Renaissance Florence on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Margrave Hugh "the Great" of Tuscany chose Florence as his residence instead of Lucca in about 1000 CE. This initiated a
Margrave Hugh "the Great" of Tuscany chose Florence as his residence instead of Lucca in about 1000 CE. This initiated a  Political conflict did not, however, prevent the city's rise to become one of the most powerful and prosperous in Europe, assisted by its own strong gold currency. The "fiorino d'oro" of the
Political conflict did not, however, prevent the city's rise to become one of the most powerful and prosperous in Europe, assisted by its own strong gold currency. The "fiorino d'oro" of the 
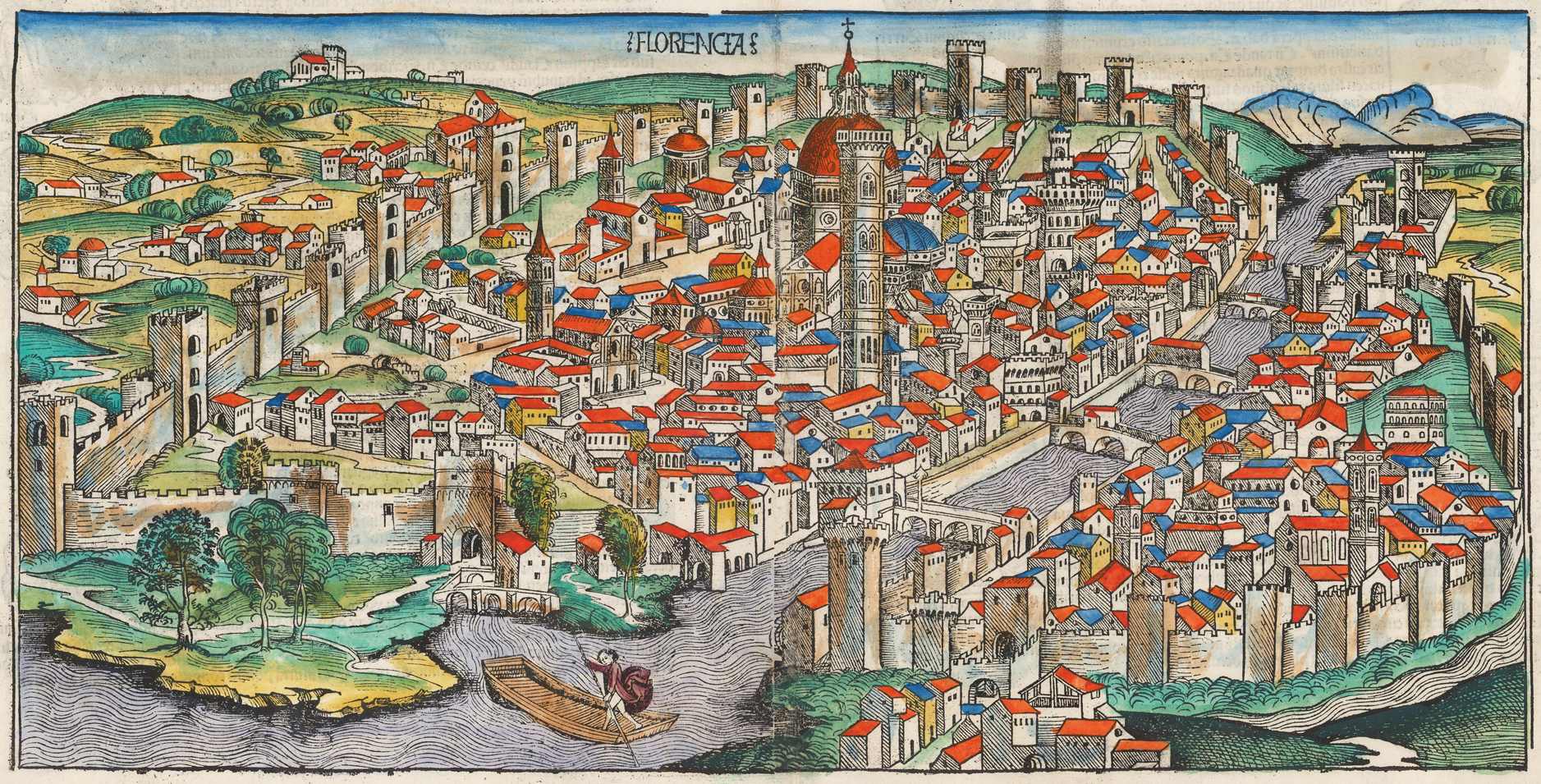 After Lorenzo's death in 1492, his son
After Lorenzo's death in 1492, his son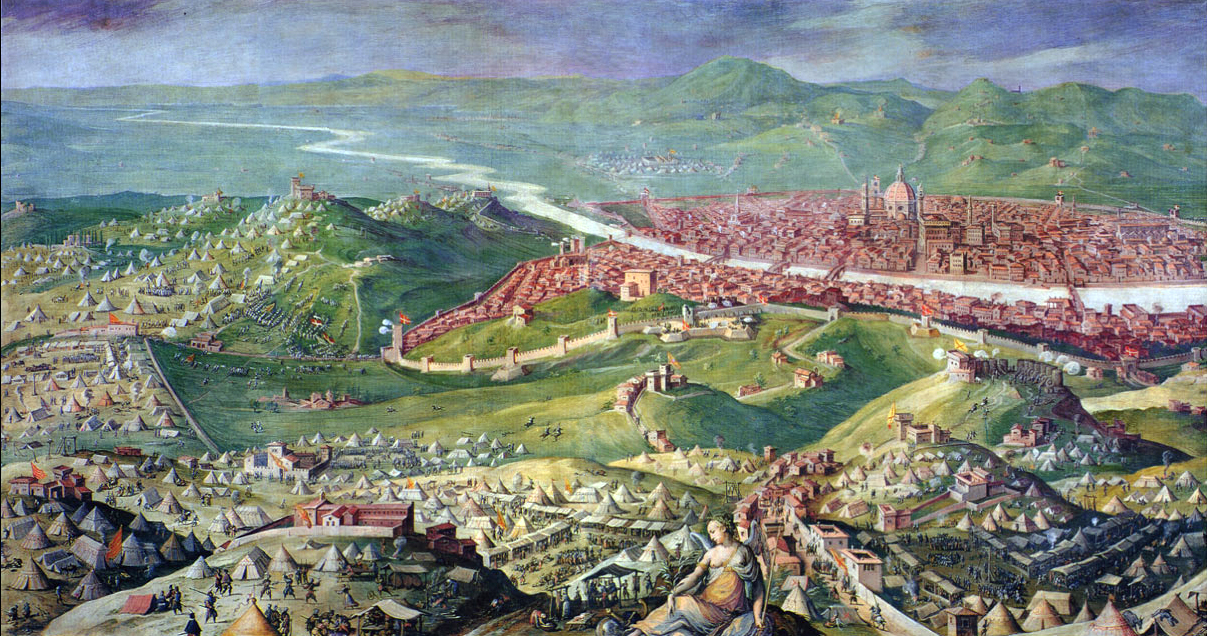  The 10-month
The 10-month
 The extinction of the Medici line and the accession in 1737 of Francis Stephen, duke of Lorraine, the husband of
The extinction of the Medici line and the accession in 1737 of Francis Stephen, duke of Lorraine, the husband of  Florence replaced
Florence replaced
, whilst Americans are about south of the cit
On November 4, 1966, the Flood of the River Arno in Florence, Arno flooded parts of the city centre, killing at least 40 and damaging millions of art treasures and rare books. There was no warning from the authorities who knew the flood was coming except a phone call to the jewellers on the Ponte Vecchio. Volunteers from around the world came to help rescue the books and art, and the effort inspired multiple new methods of
excerpt and text search
* Goldthwaite, Richard A. ''The Economy of Renaissance Florence'' (2009) * Hibbert, Christopher, ''Florence: The Biography of a City'', Penguin Books, 1994. * Holmes, George. ''The Florentine Enlightenment, 1400-50'' (1969) * Najemy. John M. ''A History of Florence 1200-1575'' (2008
excerpt and text search
SCRC 311 Cochran Ledger of Debtors and Creditors at OPenn
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Florence

Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico an ...
( it, Firenze) weathered the decline of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
to emerge as a financial hub of Europe, home to several bank
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
Because ...
s including that of the politically powerful Medici family
The House of Medici ( , ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici, in the Republic of Florence during the first half of the 15th century. The family originated in the Muge ...
. The city's wealth supported the development of art during the Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance ( it, Rinascimento ) was a period in Italian history covering the 15th and 16th centuries. The period is known for the initial development of the broader Renaissance culture that spread across Europe and marked the trans ...
, and tourism attracted by its rich history continues today.
Prehistoric origins
For much of theQuaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
Age, the Florence-Prato
Prato ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, Italy, the capital of the Province of Prato. The city lies in the north east of Tuscany, at the foot of Monte Retaia, elevation , the last peak in the Calvana chain. With more than 200,000 i ...
-Pistoia
Pistoia (, is a city and ''comune'' in the Italian region of Tuscany, the capital of a province of the same name, located about west and north of Florence and is crossed by the Ombrone Pistoiese, a tributary of the River Arno. It is a typi ...
plain was occupied by a great lake bounded by Monte Albano in the west, Monte Giovi in the north and the foothills of Chianti
A Chianti wine (, also , ) is any wine produced in the Chianti region of central Tuscany. It was historically associated with a squat bottle enclosed in a straw basket, called a ''fiasco'' ("flask"; ''pl. fiaschi''). However, the ''fiasco'' is ...
in the south. Even after most of the water had receded, the plain, above sea level, was strewn with ponds and marshes that remained until the 18th century, when the land was reclaimed. Most of the marshland was in the region of Campi Bisenzio
Campi Bisenzio is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Florence in the Italian region Tuscany, located about northwest of Florence.
History
The word Campi in the municipality's name stems from the fields which are widespread i ...
, Signa
Signa () is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Florence in the Italian region Tuscany, located about west of Florence.
Signa borders the following municipalities: Campi Bisenzio, Carmignano, Lastra a Signa, Poggio a Caiano, ...
and Bagno a Ripoli
Bagno a Ripoli is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Florence in the Italian region Tuscany, located about southeast of Florence.
The International School of Florence has its primary school campus in the comune.
.
It is thought that there was already a settlement at the confluence of the Mugnone River with the River Arno between the 10th and 8th centuries BC. Between the 7th and 6th centuries BC, Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, rou ...
discovered and used the ford of the Arno near this confluence, closer to the hills to the north and south. A bridge or a ferry was probably constructed here, about ten metres away from the current Ponte Vecchio
The Ponte Vecchio ("Old Bridge", ) is a medieval stone closed-spandrel segmental arch bridge over the Arno River, in Florence, Italy. The only bridge in Florence spared from destruction during the Second World War, it is noted for the shops bui ...
, but closer to the ford itself. The Etruscans, however, preferred not to build cities on the plain for reasons of defence and instead settled about six kilometres away on a hill. This settlement was a precursor of the fortified centre of Vipsul (today's Fiesole
Fiesole () is a town and ''comune'' of the Metropolitan City of Florence in the Italian region of Tuscany, on a scenic height above Florence, 5 km (3 miles) northeast of that city. It has structures dating to Etruscan and Roman times.
Sin ...
), which was later connected by road to all the major Etruscan centres of Emilia
Emilia may refer to:
People
* Emilia (given name), list of people with this name
Places
* Emilia (region), a historical region of Italy. Reggio, Emilia
* Emilia-Romagna, an administrative region in Italy, including the historical regions of Emi ...
to the north and Lazio
it, Laziale
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
to the south.
Classical Florence
Some historians still assert the existence of a Pre-Roman settlement in Florence, arguing the possibility of an urban center destroyed bySulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He won the first large-scale civil war in Roman history and became the first man of the Republic to seize power through force.
Sulla had ...
.
Written history of Florence traditionally begins in 59 BC, when the Romans founded the village for army veterans, and reportedly dedicated it to the god Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
. According to some stories, the city was founded for precise political and strategic reasons; in 62 BC, Fiesole
Fiesole () is a town and ''comune'' of the Metropolitan City of Florence in the Italian region of Tuscany, on a scenic height above Florence, 5 km (3 miles) northeast of that city. It has structures dating to Etruscan and Roman times.
Sin ...
(a region in Florence) was a cove for Catiline
Lucius Sergius Catilina ( 108 BC – January 62 BC), known in English as Catiline (), was a Roman politician and soldier. He is best known for instigating the Catilinarian conspiracy, a failed attempt to violently seize control of the R ...
s, and Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman people, Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caes ...
wanted an outpost nearby to monitor the roads and communications.
The Romans built ports on the Arno
The Arno is a river in the Tuscany region of Italy. It is the most important river of central Italy after the Tiber.
Source and route
The river originates on Monte Falterona in the Casentino area of the Apennines, and initially takes a s ...
and the Mugnone
The Mugnone is a river in Italy that runs through Florence and is a tributary to the Arno. The river has been known since Roman times. The river historically flowed into the Arno near the Ponte Vecchio
The Ponte Vecchio ("Old Bridge", ) is a me ...
to create advantageous transport positions; old Florence was on the Via Cassia
The ''Via Cassia'' ("way of Cassius") was an important Roman road striking out of the ''Via Flaminia'' near the Milvian Bridge in the immediate vicinity of Rome and, passing not far from Veii, traversed Etruria. The ''Via Cassia'' passed throug ...
, forming a wedge controlling the end of the Apennine valley of the Arno and the beginning of the plain that led to the sea in the direction of Pisa
Pisa ( , or ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for its leaning tower, the cit ...
. In AD 123, a bridge was constructed over the Arno. Buildings began to accumulate around the Roman military camp, including an aqueduct (from Monte Morello
Monte Morello is the highest mountain (934 m.) in the Florentine valley, Italy. It is located to the north-west of Florence and it spreads across the borders of the municipalities of Florence, Vaglia, Sesto Fiorentino and Calenzano.
More ...
), a forum (in today's Piazza della Repubblica), spas, the Roman Theatre of Florence, and the Roman Amphitheatre of Florence, while the surrounding land was organized by centuriation Centuriation (in Latin ''centuriatio'' or, more usually, ''limitatio''), also known as Roman grid, was a method of land measurement used by the Romans. In many cases land divisions based on the survey formed a field system, often referred to in mode ...
. A nearby river port allowed trade up to Pisa. The outlines of the Roman city are still recognizable in the city's plan, notably the city walls
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
.
In AD 285, Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, grc, Διοκλητιανός, Diokletianós; c. 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed ''Iovius'', was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Gaius Valerius Diocles ...
established a commander seat in Florence who was responsible for all of Tuscia Tuscia is a historical region of Italy that comprised the territories under Etruscan influence and the name adopted for Etruria after the Roman conquest. While it later came to coincide with today's province of Viterbo, it was originally much larger ...
. Eastern merchants (some from the quarter of Oltrarno
The Oltrarno (''beyond the Arno'') is a quarter of Florence, Italy. It is located south of the River Arno. It contains part of the historic centre of Florence and many notable sites such as the church Santo Spirito di Firenze, Palazzo Pitti, Bel ...
) brought the cult of Isis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic: ''Wos'' 'a''or ''Wusa''; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingd ...
, and later Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
.
Because Florence rapidly developed over the next several centuries and into the Middle Ages, few monuments from the Roman period remain in Florence today. Some of the remaining structures include the thermal complex discovered in the Piazza della Signoria
Piazza della Signoria () is a w-shaped square in front of the Palazzo Vecchio in Florence, Italy. It was named after the Palazzo della Signoria, also called Palazzo Vecchio. It is the main point of the origin and history of the Florentine Republ ...
, the amphitheater
An amphitheatre (British English) or amphitheater (American English; both ) is an open-air venue used for entertainment, performances, and sports. The term derives from the ancient Greek ('), from ('), meaning "on both sides" or "around" and ...
(or at least its road structure), and artifacts remaining at the Florentine National Archaeological Museum and the Museo di Firenze com'era
Museo di Firenze com'era ("Museum of Florence as it was") was a history and archaeology museum, one of the civic museums of the city of Florence.
The museum was located on Via dell'Oriuolo in a former convent of the Oblates. It closed permanentl ...
(''English: The Museum of Florence as it Was'').
Early Middle Ages
The seat of abishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
from around the beginning of the 4th century CE, the city was ruled alternatively by Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
and Ostrogothic
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
potentates as the two powers fought each other for control of the city. The city would be taken by siege only to be lost again later by one of the two powers.
Peace returned under Lombard rule in the 6th century. Conquered by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Holy ...
in 774, Florence became part of the March of Tuscany
The March of Tuscany ( it, Marca di Tuscia; ) was a march of the Kingdom of Italy and the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages. Located in northwestern central Italy, it bordered the Papal States to the south, the Ligurian Sea to the west and ...
, whose capital was Lucca
Lucca ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, Central Italy, on the Serchio River, in a fertile plain near the Ligurian Sea. The city has a population of about 89,000, while its province has a population of 383,957.
Lucca is known as one o ...
. The population began to grow again and commerce prospered. In 854, Florence and Fiesole
Fiesole () is a town and ''comune'' of the Metropolitan City of Florence in the Italian region of Tuscany, on a scenic height above Florence, 5 km (3 miles) northeast of that city. It has structures dating to Etruscan and Roman times.
Sin ...
were united in one county.
Middle Ages
 Margrave Hugh "the Great" of Tuscany chose Florence as his residence instead of Lucca in about 1000 CE. This initiated a
Margrave Hugh "the Great" of Tuscany chose Florence as his residence instead of Lucca in about 1000 CE. This initiated a Golden Age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the ''Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages of Man, Ages, Gold being the first and the one during ...
of Florentine Art
Florentine painting or the Florentine School refers to artists in, from, or influenced by the naturalistic style developed in Florence in the 14th century, largely through the efforts of Giotto di Bondone, and in the 15th century the leading scho ...
. In 1013, construction was begun on the Basilica di San Miniato al Monte
San Miniato al Monte (St. Minias on the Mountain) is a basilica in Florence, central Italy, standing atop one of the highest points in the city. It has been described as one of the finest Romanesque structures in Tuscany and one of the most scenic ...
. The exterior of the baptistry
In Christian architecture the baptistery or baptistry (Old French ''baptisterie''; Latin ''baptisterium''; Greek , 'bathing-place, baptistery', from , baptízein, 'to baptize') is the separate centrally planned structure surrounding the baptismal ...
was reworked in Romanesque style between 1059 and 1128.
Florence experienced a long period of civic revival beginning in the 10th century and was governed from 1115 by an autonomous medieval commune
Medieval communes in the European Middle Ages had sworn allegiances of mutual defense (both physical defense and of traditional freedoms) among the citizens of a town or city. These took many forms and varied widely in organization and makeup.
C ...
. But the period of revival was interrupted when the city was plunged into internal strife by the 13th-century struggle between the Ghibellines
The Guelphs and Ghibellines (, , ; it, guelfi e ghibellini ) were factions supporting the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor, respectively, in the Italian city-states of Central Italy and Northern Italy.
During the 12th and 13th centuries, rivalr ...
, supporters of the German emperor
The German Emperor (german: Deutscher Kaiser, ) was the official title of the head of state and hereditary ruler of the German Empire. A specifically chosen term, it was introduced with the 1 January 1871 constitution and lasted until the offi ...
, and the pro-Papal
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
Guelphs
The Guelphs and Ghibellines (, , ; it, guelfi e ghibellini ) were factions supporting the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor, respectively, in the Italian city-states of Central Italy and Northern Italy.
During the 12th and 13th centuries, rivalr ...
after the murder of nobleman Buondelmonte del Buondelmonti for reneging on his agreement to marry one of the daughters of the Amidei
Amidei was the name of a noble family from Florence, Italy. The family was of Roman descent but lived in Florence since its foundation. They have been described by Niccolò Machiavelli as being one of the most powerful families of its time, and ...
family. In 1257, the city was ruled by a ''podestà
Podestà (, English: Potestate, Podesta) was the name given to the holder of the highest civil office in the government of the cities of Central and Northern Italy during the Late Middle Ages. Sometimes, it meant the chief magistrate of a city ...
'', the Guelph Luca Grimaldi
Luca Grimaldi (floruit, fl. 1240–1275) was a Genoa, Genoese troubadour and Guelphs and Ghibellines, Guelph politician and diplomat. None of his poetic work survives.
Jean de Nostredame listed one ''Luco ou Lucas de Grymaud, natif de Gryma ...
. The Guelphs had triumphed and soon split in turn into feuding "White" and "Black" factions led respectively by Vieri de' Cerchi
The Florentine banking family of the Cerchi, minor nobles of the Valdarno, with a seat especially at Acone near Pontassieve, settled in Florence in the early thirteenth century and increased their fortunes. The family became the heads of a conso ...
and Corso Donati Corso Donati was a leader of the Black Guelph faction in 13th- and early 14th- century Florence.
Bologna and Pistoia
In the late thirteenth century, power in Florence and the other Tuscan cities was divided between the Podestà, an outsider who ser ...
. These struggles eventually led to the exile of the White Guelphs, one of whom was the poet Dante Alighieri
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian poet, writer and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: '' ...
. This factional strife was later recorded by Dino Compagni Dino Compagni (c. 125526 February 1324) was an Italian historical writer and political figure.
Dino is an abridgement of Aldobrandino or Ildebrandino. He was born into a ''popolano'' or prosperous family of Florence, supporters of the White party o ...
, a White Guelph, in his ''Chronicles of Florence''.
 Political conflict did not, however, prevent the city's rise to become one of the most powerful and prosperous in Europe, assisted by its own strong gold currency. The "fiorino d'oro" of the
Political conflict did not, however, prevent the city's rise to become one of the most powerful and prosperous in Europe, assisted by its own strong gold currency. The "fiorino d'oro" of the Republic of Florence
The Republic of Florence, officially the Florentine Republic ( it, Repubblica Fiorentina, , or ), was a medieval and early modern state that was centered on the Italian city of Florence in Tuscany. The republic originated in 1115, when the Flo ...
, or florin
The Florentine florin was a gold coin struck from 1252 to 1533 with no significant change in its design or metal content standard during that time. It had 54 grains (3.499 grams, 0.113 troy ounce) of nominally pure or 'fine' gold with a purcha ...
, was introduced in 1252, the first European gold coin struck in sufficient quantities to play a significant commercial role since the 7th century. Many Florentine banks had branches across Europe, with able bankers and merchants such as the famous chronicler Giovanni Villani
Giovanni Villani (; 1276 or 1280 – 1348)Bartlett (1992), 35. was an Italian banker, official, diplomat and chronicler from Florence who wrote the ''Nuova Cronica'' (''New Chronicles'') on the history of Florence. He was a leading statesman ...
of the Peruzzi Company engaging in commercial transactions as far away as Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
. The florin quickly became the dominant trade coin of Western Europe, replacing silver bars in multiples of the mark. This period also saw the eclipse of Florence's formerly powerful rival Pisa
Pisa ( , or ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for its leaning tower, the cit ...
, which was defeated by Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the List of cities in Italy, sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian ce ...
in 1284 and subjugated by Florence in 1406. Power shifted from the aristocracy to the mercantile elite and members of organized guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
s after an anti-aristocratic movement, led by Giano della Bella, enacted the Ordinances of Justice
The Ordinances of Justice were a series of statutory laws enacted in the Republic of Florence of northern Italy between the years 1293 and 1295.
Description
These laws were directed against, and identified by name, particularly influential (i.e ...
in 1293.
While visiting the ruins of Rome during the jubilee
A jubilee is a particular anniversary of an event, usually denoting the 25th, 40th, 50th, 60th, and the 70th anniversary. The term is often now used to denote the celebrations associated with the reign of a monarch after a milestone number of y ...
celebration in 1300, the banker and chronicler Giovanni Villani
Giovanni Villani (; 1276 or 1280 – 1348)Bartlett (1992), 35. was an Italian banker, official, diplomat and chronicler from Florence who wrote the ''Nuova Cronica'' (''New Chronicles'') on the history of Florence. He was a leading statesman ...
(c. 1276–1348) noted the well-known history of the city, its monuments and achievements, and was then inspired to write a universal history
A universal history is a work aiming at the presentation of a history of all of mankind as a whole, coherent unit. A universal chronicle or world chronicle typically traces history from the beginning of written information about the past up to t ...
of his own city of Florence. Hence he began to record the history of Florence in a year-by-year format in his ''Nuova Cronica
The ''Nuova Cronica'' (also: ''Nova Cronica'') or '' New Chronicles'' is a 14th-century history of Florence created in a year-by-year linear format and written by the Italian banker and official Giovanni Villani (c. 1276 or 1280–1348). T ...
'', which was continued by his brother and nephew after he succumbed to the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
in 1348. Villani is praised by historians for preserving valuable information on statistics, biographies, and even events taking place throughout Europe, but his work has also drawn criticism by historians for its many inaccuracies, use of the supernatural and divine providence
In theology, Divine Providence, or simply Providence, is God's intervention in the Universe. The term ''Divine Providence'' (usually capitalized) is also used as a title of God. A distinction is usually made between "general providence", which ...
to explain the outcome of events and glorification of Florence and the papacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
.

Renaissance
In 1338, there were about 17,000 beggars in the city. Four thousand were on public relief. There were six primary schools with 10,000 pupils, including girls. Four high schools taught 600 students, including a few girls. They studied literature and philosophy. Of a population estimated at 80,000 before theBlack Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
of 1349, about 25,000 are estimated to have been engaged in the city's wool industry. In 1345, Florence was the scene of an attempted strike by wool carders (''ciompi''), who in 1378 rose up in a brief revolt against oligarchic rule known as the Revolt of the Ciompi
The Ciompi Revolt was a rebellion among unrepresented labourers which occurred in the Republic of Florence, from 1378 to 1382.Cohn, Samuel K., Jr. ''Popular Protest in Late Medieval Europe: Italy, France, and Flanders''. Manchester, Manchester UP, ...
. After their suppression, the city came under the sway of the Albizzi
The Albizzi family () was a Florentine family originally based in Arezzo, who were rivals of the Medici and Alberti families. They were at the centre of Florentine oligarchy from 1382, in the reaction that followed the Ciompi revolt, to the rise ...
family, bitter rivals of the Medici family
The House of Medici ( , ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici, in the Republic of Florence during the first half of the 15th century. The family originated in the Muge ...
, between 1382 and 1434. Cosimo de' Medici
Cosimo di Giovanni de' Medici (27 September 1389 – 1 August 1464) was an Italian banker and politician who established the Medici family as effective rulers of Florence during much of the Italian Renaissance. His power derived from his wealth ...
(1389–1464) was the first Medici family member to govern the city from behind the scenes. Although the city was technically a democracy of sorts, his power came from a vast network of patronage
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings, popes, and the wealthy have provided to artists su ...
and a political alliance to new immigrants to the city, the ''gente nuova''. The fact that the Medici were bankers to the pope also contributed to their prominence. Cosimo was succeeded by his son Piero di Cosimo de' Medici
Piero di Cosimo de' Medici (the Gouty), (Italian: ''Piero "il Gottoso"'') (1416 – 2 December 1469) was the ''de facto'' ruler of Florence from 1464 to 1469, during the Italian Renaissance.
Biography
Piero was the son of Cosimo de' Medi ...
(1416–1469), who was shortly thereafter succeeded by Cosimo's grandson, Lorenzo in 1469. Lorenzo de' Medici was a great patron of the arts who commissioned works by Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was insp ...
, Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
and Sandro Botticelli
Alessandro di Mariano di Vanni Filipepi ( – May 17, 1510), known as Sandro Botticelli (, ), was an Italian Renaissance painting, Italian painter of the Early Renaissance. Botticelli's posthumous reputation suffered until the late 19th cent ...
.
 After Lorenzo's death in 1492, his son
After Lorenzo's death in 1492, his son Piero the Unfortunate
Piero di Lorenzo de' Medici (15 February 1472 – 28 December 1503), called Piero the Fatuous or Piero the Unfortunate, was the lord of Florence from 1492 until his exile in 1494.
Early life
Piero di Lorenzo de' Medici was the eldest son of ...
took the reins of government, however his rule was short. In 1494, King Charles VIII of France
Charles VIII, called the Affable (french: l'Affable; 30 June 1470 – 7 April 1498), was King of France from 1483 to his death in 1498. He succeeded his father Louis XI at the age of 13.Paul Murray Kendall, ''Louis XI: The Universal Spider'' (Ne ...
invaded Italy and entered Tuscany on his way to claim the throne of the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
. After Piero made a submissive treaty with Charles, the Florentines responded by forcing him into exile, and the first period of Medici rule ended with the restoration of a republican government. Anti-Medici sentiment was much influenced by the teachings of the radical Dominican prior Girolamo Savonarola
Girolamo Savonarola, OP (, , ; 21 September 1452 – 23 May 1498) or Jerome Savonarola was an Italian Dominican friar from Ferrara and preacher active in Renaissance Florence. He was known for his prophecies of civic glory, the destruction of ...
. However, in due time, Savonarola lost support and was hanged in 1498. Medici rule was not restored until 1512. The Florentines drove out the Medici for a second time and re-established the Republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
on May 16, 1527.
An individual of highly unusual insight into political conditions of this time was Niccolò Machiavelli
Niccolò di Bernardo dei Machiavelli ( , , ; 3 May 1469 – 21 June 1527), occasionally rendered in English as Nicholas Machiavel ( , ; see below), was an Italian diplomat, author, philosopher and historian who lived during the Renaissance. ...
, whose prescriptions for Florence's regeneration under strong leadership have often been seen as a legitimization of political expediency and even evil. Machiavelli was tortured and exiled from Florence by the Medici family in 1513, due to accusations of conspiracy, which was exacerbated because of his ties to the previous republican government of Florence. Commissioned by the Medici, in 1520 Machiavelli wrote the ''Florentine Histories
''Florentine Histories'' ( it, Istorie fiorentine) is a historical account by Italian Renaissance political philosopher and writer Niccolò Machiavelli, first published posthumously in 1532.
Background
After the crisis of 1513, with arrests for ...
'', a history of the city.
 The 10-month
The 10-month Siege of Florence (1529–1530)
The siege of Florence took place from 24 October 1529 to 10 August 1530, at the end of the War of the League of Cognac. At the Congress of Bologna, the Medici Pope Clement VII and Emperor Charles V agreed to restore the Medici family in Flore ...
by the Spanish ended the Republic of Florence
The Republic of Florence, officially the Florentine Republic ( it, Repubblica Fiorentina, , or ), was a medieval and early modern state that was centered on the Italian city of Florence in Tuscany. The republic originated in 1115, when the Flo ...
and Alessandro de' Medici
Alessandro is both a given name and a surname, the Italian form of the name Alexander. Notable people with the name include:
People with the given name Alessandro
* Alessandro Allori (1535–1607), Italian portrait painter
* Alessandro Baricco ...
became the ruler of the city. The siege brought the destruction of its suburbs, the ruin of its export business and the confiscation of its citizens' wealth. Alessandro, who ruled from 1531 to 1537, was the first Medici to use the style Duke of Florence
The ''Duca della Repubblica Fiorentina'', rendered in English as Duke of the Florentine Republic or Duke of the Republic of Florence, was a title created in 1532 by Pope Clement VII for the Medici family (his own family), which ruled the Republic ...
, a title arranged for him in 1532 by Holy Roman Emperor Charles V
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain ( Castile and Aragon) fro ...
. In 1569, Duke Cosimo I
Cosimo I de' Medici (12 June 1519 – 21 April 1574) was the second Duke of Florence from 1537 until 1569, when he became the first Grand Duke of Tuscany, a title he held until his death.
Life
Rise to power
Cosimo was born in Florence on 12 ...
was elevated to the rank of Grand Duke of Tuscany
The rulers of Tuscany varied over time, sometimes being margraves, the rulers of handfuls of border counties and sometimes the heads of the most important family of the region.
Margraves of Tuscany, 812–1197 House of Boniface
:These were origin ...
by Pope Pius V
Pope Pius V ( it, Pio V; 17 January 1504 – 1 May 1572), born Antonio Ghislieri (from 1518 called Michele Ghislieri, O.P.), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1566 to his death in May 1572. He is v ...
. The Medici would continue to rule in Tuscany as grand dukes until 1737. After the Battle of Marciano
The Battle of Marciano (also known as the Battle of Scannagallo) occurred in the countryside of Marciano della Chiana, near Arezzo, Tuscany, on August 2, 1554, during the Italian War of 1551. The battle marked the defeat of the Republic of Sie ...
in 1554, the city's historical rival Siena
Siena ( , ; lat, Sena Iulia) is a city in Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the province of Siena.
The city is historically linked to commercial and banking activities, having been a major banking center until the 13th and 14th centuri ...
was conquered and the only remaining territory in Tuscany not ruled from Florence was the Republic of Lucca
Lucca ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, Central Italy, on the Serchio River, in a fertile plain near the Ligurian Sea. The city has a population of about 89,000, while its province has a population of 383,957.
Lucca is known as one o ...
(later a Duchy
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a Middle Ages, medieval country, territory, fiefdom, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or Queen regnant, queen in Western European tradition.
There once exis ...
).
During Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
Florence, mob
Mob or MOB may refer to:
Behavioral phenomena
* Crowd
* Smart mob, a temporary self-structuring social organization, coordinated through telecommunication
Crime and law enforcement
* American Mafia, also known as the Mob
* Irish Mob, a US crimin ...
s were both common and influential. Families were pitted against each other in a constant struggle for power. Politically, double-crossings and betrayals were not uncommon, sometimes even within families. Despite political violence, factionalism and corruption, Renaissance Florence did experiment with different forms of citizen government and power sharing arrangements. In order to reconcile the warring factions and families, a complex electoral system was developed as mechanism for sharing power. Incumbent officers and appointees carried out a secret ballot every three or four years. They committed the names of all those elected into a series of bags, one for each sesto, or sixth, of the city. One name was drawn from each bag every two months to form the highest executive authority of the city, the Signoria
A signoria () was the governing authority in many of the Italian city states during the Medieval and Renaissance periods.
The word signoria comes from ''signore'' , or "lord"; an abstract noun meaning (roughly) "government; governing authority; ...
. The selection scheme was controlled to ensure that no two members of the same family ended up in the same batch of six names.
This lottery
A lottery is a form of gambling that involves the drawing of numbers at random for a prize. Some governments outlaw lotteries, while others endorse it to the extent of organizing a national or state lottery. It is common to find some degree of ...
arrangement organized the political structure of Florence until 1434, when the Medici family took power. To maintain control, the Medici undermined the selection process by introducing a system of elected committees they could effectively manipulate by fear and favour. Civic lotteries still took place, but actual power rested with the Medicis. In 1465, a movement to reintroduce civic lotteries was halted by an extraordinary commission packed with Medici supporters.
Role in art, literature, music and science
The surge in artistic, literary, and scientific investigation that occurred in Florence in the 14th-16th centuries was facilitated by Florentines' strong economy, based on money, banking, trade, and with the display of wealth and leisure. In parallel with leisure evolving from a strong economy, the crises of theCatholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
church (especially the controversy over the French Avignon Papacy
The Avignon Papacy was the period from 1309 to 1376 during which seven successive popes resided in Avignon – at the time within the Kingdom of Burgundy-Arles, Kingdom of Arles, part of the Holy Roman Empire; now part of France – rather than i ...
and the Great Schism) along with the catastrophic effects of the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
led to a re-evaluation of medieval values, resulting in the development of a humanist
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "humani ...
culture, stimulated by the works of Petrarch
Francesco Petrarca (; 20 July 1304 – 18/19 July 1374), commonly anglicized as Petrarch (), was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.
Petrarch's rediscovery of Cicero's letters is often credited w ...
and Boccaccio
Giovanni Boccaccio (, , ; 16 June 1313 – 21 December 1375) was an Italian people, Italian writer, poet, correspondent of Petrarch, and an important Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanist. Born in the town of Certaldo, he became so we ...
. This prompted a revisitation and study of the classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, leading to the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
.
This renaissance thrived locally from about 1434 to 1534. It halted amid social, moral, and political upheaval. By then, the inspiration it had created had set the rest of Western Europe ablaze with new ideas.
Florence benefited materially and culturally from this sea-change in social consciousness
Social consciousness or social awareness, is collective consciousness shared by individuals within a society.ancient Greek drama
Ancient Greek theatre was a theatrical culture that flourished in ancient Greece from 700 BC. The city-state of Athens, which became a significant cultural, political, and religious place during this period, was its centre, where the theatre was ...
by humanist scholars led to the birth of opera
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librett ...
in the 1590s.
Modern and contemporary age
 The extinction of the Medici line and the accession in 1737 of Francis Stephen, duke of Lorraine, the husband of
The extinction of the Medici line and the accession in 1737 of Francis Stephen, duke of Lorraine, the husband of Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa Walburga Amalia Christina (german: Maria Theresia; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was ruler of the Habsburg dominions from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position ''suo jure'' (in her own right). ...
of Austria, led to Tuscany's inclusion in the territories of the Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
n crown. Austrian rule was to end in defeat at the hands of France and the Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia,The name of the state was originally Latin: , or when the kingdom was still considered to include Corsica. In Italian it is , in French , in Sardinian , and in Piedmontese . also referred to as the Kingdom of Savoy-S ...
-Piedmont in 1859, and Tuscany became a province of the united Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
in 1861.
 Florence replaced
Florence replaced Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
as Italy's capital in 1865 and, in an effort to modernise the city, the old market in the Piazza del Mercato Vecchio and many medieval houses were pulled down and replaced by a more formal street plan with newer houses. The Piazza (first renamed Piazza Vittorio Emmanuele II
en, Victor Emmanuel Maria Albert Eugene Ferdinand Thomas
, house = Savoy
, father = Charles Albert of Sardinia
, mother = Maria Theresa of Austria
, religion = Roman Catholicism
, image_size = 252px
, successio ...
, then Piazza della Repubblica, the present name) was significantly widened and a large triumphal arch was constructed at the west end. This development was unpopular and was prevented from continuing by the efforts of several British and American people living in the city. Poet Antonio Pucci had written in the 14th century, "There was never so noble a garden as when in Mercato Vecchio the eyes and tastes of the Florentines did feast." The area had, however, decayed from its original medieval splendor. A museum recording the destruction stands nearby today. The country's second capital city was superseded by Rome six years later after the withdrawal of the French troops made its addition to the kingdom possible. A very important role is played in these years by the famous Florentine café Giubbe Rosse from its foundation until the present day.
20th century
In the 19th century, the population of Florence doubled to over 230,000, and in the 20th century reached over 450,000 at one point with the growth of tourism, trade, financial services and the industry. A foreign community came to represent one-quarter of the population in the second half of the 19th century and of this period and writers such as James Irving and the pre-Raphaelite artists captured a romantic vision of the city in their works. Numerous villas of mainly English barons with their eclectic collections of art were bequeathed to the city in this era. Today they are occupied by museums such as the Horne Museum, theStibbert Museum
The Stibbert Museum ( it, Museo Stibbert) is located on via Frederick Stibbert on the hill of Montughi in Florence, Italy. The museum contains over 36,000 artifacts, including a vast collection of armour from Eastern and Western civilizations.
...
, Villa La Pietra
Villa La Pietra is a renaissance villa in the hills outside Florence, in Tuscany in central Italy. It was formerly the home of Arthur Acton and later of his son Harold Acton, on whose death in 1994 it was bequeathed to New York University. The vi ...
, etc.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the city experienced a year-long German occupation (1943–1944). On September 25, 1943, Allied bombers targeted central Florence, destroying many buildings and killing 215 civilians.
In late July 1944, the British 8th Army
The Eighth Army was an Allied field army formation of the British Army during the Second World War, fighting in the North African and Italian campaigns. Units came from Australia, British India, Canada, Czechoslovakia, Free French Forces ...
closed in as they liberated Tuscany. New Zealand troops stormed the Pian dei Cerri hills overlooking the city. After several days of fighting, German forces retreated and gave way.
During the German retreat, Florence was declared an undefended "open city
In war, an open city is a settlement which has announced it has abandoned all defensive efforts, generally in the event of the imminent capture of the city to avoid destruction. Once a city has declared itself open the opposing military will be ...
", prohibiting further shelling and bombing in accordance with the Hague Convention. On 4 August, the retreating Germans decided to detonate charges along the bridges of the Arno linking the district of Oltrarno
The Oltrarno (''beyond the Arno'') is a quarter of Florence, Italy. It is located south of the River Arno. It contains part of the historic centre of Florence and many notable sites such as the church Santo Spirito di Firenze, Palazzo Pitti, Bel ...
to the rest of the city, thus making it difficult for the New Zealand, South African and British troops to cross just before liberation. The German officer in charge of the demolitions, Gerhard Wolf
Gerhard Wolf (12 August 1896 – 23 March 1971) was a German diplomat who served as consul in Florence during World War II.
Wolf was born in Dresden, the seventh and youngest child of an attorney of family law. After serving in the military, he st ...
, ordered that the Ponte Vecchio
The Ponte Vecchio ("Old Bridge", ) is a medieval stone closed-spandrel segmental arch bridge over the Arno River, in Florence, Italy. The only bridge in Florence spared from destruction during the Second World War, it is noted for the shops bui ...
was to be spared. At 04:00 on 4 August 1944, an armored patrol of the South African Imperial Light Horse and Kimberley Regiments found the Ponte Vecchio bridge intact, crossed the bridge under heavy German shelling and subsequently became the first Allied soldiers to enter Florence. Before the war, Wolf had been a student in the city, and his decision has been honored with a memorial plaque on the bridge. Instead, an equally historic area of streets directly to the south of the bridge, including part of the Corridoio Vasariano, was destroyed using mines. Since then, the bridges have been restored exactly to their original forms using as many of the remaining materials as possible, but the buildings surrounding the Ponte Vecchio have been rebuilt in a style combining the old with modern design. The last days of battle for Florence were very intense because the Italian Fascists resistance skirmish known as ''Franchi Tiratori''. The Allied soldiers who died driving the Germans from Tuscany are buried in cemeteries outside the city, i.e. British and Commonwealth soldiers a few kilometers east of the center on the north bank of the Arn, whilst Americans are about south of the cit
On November 4, 1966, the Flood of the River Arno in Florence, Arno flooded parts of the city centre, killing at least 40 and damaging millions of art treasures and rare books. There was no warning from the authorities who knew the flood was coming except a phone call to the jewellers on the Ponte Vecchio. Volunteers from around the world came to help rescue the books and art, and the effort inspired multiple new methods of
art conservation
The conservation and restoration of cultural property focuses on protection and care of cultural property (tangible cultural heritage), including artworks, architecture, archaeology, and museum collections. Conservation activities include preve ...
. Forty years later, there were still works awaiting restoration.
On May 28, 1993, a powerful car bomb exploded in the via de Georgofili, behind the Uffizi
The Uffizi Gallery (; it, Galleria degli Uffizi, italic=no, ) is a prominent art museum located adjacent to the Piazza della Signoria in the Historic Centre of Florence in the region of Tuscany, Italy. One of the most important Italian museums ...
, killing five people, injuring numerous others and seriously damaging the Torre dei Pulci
The Torre dei Pulci is a historical tower in Florence, Italy. The tower was the residence of the Pulci family in medieval and Renaissance times, including poet Luigi Pulci. It was in origin a purely defensive tower, which was enlarged until it be ...
, the museum and parts of its collection. The blast has been attributed to the Mafia
"Mafia" is an informal term that is used to describe criminal organizations that bear a strong similarity to the original “Mafia”, the Sicilian Mafia and Italian Mafia. The central activity of such an organization would be the arbitration of d ...
.
21st century
In 2002, Florence was the seat of the firstEuropean Social Forum
The European Social Forum (ESF) was a recurring conference held by members of the alter-globalization movement (also known as the Global Justice Movement). In the first few years after it started in 2002 the conference was held every year, but late ...
. There are also several new building and cultural projects, such as that of the Parco della Musica e della Cultura, which will be a vast musical and cultural complex that is currently being built in the Parco delle Cascine
The Parco delle Cascine (Cascine Park) is a monumental and historical park in the city of Florence. The park covers an area of 160 hectares (395 acres). It has the shape of a long and narrow stripe, on the north bank of the Arno river. It extends ...
(Cascine park). It will host a lyrical theatre containing 2000 places, a concert hall for 1000 spectators, a hall with 3000 seats and an open-air amphitheatre with 3000 spaces. It will host numerous ballets, concerts, lyrical operas and numerous musical festivals. The theatre was inaugurated on April 28, 2011, in honour of the 150th anniversary of the Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
.
See also
*Medici
The House of Medici ( , ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici, in the Republic of Florence during the first half of the 15th century. The family originated in the Muge ...
*War of the Eight Saints
The War of the Eight Saints (1375–1378) was a war between Pope Gregory XI and a coalition of Italian city-states led by Florence that contributed to the end of the Avignon Papacy
The Avignon Papacy was the period from 1309 to 1376 during whic ...
*Republic of Florence
The Republic of Florence, officially the Florentine Republic ( it, Repubblica Fiorentina, , or ), was a medieval and early modern state that was centered on the Italian city of Florence in Tuscany. The republic originated in 1115, when the Flo ...
*Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany ( it, Granducato di Toscana; la, Magnus Ducatus Etruriae) was an Italian monarchy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1859, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In th ...
* Timeline of Florence
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Florence, Tuscany, Italy.
The earliest timeline of Florence, the ''Annales florentini'', was created in the 12th century.
Prior to 14th century
* 59 BCE – Roman colony founded (appr ...
References
Further reading
*Niccolò Machiavelli
Niccolò di Bernardo dei Machiavelli ( , , ; 3 May 1469 – 21 June 1527), occasionally rendered in English as Nicholas Machiavel ( , ; see below), was an Italian diplomat, author, philosopher and historian who lived during the Renaissance. ...
, ''Florentine Histories
''Florentine Histories'' ( it, Istorie fiorentine) is a historical account by Italian Renaissance political philosopher and writer Niccolò Machiavelli, first published posthumously in 1532.
Background
After the crisis of 1513, with arrests for ...
''.
* Brucker, Gene A. ''Florence: The Golden Age 1138-1737'' (1998)
* Brucker, Gene A. '' Renaissance Florence'' (2nd ed. 1983)
* Cochrane, Eric. ''Florence in the Forgotten Centuries, 1527-1800: A History of Florence and the Florentines in the Age of the Grand Dukes'' (1976)
* Crum, Roger J. and John T. Paoletti. ''Renaissance Florence: A Social History'' (2008excerpt and text search
* Goldthwaite, Richard A. ''The Economy of Renaissance Florence'' (2009) * Hibbert, Christopher, ''Florence: The Biography of a City'', Penguin Books, 1994. * Holmes, George. ''The Florentine Enlightenment, 1400-50'' (1969) * Najemy. John M. ''A History of Florence 1200-1575'' (2008
excerpt and text search
Primary sources
* Brucker, Gene A., ed. ''The Society of Renaissance Florence: A Documentary Study'' (1971)Other readings
*Linda Proud
Linda Proud (born 1949) is a British author of historical fiction. She is best known for ''The Botticelli Trilogy'', which is set in late fifteenth-century Florence.
Early life and career
Proud was born in Hertfordshire and was an only child. As ...
's trilogy of novels beginning with ''A Tabernacle for the Sun'' gives an excellent introduction to Renaissance Florence, its culture, history and philosophy. http://www.lindaproud.com/
*Eve Borsook, ''Companion Guide to Florence'', is a very in-depth guide to the city and the history of its districts and buildings.
*Oliver Dowlen, ''Sorted: Civic Lotteries and the Future of Public Participation.'' (MASS LBP: Toronto, 2008)
External links
SCRC 311 Cochran Ledger of Debtors and Creditors at OPenn
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Florence
Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico an ...