Perm, Russia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The city is a major administrative, industrial, scientific, and cultural centre. The leading industries include machinery,
The city is a major administrative, industrial, scientific, and cultural centre. The leading industries include machinery,
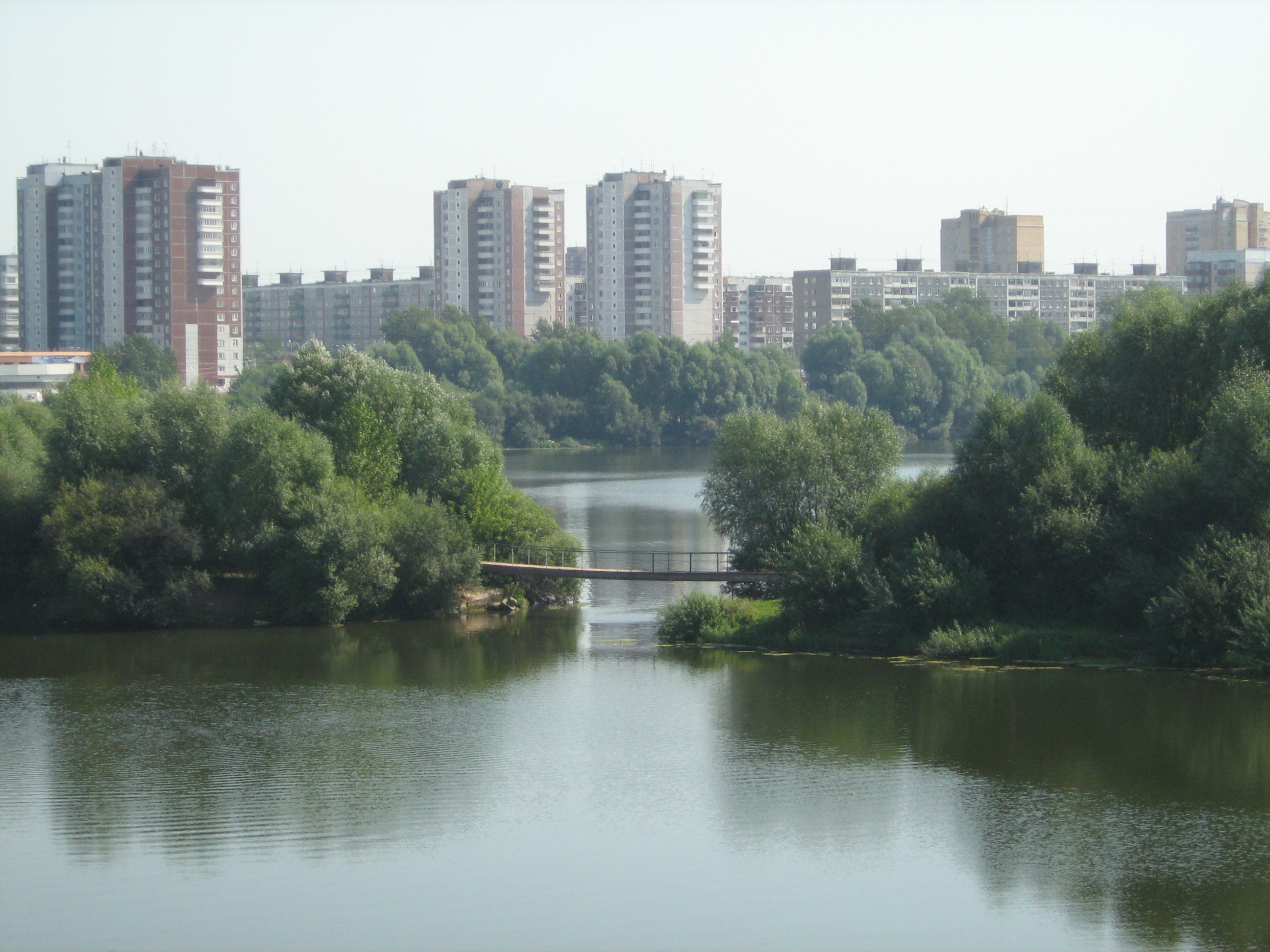

 For administrative purposes, Perm is divided into seven city districts:
For administrative purposes, Perm is divided into seven city districts:
Perm City Administration The largest industries in the city are electric power engineering, oil and gas refining, machine building, chemicals and petrochemicals, forestry processing, printing and food industry.English version
City of Perm. Department of Industrial Policy, Investment and Entrepreneurship Several major industrial companies are located in Perm:
— Perm regional server. Perm is served by the international airport Bolshoye Savino, which is located southwest of the city. Perm's public transit network includes
Perm asv2019-05 img17 bus at Razgulay stop.jpg, LiAZ-5292 (
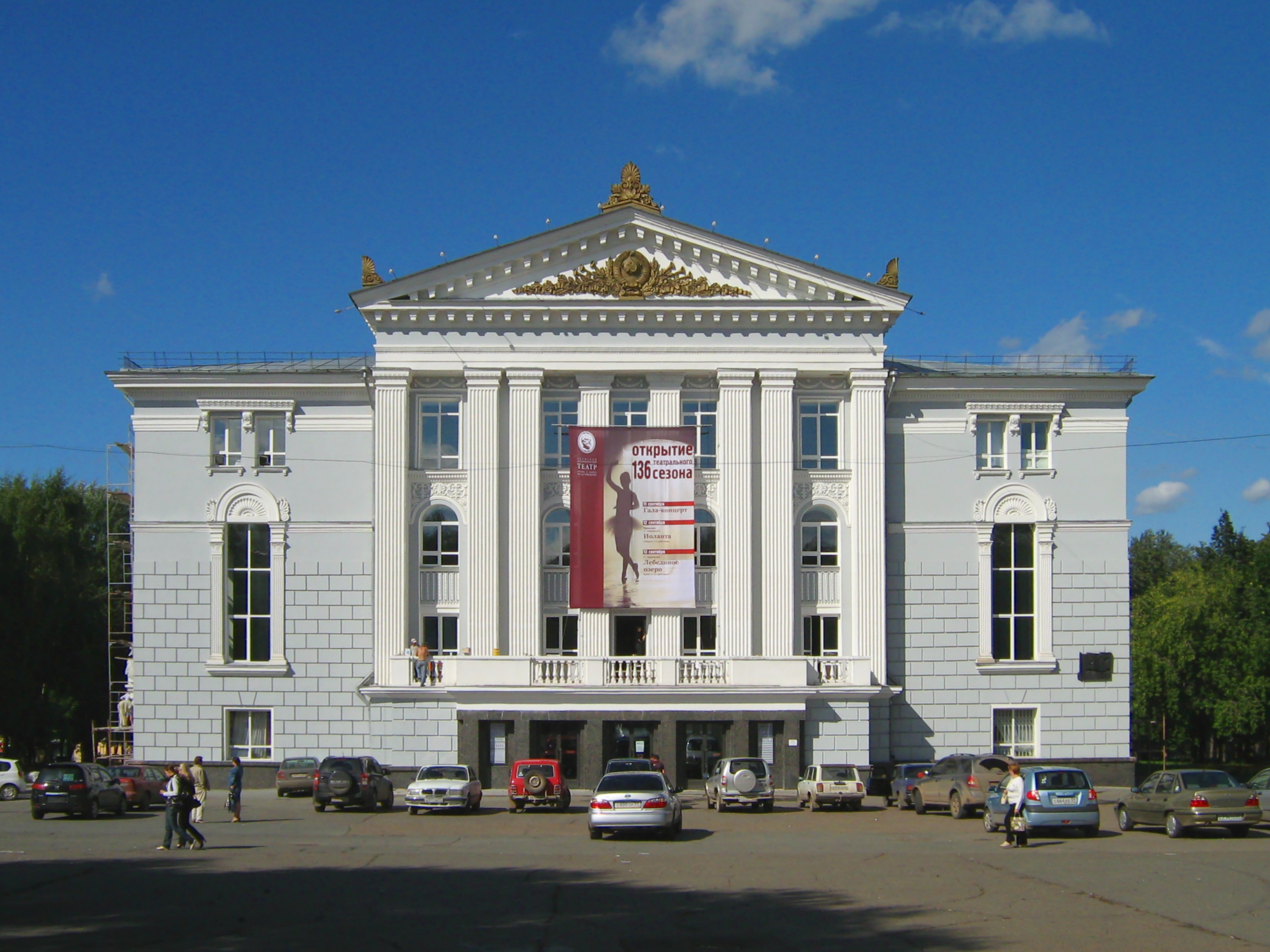
 The Perm Opera and Ballet House is one of the best in Russia. There are many other theatres in Perm, including the Drama Theater, the Puppet Theatre, the Theatre for Young Spectators, the Theatre "Stage Molot", and the ''mystical'' At the Bridge Theatre.
Among the cities museums and galleries, the
The Perm Opera and Ballet House is one of the best in Russia. There are many other theatres in Perm, including the Drama Theater, the Puppet Theatre, the Theatre for Young Spectators, the Theatre "Stage Molot", and the ''mystical'' At the Bridge Theatre.
Among the cities museums and galleries, the
— РИА «Новый Регион».
Perm State UniversityPerm State Technical UniversityPerm State Pharmaceutical AcademyPerm State Agricultural AcademyPerm State Choreographic School
 *
*
(rus)
Official website of Perm
Official website of the Perm City Duma
Street View of PermPerm Chamber of Commerce and IndustryThe Western Ural Photographic Album
Virtual museum of Romanov in PermThe city of Perm - The poem of the townArticle about Perm Ballet
* ttp://www.operm.ru Unofficial website of Perm {{Authority control Permsky Uyezd Populated places established in 1723 History of Ural 1723 establishments in the Russian Empire 1723 establishments in Europe Populated places on the Kama River
Perm (russian: Пермь, p=pʲermʲ), previously known as Yagoshikha (Ягошиха) (1723–1781), and Molotov (Молотов) (1940–1957), is the largest city and the

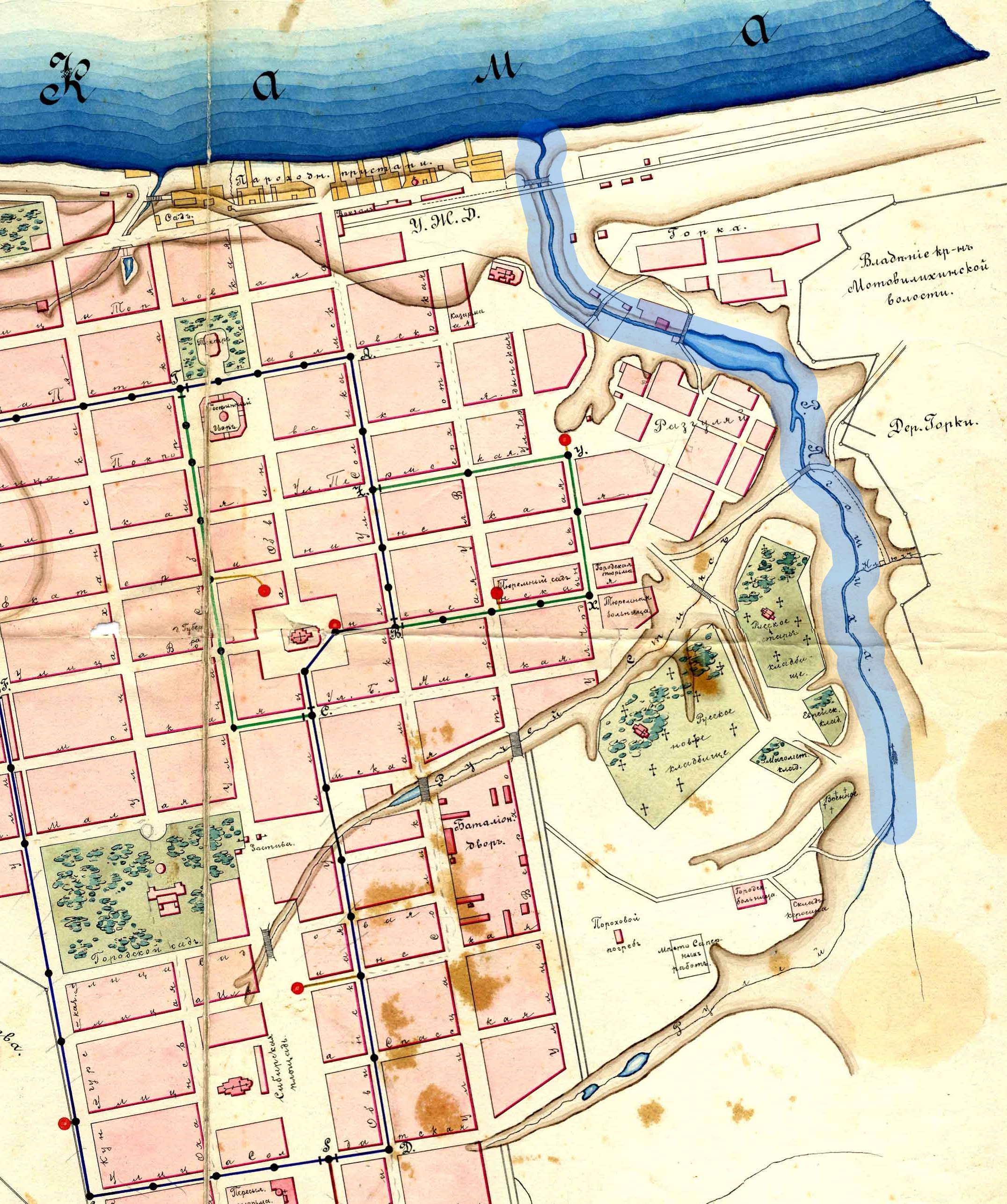 The city is located on the bank of the
The city is located on the bank of the
 After the outbreak of the
After the outbreak of the Sergey Prokudin-Gorsky
Sergey Mikhaylovich Prokudin-Gorsky ( rus, Сергей Михайлович Прокудин-Горский, p=sʲɪrˈɡʲej mʲɪxəjɫəvʲɪtɕ prəkudʲin ˈɡorskʲɪj, a=ru-Prokudin-Gorskii.ogg; – September 27, 1944) was a Ru ...
, taken in 1910" widths="175">
File:Sergei Mikhailovich Prokudin-Gorskii - City of Perm. General view (1910).jpg, General view of City of Perm
File:Sergei Mikhailovich Prokudin-Gorskii - General view of the city of Perm from Gorodskie Gorki (1910).jpg, General view of the city of Perm from Gorodskiye Gorki
File:Sergei Mikhailovich Prokudin-Gorskii - Razguliai, outskirts of the city of Perm (1910).jpg, Razgulyay, outskirts of the city of Perm
File:Perm. Mary Magdalene Church.png, Mary Magdalene Church of the city Perm
File:Prokudin-Gorsky - Perm. Summertime location of the exchange.jpg, Summertime location of the exchange in the city Perm
File:Prokudin-Gorskii - Staro-Sibirskaia Gate in the city of Perm.jpg, Prokudin-Gorsky — Staro-Sibirskaya Gate in the city of Perm
File:Prokudin-Gorskii-25.jpg, Kama River near Perm. The bridge still stands today, but another similar bridge has been built alongside it. Both are painted white.
File:Prokudin-Gorsky - Perm. Headquarters of the Ural Railway Administration.jpg, Headquarters of the Ural Railway Administration in the city of Perm
administrative centre
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.
In countries with French as administrative language (such as Belgium, Lu ...
of Perm Krai
Perm Krai (russian: Пе́рмский край, r=Permsky kray, p=ˈpʲɛrmskʲɪj ˈkraj, ''Permsky krai'', , ''Perem lador'') is a federal subject of Russia (a krai) that came into existence on December 1, 2005 as a result of the 2004 refe ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
. The city is located on the banks of the Kama River
The Kama (russian: Ка́ма, ; tt-Cyrl, Чулман, ''Çulman''; udm, Кам) is a long«Река � ...
, near the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
, covering an area of , with a population of over one million residents. Perm is the fifteenth-largest city in Russia, and the fifth-largest city in the Volga Federal District
Volga (Privolzhsky) Federal District (russian: Приво́лжский федера́льный о́круг, ''Privolzhsky federalny okrug'') is one of the eight federal districts of Russia. It forms the southeastern part of European Russia. ...
.
In 1723, a copper-smelting works was founded at the village of ''Yagoshikha''. In 1781 the settlement of Yagoshikha became the town of ''Perm''. Perm's position on the navigable Kama River, leading to the Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the List of rivers of Europe#Rivers of Europe by length, longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Cas ...
, and on the Siberian Route
The Siberian Route (russian: Сибирский тракт; ''Sibirsky trakt''), also known as the Moscow Highway (, Московский тракт) and Great Highway (, Большой тракт), was a historic route that connected European Russ ...
across the Ural Mountains, helped it become an important trade and manufacturing centre. It also lay along the Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR; , , ) connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the ea ...
. Perm grew considerably as industrialization proceeded in the Urals during the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
period, and in 1940 was named ''Molotov'' in honour of Vyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Mikhaylovich Molotov. ; (;. 9 March Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">O._S._25_February.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O. S. 25 February">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dat ...
. In 1957 the city returned to its historical name.
Modern Perm is still a major railway hub and one of the chief industrial centers of the Urals region. The city's diversified metallurgical and engineering industries produce equipment and machine tools for the petroleum and coal industries, as well as agricultural machinery. A major petroleum refinery uses oil transported by pipeline from the West Siberian oilfields, and the city's large chemical industry makes fertilizers and dyes. The city's institutions of higher education include the Perm A.M. Gorky State University, founded in 1916.
Etymology
The name ''Perm'' is ofUralic
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian (w ...
etymology ( Komi-Permyak: Перем, ''Perem''; kv, Перым, ''Perym''). Komi is a member of the Permic
The Permic or Permian languages are a branch of the Uralic language family. They are spoken in several regions to the west of the Ural Mountains within the Russian Federation. The total number of speakers is around 950,000, of which around 550,00 ...
branch of the Uralic languages, which is also named for Perm. In Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
and Vepsian
Veps, or Vepsians (Vepsian language, Veps: ''vepsläižed''), are a Baltic Finns, Finnic people who speak the Veps language, which belongs to the Finnic languages, Finnic branch of the Uralic languages.
According to the 2002 census, there were 8 ...
''perämaa'' means "far-away land"; similarly, in Hungarian ''perem'' means "edge" or "verge". The geologic period
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronol ...
of the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleoz ...
takes its name from the toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
.
Geography

 The city is located on the bank of the
The city is located on the bank of the Kama River
The Kama (russian: Ка́ма, ; tt-Cyrl, Чулман, ''Çulman''; udm, Кам) is a long«Река � ...
upon hilly terrain. The Kama is the main tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage ...
of the Volga River
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the List of rivers of Europe#Rivers of Europe by length, longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Cas ...
and is one of the deepest and most picturesque rivers of Russia. This river is the waterway which grants the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
access to the White Sea
The White Sea (russian: Белое море, ''Béloye móre''; Karelian and fi, Vienanmeri, lit. Dvina Sea; yrk, Сэрако ямʼ, ''Serako yam'') is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is su ...
, Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
, Sea of Azov
The Sea of Azov ( Crimean Tatar: ''Azaq deñizi''; russian: Азовское море, Azovskoye more; uk, Азовське море, Azovs'ke more) is a sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch, ...
, Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
, and Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
. The Kama divides the city into two parts: the central part and the right bank part. The city stretches for along the Kama and across it. The city street grid parallels the Kama River, travelling generally east-west, while other main streets run perpendicularly to those following the river. The grid pattern accommodates the hills of the city where it crosses them.
Another distinguishing feature of the city's relief is the large number of small rivers and brooks. The largest of them are the Mulyanka, the Yegoshikha, the Motovilikha
Motovilikhinsky City District (russian: Мотови́лихинский район) is one of the seven city districts of the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Perm, Russia, Perm in Perm Krai, Russia. Population: It is the second ...
(all are on the left bank of Kama River), and the Gayva (on the right bank).
Perm has a continental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 north), within large landmasses where prevailing winds blow overland bringing som ...
with warm summers and long, cold winters.
History
Perm is located in the old Permiak area. Perm was first mentioned as the village of Yagoshikha () in 1647; however, the history of the modern city of Perm starts with the development of theUral region
Ural (russian: Урал) is a geographical region located around the Ural Mountains, between the East European and West Siberian plains. It is considered a part of Eurasian Steppe, extending approximately from the North to the South; from the A ...
by Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
. Vasily Tatishchev
Vasily Nikitich Tatishchev (russian: Васи́лий Ники́тич Тати́щев) (19 April 1686 – 15 July 1750) was a prominent Russian Imperial statesman, historian, philosopher, and ethnographer, best remembered as the author of the ...
, appointed by the Tsar as a chief manager of Ural factories, founded Perm together with another major centre of the Ural region, Yekaterinburg
Yekaterinburg ( ; rus, Екатеринбург, p=jɪkətʲɪrʲɪnˈburk), alternatively romanized as Ekaterinburg and formerly known as Sverdlovsk ( rus, Свердло́вск, , svʲɪrˈdlofsk, 1924–1991), is a city and the administra ...
.
In the 19th century, Perm became a major trade and industrial centre with a population of more than 20,000 people in the 1860s, with several metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
, paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distributed ...
, and steamboat
A steamboat is a boat that is marine propulsion, propelled primarily by marine steam engine, steam power, typically driving propellers or Paddle steamer, paddlewheels. Steamboats sometimes use the ship prefix, prefix designation SS, S.S. or S/S ...
producing factories, including one owned by a British entrepreneur. In 1870, an opera theatre was opened in the city, and in 1871 the first phosphoric factory in Russia was built. In 1916, Perm State University
Perm State University (now Perm State National Research University; russian: Пермский университет, Пермский государственный университет, , romanised: , ) or PSU, PSNRU (russian: ПГУ, , ...
—a major educational institution in modern Russia—was opened.

 After the outbreak of the
After the outbreak of the Russian Civil War
, date = October Revolution, 7 November 1917 – Yakut revolt, 16 June 1923{{Efn, The main phase ended on 25 October 1922. Revolt against the Bolsheviks continued Basmachi movement, in Central Asia and Tungus Republic, the Far East th ...
, Perm became a prime target for both sides because of its military munitions
Ammunition (informally ammo) is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. Ammunition is both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines) and the component parts of other weap ...
factories. It was heavily rumored from July-September 1918 that the Tsarina Alexandra Feodorovna and her four daughters were imprisoned at the perception and Berezine buildings. According to the File on the Tsar, the Grand Duchess Anastasia
Grand may refer to:
People with the name
* Grand (surname)
* Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor
* Grand Mixer DXT, American turntablist
* Grand Puba (born 1966), American rapper
Places
* Grand, Oklahoma
* Grand, Vosges, village and co ...
would have attempted to flee. On December 25, 1918, the Siberian White Army
The White Army (russian: Белая армия, Belaya armiya) or White Guard (russian: Бѣлая гвардія/Белая гвардия, Belaya gvardiya, label=none), also referred to as the Whites or White Guardsmen (russian: Бѣлогв� ...
under Anatoly Pepelyayev
Anatoly Nikolayevich Pepelyayev (russian: Анатолий Николаевич Пепеляев; , in Tomsk – 14 January 1938) was a White Russian general who led the Siberian armies of Admiral Kolchak during the Russian Civil War. His ...
(who acknowledged the authority of the Omsk
Omsk (; rus, Омск, p=omsk) is the administrative center and largest city of Omsk Oblast, Russia. It is situated in southwestern Siberia, and has a population of over 1.1 million. Omsk is the third largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk ...
Government of Aleksandr Kolchak
Alexander Vasilyevich Kolchak (russian: link=no, Александр Васильевич Колчак; – 7 February 1920) was an Imperial Russian admiral, military leader and polar explorer who served in the Imperial Russian Navy and fought ...
), took Perm. On July 1, 1919, the city was retaken by the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
.
Soviet period
In the 1930s, Perm grew as a major industrial city withaviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air ...
, shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
, and chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wi ...
factories built during that period. During the Great Patriotic War
The Eastern Front of World War II was a theatre of conflict between the European Axis powers against the Soviet Union (USSR), Poland and other Allies, which encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northeast Europe (Baltics), and Sout ...
(World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
), Perm was a vital center of artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
production in the Soviet Union. During the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, Perm became a closed city
A closed city or closed town is a settlement where travel or residency restrictions are applied so that specific authorization is required to visit or remain overnight. Such places may be sensitive military establishments or secret research ins ...
.
Modern city
 The city is a major administrative, industrial, scientific, and cultural centre. The leading industries include machinery,
The city is a major administrative, industrial, scientific, and cultural centre. The leading industries include machinery, defence
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense industr ...
, oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
production (about 3% of Russian output), oil refining
{{Unreferenced, date=December 2009
Refining (also perhaps called by the mathematical term affining) is the process of purification of a (1) substance or a (2) form. The term is usually used of a natural resource that is almost in a usable form, b ...
, chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wi ...
and petrochemical, timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
and wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin th ...
processing and the food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is inge ...
industry.
On 20 September 2021, a mass shooting occurred at Perm State University
Perm State University (now Perm State National Research University; russian: Пермский университет, Пермский государственный университет, , romanised: , ) or PSU, PSNRU (russian: ПГУ, , ...
, resulting in six fatalities and 47 injuries.
Administrative and municipal status
Perm is theadministrative centre
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.
In countries with French as administrative language (such as Belgium, Lu ...
of the krai
A krai or kray (; russian: край, , ''kraya'') is one of the types of federal subjects of modern Russia, and was a type of geographical administrative division in the Russian Empire and the Russian SFSR.
Etymologically, the word is relate ...
and, within the framework of administrative divisions, it also serves as the administrative center of Permsky District
Perm District (russian: Пе́рмский райо́н, ) is an administrative district (raion), one of the thirty-three in Perm Krai, Russia.Law #416-67 Population - 116,353 (2021)
Geography
The Perm district is located in the suburban area o ...
, even though it is not a part of it.Law #416-67 As an administrative division, it is, together with two rural localities, incorporated separately as the city of krai significance of Perm—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
. As a municipal division, the city of krai significance of Perm is incorporated as Perm Urban Okrug.Law #2038-446
City divisions

 For administrative purposes, Perm is divided into seven city districts:
For administrative purposes, Perm is divided into seven city districts:
Economy
Perm has the largest industrial output among cities in the Urals, ahead ofYekaterinburg
Yekaterinburg ( ; rus, Екатеринбург, p=jɪkətʲɪrʲɪnˈburk), alternatively romanized as Ekaterinburg and formerly known as Sverdlovsk ( rus, Свердло́вск, , svʲɪrˈdlofsk, 1924–1991), is a city and the administra ...
, Chelyabinsk
Chelyabinsk ( rus, Челя́бинск, p=tɕɪˈlʲæbʲɪnsk, a=Ru-Chelyabinsk.ogg; ba, Силәбе, ''Siläbe'') is the administrative center and largest city of Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia. It is the seventh-largest city in Russia, with a ...
and Ufa
Ufa ( ba, Өфө , Öfö; russian: Уфа́, r=Ufá, p=ʊˈfa) is the largest city and capital of Bashkortostan, Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Belaya and Ufa rivers, in the centre-north of Bashkortostan, on hills forming the ...
, although Perm has a smaller population than these. Thirty-five per cent of Perm Oblast Until 1 December 2005, Perm Oblast (russian: Пе́рмская о́бласть) was a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) in Privolzhsky (Volga) Federal District. According to the results of the referendum held in October 2004, Perm Oblast was ...
's industry is located in Perm.IndustryPerm City Administration The largest industries in the city are electric power engineering, oil and gas refining, machine building, chemicals and petrochemicals, forestry processing, printing and food industry.English version
City of Perm. Department of Industrial Policy, Investment and Entrepreneurship Several major industrial companies are located in Perm:
Perm Motors
Perm or PERM may refer to:
Places
*Perm, Russia, a city in Russia
** Permsky District, the district
**Perm Krai, a federal subject of Russia since 2005
**Perm Oblast, a former federal subject of Russia 1938–2005
**Perm Governorate, an administra ...
and Aviadvigatel
UEC-Aviadvigatel JSC (Russian: АО "ОДК-Авиадвигатель", lit. Aeroengine) is a Russian developer and builder of aircraft engines, most notably jet engines for commercial aircraft. Based at the Perm Engine Plant, its products powe ...
, major suppliers of engines to the Russian aircraft industry; rocket engine company Proton-PM
OJSC Proton-PM ( Russian: ) is a Russian engine and heavy machinery manufacturing plant. It is located in the city of Perm, in the Perm Krai, on the bank of the Kama River. It started in 1958 as the specialized branch of Plant No. 19 named after ...
, which will mass-produce the RD-191 engine for the upcoming Angara rocket family
The Angara rocket family (Russian: Ангара) is a family of launch vehicles being developed by the Moscow-based Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center. The launch vehicles are to put between and into low Earth orbit and are ...
; electric engineering firms Morion JSC, Perm Scientific and Industrial Group, and Perm Electrical Engineering Plant; Russia's largest exporter of cables and wires, JSC KAMKABEL; and oil and natural gas companies such as LUKoil
The PJSC Lukoil Oil Company ( stylized as LUKOIL or ЛУКОЙЛ in Cyrillic script) is a Russian multinational energy corporation headquartered in Moscow, specializing in the business of extraction, production, transport, and sale of petrol ...
-Perm Ltd. and LUKoilPernefteprodukt Ltd.
Transportation
Perm is an important railway junction on theTrans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR; , , ) connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the ea ...
with lines radiating to Central Russia
Central Russia is, broadly, the various areas in European Russia.
Historically, the area of Central Russia varied based on the purpose for which it is being used. It may, for example, refer to European Russia (except the North Caucasus and ...
, the north part of the Urals
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through European ...
, and the far east of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
. Perm has two major railway stations, the historical Perm I and the modern Perm II. The Kama River
The Kama (russian: Ка́ма, ; tt-Cyrl, Чулман, ''Çulman''; udm, Кам) is a long«Река � ...
is an important direct link between the European part of Russia to the sea ports on the White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
, Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
* Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originati ...
, Azov
Azov (russian: Азов), previously known as Azak,
is a town in Rostov Oblast, Russia, situated on the Don River just from the Sea of Azov, which derives its name from the town. Population:
History
Early settlements in the vicinity
The mo ...
, Black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white have o ...
, and Caspian Caspian can refer to:
*The Caspian Sea
*The Caspian Depression, surrounding the northern part of the Caspian Sea
*The Caspians, the ancient people living near the Caspian Sea
*Caspian languages, collection of languages and dialects of Caspian peopl ...
seas.Transport infrastructure— Perm regional server. Perm is served by the international airport Bolshoye Savino, which is located southwest of the city. Perm's public transit network includes
tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
, bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
, and city-railway routes. The formerly important trolleybus
A trolleybus (also known as trolley bus, trolley coach, trackless trolley, trackless tramin the 1910s and 1920sJoyce, J.; King, J. S.; and Newman, A. G. (1986). ''British Trolleybus Systems'', pp. 9, 12. London: Ian Allan Publishing. .or troll ...
service was discontinued in July 2019.
CNG
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is a fuel gas mainly composed of methane (CH4), compressed to less than 1% of the volume it occupies at standard atmospheric pressure. It is stored and distributed in hard containers at a pressure of , usually in cy ...
motor version) city bus
Perm asv2019-05 img19 trolley at Razgulay stop.jpg, Trolza-5265 low-floor trolleybus
Perm asv2019-05 img70 tram in Motovilikha.jpg, AKSM-60102 tram
Perm asv2019-05 img56 Perm-II station.jpg, Perm II railway station
Perm asv2019-05 img32 Perm-I station.jpg, Perm I railway station
Bolshoe_Savino_(new_terminal).jpg, Perm International Airport
Perm International Airport (russian: Международный аэропорт Пермь) is an international airport located at Bolshoye Savino, southwest of the city of Perm, Russia. It is the only airport in Perm Krai with scheduled comme ...
Proposed metro system
The ''Perm Metro'' is a planned construction of a metro system which has been considered. The first plans date back to the 1970s. A feasibility study was compiled in 1990 but economic difficulties during the decade prevented its final planning and construction. The plans were revitalised in the early 2000s, but a lack of funding hampered the project and plans were once again put on hold. Light rail has also been considered.Culture

 The Perm Opera and Ballet House is one of the best in Russia. There are many other theatres in Perm, including the Drama Theater, the Puppet Theatre, the Theatre for Young Spectators, the Theatre "Stage Molot", and the ''mystical'' At the Bridge Theatre.
Among the cities museums and galleries, the
The Perm Opera and Ballet House is one of the best in Russia. There are many other theatres in Perm, including the Drama Theater, the Puppet Theatre, the Theatre for Young Spectators, the Theatre "Stage Molot", and the ''mystical'' At the Bridge Theatre.
Among the cities museums and galleries, the Perm State Art Gallery
Perm or PERM may refer to:
Places
*Perm, Russia, a city in Russia
**Permsky District, the district
**Perm Krai, a federal subject of Russia since 2005
**Perm Oblast, a former federal subject of Russia 1938–2005
**Perm Governorate, an administrat ...
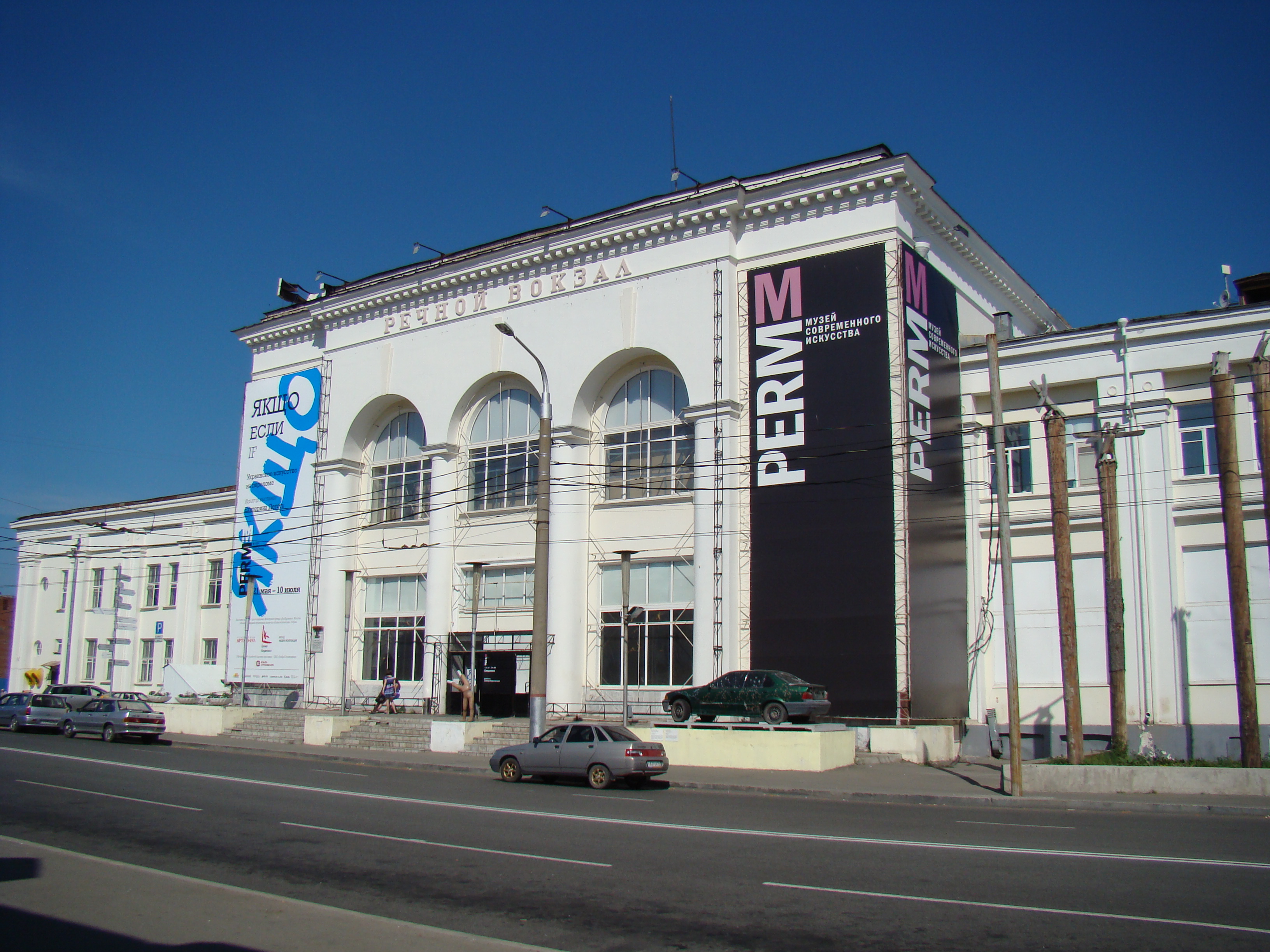
is recognised for its outstanding collections of art, including paintings from 15th- to 18th-century art movements, and wooden sculptures from the region. It is housed in a notable early 19th-century structure, once an orthodox cathedral. The spire of the museum towers over the rest of Perm, as it is situated on the Komsomolsky Prospect. Perm is receiving attention from the development of the new Museum of Contemporary Art, Perm Museum of Contemporary Art
Perm Museum of Contemporary Art (PERMM) (russian: Пермский музей современного искусства (ПЕРММ)) is an art gallery in Perm, Perm Krai, Russia, that officially opened in spring 2009. It holds changing exhibit ...
(PERMM) which officially opened in March 2009.
The RAV Vast steel tongue drum was invented in Perm by Andrey Remyannikov. This instrument is unique in the tongue drum and handpan
250px, A handpan from the first production run of Pantheon Steel.
Handpan is a term for a group of musical instruments that are classified as a subset of the steelpan. Several handpan makers and brands have emerged in recent years, resulting f ...
world because each note has multiple harmonic overtone
An overtone is any resonant frequency above the fundamental frequency of a sound. (An overtone may or may not be a harmonic) In other words, overtones are all pitches higher than the lowest pitch within an individual sound; the fundamental i ...
s that resonate with other notes in the drum. The sound consequently has long sustain and reverberation
Reverberation (also known as reverb), in acoustics, is a persistence of sound, after a sound is produced. Reverberation is created when a sound or signal is reflected causing numerous reflections to build up and then decay as the sound is abso ...
.
The Legend of Perm Bear or The Walking Bear is a sculpture depicting a walking bear
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae. They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Nor ...
, which is also shown on the city's coat of arms. It is situated in the central part of the city on Lenin Street, in front of the Organ Concert Hall and close to the building of Legislative Assembly of Perm Krai
Perm Krai (russian: Пе́рмский край, r=Permsky kray, p=ˈpʲɛrmskʲɪj ˈkraj, ''Permsky krai'', , ''Perem lador'') is a federal subject of Russia (a krai) that came into existence on December 1, 2005 as a result of the 2004 refe ...
. The author of the sculpture is Vladimir Pavlenko, a monumentalist sculptor from Nizhny Tagil
Nizhny Tagil ( rus, Нижний Тагил, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪj tɐˈgʲil) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, located east of the boundary between Asia and Europe. Population:
History
The prehistor ...
, member of the Artists' Union of Russia and UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
International Association of Arts.В центре Перми появился бурый медведь— РИА «Новый Регион».
Education
Perm is a scientific centre; some of the scientific institutes are combined in the Perm Scientific Center of the Ural Branch of theRussian Academy of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across t ...
.
Perm is a home to several major universities
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, t ...
including Perm State University
Perm State University (now Perm State National Research University; russian: Пермский университет, Пермский государственный университет, , romanised: , ) or PSU, PSNRU (russian: ПГУ, , ...
, Perm State Technical University, Perm branch of state university Higher school of economics, Perm State Teachers' Training University, Perm State Medical Academy, Perm State Pharmaceutical Academy, Perm State Agricultural Academy, The Institute of Art and Culture, Perm State Choreographic School, and others. There are also three military schools in Perm.
Education links
Perm State University
Climate
Perm has a warm summer continental climate (Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
: ''Dfb''). Winters are long, snowy and quite cold. Summers are moderately warm with cool nights, although summers are shorter than winters. Due to its far inland location, there is a distinct lack of seasonal lag
Seasonal lag is the phenomenon whereby the date of maximum average air temperature at a geographical location on a planet is delayed until some time after the date of maximum insolation (i.e. the summer solstice). This also applies to the minimum ...
resulting in rapid cooling down of the warm weather as days get shorter. This is less evident during winter.
Demographics
At the time of the official 2010 Census, the ethnic makeup of the city's population whose ethnicity was known (907,955) was:Sports
The city hosted 2002 European Amateur Boxing Championships. In 1995-2008, Perm was the location of the Ural Great basketball team — the only Russian basketball champion besides CSKA. There is also an amateurbandy
Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two teams wearing ice skates on a large ice surface (either indoors or outdoors) while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal. The international governing body for bandy is ...
team called Kama
''Kama'' (Sanskrit ) means "desire, wish, longing" in Hindu, Buddhist, Jain, and Sikh literature.Monier Williamsकाम, kāmaMonier-Williams Sanskrit English Dictionary, pp 271, see 3rd column Kama often connotes sensual pleasure, sexual ...
.
Notable people
The following people were either born in Perm or made names for themselves while residing there. *
*Tatiana Borodina
Tatiana Borodina is a Russian opera soprano.
Biography
Borodina was born in Perm. She graduated from the Perm Musical College and Saint Petersburg Conservatory in 2000.
She was a prize winner at the Young Voices of East: International Competi ...
(born ca.1972), opera soprano
*Sergei Diaghilev
Sergei Pavlovich Diaghilev ( ; rus, Серге́й Па́влович Дя́гилев, , sʲɪˈrɡʲej ˈpavləvʲɪdʑ ˈdʲæɡʲɪlʲɪf; 19 August 1929), usually referred to outside Russia as Serge Diaghilev, was a Russian art critic, pat ...
(1872–1929), ballet impresario
* Alexei Ivanov (born 1969) a Russian award-winning writer.
*Dmitry Mamin-Sibiryak
Dmitry Narkisovich Mamin-Sibiryak (russian: Дми́трий Нарки́сович Ма́мин-Сибиря́к) (October 25, 1852 – November 2, 1912) was a Russian author most famous for his novels and short stories about life in the Ur ...
(1852–1912) a Russian author of novels and short stories set in the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
.
* Tanya Mityushina (born 1993), model
*Nikolay Moiseyev
Nikolay Dmitriyevich Moiseyev (russian: Никола́й Дми́триевич Моисе́ев; December 3(16), 1902 in Perm – December 6, 1955 in Moscow) was a Soviet astronomer and expert in celestial mechanics. In 1938, he b ...
(1902–1955) a Soviet astronomer and expert in celestial mechanics
Celestial mechanics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the motions of objects in outer space. Historically, celestial mechanics applies principles of physics (classical mechanics) to astronomical objects, such as stars and planets, to ...
*Andronic Nikolsky
Archbishop Andronik (also spelled Andronic; russian: Архиепископ Андроник, secular name Vladimir Alexandrovich Nikolsky, russian: Владимир Александрович Никольский; August 1, 1870 – July 7, 191 ...
(1870–1918), first Russian Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = ru
, image = Moscow July 2011-7a.jpg
, imagewidth =
, alt =
, caption = Cathedral of Christ the Saviour in Moscow, Russia
, abbreviation = ROC
, type ...
Bishop of Kyoto, Japan
*Mikhail Osorgin
Mikhail Andreyevich Osorgin (russian: Михаи́л Андре́евич Осорги́н; real last name Ilyin (Ильи́н); 19 October 1878 – 27 November 1942) was a writer, journalist, and essayist born in the Russian Empire.
Biography
Oso ...
(1878–1942) a Russian writer, journalist and essayist.
*Natasha Poly
Natalia Sergeevna Polevshchikova (russian: Наталья Серге́евна Полевщикова; born 12 July 1985), known professionally as Natasha Poly, is a Russian supermodel. Since 2004, Poly has appeared in prominent high-fashion ad ...
(born 1985), supermodel
*Alexander Stepanovich Popov
Alexander Stepanovich Popov (sometimes spelled Popoff; russian: Алекса́ндр Степа́нович Попо́в; – ) was a Russian physicist, who was one of the first persons to invent a radio receiving device. declassified 8 Januar ...
(1859–1905), physicist; regarded locally as the inventor of radio
*Dmitry Rybolovlev
Dmitry Yevgenyevich Rybolovlev (russian: Дмитрий Евгеньевич Рыболовлев; ; born 22 November 1966) is a Russian oligarch, billionaire businessman, and investor.
Rybolovlev became chairman of the Russian fertilizer prod ...
(born 1966) a Russian oligarch, billionaire businessman and investor
*Katerina Shpitsa
Katerina Anatolievna Shpitsa (russian: Катери́на Анато́льевна Шпи́ца; born 29 October 1985) is a Russians, Russian stage and film actress. She is best known for '':ru:Катя: Военная история, Katya: Mil ...
(born 1985), actress of theatre and cinema
* Mikhail Shuisky (1883–1953), baritone opera singer
* Arkady Shvetsov (1892-1953), aircraft engine designer
*Nikolay Slavyanov
Nikolay Gavrilovich Slavyanov (russian: Никола́й Гаври́лович Славя́нов; – ) was a Russian inventor who in 1888 introduced arc welding with consumable metal electrodes, or shielded metal arc welding, the second histori ...
(1854–1897), inventor of an early method of arc welding
Arc welding is a welding process that is used to join metal to metal by using electricity to create enough heat to melt metal, and the melted metals, when cool, result in a binding of the metals. It is a type of welding that uses a welding powe ...
*Peter Struve
Peter (or Pyotr or Petr) Berngardovich Struve (russian: Пётр Бернга́рдович Стру́ве; pronounced ; 26 January 1870 in Perm, Russia, Perm – 22 February 1944 in Paris) was a Russian Political economy, political economist, ph ...
(1870–1944), political economist, philosopher and editor
*Yuri Trutnev
Yury Petrovich Trutnev (russian: Ю́рий Петро́вич Тру́тнев; born 1 March 1956) is a Russian politician who serves as a Deputy Prime Minister of Russia and Presidential Envoy to the Far Eastern Federal District since 2013. F ...
(born 1956), politician, Presidential Envoy to the Far Eastern Federal District
The Far Eastern Federal District (russian: Дальневосто́чный федера́льный о́круг, ''Dalnevostochny federalny okrug'') is the largest of the federal districts of Russia, eight federal districts of Russia but t ...
*Andrey Voronikhin
Andrey (Andrei) Nikiforovich Voronikhin (russian: Андрей Никифорович Воронихин) (28 October 1759, Novoe Usolye, Perm Oblast – 21 February 1814, Saint Petersburg) was a Russian architect and painter. As a representativ ...
(1759–1814), architect and painter
Sport
*Michael Beilin
Michael Beilin (מיכאל ביילין; born April 25, 1976) is an Israeli former Olympic Greco-Roman wrestler.
Early life
Beilin is from Perm, Russia, and is Jewish.
(born 1976), Israeli Olympic Greco-Roman wrestler
*Vladimir Chagin
Vladimir Gennadiyevich Chagin ( rus, Владимир Геннадьевич Чагин, p=vlɐˈdʲimʲɪr gʲɪˈnadʲɪɪvɪtɕ ˈtɕægʲɪn; born 5 January 1970) is a Russian rally raid driver. He has won the Dakar Rally driving Kamaz tru ...
(born 1970), a Russian rally raid
Rally raid, also known as cross-country rallying, is a form of long distance off-road racing that takes place over several days. The length of the event can be as short as 2–3 days for a cross-country baja to as long as 15 days with marathon ra ...
driver in the Dakar Rally
The Dakar Rally (or simply "The Dakar"; formerly known as the "Paris–Dakar Rally") is an annual rally raid organised by the Amaury Sport Organisation. Most events since the inception in 1978 were staged from Paris, France, to Dakar, Senegal, ...
*Alexandra Kosteniuk
Alexandra Konstantinovna Kosteniuk (russian: Алекса́ндра Константи́новна Костеню́к; born 23 April 1984) is a Russian chess grandmaster who is the former Women's World Rapid Chess Champion in 2021, and the for ...
(born 1984), 2008 Women's World Chess Champion
* Vladimirs Lubkins (born 1963), retired Latvian ice hockey player
*Tatiana Totmianina
Tatiana Ivanovna Totmianina (russian: Татьяна Ивановна Тотьмянина; born 2 November 1981) is a Russian former competitive pair skater. With partner Maxim Marinin, she is the 2006 Olympic champion, two-time World champion, ...
(born 1981), pair skater, 2006 Olympic Champion
*Maxim Trankov
Maxim Leonidovich Trankov (russian: Максим Леонидович Траньков; born 7 October 1983) is a Russian pair skater. With Tatiana Volosozhar, he is a two-time 2014 Olympic champion in the pairs and in team events, the 2013 ...
(born 1983), pairs figure skater
* Konstantin Zyryanov (born 1977), footballer with 52 caps for Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
;and
The Nobel-prize-winning writer Boris Pasternak
Boris Leonidovich Pasternak (; rus, Бори́с Леони́дович Пастерна́к, p=bɐˈrʲis lʲɪɐˈnʲidəvʲɪtɕ pəstɛrˈnak; 30 May 1960) was a Russian poet, novelist, composer and literary translator. Composed in 1917, Pa ...
(1890–1960) lived in Perm for a time, and it figures in his novel ''Doctor Zhivago
''Doctor Zhivago'' is the title of a novel by Boris Pasternak and its various adaptations.
Description
The story, in all of its forms, describes the life of the fictional Russian physician and poet Yuri Zhivago
Yuri Andreievich Zhivago is the ...
'' under the fictional name "Yuriatin" where Yuri sees Lara again in the public library.
Marketing
Perm is an example ofcity marketing
City marketing (related to city branding) or Place Marketing is the promotion of a city, or a district within it, with the aim of encouraging certain activities to take place there.
Place marketing "refers to the application of mark ...
in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, where the city also has a logo
A logo (abbreviation of logotype; ) is a graphic mark, emblem, or symbol used to aid and promote public identification and recognition. It may be of an abstract or figurative design or include the text of the name it represents as in a wordma ...
.Artemy Lebedev thought up a logo of the Perm city(rus)
Twin towns – sister cities
Perm is twinned with: *Agrigento
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one of ...
, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Italy (2012)
* Amnéville, Moselle
The Moselle ( , ; german: Mosel ; lb, Musel ) is a river that rises in the Vosges mountains and flows through north-eastern France and Luxembourg to western Germany. It is a bank (geography), left bank tributary of the Rhine, which it jo ...
, France (1992)
* Duisburg
Duisburg () is a city in the Ruhr metropolitan area of the western German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Lying on the confluence of the Rhine and the Ruhr rivers in the center of the Rhine-Ruhr Region, Duisburg is the 5th largest city in Nor ...
, North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ksh, Noodrhing-Wäßßfaale), commonly shortened to NRW (), is a States of Germany, state (''Land'') in Western Germany. With more tha ...
, Germany (2007)
* Louisville
Louisville ( , , ) is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Kentucky and the 28th most-populous city in the United States. Louisville is the historical seat and, since 2003, the nominal seat of Jefferson County, on the Indiana border.
...
, Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
, United States (1994)
* Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
, Oxfordshire
Oxfordshire is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the north west of South East England. It is a mainly rural county, with its largest settlement being the city of Oxford. The county is a centre of research and development, primarily ...
, United Kingdom (1995-2022)
* Qingdao
Qingdao (, also spelled Tsingtao; , Mandarin: ) is a major city in eastern Shandong Province. The city's name in Chinese characters literally means " azure island". Located on China's Yellow Sea coast, it is a major nodal city of the One Belt ...
, Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilizati ...
, China (2006)
See also
*Immaculate Conception Church, Perm
The Immaculate Conception Church (russian: Храм Непорочного Зачатия Пресвятой Девы Марии ) is a Catholic church in the city of Perm in the Russian Federation, built in the 1870s. It belongs to the Central D ...
* Stephen of Perm
References
Notes
Sources
* * *External links
*Official website of Perm
Official website of the Perm City Duma
Street View of Perm
Virtual museum of Romanov in Perm
* ttp://www.operm.ru Unofficial website of Perm {{Authority control Permsky Uyezd Populated places established in 1723 History of Ural 1723 establishments in the Russian Empire 1723 establishments in Europe Populated places on the Kama River