 In
In electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
, signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing '' signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, ...
, and video, ringing is oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or Periodic function, periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of Mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples o ...
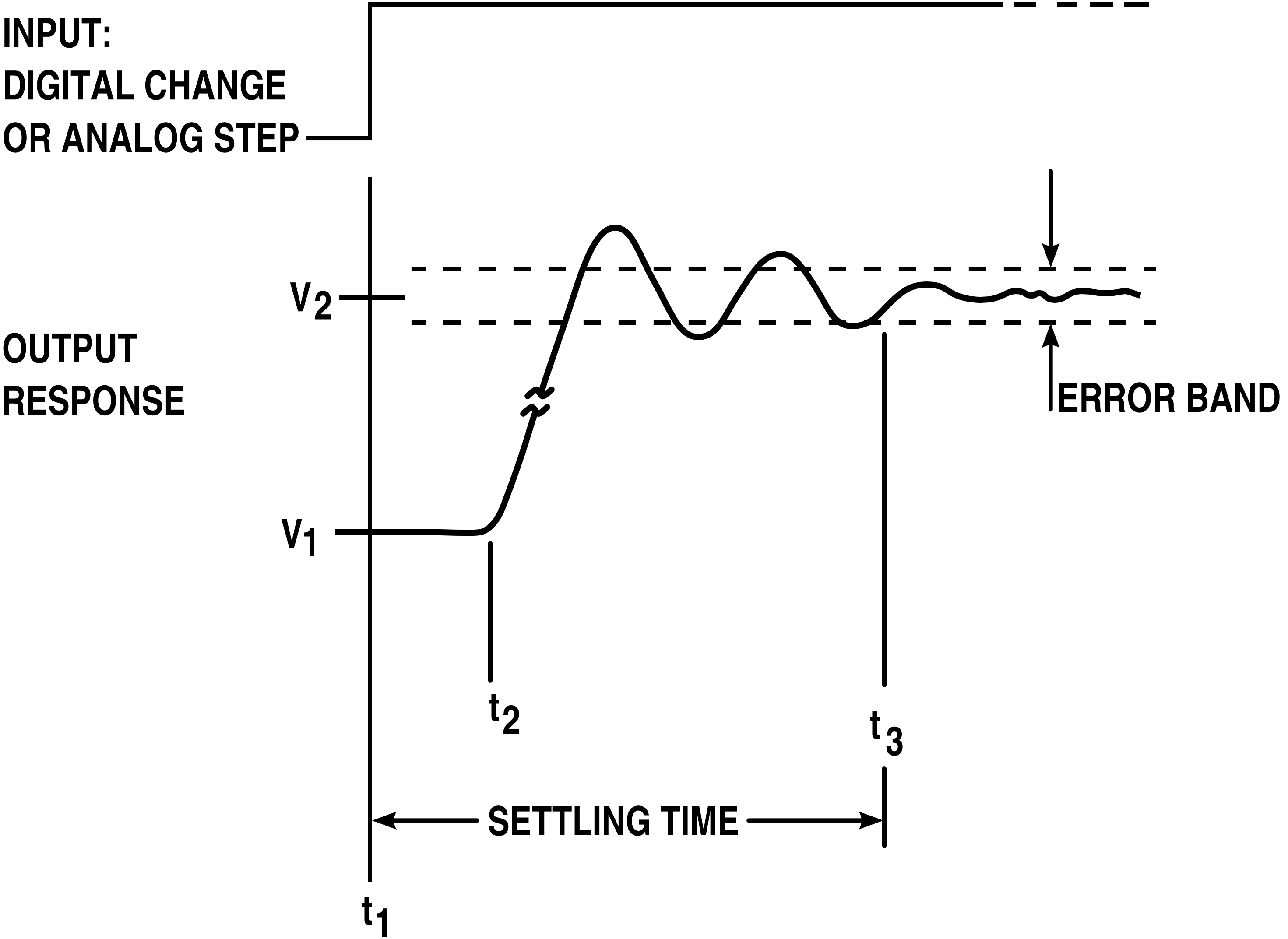
of a signal, particularly in the step response (the response to a sudden change in input). Often ringing is undesirable, but not always, as in the case of resonant inductive coupling
Resonant inductive coupling or magnetic phase synchronous coupling is a phenomenon with inductive coupling where the coupling becomes stronger when the "secondary" (load-bearing) side of the loosely coupled coil resonates. A resonant transfo ...
. It is also known as hunting. It is closely related to overshoot, often instigated as damping response following overshoot or undershoot, and thus the terms are at times conflated.
It is also known as ripple, particularly in electricity or in frequency domain
In physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time. Put simply, a time-domain graph shows how a ...
response.
Electricity
Inelectrical
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
circuits, ringing is an unwanted oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or Periodic function, periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of Mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples o ...
of a voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge t ...
or current. It happens when an electrical pulse causes the parasitic capacitances and inductances in the circuit (i.e. those that are not part of the design, but just by-products of the materials used to construct the circuit) to resonate at their characteristic frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from '' angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is ...
.Johnson, H. and Graham, M. ''High-Speed Digital Design: A Handbook of Black Magic''. 1993. pp. 88–90 Ringing artifacts are also present in square wave
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same duration at minimum and maximum. In an ideal square wave, the transitions b ...
s; see Gibbs phenomenon
In mathematics, the Gibbs phenomenon, discovered by Available on-line at:National Chiao Tung University: Open Course Ware: Hewitt & Hewitt, 1979. and rediscovered by , is the oscillatory behavior of the Fourier series of a piecewise continuou ...
.
Ringing is undesirable because it causes extra current to flow, thereby wasting energy and causing extra heating of the components; it can cause unwanted electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible ...
to be emitted; it can delay arrival at a desired final state (increase settling time); and it may cause unwanted triggering of bistable elements in digital circuit In theoretical computer science, a circuit is a model of computation in which input values proceed through a sequence of gates, each of which computes a function. Circuits of this kind provide a generalization of Boolean circuits and a mathematica ...
s. Ringy communications circuits may suffer falsing.
Ringing can be due to signal reflection
In telecommunications, signal reflection occurs when a signal is transmitted along a transmission medium, such as a copper cable or an optical fiber. Some of the signal power may be reflected back to its origin rather than being carried all t ...
, in which case it may be minimized by impedance matching
In electronics, impedance matching is the practice of designing or adjusting the input impedance or output impedance of an electrical device for a desired value. Often, the desired value is selected to maximize power transfer or minimize si ...
.
Video
In video circuits, electrical ringing causes closely spaced repeated ghosts of a vertical or diagonal edge where dark changes to light or vice versa, going from left to right. In aCRT
CRT or Crt may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Medicine and biology
* Calreticulin, a protein
*Capillary refill time, for blood to refill capillaries
*Cardiac resynchronization therapy and CRT defibrillator (CRT-D)
* Catheter-re ...
the electron beam upon changing from dark to light or vice versa instead of changing quickly to the desired intensity and staying there, overshoots and undershoots a few times. This bouncing could occur anywhere in the electronics or cabling and is often caused by or accentuated by a too high setting of the sharpness control.
Audio
Ringing can affect audio equipment in a number of ways. Audio amplifiers can produce ringing depending on their design, although the transients that can produce such ringing rarely occur in audio signals. Transducers (i.e.,microphones
A microphone, colloquially called a mic or mike (), is a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signal. Microphones are used in many applications such as telephones, hearing aids, public address systems for concert halls and publi ...
and loudspeakers
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or speaker driver) is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. A ''speaker system'', also often simply referred to as a "speaker" or "l ...
) can also ring. Mechanical ringing is more of a problem with loudspeakers as the moving masses are larger and less easily damped, but unless extreme they are difficult to audibly identify.
In digital audio, ringing can occur as a result of filters such as brickwall filter
In signal processing, a sinc filter is an idealized filter that removes all frequency components above a given cutoff frequency, without affecting lower frequencies, and has linear phase response. The filter's impulse response is a sinc functi ...
s. Here, the ringing occurs before the transient as well as after.
Signal processing
Insignal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing '' signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, ...
, "ringing" may refer to ringing artifacts
In signal processing, particularly digital image processing, ringing artifacts are artifacts that appear as spurious signals near sharp transitions in a signal. Visually, they appear as bands or "ghosts" near edges; audibly, they appear as "ec ...
: spurious signals near sharp transitions. These have a number of causes, and occur for instance in JPEG
JPEG ( ) is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images, particularly for those images produced by digital photography. The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and im ...
compression and as pre-echo in some audio compression.
See also
*Microphonics
Microphonics, microphony, or microphonism describes the phenomenon wherein certain components in electronic devices transform mechanical vibrations into an undesired electrical signal (noise). The term comes from analogy with a microphone, which ...
* Ripple (electrical)
* Impedance matching
In electronics, impedance matching is the practice of designing or adjusting the input impedance or output impedance of an electrical device for a desired value. Often, the desired value is selected to maximize power transfer or minimize si ...
References
External links
Microphony with older video cameras
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ringing (Signal) Transient response characteristics Filter theory