Red Ochre on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Ochre ( ; , ), or ocher in
Ochre ( ; , ), or ocher in
 * Yellow ochre, , is a
* Yellow ochre, , is a
File:LimoniteUSGOV.jpg, Limonite, a
File:Lascaux2.jpg, Image of a horse coloured with yellow ochre (17,300 BC) from Lascaux cave, France.
File:Pech Merle main.jpg, Image of a human hand created with red ochre in Pech Merle cave, France ( Gravettian era, 25,000 BC).
 Ochre was the most commonly used pigment for painting walls in the ancient Mediterranean world. In Ancient Greece, red ochre was called μίλτος, ''míltos'' (hence
Ochre was the most commonly used pigment for painting walls in the ancient Mediterranean world. In Ancient Greece, red ochre was called μίλτος, ''míltos'' (hence
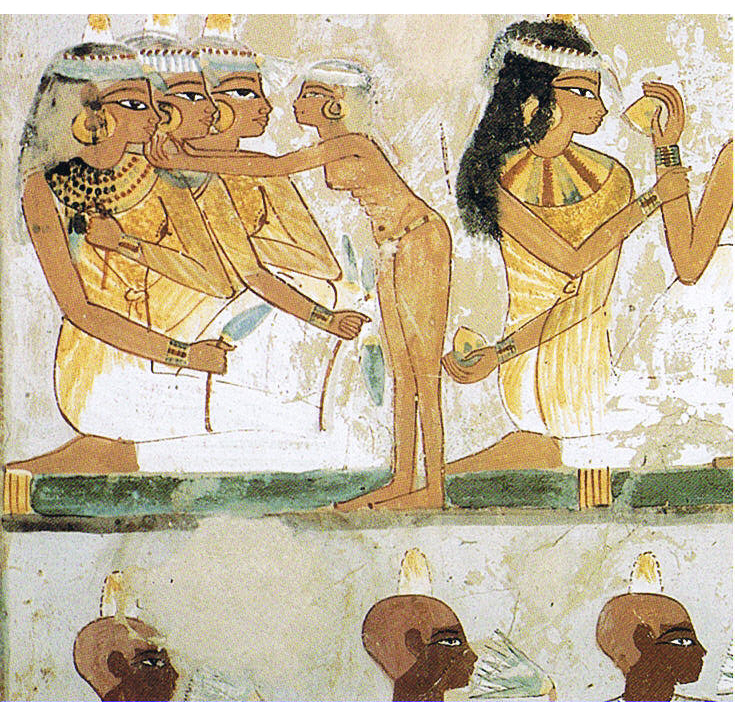 In Ancient Egypt, yellow was associated with gold, which was considered to be eternal and indestructible. The skin and bones of the gods were believed to be made of gold. The Egyptians used yellow ochre extensively in tomb painting, though occasionally they used orpiment, which made a brilliant colour, but was highly toxic, since it was made with arsenic. In tomb paintings, men were always shown with brown faces, women with yellow ochre or gold faces.
Red ochre in Ancient Egypt was used as a rouge, or lip gloss for women. Ochre-coloured lines were also discovered on the Unfinished Obelisk at the northern region of the Aswan Stone Quarry, marking work sites. Ochre clays were also used medicinally in Ancient Egypt: such use is described in the Ebers Papyrus from Egypt, dating to about 1550 BC.
In Ancient Egypt, yellow was associated with gold, which was considered to be eternal and indestructible. The skin and bones of the gods were believed to be made of gold. The Egyptians used yellow ochre extensively in tomb painting, though occasionally they used orpiment, which made a brilliant colour, but was highly toxic, since it was made with arsenic. In tomb paintings, men were always shown with brown faces, women with yellow ochre or gold faces.
Red ochre in Ancient Egypt was used as a rouge, or lip gloss for women. Ochre-coloured lines were also discovered on the Unfinished Obelisk at the northern region of the Aswan Stone Quarry, marking work sites. Ochre clays were also used medicinally in Ancient Egypt: such use is described in the Ebers Papyrus from Egypt, dating to about 1550 BC.
 Ochre pigments are plentiful across Australia, especially the Western Desert,
Ochre pigments are plentiful across Australia, especially the Western Desert,
 Red ochre has been used as a colouring agent in Africa for over 200,000 years. Women of the Himba ethnic group in Namibia use a mix of ochre and animal fat for body decoration, to achieve a reddish skin colour. The ochre mixture is also applied to their hair after braiding. Men and women of the
Red ochre has been used as a colouring agent in Africa for over 200,000 years. Women of the Himba ethnic group in Namibia use a mix of ochre and animal fat for body decoration, to achieve a reddish skin colour. The ochre mixture is also applied to their hair after braiding. Men and women of the
''Pigments through the ages''
for red ochre paint.
Aboriginal Art Online
Use of ochres in traditional Aboriginal art.
National Museum of Australia
Collection of ochre samples.
Yellow ochre
Colourlex
Red ochre
Colourlex
{{Shades of red Iron oxide pigments Shades of brown Iron ores
American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken lan ...
, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colours produced by this pigment, especially a light brownish-yellow. A variant of ochre containing a large amount of hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
, or dehydrated iron oxide, has a reddish tint known as "red ochre" (or, in some dialects, ruddle).
The word ochre also describes clays coloured with iron oxide derived during the extraction of tin and copper.
Earth pigments
Ochre is a family of earth pigments, which includes yellow ochre, red ochre, purple ochre, sienna, and umber. The major ingredient of all the ochres is iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, known aslimonite
Limonite () is an iron ore consisting of a mixture of hydrated iron(III) oxide-hydroxides in varying composition. The generic formula is frequently written as FeO(OH)·H2O, although this is not entirely accurate as the ratio of oxide to hydroxid ...
, which gives them a yellow colour.
hydrate
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was understo ...
d iron hydroxide (limonite) also called gold ochre.
* Red ochre, , takes its reddish colour from the mineral hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
, which is an anhydrous
A substance is anhydrous if it contains no water. Many processes in chemistry can be impeded by the presence of water; therefore, it is important that water-free reagents and techniques are used. In practice, however, it is very difficult to achie ...
iron oxide.
* Purple ochre is identical to red ochre chemically but of a different hue caused by different light diffraction properties associated with a greater average particle size.
* Brown ochre, also FeO(OH), ( goethite), is a partly hydrated iron oxide.
* Sienna contains both limonite and a small amount of manganese oxide (less than 5%), which makes it darker than ochre.
* Umber pigments contain a larger proportion of manganese (5-20%), which makes them a dark brown. p. 30
When natural sienna and umber pigments are heated, they are dehydrated and some of the limonite is transformed into hematite, giving them more reddish colours, called burnt sienna and burnt umber. Ochres are non-toxic and can be used to make an oil paint that dries quickly and covers surfaces thoroughly. Modern ochre pigments often are made using synthetic iron oxide. Pigments which use natural ochre pigments indicate it with the name PY-43 (Pigment yellow 43) on the label, following the Colour Index International system.
mineraloid
A mineraloid is a naturally occurring mineral-like substance that does not demonstrate crystallinity. Mineraloids possess chemical compositions that vary beyond the generally accepted ranges for specific minerals. For example, obsidian is an amor ...
containing iron hydroxide, is the main ingredient of all the ochre pigments.
File:Hematite.jpg, Hematite is a more reddish variety of iron oxide, and is the main ingredient of red ochre. When limonite is roasted, it turns partially to the more reddish hematite and becomes red ochre or burnt sienna.
File:Sentier des ocres 1.JPG, The clay hills of Roussillon, Vaucluse, in Provence have been an important source of ochre pigment since the 18th century.
Historical use in art and culture
Prehistory
Yellow and red ochre pigment was used in prehistoric and ancient times by many different civilizations on different continents. Evidence of the processing of ochre to a lesser extent, in Africa and Europe has been dated by archaeologists to 300,000 years ago, evidence of use in Australia is dated to 50,000 years ago, and new research has uncovered evidence in Asia that is dated to 40,000 years ago. Pieces of ochre engraved with abstract designs have been found at the site of the Blombos Cave in South Africa, dated to around 75,000 years ago. In Wales, thepaleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
burial called the Red Lady of Paviland from its coating of red ochre has been dated to around 33,000 years before present. Paintings of animals made with red and yellow ochre pigments have been found in paleolithic sites at Pech Merle in France (ca. 25,000 years old), and the cave of Altamira in Spain (ca. 16,500–15,000 BC). The cave of Lascaux has an image of a horse coloured with yellow ochre estimated to be 17,300 years old. Neolithic burials may have used red ochre pigments symbolically, either to represent a return to the earth or possibly as a form of ritual rebirth, in which the colour may symbolize blood and a hypothesized Great Goddess Great Goddess is the concept of an almighty goddess or mother goddess, or a matriarchal religion. Apart from various specific figures called this from various cultures, the Great Goddess hypothesis, is a postulated fertility goddess supposed to h ...
.
The Ancient Picts were said to paint themselves "Iron Red" according to the Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
historian Jordanes. Frequent references in Irish myth to "red men" ( Gaelic: Fer Dearg) make it likely that such a practice was common to the Celts of the British Isles, bog iron being particularly abundant in the midlands of Ireland
The Midland Region (coded IE063) is a NUTS Level III statistical region of Ireland. It consists of the territory of the counties of Laois, Offaly, Westmeath and Longford. The Midland Region spans 6,524 km2, 9.5% of the total area of the sta ...
.
Ochre has uses other than as paint: "tribal peoples alive today . . . use either as a way to treat animal skins or else as an insect repellent, to staunch bleeding, or as protection from the sun. Ochre may have been the first medicament."
Ancient Greece and Rome
 Ochre was the most commonly used pigment for painting walls in the ancient Mediterranean world. In Ancient Greece, red ochre was called μίλτος, ''míltos'' (hence
Ochre was the most commonly used pigment for painting walls in the ancient Mediterranean world. In Ancient Greece, red ochre was called μίλτος, ''míltos'' (hence Miltiades
Miltiades (; grc-gre, Μιλτιάδης; c. 550 – 489 BC), also known as Miltiades the Younger, was a Greek Athenian citizen known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon, as well as for his downfall afterwards. He was the son of Cim ...
: "red-haired" or "ruddy"). In ancient Athens
Athens is one of the oldest named cities in the world, having been continuously inhabited for perhaps 5,000 years. Situated in southern Europe, Athens became the leading city of Ancient Greece in the first millennium BC, and its cultural achieve ...
when Assembly was called, a contingent of public slaves would sweep the open space of the Agora
The agora (; grc, ἀγορά, romanized: ', meaning "market" in Modern Greek) was a central public space in ancient Greek city-states. It is the best representation of a city-state's response to accommodate the social and political order of t ...
with ropes dipped in ''miltos'': those citizens that loitered there instead of moving to the Assembly area would risk having their clothes stained with the paint. This prevented them from wearing these clothes in public again, as failure to attend the Assembly incurred a fine.
In England, red ochre was also known as "raddle", "reddle", or "ruddle" and was used to mark sheep and can also be used as a waxy waterproof coating on structures. The reddle was sold as a ready-made mixture to farmers and herders by travelling workers called reddlemen.
In Classical antiquity, the finest red ochre came from a Greek colony on the Black Sea where the modern city of Sinop in Turkey is located. It was carefully regulated, expensive and marked by a special seal, and this colour was called sealed Sinope. Later the Latin and Italian name sinopia was given to wide range of dark red ochre pigments. Roman triumphators painted their faces red, perhaps to imitate the red-painted flesh of statues of the Gods. The Romans used yellow ochre in their paintings to represent gold and skin tones, and as a background colour. It is found frequently in the murals of Pompeii
Pompeii (, ) was an ancient city located in what is now the ''comune'' of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried ...
.
Ancient Egypt
 In Ancient Egypt, yellow was associated with gold, which was considered to be eternal and indestructible. The skin and bones of the gods were believed to be made of gold. The Egyptians used yellow ochre extensively in tomb painting, though occasionally they used orpiment, which made a brilliant colour, but was highly toxic, since it was made with arsenic. In tomb paintings, men were always shown with brown faces, women with yellow ochre or gold faces.
Red ochre in Ancient Egypt was used as a rouge, or lip gloss for women. Ochre-coloured lines were also discovered on the Unfinished Obelisk at the northern region of the Aswan Stone Quarry, marking work sites. Ochre clays were also used medicinally in Ancient Egypt: such use is described in the Ebers Papyrus from Egypt, dating to about 1550 BC.
In Ancient Egypt, yellow was associated with gold, which was considered to be eternal and indestructible. The skin and bones of the gods were believed to be made of gold. The Egyptians used yellow ochre extensively in tomb painting, though occasionally they used orpiment, which made a brilliant colour, but was highly toxic, since it was made with arsenic. In tomb paintings, men were always shown with brown faces, women with yellow ochre or gold faces.
Red ochre in Ancient Egypt was used as a rouge, or lip gloss for women. Ochre-coloured lines were also discovered on the Unfinished Obelisk at the northern region of the Aswan Stone Quarry, marking work sites. Ochre clays were also used medicinally in Ancient Egypt: such use is described in the Ebers Papyrus from Egypt, dating to about 1550 BC.
Australia
Kimberley
Kimberly or Kimberley may refer to:
Places and historical events
Australia
* Kimberley (Western Australia)
** Roman Catholic Diocese of Kimberley
* Kimberley Warm Springs, Tasmania
* Kimberley, Tasmania a small town
* County of Kimberley, a ...
and Arnhem Land
Arnhem Land is a historical region of the Northern Territory of Australia, with the term still in use. It is located in the north-eastern corner of the territory and is around from the territory capital, Darwin. In 1623, Dutch East India Compan ...
regions, and occur in many archaeological sites. The practice of ochre painting has been prevalent among Indigenous Australian people for over 40,000 years. Pleistocene burials with red ochre date as early as 40,000 BP and ochre plays a role in expressing symbolic ideologies of the earliest arrivals to the continent. Ochre has been used for millennia by Aboriginal Australians for body decoration, sun protection, mortuary practices, cave painting, bark painting and other artwork, and the preservation of animal skins, among other uses. At Lake Mungo, in Western New South Wales, burial sites have been excavated and burial materials, including ochre-painted bones, have been dated to the arrival of people in Australia; " Mungo Man" (LM3) was buried sprinkled with red ochre at dates confidently estimated as at least 30,000 years B.P. and possibly as old as 60,000 years old.
The National Museum of Australia has a large collection of samples of ochre from many sites across Australia.
New Zealand
The Māori people of New Zealand were found to be making extensive use of mineral ochre mixed with fish oil. Ochre was the predominant colouring agent used by Maori, and was used to paint their large '' waka taua'' (war canoe). Ochre prevented the drying out of the wood in canoes and the carvings of meeting houses; later missionaries estimated that it would last for 30 years. It was also roughly smeared over the face, especially by women, to keep off insects. Solid chunks of ochre were ground on a flat but rough surfaced rock to produce the powder.Indigenous North America
InNewfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
its use is most often associated with the Beothuk, whose use of red ochre led them to be referred to as "Red Indians" by the first Europeans to Newfoundland. The Beothuk may have also used yellow ochre to colour their hair. It was also used by the Maritime Archaic as evidenced by its discovery in the graves of over 100 individuals during an archaeological excavation at Port au Choix. Its use was widespread at times in the Eastern Woodlands cultural area of Canada and the US; the Red Ocher people
The Red Ocher people were an indigenous people of North America. A series of archaeological sites located in the Upper Great Lakes, the Greater Illinois River Valley, and the Ohio River Valley in the American Midwest have been discovered to be a ...
complex refers to a specific archaeological period in the Woodlands ca. 1000–400 BC. California Native Americans such as the Tongva and Chumash were also known to use red ochre as body paint. Researchers diving into dark submerged caves on Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula have found evidence of an ambitious mining operation starting 12,000 years ago and lasting two millennia for red ochre.
Colonial North America
InNewfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
, red ochre was the pigment of choice for use in vernacular outbuildings and work buildings associated with the cod fishery. Deposits of ochre are found throughout Newfoundland, notably near Fortune Harbour and at Ochre Pit Cove. While earliest settlers may have used locally collected ochre, people were later able to purchase pre-ground ochre through local merchants, largely imported from England.
The dry ingredient, ochre, was mixed with some type of liquid raw material to create a rough paint. The liquid material was usually seal oil or cod liver oil in Newfoundland and Labrador, while Scandinavian recipes sometimes called for linseed oil
Linseed oil, also known as flaxseed oil or flax oil (in its edible form), is a colourless to yellowish oil obtained from the dried, ripened seeds of the flax plant (''Linum usitatissimum''). The oil is obtained by pressing, sometimes followed by ...
. Red ochre paint was sometimes prepared months in advance and allowed to sit, and the smell of ochre paint being prepared is still remembered today.
Variations in local recipes, shades of ore, and type of oil used resulted in regional variations in colour. Because of this, it is difficult to pinpoint an exact shade or hue of red that would be considered the traditional " fishing stage red". In the Bonavista Bay area one man maintained that seal oil mixed with the ochre gave the sails a purer red colour, while cod liver oil would give a "foxy" colour, browner in hue.
Africa
 Red ochre has been used as a colouring agent in Africa for over 200,000 years. Women of the Himba ethnic group in Namibia use a mix of ochre and animal fat for body decoration, to achieve a reddish skin colour. The ochre mixture is also applied to their hair after braiding. Men and women of the
Red ochre has been used as a colouring agent in Africa for over 200,000 years. Women of the Himba ethnic group in Namibia use a mix of ochre and animal fat for body decoration, to achieve a reddish skin colour. The ochre mixture is also applied to their hair after braiding. Men and women of the Maasai people
The Maasai (; sw, Wamasai) are a Nilotic ethnic group inhabiting northern, central and southern Kenya and northern Tanzania. They are among the best-known local populations internationally due to their residence near the many game parks of t ...
in Kenya and Tanzania have also used ochre in the same way.
Renaissance
During the Renaissance, yellow and red ochre pigments were widely used in painting panels and frescoes. The colours vary greatly from region to region, depending upon whether the local clay was richer in yellowish limonite or reddish hematite. The red earth from Pozzuoli near Naples was a salmon pink, while the pigment from Tuscany contained manganese, making it a darker reddish brown called terra di siena, or sienna earth. The 15th-century painter Cennino Cennini described the uses of ochre pigments in his famous treatise on painting. In early modern Malta, red ochre paint was commonly used on public buildings.Modern history
The industrial process for making ochre pigment was developed by the French scientist Jean-Étienne Astier in the 1780s. He was fromRoussillon
Roussillon ( , , ; ca, Rosselló ; oc, Rosselhon ) is a historical province of France that largely corresponded to the County of Roussillon and part of the County of Cerdagne of the former Principality of Catalonia. It is part of the reg ...
in the Vaucluse department of Provence, and he was fascinated by the cliffs of red and yellow clay in the region. He invented a process to make the pigment on a large scale. First the clay was extracted from open pits or mines. The raw clay contained about 10 to 20 percent ochre. Then he washed the clay to separate the grains of sand from the particles of ochre. The remaining mixture was then decanted in large basins, to further separate the ochre from the sand. The water was then drained, and the ochre was dried, cut into bricks, crushed, sifted, and then classified by colour and quality. The best quality was reserved for artists' pigments.
In Britain, ochre was mined at Brixham
Brixham is a coastal town and civil parish, the smallest and southernmost of the three main population centres (the others being Paignton and Torquay) on the coast of Torbay in the county of Devon, in the south-west of England. Commercial fish ...
, England. It became an important product for the British fishing industry, where it was combined with oil and used to coat sails to protect them from seawater, giving them a reddish colour. The ochre was boiled in great caldrons, together with tar, tallow and oak bark, the last ingredient giving the name of barking yards to the places where the hot mixture was painted on to the sails, which were then hung up to dry. In 1894, a theft case provided insights into the use of the pigment as a food adulterant in sausage roll production whereby the accused apprentice was taught to soak brown bread in red ochre, salt, and pepper
Pepper or peppers may refer to:
Food and spice
* Piperaceae or the pepper family, a large family of flowering plant
** Black pepper
* ''Capsicum'' or pepper, a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family Solanaceae
** Bell pepper
** Chili ...
to give the appearance of beef sausage for the filling.
As noted above, the industrial process for making ochre pigment was developed by the French scientist Jean-Étienne Astier in the 1780s, using the ochre mines and quarries in Roussillon
Roussillon ( , , ; ca, Rosselló ; oc, Rosselhon ) is a historical province of France that largely corresponded to the County of Roussillon and part of the County of Cerdagne of the former Principality of Catalonia. It is part of the reg ...
, Rustrel, or Gargas in the Vaucluse department of Provence, in France. Thanks to the process invented by Astier and refined by his successors, ochre pigments from Vaucluse were exported across Europe and around the world. It was not only used for artists paints and house paints; it also became an important ingredient for the early rubber industry.
Ochre from Vaucluse was an important French export until the mid-20th century, when major markets were lost due to the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ...
and the Spanish Civil War. Ochre also began to face growing competition from newly synthetic pigment industry. The quarries in Roussillon, Rustrel, the Mines of Bruoux closed one by one. Today, the last quarry in activity is in Gargas (Vaucluse) and belongs to the Société des Ocres de France.
In heraldry
Ochre, both red and yellow, appear as tinctures inSouth African heraldry
South African heraldry dates back to the 1650s, inheriting European (especially Dutch and British) heraldic traditions. Arms are borne by individuals, official bodies, local authorities, military units, and by a wide variety of organisations. ...
; the national coat of arms, adopted in 2000, includes ''red ochre'', while (yellow) ochre appears in the arms of the University of Transkei.
In Popular Culture
A reddleman named Diggory Venn was prominently described inThomas Hardy
Thomas Hardy (2 June 1840 – 11 January 1928) was an English novelist and poet. A Victorian realist in the tradition of George Eliot, he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by Romanticism, including the poetry of William Word ...
's 1878 novel entitled '' The Return of the Native''.
See also
* Falu red * Female cosmetic coalitions *Iron(III) oxide
Iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Fe2O3. It is one of the three main oxides of iron, the other two being iron(II) oxide (FeO), which is rare; and iron(II,III) oxide (Fe3O4), which also occurs naturally ...
* List of colors
* List of inorganic pigments
* Red Lady of Paviland
* Red pigments
References
Citations
Sources
* Helwig, K. Iron Oxide Pigments, in Artists’ Pigments, Berrie, B.H., Ed., National Gallery of Art Washington, 2007, pp. 38–109. * Isabelle Roelofs and Fabien Petillion, ''La couleur expliquée aux artistes'', Editions Eyrolles, (2012), . * Philip Ball, Histoire vivante des couleurs (2001), Hazan Publishers, Paris, . * Fuller, Carl; "Natural Colored Iron Oxide Pigments", pp. 281–6. In: ''Pigment Handbook'', 2nd Edition. Lewis, P. (ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1988. * Thomas, Anne Wall. ''Colors From the Earth'', New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1980. * Wreschner, Ernst E. (October 1980) "Red Ochre and Human Evolution: A Case for Discussion." ''Current Anthropology'' 21:631–644. (Comments by various authors included.) * Daniel V. Thompson (1956), The Materials and Techniques of Medieval Painting, Dover Publications, New York. . * Lara Broecke, ''Cennino Cennini's ''Il Libro dell'Arte'': a New English Translation and Commentary with Italian Transcription'', Archetype, London, 2015, . * David Bomford and Ashoka Roy (2009), A Closer Look- Colour, The National Gallery, London, .External links
''Pigments through the ages''
for red ochre paint.
Aboriginal Art Online
Use of ochres in traditional Aboriginal art.
National Museum of Australia
Collection of ochre samples.
Yellow ochre
Colourlex
Red ochre
Colourlex
{{Shades of red Iron oxide pigments Shades of brown Iron ores