right brachiocephalic vein on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The left and right brachiocephalic veins (previously called innominate veins) are major veins in the upper chest, formed by the union of each corresponding
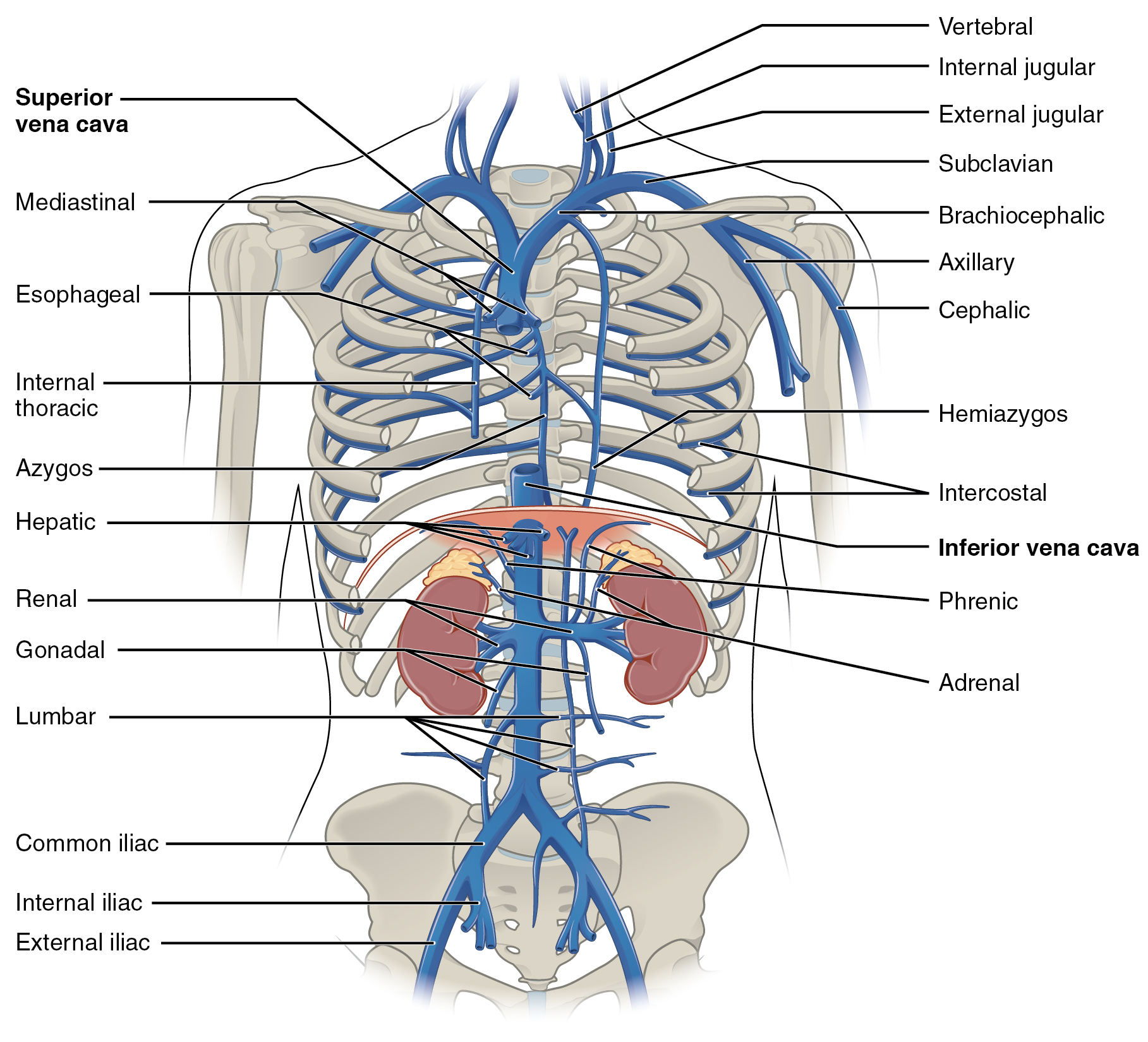 The brachiocephalic vein is formed by the confluence of the subclavian and internal jugular veins. In addition it receives drainage from:
* Left and right
The brachiocephalic vein is formed by the confluence of the subclavian and internal jugular veins. In addition it receives drainage from:
* Left and right
Image:Gray480.png, Diagram showing completion of development of the parietal veins.
Image:Gray490.png, Front view of heart and lungs.
Image:Gray562.png, The fascia and middle thyroid veins.
File:Slide2eeee.JPG, Right Brachiocephalic vein
File:Slide9eeee.JPG, Right& Left Brachiocephalic vein
File:Slide14eeee.JPG, Right& Left Brachiocephalic vein
Image:Venenwinkel.png , The brachiocephalic veins, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, azygos vein and their tributaries.
internal jugular vein
The internal jugular vein is a paired jugular vein that collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck. This vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve.
It begins in the posteri ...
and subclavian vein
The subclavian vein is a paired large vein, one on either side of the body, that is responsible for draining blood from the upper extremities, allowing this blood to return to the heart. The left subclavian vein plays a key role in the absorption ...
. This is at the level of the sternoclavicular joint
The sternoclavicular joint or sternoclavicular articulation is a synovial saddle joint between the manubrium of the sternum, and the clavicle, as well as the first rib. The joint possesses a joint capsule, and an articular disk, and is reinfor ...
. The left brachiocephalic vein is nearly always longer than the right.
These veins merge to form the superior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vein th ...
, a great vessel
Great vessels are the large vessels that bring blood to and from the heart. These are:
* Superior vena cava
* Inferior vena cava
* Pulmonary arteries
* Pulmonary veins
* Aorta
Transposition of the great vessels is a group of congenital
A b ...
, posterior to the junction of the first costal cartilage
The costal cartilages are bars of hyaline cartilage that serve to prolong the ribs forward and contribute to the elasticity of the walls of the thorax. Costal cartilage is only found at the anterior ends of the ribs, providing medial extension.
...
with the manubrium of the sternum.
The brachiocephalic veins are the major veins returning blood to the superior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vein th ...
.
Tributaries
 The brachiocephalic vein is formed by the confluence of the subclavian and internal jugular veins. In addition it receives drainage from:
* Left and right
The brachiocephalic vein is formed by the confluence of the subclavian and internal jugular veins. In addition it receives drainage from:
* Left and right internal thoracic vein
In human anatomy, the internal thoracic vein (previously known as the internal mammary vein) is a vessel that drains the chest wall and breasts.
Structure
Bilaterally, the internal thoracic vein arises from the superior epigastric vein, an ...
(Also called internal mammary veins): drain into the inferior border of their corresponding vein
* Left and right inferior thyroid veins
The inferior thyroid veins appear two, frequently three or four, in number, and arise in the venous plexus on the thyroid gland, communicating with the middle and superior thyroid veins. While the superior and middle thyroid veins serve as direc ...
: drain into the superior aspect of their corresponding veins near the confluence
* Left and right vertebral vein
The vertebral vein is formed in the suboccipital triangle, from numerous small tributaries which spring from the internal vertebral venous plexuses and issue from the vertebral canal above the posterior arch of the Atlas (anatomy), atlas.
They un ...
* Left superior intercostal vein
The superior intercostal veins are two veins that drain the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th intercostal spaces, one vein for each side of the body.
Right superior intercostal vein
The right superior intercostal vein drains the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th posterior interc ...
: drains into the left brachiocephalic veinRyan, McNicholas & Eustace "Anatomy for Diagnostic
Imaging: 3rd Edition"
Embryological origin
The left brachiocephalic vein forms from the anastomosis formed between the left and right anterior cardinal veins when the caudal portion of the left anterior cardinal vein degenerates.Additional images
See also
*Hip bone
The hip bone (os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone) is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the Ilium (bone), ...
(Innominate bone
The hip bone (os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone) is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the ilium, ischi ...
)
* Brachiocephalic artery
The brachiocephalic artery (or brachiocephalic trunk or innominate artery) is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm and the head and neck.
It is the first branch of the aortic arch. Soon after it emerges, the brachiocep ...
(Innominate artery
The brachiocephalic artery (or brachiocephalic trunk or innominate artery) is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm and the head and neck.
It is the first branch of the aortic arch. Soon after it emerges, the brachio ...
)
References