pyloric glands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The gastric glands are
 Gastric glands are mostly
Gastric glands are mostly
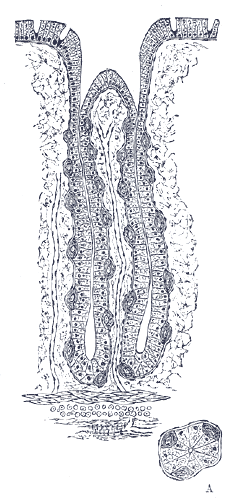 There are millions of
There are millions of
File:Illu stomach layers.jpg, Layers of stomach wall
File:Control-of-stomach-acid-sec.png, Gastric acid regulation
Image:Gray1053.png, Human
Veterinary Histology at vt.edu
* - see slide #42 * - "Esophageal-stomach junction" * - "Digestive System: Alimentary Canal: esophageal/stomach junction" {{Authority control Digestive system Stomach
gland
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland).
Structure
De ...
s in the lining
Lining may refer to:
* Lining (sewing), the process of inserting an inner layer of fabric, fur, or other material
* Lining of paintings, the process of restoration paintings by attaching a new canvas to the back of the existing one
* Brake linin ...
of the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
that play an essential role in the process of digestion. All of the glands have mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is ...
-secreting foveolar cell
Foveolar cells or surface mucous cells are mucus-producing cells which cover the inside of the stomach, protecting it from the corrosive nature of gastric acid. These cells line the gastric mucosa (mucous neck cells are found in the necks of the ...
s. Mucus lines the entire stomach, and protects the stomach lining from the effects of hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
released from other cells in the glands.
There are two types of gland in the stomach, the oxyntic gland, and the pyloric gland. The major type of gastric gland is the oxyntic gland that is present in 80 per cent of the stomach, and is often referred to simply as the ''gastric gland''. The oxyntic gland is an exocrine gland
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two ...
and contains the parietal cell
Parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells) are epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor. These cells are located in the gastric glands found in the lining of the fundus and body regions of the ...
s that produce hydrochloric acid, and intrinsic factor
Intrinsic factor (IF), cobalamin binding intrinsic factor, also known as gastric intrinsic factor (GIF), is a glycoprotein produced by the parietal cells (in humans) or chief cells (in rodents) of the stomach. It is necessary for the absorption o ...
. Intrinsic factor is necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. It is one of eight B vitamins. It is required by animals, which use it as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, in both fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It ...
.
The other type of gland in the stomach is the pyloric gland found in the pyloric region taking up the remaining 20 per cent of the stomach area. The pyloric gland secretes gastrin
Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the pyloric antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas.
Gastrin ...
from its G cell
In anatomy, the G cell or gastrin cell, is a type of cell in the stomach and duodenum that secretes gastrin. It works in conjunction with gastric chief cells and parietal cells. G cells are found deep within the pyloric glands of the stomach antrum ...
s. Pyloric glands are similar in structure to the oxyntic glands but are endocrine gland
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid ...
s with hardly any parietal cells.
Types of gland
The gastric glands are glands in the lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the process of digestion. All of the glands have mucus-secreting foveolar cells. Mucus lines the entire stomach of protects the stomach lining from the effects of hydrochloric acid released from other cells in the glands. Gastric glands are mostly
Gastric glands are mostly exocrine gland
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two ...
s and are all located beneath the gastric pit
Gastric pits are indentations in the stomach which denote entrances to 3-5"Secretions from several gastric glands flow into each gastric pit" Principals of Anatomy & Physiology 15th Ed 2017, Gerard Tortora & Bryan Derrickson tubular shaped gastric ...
s within the gastric mucosa
The gastric mucosa is the mucous membrane layer of the stomach, which contains the glands and the gastric pits. In humans, it is about 1 mm thick, and its surface is smooth, soft, and velvety. It consists of simple columnar epithelium, lamin ...
—the mucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
of the stomach. The gastric mucosa is pitted with innumerable gastric pits which each house 3-5 gastric glands. The cells of the exocrine glands are foveolar (mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is ...
), chief cells In human anatomy, there are three types of chief cells, the gastric chief cell, the parathyroid chief cell, and the type 1 chief cells found in the carotid body.
Cell types
The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell) is a ...
, and parietal cell
Parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells) are epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor. These cells are located in the gastric glands found in the lining of the fundus and body regions of the ...
s.
The other type of gastric gland is the pyloric gland
The gastric glands are glands in the lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the process of digestion. All of the glands have mucus-secreting foveolar cells. Mucus lines the entire stomach, and protects the stomach lining from the ...
which is an endocrine gland
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid ...
that secretes the hormone gastrin
Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the pyloric antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas.
Gastrin ...
produced by its G cell
In anatomy, the G cell or gastrin cell, is a type of cell in the stomach and duodenum that secretes gastrin. It works in conjunction with gastric chief cells and parietal cells. G cells are found deep within the pyloric glands of the stomach antrum ...
s.
The cardiac glands are found in the cardia
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is ...
of the stomach which is the part nearest to the heart, enclosing the opening where the esophagus joins to the stomach. Only cardiac glands are found here and they primarily secrete mucus. They are fewer in number than the other gastric glands and are more shallowly positioned in the mucosa. There are two kinds - either simple tubular with short ducts or compound racemose resembling the duodenal
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
Brunner's glands
Brunner's glands (or duodenal glands) are compound tubular submucosal glands found in that portion of the duodenum which is above the hepatopancreatic sphincter (i.e sphincter of Oddi). It also contains submucosa which creates special glands. ...
.
The fundic glands (or ''oxyntic glands''), are found in the fundus and body of the stomach. They are simple almost straight tubes, two or more of which open into a single duct. ''Oxyntic'' means acid-secreting and they secrete hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
(HCl) and intrinsic factor
Intrinsic factor (IF), cobalamin binding intrinsic factor, also known as gastric intrinsic factor (GIF), is a glycoprotein produced by the parietal cells (in humans) or chief cells (in rodents) of the stomach. It is necessary for the absorption o ...
.
The pyloric glands are located in the antrum ''This is a disambiguation page for the biological term. For the 2018 horror movie, see Antrum (film)''
In biology, antrum is a general term for a cavity or chamber, which may have specific meaning in reference to certain organs or sites in the bod ...
of the pylorus
The pylorus ( or ), or pyloric part, connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the ''pyloric antrum'' (opening to the body of the stomach) and the ''pyloric canal'' (opening to the duodenum). The ''pylori ...
. They secrete gastrin
Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the pyloric antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas.
Gastrin ...
produced by their G cells
In anatomy, the G cell or gastrin cell, is a type of cell in the stomach and duodenum that secretes gastrin. It works in conjunction with gastric chief cells and parietal cells. G cells are found deep within the pyloric glands of the stomach antrum ...
.
Types of cell
 There are millions of
There are millions of gastric pit
Gastric pits are indentations in the stomach which denote entrances to 3-5"Secretions from several gastric glands flow into each gastric pit" Principals of Anatomy & Physiology 15th Ed 2017, Gerard Tortora & Bryan Derrickson tubular shaped gastric ...
s in the gastric mucosa and their necessary narrowness determines the tubular form of the gastric gland. More than one tube allows for the accommodation of more than one cell type. The form of each gastric gland is similar; they are all described as having a neck region that is closest to the pit entrance, and basal regions on the lower parts of the tubes. The epithelium from the gastric mucosa travels into the pit and at the neck the epithelial cells change to short columnar granular cells. These cells almost fill the tube and the remaining lumen is continued as a very fine channel.
Cells found in the gastric glands include foveolar cell
Foveolar cells or surface mucous cells are mucus-producing cells which cover the inside of the stomach, protecting it from the corrosive nature of gastric acid. These cells line the gastric mucosa (mucous neck cells are found in the necks of the ...
s, chief cell In human anatomy, there are three types of chief cells, the gastric chief cell, the parathyroid chief cell, and the type 1 chief cells found in the carotid body.
Cell types
The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell) is a ...
s, parietal cell
Parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells) are epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor. These cells are located in the gastric glands found in the lining of the fundus and body regions of the ...
s, G cells
In anatomy, the G cell or gastrin cell, is a type of cell in the stomach and duodenum that secretes gastrin. It works in conjunction with gastric chief cells and parietal cells. G cells are found deep within the pyloric glands of the stomach antrum ...
, enterochromaffin-like cell
Enterochromaffin-like cells or ECL cells are a type of neuroendocrine cell found in the gastric glands of the gastric mucosa beneath the epithelium, in particular in the vicinity of parietal cells, that aid in the production of gastric acid via th ...
s (ECLs), etc. The first cells of all of the glands are foveolar cells in the neck region–also called ''mucous neck cells'' that produce mucus. This is thought to be different from the mucus produced by the gastric mucosa.
Fundic glands found in the fundus and also in the body have another two cell types–gastric chief cell In human anatomy, there are three types of chief cells, the gastric chief cell, the parathyroid chief cell, and the type 1 chief cells found in the carotid body.
Cell types
The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell) is a ...
s and parietal cell
Parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells) are epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor. These cells are located in the gastric glands found in the lining of the fundus and body regions of the ...
s (oxyntic cells).
* Surface mucous cell
Foveolar cells or surface mucous cells are mucus-producing cells which cover the inside of the stomach, protecting it from the corrosive nature of gastric acid. These cells line the gastric mucosa (mucous neck cells are found in the necks of the ...
(foveolar cell) – They are mucous producing cells which cover the inside of the stomach, protecting it from the corrosive nature of gastric acid. These cells line the gastric mucosa.
*Mucous neck cell
Foveolar cells or surface mucous cells are mucus-producing cell (biology), cells which cover the inside of the stomach, protecting it from the corrosive nature of gastric acid. These cells line the gastric mucosa (mucous neck cells are found in t ...
– Mucous neck cells are located within gastric glands, interspersed between parietal cells. These are shorter than their surface counterpart and contain lesser quantities of mucin granules in their apical surface.
* Chief cells In human anatomy, there are three types of chief cells, the gastric chief cell, the parathyroid chief cell, and the type 1 chief cells found in the carotid body.
Cell types
The gastric chief cell (also known as a zymogenic cell or peptic cell) is a ...
(zymogen cells/peptic cells) – They are found in the basal regions of the gland and release proenzymes or zymogens
In biochemistry, a zymogen (), also called a proenzyme (), is an inactive precursor of an enzyme. A zymogen requires a biochemical change (such as a hydrolysis reaction revealing the active site, or changing the configuration to reveal the active ...
– pepsinogen
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, whe ...
(precursor to pepsin
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, w ...
), and prorennin (precursor to rennin
Chymosin or rennin is a protease found in rennet. It is an aspartic endopeptidase belonging to MEROPS A1 family. It is produced by newborn ruminant animals in the lining of the abomasum to curdle the milk they ingest, allowing a longer residen ...
or chymosin). Prorennin is secreted in young mammals (childhood stage). It is not secreted in adult mammals. Chief cells also produce small amounts of gastric lipase
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach ...
. Gastric lipase contributes little to digestion of fat.
* Parietal cell
Parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells) are epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor. These cells are located in the gastric glands found in the lining of the fundus and body regions of the ...
s ("parietal" means "relating to a wall"), also known as oxyntic cells are most numerous on the side walls of the gastric glands. The parietal cells secrete hydrochloric acid, the main component of gastric acid
Gastric acid, gastric juice, or stomach acid is a digestive fluid formed within the stomach lining. With a pH between 1 and 3, gastric acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins by activating digestive enzymes, which together break down the ...
. This needs to be readily available for the stomach in a plentiful supply, and so from their positions in the walls, their secretory networks of fine channels called canaliculi can project and ingress into all the regions of the gastric-pit lumen. Another important secretion of the parietal cells is castle's intrinsic factor. Intrinsic factor is a glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos ...
essential for the absorption of vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. It is one of eight B vitamins. It is required by animals, which use it as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, in both fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It ...
. The parietal cells also produce and release bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochemic ...
ions in response to histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Since histamine was discovered in ...
release from the nearby ECLs, and so serve a crucial role in the pH buffering system.
* Enteroendocrine cell
Enteroendocrine cells are specialized cells of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas with endocrine function. They produce gastrointestinal hormones or peptides in response to various stimuli and release them into the bloodstream for systemic ef ...
s or argentaffin cells – They are usually present in the basal parts of the gastric glands, which is differentiated into three cell types – enterochromaffin like cells (ECL cells), G-cells, and D-cells.
** Enterochromaffin like cells (ECL cells) – They release serotonin and histamine. These cells store and release histamine when the pH of the stomach becomes too high. The release of histamine is stimulated by the secretion of gastrin
Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the pyloric antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas.
Gastrin ...
from the G cells. Histamine promotes the production and release of HCL from the parietal cells to the blood and protons to the stomach lumen. When the stomach pH decreases (becomes more acidic), the ECLs stop releasing histamine.
** G cells – They secrete gastrin
Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the pyloric antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas.
Gastrin ...
hormone. Gastrin stimulates the gastric glands to release gastric juice. These cells are mostly found in pyloric glands in the antrum of the pylorus
The pylorus ( or ), or pyloric part, connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the ''pyloric antrum'' (opening to the body of the stomach) and the ''pyloric canal'' (opening to the duodenum). The ''pylori ...
; some are found in the duodenum and other tissues. The gastric pits of these glands are much deeper than the others and here the gastrin is secreted into the bloodstream not the lumen.
** D-cells – D-cells secrete somatostatin
Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-couple ...
. Somatostatin suppresses the release of hormones from the digestive tract.
Clinical significance
Fundic gland polyposis
Fundic gland polyposis is a medical syndrome where the fundus and the body of the stomach develop many fundic gland polyps. The condition has been described both in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and attenuated variants (AFAP) ...
is a medical syndrome where the fundus and the body of the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
develop many fundic gland
The gastric glands are glands in the lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the process of digestion. All of the glands have mucus-secreting foveolar cells. Mucus lines the entire stomach, and protects the stomach lining from the e ...
polyps
A polyp in zoology is one of two forms found in the phylum Cnidaria, the other being the medusa. Polyps are roughly cylindrical in shape and elongated at the axis of the vase-shaped body. In solitary polyps, the aboral (opposite to oral) end is ...
.
Pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia is a type of vitamin B12 deficiency anemia, a disease in which not enough red blood cells are produced due to the malabsorption of vitamin B12. Malabsorption in pernicious anemia results from the lack or loss of intrinsic fa ...
is caused when damaged parietal cells fail to produce the intrinsic factor necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12. This is the most common cause of vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have few or absent symp ...
.
See also
* Zollinger-Ellison syndromeAdditional images
cardiac glands
The gastric glands are glands in the gastric mucosa, lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the digestion, process of digestion. All of the glands have mucus-secreting foveolar cells. Mucus lines the entire stomach, and protects the ...
(at cardia
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is ...
)
Image:Gray1054.png, Human pyloric glands
The gastric glands are glands in the lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the process of digestion. All of the glands have mucus-secreting foveolar cells. Mucus lines the entire stomach, and protects the stomach lining from the ...
(at pylorus
The pylorus ( or ), or pyloric part, connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the ''pyloric antrum'' (opening to the body of the stomach) and the ''pyloric canal'' (opening to the duodenum). The ''pylori ...
)
Image:Gray1055.png, Human fundic glands
The gastric glands are glands in the lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the process of digestion. All of the glands have mucus-secreting foveolar cells. Mucus lines the entire stomach, and protects the stomach lining from the e ...
(at fundus)
References
External links
* - "Fundic stomach" * - "Mammal, ruminant stomach (LM, High)" * - "Digestive System: Alimentary Canal - fundic stomach"Veterinary Histology at vt.edu
* - see slide #42 * - "Esophageal-stomach junction" * - "Digestive System: Alimentary Canal: esophageal/stomach junction" {{Authority control Digestive system Stomach