Red Terror on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Red Terror (russian: Красный террор, krasnyj terror) in
"The Red Terror"
''Russian Revolution''. Alpha History. Retrieved 4 August 2021. and lasted until 1922. Arising after
The Red Terror
" ''ThoughtCo''. Retrieved March 24, 2021. and sought to eliminate
Soviet Russia
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
was a campaign of political repression
Political repression is the act of a state entity controlling a citizenry by force for political reasons, particularly for the purpose of restricting or preventing the citizenry's ability to take part in the political life of a society, thereb ...
and executions
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that t ...
carried out by the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
, chiefly through the Cheka
The All-Russian Extraordinary Commission ( rus, Всероссийская чрезвычайная комиссия, r=Vserossiyskaya chrezvychaynaya komissiya, p=fsʲɪrɐˈsʲijskəjə tɕrʲɪzvɨˈtɕæjnəjə kɐˈmʲisʲɪjə), abbreviated ...
, the Bolshevik secret police
Secret police (or political police) are intelligence, security or police agencies that engage in covert operations against a government's political, religious, or social opponents and dissidents. Secret police organizations are characteristic of ...
. It started in late August 1918 after the beginning of the Russian Civil War
, date = October Revolution, 7 November 1917 – Yakut revolt, 16 June 1923{{Efn, The main phase ended on 25 October 1922. Revolt against the Bolsheviks continued Basmachi movement, in Central Asia and Tungus Republic, the Far East th ...
Llewellyn, Jennifer; McConnell, Michael; Thompson, Steve (11 August 2019)"The Red Terror"
''Russian Revolution''. Alpha History. Retrieved 4 August 2021. and lasted until 1922. Arising after
assassination attempts on Vladimir Lenin
Several attempts are known to have been made on Vladimir Lenin's life. The most famous of them was committed on August 30, 1918, by the Socialist Revolutionary Party member Fanny Kaplan, as a result of which Lenin was seriously wounded.
Direct as ...
and Petrograd Cheka leader Moisei Uritsky
Moisei Solomonovich Uritsky ( ua, Мойсей Соломонович Урицький; russian: Моисей Соломонович Урицкий; – 30 August 1918) was a Bolshevik revolutionary leader in Russia. After the October Revol ...
, the latter of which was successful, the Red Terror was modeled on the Reign of Terror
The Reign of Terror (french: link=no, la Terreur) was a period of the French Revolution when, following the creation of the First Republic, a series of massacres and numerous public executions took place in response to revolutionary fervour, ...
of the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
,Wilde, Robert. 2019 February 20.The Red Terror
" ''ThoughtCo''. Retrieved March 24, 2021. and sought to eliminate
political dissent
Political dissent is a dissatisfaction with or opposition to the policies of a governing body. Expressions of dissent may take forms from vocal disagreement to civil disobedience to the use of violence. More broadly, the term is usually applied to Bolshevik political repression throughout the Civil War (1917–1922), as distinguished from the
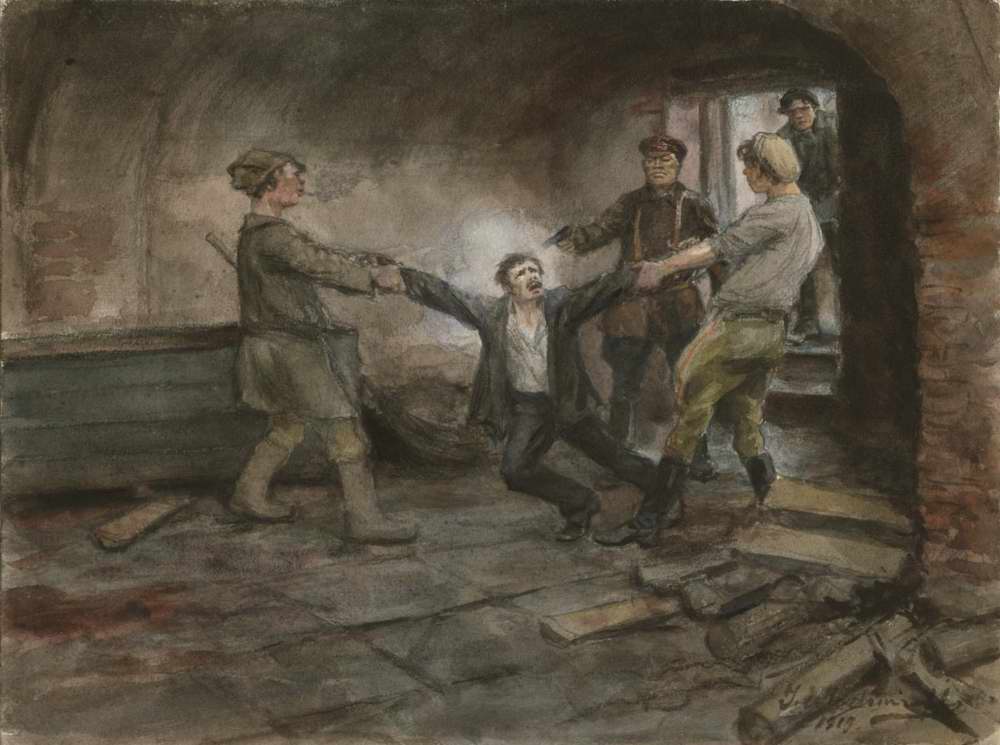
 While recovering from his wounds, Lenin instructed: "It is necessary – secretly and ''urgently'' to prepare the terror." Christopher Andrew and
While recovering from his wounds, Lenin instructed: "It is necessary – secretly and ''urgently'' to prepare the terror." Christopher Andrew and
White Terror
White Terror is the name of several episodes of mass violence in history, carried out against anarchists, communists, socialists, liberals, revolutionaries, or other opponents by conservative or nationalist groups. It is sometimes contrasted wit ...
carried out by the White Army
The White Army (russian: Белая армия, Belaya armiya) or White Guard (russian: Бѣлая гвардія/Белая гвардия, Belaya gvardiya, label=none), also referred to as the Whites or White Guardsmen (russian: Бѣлогв� ...
(Russian and non-Russian groups opposed to Bolshevik rule) against their political enemies, including the Bolsheviks.
Estimates for the total number of victims of Bolshevik repression vary widely in numbers and scope. One source gives estimates of 28,000 executions per year from December 1917 to February 1922. Estimates for the number of people shot during the initial period of the Red Terror are at least 10,000. Estimates for the whole period go for a low of 50,000Stone, Bailey (2013). ''The Anatomy of Revolution Revisited: A Comparative Analysis of England, France, and Russia''. Cambridge University Press. p. 335. to highs of 140,000 and 200,000 executed. The most reliable estimations for the number of executions in total put the number at about 100,000.
Bolshevik justification
The Red Terror inSoviet Russia
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
was justified in Soviet historiography
Soviet historiography is the methodology of history studies by historians in the Soviet Union (USSR). In the USSR, the study of history was marked by restrictions imposed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU). Soviet historiography i ...
as a wartime campaign against counter-revolutionaries
A counter-revolutionary or an anti-revolutionary is anyone who opposes or resists a revolution, particularly one who acts after a revolution in order to try to overturn it or reverse its course, in full or in part. The adjective "counter-revoluti ...
during the Russian Civil War of 1918–1921, targeting those who sided with the Whites (White Army
The White Army (russian: Белая армия, Belaya armiya) or White Guard (russian: Бѣлая гвардія/Белая гвардия, Belaya gvardiya, label=none), also referred to as the Whites or White Guardsmen (russian: Бѣлогв� ...
). Bolsheviks referred to any anti-Bolshevik factions as Whites, regardless of whether those factions actually supported the White movement cause. Leon Trotsky
Lev Davidovich Bronstein. ( – 21 August 1940), better known as Leon Trotsky; uk, link= no, Лев Давидович Троцький; also transliterated ''Lyev'', ''Trotski'', ''Trotskij'', ''Trockij'' and ''Trotzky''. (), was a Russian ...
described the context in 1920:
He then contrasted the terror with the revolution and provided the Bolshevik's justification for it:
Martin Latsis
Martin Ivanovich Latsis (russian: Мартын Иванович Лацис, lv, Mārtiņš Lācis, born Jānis Sudrabs, russian: Ян Фридрихович Судрабс, translit=Yan Fridrikhovich Sudrabs) (December 14, 1888 – February 11, ...
, chief of the Ukrainian Cheka
The All-Russian Extraordinary Commission ( rus, Всероссийская чрезвычайная комиссия, r=Vserossiyskaya chrezvychaynaya komissiya, p=fsʲɪrɐˈsʲijskəjə tɕrʲɪzvɨˈtɕæjnəjə kɐˈmʲisʲɪjə), abbreviated ...
, stated in the newspaper ''Red Terror'':
The bitter struggle was described succinctly from the Bolshevik point of view by Grigory Zinoviev in mid-September 1918:
A completely different point of view from those of the Bolsheviks was expressed in November 1918 by the Left Socialist Revolutionary leader Maria Spiridonova
Maria Alexandrovna Spiridonova (russian: Мари́я Алекса́ндровна Спиридо́нова; 16 October 1884 – 11 September 1941) was a Narodnik-inspired Russian revolutionary. In 1906, as a novice member of a local combat group ...
, at the time in prison awaiting trial. In her Open Letter to the Central Executive of the Bolshevik party, she wrote in particular:

History
The Red Terror campaign is considered to have officially begun between 17 and 30 August 1918 as retribution for two assassination attempts (one of which was successful). The official decree of a "Red Terror," however, came a few days later, in September.Background
In December 1917Felix Dzerzhinsky
Felix Edmundovich Dzerzhinsky ( pl, Feliks Dzierżyński ; russian: Фе́ликс Эдму́ндович Дзержи́нский; – 20 July 1926), nicknamed "Iron Felix", was a Bolshevik revolutionary and official, born into Poland, Polish n ...
was appointed to the duty of rooting out counterrevolutionary
A counter-revolutionary or an anti-revolutionary is anyone who opposes or resists a revolution, particularly one who acts after a revolution in order to try to overturn it or reverse its course, in full or in part. The adjective "counter-revoluti ...
threats to the Soviet government
The Government of the Soviet Union ( rus, Прави́тельство СССР, p=prɐˈvʲitʲɪlʲstvə ɛs ɛs ɛs ˈɛr, r=Pravítelstvo SSSR, lang=no), formally the All-Union Government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, commonly ab ...
. He was the director of the All-Russian Extraordinary Commission (aka Cheka
The All-Russian Extraordinary Commission ( rus, Всероссийская чрезвычайная комиссия, r=Vserossiyskaya chrezvychaynaya komissiya, p=fsʲɪrɐˈsʲijskəjə tɕrʲɪzvɨˈtɕæjnəjə kɐˈmʲisʲɪjə), abbreviated ...
), a predecessor of the KGB that served as the secret police
Secret police (or political police) are intelligence, security or police agencies that engage in covert operations against a government's political, religious, or social opponents and dissidents. Secret police organizations are characteristic of ...
for the Soviets.
From early 1918 Bolsheviks started physical elimination of opposition and other socialist and revolutionary fractions:
On 11 August 1918, prior to the events that would officially catalyze the Terror, Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 19 ...
had sent telegrams "to introduce mass terror" in Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod ( ; rus, links=no, Нижний Новгород, a=Ru-Nizhny Novgorod.ogg, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪj ˈnovɡərət ), colloquially shortened to Nizhny, from the 13th to the 17th century Novgorod of the Lower Land, formerly known as Gork ...
in response to a suspected civilian uprising there, and to "crush" landowners in Penza
Penza ( rus, Пе́нза, p=ˈpʲɛnzə) is the largest city and administrative center of Penza Oblast, Russia. It is located on the Sura River, southeast of Moscow. As of the 2010 Census, Penza had a population of 517,311, making it the 38th-l ...
who resisted, sometimes violently, the requisitioning of their grain by military detachments:
On 17 August 1918, Petrograd
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
Cheka leader Moisei Uritsky
Moisei Solomonovich Uritsky ( ua, Мойсей Соломонович Урицький; russian: Моисей Соломонович Урицкий; – 30 August 1918) was a Bolshevik revolutionary leader in Russia. After the October Revol ...
was assassinated by Leonid Kannegisser; shortly after, on August 30, Fanni Kaplan
Fanny Efimovna Kaplan (russian: Фа́нни Ефи́мовна Капла́н, links=no; real name Feiga Haimovna Roytblat, ; February 10, 1890 – September 3, 1918) was a Ukrainian Jewish woman, Socialist-Revolutionary, and early Soviet dissi ...
unsuccessfully attempted to assassinate Vladimir Lenin.
These attacks would finally persuade the government to heed Dzerzhinsky's lobbying for greater internal security. The campaign of mass repressions would officially begin thereafter as retribution.
Repression begins
 While recovering from his wounds, Lenin instructed: "It is necessary – secretly and ''urgently'' to prepare the terror." Christopher Andrew and
While recovering from his wounds, Lenin instructed: "It is necessary – secretly and ''urgently'' to prepare the terror." Christopher Andrew and Vasili Mitrokhin
Vasili Nikitich Mitrokhin (russian: link=no, Васи́лий Ники́тич Митро́хин; March 3, 1922 – January 23, 2004) was a major and senior archivist for the Soviet Union's foreign intelligence service, the First Chief Di ...
(2000). The Mitrokhin Archive
The "Mitrokhin Archive" is a collection of handwritten notes which were secretly made by the KGB archivist Vasili Mitrokhin during the thirty years in which he served as a KGB archivist in the foreign intelligence service and the First Chief Dir ...
: The KGB in Europe and the West. Gardners Books. , page 34. In immediate response to the two attacks, Chekists killed approximately 1,300 "bourgeois hostages" held in Petrograd
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
and Kronstadt
Kronstadt (russian: Кроншта́дт, Kronshtadt ), also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt or Kronštádt (from german: link=no, Krone for " crown" and ''Stadt'' for "city") is a Russian port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city ...
prisons.
Bolshevik newspapers were especially integral to instigating an escalation in state violence: on August 31, the state-controlled media launched the repressive campaign through incitement of violence. One article appearing in ''Pravda
''Pravda'' ( rus, Правда, p=ˈpravdə, a=Ru-правда.ogg, "Truth") is a Russian broadsheet newspaper, and was the official newspaper of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, when it was one of the most influential papers in the co ...
'' exclaimed: "the time has come for us to crush the bourgeoisie or be crushed by it.... The anthem of the working class will be a song of hatred and revenge!" The next day, the newspaper ''Krasnaia Gazeta'' stated that "only rivers of blood can atone for the blood of Lenin and Uritsky."
The first official announcement of a Red Terror was published in ''Izvestia
''Izvestia'' ( rus, Известия, p=ɪzˈvʲesʲtʲɪjə, "The News") is a daily broadsheet newspaper in Russia. Founded in 1917, it was a newspaper of record in the Soviet Union until the Soviet Union's dissolution in 1991, and describes ...
'' on September 3, titled "Appeal to the Working Class", calling for the workers to "crush the hydra of counter-revolution
A counter-revolutionary or an anti-revolutionary is anyone who opposes or resists a revolution, particularly one who acts after a revolution in order to try to overturn it or reverse its course, in full or in part. The adjective "counter-revoluti ...
with massive terror!"; it would also make clear that "anyone who dares to spread the slightest rumor against the Soviet regime
The political system of the Soviet Union took place in a federal single-party soviet socialist republic framework which was characterized by the superior role of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU), the only party permitted by the Co ...
will be arrested immediately and sent to a concentration camp
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simply ...
". ''Izvestia'' also reported that, in the 4 days since the attempt on Lenin, over 500 hostages had been executed in Petrograd
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
alone.
Subsequently, on September 5, the Central Committee of the Bolshevik government Under the leadership of Russian communist Vladimir Lenin, the Bolshevik Party seized power in the Russian Republic during a coup known as the October Revolution. Overthrowing the pre-existing Provisional Government, the Bolsheviks established a new ...
issued a decree "On Red Terror", prescribing "mass shooting” to be "inflicted without hesitation;" the decree ordered the Cheka
The All-Russian Extraordinary Commission ( rus, Всероссийская чрезвычайная комиссия, r=Vserossiyskaya chrezvychaynaya komissiya, p=fsʲɪrɐˈsʲijskəjə tɕrʲɪzvɨˈtɕæjnəjə kɐˈmʲisʲɪjə), abbreviated ...
"to secure the Soviet Republic from the class enemies by isolating them in concentration camps", as well as stating that counter-revolutionaries "must be executed by shooting ndthat the names of the executed and the reasons of the execution must be made public."
The government executed 500 "representatives of overthrown classes" (kulak
Kulak (; russian: кула́к, r=kulák, p=kʊˈlak, a=Ru-кулак.ogg; plural: кулаки́, ''kulakí'', 'fist' or 'tight-fisted'), also kurkul () or golchomag (, plural: ), was the term which was used to describe peasants who owned ove ...
s) immediately after the assassination of Uritsky. Soviet commissar Grigory Petrovsky
Grigory Ivanovich Petrovsky (russian: Григо́рий Ива́нович Петро́вский, uk, Григо́рій Іва́нович Петро́вський, translit=Hryhorii Ivanovych Petrovskyi) (3 February 1878 - 9 January 1958) wa ...
called for an expansion of the Terror and an "immediate end of looseness and tenderness."
In October 1918, Cheka commander Martin Latsis
Martin Ivanovich Latsis (russian: Мартын Иванович Лацис, lv, Mārtiņš Lācis, born Jānis Sudrabs, russian: Ян Фридрихович Судрабс, translit=Yan Fridrikhovich Sudrabs) (December 14, 1888 – February 11, ...
likened the Red Terror to a class war
Class War is an anarchist group and newspaper established by Ian Bone and others in 1983 in the United Kingdom. An incarnation of Class War was briefly registered as a political party for the purposes of fighting the 2015 United Kingdom gener ...
, explaining that "we are destroying the ''bourgeoisie'' as a class."
On October 15, the leading Chekist Gleb Bokii
Gleb Ivanovich Bokii ( ukr, Гліб Іванович Бокій; russian: Глеб Иванович Бокий; 21 June 1879 – 15 November 1937) was a Ukrainian Communist political activist, revolutionary, and paranormal investigatorZnamenski ...
, summing up the officially-ended Red Terror, reported that, in Petrograd, 800 alleged enemies had been shot and another 6,229 imprisoned. Casualties in the first two months were between 10,000 and 15,000 based on lists of summarily executed
A summary execution is an execution in which a person is accused of a crime and immediately killed without the benefit of a full and fair trial. Executions as the result of summary justice (such as a drumhead court-martial) are sometimes include ...
people published in newspaper ''Cheka Weekly'' and other official press. A declaration ''About the Red Terror'' by the Sovnarkom
The Councils of People's Commissars (SNK; russian: Совет народных комиссаров (СНК), ''Sovet narodnykh kommissarov''), commonly known as the ''Sovnarkom'' (Совнарком), were the highest executive authorities of ...
on 5 September 1918 stated:
As the Russian Civil War
, date = October Revolution, 7 November 1917 – Yakut revolt, 16 June 1923{{Efn, The main phase ended on 25 October 1922. Revolt against the Bolsheviks continued Basmachi movement, in Central Asia and Tungus Republic, the Far East th ...
progressed, significant numbers of prisoners, suspects and hostages were executed because they belonged to the "possessing classes". Numbers are recorded for cities occupied by the Bolsheviks:
InInKharkov Kharkiv ( uk, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest city and municipality in Ukraine.there were between 2,000 and 3,000 executions in February–June 1919, and another 1,000–2,000 when the town was taken again in December of that year; inRostov-on-Don Rostov-on-Don ( rus, Ростов-на-Дону, r=Rostov-na-Donu, p=rɐˈstof nə dɐˈnu) is a port city and the administrative centre of Rostov Oblast and the Southern Federal District of Russia. It lies in the southeastern part of the East Eu ..., approximately 1,000 in January 1920; inOdessa Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrativ ..., 2,200 in May–August 1919, then 1,500–3,000 between February 1920 and February 1921; inKiev Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ..., at least 3,000 in February–August 1919; in Ekaterinodar, at least 3,000 between August 1920 and February 1921; In Armavir, a small town in Kuban, between 2,000 and 3,000 in August–October 1920. The list could go on and on.
Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
, Béla Kun
Béla Kun (born Béla Kohn; 20 February 1886 – 29 August 1938) was a Hungarian communist revolutionary and politician who governed the Hungarian Soviet Republic in 1919. After attending Franz Joseph University at Kolozsvár (today Cluj-Napo ...
and Rosalia Zemlyachka
Rosalia Samoilovna Zemlyachka, née Zalkind (russian: link=no, Розалия Самойловна Землячка, рожд. Залкинд; 20 March 187621 January 1947) was a Russian revolutionary and Soviet politician. As a revolutionary, she ...
, with Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 19 ...
's approval, had 50,000 White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White o ...
prisoners of war and civilians summarily executed by shooting or hanging after the defeat of general Pyotr Wrangel
Baron Pyotr Nikolayevich Wrangel (russian: Пётр Никола́евич барон Вра́нгель, translit=Pëtr Nikoláevič Vrángel', p=ˈvranɡʲɪlʲ, german: Freiherr Peter Nikolaus von Wrangel; April 25, 1928), also known by his ni ...
at the end of 1920. They had been promised amnesty if they would surrender. This is one of the largest massacres in the Civil War.
On 16 March 1919, all military detachments of the Cheka were combined in a single body, the Troops for the Internal Defense of the Republic, which numbered 200,000 in 1921. These troops policed labor camps, ran the Gulag
The Gulag, an acronym for , , "chief administration of the camps". The original name given to the system of camps controlled by the GPU was the Main Administration of Corrective Labor Camps (, )., name=, group= was the government agency in ...
system, conducted prodrazvyorstka
''Prodrazvyorstka'', also transliterated ''Prodrazverstka'' ( rus, продразвёрстка, p=prədrɐˈzvʲɵrstkə, short for , ) was a policy and campaign of confiscation of grain and other agricultural products from peasants at nominal ...
(requisitions of food), and put down peasant rebellions, riots by workers, and mutinies in the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
(which was plagued by desertions).
One of the main organizers of the Red Terror for the Bolshevik government was 2nd-Grade Army Commissar Yan Karlovich Berzin
Yan (Ian) Karlovich Berzin (russian: Ян Карлович Берзин; lv, Jānis Bērziņš; real name Pēteris Ķuzis; , Kreis Riga (now in Zaube parish), the Russian Empire – 29 July 1938, Moscow, the USSR), was a Latvian Soviet commun ...
(1889–1938), whose real name was Pēteris Ķuzis. He took part in the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key moment ...
of 1917 and afterwards worked in the central apparatus of the Cheka. During the Red Terror, Berzin initiated the system of taking and shooting hostages to stop desertions and other "acts of disloyalty and sabotage". As chief of a special department of the Latvian Red Army (later the 15th Army), Berzin played a part in the suppression of the Russian sailors' mutiny at Kronstadt in March 1921. He particularly distinguished himself in the course of the pursuit, capture, and killing of captured sailors.
Repressions
Among the victims of the Red Terror were tsarists, liberals, non-Bolsheviksocialists
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the eco ...
, members of the clergy, ordinary criminals
In ordinary language, a crime is an unlawful act punishable by a State (polity), state or other authority. The term ''crime'' does not, in modern criminal law, have any simple and universally accepted definition,Farmer, Lindsay: "Crime, definit ...
, counter-revolutionaries
A counter-revolutionary or an anti-revolutionary is anyone who opposes or resists a revolution, particularly one who acts after a revolution in order to try to overturn it or reverse its course, in full or in part. The adjective "counter-revoluti ...
, and other political dissidents
Political dissent is a dissatisfaction with or opposition to the policies of a governing body. Expressions of dissent may take forms from vocal disagreement to civil disobedience to the use of violence.industrial workers who failed to meet
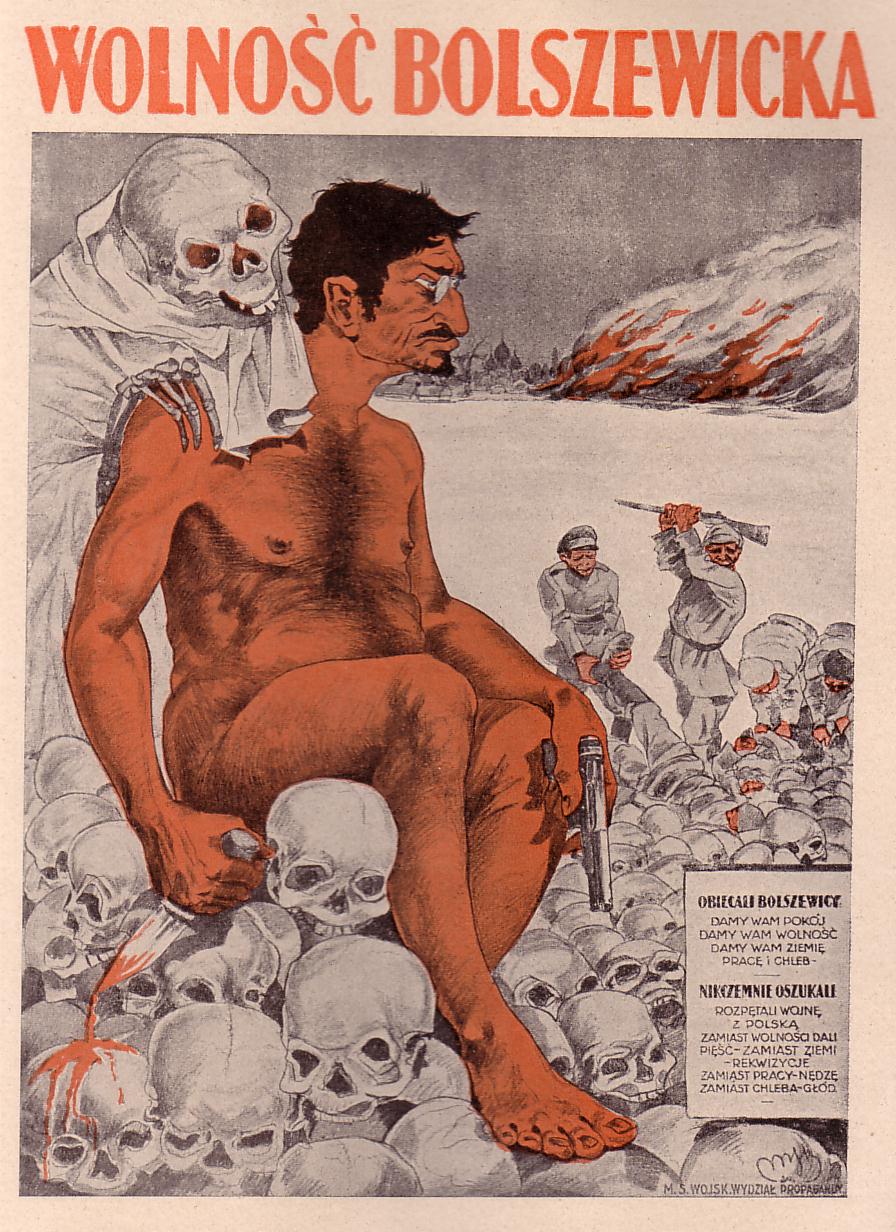 The
The
page 156
/ref> An estimated 3,000 were put to death in 1918 alone.
production quota
A production quota is a goal for the production of a good. It is typically set by a government or an organization, and can be applied to an individual worker, firm, industry or country. Quotas can be set high to encourage production, or can be u ...
s were also targeted.
The first victims of the Terror were the Socialist Revolutionaries
The Socialist Revolutionary Party, or the Party of Socialist-Revolutionaries (the SRs, , or Esers, russian: эсеры, translit=esery, label=none; russian: Партия социалистов-революционеров, ), was a major politi ...
(SR). Over the months of the campaign, over 800 SR members were executed, while thousands more were driven into exile or detained in labor camps. In a matter of weeks, executions carried out by the Cheka doubled or tripled the amount of death sentences pronounced by the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
over its 92-year period from 1825 to 1917. While the Socialist Revolutionaries were initially the primary targets of the terror, most of its victims were associated with the Tsarist autocracy.
Peasants
Internal Troops
The Internal Troops, full name Internal Troops of the Ministry for Internal Affairs (MVD) (russian: Внутренние войска Министерства внутренних дел, Vnutrenniye Voiska Ministerstva Vnutrennikh Del; abbreviat ...
of the Cheka and the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
practiced the terror tactics of taking and executing numerous hostages, often in connection with desertions of forcefully mobilized peasants. According to Orlando Figes
Orlando Guy Figes () is a British historian and writer. Until his retirement, he was Professor of History at Birkbeck College, University of London.
Figes is known for his works on Russian history, such as '' A People's Tragedy'' (1996), ''Nata ...
, more than 1 million people deserted from the Red Army in 1918, around 2 million people deserted in 1919, and almost 4 million deserters escaped from the Red Army in 1921. Around 500,000 deserters were arrested in 1919 and close to 800,000 in 1920 by Cheka troops and special divisions created to combat desertions. Thousands of deserters were killed, and their families were often taken hostage. According to Lenin's instructions,
In September 1918, in just twelve provinces of Russia, 48,735 deserters and 7,325 brigands were arrested: 1,826 were executed and 2,230 were deported. A typical report from a Cheka department stated:
Estimates suggest that during the suppression of the Tambov Rebellion
The Tambov Rebellion of 1920–1921 was one of the largest and best-organized peasant rebellions challenging the Bolshevik government during the Russian Civil War. The uprising took place in the territories of the modern Tambov Oblast and part ...
of 1920–1921, around 100,000 peasant rebels and their families were imprisoned or deported and perhaps 15,000 executed.
This campaign marked the beginning of the Gulag
The Gulag, an acronym for , , "chief administration of the camps". The original name given to the system of camps controlled by the GPU was the Main Administration of Corrective Labor Camps (, )., name=, group= was the government agency in ...
, and some scholars have estimated that 70,000 were imprisoned by September 1921 (this number excludes those in several camps in regions that were in revolt, such as Tambov). Conditions in these camps led to high mortality rates, and "repeated massacres" took place. The Cheka at the Kholmogory camp adopted the practice of drowning bound prisoners in the nearby Dvina river. Occasionally, entire prisons were "emptied" of inmates via mass shootings prior to abandoning a town to White forces.
Industrial workers
On 16 March 1919, Cheka stormed the Putilov factory. More than 900 workers who went to a strike were arrested, of whom more than 200 were executed without trial during the next few days. Numerous strikes took place in the spring of 1919 in cities of Tula, Oryol,Tver
Tver ( rus, Тверь, p=tvʲerʲ) is a city and the administrative centre of Tver Oblast, Russia. It is northwest of Moscow. Population:
Tver was formerly the capital of a powerful medieval state and a model provincial town in the Russian ...
, Ivanovo and Astrakhan
Astrakhan ( rus, Астрахань, p=ˈastrəxənʲ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in Southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of the ...
. Starving workers sought to obtain food rations matching those of Red Army soldiers. They also demanded the elimination of privileges for Bolsheviks, freedom of the press, and free elections. The Cheka mercilessly suppressed all strikes, using arrests and executions.
In the city of Astrakhan, a revolt led by the White Guard forces broke out. In preparing this revolt, the Whites managed to smuggle more than 3000 rifles and machine guns into the city. The leaders of the plot decided to act on the night 9–10 March 1919. The rebels were joined by wealthy peasants from the villages, which suppressed the Committees of the Poor, and committed massacres against rural activists. Eyewitnesses reported atrocities in villages such as Ivanchug, Chagan, Karalat. In response, Soviet forces led by Kirov undertook to suppress this revolt in the villages, and together with the Committees of the Poor restored Soviet power. The revolt in Astrakhan was brought under control by 10 March, and completely defeated by the 12th. More than 184 were sentenced to death, including monarchists, and representatives of the Kadets, Left-Socialist Revolutionaries, repeat offenders, and persons shown to have links with British and American intelligence services. The opposition media with political opponents like Chernov, and Melgunov, and others would later say that between 2,000 and 4,000 were shot or drowned from 12 to 14 of March 1919.
However, strikes continued. Lenin had concerns about the tense situation regarding workers in the Ural region
Ural (russian: Урал) is a geographical region located around the Ural Mountains, between the East European and West Siberian plains. It is considered a part of Eurasian Steppe, extending approximately from the North to the South; from the A ...
. On 29 January 1920, he sent a telegram to Vladimir Smirnov stating "I am surprised that you are taking the matter so lightly, and are not immediately executing large numbers of strikers for the crime of sabotage".
At these times, there were numerous reports that Cheka interrogators used torture. At Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrativ ...
the Cheka tied White officers to planks and slowly fed them into furnaces or tanks of boiling water; in Kharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, wikt:Харків, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in Ukraine.Voronezh
Voronezh ( rus, links=no, Воро́неж, p=vɐˈronʲɪʂ}) is a city and the administrative centre of Voronezh Oblast in southwestern Russia straddling the Voronezh River, located from where it flows into the Don River. The city sits on the ...
Cheka rolled naked people around in barrels studded internally with nails; victims were crucified or stoned to death at Dnipropetrovsk; the Cheka at Kremenchuk
Kremenchuk (; uk, Кременчу́к, Kremenchuk ) is an industrial city in central Ukraine which stands on the banks of the Dnipro River. The city serves as the administrative center of the Kremenchuk Raion (district) in Poltava Oblast (pr ...
impaled members of the clergy and buried alive rebelling peasants; in Oryol, water was poured on naked prisoners bound in the winter streets until they became living ice statues; in Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
, Chinese Cheka detachments placed rats in iron tubes sealed at one end with wire netting and the other placed against the body of a prisoner, with the tubes being heated until the rats gnawed through the victim's body in an effort to escape.
Executions took place in prison cellars or courtyards, or occasionally on the outskirts of town, during the Red Terror and Russian Civil War
, date = October Revolution, 7 November 1917 – Yakut revolt, 16 June 1923{{Efn, The main phase ended on 25 October 1922. Revolt against the Bolsheviks continued Basmachi movement, in Central Asia and Tungus Republic, the Far East th ...
. After the condemned were stripped of their clothing and other belongings, which were shared among the Cheka executioners, they were either machine-gunned in batches or dispatched individually with a revolver. Those killed in prison were usually shot in the back of the neck as they entered the execution cellar, which became littered with corpses and soaked with blood. Victims killed outside the town were moved by truck, bound and gagged, to their place of execution, where they sometimes were made to dig their own graves.
According to Edvard Radzinsky, "it became a common practice to take a husband hostage and wait for his wife to come and purchase his life with her body". During decossackization, there were massacres, according to historian Robert Gellately
Robert Gellately (born 1943) is a Canadian academic and noted authority on the history of modern Europe, particularly during World War II and the Cold War era.
Education and career
He earned his B.A., B.Ed., and M.A. degrees at Memorial Unive ...
, "on an unheard of scale". The Pyatigorsk
Pyatigorsk (russian: Пятиго́рск; Circassian: Псыхуабэ, ''Psıxwabæ'') is a city in Stavropol Krai, Russia located on the Podkumok River, about from the town of Mineralnye Vody where there is an international airport and about ...
Cheka organized a "day of Red Terror" to execute 300 people in one day, and took quotas from each part of town. According to the Chekist , the Cheka in Kislovodsk
Kislovodsk (russian: Кислово́дск, lit. ''sour waters''; ; krc, Ачысуу) is a spa city in Stavropol Krai, Russia, in the North Caucasus region of Russia which is located between the Black and Caspian Seas.
Population:
History
I ...
, "for lack of a better idea", killed all the patients in the hospital. In October 1920 alone more than 6,000 people were executed. Gellately adds that Communist leaders "sought to justify their ethnic-based massacres by incorporating them into the rubric of the 'class struggle.
Clergy and religious
Members of the clergy were subjected to particularly brutal abuse. According to documents cited byAlexander Yakovlev
Alexander Nikolayevich Yakovlev (russian: Алекса́ндр Никола́евич Я́ковлев; 2 December 1923 – 18 October 2005) was a Soviet and Russian politician, diplomat, and historian. A member of the Politburo and Secreta ...
, then head of the Presidential Committee for the Rehabilitation of Victims of Political Repression, priests, monks and nuns were crucified, thrown into cauldrons of boiling tar, scalped, strangled, given Communion with melted lead and drowned in holes in the ice.Alexander Nikolaevich Yakovlev
Alexander Nikolayevich Yakovlev (russian: Алекса́ндр Никола́евич Я́ковлев; 2 December 1923 – 18 October 2005) was a Soviet and Russian politician, diplomat, and historian. A member of the Politburo and Secreta ...
. ''A Century of Violence in Soviet Russia.'' Yale University Press
Yale University Press is the university press of Yale University. It was founded in 1908 by George Parmly Day, and became an official department of Yale University in 1961, but it remains financially and operationally autonomous.
, Yale Universi ...
, 2002.page 156
/ref> An estimated 3,000 were put to death in 1918 alone.
Interpretations by historians
Historians such asStéphane Courtois
Stéphane Courtois (born 25 November 1947) is a French historian and university professor, a director of research at the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS), professor at the Catholic Institute of Higher Studies (ICES) in La Ro ...
and Richard Pipes have argued that the Bolsheviks needed to use terror to stay in power because they lacked popular support.Richard Pipes, ''Communism: A History'' (2001), , p. 39. Although the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
dominated among workers, soldiers and in their revolutionary soviets
Soviet people ( rus, сове́тский наро́д, r=sovyétsky naród), or citizens of the USSR ( rus, гра́ждане СССР, grázhdanye SSSR), was an umbrella demonym for the population of the Soviet Union.
Nationality policy in ...
, they won less than a quarter of the popular vote in elections for the Constituent Assembly held soon after the October Revolution, since they commanded much less support among the peasantry. The Constituent Assembly elections predated the split between the Right SRs, who had opposed the Bolsheviks, and the Left SRs
The Party of Left Socialist-Revolutionaries (russian: Партия левых социалистов-революционеров-интернационалистов) was a revolutionary socialist political party formed during the Russian Revo ...
, who were their coalition partners, consequentially many peasant votes intended for the latter went to the SRs. Massive strikes by Russian workers were "mercilessly" suppressed during the Red Terror.
According to Richard Pipes, terror was inevitably justified by Lenin's belief that human lives were expendable in the cause of building the new order of communism. Pipes has quoted Marx's observation of the class struggles in 19th century France: "The present generation resembles the Jews whom Moses led through the wilderness. It must not only conquer a new world, it must also ''perish'' in order to make room for the people who are fit for a new world", but noted that neither Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
nor Friedrich Engels
Friedrich Engels ( ,"Engels"
''
 The Red Terror was significant because it was the first of numerous Communist terror campaigns which were waged in Soviet Russia and many other countries. It also triggered the
The Red Terror was significant because it was the first of numerous Communist terror campaigns which were waged in Soviet Russia and many other countries. It also triggered the BBC Article
/ref> The situation was also called a "Red Terror" by the media. * Finnish Red Terror — the 1918 Civil War in
marxists.org
*
by Yuliy Osipovich Martov, June/July 1918
The Record of the Red Terror
by
More 'red terror' remains found in Russia
''
Robert Conquest
George Robert Acworth Conquest (15 July 1917 – 3 August 2015) was a British historian and poet.
A long-time research fellow at Stanford University's Hoover Institution, Conquest was most notable for his work on the Soviet Union. His books ...
was convinced that "unprecedented terror must seem necessary to ideologically motivated attempts to transform society massively and speedily, against its natural possibilities."Robert Conquest, ''Reflections on a Ravaged Century'' (2000), , p. 101.
Orlando Figes
Orlando Guy Figes () is a British historian and writer. Until his retirement, he was Professor of History at Birkbeck College, University of London.
Figes is known for his works on Russian history, such as '' A People's Tragedy'' (1996), ''Nata ...
' view was that Red Terror was implicit, not so much in Marxism itself, but in the tumultuous violence of the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ...
. He noted that there were a number of Bolsheviks, led by Lev Kamenev, Nikolai Bukharin, and Mikhail Olminsky
Mikhail Stepanovich Olminsky ( rus, Михаил Степанович Ольминский) (15 October, 1863 – May 8, 1933) (real surname: Aleksandrov) was a prominent Russian Bolshevik particularly involved with Party history and also an acti ...
, who criticized the actions and warned that thanks to "Lenin's violent seizure of power and his rejection of democracy," the Bolsheviks would be "forced to turn increasingly to terror to silence their political critics and subjugate a society they could not control by other means." Figes also asserts that the Red Terror "erupted from below. It was an integral element of the social revolution from the start. The Bolsheviks encouraged but did not create this mass terror. The main institutions of the Terror were all shaped, at least in part, in response to these pressures from below."
The German Marxist Karl Kautsky
Karl Johann Kautsky (; ; 16 October 1854 – 17 October 1938) was a Czech-Austrian philosopher, journalist, and Marxist theorist. Kautsky was one of the most authoritative promulgators of orthodox Marxism after the death of Friedrich Engels i ...
pleaded with Lenin against using violence as a form of terrorism because it was indiscriminate, intended to frighten the civilian population and included the taking and executing hostages: "Among the phenomena for which Bolshevism has been responsible, terrorism, which begins with the abolition of every form of freedom of the Press, and ends in a system of wholesale execution, is certainly the most striking and the most repellent of all."
In ''The Black Book of Communism
''The Black Book of Communism: Crimes, Terror, Repression'' is a 1997 book by Stéphane Courtois, Andrzej Paczkowski, Nicolas Werth, Jean-Louis Margolin, and several other European academics documenting a history of political repression by co ...
'', Nicolas Werth
Nicolas Werth (born 1950 in Paris) is a French historian.
Biography
Werth is a scholar of communist studies. He is the son of Alexander Werth, a Russian born British journalist and writer who lived in the USSR during World War II.
Work
Nico ...
contrasts the Red and White Terrors, noting the former was the official policy of the Bolshevik government:
The Bolshevik policy of terror was more systematic, better organized, and targeted at whole social classes. Moreover, it had been thought out and put into practice before the outbreak of the civil war. The White Terror was never systematized in such a fashion. It was almost invariably the work of detachments that were out of control, and taking measures not officially authorized by the military command that was attempting, without much success, to act as a government. If one discounts the pogroms, which Denikin himself condemned, the White Terror most often was a series of reprisals by the police acting as a sort of military counterespionage force. The Cheka and the Troops for the Internal Defense of the Republic were a structured and powerful instrument of repression of a completely different order, which had support at the highest level from the Bolshevik regime.James Ryan points out that Lenin never advocated for the physical extermination of the entire bourgeoisie as a class, just the execution of those who were actively involved in opposing and undermining Bolshevik rule. He did intend to bring about "the overthrow and complete abolition of the bourgeoisie", but through non-violent political and economic means.
Leszek Kołakowski
Leszek Kołakowski (; ; 23 October 1927 – 17 July 2009) was a Polish philosopher and historian of ideas. He is best known for his critical analyses of Marxist thought, especially his three-volume history, '' Main Currents of Marxism'' (1976 ...
noted that while Bolsheviks (especially Lenin) were very much focused on the Marxian concept of "violent revolution" and dictatorship of the proletariat
In Marxist philosophy, the dictatorship of the proletariat is a condition in which the proletariat holds state power. The dictatorship of the proletariat is the intermediate stage between a capitalist economy and a communist economy, whereby the ...
long before the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key moment ...
, implementation of the dictatorship was clearly defined by Lenin as early as in 1906, when he argued it must involve "unlimited power based on force and not on law," power that is "absolutely unrestricted by any rules whatever and based directly on violence." In ''The State and Revolution
''The State and Revolution'' (1917) is a book by Vladimir Lenin describing the role of the state in society, the necessity of proletarian revolution, and the theoretic inadequacies of social democracy in achieving revolution to establish the dicta ...
'' of 1917, Lenin once again reiterated the arguments raised by Marx and Engels calling for use of terror. Voices such as Kautsky calling for moderate use of violence met "furious reply" from Lenin in ''The Proletarian Revolution and the Renegade Kautsky
''The Proletarian Revolution and the Renegade Kautsky'' (most frequently published as ''The Dictatorship of the Proletariat and the Renegade Kautsky)'' is a work by Vladimir Lenin written in October and November 1918 defending the Bolsheviks agai ...
'' (1918). Another theoretical and systematic argument in favor of organized terror in response to Kautsky's reservations was written by Trotsky
Lev Davidovich Bronstein. ( – 21 August 1940), better known as Leon Trotsky; uk, link= no, Лев Давидович Троцький; also transliterated ''Lyev'', ''Trotski'', ''Trotskij'', ''Trockij'' and ''Trotzky''. (), was a Russian M ...
in '' The Defense of Terrorism'' (1921). Trotsky argued that in the light of historical materialism, it is sufficient that the violence is successful for it to justify its rightness. Trotsky also introduced and provided ideological justification for many of the future features characterizing the Bolshevik system such as "militarization of labor" and concentration camps.
Historical significance
Russian Civil War
, date = October Revolution, 7 November 1917 – Yakut revolt, 16 June 1923{{Efn, The main phase ended on 25 October 1922. Revolt against the Bolsheviks continued Basmachi movement, in Central Asia and Tungus Republic, the Far East th ...
according to historian Richard Pipes. Menshevik
The Mensheviks (russian: меньшевики́, from меньшинство 'minority') were one of the three dominant factions in the Russian socialist movement, the others being the Bolsheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries.
The factions eme ...
Julius Martov wrote about Red Terror:
The beast has licked hot human blood. The man-killing machine is brought into motion ... But blood breeds blood ... We witness the growth of the bitterness of the civil war, the growing bestiality of men engaged in it.The term 'Red Terror' was later used in reference to other campaigns of violence which were waged by communist or communist-affiliated groups. Some other events which were also called "Red Terrors" include: * Hungarian Red Terror — the execution of 590 people who were accused of being involved in the counterrevolutionary ''coup'' against the
Hungarian Soviet Republic
The Socialist Federative Republic of Councils in Hungary ( hu, Magyarországi Szocialista Szövetséges Tanácsköztársaság) (due to an early mistranslation, it became widely known as the Hungarian Soviet Republic in English-language sources ( ...
on 24 June 1919.
* Spanish Red Terror — assassinations which were carried out during the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, lin ...
.
* Red Terror (Greece) — a campaign of repression which was waged in Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
by the Communist organizations of the Greek Resistance (during the Axis occupation of Greece which coincided with World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
) and the Greek Civil War
The Greek Civil War ( el, ο Eμφύλιος �όλεμος ''o Emfýlios'' 'Pólemos'' "the Civil War") took place from 1946 to 1949. It was mainly fought against the established Kingdom of Greece, which was supported by the United Kingdom ...
(1943–49).
* Ethiopian Red Terror — a campaigned of repression which was waged by the Derg during the rule of Mengistu Haile Mariam
Mengistu Haile Mariam ( am, መንግሥቱ ኀይለ ማሪያም, pronunciation: ; born 21 May 1937) is an Ethiopian politician and former army officer who was the head of state of Ethiopia from 1977 to 1991 and General Secretary of the Wor ...
.
* Chinese Red Terror — a campaign of repression which is believed to have begun with the Red August
Red August (), originally meaning August 1966 of the Cultural Revolution, is a term used to indicate a series of massacres in Beijing which mainly took place during the period. According to the official statistics in 1980, from August to Septembe ...
of the Cultural Revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a sociopolitical movement in the People's Republic of China (PRC) launched by Mao Zedong in 1966, and lasting until his death in 1976. Its stated goal ...
. According to Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
himself: "Red terror ought to be our reply to these counter-revolutionaries. We must, especially in the war zones and in the border areas, deal immediately, swiftly with every kind of counter-revolutionary activity."
* Indian Red Terror — a name which was given to the "Nandigram violence
Nandigram Violence refers to the violence in Nandigram, West Bengal, India, in 2007 due to the land acquisition for a project taken up by the CPI(M)-led Government of West Bengal to create a chemical hub, a type of special economic zone (S ...
" (November 2007) in Nandigram
Nandigram is a census town in the Nandigram I Community Development Block of the Haldia subdivision in the Purba Medinipur district of the Indian state of West Bengal.
In 2007, the West Bengal government allowed the Salim Group to set up a ch ...
, West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fourt ...
, critics use it in order to allude to the actions of the local administration Communist Party of India
Communist Party of India (CPI) is the oldest Marxist–Leninist communist party in India and one of the nine national parties in the country. The CPI was founded in modern-day Kanpur (formerly known as Cawnpore) on 26 December 1925.
H ...
, the ruling party in West Bengal./ref> The situation was also called a "Red Terror" by the media. * Finnish Red Terror — the 1918 Civil War in
Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
.
* Yugoslavian Red Terror — another name for the period from 1941 to 1942 in Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
known as the "Leftist errors
Leftist errors ( sh, leva/lijeva skretanja) was a term used by the Communist Party of Yugoslavia (CPY) to describe radical policies and strategies – described as the Red Terror (''Crveni Teror'') by others – pursued by self-described Left-wi ...
."
See also
Notes
References and further reading
See also: ' * * * * * * * * See also text omarxists.org
*
External links
by Yuliy Osipovich Martov, June/July 1918
The Record of the Red Terror
by
Sergei Melgunov
Sergei Petrovich Melgunov (russian: Серге́й Петро́вич Мельгуно́в) (December 24 or 25, 1879 – May 26, 1956) was a Russian historian, publicist and politician best known for his opposition to the Soviet government and ...
More 'red terror' remains found in Russia
UPI
United Press International (UPI) is an American international news agency whose newswires, photo, news film, and audio services provided news material to thousands of newspapers, magazines, radio and television stations for most of the 20th c ...
, July 19, 2010.
{{Terrorism topics
Mass murder in 1918
Political and cultural purges
Political repression in the Soviet Union
Communist terrorism
Politicides
Russian Civil War
Soviet war crimes
*
War crimes in Russia