Qianosuchus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Qianosuchus'' is an
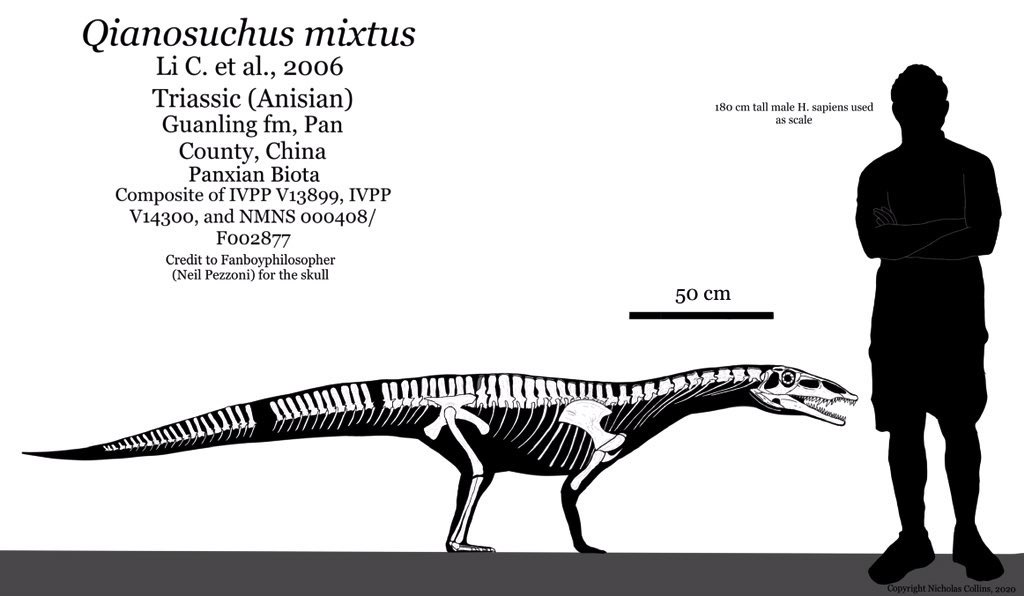 ''Qianosuchus'' had a skull around 33 cm (13 inches) long, with an elongated snout. The
''Qianosuchus'' had a skull around 33 cm (13 inches) long, with an elongated snout. The
 ''Qianosuchus'' was well adapted to a semi-marine lifestyle, with a laterally compressed tail and tall neural spines providing a greater surface area, indicating an animal reliant on its undulating tail for propulsion. Its tail is actually more expanded than those of several other marine reptiles such as ''
''Qianosuchus'' was well adapted to a semi-marine lifestyle, with a laterally compressed tail and tall neural spines providing a greater surface area, indicating an animal reliant on its undulating tail for propulsion. Its tail is actually more expanded than those of several other marine reptiles such as ''
Hmnh.org: Triassic archosaur Qianosuchus was an ancient mariner
{{Taxonbar, from=Q593059 Poposauroids Triassic archosaurs Middle Triassic reptiles of Asia Anisian life Fossil taxa described in 2006 Anisian genus first appearances Guanling Formation Prehistoric pseudosuchian genera
extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of aquatic poposauroid
Poposauroidea is a clade of advanced pseudosuchians (archosaurs closer to crocodilians than to dinosaurs). It includes poposaurids, shuvosaurids, ctenosauriscids, and other unusual pseudosuchians such as ''Qianosuchus'' and ''Lotosaurus''. How ...
archosaur
Archosauria () is a clade of diapsids, with birds and crocodilians as the only living representatives. Archosaurs are broadly classified as reptiles, in the cladistic sense of the term which includes birds. Extinct archosaurs include non-avian d ...
from the middle Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period ...
(Anisian
In the geologic timescale, the Anisian is the lower stage or earliest age of the Middle Triassic series or epoch and lasted from million years ago until million years ago. The Anisian Age succeeds the Olenekian Age (part of the Lower Triassic Ep ...
) Guanling Formation
The Guanling Formation is a Middle Triassic (Anisian or Pelsonian in the regional chronostratigraphy) geologic formation in southwestern China.
Description
The formation encompasses two members. The first member is primarily calcareous muds ...
of Pan County
Panzhou () is a county-level city in southwestern Guizhou province, China, on the border with Yunnan province to the west. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Liupanshui.
Administrative divisions
As of 2017, Panzhou is ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. It is represented by two nearly complete skeletons and a crushed skull preserved in the limestone. ''Qianosuchus'' was at least 3 metres long, and had several skeletal adaptations which indicate a semi-marine lifestyle, similar to modern-day saltwater crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats and brackish wetlands from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaic region to northern Australia and Micronesia. It has been listed ...
s. These adaptations have not been seen in any other archosaur from the Triassic.
Description
 ''Qianosuchus'' had a skull around 33 cm (13 inches) long, with an elongated snout. The
''Qianosuchus'' had a skull around 33 cm (13 inches) long, with an elongated snout. The rostrum
Rostrum may refer to:
* Any kind of a platform for a speaker:
**dais
**pulpit
* Rostrum (anatomy), a beak, or anatomical structure resembling a beak, as in the mouthparts of many sucking insects
* Rostrum (ship), a form of bow on naval ships
* Ros ...
formed by the premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has b ...
is shallow at the front of the skull but deepens posteriorly. Each premaxilla has nine long teeth, and the maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
e bear eighteen teeth each. All the teeth are laterally compressed, curved backwards and serrated, like those of most other carnivorous archosaurs. The nares are expanded and elongated and almost collide with the antorbital fenestra
An antorbital fenestra (plural: fenestrae) is an opening in the skull that is in front of the eye sockets. This skull character is largely associated with archosauriforms, first appearing during the Triassic Period. Among extant archosaurs, bird ...
e, meaning that the septum (bony wall) between them is thin and lightweight. Unusually, the jugal
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species.
Anatomy ...
forms no part of the border of the antorbital fenestra. Each orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a p ...
had a large and well-developed sclerotic ring
Sclerotic rings are rings of bone found in the eyes of many animals in several groups of vertebrates, except for mammals and crocodilians. They can be made up of single bones or multiple segments and take their name from the sclera. They are bel ...
in it, which would have reinforced the eyeball under pressure when ''Qianosuchus'' was diving. The frontal bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, par ...
s have deep fossae (depressions) on their upper surface, which stretch backwards to the sutures with the parietals. Another such fossa is present between the two parietals themselves. The dentary
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movabl ...
turns down very slightly at the tip; a precise tooth count is unknown due to the bone being hidden by the maxillary teeth in the fossils. The hyoid bones are long and slender, with slightly expanded ends.
''Qianosuchus'' had nine cervical
In anatomy, cervical is an adjective that has two meanings:
# of or pertaining to any neck.
# of or pertaining to the female cervix: i.e., the ''neck'' of the uterus.
*Commonly used medical phrases involving the neck are
**cervical collar
**cerv ...
, fifteen dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
* Dorsal c ...
, two sacral
Sacral may refer to:
*Sacred
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. The property ...
and at least 50 caudal vertebrae
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic ...
. The posterior end of the tail is missing in both skeletons. The neural spines
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic ...
grow taller posteriorly (further down the tail), making the caudal vertebrae tall but thin in that area. The first 23 caudal vertebrae have transverse processes
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic i ...
, but these processes are lost further back. The vertebral centra grow shorter posteriorly, making the tail more flexible than the neck. Some of the more anterior caudal vertebrae have chevron bones ventral to them which also increase the height of the tail. All presacral vertebrae have small osteoderm
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amp ...
s at the top of their neural spines. The cervical rib
A cervical rib in humans is an extra rib which arises from the seventh cervical vertebra. Their presence is a congenital abnormality located above the normal first rib. A cervical rib is estimated to occur in 0.2% to 0.5% (1 in 200 to 500) of th ...
s are elongate, at least four times the length of their corresponding centra, and may have had strong muscles attached enabling it to create suction in its throat while lunging forward at prey by expanding the oesophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the ...
. The dorsal ribs are expanded and pachyostotic
Pachyostosis is a non-pathological condition in vertebrate animals in which the bones experience a thickening, generally caused by extra layers of lamellar bone. It often occurs together with bone densification (osteosclerosis), reducing inner ca ...
at their distal ends.
''Qianosuchus scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eithe ...
e were thin and short, but had an extremely broad dorsal blade. Its coracoid bones were oval-shaped and quite thin, while its clavicle
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the rig ...
s articulated almost at right angles with the interclavicle
An interclavicle is a bone which, in most tetrapods, is located between the clavicles. Therian mammals ( marsupials and placentals) are the only tetrapods which never have an interclavicle, although some members of other groups also lack one. In th ...
to form an L-shaped outline from the side. The humeri
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a round ...
were slender and lightly built, and almost totally straight. Neither partial skeleton has preserved the forelimbs below the elbows.
The pelvic girdle
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The p ...
is similar to that of closely related but more terrestrial archosaurs, with the large posterior process and small anterior process on the ilium. The pubis had a deep foramen close to the proximal end, while the distal end of the thinner and shorter ischium
The ischium () form ...
was slightly expanded. The femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with ...
was weakly sigmoid, and the fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is ...
and tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
were almost exactly the same length. The calcaneum
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel) or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.
...
had a hemicylindrical condyle and a broad calcaneal tuber, while the astragalus
''Astragalus'' is a large genus of over 3,000 species of herbs and small shrubs, belonging to the legume family Fabaceae and the subfamily Faboideae. It is the largest genus of plants in terms of described species. The genus is native to tempe ...
had a convex facet for the tibia. Five metatarsals
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medi ...
and two tarsals are known, with the fifth metatarsal slightly hooked.
Paleobiology
 ''Qianosuchus'' was well adapted to a semi-marine lifestyle, with a laterally compressed tail and tall neural spines providing a greater surface area, indicating an animal reliant on its undulating tail for propulsion. Its tail is actually more expanded than those of several other marine reptiles such as ''
''Qianosuchus'' was well adapted to a semi-marine lifestyle, with a laterally compressed tail and tall neural spines providing a greater surface area, indicating an animal reliant on its undulating tail for propulsion. Its tail is actually more expanded than those of several other marine reptiles such as ''Hupehsuchus
''Hupehsuchus'' is an extinct genus of small marine reptiles, about 1 m (3 ft) long, found in the area of Hubei in China. This marine reptile lived in the Olenekian stage of the Early Triassic period.
Description
''Hupehsuchus'' w ...
'' and the modern marine iguana
The marine iguana (''Amblyrhynchus cristatus''), also known as the sea iguana, saltwater iguana, or Galápagos marine iguana, is a species of iguana found only on the Galápagos Islands (Ecuador). Unique among modern lizards, it is a marine repti ...
, so ''Qianosuchus'' was almost certainly a competent swimmer. The thin scapulae and coracoids are also seen in many marine reptiles such as ichthyosaur
Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia ('fish flippers' – a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1842, altho ...
s and mosasaurs
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Greek ' meaning 'lizard') comprise a group of extinct, large marine reptiles from the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on th ...
, while the long neck and reduced dermal armour are seen in marine reptiles such as ''Tanystropheus
''Tanystropheus'' (Greek ~ 'long' + 'hinged') is an extinct archosauromorph reptile from the Middle and Late Triassic epochs. It is recognisable by its extremely elongated neck, which measured long—longer than its body and tail combined. T ...
.'' However, its pelvic girdle and large, relatively unspecialized legs would have allowed ''Qianosuchus'' to walk around on land as well, and may well have had an erect or semi-erect posture, based on the ankle joint. All this suggests that ''Qianosuchus'' lived a semi-aquatic lifestyle in and around the shallow seas where it lived, hunting either on water or on land.
References
External links
Hmnh.org: Triassic archosaur Qianosuchus was an ancient mariner
{{Taxonbar, from=Q593059 Poposauroids Triassic archosaurs Middle Triassic reptiles of Asia Anisian life Fossil taxa described in 2006 Anisian genus first appearances Guanling Formation Prehistoric pseudosuchian genera