Rail transport in Estonia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
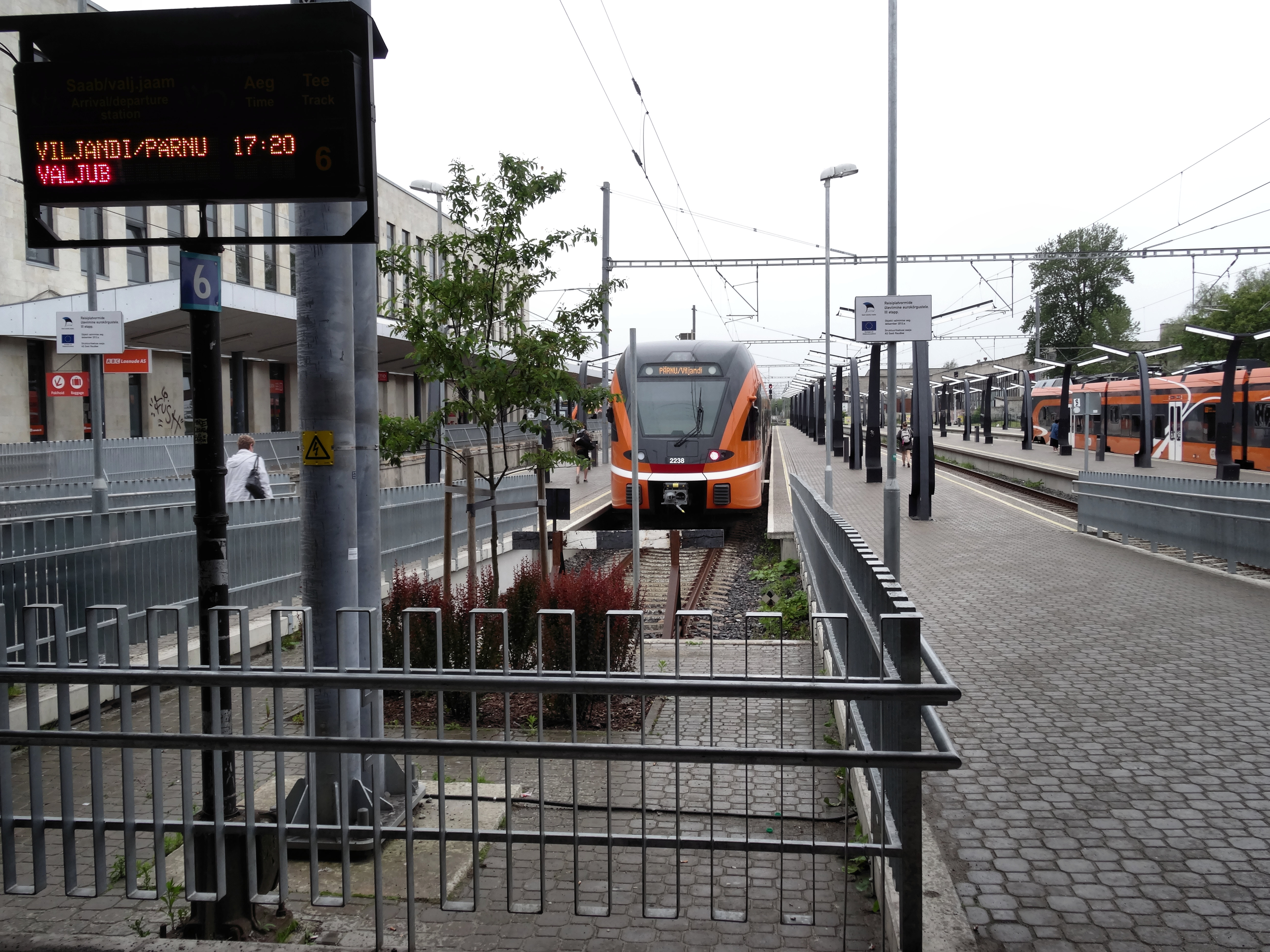

 The rail transport system in Estonia consists of about of
The rail transport system in Estonia consists of about of
 * Total length: circa 1,200 km, of which 900 km in public use
* Gauge:
* Total length: circa 1,200 km, of which 900 km in public use
* Gauge:

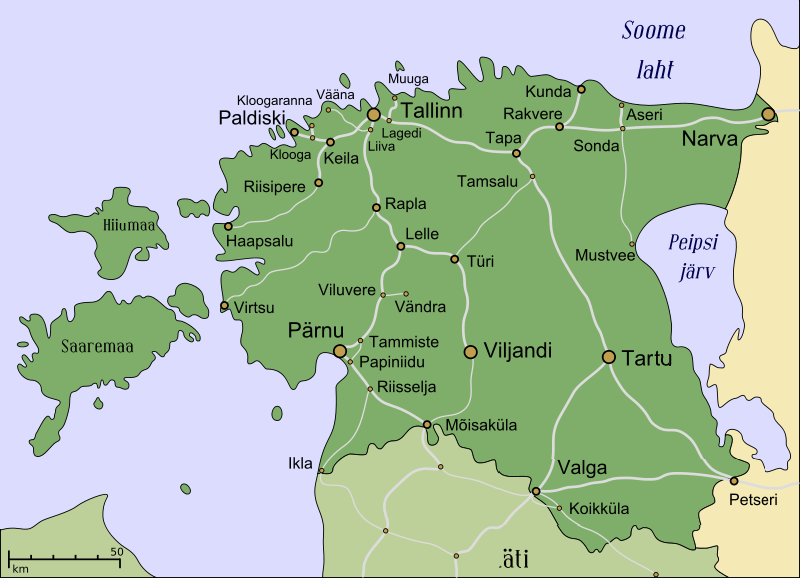

 Owned by AS Eesti Raudtee:
*
Owned by AS Eesti Raudtee:
*
Passenger trains are operated by Elron (Tallinn– Aegviidu, Tallinn–Tartu, Tallinn–
Passenger trains are operated by Elron (Tallinn–Tartu and Tartu–
Passenger trains between
Passenger trains are operated by Elron (Tartu– Koidula route). * Valga–Pechory, . Part of
The line is used only by freight trains. Owned by Edelaraudtee Infrastruktuuri AS: * Tallinn–
The Joint Stock Company Spacecom
''www.spacecom.ee''
Passenger services are offered by three operators:
* Elron, domestic routes
*
Division of railways at Estonian Technical Surveillance Authority
— Web pages containing various statistical information about the railway network and operations in Estonia.
Map of public railways and railway stations
(link broken)
National railway company Eesti Raudtee
Estonian Railway Museum in Haapsalu (history page)
Estonian private Railway Company "GoRail" official website
{{Rail transport in Europe
railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
lines, of which are currently in public use. The infrastructure of the railway network is mostly owned by the state and is regulated and surveyed by the Estonian Technical Surveillance Authority ( et, Tehnilise Järelevalve Amet).
All public railways in Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
are (Russian gauge
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
), the same as in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, and Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
. The gauge
Gauge ( or ) may refer to:
Measurement
* Gauge (instrument), any of a variety of measuring instruments
* Gauge (firearms)
* Wire gauge, a measure of the size of a wire
** American wire gauge, a common measure of nonferrous wire diameter, ...
used in Estonia is also compatible with Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
's gauge. Sometimes it is defined to be (see Rail gauge in Estonia), for example when buying track maintenance or vehicles from Finland.
Railways in Estonia today are used mostly for freight transport, but also for passenger traffic, with 8.3 million passengers reported in 2019. Passenger transport is most frequent near Tallinn, centred on the main Tallinn Baltic Station
Baltic Station ( et, Balti jaam) is the main railway station in Tallinn, Estonia. All local commuter, long-distance and international trains depart from the station.
The station has seven platforms, of which two are situated apart from the res ...
.
The Tallinn to Tartu railway is due to be electrified by 2024, with electrification of the remaining network expected to be completed by 2028. 16 new electric trains manufactured by Škoda Transportation
Škoda Transportation a.s. is a Czech engineering company that continues the legacy of Škoda Works' rolling stock manufacturing that started at the end of 19th century in Plzeň. Following the first world war, the Works commenced locomotive p ...
are due to come into service starting 2024.
History
Network
 * Total length: circa 1,200 km, of which 900 km in public use
* Gauge:
* Total length: circa 1,200 km, of which 900 km in public use
* Gauge: Russian gauge
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
* Electrified: .
The Estonian railway network is owned by the state-owned company AS Eesti Raudtee and the private company Edelaraudtee
Edelaraudtee (''Southwestern railway'') is an Estonian railway operator founded in 1997. AS Edelaraudtee operates freight services on lines from Tallinn to Rapla, Pärnu & Viljandi owned by Edelaraudtee Infrastruktuuri AS.
Until 2014, the com ...
Infrastruktuuri AS. These railway network infrastructure operators provide all railway network services for railway operators running freight and passenger services. AS Eesti Raudtee provides approximately of track, of which is double track
A double-track railway usually involves running one track in each direction, compared to a single-track railway where trains in both directions share the same track.
Overview
In the earliest days of railways in the United Kingdom, most lin ...
and is electrified
Electrification is the process of powering by electricity and, in many contexts, the introduction of such power by changing over from an earlier power source.
The broad meaning of the term, such as in the history of technology, economic history ...
. Edelaraudtee Infrastruktuuri AS maintains of track which consists of of main line and of station line.
Main lines

Tallinn–Narva railway
The Tallinn–Narva railway is located in Northern Estonia, Estonia and is the oldest railway (built in 1870) in Estonia with a total length of 211 km. A significant part of the railway load consists of freight trains (such as oil trains) f ...
, . This line was completed in 1870. It was originally a part of the railway network of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, connecting Paldiski
Paldiski is a town and Baltic Sea port situated on the Pakri Peninsula of northwestern Estonia. Since 2017, it's the administrative centre of Lääne-Harju Parish of Harju County. Previously a village of Estonia-Swedes known by the historical ...
to St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
via Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju ' ...
and Narva
Narva, russian: Нарва is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in Ida-Viru County, Ida-Viru county, at the Extreme points of Estonia, eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva (river), Narva river which ...
. Passenger trains are operated by Elron (Tallinn– Aegviidu, Tallinn–Tartu, Tallinn–
Rakvere
Rakvere is a town in northern Estonia and the administrative centre of the Lääne-Viru ''maakond'' (county), 20 km south of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea. Rakvere is the 8th most populous urban area in Estonia. Rakvere has a tota ...
and Tallinn–Narva routes) and by GO Rail
GoRail is a rail freight operator in Estonia, and also offers related training services. Until commencing offering freight services in 2019 it was a passenger service operator, and until 2020 it operated the only direct international passenge ...
(international trains to Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
and St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, Russia).
* Tallinn–Keila
Keila (german: Kegel) is a town and an urban municipality in Harju County in north-western Estonia, 25 km southwest of Tallinn. Keila is also the location of administrative buildings of the surrounding Keila Parish, a rural municipality se ...
–Paldiski
Paldiski is a town and Baltic Sea port situated on the Pakri Peninsula of northwestern Estonia. Since 2017, it's the administrative centre of Lääne-Harju Parish of Harju County. Previously a village of Estonia-Swedes known by the historical ...
, . Passenger trains are operated by Elron (Tallinn–Pääsküla
Pääsküla (Estonian for ''"Passage Village"'') is a subdistrict ( et, asum) in the district of Nõmme, Tallinn, the capital of Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It i ...
, Tallinn–Keila, Tallinn–Paldiski and Tallinn–Klooga-rand
Kloogaranna is a village in Lääne-Harju Parish, Harju County, Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finl ...
routes).
* Keila–Turba, Estonia
Turba is a small borough ( et, alevik) in Saue Parish, Harju County, Estonia. Prior to the administrative reform of Estonian local governments in March 2017, Turba belonged to Nissi Parish
Nissi Parish ( et, Nissi vald) was a rural municipalit ...
, . This line is part of the former Keila–Haapsalu
Haapsalu () is a seaside resort town located on the west coast of Estonia. It is the administrative centre of Lääne County, and on 1 January 2020 it had a population of 9,375.
Description
Haapsalu has been well known for centuries for its w ...
line, that was completed in 1905. The Riisipere–Haapsalu section was abandoned in 2004, but rebuilt as far as Turba during 2019, as a first step towards eventually re-opening the line to Haapsalu
Haapsalu () is a seaside resort town located on the west coast of Estonia. It is the administrative centre of Lääne County, and on 1 January 2020 it had a population of 9,375.
Description
Haapsalu has been well known for centuries for its w ...
(and possibly the port at Rohuküla ). Passenger trains are operated by Elron (Tallinn–Riisipere route).
* Tapa
Tapa, TAPA, Tapas or Tapasya may refer to:
Media
*Tapas (website), a webtoon site, formerly known as Tapastic
* ''Tapas'' (film), a 2005 Spanish film
* ''Tapasya'' (1976 film), an Indian Hindi-language film
* ''Tapasya'' (1992 film), a Nepalese f ...
–Tartu
Tartu is the second largest city in Estonia after the Northern European country's political and financial capital, Tallinn. Tartu has a population of 91,407 (as of 2021). It is southeast of Tallinn and 245 kilometres (152 miles) northeast of ...
, . Completed in 1877.Passenger trains are operated by Elron (Tallinn–Tartu and Tartu–
Jõgeva
Jõgeva (german: Laisholm) is a small town in Estonia with a population of around 5000 people. It is the capital of Jõgeva Parish and Jõgeva County.
History
Jõgeva was first mentioned in 1599 as ''Jagiwa'' manor, being established only rec ...
routes).
* Tartu– Valga, 82.5 km. Completed in 1887. International connection from Valga in Estonia to Valka
Valka (; german: Walk) is a town and municipality in northern Latvia, on the border with Estonia along both banks of the river Pedele.
Valka and the Estonian town Valga are twins, separated by the Estonian/Latvian border but using the slogan "O ...
in Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
. Passenger trains between
Tartu
Tartu is the second largest city in Estonia after the Northern European country's political and financial capital, Tallinn. Tartu has a population of 91,407 (as of 2021). It is southeast of Tallinn and 245 kilometres (152 miles) northeast of ...
and Valga are operated by Elron. Passenger trains between Valga and Riga
Riga (; lv, Rīga , liv, Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city of Latvia and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Ba ...
are operated by Latvian Railways
JSC Latvian Railway ( lv, Latvijas dzelzceļš or LDz) was established on 2 September 1991 and is seen as the successor of the Latvian Railway Board (Latvian Railways) which was established on 5 August 1919.
Latvijas dzelzceļš is a state-owned ...
.
* Tartu–Pechory
Pechory (russian: Печо́ры; Estonian and Seto: ') is a town and the administrative centre of Pechorsky District in the Pskov Oblast, Russia. Its population in the 2010 Census was 11,195, having fallen from 13,056 recorded in ...
, . Built between 1929 and 1931. International connection from Koidula railway station
Koidula railway station ( et, Koidula raudteejaam) is a railway station in Koidula, Estonia, on the Russian border. It merges the Tartu–Pechory and Valga–Pechory railways just before the Russian border (Pechory is located straight after the ...
( Koidula) in Estonia to Pechory in Russia.Passenger trains are operated by Elron (Tartu– Koidula route). * Valga–Pechory, . Part of
Riga
Riga (; lv, Rīga , liv, Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city of Latvia and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Ba ...
–Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=pskov-ru.ogg, p=pskof; see also names in other languages) is a city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, located about east of the Estonian border, on the Velikaya River. Population ...
railway, opened to regular traffic in 1889. International connection from Koidula railway station
Koidula railway station ( et, Koidula raudteejaam) is a railway station in Koidula, Estonia, on the Russian border. It merges the Tartu–Pechory and Valga–Pechory railways just before the Russian border (Pechory is located straight after the ...
in Estonia to Pechory in Russia. The line is used only by freight trains. Owned by Edelaraudtee Infrastruktuuri AS: * Tallinn–
Lelle
Lelle is a small borough (') in Kehtna Parish, Rapla County, in central Estonia. It has a station on the Tallinn - Viljandi railway line operated by Elron, and until December 2018 was the junction with the former branch to Pärnu. As of 2011 C ...
–(Pärnu
Pärnu () is the fourth largest city in Estonia. Situated in southwest Estonia, Pärnu is located south of the Estonian capital, Tallinn, and west of Estonia's second largest city, Tartu. The city sits off the coast of Pärnu Bay, an inlet o ...
)–(Mõisaküla
Mõisaküla ( lv, Muižciems; Meizakila) is a town in southern Estonia, part of Mulgi Parish of Viljandi County, just next to the border of Latvia. It is considered to be the smallest town in Estonia.
The town has 32 streets, with the total le ...
), (formerly 190.0 km). There was an international connection from Mõisaküla to Latvia, but the stretch Pärnu–Mõisaküla was abandoned in 2008. The Lelle-Pärnu section was permanently closed for passenger operations on 9 December 2018 as it required a €17 million refurbishment. A rail service to Pärnu station will be resumed with the opening of the Rail Baltica
Rail Baltica (also known as Rail Baltic in Estonia) is a high-speed railway under construction between Warsaw, Poland and Tallinn, Estonia, with further connections to Finland via Baltic Sea cruiseferries or the proposed Helsinki–Tallinn Tunn ...
line.
* Lelle–Viljandi
Viljandi (, german: Fellin, sv, Fellin) is a town and municipality in southern Estonia with a population of 17,407 in 2019. It is the capital of Viljandi County and is geographically located between two major Estonian cities, Pärnu and Tartu ...
, . This line connects Viljandi to the Tallinn–Pärnu line via Lelle.
Major industrial railways
* Põlevkivi Raudtee (''oil shale railway'') maintains over of track inIda-Virumaa
Ida-Viru County ( et, Ida-Viru maakond or ''Ida-Virumaa'') is one of 15 counties of Estonia. It is the most north-eastern part of the country. The county contains large deposits of oil shale - the main mineral mined in Estonia. Oil shale is used ...
. Main use of the network is transporting oil shale
Oil shale is an organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rock containing kerogen (a solid mixture of organic chemical compounds) from which liquid hydrocarbons can be produced. In addition to kerogen, general composition of oil shales constitute ...
from underground and open-cast mines to the Narva Power Plants
The Narva Power Plants ( et, Narva Elektrijaamad) are a power generation complex in and near Narva in Estonia, near the border with Leningrad Oblast, Russia. The complex consists of the world's two largest oil shale-fired thermal power plants, ...
. The company is a subsidiary of Eesti Põlevkivi, which itself is a subsidiary of Eesti Energia
Eesti Energia AS is a public limited energy company in Estonia with its headquarters in Tallinn. It is the world's biggest oil shale to energy company. The company was founded in 1939. As of 2014, it operates in Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Fi ...
, owned by the state.
* Rakvere
Rakvere is a town in northern Estonia and the administrative centre of the Lääne-Viru ''maakond'' (county), 20 km south of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea. Rakvere is the 8th most populous urban area in Estonia. Rakvere has a tota ...
– Kunda, . Built in 1896, this line connects the industrial town of Kunda to the Tallinn–Tapa–Narva line. The line is owned by private company Kunda Trans.
Connections to adjacent countries
Daily passenger service connectTallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju ' ...
with Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
(night train; travel time is 15 hours) through Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, operated by the Russian Railways.
As of summer 2016 three daily trains operated by Latvian Railways
JSC Latvian Railway ( lv, Latvijas dzelzceļš or LDz) was established on 2 September 1991 and is seen as the successor of the Latvian Railway Board (Latvian Railways) which was established on 5 August 1919.
Latvijas dzelzceļš is a state-owned ...
connect Riga
Riga (; lv, Rīga , liv, Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city of Latvia and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Ba ...
(Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
) to Valga (Estonia). The other railway lines to neighbouring countries are not used for direct passenger traffic at the moment. It is possible to travel between Tallinn and Riga with train change at Valga, and the timetables of Tallinn–Valga and Valga–Riga are adjusted for that purpose, but this still takes a long time compared to bus (travel time about 5 hours) or air.
Historic train routes are Tallinn–Moscow via Tartu–Pechory, and Riga–St. Petersburg, which passed through Estonia from Valka, Latvia to Valga, Estonia–Võru
Võru (; vro, Võro; german: Werro) is a town and a municipality in south-eastern Estonia. It is the capital of Võru County and the centre of Võru Parish.
History
Võru was founded on 21 August 1784, according to the wish of the Empress Cather ...
–Piusa
Piusa is a village in Võru Parish, Võru County, in southeastern Estonia. It is located on the left bank of the river Piusa, near the border of Russia.
Piusa is famous for its sand caves along the river.
Sand quarries for glass production ar ...
–Pechory, Russia. Both were closed in the 1990s.
There are plans for a new high-speed line Tallinn–Riga (continuing to Poland), Rail Baltica
Rail Baltica (also known as Rail Baltic in Estonia) is a high-speed railway under construction between Warsaw, Poland and Tallinn, Estonia, with further connections to Finland via Baltic Sea cruiseferries or the proposed Helsinki–Tallinn Tunn ...
, planned to be in operation around 2025.
Railway links with adjacent countries
* Same gauge: **Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
– yes
*** at Valga – diesel trains only
** Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
– yes
*** at Narva
Narva, russian: Нарва is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in Ida-Viru County, Ida-Viru county, at the Extreme points of Estonia, eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva (river), Narva river which ...
– diesel trains only
*** at Koidula – diesel trains only
Operators
Freight trains are operated byEesti Raudtee
Eesti Raudtee or EVR is the national railway infrastructure company of Estonia. It owns a network of of broad gauge () railway throughout the country, including the used by the Elron commuter trains around Tallinn. Its sole shareholder is th ...
and private companies including Estonian Railway Services (E.R.S. AS), and Spacecom.''www.spacecom.ee''
Russian Railways
Russian Railways (russian: link=no, ОАО «Российские железные дороги» (ОАО «РЖД»), OAO Rossiyskie zheleznye dorogi (OAO RZhD)) is a Russian fully state-owned vertically integrated railway company, both manag ...
, Tallinn–Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
and Tallinn–Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
* Pasažieru vilciens
Pasažieru vilciens ("Passenger train", abbreviated: PV) is the only passenger-carrying railway company in Latvia, operating both electric locomotive, electric and diesel trains on various lines throughout the country. It was formed in November 20 ...
, Valga–Riga
Riga (; lv, Rīga , liv, Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city of Latvia and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Ba ...
See also
*Narrow gauge railways in Estonia
All Estonian narrow-gauge railways were built at the gauge of .
The TU2 pages Four museum lines and some industrial peat rai ...
* The TU2 pages Four museum lines and some industrial peat rai ...
Rail Baltica
Rail Baltica (also known as Rail Baltic in Estonia) is a high-speed railway under construction between Warsaw, Poland and Tallinn, Estonia, with further connections to Finland via Baltic Sea cruiseferries or the proposed Helsinki–Tallinn Tunn ...
* Rail transport by country
This page provides an index of articles on rail transport by country.
International railway organisations
* International Union of Railways (UIC)
* International Union of Public Transport (UITP)
* Association of American Railways (AAR)
Afri ...
* Transport in Estonia
Transport in Estonia relies mainly on road and rail networks.
Roads
*Total: 57,565 km (including 16,465 km of national roads)
*Paved: 12,926 km (including 99 km of limited-access roads)
National roads
National roads for ...
References
External links
Division of railways at Estonian Technical Surveillance Authority
— Web pages containing various statistical information about the railway network and operations in Estonia.
Map of public railways and railway stations
(link broken)
National railway company Eesti Raudtee
Estonian Railway Museum in Haapsalu (history page)
Estonian private Railway Company "GoRail" official website
{{Rail transport in Europe