a 78-rpm
record player), smoke cigarettes, blow up balloons, and move its head and arms. The body consisted of a steel gear, cam and motor skeleton covered by an aluminum skin. In 1928, Japan's first robot,
Gakutensoku
Gakutensoku (學天則, Japanese for "learning from the laws of nature"), the first robot to be built in the East, was created in Osaka in the late 1920s. The robot was designed and manufactured by biologist Makoto Nishimura (1883–1956, father ...
, was designed and constructed by biologist Makoto Nishimura.
Modern autonomous robots
The first electronic autonomous robots with complex behaviour were created by
William Grey Walter of the
Burden Neurological Institute at
Bristol, England in 1948 and 1949. He wanted to prove that rich connections between a small number of
brain cells
Brain cells make up the functional tissue of the brain. The rest of the brain tissue is structural or connective called the stroma which includes blood vessels. The two main types of cells in the brain are neurons, also known as nerve cells, an ...
could give rise to very complex
behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as wel ...
s – essentially that the secret of how the brain worked lay in how it was wired up. His first robots, named ''Elmer'' and ''Elsie'', were constructed between 1948 and 1949 and were often described as ''tortoises'' due to their shape and slow rate of movement. The three-wheeled tortoise robots were capable of
phototaxis, by which they could find their way to a recharging station when they ran low on battery power.
Walter stressed the importance of using purely
analogue electronics to
simulate
A simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. Simulations require the use of Conceptual model, models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or proc ...
brain processes at a time when his contemporaries such as
Alan Turing and
John von Neumann were all turning towards a view of mental processes in terms of
digital
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Technology and computing Hardware
*Digital electronics, electronic circuits which operate using digital signals
**Digital camera, which captures and stores digital i ...
computation
Computation is any type of arithmetic or non-arithmetic calculation that follows a well-defined model (e.g., an algorithm).
Mechanical or electronic devices (or, historically, people) that perform computations are known as ''computers''. An es ...
. His work inspired subsequent generations of robotics researchers such as
Rodney Brooks,
Hans Moravec
Hans Peter Moravec (born November 30, 1948, Kautzen, Austria) is an adjunct faculty member at the Robotics Institute of Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, USA. He is known for his work on robotics, artificial intelligence, and writings on ...
and
Mark Tilden. Modern incarnations of Walter's ''turtles'' may be found in the form of
BEAM robotics.

The first digitally operated and programmable robot was invented by
George Devol in 1954 and was ultimately called the
Unimate. This ultimately laid the foundations of the modern robotics industry. Devol sold the first Unimate to
General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
in 1960, and it was installed in 1961 in a plant in
Trenton, New Jersey to lift hot pieces of metal from a
die casting machine and stack them. Devol's patent for the first digitally operated programmable robotic arm represents the foundation of the modern robotics industry.
The first
palletizing robot was introduced in 1963 by the Fuji Yusoki Kogyo Company. In 1973, a robot with six electromechanically driven axes was patented by
KUKA robotics in Germany, and the
programmable universal manipulation arm was invented by
Victor Scheinman in 1976, and the design was sold to
Unimation.
Commercial and industrial robots are now in widespread use performing jobs more cheaply or with greater accuracy and reliability than humans. They are also employed for jobs which are too dirty, dangerous or dull to be suitable for humans. Robots are widely used in manufacturing, assembly and packing, transport, earth and space exploration, surgery, weaponry, laboratory research, and mass production of consumer and industrial goods.
Future development and trends
Various techniques have emerged to develop the science of robotics and robots. One method is
evolutionary robotics, in which a number of differing robots are submitted to tests. Those which perform best are used as a model to create a subsequent "generation" of robots. Another method is
developmental robotics, which tracks changes and development within a single robot in the areas of problem-solving and other functions. Another new type of robot is just recently introduced which acts both as a smartphone and robot and is named RoboHon.
As robots become more advanced, eventually there may be a standard computer operating system designed mainly for robots.
Robot Operating System is an open-source set of programs being developed at
Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is consider ...
, the
Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the
Technical University of Munich, Germany, among others. ROS provides ways to program a
robot's navigation and limbs regardless of the specific hardware involved. It also provides high-level commands for items like
image recognition and even opening doors. When ROS boots up on a robot's computer, it would obtain data on attributes such as the length and movement of robots' limbs. It would relay this data to higher-level algorithms. Microsoft is also developing a "Windows for robots" system with its Robotics Developer Studio, which has been available since 2007.
Japan hopes to have full-scale commercialization of service robots by 2025. Much technological research in Japan is led by Japanese government agencies, particularly the Trade Ministry.
Many future applications of robotics seem obvious to people, even though they are well beyond the capabilities of robots available at the time of the prediction.
As early as 1982 people were confident that someday robots would: 1. Clean parts by removing
molding flash
Flash, also known as flashing, is excess material attached to a molded, forged, or cast product, which must usually be removed. This is typically caused by leakage of the material between the two surfaces of a mold (beginning along the parting l ...
2. Spray paint automobiles with absolutely no human presence 3. Pack things in boxes—for example, orient and nest chocolate candies in candy boxes 4. Make electrical
cable harness 5. Load trucks with boxes—a
packing problem 6. Handle soft goods, such as garments and shoes 7. Shear sheep 8.
prosthesis
In medicine, a prosthesis (plural: prostheses; from grc, πρόσθεσις, prósthesis, addition, application, attachment), or a prosthetic implant, is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through trau ...
9. Cook fast food and work in other service industries 10. Household robot.
Generally such predictions are overly optimistic in timescale.
New functionalities and prototypes
In 2008,
Caterpillar Inc. developed a dump truck which can drive itself without any human operator. Many analysts believe that self-driving trucks may eventually revolutionize logistics. By 2014, Caterpillar had a self-driving dump truck which is expected to greatly change the process of mining. In 2015, these Caterpillar trucks were actively used in mining operations in Australia by the mining company
Rio Tinto Coal Australia
Rio Tinto Coal Australia (RTCA) was an Australian coal mining organisation, that was part of the worldwide Rio Tinto Group. In 2018, Rio Tinto completed the sale of its remaining assets
RTCA Operations
RTCA Queensland Operations
Blair ...
. Some analysts believe that within the next few decades, most trucks will be self-driving.
A literate or 'reading robot' named Marge has intelligence that comes from software. She can read newspapers, find and correct misspelled words, learn about banks like Barclays, and understand that some restaurants are better places to eat than others.
Baxter is a new robot introduced in 2012 which learns by guidance. A worker could teach Baxter how to perform a task by moving its hands in the desired motion and having Baxter memorize them. Extra dials, buttons, and controls are available on Baxter's arm for more precision and features. Any regular worker could program Baxter and it only takes a matter of minutes, unlike usual industrial robots that take extensive programs and coding to be used. This means Baxter needs no programming to operate. No software engineers are needed. This also means Baxter can be taught to perform multiple, more complicated tasks. Sawyer was added in 2015 for smaller, more precise tasks.
Prototype cooking robots have been developed and could be programmed for autonomous, dynamic and adjustable preparation of discrete meals.
Etymology
The word ''robot'' was introduced to the public by the
Czech interwar
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the First World War to the beginning of the Second World War. The interwar period was relativel ...
writer
Karel Čapek in his play ''
R.U.R. (Rossum's Universal Robots)
''R.U.R.'' is a 1920 science-fiction play by the Czech writer Karel Čapek. "R.U.R." stands for (Rossum's Universal Robots, a phrase that has been used as a subtitle in English versions). The play had its world premiere on 2 January 1921 in H ...
'', published in 1920.
The play begins in a factory that uses a chemical substitute for protoplasm to manufacture living, simplified people called ''robots.'' The play does not focus in detail on the technology behind the creation of these living creatures, but in their appearance they prefigure modern ideas of
androids, creatures who can be mistaken for humans. These mass-produced workers are depicted as efficient but emotionless, incapable of original thinking and indifferent to self-preservation. At issue is whether the robots are being
exploited and the consequences of human dependence upon commodified labor (especially after a number of specially-formulated robots achieve self-awareness and incite robots all around the world to rise up against the humans).
Karel Čapek himself did not coin the word. He wrote a short letter in reference to an
etymology in the ''
Oxford English Dictionary'' in which he named his brother, the painter and writer
Josef Čapek, as its actual originator.
In an article in the Czech journal ''
Lidové noviny'' in 1933, he explained that he had originally wanted to call the creatures ''laboři'' ("workers", from
Latin ''labor''). However, he did not like the word, and sought advice from his brother Josef, who suggested "roboti". The word ''robota'' means literally "
corvée", "serf labor", and figuratively "drudgery" or "hard work" in
Czech and also (more general) "work", "labor" in many
Slavic languages (e.g.:
Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
,
Russian,
Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguat ...
,
Slovak,
Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
,
Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North M ...
,
Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
, archaic Czech, as well as ''robot'' in
Hungarian). Traditionally the ''robota'' (Hungarian ''robot'') was the work period a serf (
corvée) had to give for his lord, typically 6 months of the year. The origin of the word is the
Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic () was the first Slavic languages, Slavic literary language.
Historians credit the 9th-century Byzantine Empire, Byzantine missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius with Standard language, standardizing the lan ...
(
Old Bulgarian) ''rabota'' "servitude" ("work" in contemporary Bulgarian and Russian), which in turn comes from the
Proto-Indo-European root ''*orbh-''. ''Robot'' is
cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words in different languages that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymology, etymological ancestor in a proto-language, common parent language. Because language c ...
with the German root ''Arbeit'' (work).
English pronunciation of the word has evolved relatively quickly since its introduction. In the U.S. during the late '30s to early '40s the second syllable was pronounced with a long "O" like "row-boat." By the late '50s to early '60s, some were pronouncing it with a short "U" like "row-but" while others used a softer "O" like "row-bought." By the '70s, its current pronunciation "row-bot" had become predominant.
The word
robotics, used to describe this field of study,
was coined by the science fiction writer
Isaac Asimov
yi, יצחק אזימאװ
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Petrovichi, Russian SFSR
, spouse =
, relatives =
, children = 2
, death_date =
, death_place = Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
, nationality = Russian (1920–1922)Soviet (192 ...
. Asimov created the "''
Three Laws of Robotics''" which are a recurring theme in his books. These have since been used by many others to define laws used in fiction. (The three laws are pure fiction, and no technology yet created has the ability to understand or follow them, and in fact most robots serve military purposes, which run quite contrary to the first law and often the third law. "People think about Asimov's laws, but they were set up to point out how a simple ethical system doesn't work. If you read the short stories, every single one is about a failure, and they are totally impractical," said Dr. Joanna Bryson of the University of Bath.)
Modern robots

Mobile robot
Mobile robots have the capability to move around in their environment and are not fixed to one physical location. An example of a mobile robot that is in common use today is the ''automated guided vehicle'' or ''automatic guided vehicle'' (AGV). An AGV is a mobile robot that follows markers or wires in the floor, or uses vision or lasers.
AGVs are discussed later in this article.
Mobile robots are also found in industry, military and security environments. They also appear as consumer products, for entertainment or to perform certain tasks like vacuum cleaning. Mobile robots are the focus of a great deal of current research and almost every major university has one or more labs that focus on mobile robot research.
Mobile robots are usually used in tightly controlled environments such as on
assembly lines because they have difficulty responding to unexpected interference. Because of this most humans rarely encounter robots. However
domestic robots for cleaning and maintenance are increasingly common in and around homes in developed countries. Robots can also be found in
military applications.
Industrial robots (manipulating)
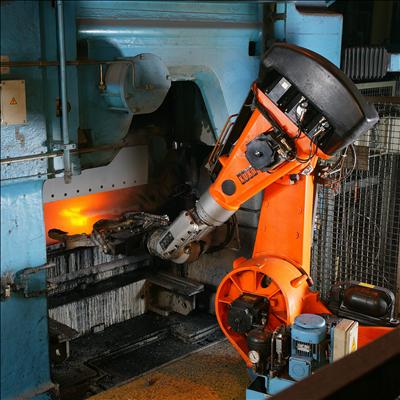

Industrial robots usually consist of a
jointed arm
A robotic arm is a type of mechanical arm, usually programmable, with similar functions to a human arm; the arm may be the sum total of the mechanism or may be part of a more complex robot. The links of such a manipulator are connected by joints ...
(multi-linked manipulator) and an
end effector
In robotics, an end effector is the device at the end of a robotic arm, designed to interact with the environment. The exact nature of this device depends on the application of the robot.
In the strict definition, which originates from serial ro ...
that is attached to a fixed surface. One of the most common type of end effector is a
gripper
A ''gripper'' is something that grips things or makes it easier to grip things. It may refer to:
* grippers, tools for building hand strength
* a Robot end effector, the "hand" of a robot
* a person working in a grip (job)
In the United States, ...
assembly.
The
International Organization for Standardization gives a definition of a manipulating industrial robot in
ISO 8373 ISO 8373 Manipulating industrial robots – Vocabulary
It is the ISO standard that defines terms relevant to manipulating industrial robots operated in a manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equ ...
:
"an automatically controlled, reprogrammable, multipurpose, manipulator programmable in three or more axes, which may be either fixed in place or mobile for use in industrial automation applications."
This definition is used by the
International Federation of Robotics, the European Robotics Research Network (EURON) and many national standards committees.
Service robot
Most commonly industrial robots are fixed robotic arms and manipulators used primarily for production and distribution of goods. The term "service robot" is less well-defined. The
International Federation of Robotics has proposed a tentative definition, "A service robot is a robot which operates semi- or fully autonomously to perform services useful to the well-being of humans and equipment, excluding manufacturing operations."
Educational (interactive) robots
Robots are used as educational assistants to teachers. From the 1980s, robots such as
turtles were used in schools and programmed using the
Logo language.
There are
robot kit
A robot kit is a special construction kit for building robots, especially autonomous mobile robots.
Toy robot kits are also supplied by several companies. They are mostly made of plastics elements like Lego Mindstorms, rero Reconfigurable Robo ...
s like
Lego Mindstorms,
BIOLOID
The ROBOTIS BIOLOID is a hobbyist and educational robot kit produced by the Korean robot manufacturer ROBOTIS. The BIOLOID platform consists of components and small, modular servomechanisms called the AX-12A Dynamixels, which can be used in a da ...
, OLLO from ROBOTIS, or BotBrain Educational Robots can help children to learn about mathematics, physics, programming, and electronics. Robotics have also been introduced into the lives of elementary and high school students in the form of
robot competitions with the company
FIRST
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
(For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology). The organization is the foundation for the
FIRST Robotics Competition,
FIRST Tech Challenge
FIRST Tech Challenge (FTC), formerly known as FIRST Vex Challenge, is a robotics competition for students in grades 7–12 to compete head to head, by designing, building, and programming a robot to compete in an alliance format against other te ...
,
FIRST Lego League Challenge
The ''FIRST'' LEGO League Challenge (formerly known as ''FIRST'' LEGO League) is an international competition organized by ''FIRST'' for elementary and middle school students (ages 9–14 in the United States and Canada, 9–16 elsewhere).
Each y ...
and
FIRST Lego League Explore
FIRST LEGO League Explore (FLLE) (formerly known as FIRST LEGO League Jr.) is a non-competitive robotics program designed for children ages six to ten. It is one of the programs established by FIRST.
FIRST LEGO League Explore follows the same the ...
competitions.
There have also been robots such as the teaching computer, Leachim (1974). Leachim was an early example of speech synthesis using the using the
Diphone synthesis
Speech synthesis is the artificial production of human speech. A computer system used for this purpose is called a speech synthesizer, and can be implemented in software or hardware products. A text-to-speech (TTS) system converts normal languag ...
method.
2-XL
2-XL (2-XL Robot, 2XL Robot, 2-XL Toy) is an educational toy robot that was marketed from 1978–1981 by the Mego Corporation, and from 1992–1995 by Tiger Electronics. 2-XL was the first "smart-toy" in that it exhibited rudimentary intelligenc ...
(1976) was a robot shaped game / teaching toy based on branching between audible tracks on an
8-track tape player, both invented by
Michael J. Freeman
Michael J. Freeman (born 1947) is an American inventor who works in trend analysis, advanced behavioral systems, programming of smart toys, cable television and robotics. He was a professor at three American universities and a consultant to busine ...
. Later, the 8-track was upgraded to tape cassettes and then to digital.
Modular robot
Modular robots are a new breed of robots that are designed to increase the use of robots by modularizing their architecture. The functionality and effectiveness of a modular robot is easier to increase compared to conventional robots. These robots are composed of a single type of identical, several different identical module types, or similarly shaped modules, which vary in size. Their architectural structure allows hyper-redundancy for modular robots, as they can be designed with more than 8 degrees of freedom (DOF). Creating the programming,
inverse kinematics
In computer animation and robotics, inverse kinematics is the mathematical process of calculating the variable joint parameters needed to place the end of a kinematic chain, such as a robot manipulator or animation character's skeleton, in a g ...
and dynamics for modular robots is more complex than with traditional robots. Modular robots may be composed of L-shaped modules, cubic modules, and U and H-shaped modules. ANAT technology, an early modular robotic technology patented by Robotics Design Inc., allows the creation of modular robots from U and H shaped modules that connect in a chain, and are used to form heterogeneous and homogenous modular robot systems. These "ANAT robots" can be designed with "n" DOF as each module is a complete motorized robotic system that folds relatively to the modules connected before and after it in its chain, and therefore a single module allows one degree of freedom. The more modules that are connected to one another, the more degrees of freedom it will have. L-shaped modules can also be designed in a chain, and must become increasingly smaller as the size of the chain increases, as payloads attached to the end of the chain place a greater strain on modules that are further from the base. ANAT H-shaped modules do not suffer from this problem, as their design allows a modular robot to distribute pressure and impacts evenly amongst other attached modules, and therefore payload-carrying capacity does not decrease as the length of the arm increases. Modular robots can be manually or self-reconfigured to form a different robot, that may perform different applications. Because modular robots of the same architecture type are composed of modules that compose different modular robots, a snake-arm robot can combine with another to form a dual or quadra-arm robot, or can split into several mobile robots, and mobile robots can split into multiple smaller ones, or combine with others into a larger or different one. This allows a single modular robot the ability to be fully specialized in a single task, as well as the capacity to be specialized to perform multiple different tasks.
Modular robotic technology is currently being applied in hybrid transportation,
industrial automation,
duct cleaning
and handling. Many research centres and universities have also studied this technology, and have developed prototypes.
Collaborative robots
A ''collaborative robot'' or ''
cobot'' is a robot that can safely and effectively interact with human workers while performing simple industrial tasks. However, end-effectors and other environmental conditions may create hazards, and as such risk assessments should be done before using any industrial motion-control application.
The collaborative robots most widely used in industries today are manufactured by
Universal Robots in Denmark.
Rethink Robotics—founded by
Rodney Brooks, previously with
iRobot—introduced
Baxter in September 2012; as an
industrial robot designed to safely interact with neighboring human workers, and be programmable for performing simple tasks.
Baxters stop if they detect a human in the way of their robotic arms and have prominent off switches. Intended for sale to small businesses, they are promoted as the robotic analogue of the personal computer.
, 190 companies in the US have bought Baxters and they are being used commercially in the UK.
Robots in society

Roughly half of all the robots in the world are in Asia, 32% in Europe, and 16% in North America, 1% in
Australasia and 1% in Africa. 40% of all the robots in the world are in Japan, making Japan the country with the highest number of robots.
Autonomy and ethical questions

As robots have become more advanced and sophisticated, experts and academics have increasingly explored the questions of what ethics might govern robots' behavior,
and whether robots might be able to claim any kind of social, cultural, ethical or legal rights. One scientific team has said that it was possible that a robot brain would exist by 2019. Others predict robot intelligence breakthroughs by 2050. Recent advances have made robotic behavior more sophisticated. The social impact of intelligent robots is subject of a 2010 documentary film called ''
Plug & Pray''.
Vernor Vinge has suggested that a moment may come when computers and robots are smarter than humans. He calls this "
the Singularity".
He suggests that it may be somewhat or possibly very dangerous for humans. This is discussed by a philosophy called
Singularitarianism
Singularitarianism is a movement defined by the belief that a technological singularity—the creation of superintelligence—will likely happen in the medium future, and that deliberate action ought to be taken to ensure that the singularity ben ...
.
In 2009, experts attended a conference hosted by the
Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) to discuss whether computers and robots might be able to acquire any autonomy, and how much these abilities might pose a threat or hazard. They noted that some robots have acquired various forms of semi-autonomy, including being able to find power sources on their own and being able to independently choose targets to attack with weapons. They also noted that some computer viruses can evade elimination and have achieved "cockroach intelligence." They noted that self-awareness as depicted in science-fiction is probably unlikely, but that there were other potential hazards and pitfalls.
Various media sources and scientific groups have noted separate trends in differing areas which might together result in greater robotic functionalities and autonomy, and which pose some inherent concerns.
Military robots
Some experts and academics have questioned the use of robots for military combat, especially when such robots are given some degree of autonomous functions. There are also concerns about technology which might allow some armed robots to be controlled mainly by other robots. The US Navy has funded a report which indicates that, as
military robots become more complex, there should be greater attention to implications of their ability to make autonomous decisions. One researcher states that autonomous robots might be more humane, as they could make decisions more effectively. However, other experts question this.
One robot in particular, the
EATR, has generated public concerns
over its fuel source, as it can continually refuel itself using organic substances.
Although the engine for the EATR is designed to run on
biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
and vegetation specifically selected by its sensors, which it can find on battlefields or other local environments, the project has stated that chicken fat can also be used.
Manuel De Landa
Manuel DeLanda (born 1952) is a Mexican- American writer, artist and philosopher who has lived in New York since 1975. He is a lecturer in architecture at the Princeton University School of Architecture and the University of Pennsylvania School ...
has noted that "smart missiles" and autonomous bombs equipped with artificial perception can be considered robots, as they make some of their decisions autonomously. He believes this represents an important and dangerous trend in which humans are handing over important decisions to machines.
Relationship to unemployment
For centuries, people have predicted that machines would make
workers obsolete and increase unemployment, although the causes of unemployment are usually thought to be due to social policy.
A recent example of human replacement involves Taiwanese technology company
Foxconn who, in July 2011, announced a three-year plan to replace workers with more robots. At present the company uses ten thousand robots but will increase them to a million robots over a three-year period.
Lawyers have speculated that an increased prevalence of robots in the workplace could lead to the need to improve redundancy laws.
Kevin J. Delaney said "Robots are taking human jobs. But Bill Gates believes that governments should tax companies’ use of them, as a way to at least temporarily slow the spread of automation and to fund other types of employment." The
robot tax would also help pay a guaranteed living wage to the displaced workers.
The
World Bank's
World Development Report 2019 puts forth evidence showing that while automation displaces workers, technological innovation creates more new industries and jobs on balance.
Contemporary uses

At present, there are two main types of robots, based on their use:
general-purpose autonomous robots and dedicated robots.
Robots can be classified by their
specificity of purpose. A robot might be designed to perform one particular task extremely well, or a range of tasks less well. All robots by their nature can be re-programmed to behave differently, but some are limited by their physical form. For example, a factory robot arm can perform jobs such as cutting, welding, gluing, or acting as a fairground ride, while a pick-and-place robot can only populate printed circuit boards.
General-purpose autonomous robots
General-purpose autonomous robots can perform a variety of functions independently. General-purpose autonomous robots typically can navigate independently in known spaces, handle their own re-charging needs, interface with electronic doors and elevators and perform other basic tasks. Like computers, general-purpose robots can link with networks, software and accessories that increase their usefulness. They may recognize people or objects, talk, provide companionship, monitor environmental quality, respond to alarms, pick up supplies and perform other useful tasks. General-purpose robots may perform a variety of functions simultaneously or they may take on different roles at different times of day. Some such robots try to mimic human beings and may even resemble people in appearance; this type of robot is called a humanoid robot. Humanoid robots are still in a very limited stage, as no humanoid robot can, as of yet, actually navigate around a room that it has never been in. Thus, humanoid robots are really quite limited, despite their intelligent behaviors in their well-known environments.
Factory robots
Car production
Over the last three decades,
automobile factories
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded as t ...
have become dominated by robots. A typical factory contains hundreds of
industrial robots working on fully automated production lines, with one robot for every ten human workers. On an automated production line, a vehicle chassis on a conveyor is
welded,
glued, painted and finally assembled at a sequence of robot stations.
Packaging
Industrial robots are also used extensively for palletizing and packaging of manufactured goods, for example for rapidly taking drink cartons from the end of a conveyor belt and placing them into boxes, or for loading and unloading machining centers.
Electronics
Mass-produced
printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in Electrical engineering, electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a L ...
s (PCBs) are almost exclusively manufactured by pick-and-place robots, typically with
SCARA manipulators, which remove tiny
electronic component
An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not ...
s from strips or trays, and place them on to PCBs with great accuracy. Such robots can place hundreds of thousands of components per hour, far out-performing a human in speed, accuracy, and reliability.
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs)

Mobile robots, following markers or wires in the floor, or using vision
or lasers, are used to transport goods around large facilities, such as warehouses, container ports, or hospitals.
= Early AGV-style robots
=
Limited to tasks that could be accurately defined and had to be performed the same way every time. Very little feedback or intelligence was required, and the robots needed only the most basic
exteroceptors (sensors). The limitations of these AGVs are that their paths are not easily altered and they cannot alter their paths if obstacles block them. If one AGV breaks down, it may stop the entire operation.
= Interim AGV technologies
=
Developed to deploy triangulation from beacons or bar code grids for scanning on the floor or ceiling. In most factories, triangulation systems tend to require moderate to high maintenance, such as daily cleaning of all beacons or bar codes. Also, if a tall pallet or large vehicle blocks beacons or a bar code is marred, AGVs may become lost. Often such AGVs are designed to be used in human-free environments.
= Intelligent AGVs (i-AGVs)
=
Such as SmartLoader, SpeciMinder, ADAM, Tug Eskorta, and MT 400 with Motivity are designed for people-friendly workspaces. They navigate by recognizing natural features.
3D scanner
3D scanning is the process of analyzing a real-world object or environment to collect data on its shape and possibly its appearance (e.g. color). The collected data can then be used to construct digital 3D modelling, 3D models.
A 3D scanner can ...
s or other means of sensing the environment in two or three dimensions help to eliminate cumulative
errors in
dead-reckoning
In navigation, dead reckoning is the process of calculating current position of some moving object by using a previously determined position, or fix, and then incorporating estimates of speed, heading direction, and course over elapsed time. ...
calculations of the AGV's current position. Some AGVs can create maps of their environment using scanning lasers with
simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) and use those maps to navigate in real time with other
path planning
Motion planning, also path planning (also known as the navigation problem or the piano mover's problem) is a computational problem to find a sequence of valid configurations that moves the object from the source to destination. The term is used ...
and obstacle avoidance algorithms. They are able to operate in complex environments and perform non-repetitive and non-sequential tasks such as transporting
photomasks in a semiconductor lab, specimens in hospitals and goods in warehouses. For dynamic areas, such as warehouses full of pallets, AGVs require additional strategies using three-dimensional sensors such as
time-of-flight or
stereovision
Stereopsis () is the component of depth perception retrieved through binocular vision.
Stereopsis is not the only contributor to depth perception, but it is a major one. Binocular vision happens because each eye receives a different image becaus ...
cameras.
Dirty, dangerous, dull, or inaccessible tasks
There are many jobs that humans would rather leave to robots. The job may be boring, such as
domestic cleaning or
sports field line marking, or dangerous, such as exploring inside a
volcano. Other jobs are physically inaccessible, such as exploring another
planet, cleaning the inside of a long pipe, or performing
laparoscopic
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.Medli ...
surgery.
Space probes
Almost every unmanned
space probe ever launched was a robot. Some were launched in the 1960s with very limited abilities, but their ability to fly and land (in the case of
Luna 9) is an indication of their status as a robot. This includes the
Voyager probe
The Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two robotic interstellar probes, ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2''. They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable alignment of Jupiter and Saturn, to fly near th ...
s and the Galileo probes, among others.
Telerobots
 Teleoperated robots
Teleoperated robots, or telerobots, are devices
remotely operated from a distance by a human operator rather than following a predetermined sequence of movements, but which has semi-autonomous behaviour. They are used when a human cannot be present on site to perform a job because it is dangerous, far away, or inaccessible. The robot may be in another room or another country, or may be on a very different scale to the operator. For instance, a laparoscopic surgery robot allows the surgeon to work inside a human patient on a relatively small scale compared to open surgery, significantly shortening recovery time.
They can also be used to avoid exposing workers to the hazardous and tight spaces such as in
duct cleaning. When disabling a bomb, the operator sends a small robot to disable it. Several authors have been using a device called the Longpen to sign books remotely. Teleoperated robot aircraft, like the Predator
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle, are increasingly being used by the military. These pilotless drones can search terrain and fire on targets. Hundreds of robots such as
iRobot's
Packbot and the
Foster-Miller TALON are being used in
Iraq and
Afghanistan by the
U.S. military
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the ...
to defuse roadside bombs or
improvised explosive devices (IEDs) in an activity known as
explosive ordnance disposal (EOD).
Automated fruit harvesting machines
Robots are used to
automate picking fruit on orchards at a cost lower than that of human pickers.
Domestic robots
 Domestic robots
Domestic robots are simple robots dedicated to a single task work in home use. They are used in simple but often disliked jobs, such as
vacuum cleaning
A vacuum cleaner, also known simply as a vacuum or a hoover, is a device that causes suction in order to remove dirt from floors, upholstery, draperies, and other surfaces. It is generally electrically driven.
The dirt is collected by either a ...
,
floor washing, and
lawn mowing
A lawn mower (also known as a mower, grass cutter or lawnmower) is a device utilizing one or more revolving blades (or a reel) to cut a grass surface to an even height. The height of the cut grass may be fixed by the design of the mower, but g ...
. An example of a domestic robot is a
Roomba
Roomba is a series of autonomous robotic vacuum cleaners made by the company iRobot. Introduced in September 2002, they have a set of sensors that enable them to navigate the floor area of a home. These sensors can detect the presence of obstac ...
.
Military robots
Military robots include the
SWORDS robot
The Foster-Miller TALON remotely operated vehicle is a small, tracked military robot designed for missions ranging from reconnaissance to combat. It is made by American robotics company Qinetiq-NA, a subsidiary of Qinetiq.
Overview
Foster-Mill ...
which is currently used in ground-based combat. It can use a variety of weapons and there is some discussion of giving it some degree of autonomy in battleground situations.
Unmanned combat air vehicles (UCAVs), which are an upgraded form of
UAVs, can do a wide variety of missions, including combat. UCAVs are being designed such as the
BAE Systems Mantis
The BAE Systems Mantis Unmanned Autonomous System Advanced Concept Technology Demonstrator is a British demonstrator programme for Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) technology. The Mantis is a twin-engine, turboprop-powered UCAV with a wingsp ...
which would have the ability to fly themselves, to pick their own course and target, and to make most decisions on their own. The
BAE Taranis is a UCAV built by Great Britain which can fly across continents without a pilot and has new means to avoid detection.
Flight trials are expected to begin in 2011.
The
AAAI has studied this topic in depth
and its president has commissioned a study to look at this issue.
Some have suggested a need to build "
Friendly AI", meaning that the advances which are already occurring with AI should also include an effort to make AI intrinsically friendly and humane. Several such measures reportedly already exist, with robot-heavy countries such as Japan and South Korea
having begun to pass regulations requiring robots to be equipped with safety systems, and possibly sets of 'laws' akin to Asimov's
Three Laws of Robotics. An official report was issued in 2009 by the Japanese government's Robot Industry Policy Committee. Chinese officials and researchers have issued a report suggesting a set of ethical rules, and a set of new legal guidelines referred to as "Robot Legal Studies."
Some concern has been expressed over a possible occurrence of robots telling apparent falsehoods.
Mining robots
Mining robots are designed to solve a number of problems currently facing the mining industry, including skills shortages, improving productivity from declining ore grades, and achieving environmental targets. Due to the hazardous nature of mining, in particular
underground mining, the prevalence of autonomous, semi-autonomous, and tele-operated robots has greatly increased in recent times. A number of vehicle manufacturers provide autonomous trains, trucks and
loaders that will load material, transport it on the mine site to its destination, and unload without requiring human intervention. One of the world's largest mining corporations,
Rio Tinto, has recently expanded its autonomous truck fleet to the world's largest, consisting of 150 autonomous
Komatsu trucks, operating in
Western Australia. Similarly,
BHP has announced the expansion of its autonomous drill fleet to the world's largest, 21 autonomous
Atlas Copco drills.
Drilling,
longwall
Longwall mining is a form of underground coal mining where a long wall of coal is mined in a single slice (typically thick). The longwall panel (the block of coal that is being mined) is typically long (but can be upto long) and wide.
Histor ...
and
rockbreaking machines are now also available as autonomous robots. The
Atlas Copco Rig Control System can autonomously execute a drilling plan on a
drilling rig, moving the rig into position using GPS, set up the drill rig and drill down to specified depths. Similarly, the
Transmin
Transmin is an Australian privately owned company specialising in bulk materials handling equipment and related products headquartered in Malaga, Western Australia, 15 kilometres north of Perth, Western Australia, that provides engineered equip ...
Rocklogic system can automatically plan a path to position a rockbreaker at a selected destination. These systems greatly enhance the safety and efficiency of mining operations.
Healthcare
Robots in healthcare have two main functions. Those which assist an individual, such as a sufferer of a disease like Multiple Sclerosis, and those which aid in the overall systems such as pharmacies and hospitals.
Home automation for the elderly and disabled
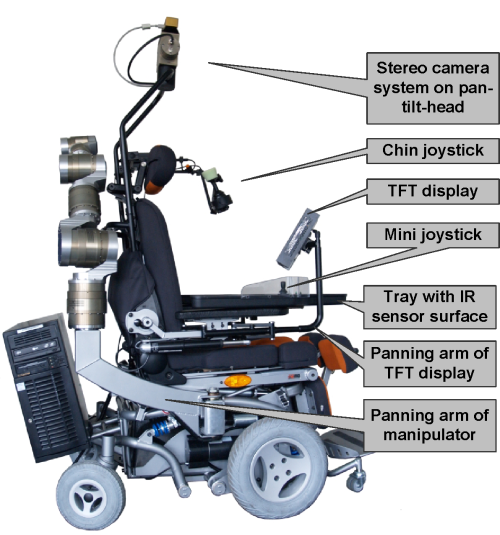
Robots used in
home automation
Home automation or domotics is building automation for a home, called a smart home or smart house. A home automation system will monitor and/or control home attributes such as lighting, climate, entertainment systems, and appliances. It m ...
have developed over time from simple basic robotic assistants, such as the
Handy 1,
through to semi-autonomous robots, such as
FRIEND which can assist the elderly and disabled with common tasks.
The population is
aging
Ageing ( BE) or aging ( AE) is the process of becoming older. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi, whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In ...
in many countries, especially Japan, meaning that there are increasing numbers of elderly people to care for, but relatively fewer young people to care for them. Humans make the best carers, but where they are unavailable, robots are gradually being introduced.
FRIEND is a semi-autonomous robot designed to support
disabled and
elderly
Old age refers to ages nearing or surpassing the life expectancy of human beings, and is thus the end of the human life cycle. Terms and euphemisms for people at this age include old people, the elderly (worldwide usage), OAPs (British usage ...
people in their daily life activities, like preparing and serving a meal. FRIEND make it possible for
patients who are
paraplegic
Paraplegia, or paraparesis, is an impairment in motor or sensory function of the lower extremities. The word comes from Ionic Greek ()
"half-stricken". It is usually caused by spinal cord injury or a congenital condition that affects the neural ...
, have muscle diseases or serious
paralysis
Paralysis (also known as plegia) is a loss of motor function in one or more muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 50 ...
(due to strokes etc.), to perform tasks without help from other people like therapists or nursing staff.
Pharmacies
Script Pro manufactures a robot designed to help pharmacies fill prescriptions that consist of oral solids or
medications
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and rel ...
in pill form. The pharmacist or
pharmacy technician
A pharmacy technician performs pharmacy-related functions, working collaboratively with a licensed pharmacist. Training, certification, licensing, and actual practice of pharmacy technicians varies not only worldwide but in some countries regional ...
enters the prescription information into its information system. The system, upon determining whether or not the drug is in the robot, will send the information to the robot for filling. The robot has 3 different size vials to fill determined by the size of the pill. The robot technician, user, or pharmacist determines the needed size of the vial based on the tablet when the robot is stocked. Once the vial is filled it is brought up to a conveyor belt that delivers it to a holder that spins the vial and attaches the patient label. Afterwards it is set on another conveyor that delivers the patient's medication vial to a slot labeled with the patient's name on an LED read out. The pharmacist or technician then checks the contents of the vial to ensure it's the correct drug for the correct patient and then seals the vials and sends it out front to be picked up.
McKesson's Robot RX is another healthcare robotics product that helps pharmacies dispense thousands of medications daily with little or no errors. The robot can be ten feet wide and thirty feet long and can hold hundreds of different kinds of medications and thousands of doses. The pharmacy saves many resources like staff members that are otherwise unavailable in a resource scarce industry. It uses an
electromechanical head coupled with a
pneumatic
Pneumatics (from Greek ‘wind, breath’) is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air.
Pneumatic systems used in Industrial sector, industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A central ...
system to capture each dose and deliver it to either its stocked or dispensed location. The head moves along a single axis while it rotates 180 degrees to pull the medications. During this process it uses
barcode technology to verify it's pulling the correct drug. It then delivers the drug to a patient specific bin on a conveyor belt. Once the bin is filled with all of the drugs that a particular patient needs and that the robot stocks, the bin is then released and returned out on the conveyor belt to a technician waiting to load it into a cart for delivery to the floor.
Research robots
While most robots today are installed in factories or homes, performing labour or life saving jobs, many new types of robot are being developed in
laboratories
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicia ...
around the world. Much of the research in robotics focuses not on specific industrial tasks, but on investigations into new types of robot, alternative ways to think about or design robots, and new ways to manufacture them. It is expected that these new types of robot will be able to solve real world problems when they are finally realized.
Bionic and biomimetic robots
One approach to designing robots is to base them on animals.
BionicKangaroo was designed and engineered by studying and applying the physiology and methods of locomotion of a kangaroo.
Nanorobots
Nanorobotics is the
emerging technology field of creating machines or robots whose components are at or close to the microscopic scale of a
nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re ...
(10
−9 meters). Also known as "nanobots" or "nanites", they would be constructed from
molecular machine
A molecular machine, nanite, or nanomachine is a molecular component that produces quasi-mechanical movements (output) in response to specific stimuli (input). In cellular biology, macromolecular machines frequently perform tasks essential for l ...
s. So far, researchers have mostly produced only parts of these complex systems, such as bearings, sensors, and
synthetic molecular motors
Synthetic molecular motors are molecular machines capable of continuous directional rotation under an energy input. Although the term "molecular motor" has traditionally referred to a naturally occurring protein that induces motion (via protein d ...
, but functioning robots have also been made such as the entrants to the Nanobot Robocup contest. Researchers also hope to be able to create entire robots as small as viruses or bacteria, which could perform tasks on a tiny scale. Possible applications include micro surgery (on the level of individual
cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
),
utility fog, manufacturing, weaponry and cleaning. Some people have suggested that if there were nanobots which could reproduce, the earth would turn into "
grey goo", while others argue that this hypothetical outcome is nonsense.
Reconfigurable robots
A few researchers have investigated the possibility of creating robots which can
alter their physical form to suit a particular task, like the fictional
T-1000. Real robots are nowhere near that sophisticated however, and mostly consist of a small number of cube shaped units, which can move relative to their neighbours. Algorithms have been designed in case any such robots become a reality.
Robotic, mobile laboratory operators
In July 2020 scientists reported the development of a mobile robot chemist and demonstrate that it can assist in experimental searches. According to the scientists their strategy was
automating the researcher rather than the instruments – freeing up time for the human researchers to think creatively – and could identify photocatalyst mixtures for hydrogen production from water that were six times more active than initial formulations. The modular robot can operate laboratory instruments, work nearly around the clock, and autonomously make decisions on his next actions depending on experimental results.
Soft-bodied robots
Robots with
silicone
A silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer made up of siloxane (−R2Si−O−SiR2−, where R = organic group). They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking ...
bodies and flexible actuators (
air muscles,
electroactive polymers
file:EAP-example2.png, (a) Cartoon drawing of an EAP gripping device.(b) A voltage is applied and the EAP fingers deform in order to release the ball.(c) When the voltage is removed, the EAP fingers return to their original shape and grip the ball
...
, and
ferrofluids) look and feel different from robots with rigid skeletons, and can have different behaviors. Soft, flexible (and sometimes even squishy) robots are often designed to mimic the biomechanics of animals and other things found in nature, which is leading to new applications in medicine, care giving, search and rescue, food handling and manufacturing, and scientific exploration.
Swarm robots
Inspired by
colonies of insects such as
ants and
bees
Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey. Bees are a monophyletic lineage within the superfamil ...
, researchers are modeling the behavior of
swarms of thousands of tiny robots which together perform a useful task, such as finding something hidden, cleaning, or spying. Each robot is quite simple, but the
emergent behavior
In philosophy, systems theory, science, and art, emergence occurs when an entity is observed to have properties its parts do not have on their own, properties or behaviors that emerge only when the parts interact in a wider whole.
Emergence ...
of the swarm is more complex. The whole set of robots can be considered as one single distributed system, in the same way an ant colony can be considered a
superorganism, exhibiting
swarm intelligence
Swarm intelligence (SI) is the collective behavior of decentralized, self-organized systems, natural or artificial. The concept is employed in work on artificial intelligence. The expression was introduced by Gerardo Beni and Jing Wang in 1989, in ...
. The largest swarms so far created include the iRobot swarm, the SRI/MobileRobots CentiBots project and the Open-source Micro-robotic Project swarm, which are being used to research collective behaviors. Swarms are also more resistant to failure. Whereas one large robot may fail and ruin a mission, a swarm can continue even if several robots fail. This could make them attractive for space exploration missions, where failure is normally extremely costly.
Haptic interface robots
Robotics also has application in the design of
virtual reality interfaces. Specialized robots are in widespread use in the
haptic research community. These robots, called "haptic interfaces", allow touch-enabled user interaction with real and virtual environments. Robotic forces allow simulating the mechanical properties of "virtual" objects, which users can experience through their sense of
touch.
Contemporary art and sculpture
Robots are used by contemporary artists to create works that include mechanical automation. There are many branches of robotic art, one of which is robotic installation art, a type of
installation art that is programmed to respond to viewer interactions, by means of computers, sensors and actuators. The future behavior of such installations can therefore be altered by input from either the artist or the participant, which differentiates these artworks from other types of
kinetic art.
Le Grand Palais
The Grand Palais des Champs-Élysées ( en, Great Palace of the Elysian Fields), commonly known as the Grand Palais (English: Great Palace), is a historic site, exhibition hall and museum complex located at the Champs-Élysées in the 8th arro ...
in Paris organized an exhibition "Artists & Robots", featuring artworks created by more than forty artists with the help of robots in 2018.
Robots in popular culture

Literature
Robotic characters,
androids (artificial men/women) or
gynoids (artificial women), and
cyborgs (also "
bionic
Bionics or biologically inspired engineering is the application of biological methods and systems found in nature to the study and design of engineering systems and modern technology.
The word ''bionic'', coined by Jack E. Steele in August 1 ...
men/women", or humans with significant mechanical enhancements) have become a staple of science fiction.
The first reference in Western literature to mechanical servants appears in
Homer's ''
Iliad''. In Book XVIII,
Hephaestus, god of fire, creates new armor for the hero Achilles, assisted by robots.
According to the
Rieu translation, "Golden maidservants hastened to help their master. They looked like real women and could not only speak and use their limbs but were endowed with intelligence and trained in handwork by the immortal gods." The words "robot" or "android" are not used to describe them, but they are nevertheless mechanical devices human in appearance. "The first use of the word Robot was in Karel Čapek's play R.U.R. (Rossum's Universal Robots) (written in 1920)". Writer Karel Čapek was born in Czechoslovakia (Czech Republic).
Possibly the most prolific author of the twentieth century was
Isaac Asimov
yi, יצחק אזימאװ
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Petrovichi, Russian SFSR
, spouse =
, relatives =
, children = 2
, death_date =
, death_place = Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
, nationality = Russian (1920–1922)Soviet (192 ...
(1920–1992)
who published over five-hundred books.
Asimov is probably best remembered for his science-fiction stories and especially those about robots, where he placed robots and their interaction with society at the center of many of his works. Asimov carefully considered the problem of the ideal set of instructions robots might be given to lower the risk to humans, and arrived at his
Three Laws of Robotics: a robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm; a robot must obey orders given it by human beings, except where such orders would conflict with the First Law; and a robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict with the First or Second Law. These were introduced in his 1942 short story "Runaround", although foreshadowed in a few earlier stories. Later, Asimov added the Zeroth Law: "A robot may not harm humanity, or, by inaction, allow humanity to come to harm"; the rest of the laws are modified sequentially to acknowledge this.
According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary,'' the first passage in Asimov's short story "
Liar!" (1941) that mentions the First Law is the earliest recorded use of the word ''
robotics''. Asimov was not initially aware of this; he assumed the word already existed by analogy with ''mechanics,'' ''hydraulics,'' and other similar terms denoting branches of applied knowledge.
Films
Robots appear in many films. Most of the robots in cinema are fictional. Two of the most famous are
R2-D2 and
C-3PO from the ''
Star Wars
''Star Wars'' is an American epic film, epic space opera multimedia franchise created by George Lucas, which began with the Star Wars (film), eponymous 1977 film and quickly became a worldwide popular culture, pop-culture Cultural impact of S ...
'' franchise.
Sex robots
The concept of humanoid
sex robot
Sex robots or sexbots are anthropomorphic robotic sex dolls that have a humanoid form, human-like movement or behavior, and some degree of artificial intelligence. , although elaborately instrumented sex dolls have been created by a number of i ...
s has drawn public attention and elicited debate regarding their supposed benefits and potential effects on society. Opponents argue that the introduction of such devices would be socially harmful, and demeaning to women and children,
while proponents cite their potential therapeutical benefits, particularly in aiding people with
dementia or
depression.
Problems depicted in popular culture
Fears and concerns about robots have been repeatedly expressed in a wide range of books and films. A common theme is the development of a master race of conscious and highly intelligent robots, motivated to take over or destroy the human race. ''
Frankenstein'' (1818), often called the first science fiction novel, has become synonymous with the theme of a robot or android advancing beyond its creator.
Other works with similar themes include ''
The Mechanical Man'', ''
The Terminator
''The Terminator'' is a 1984 American science fiction action film directed by James Cameron. It stars Arnold Schwarzenegger as the Terminator, a cyborg assassin sent back in time from 2029 to 1984 to kill Sarah Connor (Linda Hamilton), whos ...
'', ''
Runaway
Runaway, Runaways or Run Away may refer to:
Engineering
* Runaway reaction, a chemical reaction releasing more heat than what can be removed and becoming uncontrollable
* Thermal runaway, self-increase of the reaction rate of an exothermic proce ...
'', ''
RoboCop
''RoboCop'' is a 1987 American science fiction action film directed by Paul Verhoeven and written by Edward Neumeier and Michael Miner. The film stars Peter Weller, Nancy Allen, Daniel O'Herlihy, Ronny Cox, Kurtwood Smith, and Miguel Ferre ...
'', the
Replicators in ''Stargate'', the
Cylons in ''
Battlestar Galactica
''Battlestar Galactica'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Glen A. Larson. The franchise began with the Battlestar Galactica (1978 TV series), original television series in 1978, and was followed by a short-run sequel se ...
'', the
Cybermen
The Cybermen are a fictional race of cyborgs principally portrayed in the British science fiction television programme '' Doctor Who''. The Cybermen are a species of space-faring cyborgs who often forcefully and painfully convert human beings ...
and
Daleks in ''
Doctor Who
''Doctor Who'' is a British science fiction television series broadcast by the BBC since 1963. The series depicts the adventures of a Time Lord called the Doctor, an extraterrestrial being who appears to be human. The Doctor explores the u ...
'', ''
The Matrix'', ''
Enthiran'' and ''
I, Robot
''I, Robot'' is a fixup (compilation) novel of science fiction short stories or essays by American writer Isaac Asimov. The stories originally appeared in the American magazines ''Super Science Stories'' and ''Astounding Science Fiction'' betw ...
''. Some fictional robots are programmed to kill and destroy; others gain superhuman intelligence and abilities by upgrading their own software and hardware. Examples of popular media where the robot becomes evil are ''
2001: A Space Odyssey'', ''
Red Planet'' and ''
Enthiran''.
The 2017 game ''
Horizon Zero Dawn
''Horizon Zero Dawn'' is a 2017 action role-playing game developed by Guerrilla Games and published by Sony Interactive Entertainment. The plot follows Aloy, a young hunter in a world overrun by machines, who sets out to uncover her past. The ...
'' explores themes of robotics in warfare,
robot ethics
Robot ethics, sometimes known as "roboethics", concerns ethical problems that occur with robots, such as whether robots pose a threat to humans in the long or short run, whether some ''uses'' of robots are problematic (such as in healthcare or as ...
, and the
AI control problem
In the field of artificial intelligence (AI), AI alignment research aims to steer AI systems towards their designers’ intended goals and interests. An ''aligned'' AI system advances the intended objective; a ''misaligned'' AI system is compete ...
, as well as the positive or negative impact such technologies could have on the environment.
Another common theme is the reaction, sometimes called the "
uncanny valley", of unease and even revulsion at the sight of robots that mimic humans too closely.
More recently, fictional representations of artificially intelligent robots in films such as ''
A.I. Artificial Intelligence'' and ''
Ex Machina'' and the 2016 TV adaptation of ''
Westworld'' have engaged audience sympathy for the robots themselves.
See also
*
Index of robotics articles
Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots. Robotics is related to the sciences of electronics, engineering, mechanics, and computer soft ...
*
Outline of robotics
following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to robotics:
Robotics is a branch of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering and computer science that deals with the design, construction, operation, and application o ...
*
Artificial intelligence
*
William Grey Walter
Specific robotics concepts
*
Robot locomotion
*
Simultaneous localization and mapping
*
Tactile sensor
*
Teleoperation
*
Uncanny valley
*
von Neumann machine
*
Wake-up robot problem In robotics, the wake-up robot problem refers to a situation where an autonomous robot is carried to an arbitrary location and put to operation, and the robot must localize itself without any prior knowledge.
The wake-up robot problem is closely r ...
*
Neuromorphic engineering
Robotics methods and categories
*
Cognitive robotics
Cognitive Robotics or Cognitive Technology is a subfield of robotics concerned with endowing a robot with intelligent behavior by providing it with a processing architecture that will allow it to learn and reason about how to behave in response t ...
*
Companion robot A companion robot is a robot created for the purposes of creating real or apparent companionship for human beings. Target markets for companion robots include the elderly and single children.
Examples
There are several companion robot prototypes ...
*
Domestic robot
*
Epigenetic robotics
Developmental robotics (DevRob), sometimes called epigenetic robotics, is a scientific field which aims at studying the developmental mechanisms, architectures and constraints that allow lifelong and open-ended learning of new skills and new knowl ...
*
Evolutionary robotics
*
Humanoid robot
*
Autonomous robot
*
Microbotics
Microbotics (or microrobotics) is the field of miniature robotics, in particular mobile robots with characteristic dimensions less than 1 mm. The term can also be used for robots capable of handling micrometer size components.
History
Microb ...
*
Robot control
Specific robots and devices
*
AIBO
*
Autonomous spaceport drone ship
*
Driverless car
*
Friendly Robotics
Robomow (also known as Friendly Robotics) is a manufacturer of robotic lawn mowers. Founded in Even Yehuda, Israel in 1995 by Udi Peless and Shai Abramson, the company provides robotic lawnmowers to the United States and Europe, with prices rangi ...
*
Lely Juno family
The Lely Juno family is a family of robot series produced by Excel Dairy Services, headquartered in the Netherlands. The robots' main function and purpose is to provide labor on farms such as supplying food to cows
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') ...
*
Liquid handling robot
A liquid handling robot is used to automate workflows in life science laboratories. It is a robot that dispenses a selected quantity of reagent, samples or other liquid to a designated container.
Introduction
Liquid handling plays a pivo ...
*
Paro (robot)
PARO is a therapeutic robot baby harp seal, intended to be very cute and to have a calming effect on and elicit emotional responses in patients of hospitals and nursing homes, similar to animal-assisted therapy except using robots.
History
Paro ...
*
PatrolBot
*
RoboBee
*
Roborior
Roborior is a robot manufactured by the robotics company Tmsuk and marketed by Sanyo. It is used both for lighting and guarding homes. Roborior is roughly the size of a watermelon and can produce different hues of color ranging from blue, purple, ...
*
Robot App Store
The Robot App Store is a digital application distribution platform for applications for robots opened to the public on late 2011. The service allows users to browse and download applications that were developed for robots, and published through th ...
Other related articles
*
Unmanned vehicle
An uncrewed vehicle or unmanned vehicle is a vehicle without a person on board. Uncrewed vehicles can either be under telerobotic control—remote controlled or remote guided vehicles—or they can be autonomously controlled—autonomous vehicl ...
*
Remote control vehicle
A remote-control vehicle is defined as any vehicle that is teleoperated by a means that does not restrict its motion with an origin external to the device. This is often a radio-control device, a cable between the controller and the vehicle, o ...
*
Automated guided vehicle
Further reading
*
See this humanoid robot artist sketch drawings from sight (CNN, Video, 2019)* Margolius, Ivan. 'The Robot of Prague', Newsletter, The Friends of Czech Heritage no. 17, Autumn 2017, pp. 3 – 6. https://czechfriends.net/images/RobotsMargoliusJul2017.pdf
* Glaser, Horst Albert and Rossbach, Sabine: The Artificial Human, Frankfurt/M., Bern, New York 201
"A Tragical History"*
Gutkind, L. (2006). ''
Almost Human: Making Robots Think''. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, Inc.
* Craig, J.J. (2005). ''Introduction to Robotics'', Pearson Prentice Hall. Upper Saddle River, NJ.
* Tsai, L. W. (1999). ''Robot Analysis''. Wiley. New York.
* Sotheby's New York. ''The Tin Toy Robot Collection of Matt Wyse'' (1996)
*
DeLanda, Manuel. ''
War in the Age of Intelligent Machines
''War in the Age of Intelligent Machines'' (1991) is a book by Manuel DeLanda, in which he traces the history of warfare and the history of technology.
It is influenced in part by Michel Foucault's '' Discipline and Punish'' (1978) and also rei ...
''. 1991. Swerve. New York.
*
Needham, Joseph
Noel Joseph Terence Montgomery Needham (; 9 December 1900 – 24 March 1995) was a British biochemist, historian of science and sinologist known for his scientific research and writing on the history of Chinese science and technology, init ...
(1986). ''
Science and Civilization in China
''Science and Civilisation in China'' (1954–present) is an ongoing series of books about the history of science and technology in China published by Cambridge University Press. It was initiated and edited by British historian Joseph Needham ( ...
: Volume 2''. Taipei: Caves Books Ltd.
* Cheney, Margaret
989:123(1981). ''Tesla, Man Out of Time''. Dorset Press. New York.
* Čapek, Karel (1920).
R.U.R.', Aventinum, Prague.
* TechCast Article Series, Jason Rupinski and Richard Mix
"Public Attitudes to Androids: Robot Gender, Tasks, & Pricing"
References
External links
*
Journal of Field Robotics
{{Authority control
Czech words and phrases
Science in popular culture
1920s neologisms

 A robot is a
A robot is a  The 11th century Lokapannatti tells of how the Buddha's relics were protected by mechanical robots (bhuta vahana yanta), from the kingdom of Roma visaya (Rome); until they were disarmed by King Ashoka.
In ancient China, the 3rd-century text of the ''Lie Zi'' describes an account of humanoid automata, involving a much earlier encounter between Chinese emperor
The 11th century Lokapannatti tells of how the Buddha's relics were protected by mechanical robots (bhuta vahana yanta), from the kingdom of Roma visaya (Rome); until they were disarmed by King Ashoka.
In ancient China, the 3rd-century text of the ''Lie Zi'' describes an account of humanoid automata, involving a much earlier encounter between Chinese emperor  In Renaissance Italy, Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519) sketched plans for a humanoid robot around 1495. Da Vinci's notebooks, rediscovered in the 1950s, contained detailed drawings of a mechanical knight now known as Leonardo's robot, able to sit up, wave its arms and move its head and jaw. The design was probably based on anatomical research recorded in his '' Vitruvian Man''. It is not known whether he attempted to build it. According to '' Encyclopædia Britannica'', Leonardo da Vinci may have been influenced by the classic automata of al-Jazari.
In Japan, complex animal and human automata were built between the 17th to 19th centuries, with many described in the 18th century ''Karakuri zui'' (''Illustrated Machinery'', 1796). One such automaton was the
In Renaissance Italy, Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519) sketched plans for a humanoid robot around 1495. Da Vinci's notebooks, rediscovered in the 1950s, contained detailed drawings of a mechanical knight now known as Leonardo's robot, able to sit up, wave its arms and move its head and jaw. The design was probably based on anatomical research recorded in his '' Vitruvian Man''. It is not known whether he attempted to build it. According to '' Encyclopædia Britannica'', Leonardo da Vinci may have been influenced by the classic automata of al-Jazari.
In Japan, complex animal and human automata were built between the 17th to 19th centuries, with many described in the 18th century ''Karakuri zui'' (''Illustrated Machinery'', 1796). One such automaton was the  Remotely operated vehicles were demonstrated in the late 19th century in the form of several types of remotely controlled torpedoes. The early 1870s saw remotely controlled torpedoes by
Remotely operated vehicles were demonstrated in the late 19th century in the form of several types of remotely controlled torpedoes. The early 1870s saw remotely controlled torpedoes by  In 1928, one of the first humanoid robots, Eric, was exhibited at the annual exhibition of the Model Engineers Society in London, where it delivered a speech. Invented by W. H. Richards, the robot's frame consisted of an aluminium body of armour with eleven electromagnets and one motor powered by a twelve-volt power source. The robot could move its hands and head and could be controlled through remote control or voice control. Both Eric and his "brother" George toured the world.
Westinghouse Electric Corporation built Televox in 1926; it was a cardboard cutout connected to various devices which users could turn on and off. In 1939, the humanoid robot known as Elektro was debuted at the
In 1928, one of the first humanoid robots, Eric, was exhibited at the annual exhibition of the Model Engineers Society in London, where it delivered a speech. Invented by W. H. Richards, the robot's frame consisted of an aluminium body of armour with eleven electromagnets and one motor powered by a twelve-volt power source. The robot could move its hands and head and could be controlled through remote control or voice control. Both Eric and his "brother" George toured the world.
Westinghouse Electric Corporation built Televox in 1926; it was a cardboard cutout connected to various devices which users could turn on and off. In 1939, the humanoid robot known as Elektro was debuted at the  The first digitally operated and programmable robot was invented by George Devol in 1954 and was ultimately called the Unimate. This ultimately laid the foundations of the modern robotics industry. Devol sold the first Unimate to
The first digitally operated and programmable robot was invented by George Devol in 1954 and was ultimately called the Unimate. This ultimately laid the foundations of the modern robotics industry. Devol sold the first Unimate to  The word ''robot'' was introduced to the public by the Czech
The word ''robot'' was introduced to the public by the Czech 
 Industrial robots usually consist of a
Industrial robots usually consist of a  Roughly half of all the robots in the world are in Asia, 32% in Europe, and 16% in North America, 1% in Australasia and 1% in Africa. 40% of all the robots in the world are in Japan, making Japan the country with the highest number of robots.
Roughly half of all the robots in the world are in Asia, 32% in Europe, and 16% in North America, 1% in Australasia and 1% in Africa. 40% of all the robots in the world are in Japan, making Japan the country with the highest number of robots.
 As robots have become more advanced and sophisticated, experts and academics have increasingly explored the questions of what ethics might govern robots' behavior, and whether robots might be able to claim any kind of social, cultural, ethical or legal rights. One scientific team has said that it was possible that a robot brain would exist by 2019. Others predict robot intelligence breakthroughs by 2050. Recent advances have made robotic behavior more sophisticated. The social impact of intelligent robots is subject of a 2010 documentary film called '' Plug & Pray''.
Vernor Vinge has suggested that a moment may come when computers and robots are smarter than humans. He calls this " the Singularity". He suggests that it may be somewhat or possibly very dangerous for humans. This is discussed by a philosophy called
As robots have become more advanced and sophisticated, experts and academics have increasingly explored the questions of what ethics might govern robots' behavior, and whether robots might be able to claim any kind of social, cultural, ethical or legal rights. One scientific team has said that it was possible that a robot brain would exist by 2019. Others predict robot intelligence breakthroughs by 2050. Recent advances have made robotic behavior more sophisticated. The social impact of intelligent robots is subject of a 2010 documentary film called '' Plug & Pray''.
Vernor Vinge has suggested that a moment may come when computers and robots are smarter than humans. He calls this " the Singularity". He suggests that it may be somewhat or possibly very dangerous for humans. This is discussed by a philosophy called  At present, there are two main types of robots, based on their use: general-purpose autonomous robots and dedicated robots.
Robots can be classified by their specificity of purpose. A robot might be designed to perform one particular task extremely well, or a range of tasks less well. All robots by their nature can be re-programmed to behave differently, but some are limited by their physical form. For example, a factory robot arm can perform jobs such as cutting, welding, gluing, or acting as a fairground ride, while a pick-and-place robot can only populate printed circuit boards.
At present, there are two main types of robots, based on their use: general-purpose autonomous robots and dedicated robots.
Robots can be classified by their specificity of purpose. A robot might be designed to perform one particular task extremely well, or a range of tasks less well. All robots by their nature can be re-programmed to behave differently, but some are limited by their physical form. For example, a factory robot arm can perform jobs such as cutting, welding, gluing, or acting as a fairground ride, while a pick-and-place robot can only populate printed circuit boards.
 Mobile robots, following markers or wires in the floor, or using vision or lasers, are used to transport goods around large facilities, such as warehouses, container ports, or hospitals.
Mobile robots, following markers or wires in the floor, or using vision or lasers, are used to transport goods around large facilities, such as warehouses, container ports, or hospitals.
 Teleoperated robots, or telerobots, are devices remotely operated from a distance by a human operator rather than following a predetermined sequence of movements, but which has semi-autonomous behaviour. They are used when a human cannot be present on site to perform a job because it is dangerous, far away, or inaccessible. The robot may be in another room or another country, or may be on a very different scale to the operator. For instance, a laparoscopic surgery robot allows the surgeon to work inside a human patient on a relatively small scale compared to open surgery, significantly shortening recovery time. They can also be used to avoid exposing workers to the hazardous and tight spaces such as in duct cleaning. When disabling a bomb, the operator sends a small robot to disable it. Several authors have been using a device called the Longpen to sign books remotely. Teleoperated robot aircraft, like the Predator Unmanned Aerial Vehicle, are increasingly being used by the military. These pilotless drones can search terrain and fire on targets. Hundreds of robots such as iRobot's Packbot and the Foster-Miller TALON are being used in Iraq and Afghanistan by the
Teleoperated robots, or telerobots, are devices remotely operated from a distance by a human operator rather than following a predetermined sequence of movements, but which has semi-autonomous behaviour. They are used when a human cannot be present on site to perform a job because it is dangerous, far away, or inaccessible. The robot may be in another room or another country, or may be on a very different scale to the operator. For instance, a laparoscopic surgery robot allows the surgeon to work inside a human patient on a relatively small scale compared to open surgery, significantly shortening recovery time. They can also be used to avoid exposing workers to the hazardous and tight spaces such as in duct cleaning. When disabling a bomb, the operator sends a small robot to disable it. Several authors have been using a device called the Longpen to sign books remotely. Teleoperated robot aircraft, like the Predator Unmanned Aerial Vehicle, are increasingly being used by the military. These pilotless drones can search terrain and fire on targets. Hundreds of robots such as iRobot's Packbot and the Foster-Miller TALON are being used in Iraq and Afghanistan by the  Domestic robots are simple robots dedicated to a single task work in home use. They are used in simple but often disliked jobs, such as
Domestic robots are simple robots dedicated to a single task work in home use. They are used in simple but often disliked jobs, such as  Robots used in
Robots used in 
 Fears and concerns about robots have been repeatedly expressed in a wide range of books and films. A common theme is the development of a master race of conscious and highly intelligent robots, motivated to take over or destroy the human race. '' Frankenstein'' (1818), often called the first science fiction novel, has become synonymous with the theme of a robot or android advancing beyond its creator.
Other works with similar themes include '' The Mechanical Man'', ''
Fears and concerns about robots have been repeatedly expressed in a wide range of books and films. A common theme is the development of a master race of conscious and highly intelligent robots, motivated to take over or destroy the human race. '' Frankenstein'' (1818), often called the first science fiction novel, has become synonymous with the theme of a robot or android advancing beyond its creator.
Other works with similar themes include '' The Mechanical Man'', ''