Rhythm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rhythm (from
 In his television series ''How Music Works'', Howard Goodall presents theories that human rhythm recalls the regularity with which we walk and the heartbeat. Other research suggests that it does not relate to the heartbeat directly, but rather the speed of emotional affect, which also influences heartbeat. Yet other researchers suggest that since certain features of human music are widespread, it is "reasonable to suspect that beat-based rhythmic processing has ancient evolutionary roots". Justin London writes that musical metre "involves our initial perception as well as subsequent anticipation of a series of beats that we abstract from the rhythm surface of the music as it unfolds in time". The "perception" and "abstraction" of rhythmic measure is the foundation of human instinctive musical participation, as when we divide a series of identical clock-ticks into "tick-tock-tick-tock".
In his television series ''How Music Works'', Howard Goodall presents theories that human rhythm recalls the regularity with which we walk and the heartbeat. Other research suggests that it does not relate to the heartbeat directly, but rather the speed of emotional affect, which also influences heartbeat. Yet other researchers suggest that since certain features of human music are widespread, it is "reasonable to suspect that beat-based rhythmic processing has ancient evolutionary roots". Justin London writes that musical metre "involves our initial perception as well as subsequent anticipation of a series of beats that we abstract from the rhythm surface of the music as it unfolds in time". The "perception" and "abstraction" of rhythmic measure is the foundation of human instinctive musical participation, as when we divide a series of identical clock-ticks into "tick-tock-tick-tock".
 Joseph Jordania recently suggested that the sense of rhythm was developed in the early stages of
Joseph Jordania recently suggested that the sense of rhythm was developed in the early stages of  The establishment of a basic beat requires the perception of a regular sequence of distinct short-duration pulses and, as a subjective perception of loudness is relative to background noise levels, a pulse must decay to silence before the next occurs if it is to be really distinct. For this reason, the fast-transient sounds of percussion instruments lend themselves to the definition of rhythm. Musical cultures that rely upon such instruments may develop multi-layered
The establishment of a basic beat requires the perception of a regular sequence of distinct short-duration pulses and, as a subjective perception of loudness is relative to background noise levels, a pulse must decay to silence before the next occurs if it is to be really distinct. For this reason, the fast-transient sounds of percussion instruments lend themselves to the definition of rhythm. Musical cultures that rely upon such instruments may develop multi-layered
 Most music, dance and oral poetry establishes and maintains an underlying "metric level", a basic unit of time that may be audible or implied, the
Most music, dance and oral poetry establishes and maintains an underlying "metric level", a basic unit of time that may be audible or implied, the
 A durational pattern that synchronises with a
A durational pattern that synchronises with a
 The study of rhythm, stress, and pitch in
The study of rhythm, stress, and pitch in  Dance music has instantly recognizable patterns of beats built upon a characteristic tempo and measure. The Imperial Society of Teachers of Dancing defines the
Dance music has instantly recognizable patterns of beats built upon a characteristic tempo and measure. The Imperial Society of Teachers of Dancing defines the  The general classifications of ''metrical rhythm'', ''measured rhythm'', and ''free rhythm'' may be distinguished. Metrical or divisive rhythm, by far the most common in Western music calculates each time value as a multiple or fraction of the beat. Normal accents re-occur regularly providing systematical grouping (measures). Measured rhythm ( additive rhythm) also calculates each time value as a multiple or fraction of a specified time unit but the accents do not recur regularly within the cycle. Free rhythm is where there is neither, such as in Christian chant, which has a basic pulse but a freer rhythm, like the rhythm of prose compared to that of verse. ''See Free time (music)''.
Finally some music, such as some graphically scored works since the 1950s and non-European music such as Honkyoku repertoire for
The general classifications of ''metrical rhythm'', ''measured rhythm'', and ''free rhythm'' may be distinguished. Metrical or divisive rhythm, by far the most common in Western music calculates each time value as a multiple or fraction of the beat. Normal accents re-occur regularly providing systematical grouping (measures). Measured rhythm ( additive rhythm) also calculates each time value as a multiple or fraction of a specified time unit but the accents do not recur regularly within the cycle. Free rhythm is where there is neither, such as in Christian chant, which has a basic pulse but a freer rhythm, like the rhythm of prose compared to that of verse. ''See Free time (music)''.
Finally some music, such as some graphically scored works since the 1950s and non-European music such as Honkyoku repertoire for
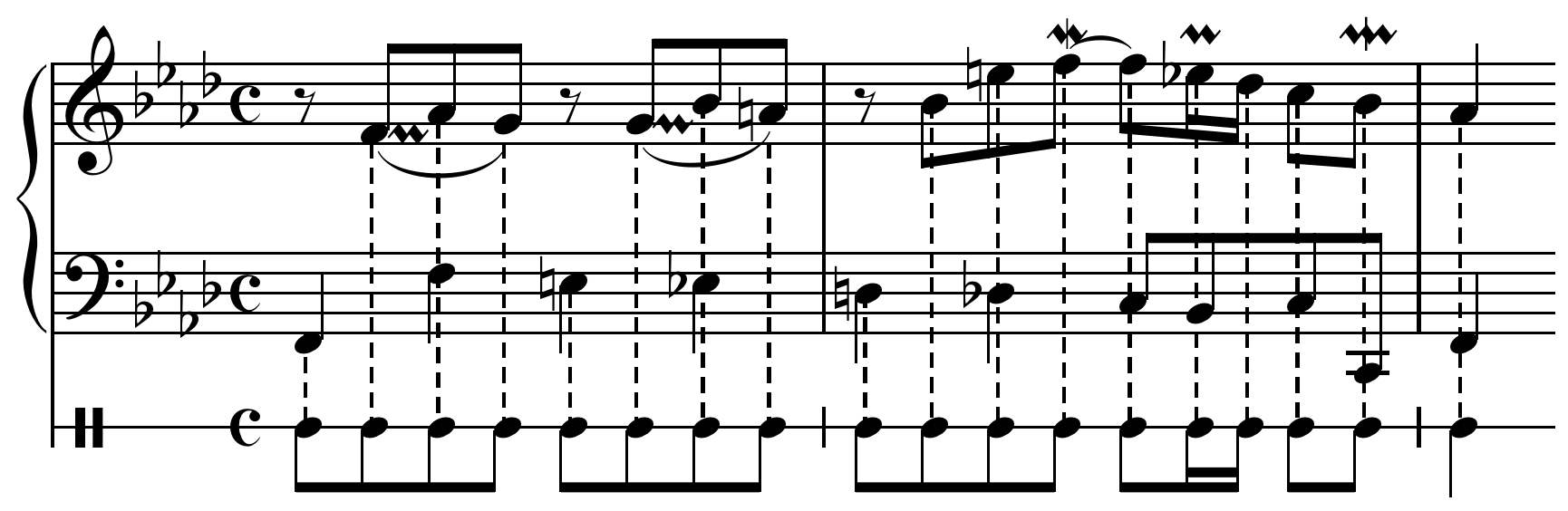 A ''composite rhythm'' is the durations and patterns (rhythm) produced by amalgamating all sounding
A ''composite rhythm'' is the durations and patterns (rhythm) produced by amalgamating all sounding
 In the
In the
The Development of Rhythmic Organization in Indian Classical Music
MA dissertation, School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London. * Lewis, Andrew (2005). ''Rhythm—What it is and How to Improve Your Sense of It''. San Francisco
RhythmSource
Press. . * Mazzola, Guerino (2017). ''The Topos of Music, Vol. I''. Heidelberg: Springer. . * * Palmer, John (2013). ''Rhythm to Go'', Vision Edition and CE Books. A fast-track collection of graded exercises from elementary to advanced level divided in four sections and including an additional chapter with rhythmic structures used in contemporary music. * Petersen, Peter (2013). ''Music and Rhythm: Fundamentals, History, Analysis.'' New York: Peter Lang. * Scholes, Percy (1977a). "Form", in ''The Oxford Companion to Music'', 6th corrected reprint of the 10th ed. (1970), revised and reset, edited by John Owen Ward. London and New York: Oxford University Press. . * Williams, C. F. A., ''The Aristoxenian Theory of Musical Rhythm'', (Cambridge Library Collection—Music), Cambridge University Press; first edition, 2009. * Van Der, Horst F. (1963). ''Maat en Ritme'', Broekmans & Van Poppel, . A collection of graded exercises in two volumes, from elementary to advanced level. *
'Rhythm of Prose', William Morrison Patterson ,Columbia University Press 1917
* ttp://www.signosemio.com/semiotics-of-rhythm.asp Louis Hébert, "A Little Semiotics of Rhythm. Elements of Rhythmology", in ''Signo'' {{Authority control * Cognitive musicology Musical terminology Patterns
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry") generally means a " movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular recurrence or pattern in time can apply to a wide variety of cyclical natural phenomena having a periodicity or frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from '' angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is ...
of anything from microseconds to several seconds (as with the riff
A riff is a repeated chord progression or refrain in music (also known as an ostinato figure in classical music); it is a pattern, or melody, often played by the rhythm section instruments or solo instrument, that forms the basis or accompanim ...
in a rock music song); to several minutes or hours, or, at the most extreme, even over many years.
Rhythm is related to and distinguished from pulse, meter, and beats:
In the performance arts, rhythm is the timing of events on a human scale; of musical sounds and silences that occur over time, of the steps of a dance, or the meter of spoken language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
and poetry. In some performing arts, such as hip hop music, the rhythmic delivery of the lyrics is one of the most important elements of the style. Rhythm may also refer to visual presentation, as "timed movement through space" and a common language of pattern
A pattern is a regularity in the world, in human-made design, or in abstract ideas. As such, the elements of a pattern repeat in a predictable manner. A geometric pattern is a kind of pattern formed of geometric shapes and typically repeated li ...
unites rhythm with geometry. For example, architects
An architect is a person who plans, designs and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that h ...
often speak of the rhythm of a building, referring to patterns in the spacing of windows, columns, and other elements of the façade
A façade () (also written facade) is generally the front part or exterior of a building. It is a loan word from the French (), which means 'frontage' or ' face'.
In architecture, the façade of a building is often the most important aspect ...
. In recent years, rhythm and meter have become an important area of research among music scholars. Recent work in these areas includes books by Maury Yeston
Maury Yeston (born October 23, 1945) is an American composer, lyricist and music theorist.
He is known as the initiator of new Broadway musicals and writing their music and lyrics, as well as a classical orchestral and ballet composer, Yale Un ...
, Fred Lerdahl and Ray Jackendoff
Ray Jackendoff (born January 23, 1945) is an American linguist. He is professor of philosophy, Seth Merrin Chair in the Humanities and, with Daniel Dennett, co-director of the Center for Cognitive Studies at Tufts University. He has always stra ...
, Jonathan Kramer
Jonathan Donald Kramer (December 7, 1942, Hartford, Connecticut – June 3, 2004, New York City) was an American composer and music theorist.
Biography
Kramer received his B.A. magna cum laude from Harvard University (1965) and his MA and ...
, Christopher Hasty, Godfried Toussaint
Godfried Theodore Patrick Toussaint (1944 – July 2019) was a Canadian computer scientist, a professor of computer science, and the head of the Computer Science Program at New York University Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirate ...
, William Rothstein, Joel Lester, and Guerino Mazzola.
Anthropology
 In his television series ''How Music Works'', Howard Goodall presents theories that human rhythm recalls the regularity with which we walk and the heartbeat. Other research suggests that it does not relate to the heartbeat directly, but rather the speed of emotional affect, which also influences heartbeat. Yet other researchers suggest that since certain features of human music are widespread, it is "reasonable to suspect that beat-based rhythmic processing has ancient evolutionary roots". Justin London writes that musical metre "involves our initial perception as well as subsequent anticipation of a series of beats that we abstract from the rhythm surface of the music as it unfolds in time". The "perception" and "abstraction" of rhythmic measure is the foundation of human instinctive musical participation, as when we divide a series of identical clock-ticks into "tick-tock-tick-tock".
In his television series ''How Music Works'', Howard Goodall presents theories that human rhythm recalls the regularity with which we walk and the heartbeat. Other research suggests that it does not relate to the heartbeat directly, but rather the speed of emotional affect, which also influences heartbeat. Yet other researchers suggest that since certain features of human music are widespread, it is "reasonable to suspect that beat-based rhythmic processing has ancient evolutionary roots". Justin London writes that musical metre "involves our initial perception as well as subsequent anticipation of a series of beats that we abstract from the rhythm surface of the music as it unfolds in time". The "perception" and "abstraction" of rhythmic measure is the foundation of human instinctive musical participation, as when we divide a series of identical clock-ticks into "tick-tock-tick-tock".
 Joseph Jordania recently suggested that the sense of rhythm was developed in the early stages of
Joseph Jordania recently suggested that the sense of rhythm was developed in the early stages of hominid
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the e ...
evolution by the forces of natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
. Plenty of animals walk rhythmically and hear the sounds of the heartbeat in the womb, but only humans have the ability to be engaged ( entrained) in rhythmically coordinated vocalizations and other activities. According to Jordania, development of the sense of rhythm was central for the achievement of the specific neurological state of the battle trance, crucial for the development of the effective defense system of early hominids. Rhythmic war cry, rhythmic drumming by shaman
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a Spirit world (Spiritualism), spirit world through Altered state of consciousness, altered states of consciousness, such as tranc ...
s, rhythmic drilling
Drilling is a cutting process where a drill bit is spun to cut a hole of circular cross-section in solid materials. The drill bit is usually a rotary cutting tool, often multi-point. The bit is pressed against the work-piece and rotated at ...
of the soldiers and contemporary professional combat forces listening to the heavy rhythmic rock music all use the ability of rhythm to unite human individuals into a shared collective identity
Collective identity is the shared sense of belonging to a group.
In sociology
In 1989, Alberto Melucci published ''Nomads of the Present'', which introduces his model of collective identity based on studies of the social movements of the 1980 ...
where group members put the interests of the group above their individual interests and safety.
Some types of parrots can know rhythm. Neurologist Oliver Sacks states that chimpanzees and other animals show no similar appreciation of rhythm yet posits that human affinity for rhythm is fundamental, so that a person's sense of rhythm cannot be lost (e.g. by stroke). "There is not a single report of an animal being trained to tap, peck, or move in synchrony with an auditory beat", Sacks write, "No doubt many pet lovers will dispute this notion, and indeed many animals, from the Lipizzaner horses of the Spanish Riding School
The Spanish Riding School (german: Spanische Hofreitschule) is an Austrian institution dedicated to the preservation of classical dressage and the training of Lipizzaner horses, based in Vienna, Austria, whose performances in the Hofburg are al ...
of Vienna to performing circus animals appear to 'dance' to music. It is not clear whether they are doing so or are responding to subtle visual or tactile cues from the humans around them." Human rhythmic arts are possibly to some extent rooted in courtship ritual.
 The establishment of a basic beat requires the perception of a regular sequence of distinct short-duration pulses and, as a subjective perception of loudness is relative to background noise levels, a pulse must decay to silence before the next occurs if it is to be really distinct. For this reason, the fast-transient sounds of percussion instruments lend themselves to the definition of rhythm. Musical cultures that rely upon such instruments may develop multi-layered
The establishment of a basic beat requires the perception of a regular sequence of distinct short-duration pulses and, as a subjective perception of loudness is relative to background noise levels, a pulse must decay to silence before the next occurs if it is to be really distinct. For this reason, the fast-transient sounds of percussion instruments lend themselves to the definition of rhythm. Musical cultures that rely upon such instruments may develop multi-layered polyrhythm
Polyrhythm is the simultaneous use of two or more rhythms that are not readily perceived as deriving from one another, or as simple manifestations of the same meter. The rhythmic layers may be the basis of an entire piece of music ( cross-rhyt ...
and simultaneous rhythms in more than one time signature, called polymeter. Such are the cross-rhythms of Sub-Saharan Africa and the interlocking ''kotekan'' rhythms of the gamelan.
For information on rhythm in Indian music see Tala (music). For other Asian approaches to rhythm see Rhythm in Persian music, Rhythm in Arabic music and ''Usul''—Rhythm in Turkish music and Dumbek rhythms.
Terminology
Pulse, beat and measure
pulse
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the ...
or ''tactus'' of the mensural level, or ''beat level'', sometimes simply called the beat. This consists of a (repeating) series of identical yet distinct periodic short-duration stimuli perceived as points in time. The "beat" pulse is not necessarily the fastest or the slowest component of the rhythm but the one that is perceived as fundamental: it has a tempo
In musical terminology, tempo ( Italian, 'time'; plural ''tempos'', or ''tempi'' from the Italian plural) is the speed or pace of a given piece. In classical music, tempo is typically indicated with an instruction at the start of a piece (ofte ...
to which listeners entrain as they tap their foot or dance to a piece of music. It is currently most often designated as a crotchet or quarter note
A quarter note (American) or crotchet ( ) (British) is a musical note played for one quarter of the duration of a whole note (or semibreve). Quarter notes are notated with a filled-in oval note head and a straight, flagless stem. The stem ...
in western notation (see time signature
The time signature (also known as meter signature, metre signature, or measure signature) is a notational convention used in Western culture, Western musical notation to specify how many beat (music), beats (pulses) are contained in each measu ...
). Faster levels are ''division levels'', and slower levels are ''multiple levels''. Maury Yeston
Maury Yeston (born October 23, 1945) is an American composer, lyricist and music theorist.
He is known as the initiator of new Broadway musicals and writing their music and lyrics, as well as a classical orchestral and ballet composer, Yale Un ...
clarified "Rhythms of recurrence" arise from the interaction of two levels of motion, the faster providing the pulse and the slower organizing the beats into repetitive groups. "Once a metric hierarchy has been established, we, as listeners, will maintain that organization as long as minimal evidence is present".
Unit and gesture
 A durational pattern that synchronises with a
A durational pattern that synchronises with a pulse
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the ...
or pulses on the underlying metric level
In music, metre ( Commonwealth spelling) or meter (American spelling) refers to regularly recurring patterns and accents such as bars and beats. Unlike rhythm, metric onsets are not necessarily sounded, but are nevertheless implied by the perfo ...
may be called a ''rhythmic unit''. These may be classified as:
*Metric – even patterns, such as steady eighth note
180px, Figure 1. An eighth note with stem extending up, an eighth note with stem extending down, and an eighth rest.
180px, Figure 2. Four eighth notes beamed together.
An eighth note ( American) or a quaver ( British) is a musical note pl ...
s or pulses;
*Intrametric – confirming patterns, such as dotted eighth-sixteenth note
Figure 1. A 16th note with stem facing up, a 16th note with stem facing down, and a 16th rest.
Figure 2. Four 16th notes beamed together.
In music, a 1/16, sixteenth note ( American) or semiquaver ( British) is a note played for half the d ...
and swing
Swing or swinging may refer to:
Apparatus
* Swing (seat), a hanging seat that swings back and forth
* Pendulum, an object that swings
* Russian swing, a swing-like circus apparatus
* Sex swing, a type of harness for sexual intercourse
* Swing rid ...
patterns;
*Contrametric – non-confirming, or syncopated patterns; and
*Extrametric – irregular patterns, such as tuplet
In music, a tuplet (also irrational rhythm or groupings, artificial division or groupings, abnormal divisions, irregular rhythm, gruppetto, extra-metric groupings, or, rarely, contrametric rhythm) is "any rhythm that involves dividing the beat ...
s.
A rhythmic gesture is any durational pattern that, in contrast to the rhythmic unit, does not occupy a period of time equivalent to a pulse or pulses on an underlying metric level. It may be described according to its beginning and ending or by the rhythmic units it contains. Rhythms that begin on a strong pulse are ''thetic'', those beginning on a weak pulse are ''anacrustic'' and those beginning after a rest or tied-over note are called ''initial rest''. Endings on a strong pulse are ''strong'', on a weak pulse, ''weak'' and those that end on a strong or weak upbeat are ''upbeat''.
Alternation and repetition
Rhythm is marked by the regulated succession of opposite elements: the dynamics of the strong and weak beat, the played beat and the inaudible but implied rest beat, or the long and short note. As well as perceiving rhythm humans must be able to anticipate it. This depends onrepetition
Repetition may refer to:
*Repetition (rhetorical device), repeating a word within a short space of words
* Repetition (bodybuilding), a single cycle of lifting and lowering a weight in strength training
*Working title for the 1985 slasher film '' ...
of a pattern that is short enough to memorize.
The alternation of the strong and weak beat is fundamental to the ancient language of poetry, dance and music. The common poetic term "foot" refers, as in dance, to the lifting and tapping of the foot in time. In a similar way musicians speak of an upbeat and a downbeat and of the "on" and "off" beat. These contrasts naturally facilitate a dual hierarchy of rhythm and depend on repeating patterns of duration, accent and rest forming a "pulse-group" that corresponds to the poetic foot. Normally such pulse-groups are defined by taking the most accented beat as the first and counting
Counting is the process of determining the number of elements of a finite set of objects, i.e., determining the size of a set. The traditional way of counting consists of continually increasing a (mental or spoken) counter by a unit for every elem ...
the pulses until the next accent. A rhythm that accents another beat and de-emphasises the downbeat as established or assumed from the melody or from a preceding rhythm is called syncopated rhythm.
Normally, even the most complex of meters may be broken down into a chain of duple and triple pulses either by addition or division. According to Pierre Boulez
Pierre Louis Joseph Boulez (; 26 March 1925 – 5 January 2016) was a French composer, conductor and writer, and the founder of several musical institutions. He was one of the dominant figures of post-war Western classical music.
Born in Mon ...
, beat structures beyond four, in western music, are "simply not natural".
Tempo and duration
The tempo of the piece is the speed or frequency of the ''tactus'', a measure of how quickly the beat flows. This is often measured in 'beats per minute' ( bpm): 60 bpm means a speed of one beat per second, a frequency of 1 Hz. A rhythmic unit is a durational pattern that has a period equivalent to a pulse or several pulses. The duration of any such unit is inversely related to its tempo. Musical sound may be analyzed on five different time scales, which Moravscik has arranged in order of increasing duration. *Supershort: a single cycle of an audible wave, approximately – second (30–10,000 Hz or more than 1,800 bpm). These, though rhythmic in nature, are not perceived as separate events but as continuous musical pitch. *Short: of the order of one second (1 Hz, 60 bpm, 10–100,000 audio cycles). Musical tempo is generally specified in the range 40 to 240 beats per minute. A continuous pulse cannot be perceived as a musical beat if it is faster than 8–10 per second (8–10 Hz, 480–600 bpm) or slower than 1 per 1.5–2 seconds (0.6–0.5 Hz, 40–30 bpm). Too fast a beat becomes adrone
Drone most commonly refers to:
* Drone (bee), a male bee, from an unfertilized egg
* Unmanned aerial vehicle
* Unmanned surface vehicle, watercraft
* Unmanned underwater vehicle or underwater drone
Drone, drones or The Drones may also refer to:
...
, too slow a succession of sounds seems unconnected. This time frame roughly corresponds to the human heart rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and e ...
and to the duration of a single step, syllable or rhythmic gesture.
*Medium: ≥ few seconds, this median durational level "defines rhythm in music" as it allows the definition of a rhythmic unit, the arrangement of an entire sequence of accented, unaccented and silent or " rest" pulses into the cells of a ''measure'' that may give rise to the "briefest intelligible and self-existent musical unit", a ''motif
Motif may refer to:
General concepts
* Motif (chess composition), an element of a move in the consideration of its purpose
* Motif (folkloristics), a recurring element that creates recognizable patterns in folklore and folk-art traditions
* Moti ...
'' or '' figure''. This may be further organized, by repetition and variation, into a definite ''phrase'' that may characterise an entire genre of music, dance or poetry and that may be regarded as the fundamental formal unit of music.
*Long: ≥ many seconds or a minute, corresponding to a durational unit that "consists of musical phrases"—which may make up a melody, a formal section, a poetic stanza or a characteristic sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is called ...
of dance moves and steps. Thus the temporal regularity of musical organisation includes the most elementary levels of musical form
In music, ''form'' refers to the structure of a musical composition or performance. In his book, ''Worlds of Music'', Jeff Todd Titon suggests that a number of organizational elements may determine the formal structure of a piece of music, suc ...
.
*Very long: ≥ minutes or many hours, musical compositions or subdivisions of compositions.
Curtis Roads takes a wider view by distinguishing nine-time scales, this time in order of decreasing duration. The first two, the infinite
Infinite may refer to:
Mathematics
*Infinite set, a set that is not a finite set
*Infinity, an abstract concept describing something without any limit
Music
*Infinite (group)
Infinite ( ko, 인피니트; stylized as INFINITE) is a South Ko ...
and the supra musical, encompass natural periodicities of months, years, decades, centuries, and greater, while the last three, the sample and subsample, which take account of digital and electronic rates "too brief to be properly recorded or perceived", measured in millionths of seconds (microsecond
A microsecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one millionth (0.000001 or 10−6 or ) of a second. Its symbol is μs, sometimes simplified to us when Unicode is not available.
A microsecond is equal to 100 ...
s), and finally the infinitesimal or infinitely brief, are again in the extra-musical domain. Roads' Macro level, encompassing "overall musical architecture or form
Form is the shape, visual appearance, or configuration of an object. In a wider sense, the form is the way something happens.
Form also refers to:
* Form (document), a document (printed or electronic) with spaces in which to write or enter dat ...
" roughly corresponds to Moravcsik's "very long" division while his Meso level, the level of "divisions of form" including movements, sections, phrases taking seconds or minutes, is likewise similar to Moravcsik's "long" category. Roads' Sound object: "a basic unit of musical structure" and a generalization of note ( Xenakis' mini structural time scale); fraction of a second to several seconds, and his Microsound (see granular synthesis) down to the threshold of audible perception; thousandths to millionths of seconds, are similarly comparable to Moravcsik's "short" and "supershort" levels of duration.
Rhythm–tempo interaction
One difficulty in defining rhythm is the dependence of its perception on tempo, and, conversely, the dependence of tempo perception on rhythm. Furthermore, the rhythm–tempo interaction is context dependent, as explained by Andranik Tangian using an example of the leading rhythm of ″Promenade″ from Moussorgsky's '' Pictures at an Exhibition'':( This rhythm is perceived as it is rather than as the first three events repeated at a double tempo (denoted as R012 = repeat from 0, one time, twice faster): However, the motive with this rhythm in the Moussorgsky's piece is rather perceived as a repeat This context-dependent perception of rhythm is explained by the principle of correlative perception, according to which data are perceived in the simplest way. From the viewpoint ofKolmogorov
Andrey Nikolaevich Kolmogorov ( rus, Андре́й Никола́евич Колмого́ров, p=ɐnˈdrʲej nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪtɕ kəlmɐˈɡorəf, a=Ru-Andrey Nikolaevich Kolmogorov.ogg, 25 April 1903 – 20 October 1987) was a Sovi ...
's complexity theory, this means such a representation of the data that minimizes the amount of memory.
The example considered suggests two alternative representations of the same rhythm: as it is, and as the rhythm-tempo interaction – a two-level representation in terms of a generative rhythmic pattern and a "tempo curve". Table 1 displays these possibilities both with and without pitch, assuming that one duration requires one byte of information, one byte is needed for the pitch of one tone, and invoking the repeat algorithm with its parameters R012 takes four bytes. As shown in the bottom row of the table, the rhythm without pitch requires fewer bytes if it is "perceived" as it is, without repetitions and tempo leaps. On the contrary, its melodic version requires fewer bytes if the rhythm is "perceived" as being repeated at a double tempo.
Thus, the loop of interdependence of rhythm and tempo is overcome due to the simplicity criterion, which "optimally" distributes the complexity of perception between rhythm and tempo. In the above example, the repetition is recognized because of additional repetition of the melodic contour, which results in a certain redundancy of the musical structure, making the recognition of the rhythmic pattern "robust" under tempo deviations. Generally speaking, the more redundant the "musical support" of a rhythmic pattern, the better its recognizability under augmentations and diminutions, that is, its distortions are perceived as tempo variations rather than rhythmic changes:
Metric structure
 The study of rhythm, stress, and pitch in
The study of rhythm, stress, and pitch in speech
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
is called prosody (see also: prosody (music)): it is a topic in linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Lingu ...
and poetics, where it means the number of lines in a verse, the number of syllables in each line and the arrangement of those syllables as long or short, accented or unaccented. Music inherited the term " meter or metre" from the terminology of poetry.)
The metric structure of music includes meter, tempo and all other rhythmic aspects that produce temporal regularity against which the foreground details or durational patterns of the music are projected. The terminology of western music is notoriously imprecise in this area. MacPherson preferred to speak of "time" and "rhythmic shape", Imogen Holst of "measured rhythm".
 Dance music has instantly recognizable patterns of beats built upon a characteristic tempo and measure. The Imperial Society of Teachers of Dancing defines the
Dance music has instantly recognizable patterns of beats built upon a characteristic tempo and measure. The Imperial Society of Teachers of Dancing defines the tango
Tango is a partner dance and social dance that originated in the 1880s along the Río de la Plata, the natural border between Argentina and Uruguay. The tango was born in the impoverished port areas of these countries as the result of a combina ...
, for example, as to be danced in time at approximately 66 beats per minute. The basic slow step forwards or backwards, lasting for one beat, is called a "slow", so that a full "right–left" step is equal to one measure. (''See Rhythm and dance
Dance is a performing art form consisting of sequences of movement, either improvised or purposefully selected. This movement has aesthetic and often symbolic value. Dance can be categorized and described by its choreography, by its repertoire ...
''.)
shakuhachi
A is a Japanese and ancient Chinese longitudinal, end-blown flute that is made of bamboo.
The bamboo end-blown flute now known as the was developed in Japan in the 16th century and is called the .
, may be considered ''ametric''. ''Senza misura'' is an Italian musical term for "without meter", meaning to play without a beat, using time to measure how long it will take to play the bar.
Composite rhythm
 A ''composite rhythm'' is the durations and patterns (rhythm) produced by amalgamating all sounding
A ''composite rhythm'' is the durations and patterns (rhythm) produced by amalgamating all sounding parts
Part, parts or PART may refer to:
People
*Armi Pärt (born 1991), Estonian handballer
* Arvo Pärt (born 1935), Estonian classical composer
*Brian Part (born 1962), American child actor
*Dealtry Charles Part (1882–1961), sheriff (1926–1927) a ...
of a musical texture. In music of the common practice period, the composite rhythm usually confirms the meter
The metre ( British spelling) or meter ( American spelling; see spelling differences) (from the French unit , from the Greek noun , "measure"), symbol m, is the primary unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), though its pr ...
, often in metric or even-note patterns identical to the pulse
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the ...
on a specific metric level. White defines ''composite rhythm'' as, "the resultant overall rhythmic articulation among all the voices of a contrapuntal texture". This concept was concurrently defined as "attack point rhythm" by Maury Yeston
Maury Yeston (born October 23, 1945) is an American composer, lyricist and music theorist.
He is known as the initiator of new Broadway musicals and writing their music and lyrics, as well as a classical orchestral and ballet composer, Yale Un ...
in 1976 as "the extreme rhythmic foreground of a composition – the absolute surface of articulated movement".
African music
 In the
In the Griot
A griot (; ; Manding: jali or jeli (in N'Ko: , ''djeli'' or ''djéli'' in French spelling); Serer: kevel or kewel / okawul; Wolof: gewel) is a West African historian, storyteller, praise singer, poet, and/or musician.
The griot is a repos ...
tradition of Africa everything related to music has been passed on orally. Babatunde Olatunji (1927–2003) developed a simple series of spoken sounds for teaching the rhythms of the hand-drum, using six vocal sounds, "Goon, Doon, Go, Do, Pa, Ta", for three basic sounds on the drum, each played with either the left or the right hand. The debate about the appropriateness of staff notation for African music is a subject of particular interest to outsiders while African scholars from Kyagambiddwa to Kongo have, for the most part, accepted the conventions and limitations of staff notation, and produced transcriptions to inform and enable discussion and debate.
John Miller has argued that West African music is based on the tension between rhythms, polyrhythm
Polyrhythm is the simultaneous use of two or more rhythms that are not readily perceived as deriving from one another, or as simple manifestations of the same meter. The rhythmic layers may be the basis of an entire piece of music ( cross-rhyt ...
s created by the simultaneous sounding of two or more different rhythms, generally one dominant rhythm interacting with one or more independent competing rhythms. These often oppose or complement each other and the dominant rhythm. Moral values underpin a musical system based on repetition of relatively simple patterns that meet at distant cross-rhythmic intervals and on call-and-response form. Collective utterances such as proverbs or lineages appear either in phrases translated into "drum talk" or in the words of songs. People expect musicians to stimulate participation by reacting to people dancing. Appreciation of musicians is related to the effectiveness of their upholding community values.
Indian music
Indian music has also been passed on orally. Tabla players would learn to speak complex rhythm patterns and phrases before attempting to play them. Sheila Chandra, an English pop singer of Indian descent, made performances based on her singing these patterns. InIndian classical music
Indian classical music is the classical music of the Indian subcontinent. It has two major traditions: the North Indian classical music known as ''Hindustani'' and the South Indian expression known as '' Carnatic''. These traditions were not ...
, the Tala
Tala may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Tala (comics), a fictional character in DC comics
*''Tala'', a 1938 volume of poetry by Gabriela Mistral
*Tala (music), a rhythmic pattern in Indian classical music
* "Tala" (song), by Sarah Geronimo ...
of a composition is the rhythmic pattern over which the whole piece is structured.
Western music
In the 20th century, composers likeIgor Stravinsky
Igor Fyodorovich Stravinsky (6 April 1971) was a Russian composer, pianist and conductor, later of French (from 1934) and American (from 1945) citizenship. He is widely considered one of the most important and influential composers of the ...
, Béla Bartók
Béla Viktor János Bartók (; ; 25 March 1881 – 26 September 1945) was a Hungarian composer, pianist, and ethnomusicologist. He is considered one of the most important composers of the 20th century; he and Franz Liszt are regarded as Hun ...
, Philip Glass
Philip Glass (born January 31, 1937) is an American composer and pianist. He is widely regarded as one of the most influential composers of the late 20th century. Glass's work has been associated with minimalism, being built up from repetitive ...
, and Steve Reich
Stephen Michael Reich ( ; born October 3, 1936) is an American composer known for his contribution to the development of minimal music in the mid to late 1960s. Reich's work is marked by its use of repetitive figures, slow harmonic rhythm, ...
wrote more rhythmically complex music using odd meters, and techniques such as phasing and additive rhythm. At the same time, modernists such as Olivier Messiaen
Olivier Eugène Prosper Charles Messiaen (, ; ; 10 December 1908 – 27 April 1992) was a French composer, organist, and ornithologist who was one of the major composers of the 20th century. His music is rhythmically complex; harmonical ...
and his pupils used increased complexity to disrupt the sense of a regular beat, leading eventually to the widespread use of irrational rhythms in New Complexity. This use may be explained by a comment of John Cage's where he notes that regular rhythms cause sounds to be heard as a group rather than individually; the irregular rhythms highlight the rapidly changing pitch relationships that would otherwise be subsumed into irrelevant rhythmic groupings. La Monte Young also wrote music in which the sense of a regular beat is absent because the music consists only of long sustained tones (drones
Drone most commonly refers to:
* Drone (bee), a male bee, from an unfertilized egg
* Unmanned aerial vehicle
* Unmanned surface vehicle, watercraft
* Unmanned underwater vehicle or underwater drone
Drone, drones or The Drones may also refer to:
...
). In the 1930s, Henry Cowell
Henry Dixon Cowell (; March 11, 1897 – December 10, 1965) was an American composer, writer, pianist, publisher and teacher. Marchioni, Tonimarie (2012)"Henry Cowell: A Life Stranger Than Fiction" ''The Juilliard Journal''. Retrieved 19 June 20 ...
wrote music involving multiple simultaneous periodic rhythms and collaborated with Leon Theremin
Leon Theremin (born Lev Sergeyevich Termen rus, Лев Сергеевич Термéн, p=ˈlʲef sʲɪrˈɡʲejɪvʲɪtɕ tɨrˈmʲen; – 3 November 1993) was a Russian and Soviet inventor, most famous for his invention of the theremin, one o ...
to invent the rhythmicon, the first electronic rhythm machine, in order to perform them. Similarly, Conlon Nancarrow wrote for the player piano
A player piano (also known as a pianola) is a self-playing piano containing a pneumatic or electro-mechanical mechanism, that operates the piano action via programmed music recorded on perforated paper or metallic rolls, with more modern i ...
.
Linguistics
Inlinguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Lingu ...
, rhythm or isochrony is one of the three aspects of prosody, along with stress and intonation. Languages can be categorized according to whether they are syllable-timed, mora-timed, or stress-timed. Speakers of syllable-timed languages such as Spanish and Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
put roughly equal time on each syllable; in contrast, speakers of stressed-timed languages such as English and Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin (; ) is a group of Chinese (Sinitic) dialects that are natively spoken across most of northern and southwestern China. The group includes the Beijing dialect, the basis of the phonology of Standard Chinese, the official language ...
put roughly equal time lags between stressed syllables, with the timing of the unstressed syllables in between them being adjusted to accommodate the stress timing.
Narmour, cited in describes three categories of prosodic rules that create rhythmic successions that are additive (same duration repeated), cumulative (short-long), or countercumulative (long-short). Cumulation is associated with closure or relaxation, countercumulation with openness or tension, while additive rhythms are open-ended and repetitive. Richard Middleton points out this method cannot account for syncopation
In music, syncopation is a variety of rhythms played together to make a piece of music, making part or all of a tune or piece of music off-beat. More simply, syncopation is "a disturbance or interruption of the regular flow of rhythm": a "plac ...
and suggests the concept of transformation.
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * . * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Giger, Peter (1993). ''Die Kunst des Rhythmus'', Schott Music. A theoretical approach to western and non-western rhythms. * * * Humble, M. (2002)The Development of Rhythmic Organization in Indian Classical Music
MA dissertation, School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London. * Lewis, Andrew (2005). ''Rhythm—What it is and How to Improve Your Sense of It''. San Francisco
RhythmSource
Press. . * Mazzola, Guerino (2017). ''The Topos of Music, Vol. I''. Heidelberg: Springer. . * * Palmer, John (2013). ''Rhythm to Go'', Vision Edition and CE Books. A fast-track collection of graded exercises from elementary to advanced level divided in four sections and including an additional chapter with rhythmic structures used in contemporary music. * Petersen, Peter (2013). ''Music and Rhythm: Fundamentals, History, Analysis.'' New York: Peter Lang. * Scholes, Percy (1977a). "Form", in ''The Oxford Companion to Music'', 6th corrected reprint of the 10th ed. (1970), revised and reset, edited by John Owen Ward. London and New York: Oxford University Press. . * Williams, C. F. A., ''The Aristoxenian Theory of Musical Rhythm'', (Cambridge Library Collection—Music), Cambridge University Press; first edition, 2009. * Van Der, Horst F. (1963). ''Maat en Ritme'', Broekmans & Van Poppel, . A collection of graded exercises in two volumes, from elementary to advanced level. *
External links
'Rhythm of Prose', William Morrison Patterson ,Columbia University Press 1917
* ttp://www.signosemio.com/semiotics-of-rhythm.asp Louis Hébert, "A Little Semiotics of Rhythm. Elements of Rhythmology", in ''Signo'' {{Authority control * Cognitive musicology Musical terminology Patterns