Pulli settlement on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
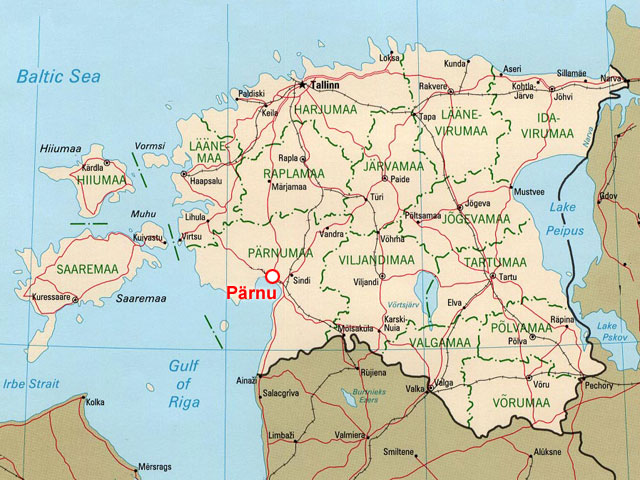
 Pulli settlement, located on the right bank of the
Pulli settlement, located on the right bank of the  The Pulli settlement was discovered in 1967 during excavation of sand from the right bank of the Pärnu river. Archaeological excavations were carried out in 1968-73 and 1975-76 by the Estonian archaeologist L. Jaanits.
Three reliable
The Pulli settlement was discovered in 1967 during excavation of sand from the right bank of the Pärnu river. Archaeological excavations were carried out in 1968-73 and 1975-76 by the Estonian archaeologist L. Jaanits.
Three reliable
 Early
Early
Story of Pulli settlement discovery
(in Estonian)
Early Holocene coastal settlements and palaeoenvironment on the shore of the Baltic Sea at Pärnu, southwestern Estonia
- PDF
(archive.org) * ttps://web.archive.org/web/20071111130356/http://www.pernau.ee/lkd/esemed/pulli.php Pärnu museum, Pulli settlement(in Estonian, archive.org) {{Coord, 58.4192, N, 24.6756, E, source:wikidata, display=title Archaeological sites in Estonia Gulf of Riga Tori Parish Populated coastal places in Estonia Populated places established in the 9th millennium BC 9th-millennium BC establishments Archaeology of Estonia Prehistory of Europe

 Pulli settlement, located on the right bank of the
Pulli settlement, located on the right bank of the Pärnu River
Pärnu () is the fourth largest city in Estonia. Situated in southwest Estonia, Pärnu is located south of the Estonian capital, Tallinn, and west of Estonia's second largest city, Tartu. The city sits off the coast of Pärnu Bay, an inlet o ...
, is the oldest known human settlement in Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
. It is two kilometers from the town of Sindi Sindi may refer to:
*Sindi people, an ancient people of the Taman Peninsula, nowadays Russia
*Sindi, Estonia, a town in Pärnu County, Estonia
*Sindi, Maharashtra, a town and municipal council in Wardha District, Maharashtra, India
Persons with th ...
, which is 14 kilometers from Pärnu
Pärnu () is the fourth largest city in Estonia. Situated in southwest Estonia, Pärnu is located south of the Estonian capital, Tallinn, and west of Estonia's second largest city, Tartu. The city sits off the coast of Pärnu Bay, an inlet o ...
. According to radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
, Pulli was settled around 11,000 years ago, at the beginning of the 9th millennium BC
The 9th millennium BC spanned the years 9000 BC to 8001 BC (11 to 10 thousand years ago). In chronological terms, it is the first full millennium of the current Holocene epoch that is generally reckoned to have begun by 9700 BC (11.7 thousand ...
. A dog tooth found at the Pulli settlement is the first evidence for the existence of the domesticated dog in the territory of Estonia.
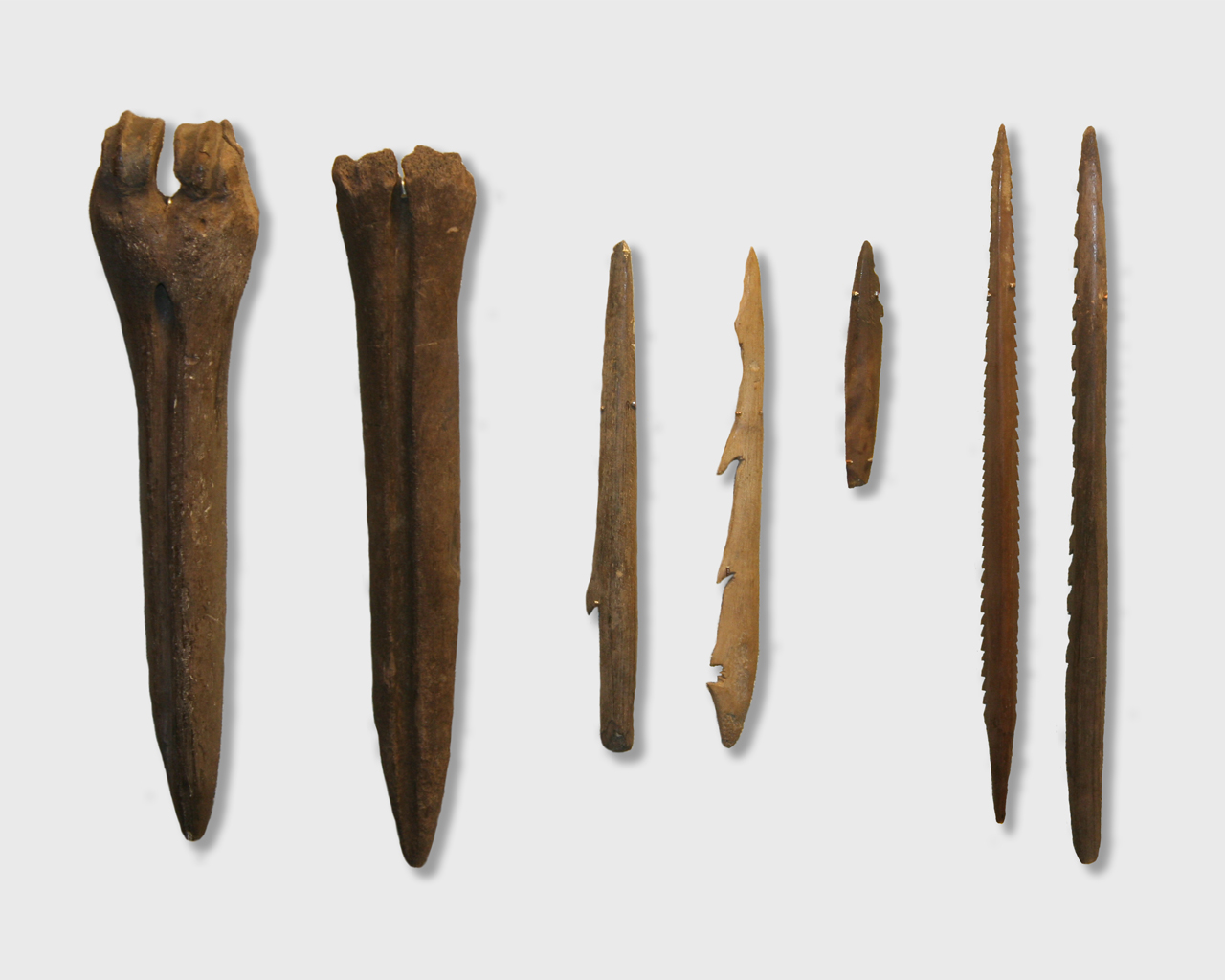
In all, 1175 items used by people of the Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
period were excavated at the Pulli settlement, among them tools mostly made of flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start fir ...
, especially arrow
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers c ...
heads. A few items made of bone were found too, such as fishhooks and accessories made of animal claws.
In the Baltic area, the best sources of flint were on the south and southeast of the Baltic, in present-day Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
and Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
and in Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
. There are few natural sources of flint in the territory of Estonia. However, black flint of high quality from southern Lithuania and Belarus is identical with examples found at the Pulli settlement.
The people who lived at Pulli probably moved there from the south after the ice had melted, moving along the Daugava river
, be, Заходняя Дзвіна (), liv, Vēna, et, Väina, german: Düna
, image = Fluss-lv-Düna.png
, image_caption = The drainage basin of the Daugava
, source1_location = Valdai Hills, Russia
, mouth_location = Gulf of Riga, Baltic Se ...
in Latvia, then along the Latvian-Estonian coast of the Baltic Sea, and finally to the mouth of the Pärnu river. In 9000 BC, the Pulli settlement was located exactly where the Pärnu river then flowed into the Baltic sea; today it is about 14-16 kilometers upstream from the sea.
Through almost the entire Stone Age, the Estonian area is clearly discernible as an original technocomplex, in which quartz dominates as the material for small tools produced by a splitting technique. The only exception is the Pulli site with its extensive use of imported flint.
 The Pulli settlement was discovered in 1967 during excavation of sand from the right bank of the Pärnu river. Archaeological excavations were carried out in 1968-73 and 1975-76 by the Estonian archaeologist L. Jaanits.
Three reliable
The Pulli settlement was discovered in 1967 during excavation of sand from the right bank of the Pärnu river. Archaeological excavations were carried out in 1968-73 and 1975-76 by the Estonian archaeologist L. Jaanits.
Three reliable carbon-14
Carbon-14, C-14, or radiocarbon, is a radioactive isotope of carbon with an atomic nucleus containing 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Its presence in organic materials is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method pioneered by Willard Libby and coll ...
dates come from the oldest known settlement site of Pulli, from the beginning of the Mesolithic: 9620±120 (Hel-2206A), 9600±120 (TA-245) and 9575±115 (TA-176) 14C years ( Raukas et al. 1995:121). These belong, with a probability of 95.4%, to the period 9300–8600 cal. BC, which makes the average 8950 cal BC — considering the probability of 68.2%, an even 9000 years cal BC. The Mesolithic archaeological complex in the Eastern Baltic bears the common name of the Kunda culture
The Kunda culture, originating from the Swiderian culture, comprised mesolithic hunter-gatherer communities of the Baltic forest zone extending eastwards through Latvia into northern Russia, dating to the period 8500–5000 BC according to cal ...
.
Science
 Early
Early Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
coastal settlements and palaeoenvironment on the shore of the Baltic Sea at Pärnu, southwestern Estonia.
Studies were conducted on 16 sections of buried organic matter (pre-Ancylus Lake
Ancylus Lake is a name given by geologists to a large freshwater lake that existed in northern Europe approximately from 9500 to 8000 years B.C being in effect one of various predecessors to the modern Baltic Sea.
Origin, evolution and demise
The ...
and pre-Littorina Sea
Littorina Sea (also Litorina Sea) is a geological brackish water stage of the Baltic Sea, which existed around 7500–4000 BP and followed the Mastogloia Sea, a transitional stage of the Ancylus Lake.
This stage and form of the body of wat ...
) and associated Stone Age cultural layers in the Pärnu area of southwestern Estonia. Buried organic beds are each part of a sedimentary sequence that is repeated, forming two overlying sets of an orderly succession of five layers. The organic sedimentation of the lower set (set 1) occurred about 10,800–10,200 years BP
Before Present (BP) years, or "years before present", is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Becau ...
, and that of the upper set (set 2) about 9450–7800 years BP. Associated with set 1 is the Early Mesolithic settlement of Pulli and with set 2 are the Stone Age cultural layers at Sindi-Lodja.
The Early and Middle Mesolithic sites in Estonia are concentrated on shores of rivers and lakes to use resources. The hunters and fishermen followed the ancient Pärnu river downstream to the receding shoreline of the Yoldia Sea. After about 10,700 years BP they were forced to retreat inland in front of the transgressive Ancylus Lake shore, which first inundated the Paikuse area about 10,400 years BP, and Pulli and higher sites about 10,200 years BP. The total amplitude of the transgression preceded 11m and reached up to 14m a.s.l. in the area. The Littorina Sea
Littorina Sea (also Litorina Sea) is a geological brackish water stage of the Baltic Sea, which existed around 7500–4000 BP and followed the Mastogloia Sea, a transitional stage of the Ancylus Lake.
This stage and form of the body of wat ...
transgression reached 7m a.s.l. after 8000–7800 years BP. The Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
, Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
and modern sites on top of each other in the Pärnu area may suggest that, although years apart, they were inhabited by the same group of people who stayed in the area and moved back and forth together with the shifting shoreline of the Baltic Sea.
See also
* Last glacial period (The most recentglacial period
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
that ended about 10,000 years ago.)
* Epipaleolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are someti ...
* Kunda culture
The Kunda culture, originating from the Swiderian culture, comprised mesolithic hunter-gatherer communities of the Baltic forest zone extending eastwards through Latvia into northern Russia, dating to the period 8500–5000 BC according to cal ...
* Prehistoric Europe
Prehistoric Europe is Europe with human presence but before the start of recorded history, beginning in the Lower Paleolithic. As history progresses, considerable regional irregularities of cultural development emerge and increase. The region o ...
References
External links
Story of Pulli settlement discovery
(in Estonian)
Early Holocene coastal settlements and palaeoenvironment on the shore of the Baltic Sea at Pärnu, southwestern Estonia
(archive.org) * ttps://web.archive.org/web/20071111130356/http://www.pernau.ee/lkd/esemed/pulli.php Pärnu museum, Pulli settlement(in Estonian, archive.org) {{Coord, 58.4192, N, 24.6756, E, source:wikidata, display=title Archaeological sites in Estonia Gulf of Riga Tori Parish Populated coastal places in Estonia Populated places established in the 9th millennium BC 9th-millennium BC establishments Archaeology of Estonia Prehistory of Europe