Quadratus Femoris Muscle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The quadratus femoris is a flat, quadrilateral
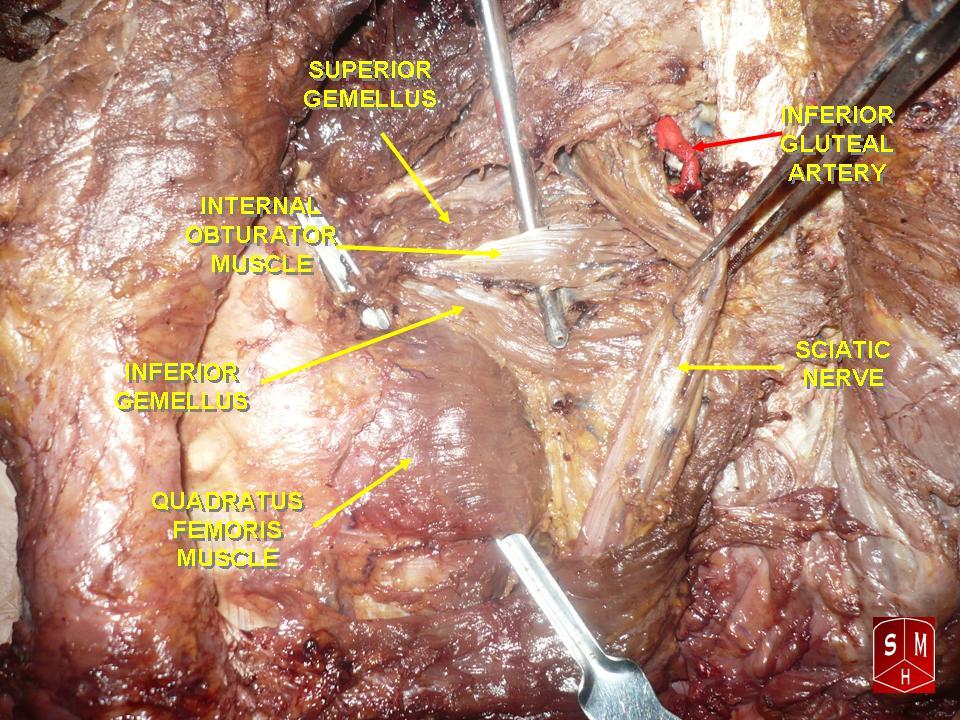
File:Gray245.png, Right femur. Posterior surface.
File:Gray344.png, Structures surrounding right hip-joint.
File:Gray832.png, Nerves of the right lower extremity Posterior view.
File:Slide6hh.JPG, Quadratus femoris muscle
File:Slide1BIBI.JPG, Muscles of Thigh. Anterior views.
PTCentral
* {{Authority control Hip muscles Hip lateral rotators Deep lateral rotators of the hip Muscles of the lower limb
skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
. Located on the posterior side of the hip joint, it is a strong external rotator
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative ...
and adductor of the thigh, but also acts to stabilize the femoral head in the acetabulum
The acetabulum (), also called the cotyloid cavity, is a concave surface of the pelvis. The head of the femur meets with the pelvis at the acetabulum, forming the hip joint.
Structure
There are three bones of the ''os coxae'' (hip bone) that c ...
. Quadratus femoris use in the Meyer's muscle pedicle grafting to prevent avascular necrosis of femur head.
Course
It originates on the lateral border of theischial tuberosity
The ischial tuberosity (or tuberosity of the ischium, tuber ischiadicum), also known colloquially as the sit bones or sitz bones, or as a pair the sitting bones, is a large swelling posteriorly on the superior ramus of the ischium. It marks th ...
of the ischium
The ischium () form ...
of the pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
. From there, it passes laterally to its insertion on the posterior side of the head of the femur: the quadrate tubercle
The quadrate tubercle is a small tubercle found upon the upper part of the femur. It serves as a point of insertion of the quadratus femoris muscle, along with the intertrochanteric crest and the linea quadrata.
Structure
The quadrate tubercle ...
on the intertrochanteric crest and along the quadrate line
A slight ridge is sometimes seen commencing about the middle of the intertrochanteric crest, and reaching vertically downward for about 5 cm. along the back part of the body: it is called the linea quadrata (or quadrate line), and gives attach ...
, the vertical line which runs downward to bisect the lesser trochanter on the medial side of the femur. Along its course, quadratus is aligned edge to edge with the inferior gemellus
The gemelli muscles are the inferior gemellus muscle
and the superior gemellus muscle, two small accessory fasciculi to the tendon of the internal obturator muscle. The gemelli muscles belong to the lateral rotator group of six muscles of the hip ...
above and the adductor magnus below, so that its upper and lower borders run horizontal and parallel.
At its origin, the upper margin of the adductor magnus is separated from it by the terminal branches of the medial femoral circumflex
The medial circumflex femoral artery (internal circumflex artery, medial femoral circumflex artery) is an artery in the upper thigh that arises from the profunda femoris artery''.''
Damage to the artery following a femoral neck fracture may lead ...
vessels.
A bursa
( grc-gre, Προῦσα, Proûsa, Latin: Prusa, ota, بورسه, Arabic:بورصة) is a city in northwestern Turkey and the administrative center of Bursa Province. The fourth-most populous city in Turkey and second-most populous in the ...
is often found between the front of this muscle and the lesser trochanter. Sometimes absent.
Clinical significance
Groin pain can be a disabling ailment with many potential root causes: one such cause, often overlooked, is quadratus femoris tendinitis.Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
can show abnormal signal intensity at the insertion of the right quadratus femoris tendon, which suggests inflammation of the area. Since the muscle works to laterally rotate and adduct the femur, actions involving the lower body can strain the muscle. In addition, patients present with hip pain and an increased signal intensity of the MRI of the quadratus femoris have been shown to also have a significantly narrower ischiofemoral space compared to the general populace. The ischiofemoral impingement may be a cause of the hip pain associated with quadratus femoris tendinitis. 
Additional images
Notes
References
* * (ISBN for the Americas 1-58890-159-9.) *External links
PTCentral
* {{Authority control Hip muscles Hip lateral rotators Deep lateral rotators of the hip Muscles of the lower limb