Richard Nugent O'Connor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
General Sir Richard Nugent O'Connor, (21 August 1889 – 17 June 1981) was a senior British Army officer who fought in both the
At the end of the war, O'Connor reverted to his rank of captain and served as regimental adjutant from April to December 1919.
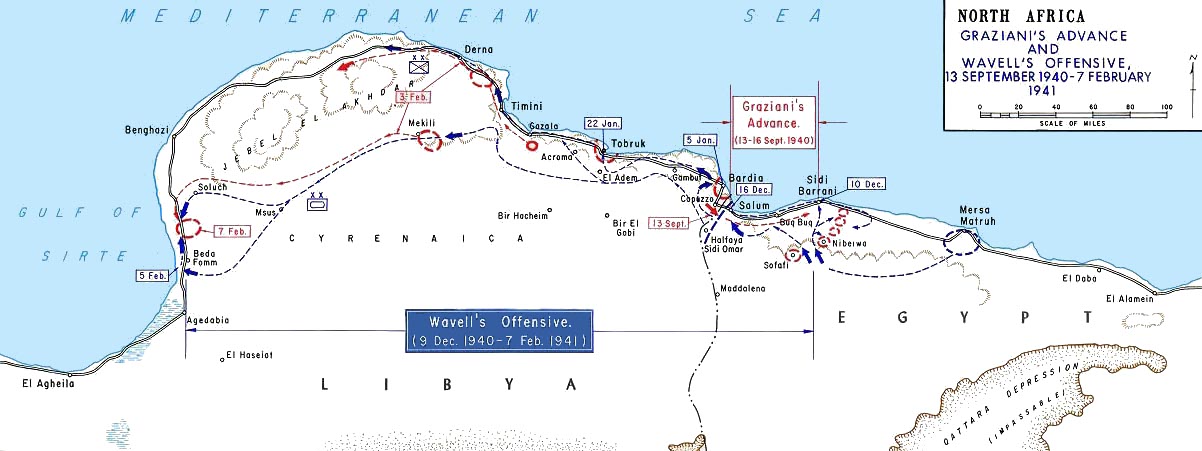 Italy declared war on Britain and France on 10 June 1940 and, soon after, O'Connor was appointed commander of the Western Desert Force. He was tasked by
Italy declared war on Britain and France on 10 June 1940 and, soon after, O'Connor was appointed commander of the Western Desert Force. He was tasked by  During November, O'Connor was appointed an acting lieutenant-general in recognition of the increased size of his command.
The counteroffensive, Operation Compass, began on 8 December 1940. O'Connor's relatively small force of 31,000 men, 275 tanks and 120 artillery pieces, ably supported by an RAF wing and the Royal Navy, broke through a gap in the Italian defences at Sidi Barrani near the coast. The Desert Force cut a swath through the Italian rear areas, stitching its way between the desert and the coast, capturing strongpoint after strongpoint by cutting off and isolating them. The Italian guns proved to be no match for the heavy British Matilda tanks and their shells bounced off the armour. By mid-December the Italians had been pushed completely out of Egypt, leaving behind 38,000 prisoners and large stores of equipment.
The Desert Force paused to rest briefly before continuing the assault into Italian Libya against the remainder of Graziani's disorganised army. At that point, the Commander-in-Chief Middle East General Sir Archibald Wavell ordered the 4th Indian Division withdrawn to spearhead the invasion of Italian East Africa.Keegan (2005), p. 191 This veteran division was to be replaced by the inexperienced
During November, O'Connor was appointed an acting lieutenant-general in recognition of the increased size of his command.
The counteroffensive, Operation Compass, began on 8 December 1940. O'Connor's relatively small force of 31,000 men, 275 tanks and 120 artillery pieces, ably supported by an RAF wing and the Royal Navy, broke through a gap in the Italian defences at Sidi Barrani near the coast. The Desert Force cut a swath through the Italian rear areas, stitching its way between the desert and the coast, capturing strongpoint after strongpoint by cutting off and isolating them. The Italian guns proved to be no match for the heavy British Matilda tanks and their shells bounced off the armour. By mid-December the Italians had been pushed completely out of Egypt, leaving behind 38,000 prisoners and large stores of equipment.
The Desert Force paused to rest briefly before continuing the assault into Italian Libya against the remainder of Graziani's disorganised army. At that point, the Commander-in-Chief Middle East General Sir Archibald Wavell ordered the 4th Indian Division withdrawn to spearhead the invasion of Italian East Africa.Keegan (2005), p. 191 This veteran division was to be replaced by the inexperienced  In early January 1941, the Western Desert Force was redesignated XIII Corps. On 9 January, the offensive resumed. By 12 January the strategic fortress port of Tobruk was surrounded. On 22 January it fell and another 27,000 Italian
In early January 1941, the Western Desert Force was redesignated XIII Corps. On 9 January, the offensive resumed. By 12 January the strategic fortress port of Tobruk was surrounded. On 22 January it fell and another 27,000 Italian

 On 21 January 1944 O'Connor became commander of
On 21 January 1944 O'Connor became commander of
First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and Second World Wars, and commanded the Western Desert Force in the early years of the Second World War. He was the field commander for Operation Compass, in which his forces destroyed a much larger Italian army – a victory which nearly drove the Axis from Africa, and in turn, led Adolf Hitler to send the Afrika Korps under Erwin Rommel
Johannes Erwin Eugen Rommel () (15 November 1891 – 14 October 1944) was a German field marshal during World War II. Popularly known as the Desert Fox (, ), he served in the ''Wehrmacht'' (armed forces) of Nazi Germany, as well as servi ...
to try to reverse the situation. O'Connor was captured by a German reconnaissance patrol during the night of 7 April 1941 and spent over two years in an Italian prisoner of war camp
A prisoner-of-war camp (often abbreviated as POW camp) is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured by a belligerent power in time of war.
There are significant differences among POW camps, internment camps, and military prisons. ...
. He eventually escaped after the fall of Mussolini in the autumn of 1943. In 1944 he commanded VIII Corps 8th Corps, Eighth Corps, or VIII Corps may refer to:
* VIII Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperial French army during the Napoleonic Wars
*VIII Army Corps (German Confederation)
* VIII Corps (German Empire), a unit of the Imperial German Army ...
in the Battle of Normandy and later during Operation Market Garden
Operation Market Garden was an Allies of World War II, Allied military operation during the World War II, Second World War fought in the Netherlands from 17 to 27 September 1944. Its objective was to create a Salient (military), salient into G ...
. In 1945 he was General Officer in Command of the Eastern Command in India and then, in the closing days of British rule in the subcontinent, he headed Northern Command. His final job in the army was Adjutant-General to the Forces in London, in charge of the British Army's administration, personnel and organisation.
In honour of his war service, O'Connor was recognised with the highest level of knighthood in two different orders of chivalry
An order of chivalry, order of knighthood, chivalric order, or equestrian order is an order of knights, typically founded during or inspired by the original Catholic military orders of the Crusades ( 1099–1291) and paired with medieval concep ...
. He was also awarded the Distinguished Service Order (twice), the Military Cross, the French Croix de Guerre
The ''Croix de Guerre'' (, ''Cross of War'') is a military decoration of France. It was first created in 1915 and consists of a square-cross medal on two crossed swords, hanging from a ribbon with various degree pins. The decoration was first awa ...
and the Legion of Honour, and served as aide-de-camp to King George VI
George VI (Albert Frederick Arthur George; 14 December 1895 – 6 February 1952) was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth from 11 December 1936 until his death in 1952. He was also the last Emperor of Ind ...
. He was also mentioned in despatches
To be mentioned in dispatches (or despatches, MiD) describes a member of the armed forces whose name appears in an official report written by a superior officer and sent to the high command, in which their gallant or meritorious action in the face ...
nine times for actions in the First World War, once in Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
in 1939 and three times in the Second World War.
Early life
O'Connor was born inSrinagar
Srinagar (English: , ) is the largest city and the summer capital of Jammu and Kashmir, India. It lies in the Kashmir Valley on the banks of the Jhelum River, a tributary of the Indus, and Dal and Anchar lakes. The city is known for its natu ...
, Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
, India, on 21 August 1889. His father was a major
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
in the Royal Irish Fusiliers
The Royal Irish Fusiliers (Princess Victoria's) was an Irish line infantry regiment of the British Army, formed by the amalgamation of the 87th (Prince of Wales's Irish) Regiment of Foot and the 89th (Princess Victoria's) Regiment of Foot in ...
, and his mother was the daughter of a former governor of India's central provinces.Keegan (2005), p. 185 He attended Tonbridge Castle School in 1899 and The Towers School in Crowthorne in 1902. In 1903, after his father's death in an accident, he moved to Wellington College Wellington College may refer to:
*Wellington College, Berkshire, an independent school in Crowthorne, Berkshire, England
** Wellington College International Shanghai
** Wellington College International Tianjin
*Wellington College, Wellington, New Z ...
and thereafter to the Royal Military College, Sandhurst in 1908. In September of the following year he was commissioned, as a second lieutenant
Second lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces, comparable to NATO OF-1 rank.
Australia
The rank of second lieutenant existed in the military forces of the Australian colonies and Australian Army until ...
and posted to the 2nd Battalion, Cameronians (Scottish Rifles)
The Cameronians (Scottish Rifles) was a rifle regiment of the British Army, the only regiment of rifles amongst the Scottish regiments of infantry. It was formed in 1881 under the Childers Reforms by the amalgamation of the 26th Cameronian Reg ...
. He maintained close ties with the regiment for the rest of his life. In January 1910, the battalion was rotated to Colchester, where he received signals and rifle training. It was then stationed in Malta from 1911 to 1912 where O'Connor served as regimental signals officer.
First World War
During the First World War, O'Connor served as signals officer of 22 Brigade in the 7th Division andcaptain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
in command of 7th Division's Signals Company. From October 1916, as a captain and later as a brevet
Brevet may refer to:
Military
* Brevet (military), higher rank that rewards merit or gallantry, but without higher pay
* Brevet d'état-major, a military distinction in France and Belgium awarded to officers passing military staff college
* Aircre ...
major, he served as brigade major of 91 Brigade, 7th Division. He was awarded the Military Cross in February 1915. In March of that year he saw action at Arras
Arras ( , ; pcd, Aro; historical nl, Atrecht ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais Departments of France, department, which forms part of the regions of France, region of Hauts-de-France; before the regions of France#Reform and mergers of ...
and Bullecourt
Bullecourt () is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region in France.
Geography
Bullecourt lies on the Upper Cretaceous plain of Artois between Arras and Bapaume and east of the A1 motorway. Thisatellite photographs ...
. O'Connor was awarded the Distinguished Service Order (DSO) and appointed brevet lieutenant-colonel in command of 2nd Infantry Battalion of the Honourable Artillery Company, part of the 7th Division, in June 1917. In November, the division was ordered to support the Italians against the Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
forces at the River Piave which then formed part of the Italian Front. In late October 1918 the 2nd Battalion captured the island of Grave di Papadopoli
A grave is a location where a dead body (typically that of a human, although sometimes that of an animal) is buried or interred after a funeral. Graves are usually located in special areas set aside for the purpose of burial, such as gravey ...
on the Piave River for which O'Connor received the Italian Silver Medal of Military Valor and a Bar
Bar or BAR may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bar (establishment), selling alcoholic beverages
* Candy bar
* Chocolate bar
Science and technology
* Bar (river morphology), a deposit of sediment
* Bar (tropical cyclone), a layer of cloud
* Bar (u ...
to his DSO.Papers of General Sir Richard O'ConnorAt the end of the war, O'Connor reverted to his rank of captain and served as regimental adjutant from April to December 1919.
Between the wars
O'Connor attended theStaff College, Camberley
Staff College, Camberley, Surrey, was a staff college for the British Army and the presidency armies of British India (later merged to form the Indian Army). It had its origins in the Royal Military College, High Wycombe, founded in 1799, which i ...
in 1920. O'Connor's other service in the years between the world wars included an appointment from 1921 to 1924 as brigade major of the Experimental Brigade (or 5 Brigade) under the command of J. F. C. Fuller
Major-General John Frederick Charles "Boney" Fuller (1 September 1878 – 10 February 1966) was a senior British Army officer, military historian, and strategist, known as an early theorist of modern armoured warfare, including categorising pr ...
, which was formed to test methods and procedures for using tanks and aircraft in co-ordination with infantry and artillery.
He returned to his old unit, the Cameronians (Scottish Rifles)
The Cameronians (Scottish Rifles) was a rifle regiment of the British Army, the only regiment of rifles amongst the Scottish regiments of infantry. It was formed in 1881 under the Childers Reforms by the amalgamation of the 26th Cameronian Reg ...
, as adjutant
Adjutant is a military appointment given to an officer who assists the commanding officer with unit administration, mostly the management of human resources in an army unit. The term is used in French-speaking armed forces as a non-commission ...
from February 1924 to 1925. From 1925 to 1927 he served as a company commander at Sandhurst.Keegan (2005), p. 199 He returned to the Staff College, Camberley as an instructor from October 1927 to January 1930. In 1930 O'Connor again served with the 1st Battalion, Cameronians (Scottish Rifles) in Egypt and from 1931 to 1932 in Lucknow, India. From April 1932 to January 1935 he was a general staff officer, grade 2 at the War Office. He attended the Imperial Defence College in London in 1935. In April 1936 O'Connor was promoted to full colonel
The colonel () in the United States Army, Marine Corps, Air Force and Space Force, is the most senior field-grade military officer rank, immediately above the rank of lieutenant colonel and just below the rank of brigadier general. Colonel i ...
and appointed temporary brigadier to assume command of the Peshawar Brigade
The Peshawar Brigade was an infantry brigade formation of the Indian Army during World War II. It was formed in December 1907, for service on the North West Frontier. During World War II it was normal practice for newly formed battalions to be po ...
in north west India. In September 1938 O'Connor was promoted to major-general and appointed General Officer Commanding 7th Infantry Division in Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
, along with the additional responsibility as Military Governor of Jerusalem. For his services in Palestine O'Connor was mentioned in despatches.
In August 1939, shortly before the outbreak of the Second World War, the 7th Division was transferred to the fortress at Mersa Matruh, Egypt, where O'Connor was concerned with defending the area against a potential attack from the massed forces of the Italian Tenth Army
The 10th Army ( it, 10ª Armata) was a field army of the Royal Italian Army, which fought in World War I and in Italian North Africa during World War II.
World War I Formation
After the Battle of Caporetto (November 1917) the Italian Army (Re ...
over the border in Libya. The 7th Division later converted to become the 6th Division in November 1939. He was appointed a Companion of the Order of the Bath
Companion may refer to:
Relationships Currently
* Any of several interpersonal relationships such as friend or acquaintance
* A domestic partner, akin to a spouse
* Sober companion, an addiction treatment coach
* Companion (caregiving), a caregive ...
in July 1940.
Second World War
Italian Offensive and Operation Compass
 Italy declared war on Britain and France on 10 June 1940 and, soon after, O'Connor was appointed commander of the Western Desert Force. He was tasked by
Italy declared war on Britain and France on 10 June 1940 and, soon after, O'Connor was appointed commander of the Western Desert Force. He was tasked by Lieutenant-General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the ...
Henry Maitland Wilson, commander of the British troops in Egypt, to push the Italian force out of Egypt, to protect the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
and British interests from attack.
On 13 September, Graziani struck: his leading divisions advanced sixty miles into Egypt where they reached the town of Sidi Barrani and, short of supplies, began to dig in. O'Connor then began to prepare for a counterattack. He had the 7th Armoured Division and the Indian 4th Infantry Division
The 4th Indian Infantry Division, also known as the Red Eagle Division, is an infantry division of the Indian Army. This division of the British Indian Army was formed in Egypt in 1939 during the Second World War. During the Second World War, ...
along with two brigades. British and Commonwealth troops in Egypt totalled around 36,000 men. The Italians had nearly five times as many troops along with hundreds more tanks and artillery pieces and the support of a much larger air force. Meanwhile, small raiding columns were sent out from the 7th Armoured and newly formed Long Range Desert Group to probe, harass, and disrupt the Italians (this marked the start of what became the Special Air Service
The Special Air Service (SAS) is a special forces unit of the British Army. It was founded as a regiment in 1941 by David Stirling and in 1950, it was reconstituted as a corps. The unit specialises in a number of roles including counter-terro ...
). The Royal Navy and Royal Air Force supported by bombarding enemy strongpoints, airfields and rear areas.Keegan (2005), p. 189
 During November, O'Connor was appointed an acting lieutenant-general in recognition of the increased size of his command.
The counteroffensive, Operation Compass, began on 8 December 1940. O'Connor's relatively small force of 31,000 men, 275 tanks and 120 artillery pieces, ably supported by an RAF wing and the Royal Navy, broke through a gap in the Italian defences at Sidi Barrani near the coast. The Desert Force cut a swath through the Italian rear areas, stitching its way between the desert and the coast, capturing strongpoint after strongpoint by cutting off and isolating them. The Italian guns proved to be no match for the heavy British Matilda tanks and their shells bounced off the armour. By mid-December the Italians had been pushed completely out of Egypt, leaving behind 38,000 prisoners and large stores of equipment.
The Desert Force paused to rest briefly before continuing the assault into Italian Libya against the remainder of Graziani's disorganised army. At that point, the Commander-in-Chief Middle East General Sir Archibald Wavell ordered the 4th Indian Division withdrawn to spearhead the invasion of Italian East Africa.Keegan (2005), p. 191 This veteran division was to be replaced by the inexperienced
During November, O'Connor was appointed an acting lieutenant-general in recognition of the increased size of his command.
The counteroffensive, Operation Compass, began on 8 December 1940. O'Connor's relatively small force of 31,000 men, 275 tanks and 120 artillery pieces, ably supported by an RAF wing and the Royal Navy, broke through a gap in the Italian defences at Sidi Barrani near the coast. The Desert Force cut a swath through the Italian rear areas, stitching its way between the desert and the coast, capturing strongpoint after strongpoint by cutting off and isolating them. The Italian guns proved to be no match for the heavy British Matilda tanks and their shells bounced off the armour. By mid-December the Italians had been pushed completely out of Egypt, leaving behind 38,000 prisoners and large stores of equipment.
The Desert Force paused to rest briefly before continuing the assault into Italian Libya against the remainder of Graziani's disorganised army. At that point, the Commander-in-Chief Middle East General Sir Archibald Wavell ordered the 4th Indian Division withdrawn to spearhead the invasion of Italian East Africa.Keegan (2005), p. 191 This veteran division was to be replaced by the inexperienced 6th Australian Division
The 6th Division was an infantry division of the Australian Army. It was raised briefly in 1917 during World War I, but was broken up to provide reinforcements before seeing action. It was not re-raised until the outbreak of World War II, when ...
, which, although tough, was untrained for desert warfare. Despite this setback, the offensive continued with minimal delay. By the end of 6 December the Australians besieged and took Bardia along with 40,000 more prisoners and 400 guns.
 In early January 1941, the Western Desert Force was redesignated XIII Corps. On 9 January, the offensive resumed. By 12 January the strategic fortress port of Tobruk was surrounded. On 22 January it fell and another 27,000 Italian
In early January 1941, the Western Desert Force was redesignated XIII Corps. On 9 January, the offensive resumed. By 12 January the strategic fortress port of Tobruk was surrounded. On 22 January it fell and another 27,000 Italian POW
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war ...
s were taken along with valuable supplies, food, and weapons. As Tobruk fell it was decided to have XIII Corps answerable directly to Wavell at HQ Middle East Command, removing HQ British troops Egypt from the chain of command. On 26 January the remaining Italian divisions in eastern Libya began to retreat to the northwest along the coast. O'Connor promptly moved to pursue and cut them off, sending his armour southwest through the desert in a wide flanking movement, while the infantry gave chase along the coast to the north. The lightly armoured advance units of 4th Armoured Brigade arrived at Beda Fomm before the fleeing Italians on 5 February, blocking the main coast road and their route of escape. Two days later, after a costly and failed attempt to break through the blockade, and with the main British infantry force fast bearing down on them from Benghazi
Benghazi () , ; it, Bengasi; tr, Bingazi; ber, Bernîk, script=Latn; also: ''Bengasi'', ''Benghasi'', ''Banghāzī'', ''Binghāzī'', ''Bengazi''; grc, Βερενίκη (''Berenice'') and ''Hesperides''., group=note (''lit. Son of he Ghazi ...
to the north, the demoralised, exhausted Italians unconditionally capitulated. O'Connor and Eric Dorman-Smith cabled back to Wavell, "Fox killed in the open..."
In two months, the XIII Corps/Western Desert Force had advanced over , destroyed an entire Italian army of ten divisions, taken over 130,000 prisoners, 400 tanks and 1,292 guns at the cost of 500 killed and 1,373 wounded. In recognition of this, O'Connor was made a Knight Commander of the Order of the Bath.
Reversal and capture
In a strategic sense, however, the victory of Operation Compass was not yet complete; the Italians still controlled most of Libya and possessed forces which would have to be dealt with. The Axis foothold in North Africa would remain a potential threat to Egypt and the Suez Canal so long as this situation continued. O'Connor was aware of this and urged Wavell to allow him to push on toTripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in ...
with all due haste to finish off the Italians. Wavell concurred as did Lieutenant-General Sir Henry Maitland Wilson, now the military governor of Cyrenaica, and XIII Corps resumed its advance. However, O'Connor's new offensive would prove short-lived: when the corps reached El Agheila, just to the southwest of Beda Fomm, Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from 1 ...
ordered the advance to halt there. The Axis had invaded Greece and Wavell was ordered to send all available forces there as soon as possible to oppose this. Wavell took the 6th Australian Division, along with part of 7th Armoured Division and most of the supplies and air support for this ultimately doomed operation. XIII Corps HQ was wound down and in February 1941 O'Connor was appointed General Officer Commanding-in-Chief the British Troops in Egypt
British Troops in Egypt was a command of the British Army.
History
A British Army commander was appointed in the late 19th century after the Anglo-Egyptian War in 1882. The British Army remained in Egypt throughout the First World War and, after t ...
.
Matters were soon to become much worse for the British. By March 1941, Hitler had dispatched General Erwin Rommel
Johannes Erwin Eugen Rommel () (15 November 1891 – 14 October 1944) was a German field marshal during World War II. Popularly known as the Desert Fox (, ), he served in the ''Wehrmacht'' (armed forces) of Nazi Germany, as well as servi ...
along with the Afrika Korps to bolster the Italians in Libya. Wavell and O'Connor now faced a formidable foe under a commander whose cunning, resourcefulness, and daring would earn him the nickname "the Desert Fox". Rommel wasted little time in launching his own offensive on 31 March. The inexperienced 2nd Armoured Division was soundly defeated and on 2 April Wavell came forward to review matters with Lieutenant-General Sir Philip Neame, by now the commander of British and Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
troops in Cyrenaica (Wilson having left to command the Allied expeditionary force in Greece). O'Connor was called forward and arrived from Cairo the next day, but declined to assume Neame's command because of his lack of familiarity with the prevailing conditions. However, he agreed to stay to advise.
On 6 April O'Connor and Neame, while travelling to their headquarters which had been withdrawn from Maraua to Timimi, were captured by a German patrol near Martuba.

Captivity and escape
O'Connor spent the next two and a half years as a prisoner of war, mainly at theCastello di Vincigliata
Vincigliata Castle (Italian: ''Castello di Vincigliata'') is a medieval castle which stands on a rocky hill to the east of Fiesole in the Italian region of Tuscany. In the mid-nineteenth century the building, which had fallen into a ruinous state ...
near Florence, Italy. Here he and Neame were in the company of such figures as Major-General Sir Adrian Carton de Wiart and Air Vice Marshal Owen Tudor Boyd. Although the conditions of their imprisonment were not unpleasant, the officers soon formed an escape club and began planning a break-out. Their first attempt, a simple attempt to climb over the castle walls, resulted in a month's solitary confinement. The second attempt, by an escape tunnel built between October 1942 and March 1943, had some success, with two New Zealander brigadiers, James Hargest and Reginald Miles, reaching Switzerland. O'Connor and Carton de Wiart, travelling on foot, were at large for a week but were captured near Bologna in the Po Valley. Once again, a month's solitary confinement was the result.
It was only after the Italian surrender in September 1943 that the final, successful, attempt was made. With help from the Italian resistance movement
The Italian resistance movement (the ''Resistenza italiana'' and ''la Resistenza'') is an umbrella term for the Italian resistance groups who fought the occupying forces of Nazi Germany and the fascist collaborationists of the Italian Social ...
, Boyd, O'Connor and Neame escaped while being transferred from Vincigliati. After a failed rendezvous with a submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
, they arrived by boat at Termoli
Termoli (Neapolitan language, Molisano: ''Térmëlë'') is a town and ''comune'' (municipality) on the south Adriatic coast of Italy, in the province of Campobasso, region of Molise. It has a population of around 32,000, having expanded quickly af ...
, then went on to Bari
Bari ( , ; nap, label= Barese, Bare ; lat, Barium) is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Bari and of the Apulia region, on the Adriatic Sea, southern Italy. It is the second most important economic centre of mainland Southern Italy a ...
where they were welcomed as guests by General Sir Harold Alexander, commanding the Allied Armies in Italy (AAI), then fighting on the Italian Front, along with the American General Dwight D. Eisenhower, on 21 December 1943. Upon his return to Britain, O'Connor was presented with the knighthood he had been awarded in 1941 and promoted to lieutenant-general. Montgomery suggested that O'Connor be his successor as British Eighth Army
The Eighth Army was an Allied field army formation of the British Army during the Second World War, fighting in the North African and Italian campaigns. Units came from Australia, British India, Canada, Czechoslovakia, Free French Forces, ...
commander, but that post was instead given to Oliver Leese and O'Connor was given a corps to command.
VIII Corps and Normandy
 On 21 January 1944 O'Connor became commander of
On 21 January 1944 O'Connor became commander of VIII Corps 8th Corps, Eighth Corps, or VIII Corps may refer to:
* VIII Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperial French army during the Napoleonic Wars
*VIII Army Corps (German Confederation)
* VIII Corps (German Empire), a unit of the Imperial German Army ...
, which consisted of the Guards Armoured Division, 11th Armoured Division
The 11th Armoured Division was an armoured division of the British Army which was created in March 1941 during the Second World War. The division was formed in response to the unanticipated success of the German panzer divisions. The 11th Armou ...
, 15th (Scottish) Infantry Division
The 15th (Scottish) Infantry Division was an infantry division of the British Army that served during the Second World War. It was raised on 2 September 1939, the day before war was declared, as part of the Territorial Army (TA) and served in ...
, along with 6th Guards Tank Brigade, 8th Army Group Royal Artillery and 2nd Household Cavalry Regiment
The Household Cavalry Composite Regiment was a temporary, wartime-only, cavalry regiment of the British Army consisting of personnel drawn from the 1st Life Guards, 2nd Life Guards and Royal Horse Guards. It was active in 1882 for service in the ...
. The corps formed part of the British Second Army, commanded by Lieutenant-General Miles Dempsey, which itself was part of the Anglo-Canadian 21st Army Group
The 21st Army Group was a British headquarters formation formed during the Second World War. It controlled two field armies and other supporting units, consisting primarily of the British Second Army and the First Canadian Army. Established in ...
, commanded by General Sir Bernard Montgomery, a friend who had also been a fellow instructor at the Staff College, Camberley in the 1920s, in addition to having served together in Palestine some years before. O'Connor's new command was to take part in Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allies of World War II, Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Front (World War II), Western Europe during World War II. The operat ...
, the Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
invasion of German-occupied France
The Military Administration in France (german: Militärverwaltung in Frankreich; french: Occupation de la France par l'Allemagne) was an interim occupation authority established by Nazi Germany during World War II to administer the occupied zo ...
, although it was not scheduled for the initial landings as it was to form part of the second wave to go ashore.
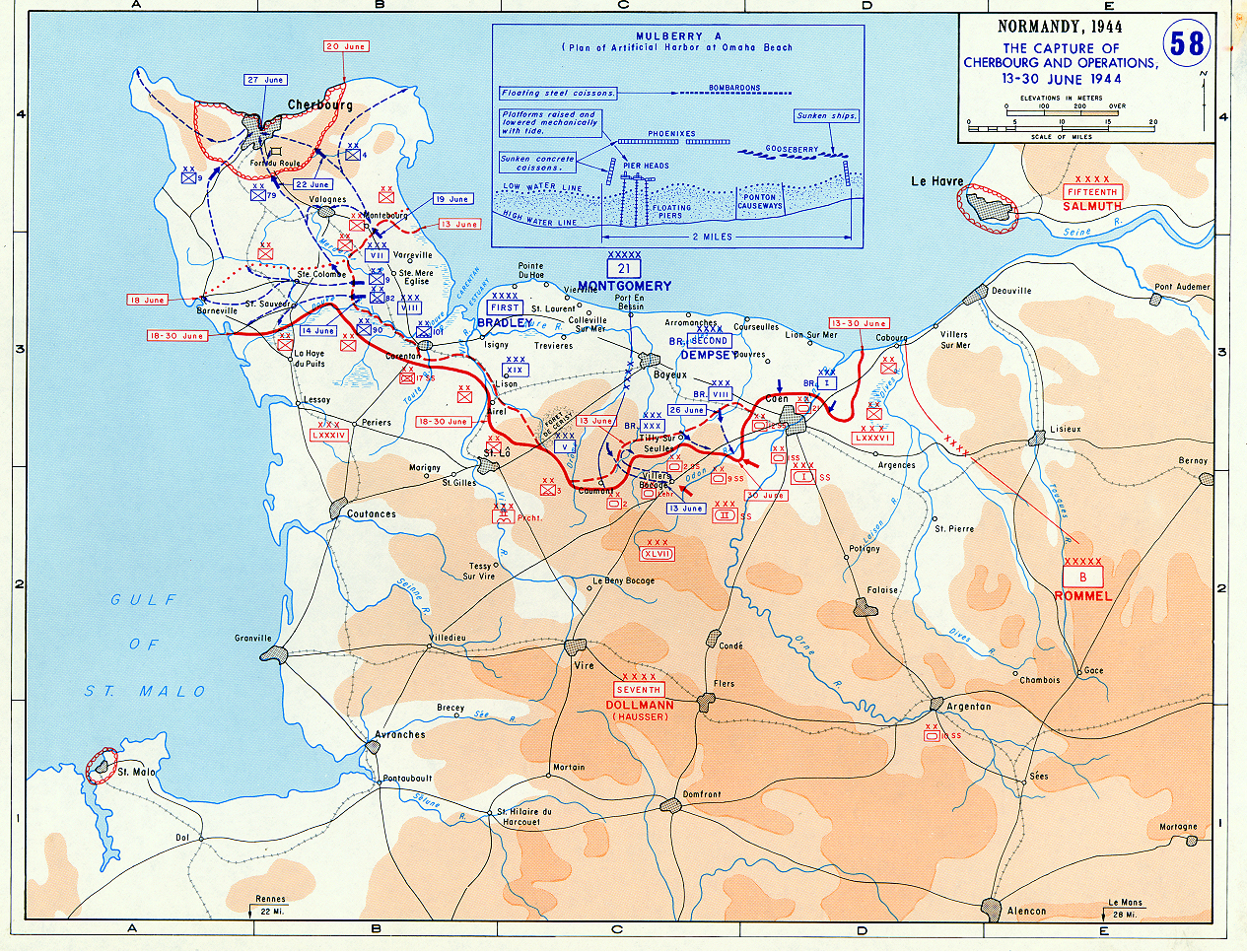
On 11 June 1944, five days after the initial landings in Normandy, O'Connor and the leading elements of VIII Corps arrived in Normandy in the sector around Caen
Caen (, ; nrf, Kaem) is a commune in northwestern France. It is the prefecture of the department of Calvados. The city proper has 105,512 inhabitants (), while its functional urban area has 470,000,hard fighting during the next few weeks. O'Connor's first mission (with the
43rd (Wessex) Infantry Division
The 43rd (Wessex) Infantry Division was an infantry division of Britain's Territorial Army (TA). The division was first formed in 1908, as the Wessex Division. During the First World War, it was broken-up and never served as a complete formatio ...
under command, replacing the Guards Armoured Division) was to mount Operation Epsom, a break out from the bridgehead established by the 3rd Canadian Infantry Division
The 3rd Canadian Division is a formation of the Canadian Army responsible for the command and mobilization of all army units in the provinces of Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta and British Columbia, as well as all units extending westwards from th ...
, cross the Odon and Orne rivers, then secure the high-ground positions northeast of Bretteville-sur-Laize and cut Caen off from the south. The break-out and river crossings were accomplished promptly. The army group commander, Montgomery, congratulated O'Connor and his VIII Corps on their success. But cutting off Caen would prove much harder. VIII Corps was pushed back over the Orne. O'Connor tried to re-establish a bridgehead during Operation Jupiter with the 43rd (Wessex) Division, but met with little success. Although the operation had failed to achieve its tactical objectives, Montgomery was pleased with the strategic benefits in the commitment and fixing of the German armoured reserves to the Caen sector.
After being withdrawn into reserve on 12 July, the next major action for VIII Corps would be Operation Goodwood
Operation Goodwood was a British offensive during the Second World War, which took place between 18 and 20 July 1944 as part of the larger battle for Caen in Normandy, France. The objective of the operation was a limited attack to the south, ...
, for which the corps was stripped of its infantry divisions but had a third armoured division ( 7th Armoured Division) attached. The attack began on 18 July with a massive aerial bombardment by the 9th USAAF, and ended on 20 July with a three-pronged drive to capture Bras and Hubert-Folie
Hubert-Folie () is a former commune in the Calvados department in the Normandy region in northwestern France. On 1 January 2019, it was merged into the new commune Castine-en-Plaine.Fontenay on the left, and Bourguébus Ridge in the centre. However, the attack ground to a halt in pouring rain, turning the battlefield into a quagmire, with the major objectives still not taken, notably the Bourguebus Ridge which was the key to any break-out.
Restored to its pre-invasion formation but with
A swift drive was followed by fierce fighting to the south during the first two days of the advance, with both sides taking heavy losses. As the allies prepared to pursue the Germans from France, O'Connor learned that VIII Corps would not take part in this phase of the campaign. VIII Corps was placed in reserve, and its transport used to supply XXX Corps and
(O'Connor, 5/3/41- 5/3/44 Aug 24, 26 1944)
 O'Connor remained in command of VIII Corps, for the time being, and was given the task of supporting Lieutenant-General Brian Horrocks' XXX Corps in
O'Connor remained in command of VIII Corps, for the time being, and was given the task of supporting Lieutenant-General Brian Horrocks' XXX Corps in
Richard O’Connor Desert War.netImperial War Museum Interview
* , - , - , - , - , - , - , - , - , - , - {{DEFAULTSORT:OConnor, Richard 1889 births 1981 deaths Alumni of the Royal College of Defence Studies British Army generals of World War II British Army personnel of World War I British escapees British military personnel of the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine British World War II prisoners of war Cameronians officers Commandeurs of the Légion d'honneur Companions of the Distinguished Service Order Escapees from Italian detention Graduates of the Royal Military College, Sandhurst Graduates of the Staff College, Camberley Honourable Artillery Company officers Knights Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath Knights of the Thistle Lords High Commissioner to the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland Lord-Lieutenants of Ross and Cromarty People educated at Wellington College, Berkshire People from Srinagar Recipients of the Croix de Guerre (France) Recipients of the Military Cross Recipients of the Silver Medal of Military Valor World War II prisoners of war held by Italy Academics of the Royal Military College, Sandhurst Academics of the Staff College, Camberley
British 3rd Infantry Division
The 3rd (United Kingdom) Division is a regular army division of the British Army. It was created in 1809 by Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, as part of the Anglo-Portuguese Army, for service in the Peninsular War, and was known as the ...
attached, the corps was switched to the southwest of Caen to take part in Operation Bluecoat. 15th (Scottish) Division attacked towards Vire
Vire () is a town and a former commune in the Calvados department in the Normandy region in northwestern France. On 1 January 2016, it was merged into the new commune of Vire Normandie.
Geography
The town is located on the river Vire. Much of it ...
to the east and west of Bois du Homme in order to facilitate the American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
advance in Operation Cobrabr>(O'Connor, 5/3/25 July 29 1944)A swift drive was followed by fierce fighting to the south during the first two days of the advance, with both sides taking heavy losses. As the allies prepared to pursue the Germans from France, O'Connor learned that VIII Corps would not take part in this phase of the campaign. VIII Corps was placed in reserve, and its transport used to supply XXX Corps and
XII Corps 12th Corps, Twelfth Corps, or XII Corps may refer to:
* 12th Army Corps (France)
* XII Corps (Grande Armée), a corps of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* XII (1st Royal Saxon) Corps, a unit of the Imperial German Army
* XII (Ro ...
. His command was reduced in mid-August, with the transfer of the Guards Armoured Divisions and 11th Armoured Division to XXX Corps and 15th (Scottish) Division to XII Corps. While in reserve, O'Connor maintained an active correspondence with Montgomery, Hobart
Hobart ( ; Nuennonne/Palawa kani: ''nipaluna'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian island state of Tasmania. Home to almost half of all Tasmanians, it is the least-populated Australian state capital city, and second-small ...
and others, making suggestions for improvements of armoured vehicles and addressing various other problems such as combat fatigue
Combat stress reaction (CSR) is acute behavioral disorganization as a direct result of the trauma of war. Also known as "combat fatigue", "battle fatigue", or "battle neurosis", it has some overlap with the diagnosis of acute stress reaction used ...
. Some of his recommendations were followed up; such as for mounting "rams
In engineering, RAMS (reliability, availability, maintainability and safety)hedgerow
A hedge or hedgerow is a line of closely spaced shrubs and sometimes trees, planted and trained to form a barrier or to mark the boundary of an area, such as between neighbouring properties. Hedges that are used to separate a road from adjoini ...
countr(O'Connor, 5/3/41- 5/3/44 Aug 24, 26 1944)
Operation Market Garden, India and afterwards
 O'Connor remained in command of VIII Corps, for the time being, and was given the task of supporting Lieutenant-General Brian Horrocks' XXX Corps in
O'Connor remained in command of VIII Corps, for the time being, and was given the task of supporting Lieutenant-General Brian Horrocks' XXX Corps in Operation Market Garden
Operation Market Garden was an Allies of World War II, Allied military operation during the World War II, Second World War fought in the Netherlands from 17 to 27 September 1944. Its objective was to create a Salient (military), salient into G ...
, the plan by Montgomery to establish a bridgehead across the Rhine in the Netherlands. Following their entry into Weert at the end of September, VIII Corps prepared for and took part in Operation Aintree
The Battle of Overloon was a battle fought in the Second World War battle between Allied forces and the German Army which took place in and around the village of Overloon in the south-east of the Netherlands between 30 September and 18 October 1 ...
, the advance towards Venray and Venlo beginning on 12 October.
However, on 27 November O'Connor was removed from his post and was ordered to take over from Lieutenant-General Sir Mosley Mayne as GOC-in-C, Eastern Command, India. Smart's account says that Montgomery prompted the move for, "not being ruthless enough with his American subordinates", although Mead states that the initiative was taken by Field Marshal Sir Alan Brooke, the Chief of the Imperial General Staff (CIGS), but Montgomery made no attempt to retain O'Connor. He was succeeded as GOC VIII Corps by Major-General Evelyn Barker, a much younger man and formerly the GOC of the 49th (West Riding) Infantry Division
The 49th (West Riding) Infantry Division was an infantry division of the British Army. The division fought in the First World War in the trenches of the Western Front, in the fields of France and Flanders. During the Second World War, the divis ...
who had been one of O'Connor's students at the Staff College, Camberley in the late 1920s. This marked the end of a long and distinguished combat career, although the new job was an important one, controlling the lines of communication of the Fourteenth Army. O'Connor was mentioned in despatches for the thirteenth and final time of his career on 22 March 1945.
Having been promoted to full general in April 1945, O'Connor was appointed GOC-in-C North Western Army
The Northern Command is a Command of the Indian Army. It was originally formed as the Northern Army of the British Indian Army in 1908. It was scrapped upon India's independence in 1947 and later re-raised in 1972. Currently, the XIV Corps (Leh) ...
in India in October that year (the formation was renamed Northern Command in November of that year). From 1946 to 1947 he was Adjutant-General to the Forces and aide-de-camp general to the King. His career as adjutant general was to be short-lived, however. After a disagreement over a cancelled demobilisation for troops stationed in the Far East, O'Connor offered his resignation in September 1947, which was accepted. Montgomery, by then the CIGS in succession to Brooke, maintained that he had been sacked, rather than resigned, for being, "not up to the job." Not long after this he was installed as a Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath
The Most Honourable Order of the Bath is a British order of chivalry founded by George I on 18 May 1725. The name derives from the elaborate medieval ceremony for appointing a knight, which involved bathing (as a symbol of purification) as one ...
.
In retirement
O'Connor retired in 1948 at the age of fifty-eight. However, he maintained his links with the army and took on other responsibilities. He was Commandant of the Army Cadet Force in Scotland from 1948 to 1959; Colonel ofthe Cameronians
The Cameronians (Scottish Rifles) was a rifle regiment of the British Army, the only regiment of rifles amongst the Scottish regiment, Scottish regiments of infantry. It was formed in 1881 under the Childers Reforms by the amalgamation of the 26t ...
, 1951 to 1954; Lord lieutenant
A lord-lieutenant ( ) is the British monarch's personal representative in each lieutenancy area of the United Kingdom. Historically, each lieutenant was responsible for organising the county's militia. In 1871, the lieutenant's responsibility ...
of Ross and Cromarty
Ross and Cromarty ( gd, Ros agus Cromba), sometimes referred to as Ross-shire and Cromartyshire, is a variously defined area in the Highlands and Islands of Scotland. There is a registration county and a lieutenancy area in current use, the latt ...
from 1955 to 1964 and served as Lord High Commissioner to the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland in 1964. His first wife, Jean, died in 1959, and in 1963 he married Dorothy Russell.
In July 1971, he was created Knight of the Order of the Thistle
The Most Ancient and Most Noble Order of the Thistle is an Chivalric order, order of chivalry associated with Scotland. The current version of the Order was founded in 1687 by James II of England, King James VII of Scotland, who asserted that h ...
. O’Connor was interviewed concerning North African operations in episode 8, "The Desert: North Africa (1940–1943)”, of the acclaimed British documentary television series, '' The World at War.'' O'Connor died in London on 17 June 1981, just two months shy of his 92nd birthday.
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * *External links
* *Richard O’Connor Desert War.net
* , - , - , - , - , - , - , - , - , - , - {{DEFAULTSORT:OConnor, Richard 1889 births 1981 deaths Alumni of the Royal College of Defence Studies British Army generals of World War II British Army personnel of World War I British escapees British military personnel of the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine British World War II prisoners of war Cameronians officers Commandeurs of the Légion d'honneur Companions of the Distinguished Service Order Escapees from Italian detention Graduates of the Royal Military College, Sandhurst Graduates of the Staff College, Camberley Honourable Artillery Company officers Knights Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath Knights of the Thistle Lords High Commissioner to the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland Lord-Lieutenants of Ross and Cromarty People educated at Wellington College, Berkshire People from Srinagar Recipients of the Croix de Guerre (France) Recipients of the Military Cross Recipients of the Silver Medal of Military Valor World War II prisoners of war held by Italy Academics of the Royal Military College, Sandhurst Academics of the Staff College, Camberley