relative binding affinities on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 Agonist binding to a receptor can be characterized both in terms of how much physiological response can be triggered (that is, the efficacy) and in terms of the
Agonist binding to a receptor can be characterized both in terms of how much physiological response can be triggered (that is, the efficacy) and in terms of the 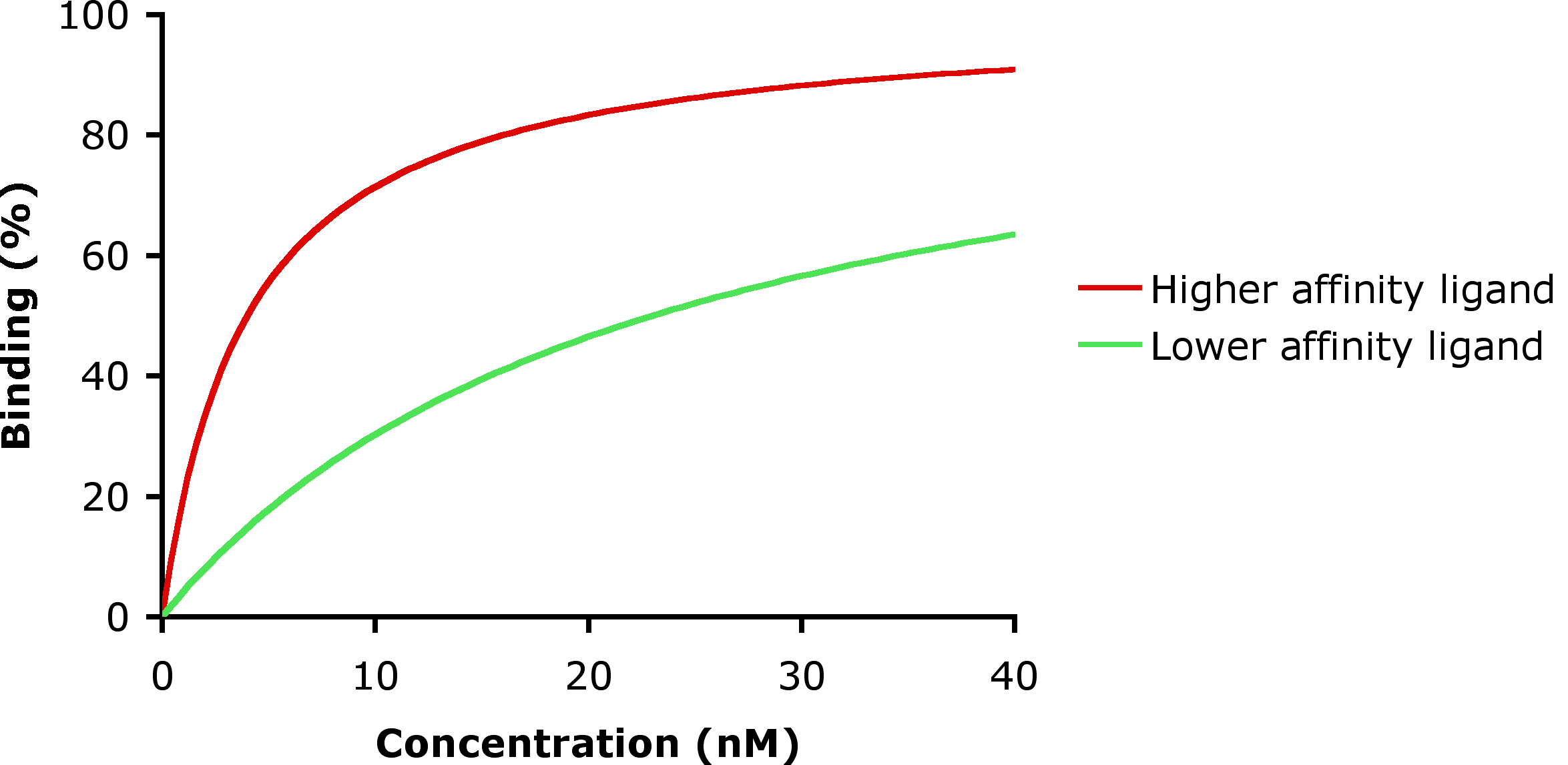 Binding affinity is most commonly determined using a
Binding affinity is most commonly determined using a
BindingDB
a public database of measured protein-ligand binding affinities.
BioLiP
a comprehensive database for ligand-protein interactions. {{DEFAULTSORT:Ligand (Biochemistry) Biomolecules Cell signaling Chemical bonding Proteins
 In
In biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology ...
and pharmacology
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemi ...
, a ligand is a substance
Substance may refer to:
* Matter, anything that has mass and takes up space
Chemistry
* Chemical substance, a material with a definite chemical composition
* Drug substance
** Substance abuse, drug-related healthcare and social policy diagnosis o ...
that forms a complex
Complex commonly refers to:
* Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe
** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each ...
with a biomolecule
A biomolecule or biological molecule is a loosely used term for molecules present in organisms that are essential to one or more typically biological processes, such as cell division, morphogenesis, or development. Biomolecules include larg ...
to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing' ...
by binding
Binding may refer to:
Computing
* Binding, associating a network socket with a local port number and IP address
* Data binding, the technique of connecting two data elements together
** UI data binding, linking a user interface element to an eleme ...
to a site
Site most often refers to:
* Archaeological site
* Campsite, a place used for overnight stay in an outdoor area
* Construction site
* Location, a point or an area on the Earth's surface or elsewhere
* Website, a set of related web pages, typi ...
on a target protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism
In chemistry, conformational isomerism is a form of stereoisomerism in which the isomers can be interconverted just by rotations about formally single bonds (refer to figure on single bond rotation). While any two arrangements of atoms in a mo ...
(conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure.
Binding occurs by intermolecular force
An intermolecular force (IMF) (or secondary force) is the force that mediates interaction between molecules, including the electromagnetic forces of attraction
or repulsion which act between atoms and other types of neighbouring particles, e.g. a ...
s, such as ionic bond
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, or between two atoms with sharply different electronegativities, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compoun ...
s, hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing ...
s and Van der Waals force
In molecular physics, the van der Waals force is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and t ...
s. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition of ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's ele ...
in metalorganic
Metal-organic compounds (jargon: metalorganics, metallo-organics) are a class of chemical compounds that contain metals and organic ligands, which confer solubility in organic solvents or volatility. Compounds with these properties find applicatio ...
and inorganic chemistry
Inorganic chemistry deals with synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disc ...
, in biochemistry it is ambiguous whether the ligand generally binds at a metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typi ...
site, as is the case in hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyte ...
. In general, the interpretation of ligand is contextual with regards to what sort of binding has been observed.
Ligand binding to a receptor protein
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a recepto ...
alters the conformation by affecting the three-dimensional shape orientation. The conformation of a receptor protein composes the functional state. Ligands include substrate
Substrate may refer to:
Physical layers
*Substrate (biology), the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the surface or medium on which an organism grows or is attached
** Substrate (locomotion), the surface over which an organism lo ...
s, inhibitor
Inhibitor or inhibition may refer to:
In biology
* Enzyme inhibitor, a substance that binds to an enzyme and decreases the enzyme's activity
* Reuptake inhibitor, a substance that increases neurotransmission by blocking the reuptake of a neurotra ...
s, activators, signaling lipids, and neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neur ...
s. The rate of binding is called affinity
Affinity may refer to:
Commerce, finance and law
* Affinity (law), kinship by marriage
* Affinity analysis, a market research and business management technique
* Affinity Credit Union, a Saskatchewan-based credit union
* Affinity Equity Part ...
, and this measurement typifies a tendency or strength of the effect. Binding affinity is actualized not only by host–guest interactions, but also by solvent effects that can play a dominant, steric
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivity of ions ...
role which drives non-covalent binding in solution. The solvent provides a chemical environment for the ligand and receptor to adapt, and thus accept or reject each other as partners.
Radioligand
A radioligand is a radioactive biochemical substance (in particular, a ligand that is radiolabeled) that is used for diagnosis or for research-oriented study of the receptor systems of the body.
In a neuroimaging application the radioligand is ...
s are radioisotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
labeled compounds used in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
as tracer
Tracer may refer to:
Science
* Flow tracer, any fluid property used to track fluid motion
* Fluorescent tracer, a substance such as 2-NBDG containing a fluorophore that is used for tracking purposes
* Histochemical tracer, a substance used for tr ...
s in PET
A pet, or companion animal, is an animal kept primarily for a person's company or entertainment rather than as a working animal, livestock, or a laboratory animal. Popular pets are often considered to have attractive appearances, intelligence ...
studies and for in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and ...
binding studies.
Receptor/ligand binding affinity
The interaction of ligands with their binding sites can be characterized in terms of a binding affinity. In general, high-affinity ligand binding results from greater attractive forces between the ligand and its receptor while low-affinity ligand binding involves less attractive force. In general, high-affinity binding results in a higher occupancy of the receptor by its ligand than is the case for low-affinity binding; theresidence time
The residence time of a fluid parcel is the total time that the parcel has spent inside a control volume (e.g.: a chemical reactor, a lake, a human body). The residence time of a set of parcels is quantified in terms of the frequency distrib ...
(lifetime of the receptor-ligand complex) does not correlate. High-affinity binding of ligands to receptors is often physiologically important when some of the binding energy can be used to cause a conformational change in the receptor, resulting in altered behavior for example of an associated ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ...
or enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
.
A ligand that can bind to and alter the function of the receptor that triggers a physiological response is called a receptor agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ago ...
. Ligands that bind to a receptor but fail to activate the physiological response are receptor antagonists
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the chief foe of the protagonist.
Etymology
The English word antagonist comes from the Greek ἀνταγωνιστής – ''antagonistēs'', "opponent, competitor, villain, enemy, riv ...
.
 Agonist binding to a receptor can be characterized both in terms of how much physiological response can be triggered (that is, the efficacy) and in terms of the
Agonist binding to a receptor can be characterized both in terms of how much physiological response can be triggered (that is, the efficacy) and in terms of the concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', '' number concentration'' ...
of the agonist that is required to produce the physiological response (often measured as EC50, the concentration required to produced the half-maximal response). High-affinity ligand binding implies that a relatively low concentration of a ligand is adequate to maximally occupy a ligand-binding site and trigger a physiological response. Receptor affinity is measured by an inhibition constant or Ki value, the concentration required to occupy 50% of the receptor. Ligand affinities are most often measured indirectly as an IC50 value from a competition binding experiment where the concentration of a ligand required to displace 50% of a fixed concentration of reference ligand is determined. The Ki value can be estimated from IC50 through the Cheng Prusoff equation. Ligand affinities can also be measured directly as a dissociation constant
In chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology, a dissociation constant (K_D) is a specific type of equilibrium constant that measures the propensity of a larger object to separate (dissociate) reversibly into smaller components, as when a complex ...
(Kd) using methods such as fluorescence quenching
Quenching refers to any process which decreases the fluorescence intensity of a given substance. A variety of processes can result in quenching, such as excited state reactions, energy transfer, complex-formation and collisional quenching. As a co ...
, isothermal titration calorimetry
Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) is a physical technique used to determine the thermodynamic parameters of interactions in solution. It is most often used to study the binding of small molecules (such as medicinal compounds) to larger macro ...
or surface plasmon resonance
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is the resonant oscillation of conduction electrons at the interface between negative and positive permittivity material in a particle stimulated by incident light. SPR is the basis of many standard tools for measu ...
.
Low-affinity binding (high Ki level) implies that a relatively high concentration of a ligand is required before the binding site is maximally occupied and the maximum physiological response to the ligand is achieved. In the example shown to the right, two different ligands bind to the same receptor binding site. Only one of the agonists shown can maximally stimulate the receptor and, thus, can be defined as a ''full agonist''. An agonist that can only partially activate the physiological response is called a ''partial agonist''. In this example, the concentration at which the full agonist (red curve) can half-maximally activate the receptor is about 5 x 10−9 Molar (nM = nanomolar).
 Binding affinity is most commonly determined using a
Binding affinity is most commonly determined using a radiolabel
A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a chemical compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide so by virtue of its radioactive decay it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tr ...
ed ligand, known as a tagged ligand. ''Homologous competitive binding experiments'' involve binding competition between a tagged ligand and an untagged ligand.
Real-time based methods, which are often label-free, such as surface plasmon resonance
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is the resonant oscillation of conduction electrons at the interface between negative and positive permittivity material in a particle stimulated by incident light. SPR is the basis of many standard tools for measu ...
, dual-polarization interferometry
Dual-polarization interferometry (DPI) is an analytical technique that probes molecular layers adsorbed to the surface of a waveguide using the evanescent wave of a laser beam. It is used to measure the conformational change in proteins, or oth ...
and multi-parametric surface plasmon resonance (MP-SPR) can not only quantify the affinity from concentration based assays; but also from the kinetics of association and dissociation, and in the later cases, the conformational change induced upon binding. MP-SPR also enables measurements in high saline dissociation buffers thanks to a unique optical setup. Microscale thermophoresis
Microscale thermophoresis (MST) is a technology for the biophysical analysis of interactions between biomolecules. Microscale thermophoresis is based on the detection of a temperature-induced change in fluorescence of a target as a function of the ...
(MST), an immobilization-free method
* was developed. This method allows the determination of the binding affinity without any limitation to the ligand's molecular weight.
For the use of statistical mechanics in a quantitative study of the
ligand-receptor binding affinity, see the comprehensive article
on the configurational partition function.
Drug potency and binding affinity
Binding affinity data alone does not determine the overall potency of a drug. Potency is a result of the complex interplay of both the binding affinity and the ligand efficacy. Ligand efficacy refers to the ability of the ligand to produce a biological response upon binding to the target receptor and the quantitative magnitude of this response. This response may be as anagonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ago ...
, antagonist, or inverse agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist.
A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse ag ...
, depending on the physiological response produced.
Selective and non-selective
Selective ligands have a tendency to bind to very limited kinds of receptor, whereas non-selective ligands bind to several types of receptors. This plays an important role inpharmacology
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemi ...
, where drugs
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalat ...
that are non-selective tend to have more adverse effects
An adverse effect is an undesired harmful effect resulting from a medication or other intervention, such as surgery. An adverse effect may be termed a " side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. The term compl ...
, because they bind to several other receptors in addition to the one generating the desired effect.
Hydrophobic ligands
For hydrophobic ligands (e.g. PIP2) in complex with a hydrophobic protein (e.g.lipid-gated ion channels
Lipid-gated ion channels are a class of ion channels whose conductance of ions through the membrane depends directly on lipids. Classically the lipids are membrane resident anionic signaling lipids that bind to the transmembrane domain on the inn ...
) determining the affinity is complicated by non-specific hydrophobic interactions. Non-specific hydrophobic interactions can be overcome when the affinity of the ligand is high. For example, PIP2 binds with high affinity to PIP2 gated ion channels.
Bivalent ligand
Bivalent ligands consist of two drug-like molecules (pharmacophores or ligands) connected by an inert linker. There are various kinds of bivalent ligands and are often classified based on what the pharmacophores target. Homobivalent ligands target two of the same receptor types. Heterobivalent ligands target two different receptor types. Bitopic ligands target an orthosteric binding sites and allosteric binding sites on the same receptor. In scientific research, bivalent ligands have been used to study receptor dimers and to investigate their properties. This class of ligands was pioneered byPhilip S. Portoghese
Philip Salvatore Portoghese (born June 4, 1931) is an American medicinal chemist who has made notable contributions to the design and synthesis of ligands targeting opioid receptors. He is a Distinguished Professor of Medicinal Chemistry at the Uni ...
and coworkers while studying the opioid receptor system. Bivalent ligands were also reported early on by Micheal Conn and coworkers for the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor. Since these early reports, there have been many bivalent ligands reported for various G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...
(GPCR) systems including cannabinoid, serotonin, oxytocin, and melanocortin receptor systems, and for GPCR
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...
- LIC systems ( D2 and nACh receptors).
Bivalent ligands usually tend to be larger than their monovalent counterparts, and therefore, not 'drug-like' as in Lipinski's rule of five
Lipinski's rule of five, also known as Pfizer's rule of five or simply the rule of five (RO5), is a rule of thumb to evaluate druglikeness or determine if a chemical compound with a certain pharmacological or biological activity has chemical pro ...
. Many believe this limits their applicability in clinical settings. In spite of these beliefs, there have been many ligands that have reported successful pre-clinical animal studies. Given that some bivalent ligands can have many advantages compared to their monovalent counterparts (such as tissue selectivity, increased binding affinity, and increased potency or efficacy), bivalents may offer some clinical advantages as well.
Mono- and polydesmic ligands
Ligands of proteins can be characterized also by the number of protein chains they bind. "Monodesmic" ligands (μόνος: single, δεσμός: binding) are ligands that bind a single protein chain, while "polydesmic" ligands (πολοί: many) are frequent in protein complexes, and are ligands that bind more than one protein chain, typically in or near protein interfaces. Recent research shows that the type of ligands and binding site structure has profound consequences for the evolution, function, allostery and folding of protein compexes.Privileged scaffold
A privileged scaffold is a molecular framework or chemical moiety that is statistically recurrent among known drugs or among a specific array of biologically active compounds. These privileged elements can be used as a basis for designing new active biological compounds or compound libraries.Methods used to study binding
Main methods to study protein–ligand interactions are principal hydrodynamic and calorimetric techniques, and principal spectroscopic and structural methods such as *Fourier transform spectroscopy
Fourier-transform spectroscopy is a measurement technique whereby spectra are collected based on measurements of the coherence of a radiative source, using time-domain or space-domain measurements of the radiation, electromagnetic or not. It ca ...
*Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after Indian physicist C. V. Raman) is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman s ...
*Fluorescence spectroscopy
Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample. It involves using a beam of light, usually ultraviolet light, that excites the elect ...
* Circular dichroism
*Nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are perturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a ...
*Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is u ...
*Atomic force microscope
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the opt ...
*Paramagnetic
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, ...
probes
*Dual polarisation interferometry
Dual-polarization interferometry (DPI) is an analytical technique that probes molecular layers adsorbed to the surface of a waveguide using the evanescent wave of a laser beam. It is used to measure the conformational change in proteins, or oth ...
* Multi-parametric surface plasmon resonance
*Ligand binding assay A ligand binding assay (LBA) is an assay, or an analytic procedure, which relies on the binding of ligand molecules to receptors, antibodies or other macromolecules. A detection method is used to determine the presence and extent of the ligand-rec ...
and radioligand binding assay
Other techniques include:
fluorescence intensity,
bimolecular fluorescence complementation,
FRET (fluorescent resonance energy transfer) / FRET quenching
surface plasmon resonance,
bio-layer interferometry Bio-layer interferometry (BLI) is an optical biosensing technology that analyzes biomolecular interactions in real-time without the need for fluorescent labeling. Alongside Surface Plasmon Resonance, BLI is one of few widely available label-free bi ...
,
Coimmunopreciptation
indirect ELISA,
equilibrium dialysis,
gel electrophoresis,
far western blot,
fluorescence polarization anisotropy,
electron paramagnetic resonance,
microscale thermophoresis
Microscale thermophoresis (MST) is a technology for the biophysical analysis of interactions between biomolecules. Microscale thermophoresis is based on the detection of a temperature-induced change in fluorescence of a target as a function of the ...
,
switchSENSE.
The dramatically increased computing power of supercomputers and personal computers has made it possible to study protein–ligand interactions also by means of computational chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulation to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of mo ...
. For example, a worldwide grid of well over a million ordinary PCs was harnessed for cancer research in the project grid.org
grid.org was a website and online community established in 2001 for cluster computing and grid computing software users. For six years it operated several different volunteer computing projects that allowed members to donate their spare computer c ...
, which ended in April 2007. Grid.org has been succeeded by similar projects such as World Community Grid
World Community Grid (WCG) is an effort to create the world's largest volunteer computing platform to tackle scientific research that benefits humanity. Launched on November 16, 2004, with proprietary Grid MP client from United Devices and addin ...
, Human Proteome Folding Project
The Human Proteome Folding Project (HPF) is a collaborative effort between New York University ( Bonneau Lab), the Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) and the University of Washington (Baker
A baker is a tradesperson who bakes and sometime ...
, Compute Against Cancer Compute Against Cancer is an initiative of Parabon Computation, Inc. powered by the Global Grid Exchange. The program provides cancer researchers access to supercomputing capabilities through Parabon’s Frontier Grid Platform. The Compute Against ...
and Folding@Home
Folding@home (FAH or F@h) is a volunteer computing project aimed to help scientists develop new therapeutics for a variety of diseases by the means of simulating protein dynamics. This includes the process of protein folding and the movements ...
.
See also
*Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ago ...
* Schild regression
In pharmacology, Schild regression analysis, named for Heinz Otto Schild, is a tool for studying the effects of agonists and antagonists on the response caused by the receptor or on ligand-receptor binding.
Dose-response curves can be constru ...
* Allosteric regulation
In biochemistry, allosteric regulation (or allosteric control) is the regulation of an enzyme by binding an effector molecule at a site other than the enzyme's active site.
The site to which the effector binds is termed the ''allosteric sit ...
* Ki Database
The Ki Database (or Ki DB) is a public domain database of published binding affinities (''K''i) of drugs and chemical compounds for receptors, neurotransmitter transporters, ion channels, and enzymes
Enzymes () are proteins that act as ...
* Docking@Home
Docking@Home was a volunteer computing project hosted by the University of Delaware and running on the Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing (BOINC) software platform. It models protein-ligand
In coordination chemistry, a l ...
* GPUGRID.net
GPUGRID is a volunteer computing project hosted by Pompeu Fabra University and running on the Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing (BOINC) software platform. It performs full-atom molecular biology simulations that are designed to ...
* DNA binding ligand
DNA-binding proteins are proteins that have DNA-binding domains and thus have a specific or general affinity for single- or double-stranded DNA. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove of B-DNA, becau ...
* BindingDB
BindingDB
is a public, web-accessible database of measured binding affinities, focusing chiefly on the interactions of proteins considered to be candidate drug-targets with ligands that are small, drug-like molecules. As of March, 2011, Bindi ...
* SAMPL Challenge
SAMPL (Statistical Assessment of the Modeling of Proteins and Ligands) is a set of community-wide blind challenges aimed to advance computational techniques as standard predictive tools in rational drug design. A broad range of biologically rele ...
References
External links
BindingDB
a public database of measured protein-ligand binding affinities.
BioLiP
a comprehensive database for ligand-protein interactions. {{DEFAULTSORT:Ligand (Biochemistry) Biomolecules Cell signaling Chemical bonding Proteins