Rice starch on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Starch or amylum is a
Starch or amylum is a
 In addition to starchy plants consumed directly, by 2008 66 million tonnes of starch were being produced per year worldwide. In 2011, production was increased to 73 million ton.
In the EU the starch industry produced about 11 million tonnes in 2011, with around 40% being used for industrial applications and 60% for food uses, most of the latter as
In addition to starchy plants consumed directly, by 2008 66 million tonnes of starch were being produced per year worldwide. In 2011, production was increased to 73 million ton.
In the EU the starch industry produced about 11 million tonnes in 2011, with around 40% being used for industrial applications and 60% for food uses, most of the latter as
 Most green plants store energy as starch, which is packed into semicrystalline granules. The extra glucose is changed into starch which is more complex than the glucose produced by plants. Young plants live on this stored energy in their roots, seeds, and fruits until it can find suitable soil in which to grow. An exception is the family
Most green plants store energy as starch, which is packed into semicrystalline granules. The extra glucose is changed into starch which is more complex than the glucose produced by plants. Young plants live on this stored energy in their roots, seeds, and fruits until it can find suitable soil in which to grow. An exception is the family
ADP-glucose
(analogous to starch). In addition to starch synthesis in plants, starch can be synthesized from non-food starch mediated by an enzyme cocktail. In this cell-free biosystem, beta-1,4-glycosidic bond-linked cellulose is partially hydrolyzed to
 While amylose was thought to be completely unbranched, it is now known that some of its molecules contain a few branch points.
Amylose is a much smaller molecule than amylopectin. About one quarter of the mass of stored starch in plants consist of amylose, although there are about 150 times more amylose than amylopectin molecules.
Accumulated starch within plants is stored in semi-crystalline granules. Each plant species has a unique starch granular size: rice starch is relatively small (about 2 μm),
While amylose was thought to be completely unbranched, it is now known that some of its molecules contain a few branch points.
Amylose is a much smaller molecule than amylopectin. About one quarter of the mass of stored starch in plants consist of amylose, although there are about 150 times more amylose than amylopectin molecules.
Accumulated starch within plants is stored in semi-crystalline granules. Each plant species has a unique starch granular size: rice starch is relatively small (about 2 μm),
 A
A
 The starch industry extracts and refines starches from seeds, roots and tubers, by wet grinding, washing, sieving and drying. Today, the main commercial refined starches are cornstarch, tapioca, arrowroot, and wheat, rice, and
The starch industry extracts and refines starches from seeds, roots and tubers, by wet grinding, washing, sieving and drying. Today, the main commercial refined starches are cornstarch, tapioca, arrowroot, and wheat, rice, and


 Starch can be hydrolyzed into simpler carbohydrates by acids, various
Starch can be hydrolyzed into simpler carbohydrates by acids, various



CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
information for workers {{Authority control Starch, Nutrition Carbohydrates Edible thickening agents Excipients Printing
polymeric
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic an ...
carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ma ...
consisting of numerous glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
units joined by glycosidic bond
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
A glycosidic bond is formed between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group ...
s. This polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wa ...
is produced by most green plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets, and is contained in large amounts in staple food
A staple food, food staple, or simply a staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for a given person or group of people, supplying a large fraction of energy needs and ...
s such as wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
es, maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
(corn), rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
, and cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively ...
(manioc).
Pure starch is a white, tasteless and odorless powder that is insoluble in cold water or alcohol. It consists of two types of molecules: the linear and helical
Helical may refer to:
* Helix, the mathematical concept for the shape
* Helical engine, a proposed spacecraft propulsion drive
* Helical spring, a coilspring
* Helical plc, a British property company, once a maker of steel bar stock
* Helicoil
A t ...
amylose
Amylose is a polysaccharide made of α-D-glucose units, bonded to each other through α(1→4) glycosidic bonds. It is one of the two components of starch, making up approximately 20–30%. Because of its tightly packed helical structure, amylose ...
and the branched amylopectin Amylopectin is a water-insoluble polysaccharide and highly branched polymer of α-glucose units found in plants. It is one of the two components of starch, the other being amylose.
Plants store starch within specialized organelles called amylopl ...
. Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin by weight. Glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one o ...
, the energy reserve of animals, is a more highly branched version of amylopectin.
In industry, starch is often converted into sugars, for example by malt
Malt is germinated cereal grain that has been dried in a process known as " malting". The grain is made to germinate by soaking in water and is then halted from germinating further by drying with hot air.
Malted grain is used to make beer, wh ...
ing. These sugars may be fermented
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
to produce ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl ...
in the manufacture of beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
, whisky
Whisky or whiskey is a type of distilled alcoholic beverage made from fermented grain mash. Various grains (which may be malted) are used for different varieties, including barley, corn, rye, and wheat. Whisky is typically aged in wooden c ...
and biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. According to the United States Energy Information Administration (E ...
. In addition, sugars produced from processed starch are used in many processed foods.
Mixing most starches in warm water produces a paste, such as wheatpaste
Wheat paste (also known as flour and water paste, flour paste, or simply paste) is a gel or liquid adhesive made from wheat flour or starch and water. It has been used since antiquity for various arts and crafts such as book binding, découpag ...
, which can be used as a thickening, stiffening or gluing agent. The principle non-food, industrial use of starch is as an adhesive in the papermaking
Papermaking is the manufacture of paper and cardboard, which are used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes. Today almost all paper is made using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a speciali ...
process. A similar paste, , can be applied to certain textile goods before ironing to stiffen them.
Etymology
The word "starch" is from its Germanic root with the meanings "strong, stiff, strengthen, stiffen". Modern German ''Stärke'' (strength) is related and referring for centuries main application, the use in textile:sizing
Sizing or size is a substance that is applied to, or incorporated into, other materials—especially papers and textiles—to act as a protective filler or glaze. Sizing is used in papermaking and textile manufacturing to change the absorption ...
yarn
Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, used in sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, ropemaking, and the production of textiles. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern manufact ...
for weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal th ...
and starching linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong, absorbent, and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. It also ...
. The Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
term for starch, "amylon" (ἄμυλον), which means "not milled", is also related. It provides the root amyl
Amyl may refer to:
* Amylum or starch, a carbohydrate
** Amylopectin, a polymer of glucose found in plants; one of two components of starch
** Amylose, a helical polymer made of α-D-glucose units; one of two components of starch
* Pentyl, a five- ...
, which is used as a prefix for several 5-carbon compounds related to or derived from starch (e.g. amyl alcohol
An amyl alcohol is any of eight alcohols with the formula C5H12O. A mixture of pentyl, amyl alcohols (also called amyl alcohol) can be obtained from fusel alcohol. Amyl alcohol is used as a solvent and in esterification, by which is produced amyl a ...
).
History
Starch grains from therhizome
In botany and dendrology, a rhizome (; , ) is a modified subterranean plant stem that sends out roots and shoots from its nodes. Rhizomes are also called creeping rootstalks or just rootstalks. Rhizomes develop from axillary buds and grow hori ...
s of ''Typha
''Typha'' is a genus of about 30 species of monocotyledonous flowering plants in the family Typhaceae. These plants have a variety of common names, in British English as bulrush or reedmace, in American English as reed, cattail, or punks, in A ...
'' (cattails, bullrushes) as flour
Flour is a powder made by grinding raw grains, roots, beans, nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredient of bread, which is a staple food for many culture ...
have been identified from grinding stone
Millstones or mill stones are stones used in gristmills, for grinding wheat or other grains. They are sometimes referred to as grindstones or grinding stones.
Millstones come in pairs: a convex stationary base known as the ''bedstone'' and ...
s in Europe dating back to 30,000 years ago. Starch grains from sorghum
''Sorghum'' () is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family (Poaceae). Some of these species are grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species is grown for grain, while many othe ...
were found on grind stones in caves in Ngalue, Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
dating up to 100,000 years ago.
Pure extracted wheat starch paste was used in Ancient Egypt possibly to glue papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, '' Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to a ...
. The extraction of starch is first described in the '' Natural History'' of Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
around AD 77–79. Romans used it also in cosmetic
Cosmetic may refer to:
*Cosmetics, or make-up, substances to enhance the beauty of the human body, apart from simple cleaning
*Cosmetic, an adjective describing beauty, aesthetics, or appearance, especially concerning the human body
*Cosmetic, a t ...
creams, to powder the hair and to thicken sauces. Persians and Indians used it to make dishes similar to gothumai wheat halva
Halva (also halvah, halwa, and other spellings, Persian : حلوا) is a type of confectionery originating from Persia and widely spread throughout the Middle East. The name is used for a broad variety of recipes, generally a thick paste made f ...
. Rice starch as surface treatment of paper has been used in paper production in China since 700 CE.
Starch industry
 In addition to starchy plants consumed directly, by 2008 66 million tonnes of starch were being produced per year worldwide. In 2011, production was increased to 73 million ton.
In the EU the starch industry produced about 11 million tonnes in 2011, with around 40% being used for industrial applications and 60% for food uses, most of the latter as
In addition to starchy plants consumed directly, by 2008 66 million tonnes of starch were being produced per year worldwide. In 2011, production was increased to 73 million ton.
In the EU the starch industry produced about 11 million tonnes in 2011, with around 40% being used for industrial applications and 60% for food uses, most of the latter as glucose syrup
Glucose syrup, also known as confectioner's glucose, is a syrup made from the hydrolysis of starch. Glucose is a sugar. Maize (corn) is commonly used as the source of the starch in the US, in which case the syrup is called "corn syrup", but glucos ...
s. In 2017 EU production was 11 million ton of which 9,4 million ton was consumed in the EU and of which 54% were starch sweeteners.
The US produced about 27.5 million tons of starch in 2017, of which about 8.2 million tons was high fructose syrup
High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), also known as glucose–fructose, isoglucose and glucose–fructose syrup, is a sweetener made from corn starch. As in the production of conventional corn syrup, the starch is broken down into glucose by enzym ...
, 6.2 million tons was glucose syrups, and 2.5 million tons were starch products. The rest of the starch was used for producing ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl ...
(1.6 billion gallons).
Energy store of plants
 Most green plants store energy as starch, which is packed into semicrystalline granules. The extra glucose is changed into starch which is more complex than the glucose produced by plants. Young plants live on this stored energy in their roots, seeds, and fruits until it can find suitable soil in which to grow. An exception is the family
Most green plants store energy as starch, which is packed into semicrystalline granules. The extra glucose is changed into starch which is more complex than the glucose produced by plants. Young plants live on this stored energy in their roots, seeds, and fruits until it can find suitable soil in which to grow. An exception is the family Asteraceae
The family Asteraceae, alternatively Compositae, consists of over 32,000 known species of flowering plants in over 1,900 genera within the order Asterales. Commonly referred to as the aster, daisy, composite, or sunflower family, Compositae w ...
(asters, daisies and sunflowers), where starch is replaced by the fructan
A fructan is a polymer of fructose molecules. Fructans with a short chain length are known as fructooligosaccharides. Fructans can be found in over 12% of the angiosperms including both monocots and dicots such as agave, artichokes, asparagus, leek ...
inulin
Inulins are a group of naturally occurring polysaccharides produced by many types of plants, industrially most often extracted from chicory. The inulins belong to a class of dietary fibers known as fructans. Inulin is used by some plants as a mea ...
. Inulin-like fructans are also present in grasses such as wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, in onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus ''Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onion ...
s and garlic
Garlic (''Allium sativum'') is a species of bulbous flowering plant in the genus ''Allium''. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chive, Allium fistulosum, Welsh onion and Allium chinense, Chinese onion. It is native to South A ...
, bananas
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", distinguis ...
, and asparagus
Asparagus, or garden asparagus, folk name sparrow grass, scientific name ''Asparagus officinalis'', is a perennial flowering plant species in the genus ''Asparagus''. Its young shoots are used as a spring vegetable.
It was once classified in ...
.
In photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
, plants use light energy to produce glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
from carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
. The glucose is used to generate the chemical energy required for general metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
, to make organic compounds such as nucleic acids
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main clas ...
, lipids
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
, proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
and structural polysaccharides such as cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
, or is stored in the form of starch granules, in amyloplast
Amyloplasts are a type of plastid, double-enveloped organelles in plant cells that are involved in various biological pathways. Amyloplasts are specifically a type of leucoplast, a subcategory for colorless, non-pigment-containing plastids. Amylopl ...
s. Toward the end of the growing season, starch accumulates in twigs of trees near the buds. Fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particu ...
, seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiospe ...
s, rhizome
In botany and dendrology, a rhizome (; , ) is a modified subterranean plant stem that sends out roots and shoots from its nodes. Rhizomes are also called creeping rootstalks or just rootstalks. Rhizomes develop from axillary buds and grow hori ...
s, and tuber
Tubers are a type of enlarged structure used as storage organs for nutrients in some plants. They are used for the plant's perennation (survival of the winter or dry months), to provide energy and nutrients for regrowth during the next growing ...
s store starch to prepare for the next growing season.
Green algae and land-plants store their starch in the plastid
The plastid (Greek: πλαστός; plastós: formed, molded – plural plastids) is a membrane-bound organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosy ...
s, while red algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority ...
, glaucophyte
The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of unicellular algae found in freshwater and moist terrestrial environments, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. The stated number of spe ...
s, cryptomonad
The cryptomonads (or cryptophytes) are a group of algae, most of which have plastids. They are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterio ...
s, dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...
s and the parasitic apicomplexa
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia) are a large phylum of parasitic alveolates. Most of them possess a unique form of organelle that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplast, and an apical complex structure. T ...
store a similar type of polysaccharide called floridean starch
Floridean starch is a type of a storage glucan found in glaucophytes and in red algae (or rhodophytes), in which it is usually the primary sink for fixed carbon from photosynthesis. It is found in grains or granules in the cell's cytoplasm and is ...
in their cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells (intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
or periplast The periplast is one of three types of cell-covering of three classes of algae. The ''Cryptomonads'' have the periplast covering. The ''Dinophyceae'' have a type called the amphiesma, and the ''Euglena'' covering is the pellicle.
Structure
The per ...
.
Glucose is soluble in water, hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are no ...
, binds with water and then takes up much space and is osmotically active; glucose in the form of starch, on the other hand, is not soluble, therefore osmotically inactive and can be stored much more compactly. The semicrystalline granules generally consist of concentric layers of amylose and amylopectin which can be made bioavailable upon cellular demand in the plant.
Glucose molecules are bound in starch by the easily hydrolyzed
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
alpha bonds. The same type of bond is found in the animal reserve polysaccharide glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one o ...
. This is in contrast to many structural polysaccharides such as chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
, cellulose and peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most ...
, which are bound by beta bonds and are much more resistant to hydrolysis.
Biosynthesis
Plants produce starch by first convertingglucose 1-phosphate
Glucose 1-phosphate (also called cori ester) is a glucose molecule with a phosphate group on the 1'-carbon. It can exist in either the α- or β- anomeric form.
Reactions of α-glucose 1-phosphate Catabolic
In glycogenolysis, it is the direct pr ...
to ADP-glucose using the enzyme glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase
In enzymology, a glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes the chemical reaction
:ATP + alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate \rightleftharpoons diphosphate + ADP-glucose
Thus, the two substrate (biochemistry), subst ...
. This step requires energy in the form of ATP. The enzyme starch synthase
In enzymology, a starch synthase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
:ADP-glucose + (1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl)n \rightleftharpoons ADP + (1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl)n+1
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ADP-glucose and a chain ...
then adds the ADP-glucose via a 1,4-alpha glycosidic bond
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
A glycosidic bond is formed between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group ...
to a growing chain of glucose residues, liberating ADP and creating amylose. The ADP-glucose is almost certainly added to the non-reducing end of the amylose polymer, as the UDP-glucose is added to the non-reducing end of glycogen during glycogen synthesis.
Starch branching enzyme
1,4-alpha-glucan-branching enzyme, also known as brancher enzyme or glycogen-branching enzyme is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''GBE1'' gene.
Glycogen branching enzyme is an enzyme that adds branches to the growing glycogen molecul ...
introduces 1,6-alpha glycosidic bonds between the amylose chains, creating the branched amylopectin. The starch debranching enzyme isoamylase
Isoamylase (, ''debranching enzyme'', ''glycogen alpha-1,6-glucanohydrolase'') is an enzyme with systematic name ''glycogen 6-alpha-D-glucanohydrolase''. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
: Hydrolysis of (1->6)-alpha-D-glucosi ...
removes some of these branches. Several isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isof ...
s of these enzymes exist, leading to a highly complex synthesis process.
Glycogen and amylopectin have similar structure, but the former has about one branch point per ten 1,4-alpha bonds, compared to about one branch point per thirty 1,4-alpha bonds in amylopectin. Amylopectin is synthesized from ADP-glucose while mammals and fungi synthesize glycogen from UDP-glucose
Uridine diphosphate glucose (uracil-diphosphate glucose, UDP-glucose) is a nucleotide sugar. It is involved in glycosyltransferase reactions in metabolism.
Functions
UDP-glucose is used in nucleotide sugar metabolism as an activated form of glu ...
; for most cases, bacteria synthesize glycogen froADP-glucose
(analogous to starch). In addition to starch synthesis in plants, starch can be synthesized from non-food starch mediated by an enzyme cocktail. In this cell-free biosystem, beta-1,4-glycosidic bond-linked cellulose is partially hydrolyzed to
cellobiose
Cellobiose is a disaccharide with the formula (C6H7(OH)4O)2O. It is classified as a reducing sugar. In terms of its chemical structure, it is derived from the condensation of a pair of β-glucose molecules forming a β(1→4) bond. It can be hyd ...
. Cellobiose phosphorylase
In enzymology, a cellobiose phosphorylase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
:cellobiose + phosphate \rightleftharpoons alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate + D-glucose
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are cellobiose and phospha ...
cleaves to glucose 1-phosphate and glucose; the other enzyme—potato alpha-glucan phosphorylase can add a glucose unit from glucose 1-phosphorylase to the non-reducing ends of starch. In it, phosphate is internally recycled. The other product, glucose, can be assimilated by a yeast. This cell-free bioprocessing does not need any costly chemical and energy input, can be conducted in aqueous solution, and does not have sugar losses.
Degradation
Starch is synthesized in plant leaves during the day and stored as granules; it serves as an energy source at night. The insoluble, highly branched starch chains have to bephosphorylated
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, whi ...
in order to be accessible for degrading enzymes. The enzyme glucan, water dikinase
In enzymology, an alpha-glucan, water dikinase () is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes the chemical reaction
:ATP + alpha-glucan + H2O \rightleftharpoons AMP + phospho-alpha-glucan + phosphate
The 3 substrate (biochemistry), substrates of this ...
(GWD) phosphorylates at the C-6 position of a glucose molecule, close to the chains 1,6-alpha branching bonds. A second enzyme, phosphoglucan, water dikinase
In enzymology, a phosphoglucan, water dikinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
:ATP + hospho-alpha-glucan+ H2O \rightleftharpoons AMP + O-phospho- hospho-alpha-glucan+ phosphate
The 3 substrates of this enzyme are ATP, p ...
(PWD) phosphorylates the glucose molecule at the C-3 position. A loss of these enzymes, for example a loss of the GWD, leads to a starch excess (sex) phenotype, and because starch cannot be phosphorylated, it accumulates in the plastids.
After the phosphorylation, the first degrading enzyme, beta-amylase
β-Amylase (EC 3.2.1.2 , saccharogen amylase, glycogenase) is an enzyme with the systematic name ''4-α-D-glucan maltohydrolase''. It catalyses the following reaction:
: Hydrolysis of (1→4)-α-D-glucosidic linkages in polysaccharides so as to ...
(BAM) can attack the glucose chain at its non-reducing end. Maltose
}
Maltose ( or ), also known as maltobiose or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond. In the isomer isomaltose, the two glucose molecules are joined with an α(1→6) bond. Maltose is the two- ...
is released as the main product of starch degradation. If the glucose chain consists of three or fewer molecules, BAM cannot release maltose. A second enzyme, disproportionating enzyme-1
In chemistry, disproportionation, sometimes called dismutation, is a redox reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation states. More generally, the term can b ...
(DPE1), combines two maltotriose molecules. From this chain, a glucose molecule is released. Now, BAM can release another maltose molecule from the remaining chain. This cycle repeats until starch is degraded completely. If BAM comes close to the phosphorylated branching point of the glucose chain, it can no longer release maltose. In order for the phosphorylated chain to be degraded, the enzyme isoamylase (ISA) is required.
The products of starch degradation are predominantly maltose and smaller amounts of glucose. These molecules are exported from the plastid to the cytosol, maltose via the maltose transporter, which if mutated (MEX1-mutant) results in maltose accumulation in the plastid. Glucose is exported via the plastidic glucose translocator
The plastid (Greek: πλαστός; plastós: formed, molded – plural plastids) is a membrane-bound organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosy ...
(pGlcT). These two sugars act as a precursor for sucrose synthesis. Sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
can then be used in the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway in the mitochondria, to generate ATP at night.
Properties
Structure

 While amylose was thought to be completely unbranched, it is now known that some of its molecules contain a few branch points.
Amylose is a much smaller molecule than amylopectin. About one quarter of the mass of stored starch in plants consist of amylose, although there are about 150 times more amylose than amylopectin molecules.
Accumulated starch within plants is stored in semi-crystalline granules. Each plant species has a unique starch granular size: rice starch is relatively small (about 2 μm),
While amylose was thought to be completely unbranched, it is now known that some of its molecules contain a few branch points.
Amylose is a much smaller molecule than amylopectin. About one quarter of the mass of stored starch in plants consist of amylose, although there are about 150 times more amylose than amylopectin molecules.
Accumulated starch within plants is stored in semi-crystalline granules. Each plant species has a unique starch granular size: rice starch is relatively small (about 2 μm), potato starch
Potato starch is starch extracted from potatoes. The cells of the root tubers of the potato plant contain leucoplasts (starch grains). To extract the starch, the potatoes are crushed, and the starch grains are released from the destroyed cells. Th ...
es have larger granules (up to 100 μm) and wheat and tapioca all in-between. Unlike other botanical sources of starch, wheat starch has a bimodal size distribution, with both smaller and larger granules ranging from 2 to 55 μm.
Some cultivated plant varieties have pure amylopectin starch without amylose, known as ''waxy starches''. The most used is waxy maize, others are glutinous rice
Glutinous rice (''Oryza sativa var. glutinosa''; also called sticky rice, sweet rice or waxy rice) is a type of rice grown mainly in Southeast and East Asia, and the northeastern regions of South Asia, which has opaque grains, very low amylose ...
and waxy potato starch
Waxy potato starch is a variety of commercially available starch composed almost entirely of amylopectin molecules, extracted from new potato varieties. Standard starch extracted from traditional potato varieties contains both amylose and amylopec ...
. Waxy starches undergo less retrogradation
Retrogradation is the landward change in position of the front of a river delta with time. This occurs when the mass balance of sediment into the delta is such that the volume of incoming sediment is less than the volume of the delta that is lost ...
, resulting in a more stable paste. A maize cultivar with a relatively high proportion of amylose starch, amylomaize Amylomaize was a term coined in the late 1940s by Robert P. Bear of Bear Hybrids Corn Company in Decatur, Illinois to describe his discovery and commercial breeding of a cornstarch with high (>50%) amylose content, also called high amylose starch. ...
, is cultivated for the use of its gel strength and for use as a resistant starch
Resistant starch (RS) is starch, including its degradation products, that escapes from digestion in the small intestine of healthy individuals. Resistant starch occurs naturally in foods, but it can also be added as part of dried raw foods, or use ...
(a starch that resists digestion) in food products.
Synthetic amylose made from cellulose has a well-controlled degree of polymerization. Therefore, it can be used as a potential drug deliver carrier.
Dissolution and gelatinization
When heated in abundant water, the granules of native starch swell and burst, the semi-crystalline structure is lost, and the smaller amylose molecules start leaching out of the granule, forming a network that holds water and increasing the mixture'sviscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
. This process is called starch gelatinization
Starch gelatinization is a process of breaking down the intermolecular bonds of starch molecules in the presence of water and heat, allowing the hydrogen bonding sites (the hydroxyl hydrogen and oxygen) to engage more water. This irreversibly d ...
. The gelatinization temperature of starch varies depending on starch cultivar, amylose/amylopectin content, and water content. Starch with water could experience complex multiphase transitions during differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) temperature scanning. For starch with excess water, a single gelatinisation endotherm can be usually observed in the low temperature range (54–73 °C). By reducing the water content (<64%) in starch, more endothermic transitions representing different structural changes can be seen because they become separated and they will move to higher temperatures. With limited water content, the swelling forces will be much less significant, and the process of gelatinization in a low moisture content environment could more accurately be defined as the "melting" of starch. Besides, the number of endotherms and enthalpies depended on amylose/amylopectin ratio, and the gelatinisation enthalpy of the amylopectin-rich starch was higher than that of the amylose-rich starch. Specifically, waxy and normal maize starches show a large gelatinization endotherm at about 70 °C; for normal maize starches, there was also a second endotherm at about 90 °C, considered as the phase transition within an amylose–lipid complex; In contrast, for high-amylose content starches (e.g. Gelose 50 and Gelose 80), there is a very broad endotherm in the temperature range between 65 and 115 °C, which is composed of the main gelatinization endotherm and the phase transition within an amylose–lipid complex.
During cooking
Cooking, cookery, or culinary arts is the art, science and craft of using heat to Outline of food preparation, prepare food for consumption. Cooking techniques and ingredients vary widely, from grilling food over an open fire to using electric ...
, the starch becomes a paste and increases further in viscosity. During cooling or prolonged storage of the paste, the semi-crystalline structure partially recovers and the starch paste thickens, expelling water. This is mainly caused by retrogradation
Retrogradation is the landward change in position of the front of a river delta with time. This occurs when the mass balance of sediment into the delta is such that the volume of incoming sediment is less than the volume of the delta that is lost ...
of the amylose. This process is responsible for the hardening of bread or staling
Staling, or "going stale", is a chemical and physical process in bread and similar foods that reduces their palatability - stale bread is dry and hard.
Mechanism and effects
Staling is not simply a drying-out process due to evaporation. One im ...
, and for the water layer on top of a starch gel ( syneresis).
Certain starches, when mixed with water, will produce a non-Newtonian fluid
A non-Newtonian fluid is a fluid that does not follow Newton's law of viscosity, i.e., constant viscosity independent of stress. In non-Newtonian fluids, viscosity can change when under force to either more liquid or more solid. Ketchup, for exa ...
sometimes nicknamed "oobleck".
Starch can also be dissolved or undergo gelation in ionic liquid
An ionic liquid (IL) is a salt in the liquid state. In some contexts, the term has been restricted to salts whose melting point is below a specific temperature, such as . While ordinary liquids such as water and gasoline are predominantly made of ...
s or metal chloride salt solutions. The thermal transition of starch is largely influenced by the ratio of ionic liquid/water. Aqueous ionic liquid with a certain ionic liquid/water ratio leads to the most effective structural disorganisation of some starches at significantly reduced temperature (even at room temperature). This phenomenon is very different from the dissolution of cellulose, as the latter occurs most efficiently in pure ionic liquids and any water contained in the ionic liquids will hinder the dissolution significantly. It is proposed that for starches with granule surface pores (e.g. millet, waxy maize, normal maize and wheat starches), the corrosion by the aqueous IL follows an inside-out pattern and the destruction to the granules is fast and even, whereas for starches with a relatively smooth surface (e.g. high-amylose maize, potato, purple yam and pea starches), the corrosion can only start from the surface and thus the change caused the aqueous IL is slow. Besides, starch, even high-amylose starch, can be fully dissolved by aqueous metal chloride salts (e.g. ZnCl2, CaCl2, and MgCl2) at moderate temperature (≤50 °C), and starch nanoparticles can form during this dissolution process.
Hydrolysis
Theenzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s that break down or hydrolyze
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
starch into the constituent sugars are known as amylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large amounts of ...
s.
Alpha-amylases are found in plants and in animals. Human saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be ...
is rich in amylase, and the pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an end ...
also secretes the enzyme. Individuals from populations with a high-starch diet tend to have more amylase genes than those with low-starch diets;
Beta-amylase cuts starch into maltose
}
Maltose ( or ), also known as maltobiose or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond. In the isomer isomaltose, the two glucose molecules are joined with an α(1→6) bond. Maltose is the two- ...
units. This process is important in the digestion of starch and is also used in brewing
Brewing is the production of beer by steeping a starch source (commonly cereal grains, the most popular of which is barley) in water and #Fermenting, fermenting the resulting sweet liquid with Yeast#Beer, yeast. It may be done in a brewery ...
, where amylase from the skin of seed grains is responsible for converting starch to maltose (Malting
Malting is the process of steeping, germinating and drying grain to convert it into malt. The malt is mainly used for brewing or whisky making, but can also be used to make malt vinegar or malt extract. Various grains are used for malting, most ...
, Mashing
In brewing and distilling, mashing is the process of combining a mix of ground grains – typically malted barley with supplementary grains such as corn, sorghum, rye, or wheat – known as the "grain bill" with water and then heating the mixtu ...
).
Given a heat of combustion of glucose of whereas that of starch is per mole of glucose monomer, hydrolysis releases about per mole, or per gram of glucose product.
Dextrinization
If starch is subjected to dry heat, it breaks down to formdextrin
Dextrins are a group of low-molecular-weight carbohydrates produced by the hydrolysis of starch and glycogen. Dextrins are mixtures of polymers of D-glucose units linked by α-(1→4) or α-(1→6) glycosidic bonds.
Dextrins can be produced from ...
s, also called "pyrodextrins" in this context. This break down process is known as dextrinization. (Pyro)dextrins are mainly yellow to brown in color and dextrinization is partially responsible for the browning of toasted bread.
Chemical tests
triiodide
In chemistry, triiodide usually refers to the triiodide ion, . This anion, one of the polyhalogen ions, is composed of three iodine atoms. It is formed by combining aqueous solutions of iodide salts and iodine. Some salts of the anion have bee ...
(I3−) solution formed by mixing iodine and iodide (usually from potassium iodine, potassium iodide) is used to test for starch; a dark blue color indicates the presence of starch. The details of this reaction are not fully known, but recent scientific work using single crystal X-ray crystallography and comparative Raman spectroscopy suggests that the final starch-iodine complex is similar to an infinite polyiodide chain like one found in a pyrroloperylene-iodine complex. The strength of the resulting blue color depends on the amount of amylose present. Waxy starches with little or no amylose present will color red. Benedict's test and Fehling's test is also done to indicate the presence of starch.
Starch indicator solution consisting of water, starch and iodide is often used in redox titrations: in the presence of an oxidizing agent the solution turns blue, in the presence of reducing agent the blue color disappears because triiodide (I3−) ions break up into three iodide ions, disassembling the starch-iodine complex. Starch solution was used as indicator for visualizing the periodic formation and consumption of triiodide intermediate in the Briggs–Rauscher reaction, Briggs-Rauscher oscillating reaction. The starch, however, changes the Chemical kinetics, kinetics of the reaction steps involving triiodide ion.
A 0.3% Mass fraction (chemistry), w/w solution is the standard concentration for a starch indicator. It is made by adding 3 grams of soluble starch to 1 liter of heated water; the solution is cooled before use (starch-iodine complex becomes unstable at temperatures above 35 °C).
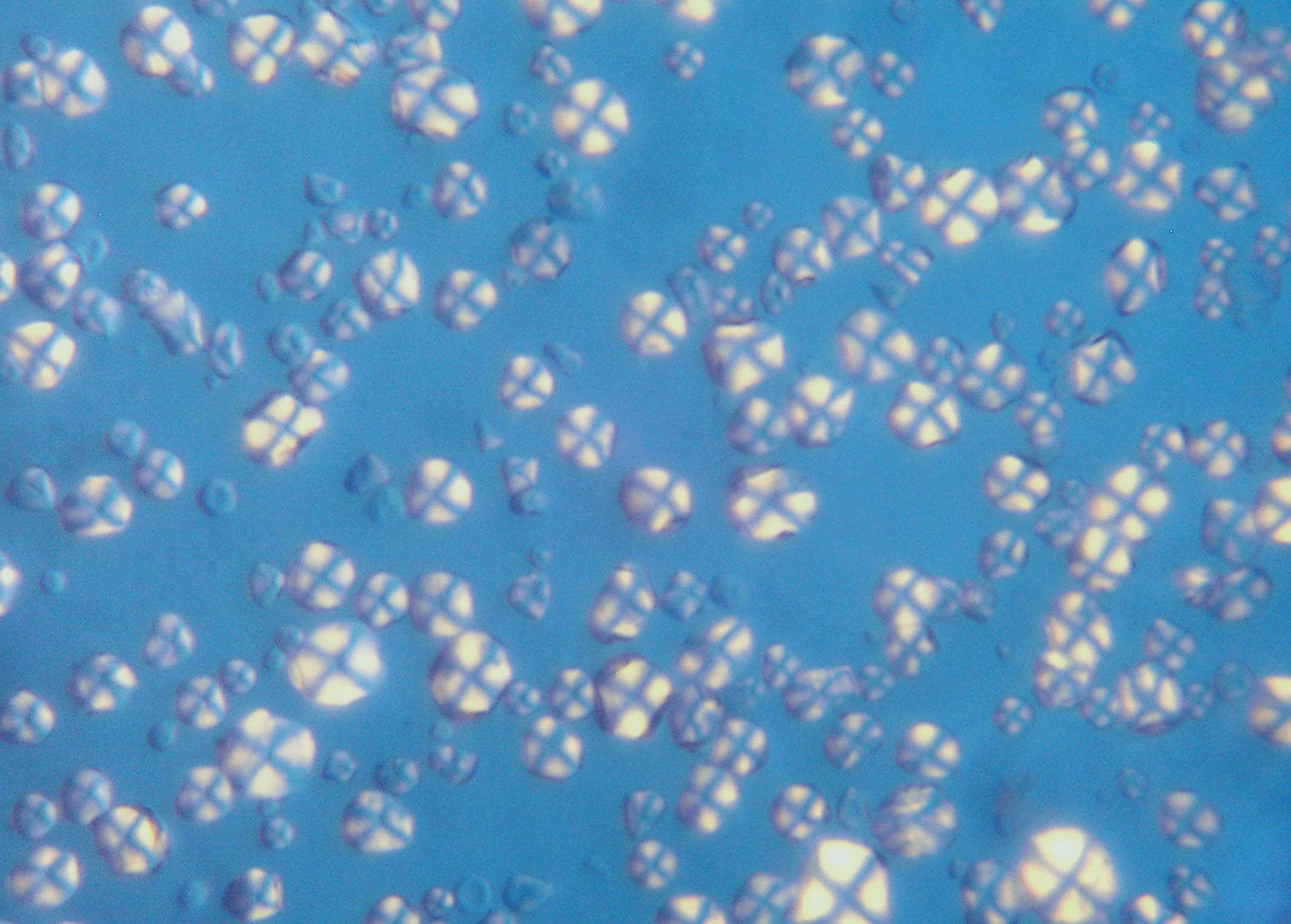
Each species of plant has a unique type of starch granules in granular size, shape and crystallization pattern. Under the microscope, starch grains stained with iodine illuminated from behind with polarized light show a distinctive Maltese cross effect (also known as extinction cross and birefringence).
Food
Starch is the most commoncarbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ma ...
in the human diet and is contained in many staple food
A staple food, food staple, or simply a staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for a given person or group of people, supplying a large fraction of energy needs and ...
s. The major sources of starch intake worldwide are the cereals (rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
, wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, and maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
) and the root vegetables (potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
es and cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively ...
). Many other starchy foods are grown, some only in specific climates, including acorns, arrowroot, arracacha, bananas, barley, breadfruit, buckwheat, canna (plant), canna, colocasia, katakuri, kudzu, Xanthosoma sagittifolium, malanga, millet, oats, oxalis tuberosa, oca, polynesian arrowroot, sago, sorghum
''Sorghum'' () is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family (Poaceae). Some of these species are grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species is grown for grain, while many othe ...
, sweet potatoes, rye, taro, chestnuts, Water caltrop, water chestnuts, Canna indica, arrowroot and yam (vegetable), yams, and many kinds of beans, such as vicia faba, favas, lentils, mung beans, peas, and chickpeas.
Before processed foods, people consumed large amounts of uncooked and unprocessed starch-containing plants, which contained high amounts of resistant starch
Resistant starch (RS) is starch, including its degradation products, that escapes from digestion in the small intestine of healthy individuals. Resistant starch occurs naturally in foods, but it can also be added as part of dried raw foods, or use ...
. Microbes within the large intestine ferment or consume the starch, producing short-chain fatty acids, which are used as energy, and support the maintenance and growth of the microbes. Upon cooking, starch is transformed from an insoluble, difficult-to-digest granule into readily accessible glucose chains with very different nutritional and functional properties.
In current diets, highly processed foods are more easily digested and release more glucose in the small intestine—less starch reaches the large intestine and more energy is absorbed by the body. It is thought that this shift in energy delivery (as a result of eating more processed foods) may be one of the contributing factors to the development of metabolic disorders of modern life, including obesity and diabetes.
The amylose/amylopectin ratio, molecular weight and molecular fine structure influences the physicochemical properties as well as energy release of different types of starches. In addition, cooking and food processing significantly impacts starch digestibility and energy release. Starch has been classified as rapidly digestible starch, slowly digestible starch and resistant starch, depending upon its digestion profile. Raw starch granules resist digestion by human enzymes and do not break down into glucose in the small intestine - they reach the large intestine instead and function as Prebiotic (nutrition), prebiotic dietary fiber. When starch granules are fully gelatinized and cooked, the starch becomes easily digestible and releases glucose quickly within the small intestine. When starchy foods are cooked and cooled, some of the glucose chains re-crystallize and become resistant to digestion again. Slowly digestible starch can be found in raw cereals, where digestion is slow but relatively complete within the small intestine. Widely used prepared foods containing starch are bread, pancakes, cereals, noodles, pasta, porridge and tortilla.
During cooking with high heat, sugars released from starch can react with amino acids via the Maillard reaction, forming advanced glycation end-products, (AGEs), contributing aromas, flavors and texture to foods. One example of a dietary AGE is acrylamide. Recent evidence suggests that the intestinal fermentation of dietary AGEs may be associated with insulin resistance, atherosclerosis, diabetes and other inflammatory diseases. This may be due to the impact of AGEs on intestinal permeability.
Starch gelatinization during cake baking can be impaired by sugar competing for water, preventing gelatinization and improving texture.
Starch production
 The starch industry extracts and refines starches from seeds, roots and tubers, by wet grinding, washing, sieving and drying. Today, the main commercial refined starches are cornstarch, tapioca, arrowroot, and wheat, rice, and
The starch industry extracts and refines starches from seeds, roots and tubers, by wet grinding, washing, sieving and drying. Today, the main commercial refined starches are cornstarch, tapioca, arrowroot, and wheat, rice, and potato starch
Potato starch is starch extracted from potatoes. The cells of the root tubers of the potato plant contain leucoplasts (starch grains). To extract the starch, the potatoes are crushed, and the starch grains are released from the destroyed cells. Th ...
es. To a lesser extent, sources of refined starch are sweet potato, sago and mung bean. To this day, starch is extracted from more than 50 types of plants.
Untreated starch requires heat to thicken or gelatinize. When a starch is pre-cooked, it can then be used to thicken instantly in cold water. This is referred to as a Starch gelatinization, pregelatinized starch.
Starch sugars


 Starch can be hydrolyzed into simpler carbohydrates by acids, various
Starch can be hydrolyzed into simpler carbohydrates by acids, various enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s, or a combination of the two. The resulting fragments are known as dextrin
Dextrins are a group of low-molecular-weight carbohydrates produced by the hydrolysis of starch and glycogen. Dextrins are mixtures of polymers of D-glucose units linked by α-(1→4) or α-(1→6) glycosidic bonds.
Dextrins can be produced from ...
s. The extent of conversion is typically quantified by ''dextrose equivalent'' (DE), which is roughly the fraction of the glycosidic bond
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
A glycosidic bond is formed between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group ...
s in starch that have been broken.
These starch sugars are by far the most common starch based food ingredient and are used as sweeteners in many drinks and foods. They include:
* Maltodextrin, a lightly hydrolyzed (DE 10–20) starch product used as a bland-tasting filler and thickener.
* Various glucose syrup
Glucose syrup, also known as confectioner's glucose, is a syrup made from the hydrolysis of starch. Glucose is a sugar. Maize (corn) is commonly used as the source of the starch in the US, in which case the syrup is called "corn syrup", but glucos ...
s (DE 30–70), also called corn syrups in the US, viscous solutions used as sweeteners and thickeners in many kinds of processed foods.
* Dextrose (DE 100), commercial glucose, prepared by the complete hydrolysis of starch.
* High fructose syrup, made by treating dextrose solutions with the enzyme glucose isomerase, until a substantial fraction of the glucose has been converted to fructose. In the U.S. high-fructose corn syrup is significantly cheaper than sugar, and is the principal sweetener used in processed foods and beverages. Fructose also has better microbiological stability. One kind of high fructose corn syrup, HFCS-55, is sweeter than sucrose because it is made with more fructose, while the sweetness of HFCS-42 is on par with sucrose.
* Sugar alcohols, such as maltitol, erythritol, sorbitol, mannitol and hydrogenated starch hydrolysate, are sweeteners made by reducing sugars.
Modified starches
A modified starch is a starch that has been chemically modified to allow the starch to function properly under conditions frequently encountered during processing or storage, such as high heat, high shear, low pH, freeze/thaw and cooling. The modified food starches are E number, E coded according to European Food Safety Authority and International Numbering System for Food Additives, INS coded Food Additives according to the Codex Alimentarius: * 1400 Dextrin * 1401 Acid-treated starch * 1402 Alkaline-treated starch * 1403 Bleached starch * 1404 Oxidized starch * 1405 Starches, enzyme-treated * 1410 Monostarch phosphate * 1412 Distarch phosphate * 1413 Phosphated distarch phosphate * 1414 Acetylation, Acetylated distarch phosphate * 1420 Starch acetate * 1422 Acetylated distarch adipate * 1440 Hydroxypropyl starch * 1442 Hydroxypropyl distarch phosphate * 1443 Hydroxypropyl distarch glycerol * 1450 Starch sodium octenyl succinate * 1451 Acetylation, Acetylated oxidized starch INS 1400, 1401, 1402, 1403 and 1405 are in the EU food ingredients without an E-number. Typical modified starches for technical applications are Paper chemicals#Cationic starch, cationic starches, hydroxyethyl starch and carboxymethylated starches.Use as food additive
As an additive for food processing, food starches are typically used as thickeners and stabilizers in foods such as puddings, custards, soups, sauces, gravies, pie fillings, and salad dressings, and to make noodles and pastas. They function as thickeners, extenders, emulsion stabilizers and are exceptional binders in processed meats. Gummed sweets such as jelly beans and wine gums are not manufactured using a mold in the conventional sense. A tray is filled with native starch and leveled. A positive mold is then pressed into the starch leaving an impression of 1,000 or so jelly beans. The jelly mix is then poured into the impressions and put onto a stove to set. This method greatly reduces the number of molds that must be manufactured.Use in pharmaceutical industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, starch is also used as an excipient, as Tablet (pharmacy), tablet disintegrant, and as binder.Resistant starch
Resistant starch is starch that escapes digestion in the small intestine of healthy individuals. High-amylose starch from wheat or corn has a higher gelatinization temperature than other types of starch, and retains its resistant starch content through baking, mild Food extrusion, extrusion and other food processing techniques. It is used as an insoluble dietary fiber in processed foods such as bread, pasta, cookies, crackers, pretzels and other low moisture foods. It is also utilized as a dietary supplement for its health benefits. Published studies have shown that resistant starch helps to improve insulin sensitivity, reduces pro-inflammatory biomarkers interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha and improves markers of colonic function. It has been suggested that resistant starch contributes to the health benefits of intact whole grains.Synthetic starch
In 2021, researchers reported the world's first Biobased economy#Agriculture, artificial synthesis of starch in the laboratory. A cell-free Biocatalysis, chemoenzymatic process was used to synthesize starch from CO2 and hydrogen. If the process is viable and can be scaled, it could substantially reduce land-, pesticide- and water-use as well as greenhouse gas emissions while increasing food security. The chemical pathway of 11 core reactions was drafted by Computational chemistry, computational pathway design and converts CO2 to starch at a rate that is ~8.5-fold higher than starch synthesis Corn starch, in maize.Non-food applications


Papermaking
Papermaking is the largest non-food application for starches globally, consuming many millions of metric tons annually. In a typical sheet of copy paper for instance, the starch content may be as high as 8%. Both chemically modified and unmodified starches are used in papermaking. In the wet part of the papermaking process, generally called the "wet-end", the starches used are cationic and have a positive charge bound to the starch polymer. These starch derivatives associate with the anionic or negatively charged paper fibers /cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
and inorganic fillers. Cationic starches together with other retention and internal sizing agents help to give the necessary strength properties to the paper web formed in the papermaking process (wet strength), and to provide strength to the final paper sheet (dry strength).
In the dry end of the papermaking process, the paper web is rewetted with a starch based solution. The process is called sizing, surface sizing. Starches used have been chemically, or enzymatically depolymerized at the paper mill or by the starch industry (oxidized starch). The size/starch solutions are applied to the paper web by means of various mechanical presses (size presses). Together with surface sizing agents the surface starches impart additional strength to the paper web and additionally provide water hold out or "size" for superior printing properties. Starch is also used in paper coatings as one of the binders for the coating formulations which include a mixture of pigments, binders and thickeners. Coated paper has improved smoothness, hardness, whiteness and gloss and thus improves printing characteristics.
Corrugated board adhesives
Corrugated board adhesives are the next largest application of non-food starches globally. Starch glues are mostly based on unmodified native starches, plus some additive such as borax and caustic soda. Part of the starch is gelatinized to carry the slurry of uncooked starches and prevent sedimentation. This opaque glue is called a SteinHall adhesive. The glue is applied on tips of the fluting. The fluted paper is pressed to paper called liner. This is then dried under high heat, which causes the rest of the uncooked starch in glue to swell/gelatinize. This gelatinizing makes the glue a fast and strong adhesive for corrugated board production.Clothing starch
Clothing or laundry starch is a liquid prepared by mixing a vegetable starch in water (unmodified starch only gels in water close to boiling point, while commercial products may not require heat), and is used in the laundry, laundering of clothes. Starch was widely used in Europe in the 16th and 17th centuries to stiffen the wide collars and Ruff (clothing), ruffs of fine linen which surrounded the necks of the well-to-do. During the 19th and early 20th century it was stylish to stiffen the collars and sleeves of men's shirts and the ruffles of women's petticoats by starching them before the clean clothes were ironing, ironed. Starch gave clothing smooth, crisp edges, and had an additional practical purpose: dirt and sweat from a person's neck and wrists would stick to the starch rather than to the fibers of the clothing. The dirt would wash away along with the starch; after laundering, the starch would be reapplied. Starch is available in Aerosol spray, spray cans, in addition to the usual granules to mix with water.Bioplastic
Starch is an important natural polymer to make bioplastics. With water and plasticisers such as glycerol, starch can be processed into so-called "thermoplastic starch" using conventional polymer processing techniques such as extrusion, injection molding and compression molding. Since materials based on only native starch have poor processibility, mechanical properties and stability, more commonly modified starches (e.g. hydroxypropyl starch) are used and starch is combined with other polymers (preferably biodegradable polymers such as polycaprolactone), as some commercial products (e.g. PLANTIC™ HP and Mater-Bi®) available on the market.
Other
Another large non-food starch application is in the construction industry, where starch is used in the gypsum wall board manufacturing process. Chemically modified or unmodified starches are added to the stucco containing primarily gypsum. Top and bottom heavyweight sheets of paper are applied to the formulation, and the process is allowed to heat and cure to form the eventual rigid wall board. The starches act as a glue for the cured gypsum rock with the paper covering, and also provide rigidity to the board. Starch is used in the manufacture of various adhesives or glues for book-binding, wallpaper adhesives, paper bag#Multiwall paper sacks, paper sack production, tube winding, Gum tape, gummed paper, envelope adhesives, school glues and bottle labeling. Starch derivatives, such as yellow dextrins, can be modified by addition of some chemicals to form a hard glue for paper work; some of those forms use borax or soda ash, which are mixed with the starch solution at to create a very good adhesive. Sodium silicate can be added to reinforce these formula. *Textile chemicals from starch: warp (weaving), warp Textile warp sizing, sizing agents are used to reduce breaking ofyarn
Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, used in sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, ropemaking, and the production of textiles. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern manufact ...
s during weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal th ...
. Starch is mainly used to size cotton based yarns. Modified starch is also used as textile printing thickener.
*In oil exploration, starch is used to adjust the viscosity of drilling fluid, which is used to lubricate the drill head and suspend the grinding residue in petroleum extraction.
*Starch is also used to make some packing peanuts, and some dropped ceiling, drop ceiling tiles.
*In the printing industry, food grade starch is used in the manufacture of anti-set-off spray powder used to separate printed sheets of paper to avoid wet ink being set-off (printing), set off.
*For body powder, powdered corn starch is used as a substitute for talcum powder, and similarly in other health and beauty products.
*Starch is used to produce various bioplastics, synthetic polymers that are biodegradable. An example is polylactic acid based on glucose from starch.
*Glucose from starch can be further fermented to biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. According to the United States Energy Information Administration (E ...
corn ethanol using the so-called wet milling process. Today most bioethanol production plants use the dry milling process to ferment corn or other feedstock directly to ethanol.
*Hydrogen production#Enzymatic hydrogen generation, Hydrogen production could use glucose from starch as the raw material, using enzymes.
Occupational safety and health
In the US the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set the legal limit (Permissible exposure limit) for starch exposure in the workplace as 15 mg/m3 total exposure and 5 mg/m3 respiratory exposure over an 8-hour workday. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has set a Recommended exposure limit (REL) of 10 mg/m3 total exposure and 5 mg/m3 respiratory exposure over an 8-hour workday.See also
* Acrylamide, which is present in fried and baked foods * Destarch * Starch analysis * Resistant starchReferences
External links
CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
information for workers {{Authority control Starch, Nutrition Carbohydrates Edible thickening agents Excipients Printing