Rigvedic Tribe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
This is a list of ancient
 *
*
 After roughly 1500 BCE
After roughly 1500 BCE
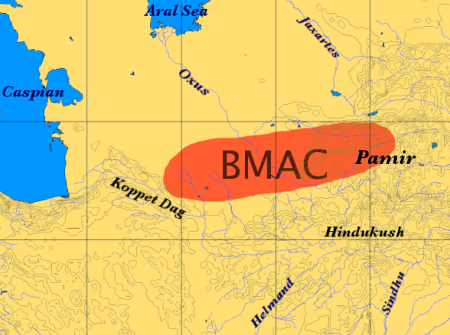
/ref> The word Druid (Gallic Celtic druides), however, is derived from Proto-Indo-European ''vid'' "to see, to know' It has also been alleged that the Rg Veda and the Puranas describe this tribe as migrating North,. However, there is nothing of this in the Rigveda and the Puranas merely mention that the Druhyu are "adjacent (āśrita) to the North". (Pratichya Āryāvarta – Western
 From roughly 1100 to 500 BCE
From roughly 1100 to 500 BCE
 ý§Æý§πý§æý§úý§®ý§™ý§¶ ‚Äì Mahajanapada
Shodasa Mahajanapadas (Sixteen Mahajanapadas)
The Mahajanapadas were sixteen great kingdoms and republics that emerged after the more powerful political entities (initially based on the territories of peoples and tribes) had conquered many others.
According to the '' Anguttara Nikaya'', ''
ý§Æý§πý§æý§úý§®ý§™ý§¶ ‚Äì Mahajanapada
Shodasa Mahajanapadas (Sixteen Mahajanapadas)
The Mahajanapadas were sixteen great kingdoms and republics that emerged after the more powerful political entities (initially based on the territories of peoples and tribes) had conquered many others.
According to the '' Anguttara Nikaya'', ''
Indo-Aryan peoples
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and int ...
and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions
Indian religions, sometimes also termed Dharmic religions or Indic religions, are the religions that originated in the Indian subcontinent. These religions, which include Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism, and Sikhism,Adams, C. J."Classification of ...
.
From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
– Indus Valley (roughly today's Punjab), Western India
Western India is a loosely defined region of India consisting of its western part. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Western Zonal Council Administrative division includes the states of Goa, Gujarat, and Maharashtra along with the Union ...
, Northern India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central ...
, Central India, and also in areas of the southern part like Sri Lanka and the Maldives
Maldives (, ; dv, ÞãÞ®ÞàÞ¨ÞÄÞ®ÞÉÞßÞáÞ∞ÞñÞ¨, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ÞãÞ®ÞàÞ¨ÞÄÞ®ÞÉÞßÞáÞ∞ÞñÞ≠ÞéÞ¨ ÞñÞ™ÞâÞ∞ÞÄÞ´ÞÉÞ®ÞáÞ∞ÞîÞß, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelag ...
through and after a complex process of migration, assimilation of other peoples and language shift.Mallory, J.P.; Douglas Q. Adams (1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. London: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers. .
Ancestors

 *
*Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction.
Knowledge of them comes chiefly from ...
(Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo- ...
speakers)
**Proto-Indo-Iranians
Indo-Iranian peoples, also known as Indo-Iranic peoples by scholars, and sometimes as Arya or Aryans from their self-designation, were a group of Indo-European peoples who brought the Indo-Iranian languages, a major branch of the Indo-European l ...
(common ancestors of the Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
, Nuristani and Indo-Aryan peoples) ( Proto-Indo-Iranian speakers)
***Proto-Indo-Aryans
The Indo-Aryan migrations were the migrations into the Indian subcontinent of Indo-Aryan peoples, an ethnolinguistic group that spoke Indo-Aryan languages, the predominant languages of today's North India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lank ...
(Proto-Indo-Aryan
Proto-Indo-Aryan (sometimes Proto-Indic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Indo-Aryan languages. It is intended to reconstruct the language of the Proto-Indo-Aryans. Being descended from Proto-Indo-Iranian (which in turn is descended f ...
speakers)
Vedic tribes
* Alina people (RV 7.18.7) * Andhras * Anu (RV 1.108.8, RV 8.10.5) * Āyu * Bhajeratha * Bhalanas * Bharatas- The Bharatas are a major Aryan clan mentioned in the Rigveda, especially in Mandala 3 attributed to the Bharata sage Vishvamitra. The entire Bharata clan is described as crossing over, with their chariots and wagons, at the confluence of the Vipash (Beas) and Shutudri (Satlej). The Bharatas are mentioned as the protagonists in the Battle of the Ten Kings in Mandala 7 (7.18 etc.), where they are on the winning side. They appear to have been successful in the early power-struggles between the various Aryan and non-Aryan clans so that they continue to dominate in post-Rigvedic texts, and later in the (Epic) tradition. "Bhārata" today is the official name of the Republic of India (see also Etymology of India). * Chedi *Dasa
''Dasa'' ( sa, ý§¶ý§æý§∏, DƒÅsa) is a Sanskrit word found in ancient Indian texts such as the ''Rigveda'' and ''Arthasastra''. It usually means "enemy" or "servant" but ''dasa'', or ''das'', also means a " servant of God", "devotee," " votary" or ...
* Dasyu
* D·πõbhƒ´ka
* Druhyus (Rigveda, RV 1.108.8, RV 8.10.5)
* Gandhara
* Gu·πÖgu
* Ikshvaku dynasty
* Krivi
* Kƒ´ka·π≠a
* Kuru
* Mahƒ´na
* Malankhara
* Maujavant
* Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
* Nahu·π£a
* Paktha
* Panis
* Pārāvata
* Parsu (Par≈õu)
* Puru (P≈´ru)
* Ru≈õama (RV Mandala 8)
* Sārasvata
* Srñjaya
* Tritsu(RV 7.18, 7.33, 7.83)
* Yadu: Of Indo-Aryan origin,Yadu is one of the five early Rigvedic tribes
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions.
From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern ...
('' panchajana'', ''panchakrishtya'' or ''panchamanusha'') mentioned in the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''s≈´ktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' ≈õruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
. The Yadus had a tribal union with the Turvasha tribe, and were frequently described together. The Yadus were a Aryan tribe. By the time of the arrival of the Puru and Bharata tribes, the Yadu-Turvashas were settled in Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: ŸæŸÜÿ¨ÿßÿ® ; ý®™ý©∞ý®úý®æý®¨ ; ; also romanised as ''PanjƒÅb'' or ''Panj-ƒÄb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
, with the Yadus possibly residing along the Yamuna River
The Yamuna ( Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Ba ...
.In Mandalas 4 and 5 of the Rigveda, the god Indra is stated to have saved the Yadu-Turvashas from drowning when they crossed rivers. In Mandala 6, the Yadu-Turvashas are stated to have been "brought from far away" by Indra. The Yadu-Turvashas are treated relatively positively in Mandalas 5, 6, and 8, and are stated to be the occasional allies and enemies of the Puru-Bharatas. In the Battle of the Ten Kings, the Yadus were defeated by Bharata chieftain Sudas.
Pancha Jana (Five tribes)
(ý§™ý§ûý•çý§ö ý§úý§®ý§æ ‚Äì '' P√°√±ca J√°nƒÅ·∏•'' / '' Pancha-janah'') The pancha Jana are five tribes inexplicitly listed together during the (ƒÄryƒÅvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
of this time, c. 1700–1500 BCE, roughly corresponds with the Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: ŸæŸÜÿ¨ÿßÿ® ; ý®™ý©∞ý®úý®æý®¨ ; ; also romanised as ''PanjƒÅb'' or ''Panj-ƒÄb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
and closer regions) (see the map of Early Vedic Period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betwe ...
)
* Anu (in the southwest part of early Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Druhyu
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions.
From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern p ...
(in the north part of early Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Puru (ancestors of the Paurava
The Pauravas were an ancient dynasty on the Indus (present-day India and Pakistan) to which King Porus may have belonged.
Porus and the Pauravas
The origins of the Pauravas are still disputed. The Pauravas may be related to the Puru tribe, due ...
) (in the centre and east parts of early Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
, including Sarasvati
Saraswati ( sa, ý§∏ý§∞ý§∏ý•çý§µý§§ý•Ä, ) is the Hindu goddess of knowledge, music, art, speech, wisdom, and learning. She is one of the Tridevi, along with the goddesses Lakshmi and Parvati.
The earliest known mention of Saraswati as a go ...
river region)
* Turvaśa (Turvasha) (in the centre and south parts of early Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
): The Turvashas ( sa, ý§§ý•Åý§∞ý•çý§µý§∂, ) were one of the five major peoples (''panchajana'', ''panchakrishtya'' or ''panchamanusha'') mentioned in the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''s≈´ktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' ≈õruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
. The Turvashas had a tribal union with the Yadu tribe, and were frequently described together. The Turvashas were a partly Indo-Aryan-acculturated Indus tribe. By the time of the arrival of the Puru and Bharata tribes, the Yadu-Turvashas were settled in Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: ŸæŸÜÿ¨ÿßÿ® ; ý®™ý©∞ý®úý®æý®¨ ; ; also romanised as ''PanjƒÅb'' or ''Panj-ƒÄb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
. By the time of the Shatapatha Brahmana
The Shatapatha Brahmana ( sa, ý§∂ý§§ý§™ý§•ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§æý§πý•çý§Æý§£ý§Æý•ç , ≈öatapatha BrƒÅhma·πáam, meaning 'BrƒÅhma·πáa of one hundred paths', abbreviated to 'SB') is a commentary on the ≈öukla (white) Yajurveda. It is attributed to the Vedic ...
(7th-6th centuries BCE), the Turvashas are linked to the Panchalas. Alfred Ludvig first conjectured that Turvƒ´ti and Vayya could have been connected with the Turvasha tribe, a notion that is still considered only speculation according to Witzel. In Mandalas 4 and 5 of the Rigveda, the god Indra is stated to have saved the Yadu-Turvashas from drowning when they crossed rivers. In Mandala 6, the Yadu-Turvashas are stated to have been "brought from far away" by Indra. The Yadu-Turvashas are treated relatively positively in Mandalas 5, 6, and 8, and are stated to be the occasional allies and enemies of the Puru-Bharatas.
* Yadu (in the southeast and south parts of early Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
Janapadas
Early Janapadas (peoples / tribes) (c. 1700–1100 BCE)
 After roughly 1500 BCE
After roughly 1500 BCE Indo-Aryan peoples
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and int ...
and tribes were swiftly expanding through ancient northern India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, therefore the number of peoples, tribes and clans was increasing (as well as the number of Indo-Aryan language speakers) and Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
was becoming a very large area (see the map on the right side).
* Aja – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
– Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Ambaśṭha – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Aṅga – Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta (Madhya-desha and Prachya Āryāvarta – Central and Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
in Vamana).
*Anu – is a Vedic Sanskrit
Vedic Sanskrit was an ancient language of the Indo-Aryan subgroup of the Indo-European language family. It is attested in the Vedas and related literature compiled over the period of the mid- 2nd to mid-1st millennium BCE. It was orally preser ...
term for one of the 5 major tribes in the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''s≈´ktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' ≈õruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
, RV 1.108.8, RV 8.10.5 (both times listed together with the Druhyu
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions.
From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern p ...
) and, much later also in the Mahabharata
The ''MahƒÅbhƒÅrata'' ( ; sa, ý§Æý§πý§æý§≠ý§æý§∞ý§§ý§Æý•ç, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, RƒÅmƒÅya·πáa''. It narrates the s ...
.Talageri, S. G. (2005). The Rigveda as a source of Indo-European history. The Indo-Aryan Controversy: Evidence and Inference in Indian History, 332. In the late Vedic period, one of the Anu kings, King Anga, is mentioned as a "chakravartin
A ''chakravarti'' ( sa, ý§öý§ïý•çý§∞ý§µý§∞ý•çý§§ý§øý§®ý•ç, ''cakravartin''; pi, cakkavatti; zh, ËΩâ˺™Áéã, ''Zhu«énl√∫nw√°ng'', "Wheel-Turning King"; , ''Zhu«énl√∫n Sh√®ngw√°ng'', "Wheel-Turning Sacred King"; ja, ˪¢Ëº™Áéã, ''Tenrin'≈ç'' ...
" ( AB 8.22). ''Ānava'', the vrddhi derivation of ''Anu'', is the name of a ruler in the Rigvedic account of the Battle of the Ten Kings (7.18.13) and at 8.4.1 with the Turvaśa (tribe). The meaning ánu "living, human" (Naighantu) cannot be substantiated for the Rigveda and may have been derived from the tribal name. (Pratichya Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Āyu –
* Bhajeratha
* Bhalana – The Bhalanas were one of the tribes that fought against Sudas in the Dasarajna
The Battle of the Ten Kings ( sa, ý§¶ý§æý§∂ý§∞ý§æý§úý•çý§û ý§Øý•Åý§¶ý•çý§ß, translit=DƒÅ≈õarƒÅj√±√° yuddh√°) is a battle, first alluded to in the 7th Mandala of the Rigveda (RV), between a Bharata king and a confederation of tribes. It resulte ...
battle. Some scholars have argued that the Bhalanas lived in Eastern Afghanistan Kabulistan
Kabulistan (Pashto: کابلستان) is a historical regional name referring to the territory that is centered on present-day Kabul Province of Afghanistan.
In many Greek and Latin sources, particularly editions of Ptolemy's ''Geography'', the ...
, and that the Bolan Pass
Bolān Pass ( ur, ) is a valley and a natural gateway, through the Toba Kakar range in Balochistan province of Pakistan, south of the Afghanistan border. The pass is an stretch of the Bolan river valley from Rindli in the south to Darwāza ...
derives its name from the Bhalanas. (Pratichya Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Bharadvāja – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Bhrigus
Bhrigu ( sa, ý§≠ý•Éý§óý•Å, ) was a rishi in Hinduism. He was one of the seven great sages, the Saptarshis, one of the many Prajapatis (the facilitators of Creation) created by Brahma. The first compiler of predictive astrology, and also the a ...
* Bheda – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Bodha – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Druhyu – The Druhyu were a people of Vedic India. They are mentioned in the Rigveda, usually together with the Anu tribe. Some early scholars have placed them in the northwestern region. The later texts, the Epic and the Puranas, locate them in the "north", that is, in Gandhara, Aratta and Setu. (Vishnu Purana IV.17) The Druhyus were driven out of the land of the seven rivers, and their next king, Gandhara, settled in a north-western region which became known as Gandhāra
Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, more precisely in present-day north-west Pakistan and parts of south-east Afghanistan. The region centered around the Peshawar Val ...
. The sons of the later Druhyu king Pracetas too settle in the "northern" (udīcya) region (Bhagavata 9.23.15–16; Visnu 4.17.5; Vayu 99.11–12; Brahmanda 3.74.11–12 and Matsya 48.9.). Recently, some writersTalageri 2000 have ahistorically asserted that the Druhyu are the ancestors of the Iranian, Greek or European peoples, or of the Celtic Druid class.Sanskrit in English/ref> The word Druid (Gallic Celtic druides), however, is derived from Proto-Indo-European ''vid'' "to see, to know' It has also been alleged that the Rg Veda and the Puranas describe this tribe as migrating North,. However, there is nothing of this in the Rigveda and the Puranas merely mention that the Druhyu are "adjacent (āśrita) to the North". (Pratichya Āryāvarta – Western
Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Gandharis (Pratichya Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
#
# (Pratichya Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Kārūṣa (Karusha) – later Cedi (Chedi) (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Keśin (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Kīkaṭa (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Kosala (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Krivi (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Kunti (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Madra
Madra (Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of north-western South Asia whose existence is attested since the Vedic period. The members of the Madra tribe were called the Madrakas.
Location
The Madras were divided into -Madra ("northe ...
(Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
**Uttara Madra (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Magadha
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was ruled ...
(Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Mahāvṛṣa (Mahavrisha) (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Mahƒ´na
*MalankharaGriffith, R. T. (2009). The Rig-Veda. The Rig Veda.
*Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
(Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Mūjavana / Maujavant (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Nahu·π£a
* Pāñcala ( Panchala) (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Pārāvata (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* P·πõthu (Prithu
Prithu (Sanskrit: ý§™ý•Éý§•ý•Å, ''P·πõthu'', lit. "large, great, important, abundant") is a sovereign ( chakravarti), featured in the Puranas. According to Hinduism, he is an avatar (incarnation) of the preserver god‚ÄîVishnu. He is also calle ...
) (Pratichya Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Pūru (Puru) (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
** Bharatas – The Bharatas are an Arya
Aryan or Arya (, Indo-Iranian *''arya'') is a term originally used as an ethnocultural self-designation by Indo-Iranians in ancient times, in contrast to the nearby outsiders known as 'non-Aryan' (*''an-arya''). In Ancient India, the term ' ...
n tribe mentioned in the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''s≈´ktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' ≈õruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
, especially in Mandala 3
The third Mandala of the Rigveda has 62 hymns, mainly to Agni and Indra. It is one of the "family books" (mandalas 2-7), the oldest core of the Rigveda, which were composed in early Vedic period (1500 - 1000 BCE). Most hymns in this book are attrib ...
attributed to the Bharata sage Vishvamitra and in and Mandala 7
The seventh Mandala of the Rigveda ("book 7", "RV 7") has 104 hymns. In the Rigveda Anukramani, all hymns in this book are attributed to ''Vashista''. Hymn 32 is additionally credited to Sakti Vashista, and hymns 101-102 (to Parjanya) are addi ...
.Frawley, D. (2001). The Rig Veda and the History of India: Rig Veda Bharata Itihasa. Aditya Prakashan. ''Bharat√°'' is also used as a name of Agni
Agni (English: , sa, ý§Öý§óý•çý§®ý§ø, translit=Agni) is a Sanskrit word meaning fire and connotes the Vedic fire deity of Hinduism. He is also the guardian deity of the southeast direction and is typically found in southeast corners of Hindu ...
(literally, "to be maintained", viz. the fire having to be kept alive by the care of men), and as a name of Rudra
Rudra (; sa, ý§∞ý•Åý§¶ý•çý§∞) is a Rigvedic deity associated with Shiva, the wind or storms, Vayu, medicine, and the hunt. One translation of the name is 'the roarer'. In the Rigveda, Rudra is praised as the 'mightiest of the mighty'. Ru ...
in RV 2.36.8. In one of the " river hymns" RV 3.33, the entire Bharata tribe is described as crossing over, with their chariots and wagons, at the confluence of the Vipash (Beas) and Shutudri (Satlej). Hymns by Vasistha in Mandala 7
The seventh Mandala of the Rigveda ("book 7", "RV 7") has 104 hymns. In the Rigveda Anukramani, all hymns in this book are attributed to ''Vashista''. Hymn 32 is additionally credited to Sakti Vashista, and hymns 101-102 (to Parjanya) are addi ...
(7.18 etc.) mention the Bharatas as the protagonists in the Battle of the Ten Kings, where they are on the winning side. They appear to have been successful in the early power-struggles between the various Arya
Aryan or Arya (, Indo-Iranian *''arya'') is a term originally used as an ethnocultural self-designation by Indo-Iranians in ancient times, in contrast to the nearby outsiders known as 'non-Aryan' (*''an-arya''). In Ancient India, the term ' ...
n and non-Aryan tribes so that they continue to dominate in post-Rigvedic texts, and later in the ( Epic) tradition, the Mahābhārata, the eponymous ancestor becomes Emperor Bharata
Bharata ( sa, ý§≠ý§∞ý§§, Bharata) is a legendary king featured in Hindu literature. He is a member of the Chandravamsha dynasty, and becomes the Chakravarti (universal monarch). He is regarded to be the ancestor of the Pandavas, the Kauravas, ...
, conqueror of 'all of India', and his tribe and kingdom is called Bhārata. "Bhārata" today is the official name of the Republic of India (see also Etymology of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
). (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*** Kuru – Ancestors of the Kaurava
''Kaurava'' is a Sanskrit term which refers to descendants of Kuru, a legendary king of India who is the ancestor of many of the characters of the epic ''Mahabharata''. Usually, the term is used for the 100 sons of King Dhritarashtra and his wi ...
(Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
**** Uttara Kuru (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*** Pandu – Ancestors of the Pandava
The Pandavas (Sanskrit: ý§™ý§æý§£ý•çý§°ý§µ, IAST: PƒÅ·πá·∏çava) refers to the five legendary brothers‚Äî Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula and Sahadeva‚Äîwho are the central characters of the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. They are acknowledge ...
(Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
** T·πõtsu (Tritsu) The Tritsus are a sub-group of the Puru who are distinct from the Bharatas mentioned in Mandala 7
The seventh Mandala of the Rigveda ("book 7", "RV 7") has 104 hymns. In the Rigveda Anukramani, all hymns in this book are attributed to ''Vashista''. Hymn 32 is additionally credited to Sakti Vashista, and hymns 101-102 (to Parjanya) are addi ...
of the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''s≈´ktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' ≈õruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
(in hymns 18, 33 and 83). Under king Sudas they defeated the confederation of ten kings led by the Bharatas at the Battle of the Ten Kings. (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
– Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Ruśama (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Śālva (Shalva) (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Sārasvata – people that dwelt the banks of the Sarasvati
Saraswati ( sa, ý§∏ý§∞ý§∏ý•çý§µý§§ý•Ä, ) is the Hindu goddess of knowledge, music, art, speech, wisdom, and learning. She is one of the Tridevi, along with the goddesses Lakshmi and Parvati.
The earliest known mention of Saraswati as a go ...
river (Pratichya Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Satvanta (Dakshina Āryāvarta – Southern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Śigru (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*≈öiva (Shiva
Shiva (; sa, ý§∂ý§øý§µ, lit=The Auspicious One, ≈öiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; …ê…¶aÀêdÙeÀê ã…ê, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
, not to be confused with the God ≈öiva
Shiva (; sa, ý§∂ý§øý§µ, lit=The Auspicious One, ≈öiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; …ê…¶aÀêdÙeÀê ã…ê, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
or Shiva
Shiva (; sa, ý§∂ý§øý§µ, lit=The Auspicious One, ≈öiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; …ê…¶aÀêdÙeÀê ã…ê, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
) (Pratichya Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Srñjaya ( Srinjaya) (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Śvikna (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Turva≈õa (Turvasa)
*Uśīnara (Ushinara) (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Vaikarṇa (Vaikarna) (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Vaṅga (Vanga) (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Varaśikha (Varashikha) (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Vaśa (Vasha) (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Vidarbha (Vidarbha
Vidarbha (Pronunciation: ãidÙ…ô…æb ±…ô is a geographical region in the east of the Indian state of Maharashtra and a proposed state of central India, comprising the state's Amravati and Nagpur divisions. Amravati Division's former name is Ber ...
, Dakshina Āryāvarta – Southern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Videha
Videha ( Prākrit: ; Pāli: ; Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of north-eastern South Asia whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The population of Videha, the Vaidehas, were initially organised into a monarchy but later ...
(Mithila Mithila may refer to:
Places
* Mithilā, a synonym for the ancient Videha state
** Mithilā (ancient city), the ancient capital city of Videha
* Mithila (region), a cultural region (historical and contemporary), now divided between India and Nepal
...
, Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Viśaṇin (Vishanin) (Pratichya Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Vṛcivanta (Vrichivanta) (Pratichya Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Yadu (Dakshina Āryāvarta – Southern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Yakṣu (Yakshu) (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
Late Janapadas (peoples / tribes) (c. 1100–500 BCE)
 From roughly 1100 to 500 BCE
From roughly 1100 to 500 BCE Indo-Aryan peoples
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and int ...
and tribes expanded even further throughout ancient northern India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
(see the map 6).
* Abhƒ´·π£aha ( Abhishaha) / Apanga (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
'') / Aupadha ('' Markandeya'') / Alasa (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Āhuka / Kuhaka ('' Markandeya'') / Kuhuka (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Alimadra / Anibhadra ('' Markandeya'') / Alibhadra (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Aṅga – (Madhya-desha and Prachya Āryāvarta – Central and Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
in ''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'')
* Āntaranarmada / Uttaranarmada ('' Markandeya''), Sunarmada (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Antargiri – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* An≈´pa / Ar≈´pa (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Annaja (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
'') – (Vindhya-prashtha Āryāvarta – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Aparānta / Purandhra (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Aparƒ´ta (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Arthapa / Atharva ('' Markandeya'') – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Aśvakūṭa – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Ātreya / Atri (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
'', ''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Audumbara / Audambara / Audumvara – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Auṇḍra – (Vindhya-prashtha Āryāvarta – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Bahirgiri – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Bhadra
''Bhadra''Feminine: sa, ý§≠ý§¶ý•çý§∞ý§æ, BhadrƒÅ is a Sanskrit word meaning 'good', 'fortune' or 'auspicious'. It is also the name of many men, women and objects in Hindu mythology.
Male Figures King of Chedi
Bhadra was a king of Chedi Kingdom ...
– (Prachya and Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Eastern and Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Bhadrakāra – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Bharadvāja – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Bhārgava – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Bharukaccha
Bharuch (), formerly known as Broach, is a city at the mouth of the river Narmada in Gujarat in western India. Bharuch is the administrative headquarters of Bharuch District.
The city of Bharuch and surroundings have been settled since time ...
/ Bhanukaccha (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Bhīrukahcha ('' Markandeya''), Dārukachchha (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''), Sahakaccha (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Bhogavardhana / Bhokardan (Dakshinapatha Āryāvarta – Southern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Bhūṣika ( Bhushika) – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Bodha / Bāhya (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
'') – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Brahmottara / Suhmottara (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Samantara (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Carmakhaṇḍika ( Charmakhandika) / Attakhaṇḍika (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Sakhe·π≠aka (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Darada – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern ''Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
'')
* Darva – (Himalayan and Northern in ''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
'' and '' Markandeya'', Parvata-shrayin and Udichya Āryāvarta – Himalayan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Da≈õeraka ( Dasheraka) / Karseruka (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Kuśeruka ('' Markandeya'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Daśamālika ( Dashamalika) / Daśanāmaka (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Daśamānika (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Da·πÖ≈õana (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Daśarṇa ( Dasharna) (Vindhya-prashtha Āryāvarta – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Druhyu
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions.
From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern p ...
/ Hrada (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Bhadra (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Durga
Durga ( sa, ý§¶ý•Åý§∞ý•çý§óý§æ, ) is a major Hindu goddess, worshipped as a principal aspect of the mother goddess Mahadevi. She is associated with protection, strength, motherhood, destruction, and wars.
Durga's legend centres around c ...
/ Durgala (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Ganaka
Kaniyar is a caste from the Indian state of Kerala. There are regional variations in the name used to define them. They are listed under the Other Backward Communities (OBC) by the Kerala Government.
Traditions of origin
Kathleen Gough has re ...
– (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Gāndhāra
Gandhar is the 3rd svara from the seven svaras of Hindustani music and Carnatic music. Gandhar is the long form of the syllable ý§ó. For simplicity in pronouncing while singing the syllable, Gandhar is pronounced as Ga (notation - G). It is als ...
/ Gandharians ('' Vaēkərəta'' in Avestan) – the people who lived in Gāndhāra
Gandhar is the 3rd svara from the seven svaras of Hindustani music and Carnatic music. Gandhar is the long form of the syllable ý§ó. For simplicity in pronouncing while singing the syllable, Gandhar is pronounced as Ga (notation - G). It is als ...
and spoke Gandhari (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Gonarda / Govinda (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Gomanta ('' Markandeya''), Mananda (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Haṃsamārga / Sarvaga (Himalayan) in ''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''; Haṃsamārga (Northern and Himalayan) in ''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
'' and '' Markandeya''; Karnamārga (Northern) and Haṃsamārga (Himalayan) in ''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''; Haṃsamārga (Himalayan) Haṃsabhaṅga (Northern) in ''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'' – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
; Parvata-shrayin Āryāvarta – Himalayan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Hāramuṣika ( Haramushika) / Hāramūrtika (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Hārapūrika (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Sāmuṣaka (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Huhuka / Samudgaka (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Sah≈´daka (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Sak·πõtraka ('' Markandeya''), ≈öahuh≈´ka (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''), Sahuh≈´ka (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Parvata-shrayin Āryāvarta – Himalayan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Ijika (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Jaguda / Jāṇgala (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Juhuḍa (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Jāguḍa ('' Markandeya'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Jāṇgala – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Jñeyamarthaka / Jñeyamallaka ('' Markandeya''), Aṅgiyamarṣaka (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''), Gopapārthiva (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kachchhika / Kāchchhīka (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Kacchƒ´ya (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Kāśmīra ('' Markandeya''), Kacchipa (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kālatoyaka – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kaliṅga (central) / Arkalinga ('' Markandeya'') – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kaliṅga (southern) – (Dakshinapatha Āryāvarta – Southern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kalitaka / Kālītaka (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Anīkaṭa ('' Markandeya''), Tālīkaṭa (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''), Kuntala (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kalivana / Kolavana (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Kālivala ('' Markandeya''), Vāridhana (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''), Kalivana (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kantakara / Kanṭakāra (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Raddhaka·π≠aka (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Bahubhadra ('' Markandeya''), Kādhara (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kāraskara / Paraṣkara (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Kaṭhākṣara ('' Markandeya''), Karandhara (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kārūṣa ( Karusha), later Cedi ( Chedi) – Southern and Vindhyan Āryāvarta (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
'') (Dakshinapatha Āryāvarta – Southern ''Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
''; Vindhya-prashtha Āryāvarta – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kāśi ( Kashi) (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kasmira (Kashmira
Kasmira was a kingdom identified as the Kashmir Valley along the Jhelum River of modern Jammu and Kashmir. During the epic ages this was one among the territories of the Naga race. The Kasmiras were allies of the Kuru king Duryodhana.
Referen ...
/ Kāmīra) – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kathas – in the River Chenab
The Chenab River () is a major river that flows in India and Pakistan, and is one of the 5 major rivers of the Punjab region. It is formed by the union of two headwaters, Chandra and Bhaga, which rise in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul regi ...
Valley (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kauśika – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Kekeya
Kekeya Kingdom (also known as Kekaya, Kaikaya, Kaikeya etc.) was a kingdom mentioned in the ancient Indian epic ''Mahabharata'' among the western kingdoms of then India. The epic ''Ramayana'' mentions one of the wives of Dasharatha, the king of Ko ...
/ Kaikeyya (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Kaikeya ('' Markandeya''), Kaikeya (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Khaśa / Khasha – Khaśa (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''), ≈öaka (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Parvata-shrayin Āryāvarta – Himalayan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kisaṇṇa – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Koṅkaṇa – (Dakshinapatha Āryāvarta – Southern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kośala (Central) – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kośala (Vindhyan) – (Vindhya-prashtha Āryāvarta – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kukkuṭa – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kul≈´ta / Ul≈´ta (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kulya – only Central in '' Markandeya''; only Southern in ''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'' and ''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'' – (Dakshinapatha Āryāvarta – Southern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
; Madhya-desha – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Kuninda
The Kingdom of Kuninda (or Kulinda in ancient literature) was an ancient central Himalayan kingdom documented from around the 2nd century BCE to the 3rd century, located in the southern areas of modern Himachal Pradesh and far western areas of U ...
/ Pulinda (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Kali·πÖga ('' Markandeya''), Kalinda (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kuśalya ( Kushalya) – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kuśūdra ( Kushudra) – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Kuthaprāvaraṇa / Kuśaprāvaraṇa (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Kuntaprāvaraṇa ('' Markandeya''), Apaprāvaraṇa (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Parvata-shrayin Āryāvarta – Himalayan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Lalhitta – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Lampāka / Lamaka (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Madguraka / Mudgara ('' Markandeya''), Mudagaraka (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Madras – in the River Chenab
The Chenab River () is a major river that flows in India and Pakistan, and is one of the 5 major rivers of the Punjab region. It is formed by the union of two headwaters, Chandra and Bhaga, which rise in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul regi ...
Valley (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Mādreya – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Magadha
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was ruled ...
/ Central and Eastern in ''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
'' and ''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'' – Magadha
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was ruled ...
(Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Maharāṣṭra ( Maharashtra) / Navarāṣṭra (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
'') – Maharashtra (Dakshinapatha Āryāvarta – Southern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Māheya – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Mālada / Mālava (Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
), Manada ('' Markandeya''), Mansāda (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Malaka – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Malavartika – Mallavarṇaka (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Mālavartin (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Mānavartika ('' Markandeya''), Baladantika (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Mālava / Western Malla (known as Malloí by the ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
and Malli by ancient Romans
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 ...
) – they were a people from southern Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: ŸæŸÜÿ¨ÿßÿ® ; ý®™ý©∞ý®úý®æý®¨ ; ; also romanised as ''PanjƒÅb'' or ''Panj-ƒÄb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
, including today's Multan
Multan (; ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, on the bank of the Chenab River. Multan is Pakistan's seventh largest city as per the 2017 census, and the major cultural, religious and economic centre of southern Punjab.
Multan is one of the old ...
city ('' Mallorum Metropolis'') and region, south of the confluence of the Jhelum, Hydaspes
The Jhelum River (/d í ∞eÀêl…ôm/) is a river in the northern Indian subcontinent. It originates at Verinag and flows through the Indian administered territory of Jammu and Kashmir, to the Pakistani-administered territory of Kashmir, and then ...
for the Greeks, and Ravi, Hydraotes for the Greeks, rivers (see map 8), they are mentioned by ancient Greek historiansIan Worthington 2014, p. 219.Peter Green 2013, p. 418. in the telling of Alexander III of Macedon
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to t ...
's or Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
( Iskandar) Mallian Campaign; Malada (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
''), Ekalavya (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
) (not the be confused with the Eastern Malla)
*Malla
Malla may refer to: Places
;Bolivia
*Malla, Bolivia, a locality
* Malla Jawira, a river
* Malla Jaqhi, a mountain
* Malla Municipality
* Malla Qullu, a mountain
;India
* Mallapuram, Tamil Nadu
*Malla (tribe), an ancient republic, one of the s ...
/ Eastern Malla / Śālva (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Māla (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Māia (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
) (not to be confused with the Mālava or Malavas
The Malavas (Brahmi script: ëÄ´ëÅÜëÄ´ëÄ∏ëÄ≠ëÄØ ''MmƒÅlava'') or Malwas were an ancient Indian tribe. Modern scholars identify them with the Mallian people (Malloi) who were settled in the Punjab region at the time of Alexander's invasion ...
of Western Ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
– Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Maṇḍala / Mālava (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Mālava ('' Markandeya'') – (Parvata-shrayin Āryāvarta – Himalayan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Māṇḍavya – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Māṣa (Masha
In Russian, Masha () is a diminutive of Maria. It has been used as a nickname or as a pet name for women named Maria or Marie. An alternative spelling in the Latin alphabet is "Macha". In Serbo-Croatian and Slovene, "Maša" is a diminutive of "Mar ...
) – (Vindhya-prashtha Āryāvarta – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Mātaṅga – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
/ Yatstha (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Mekala / Rokala (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Kevala ('' Markandeya'') – (Vindhya-prashtha Āryāvarta – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Mūka – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Nāsikya / Vāsikya (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Nāsikānta (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''), Nāsika (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Nirāhāra / Nigarhara (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Nihāra ('' Markandeya'') – (Parvata-shrayin Āryāvarta – Himalayan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Pāṇavīya – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Pāñcala ( Panchala) – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Pārada / Parita (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Pāravata (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Pa·π≠accara ( Patachchara) / ≈öatapathe≈õvara (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
'') – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Pūru (Puru) – Ancestors of the Paurava
The Pauravas were an ancient dynasty on the Indus (present-day India and Pakistan) to which King Porus may have belonged.
Porus and the Pauravas
The origins of the Pauravas are still disputed. The Pauravas may be related to the Puru tribe, due ...
(Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
**Paurava
The Pauravas were an ancient dynasty on the Indus (present-day India and Pakistan) to which King Porus may have belonged.
Porus and the Pauravas
The origins of the Pauravas are still disputed. The Pauravas may be related to the Puru tribe, due ...
– Descendants of the Puru (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*** Kuru (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – Ancestors of the Kaurava
''Kaurava'' is a Sanskrit term which refers to descendants of Kuru, a legendary king of India who is the ancestor of many of the characters of the epic ''Mahabharata''. Usually, the term is used for the 100 sons of King Dhritarashtra and his wi ...
(Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
****Kaurava
''Kaurava'' is a Sanskrit term which refers to descendants of Kuru, a legendary king of India who is the ancestor of many of the characters of the epic ''Mahabharata''. Usually, the term is used for the 100 sons of King Dhritarashtra and his wi ...
(''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – Descendants of the Kuru (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*** Pandu – Ancestors of the Pandava
The Pandavas (Sanskrit: ý§™ý§æý§£ý•çý§°ý§µ, IAST: PƒÅ·πá·∏çava) refers to the five legendary brothers‚Äî Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula and Sahadeva‚Äîwho are the central characters of the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. They are acknowledge ...
(Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
****Pandava
The Pandavas (Sanskrit: ý§™ý§æý§£ý•çý§°ý§µ, IAST: PƒÅ·πá·∏çava) refers to the five legendary brothers‚Äî Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula and Sahadeva‚Äîwho are the central characters of the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. They are acknowledge ...
– Descendants of Pandu (Udichya Āryāvarta and Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
and Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*****Arjunayana
Arjunayana, Arjunavana, Arjunavayana or Arjunayanaka was an ancient republican people located in Punjab or north-eastern Rajasthan. They emerged as a political power during the Shunga period (). In the Allahabad Pillar Inscription of Samudragupta ...
– (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
****** Tomara / Tāmasa ('' Markandeya'' and ''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Pluṣṭa ( Plushta) – (Parvata-shrayin Āryāvarta – Himalayan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Prāgjyotiṣa (Pragjyotisha
Kamarupa (; also called Pragjyotisha or Pragjyotisha-Kamarupa), an early state during the Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, was (along with Davaka) the first historical kingdom of Assam.
Though Kamarupa prevailed from 350 to ...
) – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Prava·πÖga / Plava·πÖga (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
'' and ''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Prāvijaya / Prāviṣeya (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Priyalaukika / Har·π£avardhana ('' Markandeya''), A·πÖgalaukika (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''), A·πÖgalaukika (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Puleya / Kulƒ´ya (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Pulinda ('' Markandeya''), Pulƒ´ya (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''), Pauleya (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* R≈´pasa / K≈´pasa (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), R≈´papa ('' Markandeya''), R≈´paka (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Sainika / Pidika (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), ≈ö≈´lika ('' Markandeya''), Jhillika (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Śālva ( Shalva) – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Saraja – (Vindhya-prashtha Āryāvarta – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Sārasvata – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Sauśalya ( Saushalya) – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Sauvīra – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Śaśikhādrika ( Shashikhadraka) – (Parvata-shrayin Āryāvarta – Himalayan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* ≈öatadruja ( Shatadruja) / ≈öatadrava (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* ·π¢a·π≠pura / Padgama (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), ·π¢a·π≠sura (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Pa·π≠ava ('' Markandeya''), Bahela (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Vindhya-prashtha Āryāvarta – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Sindhu
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
/ Saindhava
The Saindhavas, also known as Jayadrathas, was a Medieval Indian dynasty that ruled western Saurashtra (now in Gujarat, India) from c. 735 CE to c. 920 CE, probably in alliance with Maitrakas in its early years. Their capital was at Bhutamab ...
– (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Sirāla / Surāla (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Sumƒ´na ('' Markandeya''), Sinƒ´la (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''), Kirāta (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* ≈öudra (Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four '' varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoretically, class ser ...
/ Sudra) / Suhya (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
) (not to be confused with the Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four '' varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoretically, class ser ...
, a Varna)
* Sujaraka – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Śulakara ( Shulakara) – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Surāṣṭra (Surashtra
Saurashtra, also known as Sorath or Kathiawar, is a peninsular region of Gujarat, India, located on the Arabian Sea coast. It covers about a third of Gujarat state, notably 11 districts of Gujarat, including Rajkot District. It was formerly a ...
) / Saurāṣṭra (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Śūrpāraka / Sūrpāraka (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Sūryāraka ('' Markandeya''), Sūryāraka (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* ≈ö≈´rasena (Shurasena
Shurasena ( sa, ý§∂ý•Çý§∞ý§∏ý•áý§®, ) was an ancient Yadava ruler of Mathura. He was married to a NƒÅga (or serpent) woman named Marisha. She bore all of his children and was the cause for Vasuki‚Äôs boon to Bhima."''Surasena or shoorsaini was ...
) / Braj – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Taittrika / Taittirika (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Turasita (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Kurumini ('' Markandeya''), Tubhamina (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''), Karƒ´ti (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Taksas – in Taksasila or Taxila (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Talagana / Talagāna (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Stanapa (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Tāvakarāma (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''), Tālaśāla (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Tāmasa / Chamara (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Tomara (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
''), Tāmara (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Parvata-shrayin Āryāvarta – Himalayan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Tāmas – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Tāmralipataka – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Ta·πÖga·πáa / Apatha (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Gurguṇa ('' Markandeya'') – (Parvata-shrayin Āryāvarta – Himalayan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Taṅgaṇa / Tuṅgana ('' Markandeya'') – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Tāpasa / Svāpada ('' Markandeya''), Tāpaka (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Tilaṇga – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Traipura – (Vindhya-prashtha Āryāvarta – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Trigarta
Trigarta kingdom was an ancient kingdom in northern Indian region of the Indian subcontinent with its capital at Prasthala (modern Jalandhar), Multan and Kangra.
Trigarta was founded and ruled by the vrishni Dynasty.
Mention in Mahabharata
T ...
– (Parvata-shrayin Āryāvarta – Himalayan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Tugras – in the Sutlej river basin (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Tūrṇapāda – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Utkala – (Eastern and Central in ''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'' – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Uttamārṇa / Uttama (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Vindhya-prashtha Āryāvarta – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Vāhyatodara / Girigahvara (Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
) – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Vaidi≈õa (Vaidisha) / Vaidika (''Vayu
Vayu (, sa, ý§µý§æý§Øý•Å, ), also known as Vata and Pavana, is the Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine massenger of the gods. In the '' Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king of ...
''), Kholli≈õa (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – (Vindhya-prashtha Āryāvarta – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Vaṅga – Central and Eastern in ''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'' – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Vāṅgeya / Mārgavageya (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Rāṅgeya ('' Markandeya''), Vojñeya (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
'') – (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Vāṭadhāna – (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Vatsa
Vatsa or Vamsa (Pali and Ardhamagadhi: , literally "calf") was one of the sixteen Mahajanapadas (great kingdoms) of Uttarapatha of ancient India mentioned in the Aṅguttara Nikāya.
Location
The territory of Vatsa was located to the south o ...
/ Vamsa – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Vātsīya – (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Vemaka
The Vemaka were an ancient Indian tribe, located north of the larger tribe of the Kuninda in northern India.
They are known for their coins, as the silver coins of the Kunindas, the Vemakas and the Audumbaras closely follow the coins of the ...
– (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*Videha
Videha ( Prākrit: ; Pāli: ; Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of north-eastern South Asia whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The population of Videha, the Vaidehas, were initially organised into a monarchy but later ...
– (Prachya Āryāvarta – Eastern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
) (Mithila Mithila may refer to:
Places
* Mithilā, a synonym for the ancient Videha state
** Mithilā (ancient city), the ancient capital city of Videha
* Mithila (region), a cultural region (historical and contemporary), now divided between India and Nepal
...
/ Tirabhukti)
* Vṛka ( Vrika) – (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
* Yadu
**Haihayas
The Heheya Kingdom (also known as Haihaya, Haiheya, Heiheya _sa.html" ;"title="nowiki/> sa">ý§πý•àý§πý§Ø was a kingdom ruled by the Yadava people, who claimed to be descended from Yadu, a legendary king of Chandravamsha lineage. One of the mo ...
/ Heheya (Talajangha)
*** Avanti – Clan of the Haihayas (Central and Vindhyan Āryāvarta in ''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
'')
***Bhoja
Bhoja (reigned c. 1010–1055 CE) was an Indian king from the Paramara dynasty. His kingdom was centered around the Malwa region in central India, where his capital Dhara-nagara (modern Dhar) was located. Bhoja fought wars with nearly all ...
/ Gopta (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') (Gupta) – Clan of the Haihayas (Vindhya-prashtha Āryāvarta – Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
in ''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'')
*** Sharyatas – Clan of the Haihayas
The Heheya Kingdom (also known as Haihaya, Haiheya, Heiheya _sa.html" ;"title="nowiki/> sa">ý§πý•àý§πý§Ø was a kingdom ruled by the Yadava people, who claimed to be descended from Yadu, a legendary king of Chandravamsha lineage. One of the mo ...
.
**** Ānarta / Āvantya in '' Markandeya'', ''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'' – Subclan of the Sharyatas (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*** Tuṇḍikera / Śauṇḍikera (''Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
''), Tuṣṭikāra ('' Markandeya'') – Clan of the Haihayas
The Heheya Kingdom (also known as Haihaya, Haiheya, Heiheya _sa.html" ;"title="nowiki/> sa">ý§πý•àý§πý§Ø was a kingdom ruled by the Yadava people, who claimed to be descended from Yadu, a legendary king of Chandravamsha lineage. One of the mo ...
. (Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
*** Vƒ´tihotra / Vƒ´rahotra ('' Markandeya''), Vƒ´tahotra (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') – Clan of the Haihayas
The Heheya Kingdom (also known as Haihaya, Haiheya, Heiheya _sa.html" ;"title="nowiki/> sa">ý§πý•àý§πý§Ø was a kingdom ruled by the Yadava people, who claimed to be descended from Yadu, a legendary king of Chandravamsha lineage. One of the mo ...
(Vindhyan Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
** Cedi ( Chedi) / Chaidyas
** Shashabindu / Shashabindava –
** Vaidarbha / Vidarbha
Vidarbha (Pronunciation: ãidÙ…ô…æb ±…ô is a geographical region in the east of the Indian state of Maharashtra and a proposed state of central India, comprising the state's Amravati and Nagpur divisions. Amravati Division's former name is Ber ...
(Mahabharata
The ''MahƒÅbhƒÅrata'' ( ; sa, ý§Æý§πý§æý§≠ý§æý§∞ý§§ý§Æý•ç, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, RƒÅmƒÅya·πáa''. It narrates the s ...
) – Vidarbha
Vidarbha (Pronunciation: ãidÙ…ô…æb ±…ô is a geographical region in the east of the Indian state of Maharashtra and a proposed state of central India, comprising the state's Amravati and Nagpur divisions. Amravati Division's former name is Ber ...
(Dakshinapatha Āryāvarta – Southern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
**Yadava
The Yadava (literally, descended from Yadu) were an ancient Indian people who believed to be descended from Yadu, a legendary king of Chandravamsha lineage. The community was formed of various clans, being the Abhira, Andhaka, Vrishni, and ...
– Descendants of the Yadu
*** Ābhīra – (Udichya and Dakshinapatha Āryāvarta – Northern and Southern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
**** Northern Ābhīra (Udichya Āryāvarta – Northern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
**** Southern Ābhīra (Dakshinapatha Āryāvarta – Southern Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
***Kukura Kukura may be,
* Juraj Kukura (born 1947), Slovak actor
* Philipp Kukura (born 1978), Slovak physical chemist
* Kukur√° language, a linguistic hoax
{{dab, surname ...
–
*** Satvata –
***Vrishni
The Vrishnis (Brahmi: ''vri-shņi'') were an ancient Vedic Indian clan who were believed to be the descendants of Vrishni. It is believed that Vrishni was the son of Satvata, a descendant of Yadu, the son of Yayati. He had two wives, Gandhari a ...
–
**** Shainya / Shaineya
*Yaudheya
Yaudheya (Brahmi script: ëĨëÅÖëÄ•ëÅÇëĨ) or Yoddheya Gana (Yoddheya Republic) was an ancient militant confederation. The word Yaudheya is a derivative of the word from yodha meaning warriors.‚ÄúYaudheyas.‚Äù Ancient Communities of the Hima ...
– (Madhya-desha Āryāvarta – Central Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
)
Mahajanapadas (c. 500 BCE)
 ý§Æý§πý§æý§úý§®ý§™ý§¶ ‚Äì Mahajanapada
Shodasa Mahajanapadas (Sixteen Mahajanapadas)
The Mahajanapadas were sixteen great kingdoms and republics that emerged after the more powerful political entities (initially based on the territories of peoples and tribes) had conquered many others.
According to the '' Anguttara Nikaya'', ''
ý§Æý§πý§æý§úý§®ý§™ý§¶ ‚Äì Mahajanapada
Shodasa Mahajanapadas (Sixteen Mahajanapadas)
The Mahajanapadas were sixteen great kingdoms and republics that emerged after the more powerful political entities (initially based on the territories of peoples and tribes) had conquered many others.
According to the '' Anguttara Nikaya'', ''Digha Nikaya
Digha is a seaside resort town in the state of West Bengal, India. It lies in Purba Medinipur district and at the northern end of the Bay of Bengal. It has a low gradient with a shallow sand beach. It is a popular sea resort in West Bengal.
H ...
'', '' Chulla-Niddesa'' (Buddhist Canon
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
)
*Anga
Anga (Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of eastern South Asia whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The members of the Aṅga tribe were called the Āṅgeyas.
Counted among the "sixteen great nations" in Buddhist texts ...
*Assaka
Ashmaka (Sanskrit: ) or Assaka (Pali: ) was a Mahajanapada in ancient India which existed between 700 BCE and 425 or 345 BCE according to the Buddhist texts '' Anguttara Nikaya'' and ''Puranas''. It was located around and between the Godavar ...
(or Asmaka
Ashmaka (Sanskrit: ) or Assaka (Pali: ) was a Mahajanapadas, Mahajanapada in ancient India which existed between 700 BCE and 425 or 345 BCE according to the Buddhist texts ''Aṅguttara Nikāya, Anguttara Nikaya'' and ''Puranas''. It was loc ...
)
* Avanti
* Chetiya ( Chedi / Cedi)
* Gandhara
* Kamboja (possibly ancestral of Nuristani)
* Kashi / Kasi
KASI (1430 AM, "News Talk 1430") is a radio station licensed to serve Ames, Iowa. The station is owned by iHeartMedia, Inc. and licensed to iHM Licenses, LLC. It airs a News/Talk radio format.
The station was assigned the KASI call letters b ...
* Kosala
* Kuru
* Maccha (Matsya
Matsya ( sa, ý§Æý§§ý•çý§∏ý•çý§Ø, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya ...
)
*Magadha
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was ruled ...
*Malla
Malla may refer to: Places
;Bolivia
*Malla, Bolivia, a locality
* Malla Jawira, a river
* Malla Jaqhi, a mountain
* Malla Municipality
* Malla Qullu, a mountain
;India
* Mallapuram, Tamil Nadu
*Malla (tribe), an ancient republic, one of the s ...
* Panchala (Pañcāla
Panchala ( sa, ý§™ý§ûý•çý§öý§æý§≤, IAST: ) was an ancient kingdom of northern India, located in the Ganges-Yamuna Doab of the Upper Gangetic plain. During Late Vedic times (c. 1100‚Äì500 BCE), it was one of the most powerful states of ancien ...
)
*Surasena
Kingdom of Surasena (or Sourasena) (Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indian region corresponding to the present-day Braj region in Uttar Pradesh, with Mathura as its capital city. According to the Buddhist text '' Anguttara Nikaya'', Surasena was on ...
* Vajji ( V·πõji))
** Licchavis (tribe)
* Vamsha (Vatsa)
According to the ''Vyākhyāprajñapti
''VyƒÅkhyƒÅpraj√±apti'' ( sa, ý§µý•çý§Øý§æý§ñý•çý§Øý§æý§™ý•çý§∞ý§úý•çý§ûý§™ý•çý§§ý§ø "Exposition of Explanations"), commonly known as the ''Bhagavati S≈´tra'' (), is the fifth of the 12 Jain Agamas said to be promulgated by MahƒÅvƒ´ra. The Vyƒ ...
'' / '' Bhagavati Sutra'' ( Jain text)
* Accha
*Anga
Anga (Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of eastern South Asia whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The members of the Aṅga tribe were called the Āṅgeyas.
Counted among the "sixteen great nations" in Buddhist texts ...
* Avaha
* Bajji ( Vajji / Vriji)
** Licchavis (tribe)
* Banga / Vanga
The family Vangidae (from ''vanga'', Malagasy for the hook-billed vanga, ''Vanga curvirostris'') comprises a group of often shrike-like medium-sized birds distributed from Asia to Africa, including the vangas of Madagascar to which the family ...
*Kasi
KASI (1430 AM, "News Talk 1430") is a radio station licensed to serve Ames, Iowa. The station is owned by iHeartMedia, Inc. and licensed to iHM Licenses, LLC. It airs a News/Talk radio format.
The station was assigned the KASI call letters b ...
/ Kashi
* Kochcha
* Kosala
*Ladha
Ladha ( ps, ŸÑÿØŸá; ur, ŸÑÿØŸáÿß) or Lada is a town in South Waziristan, in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province (formerly in the Federally Administered Tribal Areas, now merged with province). Just 10 km north of Ladha is the city of Makeen, while 1 ...
/ Lata
Lata (Hindi: ý§≤ý§§ý§æ) is a Hindu/Sanskrit Indian female given name, which means "creeper" and "vine". Lata may refer to:
Notable people named Lata
*Lata Bhatt (born 1954), Indian singer.
* Lata (born 1975), Musician.
*Lata Mangeshkar (1929–2 ...
*Magadha
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was ruled ...
* Malavaka
* Malaya (located in the Malaya mountains
The Malaya Mountains were a range of mountains that were mentioned in the Hindu sacred texts like ''Matsya Purana'', the ''Kurma Purana'', the ''Vishnu Purana'', and the epics of the ''Ramayana'' and the ''Mahabharata''.
The Vishnu Purana specifi ...
, southernmost part of the Western Ghats, part of the same was called the Sahya Mountains, Southern India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territ ...
) (probably Dravidian and Non-Indo-Aryan)
* Moli / Malla
Malla may refer to: Places
;Bolivia
*Malla, Bolivia, a locality
* Malla Jawira, a river
* Malla Jaqhi, a mountain
* Malla Municipality
* Malla Qullu, a mountain
;India
* Mallapuram, Tamil Nadu
*Malla (tribe), an ancient republic, one of the s ...
*Padha
Padha is a village in Karnal district, Haryana, India with approximately 8,000 inhabitants
The main occupation is Kheti (Agriculture) and Pashupalan (cattle breeding). There is famous "Panch Thirath".
Villages in Karnal district
{{Haryana ...
* Sambhuttara
* Vaccha (Vatsa
Vatsa or Vamsa (Pali and Ardhamagadhi: , literally "calf") was one of the sixteen Mahajanapadas (great kingdoms) of Uttarapatha of ancient India mentioned in the Aṅguttara Nikāya.
Location
The territory of Vatsa was located to the south o ...
)
Mentions by Ancient Greek authors (Classical Age)
NorthwestAncient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
– Indus River Basin
* Glausae ( Glausaí) (may have been the Gandhari?)
* Malloí / Malli (known as Mālava / Western Malla by Indo-Aryans
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and intr ...
in ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
) – they were a people from southern Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: ŸæŸÜÿ¨ÿßÿ® ; ý®™ý©∞ý®úý®æý®¨ ; ; also romanised as ''PanjƒÅb'' or ''Panj-ƒÄb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
, including today's Multan
Multan (; ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, on the bank of the Chenab River. Multan is Pakistan's seventh largest city as per the 2017 census, and the major cultural, religious and economic centre of southern Punjab.
Multan is one of the old ...
city ('' Mallorum Metropolis'') and region, south of the confluence of the Jhelum, Hydaspes
The Jhelum River (/d í ∞eÀêl…ôm/) is a river in the northern Indian subcontinent. It originates at Verinag and flows through the Indian administered territory of Jammu and Kashmir, to the Pakistani-administered territory of Kashmir, and then ...
for the Greeks, and Ravi, Hydraotes for the Greeks, rivers (see map 9), they are mentioned by ancient Greek historians in the Mallian Campaign of Alexander III of Macedon
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to t ...
( Iskandar); Malada (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
''), Ekalavya (''Vamana
Vamana (), also known as Trivikrama (), Urukrama (), Upendra (), Dadhivamana (), and Balibandhana () is an avatar of the Hindu deity Vishnu. He is the fifth avatar of Vishnu, and the first Dashavatara in the Treta Yuga, after Narasimha.
Or ...
'') (Aparanta Āryāvarta – Western Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
) (not the be confused with the Eastern Malla)
* Oxydracae ( Oxydrakaí) (may have been the Śudra (Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four '' varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoretically, class ser ...
/ Sudra) / Suhya (''Brahmanda
The ''Brahmanda Purana'' ( sa, ý§¨ý•çý§∞ý§πý•çý§Æý§æý§£ý•çý§° ý§™ý•Åý§∞ý§æý§£, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas, a genre of Hindu texts. It is listed as the eighteenth Maha-Purana in almost all the anthologies. The text ...
''), not to be confused with the Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four '' varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoretically, class ser ...
, a Varna)
* Sattagydans – people that dwelt in Sattagydia
Sattagydia (Old Persian: êé∞êé´êé¶êé¢êèÅ ''Thatagu≈°'', country of the "hundred cows") was one of the easternmost regions of the Achaemenid Empire, part of its Seventh tax district according to Herodotus, along with GandƒÅrae, Dadicae and ...
(Old Persian Thataguš; th = θ, from θata – "hundred" and guš – "cows", country of the People of "Hundred Cows"), may have been an Indo-Aryan people of Sindh with Iranian influence or the opposite, an Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
people of Sindh with Indo-Aryan influence.
* Sibae / Sobii ( Sibaí / Sivaí / Sobioí / Sivioí) (may have been the Śiva
Shiva (; sa, ý§∂ý§øý§µ, lit=The Auspicious One, ≈öiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; …ê…¶aÀêdÙeÀê ã…ê, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
or Shiva
Shiva (; sa, ý§∂ý§øý§µ, lit=The Auspicious One, ≈öiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; …ê…¶aÀêdÙeÀê ã…ê, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
people of Early Janapadas
The Janapadas () (c. 1500–600 BCE) were the realms, republics (ganapada) and kingdoms (saamarajya) of the Vedic period on the Indian subcontinent. The Vedic period reaches from the late Bronze Age into the Iron Age: from about 1500 BCE to ...
?) (not to be confused with the God ≈öiva
Shiva (; sa, ý§∂ý§øý§µ, lit=The Auspicious One, ≈öiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; …ê…¶aÀêdÙeÀê ã…ê, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
or Shiva
Shiva (; sa, ý§∂ý§øý§µ, lit=The Auspicious One, ≈öiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; …ê…¶aÀêdÙeÀê ã…ê, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
)
Other regions of Ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
(''India Intra Gangem'')
* Pragii / Prasii ( Pragioí / Prasioí) (may have been the people of Prāgjyotiṣa or Pragjyotisha
Kamarupa (; also called Pragjyotisha or Pragjyotisha-Kamarupa), an early state during the Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, was (along with Davaka) the first historical kingdom of Assam.
Though Kamarupa prevailed from 350 to ...
, Pragjyotisha
Kamarupa (; also called Pragjyotisha or Pragjyotisha-Kamarupa), an early state during the Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, was (along with Davaka) the first historical kingdom of Assam.
Though Kamarupa prevailed from 350 to ...
- Kamarupa?)
Possible Indo-Aryan or other peoples / tribes / clans
*Alina (RV 7.18.7) (RV =Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''s≈´ktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' ≈õruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
) – They were one of the tribes defeated by Sudas of the Bharatas at the Dasarajna
The Battle of the Ten Kings ( sa, ý§¶ý§æý§∂ý§∞ý§æý§úý•çý§û ý§Øý•Åý§¶ý•çý§ß, translit=DƒÅ≈õarƒÅj√±√° yuddh√°) is a battle, first alluded to in the 7th Mandala of the Rigveda (RV), between a Bharata king and a confederation of tribes. It resulte ...
( Ten Kings Battle). A. A. Macdonell and A. B. Keith
Arthur Berriedale Keith (5 April 1879 – 6 October 1944) was a Scottish constitutional lawyer, scholar of Sanskrit and Indologist. He became Regius Professor of Sanskrit and Comparative Philology and Lecturer on the Constitution of the Brit ...
(1912). ''Vedic Index of Names and Subjects''. It is suggested that they lived to the north-east of the Kambojas
Kamboja ( sa, ý§ïý§Æý•çý§¨ý•ãý§ú) was a kingdom of Iron Age India that spanned parts of South and Central Asia, frequently mentioned in Sanskrit and Pali literature. Eponymous with the kingdom name, the Kambojas were an Indo-Iranian people o ...
(possible ancestors of the Nuristani that live in Nurestan
Nuristan, also spelled as Nurestan or Nooristan (Dari: ; Kamkata-vari: ), is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in the eastern part of the country. It is divided into seven districts and is Afghanistan's least populous province, w ...
) because in the 7th century CE, the land was mentioned by the Chinese pilgrim Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
. It is possible that they are connected with the Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
or Alani people who are a nomadic Iranian tribe. Alans is a dialectal cognate of Aryāna, itself derived from the root arya-, meaning 'Aryan', the common self-designation of Indo-Iranian peoples. It probably came in use in the early history of the Alans for the purpose of uniting a heterogeneous group of tribes through the invocation of a common, ancestral 'Aryan' origin. The historian S. Talageri identifies them with the Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
(Hellenes). However, the dating of the Rigveda and the hypothetical historic time for the Dasarajna
The Battle of the Ten Kings ( sa, ý§¶ý§æý§∂ý§∞ý§æý§úý•çý§û ý§Øý•Åý§¶ý•çý§ß, translit=DƒÅ≈õarƒÅj√±√° yuddh√°) is a battle, first alluded to in the 7th Mandala of the Rigveda (RV), between a Bharata king and a confederation of tribes. It resulte ...
(Battle of Ten Kings
The Battle of the Ten Kings ( sa, ý§¶ý§æý§∂ý§∞ý§æý§úý•çý§û ý§Øý•Åý§¶ý•çý§ß, translit=DƒÅ≈õarƒÅj√±√° yuddh√°) is a battle, first alluded to in the 7th Mandala of the Rigveda (RV), between a Bharata king and a confederation of tribes. It resulte ...
) occurred millennia before Hellenes were recorded in India.
*Parsu (Parśu) – The Parsus have been connected with the Persians based on the evidence of an Assyrian inscription from 844 BC referring to the Persians as Parshu, and the Behistun Inscription of Darius I of Persia referring to Parsa as the home of the Persians. Pârsâ, is the Old Persian name for the Persis region Pars province as well as the root for the term Persian.
*Shakya
Shakya ( PƒÅ·∏∑i: ; sa, ý§∂ý§æý§ïý•çý§Ø, translit=≈öƒÅkya) was an ancient eastern sub-Himalayan ethnicity and clan of north-eastern region of the Indian subcontinent, whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The Shakyas were organised ...
– a clan of Iron Age India
In the prehistory of the Indian subcontinent, the Iron Age succeeded Bronze Age India and partly corresponds with the megalithic cultures of India. Other Iron Age archaeological cultures of India were the Painted Grey Ware culture (1300–3 ...
(1st millennium BCE), habitating an area in Greater Magadha
Greater Magadha is a concept in studies of the early history of India. It is used to refer to the political and cultural sphere that developed in the lower Gangetic plains ( Johannes Bronkhorst defines the region to comprise modern day Bihar and e ...
, on the foothills of the Himalaya mountains
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...
. This is also the clan in which Siddhartha Gautama
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lu ...
(also known as Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in L ...
or Shakyamuni – Sage of the Shakyas) (c. 6th to 4th centuries BCE) was born into, whose teachings became the foundation of Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
. According to Chandra Das, the name "Shakya" is derived from the Sanskrit word "≈õakya," which means "the one who is capable". Some scholars argue that the Shakya were of Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
(Saka
The Saka ( Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who hist ...
) origin (part of the Iranian peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities.
The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separat ...
) and assimilated into Indo-Aryan peoples
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and int ...
.Christopher I. Beckwith, "Greek Buddha: Pyrrho's Encounter with Early Buddhism in Central Asia", 2016, pp 1–21
* Sogdi ( Sogdoí), people that inhabited where is today the Sibi Division
Sibi Division () is a division of Balochistan province of Pakistan. It contains the following districts: The creation of Sibi Division in 1974, the divisional offices shifted to Ziarat during the summer.
Districts
* Sibi District (created 1 ...
valley in Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. ...
, between Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. ...
and Sindh, and most of the Larkana Division
Larkana Division ( sd, لاڙڪاڻو ڊويزن) is an administrative division of the Sindh Province of Pakistan. It was created in 1980 by bifurcation of Sukkur Division. In 2000 abolished by General Pervaiz Musharraf rule but Sindh governme ...
, and parts of the Sukkur Division
Sukkur Division ( sd, سکر ڊويزن) is one of the seven administrative Divisions of the Sindh Province of Pakistan. This level of administration was abolished in 2000 but restored again on 11 July 2011.
Sukkur is the divisional headquart ...
to the west of the Indus river, in Sindh (see map 8), their main city was called Sogdorum Regia (maybe today's Sukkur
Sukkur (; ) is a city in the Pakistani province of Sindh along the western bank of the Indus River, directly across from the historic city of Rohri. Sukkur is the third largest city in Sindh after Karachi and Hyderabad, and 14th largest city ...
) by the ancient Greek and Roman authors, and was on the Indus river banks. They may have been an Indo-Aryan people of the Indus valley with a coincidental name with the Sogdians :''This category lists articles related to historical Iranian peoples''
Historical
Peoples
Iranian
Iranian
Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples ...
, or, as the name could tell, a branch of the Sogdians :''This category lists articles related to historical Iranian peoples''
Historical
Peoples
Iranian
Iranian
Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples ...
, the " Indus Sogdians", in a region of the west Indus valley.
* Kāmboja (Kamboja) (ancestors of the Nuristani and Kamboj
The Kamboj ( pa, ý®ïý©∞ý®¨ý©ãý®ú ''Kamboj'', hi, ý§ïý§Çý§¨ý•ãý§ú ''Kamboj''), also Kamboh ( ur, ALA-LC: ), is a cultivating community of the Punjab region of Pakistan and India, spanning a region from the Sutlej Valley to the north, the M ...
peoples, sometimes included in the Indo-Aryan peoples
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and int ...
, or of the Iranian Pamirian peoples – Pamiris
The Pamiris, russian: –ü–∞–º–∏ÃÅ—Ä—Ü—ã, Pam√≠rtsy, zh, s=Â∏ïÁ±≥Â∞î‰∫∫, p=P√Ým«ê'ƒõrr√©n, ur, are an Eastern Iranian ethnic group, native to the Badakhshan region of Central Asia, which includes the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region of T ...
or Badakhshani people)
Hypothetical Indo-Aryans
* Mitanni Indo-Aryans (c. 1500–1300 BCE) – hypothetical ancient people of the northernMiddle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
in the Mitanni
Mitanni (; Hittite cuneiform ; ''Mittani'' '), c. 1550–1260 BC, earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, c. 1600 BC; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat (''Hanikalbat'', ''Khanigalbat'', cuneiform ') in Assyrian records, or ''Naharin'' in ...
kingdom (part of today's far western Iran, northwestern Iraq, northern Syria and southeastern Turkey), that spoke the hypothetical Mitanni Indo-Aryan (a language that was superstrate of Hurrian
The Hurrians (; cuneiform: ; transliteration: ''·∏™u-ur-ri''; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri or Hurriter) were a people of the Bronze Age Near East. They spoke a Hurrian language and lived in Anatolia, Syria and Northern ...
, a non-Indo-European language) and merged with the Hurrians, many of them as a social elite, in the course of the Indo-Aryan migration
The Indo-Aryan migrations were the migrations into the Indian subcontinent of Indo-Aryan peoples, an ethnolinguistic group that spoke Indo-Aryan languages, the predominant languages of today's North India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lank ...
(towards West in this case).
See also
*Ramayana
The ''RƒÅmƒÅyana'' (; sa, ý§∞ý§æý§Æý§æý§Øý§£ý§Æý•ç, ) is a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th ...
*Āryāvarta
ƒÄryƒÅvarta (Sanskrit: ý§Üý§∞ý•çý§Øý§æý§µý§∞ý•çý§§, lit. "abode of the Aryas",
*Mahabharata
The ''MahƒÅbhƒÅrata'' ( ; sa, ý§Æý§πý§æý§≠ý§æý§∞ý§§ý§Æý•ç, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, RƒÅmƒÅya·πáa''. It narrates the s ...
*Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betwe ...
*Bharatavarsha
The Republic of India has two principal short names, each of which is historically significant, "India" and "Bharata". A third name, "Hindustān", is sometimes an alternative name for the region comprising most of the modern Indian states o ...
*Chakravartin
A ''chakravarti'' ( sa, ý§öý§ïý•çý§∞ý§µý§∞ý•çý§§ý§øý§®ý•ç, ''cakravartin''; pi, cakkavatti; zh, ËΩâ˺™Áéã, ''Zhu«énl√∫nw√°ng'', "Wheel-Turning King"; , ''Zhu«énl√∫n Sh√®ngw√°ng'', "Wheel-Turning Sacred King"; ja, ˪¢Ëº™Áéã, ''Tenrin'≈ç'' ...
* Bharata Khanda
*Iron Age India
In the prehistory of the Indian subcontinent, the Iron Age succeeded Bronze Age India and partly corresponds with the megalithic cultures of India. Other Iron Age archaeological cultures of India were the Painted Grey Ware culture (1300–3 ...
* Avestan geography
*History of Hinduism
The history of Hinduism covers a wide variety of related religious traditions native to the Indian subcontinent. It overlaps or coincides with the development of religion in the Indian subcontinent since the Iron Age, with some of its tradition ...
*Indo-Aryan migration
The Indo-Aryan migrations were the migrations into the Indian subcontinent of Indo-Aryan peoples, an ethnolinguistic group that spoke Indo-Aryan languages, the predominant languages of today's North India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lank ...
* Indus Valley civilization
* Janapada & Mahajanapada
The Mahājanapadas ( sa, great realm, from ''maha'', "great", and ''janapada'' "foothold of a people") were sixteen kingdoms or oligarchic republics that existed in ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE during the second urba ...
* Monarchy in ancient India
*Historicity of the Mahabharata
The ''MahƒÅbhƒÅrata'' ( ; sa, ý§Æý§πý§æý§≠ý§æý§∞ý§§ý§Æý•ç, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' RƒÅmƒÅya·πáa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kuru ...
References
Further reading
*Anthony, David W. (2007). ''The Horse The Wheel And Language. How Bronze-Age Riders From the Eurasian Steppes Shaped The Modern World''. Princeton University Press *Frawley David: ''The Rig Veda and the History of India'', 2001. (Aditya Prakashan), *Mallory, J.P.; Douglas Q. Adams (1997). ''Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture''. London: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers. *Misra, Sudama (1973). ''Janapada state in ancient India''. Vārāṇasī: Bhāratīya Vidyā Prakāśana. *Pargiter, F.E.922
__NOTOC__
Year 922 ( CMXXII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Byzantine Empire
* Summer – Battle of Constantinople: Emperor Romanos I sends Byza ...
1979. ''Ancient Indian Historical Tradition''. New Delhi: Cosmo.
*Parpola, Asko (2015), ''The Roots of Hinduism. The Early Aryans and the Indus Civilization'', Oxford University Press
*Talageri, Shrikant: ''The Rigveda: A Historical Analysis'' 2000, {{ISBN, 81-7742-010-0 --Aryan Invasion Theory and Indian Nationalism. 1993.
Indo-Aryan peoples
Lists of ancient Indo-European peoples and tribes
Lists of ancient people