Relative Biological Effectiveness on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In radiobiology, the relative biological effectiveness (often abbreviated as RBE) is the ratio of biological effectiveness of one type of ionizing radiation relative to another, given the same amount of absorbed energy. The RBE is an empirical value that varies depending on the type of ionizing radiation, the energies involved, the biological effects being considered such as cell death, and the oxygen tension of the tissues or so-called oxygen effect.
 For the purposes of computing the equivalent dose to an organ or tissue, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) has defined a standard set of radiation weighting factors (WR), formerly termed the quality factor (''Q)''. The radiation weighting factors convert absorbed dose (measured in SI units of grays or non-SI rads) into formal biological equivalent dose for radiation exposure (measured in units of sieverts or
For the purposes of computing the equivalent dose to an organ or tissue, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) has defined a standard set of radiation weighting factors (WR), formerly termed the quality factor (''Q)''. The radiation weighting factors convert absorbed dose (measured in SI units of grays or non-SI rads) into formal biological equivalent dose for radiation exposure (measured in units of sieverts or  Radiation weighting factors that go from physical energy to biological effect must not be confused with tissue weighting factors. The tissue weighting factors are used to convert an equivalent dose to a given tissue in the body, to an effective dose, a number that provides an estimation of total danger to the whole organism, as a result of the radiation dose to part of the body.
Radiation weighting factors that go from physical energy to biological effect must not be confused with tissue weighting factors. The tissue weighting factors are used to convert an equivalent dose to a given tissue in the body, to an effective dose, a number that provides an estimation of total danger to the whole organism, as a result of the radiation dose to part of the body.
 Typically the evaluation of relative biological effectiveness is done on various types of living cells grown in culture medium, including prokaryotic cells such as
Typically the evaluation of relative biological effectiveness is done on various types of living cells grown in culture medium, including prokaryotic cells such as
Relative Biological Effectiveness in Ion Beam Therapy
Radiation health effects
Application
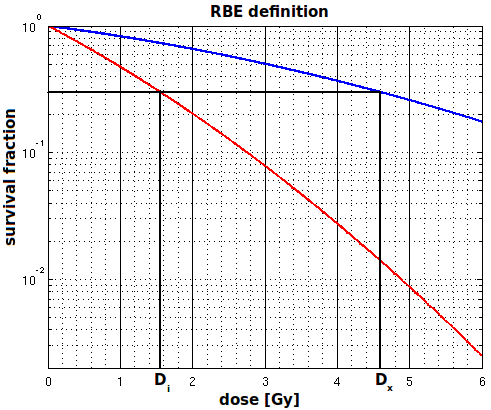
The absorbed dose can be a poor indicator of the biological effect of radiation, as the biological effect can depend on many other factors, including the type of radiation, energy, and type of tissue. The relative biological effectiveness can help give a better measure of the biological effect of radiation. The relative biological effectiveness for radiation of type ''R'' on a tissue is defined as the ratio : where ''D''''X'' is a reference absorbed dose of radiation of a standard type ''X'', and ''D''''R'' is the absorbed dose of radiation of type ''R'' that causes the same amount of biological damage. Both doses are quantified by the amount ofenergy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of hea ...
absorbed in the cells.
Different types of radiation have different biological effectiveness mainly because they transfer their energy to the tissue in different ways. Photons and beta particles have a low linear energy transfer (LET) coefficient, meaning that they ionize atoms in the tissue that are spaced by several hundred nanometers (several tenths of a micrometer Micrometer can mean:
* Micrometer (device), used for accurate measurements by means of a calibrated screw
* American spelling of micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; ...
) apart, along their path. In contrast, the much more massive alpha particles and neutrons leave a denser trail of ionized atoms in their wake, spaced about one tenth of a nanometer apart (i.e., less than one-thousandth of the typical distance between ionizations for photons and beta particles).
RBEs can be used for either cancer/hereditary risks ( stochastic) or for harmful tissue reactions ( deterministic) effects. Tissues have different RBEs depending on the type of effect. For high LET radiation (i.e., alphas and neutrons), the RBEs for deterministic effects tend to be lower than those for stochastic effects.
The concept of RBE is relevant in medicine, such as in radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiati ...
and radiotherapy, and to the evaluation of risks and consequences of radioactive contamination in various contexts, such as nuclear power plant operation, nuclear fuel disposal and reprocessing, nuclear weapons, uranium mining, and ionizing radiation safety.
Relation to radiation weighting factors (WR)
 For the purposes of computing the equivalent dose to an organ or tissue, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) has defined a standard set of radiation weighting factors (WR), formerly termed the quality factor (''Q)''. The radiation weighting factors convert absorbed dose (measured in SI units of grays or non-SI rads) into formal biological equivalent dose for radiation exposure (measured in units of sieverts or
For the purposes of computing the equivalent dose to an organ or tissue, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) has defined a standard set of radiation weighting factors (WR), formerly termed the quality factor (''Q)''. The radiation weighting factors convert absorbed dose (measured in SI units of grays or non-SI rads) into formal biological equivalent dose for radiation exposure (measured in units of sieverts or rem
Rem or REM may refer to:
Music
* R.E.M., an American rock band
* ''R.E.M.'' (EP), by Green
* "R.E.M." (song), by Ariana Grande
Organizations
* La République En Marche!, a French centrist political party
* Reichserziehungsministerium, in Nazi G ...
). However, ICRP states:
"The quantities equivalent dose and effective dose should not be used to quantify higher radiation doses or to make decisions on the need for any treatment related to tissue reactions .e., deterministic effects For such purposes, doses should be evaluated in terms of absorbed dose (in gray, Gy), and where high-LET radiations (e.g., neutrons or alpha particles) are involved, an absorbed dose, weighted with an appropriate RBE, should be used"
Radiation weighting factors are largely based on the RBE of radiation for stochastic health risks. However, for simplicity, the radiation weighting factors are not dependent on the type of tissue, and the values are conservatively chosen to be greater than the bulk of experimental values observed for the most sensitive cell types, with respect to external (external to the cell) sources. Radiation weighting factors have not been developed for internal sources of heavy ions, such as a recoil nucleus.
The ICRP 2007 standard values for relative effectiveness are given below. The higher radiation weighting factor for a type of radiation, the more damaging it is, and this is incorporated into the calculation to convert from gray to sievert units.  Radiation weighting factors that go from physical energy to biological effect must not be confused with tissue weighting factors. The tissue weighting factors are used to convert an equivalent dose to a given tissue in the body, to an effective dose, a number that provides an estimation of total danger to the whole organism, as a result of the radiation dose to part of the body.
Radiation weighting factors that go from physical energy to biological effect must not be confused with tissue weighting factors. The tissue weighting factors are used to convert an equivalent dose to a given tissue in the body, to an effective dose, a number that provides an estimation of total danger to the whole organism, as a result of the radiation dose to part of the body.
Experimental methods
 Typically the evaluation of relative biological effectiveness is done on various types of living cells grown in culture medium, including prokaryotic cells such as
Typically the evaluation of relative biological effectiveness is done on various types of living cells grown in culture medium, including prokaryotic cells such as bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, simple eukaryotic cells such as single celled plants, and advanced eukaryotic cells derived from organisms such as rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include ''Neotoma'' ( pack rats), ''Bandicota'' (bandicoot ...
s. The doses are adjusted to the LD-30 point; that is, to the amount that will cause 30% of the cells to become unable to undergo mitotic division (or, for bacteria, binary fission), thus being effectively sterilized — even if they can still carry out other cellular functions. LD-50 is more commonly used, but whoever drew the plot did not realise that the grid line closest to halfway between factors of 10 on a log plot is actually 3, not 5. LD-50 values are actually 1 gray for Carbon ions and 3 grays for photons.
The types ''R'' of ionizing radiation most considered in RBE evaluation are X-rays and gamma radiation (both consisting of photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are Massless particle, massless ...
s), alpha radiations ( helium-4 nuclei), beta radiation (electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary partic ...
s and positrons), neutron radiation, and heavy nuclei, including the fragments of nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction, reaction in which the atomic nucleus, nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller atomic nucleus, nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma ray, gamma photons, and releases a very large ...
. For some kinds of radiation, the RBE is strongly dependent on the energy of the individual particles.
Dependence on tissue type
Early on it was found that X-rays, gamma rays, and beta radiation were essentially equivalent for all cell types. Therefore, the standard radiation type ''X'' is generally an X-ray beam with 250 keV photons or cobalt-60 gamma rays. As a result, the relative biological effectiveness of beta and photon radiation is essentially 1. For other radiation types, the RBE is not a well-defined physical quantity, since it varies somewhat with the type of tissue and with the precise place of absorption within the cell. Thus, for example, the RBE for alpha radiation is 2–3 when measured onbacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, 4–6 for simple eukaryotic cells, and 6–8 for higher eukaryotic cells. According to one source it may be much higher (6500 with X rays as the reference) on ovocytes. The RBE of neutrons is 4–6 for bacteria, 8–12 for simple eukaryotic cells, and 12–16 for higher eukaryotic cells.
Dependence on source location
In the early experiments, the sources of radiation were all external to the cells that were irradiated. However, since alpha particles cannot traverse the outermost dead layer of human skin, they can do significant damage only if they come from the decay of atoms inside the body. Since the range of an alpha particle is typically about the diameter of a single eukaryotic cell, the precise location of the emitting atom in the tissue cells becomes significant. For this reason, it has been suggested that the health impact of contamination by alpha emitters might have been substantially underestimated. Measurements of RBE with external sources also neglect the ionization caused by the recoil of the parent-nucleus due to the alpha decay. While the recoil of the parent-nucleus of the decaying atom typically carries only about 2% of the energy of the alpha-particle that is emitted by the decaying atom, its range is extremely short (about 2–3 angstroms), due to its high electric charge and highmass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different element ...
. The parent nucleus is required to recoil, upon emission of an alpha particle, with a discrete kinetic energy due to conservation of momentum. Thus, all of the ionization energy from the recoil-nucleus is deposited in an extremely small volume near its original location, typically in the cell nucleus on the chromosomes, which have an affinity for heavy metals. The bulk of studies, using sources that are external to the cell, have yielded RBEs between 10 and 20. Since most of the ionization damage from the travel of the alpha particle is deposited in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
, whereas from the travel of the recoil-nucleus is on the DNA itself, it is likely greater damage is caused by the recoil nucleus than by the alpha particle itself.
History
In 1931, Failla and Henshaw reported on determination of the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of x rays and γ rays. This appears to be the first use of the term ‘RBE’. The authors noted that RBE was dependent on the experimental system being studied. Somewhat later, it was pointed out by Zirkle et al. (1952) that the biological effectiveness depends on the spatial distribution of the energy imparted and the density of ionisations per unit path length of the ionising particles. Zirkle et al. coined the term ‘linear energy transfer (LET)’ to be used in radiobiology for the stopping power, i.e. the energy loss per unit path length of a charged particle. The concept was introduced in the 1950s, at a time when the deployment of nuclear weapons and nuclear reactors spurred research on the biological effects of artificial radioactivity. It had been noticed that those effects depended both on the type and energy spectrum of the radiation, and on the kind of living tissue. The first systematic experiments to determine the RBE were conducted in that decade.See also
* Background radiation * Linear energy transfer (LET) * Theory of dual radiation actionReferences
{{reflist, 30emExternal links
Relative Biological Effectiveness in Ion Beam Therapy
Radiation health effects