refractive errors on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Refractive error is a problem with
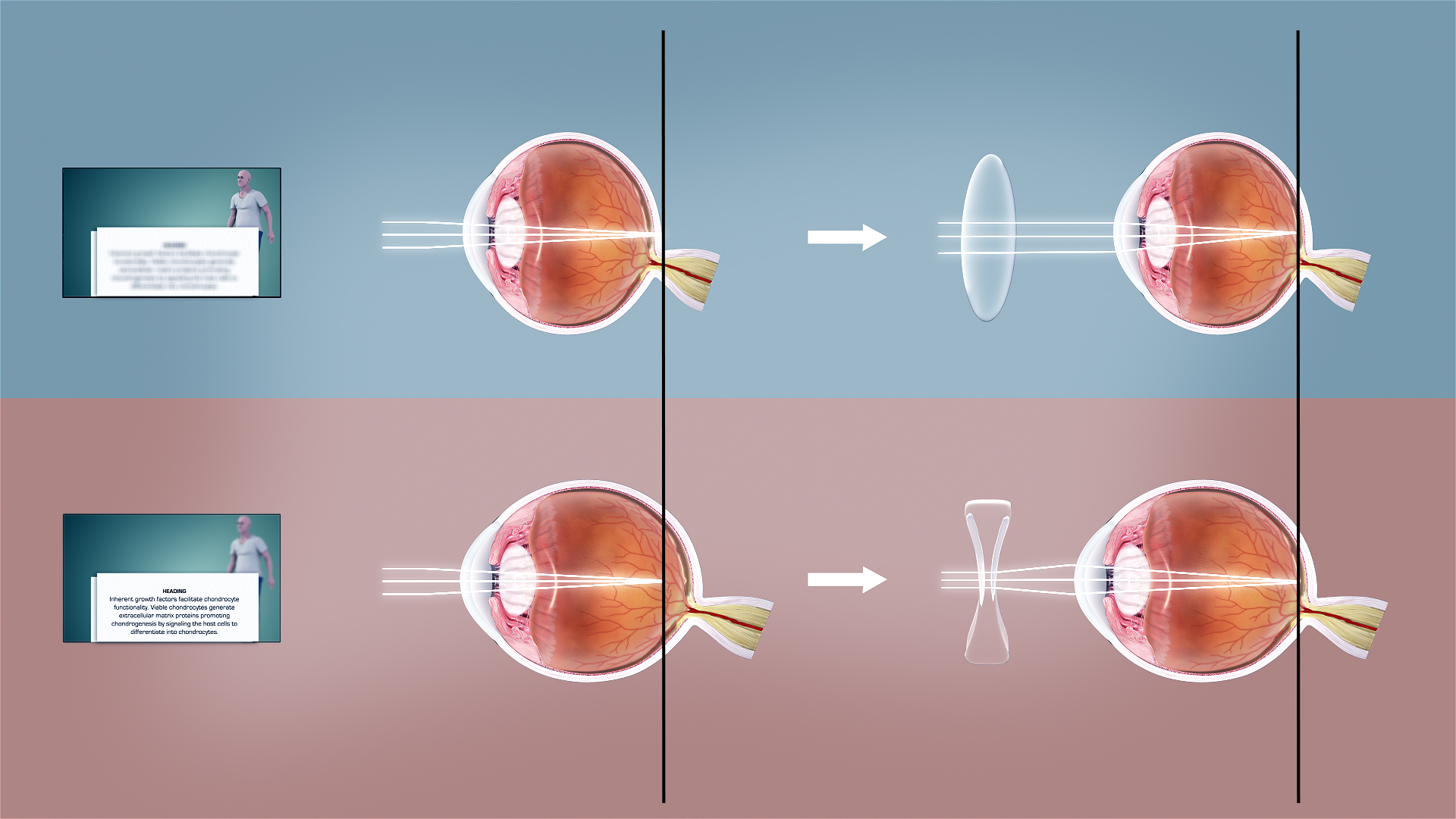 Refractive error – sometimes called "ametropia" – is when the refractive power of an eye does not match the length of the eye, so the image is focused away from the central retina, instead of directly on it.
Types of refractive error include myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia, and astigmatism.
*
Refractive error – sometimes called "ametropia" – is when the refractive power of an eye does not match the length of the eye, so the image is focused away from the central retina, instead of directly on it.
Types of refractive error include myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia, and astigmatism.
*
 Blurry vision may result from any number of conditions not necessarily related to refractive errors. The diagnosis of a refractive error is usually confirmed by an
Blurry vision may result from any number of conditions not necessarily related to refractive errors. The diagnosis of a refractive error is usually confirmed by an
 It is estimated that at least 2 billion people in the world have refractive errors. The number of people globally with refractive errors that have not been corrected was estimated at 660 million (10 per 100 people) in 2013.
Refractive errors are the first common cause of visual impairment and second most common cause of visual loss . The assessment of refractive error is now done in DALY (Disability Adjusted Life Years) which showed an 8% increase from 1990 to 2019.
The number of people globally with significant refractive errors has been estimated at one to two billion. Rates vary between regions of the world with about 25% of Europeans and 80% of Asians affected. Near-sightedness is one of the most prevalent disorders of the eye. Rates among adults are between 15 and 49% while rates among children are between 1.2 and 42%. Far-sightedness more commonly affects young children, whose eyes have yet to grow to their full length, and the elderly, who have lost the ability to compensate with their accommodation system. Presbyopia affects most people over the age of 35, and nearly 100% of people by the ages of 55–65. Uncorrected refractive error is responsible for visual impairment and disability for many people worldwide. It is one of the most common causes of
It is estimated that at least 2 billion people in the world have refractive errors. The number of people globally with refractive errors that have not been corrected was estimated at 660 million (10 per 100 people) in 2013.
Refractive errors are the first common cause of visual impairment and second most common cause of visual loss . The assessment of refractive error is now done in DALY (Disability Adjusted Life Years) which showed an 8% increase from 1990 to 2019.
The number of people globally with significant refractive errors has been estimated at one to two billion. Rates vary between regions of the world with about 25% of Europeans and 80% of Asians affected. Near-sightedness is one of the most prevalent disorders of the eye. Rates among adults are between 15 and 49% while rates among children are between 1.2 and 42%. Far-sightedness more commonly affects young children, whose eyes have yet to grow to their full length, and the elderly, who have lost the ability to compensate with their accommodation system. Presbyopia affects most people over the age of 35, and nearly 100% of people by the ages of 55–65. Uncorrected refractive error is responsible for visual impairment and disability for many people worldwide. It is one of the most common causes of
focus
Focus (: foci or focuses) may refer to:
Arts
* Focus or Focus Festival, former name of the Adelaide Fringe arts festival in East Australia Film
*Focus (2001 film), ''Focus'' (2001 film), a 2001 film based on the Arthur Miller novel
*Focus (2015 ...
ing light accurately on the retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
due to the shape of the eye
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher organisms, the ey ...
and/or cornea
The cornea is the transparency (optics), transparent front part of the eyeball which covers the Iris (anatomy), iris, pupil, and Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and Lens (anatomy), lens, the cornea ...
. The most common types of refractive error are near-sightedness
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurred vision, blurry, while close objects ...
, far-sightedness
Far-sightedness, also known as long-sightedness, hypermetropia, and hyperopia, is a condition of the eye where distant objects are seen clearly but near objects appear blurred. This blur is due to incoming light being focused behind, instead o ...
, astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. The lens and cornea of an eye without astigmatism are nearly spherical, with only a single radius of curvature, and any refractive errors ...
, and presbyopia
Presbyopia is a physiological insufficiency of optical Accommodation (vertebrate eye), accommodation associated with the aging of the human eye, eye; it results in progressively worsening ability to focus clearly on close objects. Also known as ...
. Near-sightedness results in far away objects being blurry
"Blurry" is a song by American rock band Puddle of Mudd. It was released on October 16, 2001, as the second single from the band's debut album '' Come Clean'' (2001). It was 2002's most successful rock song in the United States, topping the ''Bi ...
, far-sightedness and presbyopia result in close objects being blurry, and astigmatism causes objects to appear stretched out or blurry. Other symptoms may include double vision
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often voluntary. However, when occ ...
, headaches
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Head ...
, and eye strain
Eye strain, also medically termed as asthenopia (), is a common eye condition characterized by nonspecific symptom, non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, pain in or around the eyes, blurred vision, headache, and occasional diplopia, double vis ...
.
Near-sightedness is due to the length of the eyeball being too long; far-sightedness the eyeball too short; astigmatism the cornea being the wrong shape, while presbyopia results from aging of the lens of the eye
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
such that it cannot change shape sufficiently. Some refractive errors occur more often among those whose parents are affected. Diagnosis is by eye examination
An eye examination, commonly known as an eye test, is a series of tests performed to assess Visual acuity, vision and ability to Focus (optics), focus on and discern objects. It also includes other tests and examinations of the human eye, eyes. ...
.
Refractive errors are corrected with eyeglass
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses (American English), spectacles ( Commonwealth English), or colloquially as specs, are vision eyewear with clear or tinted lenses mounted in a frame that holds them in front of a person's eyes, typically ...
es, contact lenses
Contact lenses, or simply contacts, are thin lens (optics), lenses placed directly on the surface of the Human eye, eyes. Contact lenses are ocular prosthetic devices used by over 150 million people worldwide, and they can be worn to correct ...
, or surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
. Eyeglasses are the easiest and safest method of correction. Contact lenses can provide a wider field of vision
The visual field is "that portion of space in which objects are visible at the same moment during steady fixation of the gaze in one direction"; in ophthalmology and neurology the emphasis is mostly on the structure inside the visual field and it i ...
; however they are associated with a risk of infection. Refractive surgery
Refractive surgery is an optional eye surgery used to improve the refractive state of the eye and decrease or eliminate dependency on glasses or contact lenses. This can include various methods of surgical remodeling of the cornea ( keratomi ...
may consist of either permanently changing the shape of the cornea or, alternatively, implanting intraocular lens
An intraocular lens (IOL) is a lens (optics), lens implanted in the human eye, eye usually as part of a treatment for cataracts or for correcting other vision problems such as myopia, near-sightedness (myopia) and farsightedness, far-sightednes ...
es.
The number of people globally with refractive errors has been estimated at one to two billion. Rates vary between regions of the world with about 25% of Europeans and 80% of Asians affected. Near-sightedness is the most common disorder. Rates among adults are between 15 and 49% while rates among children are between 1.2 and 42%. Far-sightedness more commonly affects young children and the elderly. Presbyopia affects most people over the age of 35.
The number of people with refractive errors that have not been corrected was estimated at 660 million (10 per 100 people) in 2013. Of these 9.5 million were blind due to the refractive error. It is one of the most common causes of vision loss
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficul ...
along with cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens (anatomy), lens of the eye that leads to a visual impairment, decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or ...
s, macular degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred vision, blurred or vision loss, no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no sym ...
, and vitamin A deficiency
Vitamin A deficiency (VAD) or hypovitaminosis A is a lack of vitamin A in blood and tissues. It is common in poorer countries, especially among children and women of reproductive age, but is rarely seen in more developed countries. Vitamin A pla ...
.
Classification
 Refractive error – sometimes called "ametropia" – is when the refractive power of an eye does not match the length of the eye, so the image is focused away from the central retina, instead of directly on it.
Types of refractive error include myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia, and astigmatism.
*
Refractive error – sometimes called "ametropia" – is when the refractive power of an eye does not match the length of the eye, so the image is focused away from the central retina, instead of directly on it.
Types of refractive error include myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia, and astigmatism.
* Myopia
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurry, while close objects appear normal. ...
or Nearsightedness
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurry, while close objects appear normal. ...
: When the refractive power is too strong for the length of the eyeball, this is called myopia
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurry, while close objects appear normal. ...
or nearsightedness. People with myopia typically have blurry vision when viewing distant objects because the eye is refracting more than necessary. Myopia can be corrected with a concave lens, which causes the divergence of light rays before they reach the cornea.
* Hyperopia
Far-sightedness, also known as long-sightedness, hypermetropia, and hyperopia, is a condition of the eye where distant objects are seen clearly but near objects appear blurred. This blur is due to incoming light being focused behind, instead o ...
or Farsightedness
Far-sightedness, also known as long-sightedness, hypermetropia, and hyperopia, is a condition of the eye where distant objects are seen clearly but near objects appear blurred. This blur is due to incoming light being focused behind, instead o ...
: When the refractive power is too weak for the length of the eyeball, one has hyperopia
Far-sightedness, also known as long-sightedness, hypermetropia, and hyperopia, is a condition of the eye where distant objects are seen clearly but near objects appear blurred. This blur is due to incoming light being focused behind, instead o ...
or farsightedness. People with hyperopia have blurry vision when viewing near objects because the eye is unable to focus the light sufficiently. This can be corrected with convex lenses, which cause light rays to converge prior to hitting the cornea.
* Presbyopia
Presbyopia is a physiological insufficiency of optical Accommodation (vertebrate eye), accommodation associated with the aging of the human eye, eye; it results in progressively worsening ability to focus clearly on close objects. Also known as ...
: When the flexibility of the lens declines, typically due to age. The individual would experience difficulty in near vision, often relieved by reading glasses, bifocal, or progressive lenses.
* Astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. The lens and cornea of an eye without astigmatism are nearly spherical, with only a single radius of curvature, and any refractive errors ...
is when the refractive power of the eye is not uniform across the surface of the cornea because of asymmetry. In other words, the eye focuses light more strongly in one direction than another, leading to distortion of the image.
Children are typically born hyperopic and shift toward emmetropia or myopia as their eyes lengthen through childhood.
Other terminology include anisometropia
Anisometropia is a condition in which a person's eyes have substantially differing refractive power. Generally, a difference in power of one diopter (1D) is the threshold for diagnosis of the condition. Patients may have up to 3 diopters of anis ...
, when the two eyes have unequal refractive power
In optics, optical power (also referred to as dioptric power, refractive power, focal power, focusing power, or convergence power) is the degree to which a lens, mirror, or other optical system converges or diverges light. It is equal to the r ...
, and aniseikonia
Aniseikonia is an ocular condition where there is a significant difference in the perceived size of images. It can occur as an overall difference between the two eyes, or as a difference in a particular meridian. If the ocular image size in both ...
which is when the magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging the apparent size, not physical size, of something. This enlargement is quantified by a size ratio called optical magnification. When this number is less than one, it refers to a reduction in size, so ...
power between the eyes differ.
Refractive errors are typically measured using three numbers: sphere, cylinder, and axis.
* Sphere: This number denotes the strength of the lens needed to correct your vision. A "–" indicates nearsightedness while a "+" indicates farsightedness. Higher numbers indicate more power in either direction.
* Cylinder: This number denotes the amount of astigmatism, if any.
* Axis: This number notes the direction of the astigmatism and is written in degrees between 1 and 180.
An eye that has no refractive error when viewing distant objects is said to have '' emmetropia'' or be ''emmetropic'' meaning the eye is in a state in which it can focus parallel rays of light (light from distant objects) on the retina, without using any accommodation. A distant object, in this case, is defined as an object located beyond 6 meters, or 20 feet, from the eye, since the light from those objects arrives as essentially parallel rays when considering the limitations of human perception.
Risk factors
Genetics
There is evidence to suggest genetic predilection for refractive error. Individuals that have parents with certain refractive errors are more likely to have similar refractive errors. The Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) is a continuously updated catalog of human genes and genetic disorders and traits, with a particular focus on the gene-phenotype relationship. , approximately 9,000 of the over 25,000 entries in OMIM ...
) database has listed 261 genetic disorders in which myopia is one of the symptoms. Myopia may be present in heritable connective tissue disorders such as: Knobloch syndrome (OMIM 267750); Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically ha ...
(OMIM 154700); and Stickler syndrome (type 1, OMIM 108300; type 2, OMIM 604841). Myopia has also been reported in X-linked disorders caused by mutations in loci involved in retinal photoreceptor function ( NYX, RP2, MYP1) such as: autosomal recessive congenital stationary night blindness
Congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB) is a rare non-progressive retinal disorder. People with CSNB often have difficulty adapting to low light situations due to impaired photoreceptor transmission. These patients may also have reduced visu ...
( CSNB; OMIM 310500); retinitis pigmentosa
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a member of a group of genetic disorders called inherited retinal dystrophy (IRD) that cause loss of vision. Symptoms include trouble seeing at night and decreasing peripheral vision (side and upper or lower visua ...
2 (RP2; OMIM 312600); Bornholm eye disease (OMIM 310460).
Many genes that have been associated with refractive error are clustered into common biological networks involved in connective tissue growth and extracellular matrix organization. Although a large number of chromosomal localisations have been associated with myopia (MYP1-MYP17), few specific genes have been identified.
Environmental
In studies of the genetic predisposition of refractive error, there is a correlation between environmental factors and the risk of developing myopia. Myopia has been observed in individuals with visually intensive occupations.Reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of symbols, often specifically those of a written language, by means of Visual perception, sight or Somatosensory system, touch.
For educators and researchers, reading is a multifacete ...
has also been found to be a predictor of myopia in children. It has been reported that children with myopia spent significantly more time reading than non-myopic children who spent more time playing outdoors. Additionally, focusing on near objects for long periods of time - such as when reading, looking at close screens, or writing - has been associated with myopia. Socioeconomic status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is a measurement used by economics, economists and sociology, sociologsts. The measurement combines a person's work experience and their or their family's access to economic resources and social position in relation t ...
and higher levels of education have also been reported to be a risk factor for myopia. Blepharoptosis can also induce refractive errors.Normal refraction
In order to see a clear image, the eye must focus rays of light on to the light-sensing part of the eye – theretina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
, which is located in the back of the eye. This focusing – called refraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one transmission medium, medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commo ...
– is performed mainly by the cornea
The cornea is the transparency (optics), transparent front part of the eyeball which covers the Iris (anatomy), iris, pupil, and Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and Lens (anatomy), lens, the cornea ...
and the lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
, which are located at the front of the eye, the anterior segment
The anterior segment or anterior cavity is the front third of the eye that includes the structures in front of the vitreous humour: the cornea, iris, ciliary body, and lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or dispers ...
.
When an eye focuses light correctly on to the retina when viewing distant objects, this is called '' emmetropia'' or being ''emmetropic.'' This means that the refractive power of the eye matches what is needed to focus parallel rays of light onto the retina. A distant object is defined as an object located beyond 6 meters (20 feet) from the eye.
When an object is located close to the eye, the rays of light from this object no longer approach the eye parallel to each other. Consequently, the eye must ''increase'' its refractive power to bring those rays of light together on the retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
. This is called accommodation, and is accomplished by the eye thickening the lens.
Diagnosis
eye care professional
An eye care professional is an individual who provides a service related to the eyes or vision. It is any healthcare worker involved in eye care, from one with a small amount of post-secondary training to practitioners with a doctoral level of edu ...
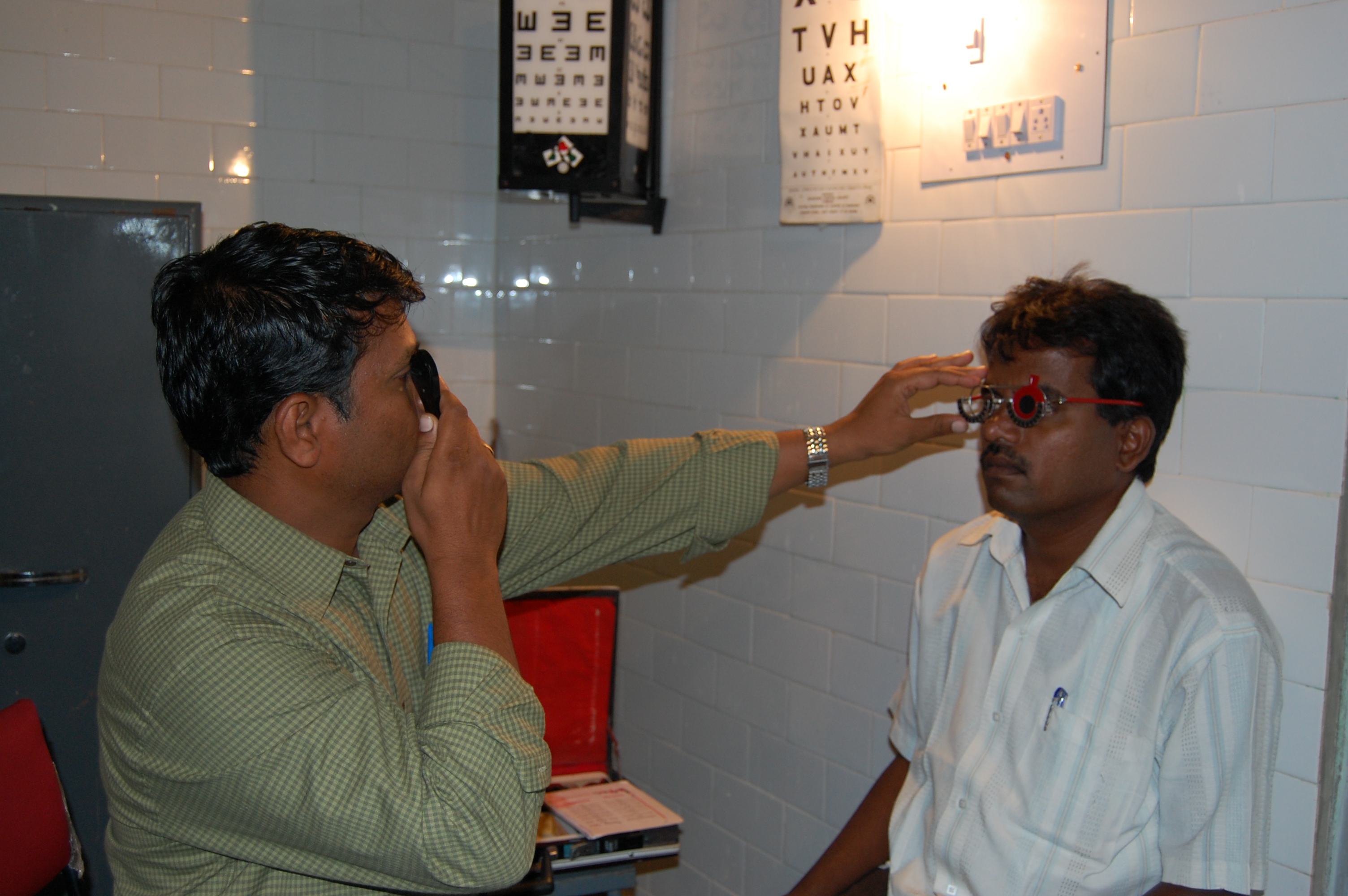
during an eye examination
An eye examination, commonly known as an eye test, is a series of tests performed to assess Visual acuity, vision and ability to Focus (optics), focus on and discern objects. It also includes other tests and examinations of the human eye, eyes. ...
using a large number of lenses of different optical powers, and often a retinoscope (a procedure entitled ''retinoscopy
Retinoscopy is a technique to obtain an objective measurement of the refractive error of a patient's eyes.
How It Works
The examiner uses a retinoscope to shine light into the patient's eye and observes the reflection (reflex) off the patient' ...
'') to measure objectively in which the person views a distant spot while the clinician changes the lenses held before the person's eye and watches the pattern of reflection of a small light shone on the eye. Following that "objective refraction" the clinician typically shows the person lenses of progressively higher or weaker powers in a process known as '' subjective refraction''.
Cycloplegic
Cycloplegia is paralysis of the ciliary muscle of the Human eye, eye, resulting in a loss of accommodation (eye), accommodation. Because of the paralysis of the ciliary muscle, the curvature of the lens can no longer be adjusted to focus on near ...
agents are frequently used to more accurately determine the amount of refractive error, particularly in children
An automated refractor
An autorefractor or automated refractor is a computer-controlled machine used during an eye examination to provide an objective measurement of a person's Refraction error, refractive error and Eyeglass prescription, prescription for glasses or con ...
is an instrument that is sometimes used in place of retinoscopy to objectively estimate a person's refractive error. Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor and its inverse can also be used to characterize eye aberrations in a higher level of resolution and accuracy.
Vision defects caused by refractive error can be distinguished from other problems using a pinhole occluder
A pinhole occluder is an opaque disk with one or more small holes through it, used by ophthalmologists, orthoptists and optometrists to test visual acuity. The occluder is a simple way to focus light, as in a pinhole camera, temporarily removing ...
, which will improve vision only in the case of refractive error.Screening
When refractive errors in children are not treated, the child may be at risk of developing ambylopia, where vision may remain permanently blurry. Because young children typically do not complain of blurry vision, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children have yearly vision screening starting at three years old so that unknown refractive errors or other ophthalmic conditions can be found and treated if deemed necessary by healthcare professionals.Management
The management of refractive error is done post-diagnosis of the condition by either optometrists, ophthalmologists, refractionists, or ophthalmic medical practitioners. How refractive errors are treated or managed depends upon the amount and severity of the condition. Those who possess mild amounts of refractive error may elect to leave the condition uncorrected, particularly if the person is asymptomatic. For those who are symptomatic,glasses
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses (American English), spectacles (Commonwealth English), or colloquially as specs, are vision eyewear with clear or tinted lenses mounted in a frame that holds them in front of a person's eyes, typically u ...
, contact lenses
Contact lenses, or simply contacts, are thin lens (optics), lenses placed directly on the surface of the Human eye, eyes. Contact lenses are ocular prosthetic devices used by over 150 million people worldwide, and they can be worn to correct ...
, refractive surgery
Refractive surgery is an optional eye surgery used to improve the refractive state of the eye and decrease or eliminate dependency on glasses or contact lenses. This can include various methods of surgical remodeling of the cornea ( keratomi ...
, or a combination are typically used.
Glasses
These are the most effective ways of correcting the refractive error. However, the availability and affordability of eyeglasses can present a difficulty for people in many low income settings of the world. Glasses also pose a challenge to children to whom they are prescribed to, due to children's tendency to not wear them as consistently as recommended. As mentioned earlier refractive errors are because of the improper focusing of the light in the retina. Eyeglasses work as an added lens of the eye serving to bend the light to bring it to focus on the retina. Depending on the eyeglasses, they serve many functions. ; Reading glasses: These are general over-the-counter glasses which can be worn for easier reading, especially for defective vision due to aging called presbyopia. ; Single vision prescription lenses: They can correct only one form of defective vision, either far-sightedness or near-sightedness. ; Multifocal lenses: The multifocal lenses can correct defective vision in multiple focus, for example: near-vision as well as far-vision. This are particularly beneficial for presbyobia.Contact lenses
Alternatively, many people choose to wear contact lenses. One style is hard contact lenses, which can distort the shape of the cornea to a desired shape. Another style, soft contact lenses, are made of silicone or hydrogel. Depending on the duration they are designed for, they may be worn daily or may be worn for an extended period of time, such as for weeks. There are a number of complication associated with contact lenses. Typically the ones that are used daily. If redness, itching, and difficulty in vision develops, the use of the lenses should be stopped immediately and the consultation of ophthalmologists may be sought.Surgery
Laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) and photo-refractive keratectomy (PRK) are popular procedures; while use of laser epithelial keratomileusis (LASEK) is increasing. Other surgical treatments for severe myopia include insertion of implants afterclear lens extraction
Clear lens extraction, also known as refractive lensectomy, custom lens replacement or refractive lens exchange is a surgical procedure in which clear lens of the human eye is removed. Unlike cataract surgery, where the cloudy lens is removed to t ...
(refractive lens exchange). Full thickness corneal graft may be a final option for patients with advanced kerataconus although currently there is interest in new techniques that involve collagen crosslinking. As with any surgical procedure complications may arise post-operatively Post-operative monitoring is normally undertaken by the specialist ophthalmic surgical clinic and optometry services. Patients are usually informed pre-operatively about what to expect and where to go if they suspect complications. Any patient reporting pain and redness after surgery should be referred urgently to their ophthalmic surgeon.
Medical treatment
Atropine has believed to slow the progression of near-sightedness and is administered in combination with multifocal lenses. These, however, need further research.Prevention
Strategies being studied to slow worsening include adjusting working conditions, increasing the time children spend outdoors, and special types of contact lenses. In children special contact lenses appear to slow worsening of nearsightedness. A number of questionnaires exist to determinequality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
impact of refractive errors and their correction.
Epidemiology
vision loss
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficul ...
along with cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens (anatomy), lens of the eye that leads to a visual impairment, decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or ...
s, macular degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred vision, blurred or vision loss, no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no sym ...
, and vitamin A deficiency
Vitamin A deficiency (VAD) or hypovitaminosis A is a lack of vitamin A in blood and tissues. It is common in poorer countries, especially among children and women of reproductive age, but is rarely seen in more developed countries. Vitamin A pla ...
.
Cost
The yearly cost of correcting refractive errors is estimated at 3.9 to 7.2 billion dollars in the United States.See also
*Dioptre
A dioptre ( British spelling) or (American spelling), symbol dpt or D, is a unit of measurement with dimension of reciprocal length, equivalent to one reciprocal metre, . It is normally used to express the optical power of a lens or curved mi ...
*Focal length
The focal length of an Optics, optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the Multiplicative inverse, inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system Converge ...
*Optical power
In optics, optical power (also referred to as dioptric power, refractive power, focal power, focusing power, or convergence power) is the degree to which a lens, mirror, or other optical system converges or diverges light. It is equal to the ...
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Refractive error Vision Disorders of ocular muscles, binocular movement, accommodation and refraction Refraction Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate Corrective lenses