Public Bus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Public transport bus services are generally based on regular operation of
Public transport bus services are generally based on regular operation of
 While there are indications of experiments with
While there are indications of experiments with
 The names of different types of bus services vary according to local tradition or marketing, although services can be classified into basic types based on route length, frequency, the purpose of use and type of bus used.
The names of different types of bus services vary according to local tradition or marketing, although services can be classified into basic types based on route length, frequency, the purpose of use and type of bus used.
 *
*
 An express bus service (also known as express commuter service, commuter bus service, or suburban bus service) is a fixed-route
An express bus service (also known as express commuter service, commuter bus service, or suburban bus service) is a fixed-route
File:HCS bus49.JPG, A
 Public transport bus services are generally based on regular operation of
Public transport bus services are generally based on regular operation of transit bus
Transit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Transit'' (1979 film), a 1979 Israeli film
* ''Transit'' (2005 film), a film produced by MTV and Staying-Alive about four people in countries in the world
* ''Transit'' (2006 film), a 2006 ...
es along a route calling at agreed bus stop
A bus stop is a place where buses stop for passengers to get on and off the bus. The construction of bus stops tends to reflect the level of usage, where stops at busy locations may have shelters, seating, and possibly electronic passenger ...
s according to a published public transport timetable.
History of buses
Origins
 While there are indications of experiments with
While there are indications of experiments with public transport
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typical ...
in Paris as early as 1662, there is evidence of a scheduled "bus route" from Market Street Market Street may refer to:
*Market Street, Cambridge, England
*Market Street, Fremantle, Western Australia, Australia
* Market Street, George Town, Penang, Malaysia
*Market Street, Manchester, England
*Market Street, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
...
in Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
to Pendleton in Salford
Salford () is a city and the largest settlement in the City of Salford metropolitan borough in Greater Manchester, England. In 2011, Salford had a population of 103,886. It is also the second and only other city in the metropolitan county afte ...
UK, started by John Greenwood John Greenwood may refer to:
Sportspeople
* John Greenwood (cricketer, born 1851) (1851–1935), English cricketer
* John Eric Greenwood (1891–1975), rugby union international who represented England
* John Greenwood (footballer) (1921–1994) ...
in 1824.
Another claim for the first public transport system for general use originated in Nantes, France
Nantes (, , ; Gallo: or ; ) is a city in Loire-Atlantique on the Loire, from the Atlantic coast. The city is the sixth largest in France, with a population of 314,138 in Nantes proper and a metropolitan area of nearly 1 million inhabitan ...
, in 1826. Stanislas Baudry, a retired army officer who had built public bath
Public baths originated when most people in population centers did not have access to private bathing facilities. Though termed "public", they have often been restricted according to gender, religious affiliation, personal membership, and other cr ...
s using the surplus heat from his flour mill on the city's edge, set up a short route between the center of town and his baths. The service started on the Place du Commerce, outside the hat shop of a M. Omnès, who displayed the motto ''Omnès Omnibus'' (Latin for "everything for everybody" or "all for all") on his shopfront. When Baudry discovered that passengers were just as interested in getting off at intermediate points as in patronizing his baths, he changed the route's focus. His new ''voiture omnibus'' ("carriage for all") combined the functions of the hired hackney carriage
A hackney or hackney carriage (also called a cab, black cab, hack or London taxi) is a carriage or car for hire. A hackney of a more expensive or high class was called a remise. A symbol of London and Britain, the black taxi is a common ...
with a stagecoach
A stagecoach is a four-wheeled public transport coach used to carry paying passengers and light packages on journeys long enough to need a change of horses. It is strongly sprung and generally drawn by four horses although some versions are draw ...
that travelled a predetermined route from inn to inn, carrying passengers and mail. His omnibus had wooden benches that ran down the sides of the vehicle; passengers entered from the rear.
In 1828, Baudry went to Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, where he founded a company under the name ''Entreprise générale des omnibus de Paris'', while his son Edmond Baudry founded two similar companies in Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefectur ...
and in Lyon
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of t ...
.
A London newspaper reported on July 4, 1829, that "the new vehicle, called the ''omnibus'', commenced running this morning from Paddington to the City", operated by George Shillibeer
George Shillibeer (11 August 1797 – 21 August 1866) was an English coachbuilder.
Biography
Shillibeer was born in St Marylebone, London the son of Abraham and Elizabeth Shillibeer. Christened in St Marys Church, Marylebone on 22 October ...
.
The first omnibus service in New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
began in 1829, when Abraham Brower, an entrepreneur who had organized volunteer fire companies, established a route along Broadway
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
starting at Bowling Green
A bowling green is a finely laid, close-mown and rolled stretch of turf for playing the game of bowls.
Before 1830, when Edwin Beard Budding of Thrupp, near Stroud, UK, invented the lawnmower, lawns were often kept cropped by grazing sheep on ...
. Other American cities soon followed suit: Philadelphia in 1831, Boston in 1835 and Baltimore in 1844. In most cases, the city governments granted a private company—generally a small stableman already in the livery
A livery is an identifying design, such as a uniform, ornament, symbol or insignia that designates ownership or affiliation, often found on an individual or vehicle. Livery will often have elements of the heraldry relating to the individual or ...
or freight-hauling business—an exclusive franchise to operate public coaches along a specified route. In return, the company agreed to maintain certain minimum levels of service.
In 1832, the New York omnibus had a rival when the first tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
s, or streetcars started operation along Bowery
The Bowery () is a street and neighborhood in Lower Manhattan in New York City. The street runs from Chatham Square at Park Row, Worth Street, and Mott Street in the south to Cooper Square at 4th Street in the north.Jackson, Kenneth L. "B ...
, which offered the excellent improvement in amenity of riding on smooth iron rails rather than clattering over granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies undergro ...
setts, called "Belgian blocks". The streetcars were financed by John Mason, a wealthy banker, and built by an Irish-American contractor, John Stephenson. The Fifth Avenue Coach Company
The Fifth Avenue Coach Company was a bus operator in Manhattan, The Bronx, Queens, and Westchester County, New York, providing public transit between 1896 and 1954 after which services were taken over by the New York City Omnibus Corporation. It ...
introduced electric buses to Fifth Avenue
Fifth Avenue is a major and prominent thoroughfare in the borough of Manhattan in New York City. It stretches north from Washington Square Park in Greenwich Village to West 143rd Street in Harlem. It is one of the most expensive shopping stre ...
in New York in 1898.
In 1831, New Yorker Washington Irving
Washington Irving (April 3, 1783 – November 28, 1859) was an American short-story writer, essayist, biographer, historian, and diplomat of the early 19th century. He is best known for his short stories "Rip Van Winkle" (1819) and " The Legen ...
remarked of Britain's Reform Act
In the United Kingdom, Reform Act is most commonly used for legislation passed in the 19th century and early 20th century to enfranchise new groups of voters and to redistribute seats in the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. ...
(finally passed in 1832): "The great reform omnibus moves but slowly." Steam bus
A steam bus is a bus powered by a steam engine. Early steam-powered vehicles designed for carrying passengers were more usually known as steam carriages, although this term was sometimes used to describe other early experimental vehicles too.
H ...
es emerged in the 1830s as competition to the horse-drawn buses.
The omnibus extended the reach of the emerging cities. The walk from the former village of Paddington
Paddington is an area within the City of Westminster, in Central London. First a medieval parish then a metropolitan borough, it was integrated with Westminster and Greater London in 1965. Three important landmarks of the district are Paddi ...
to the business heart of London in the City was a long one, even for a young man in good condition. The omnibus thus offered the suburbs more access to the inner city. The omnibus encouraged urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly t ...
. Socially, the omnibus put city-dwellers, even if for only half an hour, into previously-unheard-of physical intimacy with strangers, squeezing them together knee-to-knee. Only the very poor remained excluded. A new division in urban society now came to the fore, dividing those who kept carriages from those who did not. The idea of the "carriage trade", the folk who never set foot in the streets, who had goods brought out from the shops for their appraisal, has its origins in the omnibus crush.
Motorbus
John D. Hertz
John Daniel Hertz, Sr. (April 10, 1879October 8, 1961) was an American businessman, thoroughbred racehorse owner and breeder, and philanthropist.
Biography
Born Sándor Herz to a Jewish family in Szklabinya, Austria-Hungary (today Sklabiňa, a ...
founded the Yellow Coach Manufacturing Company
The Yellow Coach Manufacturing Company (informally Yellow Coach) was an early manufacturer of passenger buses in the United States. Between 1923 and 1943, Yellow Coach built transit buses, electric-powered trolley buses, and parlor coaches.
Fou ...
in 1923 and then sold a majority of shares to General Motors in 1925.
From the 1920s, General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
and others started buying up streetcar systems across the United States with a view to replacing them with buses in what became known as the Great American Streetcar Scandal
The General Motors streetcar conspiracy refers to the convictions of General Motors (GM) and related companies that were involved in the monopolizing of the sale of buses and supplies to National City Lines (NCL) and subsidiaries, as well as to ...
. This was accompanied by a continuing series of technical improvements: pneumatic "balloon" tires during the early 1920s, monocoque body construction in 1931, automatic transmission in 1936, diesel engines in 1936, 50+ passengers in 1948, and air suspension in 1953.
The arrest of Rosa Parks
Rosa Louise McCauley Parks (February 4, 1913 – October 24, 2005) was an American activist in the civil rights movement best known for her pivotal role in the Montgomery bus boycott. The United States Congress has honored her as "the ...
in 1955 for not giving up her seat to a white man on a public bus is considered one of the catalysts of the Civil Rights Movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination ...
within the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
.
Types of services
 The names of different types of bus services vary according to local tradition or marketing, although services can be classified into basic types based on route length, frequency, the purpose of use and type of bus used.
The names of different types of bus services vary according to local tradition or marketing, although services can be classified into basic types based on route length, frequency, the purpose of use and type of bus used.
Urban transport
 *
* Transit bus
Transit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Transit'' (1979 film), a 1979 Israeli film
* ''Transit'' (2005 film), a film produced by MTV and Staying-Alive about four people in countries in the world
* ''Transit'' (2006 film), a 2006 ...
is the most common type of public transport bus service and is used to transport large numbers of people in urban areas, or to and from the suburbs to population centres. These buses normally run on fixed routes within an urban area.
* Park and ride
A park and ride, also known as incentive parking or a commuter lot, is a parking lot with public transport connections that allows commuting, commuters and other people heading to city centres to leave their vehicles and transfer to a bus, Rail t ...
bus services are designed to provide an onward passenger journey from a parking lot
A parking lot (American English) or car park (British English), also known as a car lot, is a cleared area intended for parking vehicles. The term usually refers to an area dedicated only for parking, with a durable or semi-durable surface ...
. These may be branded as shuttle or express services, or part of the standard bus network.
* Share taxi
Share may refer to:
* Share, to make joint use of a resource (such as food, money, or space); see Sharing
* Share (finance), a stock or other financial security (such as a mutual fund)
* Share, Kwara, a town and LGA in Kwara State, Nigeria
Share m ...
bus services are designed to run as flexible high capacity vehicles usually using minibuses to any point of a person's wish instead of a fixed route. Most common examples of share taxis include public light buses
The public light bus or minibus is a public transport service in Hong Kong. It uses minibuses to serve areas that standard Hong Kong bus lines cannot reach efficiently. The vehicles are colloquially known by the code-switch ' (Van Jái) lite ...
in Hong Kong where the red topped ones act as a share taxi as opposed to green topped ones which are on fixed routes.
* Feeder bus services are designed to pick up passengers in a certain locality and take them to a transfer point where they make an onward journey on a trunk service. This can be another bus, or a rail-based service such as a tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
, rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT), also known as heavy rail or metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport generally found in urban areas. A rapid transit system that primarily or traditionally runs below the surface may be c ...
or train
In rail transport, a train (from Old French , from Latin , "to pull, to draw") is a series of connected vehicles that run along a railway track and Passenger train, transport people or Rail freight transport, freight. Trains are typically pul ...
. Feeder buses may act as part of a wider local network, or a regional coach network.
*Bus rapid transit
Bus rapid transit (BRT), also called a busway or transitway, is a bus-based public transport system designed to have much more capacity, reliability and other quality features than a conventional bus system. Typically, a BRT system includes ...
(BRT) is the application of a range of infrastructure and marketing measures to produce public transport bus services that approach the operating characteristics and capacity of rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT), also known as heavy rail or metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport generally found in urban areas. A rapid transit system that primarily or traditionally runs below the surface may be c ...
systems.
Express bus service
 An express bus service (also known as express commuter service, commuter bus service, or suburban bus service) is a fixed-route
An express bus service (also known as express commuter service, commuter bus service, or suburban bus service) is a fixed-route bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
service that is intended to run faster than normal bus services between the same two commuter or destination points, typically on longer-distance routes.
Express buses operate on a faster schedule by not making as many stops as normal bus services and often taking quicker routes, such as along freeway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms ...
s, or by using dedicated lanes or roadways. Express buses may also operate out of park and ride
A park and ride, also known as incentive parking or a commuter lot, is a parking lot with public transport connections that allows commuting, commuters and other people heading to city centres to leave their vehicles and transfer to a bus, Rail t ...
s, in some cases only during rush hour
A rush hour (American English, British English) or peak hour (Australian English) is a part of the day during which traffic congestion on roads and crowding on public transport is at its highest. Normally, this happens twice every weekday: on ...
in the peak direction.
Fare
A fare is the fee paid by a passenger for use of a public transport system: rail, bus, taxi, etc. In the case of air transport, the term airfare is often used. Fare structure is the system set up to determine how much is to be paid by various pa ...
s on express bus services may be higher than normal parallel services. Many express buses act as precursors to bus rapid transit
Bus rapid transit (BRT), also called a busway or transitway, is a bus-based public transport system designed to have much more capacity, reliability and other quality features than a conventional bus system. Typically, a BRT system includes ...
lines and employ a proof-of-payment
Proof-of-payment (POP) or proof-of-fare (POF) is an honor-based fare collection system used on many public transportation systems. Instead of checking each passenger as they enter a fare control zone, passengers are required to carry a ticket, p ...
scheme, requiring passengers to purchase tickets before boarding the bus, speeding up the service. These services may also use suburban coaches that feature amenities like comfortable seating and wireless Internet
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most ...
service, particularly on routes that travel long distances at higher speeds without stopping.
In many cases, an express bus service is identified by a letter before or after the regular route number. For example, in Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountain ...
, the letters L (as in L90), E (as in E70) and X (as in 610X or X84). L indicates that the bus runs along the normal route, while E and X indicate that the bus runs along a more direct route. In New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, express buses operate using coaches from Motor Coach Industries
Motor Coach Industries (MCI) is a North American multinational bus manufacturer, specializing in production of motorcoaches. Best known for coaches produced for intercity transit and commuter buses, MCI produces coaches for a variety of appli ...
and Prevost Car
Prevost (, , formally known as Prevost Car) is a Canadian manufacturer of touring coaches and bus shells for high-end motorhomes and specialty conversions. The company is a subsidiary of the Volvo Buses division of the Volvo Group.
History
...
, and all except the operate along highways, sometimes for a large portion of the route. For example, the Super Expresses, the all operate on highways for most of their route. Many transit systems may also use a specific number before or after the regular route number. For example, in Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the ancho ...
, the number "9" (as in 995) goes before the regular route number to display an express bus service.
Long distance transport
Long-distance coach services (US: Intercity bus line) are bus services operated over long distances between cities. These services can form the mainstay of the travel network in countries with poorrailway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
infrastructure. Different coach operators may band together on a franchise
Franchise may refer to:
Business and law
* Franchising, a business method that involves licensing of trademarks and methods of doing business to franchisees
* Franchise, a privilege to operate a type of business such as a cable television p ...
or connecting basis to offer a brand
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that distinguishes one seller's good or service from those of other sellers. Brands are used in business, marketing, and advertising for recognition and, importantly, to create an ...
ed network that covers large distances, such as Trailways
The Trailways Transportation System is an American network of approximately 70 independent bus companies that have entered into a brand licensing agreement. The company is headquartered in Fairfax, Virginia.
History
The predecessor to Trailwa ...
and National Express
National Express Group is a British multinational public transport company headquartered in Birmingham, England. It operates bus, coach, train and tram services in the United Kingdom, Ireland (National Express operates Eurolines in conjunction ...
. These networks can even operate internationally, such as Eurolines
Eurolines is a brand of intercity bus service owned by an international non-profit organisation formed under Belgian law. Using the Eurolines brand, partner bus companies operate service to over 600 destinations in 36 countries of Europe, as well ...
of Europe. Interurban bus services are primarily aimed at linking together one or more urban centres, and as such are often run as express services while travelling in the intermediate rural areas, or even only call at two terminal points as a long distance shuttle service. Some interurban services may be operated as high specification luxury services, using coaches
Coach may refer to:
Guidance/instruction
* Coach (sport), a director of athletes' training and activities
* Coaching, the practice of guiding an individual through a process
** Acting coach, a teacher who trains performers
Transportation
* Coac ...
, in order to compete with railways
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
, or link areas not rail connected. Interurban services may often terminate in central bus station
A bus station or a bus interchange is a structure where city or intercity buses stop to pick up and drop off passengers. While the term bus depot can also be used to refer to a bus station, it generally refers to a bus garage. A bus station is l ...
s rather than on street stops. Other interurban services may specifically call at intermediate village
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to ...
s and may use slower transit buses or dual purpose buses.
Specialist services
*School bus
A school bus is any type of bus owned, leased, contracted to, or operated by a school or school district. It is regularly used to transport students to and from school or school-related activities, but not including a charter bus or transit bus ...
es transport children
A child ( : children) is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. The legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person younger ...
to and from school
A school is an educational institution designed to provide learning spaces and learning environments for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compuls ...
. While many countries and school districts organise their own services, as school bus
A school bus is any type of bus owned, leased, contracted to, or operated by a school or school district. It is regularly used to transport students to and from school or school-related activities, but not including a charter bus or transit bus ...
es or charter bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
es, in some areas school bus services are implemented as special journeys on the normal public timetable, specially timed and routed to arrive and depart in coordination with the school bell
The ringing of a school bell announces important times to a school's students and staff, such as marking the beginnings and ends of the school day, class period, and breaks.
In some schools it may take the form of a physical bell, usually e ...
. Only the latter is commonly referred to as "public transport".
* Shuttle buses are any type of bus service intended primarily to shuttle passengers between two fixed points. These can be bus or coach operated, but are usually short or medium distance journeys taking less than an hour. Shuttle buses will usually link with other transport hub
A transport hub is a place where passengers and cargo are exchanged between vehicles and/or between transport modes. Public transport hubs include railway stations, rapid transit stations, bus stops, tram stops, airports and ferry slips. F ...
s, such as airport shuttle buses. A common use of a shuttle bus is in towns or cities with multiple terminal train station
A train station, railway station, railroad station or depot is a railway facility where trains stop to load or unload passengers, freight or both. It generally consists of at least one platform, one track and a station building providing suc ...
s or bus station
A bus station or a bus interchange is a structure where city or intercity buses stop to pick up and drop off passengers. While the term bus depot can also be used to refer to a bus station, it generally refers to a bus garage. A bus station is l ...
s, for passenger interconnections. "Shuttle" as a brand
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that distinguishes one seller's good or service from those of other sellers. Brands are used in business, marketing, and advertising for recognition and, importantly, to create an ...
name is applied variously across several types of service.
* Post bus
A postbus is a public bus service that is operated as part of local mail delivery as a means of providing public transport in rural areas with lower levels of patronage, where a normal bus service would be uneconomic or inefficient. Postbus ser ...
services are services that also carry mail
The mail or post is a system for physically transporting postcards, letter (message), letters, and parcel (package), parcels. A postal service can be private or public, though many governments place restrictions on private systems. Since the mid ...
, often on rural
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry typically are describ ...
routes.
* Rail replacement bus services are often charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the rec ...
ed by railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
companies as alternate means of transport for rail passengers. This can be pre-planned to cover for scheduled track maintenance
A railway track (British English and International Union of Railways, UIC terminology) or railroad track (American English), also known as permanent way or simply track, is the structure on a Rail transport, railway or railroad consisting of ...
or other planned closures, or to cover for unplanned closures such as derailment
In rail transport, a derailment occurs when a rail vehicle such as a train comes off its rails. Although many derailments are minor, all result in temporary disruption of the proper operation of the railway system and they are a potentially ...
s.
IC Bus
IC Bus (originally IC Corporation) is an American bus manufacturer. Headquartered in Lisle, Illinois, IC is a wholly owned subsidiary of Navistar International. Established in 2002 by Navistar through the reorganization of subsidiary manufact ...
CE with International 3300 chassis school bus in America
File:Free Liverpool Shuttle liveried (mo 5015), operated by Veoila Transport, Custom Coaches 'CB60 Evo II' bodied Volvo B7RLE on Moore Street in Liverpool.jpg, A shuttle bus service in Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountain ...
File:Postbus.jpg, A postbus in St. Moritz
Operation
Scheduling
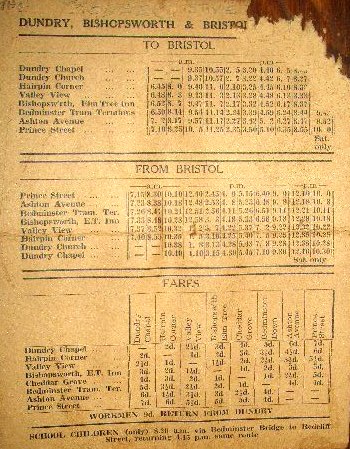
Many public bus services are run to a specifictimetable
A schedule or a timetable, as a basic time-management tool, consists of a list of times at which possible task (project management), tasks, events, or actions are intended to take place, or of a sequence of events in the chronological order ...
giving specific times of departure and arrival at waypoints along the route. These are often difficult to maintain in the event of traffic congestion
Traffic congestion is a condition in transport that is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. Traffic congestion on urban road networks has increased substantially since the 1950s. When traffic de ...
, breakdowns, on/off bus incidents, road blockages or bad weather. Predictable effects such as morning and evening rush hour
A rush hour (American English, British English) or peak hour (Australian English) is a part of the day during which traffic congestion on roads and crowding on public transport is at its highest. Normally, this happens twice every weekday: on ...
traffic are often accounted for in timetables using the past experience of the effects, although this then prevents the opportunity for drafting a ‘clock face’ timetable where the time of a bus is predictable at any time through the day. Predictable short term increases in passenger numbers may be dealt with by providing “duplicate” buses, where two or more buses operate the same slot in the timetable. Unpredictable problems resulting in delays and gaps in the timetabled service may be dealt with by ‘turning’ a bus early before it reaches it terminus
Terminus may refer to:
* Bus terminus, a bus station serving as an end destination
* Terminal train station or terminus, a railway station serving as an end destination
Geography
*Terminus, the unofficial original name of Atlanta, Georgia, United ...
, so that it can fill a gap in the opposite direction, meaning any passengers on the turned bus need to disembark and continue on a following bus. Also, depending on the location of the bus depot
A bus garage, also known as a bus depot, bus base or bus barn, is a facility where buses are stored and maintained. In many conurbations, bus garages are on the site of former car barns or tram sheds, where trams (streetcars) were stored, and ...
, replacement buses may be dispatched from the depot to fill in other gaps, starting the timetable part way along the route.
There is a common cliché
A cliché ( or ) is an element of an artistic work, saying, or idea that has become overused to the point of losing its original meaning or effect, even to the point of being weird or irritating, especially when at some earlier time it was consi ...
that people “wait all day, and then three come along at once”, in relation to a phenomenon where evenly timetabled bus services can develop a gap in service followed by buses turning up almost simultaneously. This occurs when the rush hour begins and numbers of passengers at a stop increases, increasing the loading time, and thus delay scheduled service. The following bus then catches up because it begins to be delayed less at stops due to fewer passengers waiting. This is called bus bunching
In public transport, bus bunching, clumping, convoying, piggybacking or platooning is a phenomenon whereby two or more transit vehicles (such as buses or trains) that were scheduled at regular intervals along a common route instead bunch togethe ...
. This is prevented in some cities such as Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
by assigning every stop arrival times where scheduled buses should arrive no earlier than specified.
Some services may have no specific departure times, the timetable giving the frequency of service on a route at particular phases of the day. This may be specified with departure times, but the over-riding factor is ensuring the regularity of buses arriving at stops. These are often the more frequent services, up to the busiest bus rapid transit
Bus rapid transit (BRT), also called a busway or transitway, is a bus-based public transport system designed to have much more capacity, reliability and other quality features than a conventional bus system. Typically, a BRT system includes ...
schemes. For headway-based schemes, problems can be managed by changing speed, delaying at stops and leap-frog
Leapfrog is a children's game in which players vault over each other's stooped backs.
History
Games of this sort have been called by this name since at least the late sixteenth century.level of adherence to timetables, and how often timetables may be changed. Operators and authorities may employ on-street bus inspectors to monitor adherence in real time. Service operators often have a control room, or in the case of large operations, route controllers, who can monitor the level of service on routes and can take remedial action if problems occur. This was made easier with the technological advances of
 The level and reliability of bus services are often dependent on the quality of the local road network and levels of
The level and reliability of bus services are often dependent on the quality of the local road network and levels of
 Bus drivers may be required to conduct
Bus drivers may be required to conduct
two way radio
A two-way radio is a radio that can both transmit and receive radio waves (a transceiver), unlike a broadcast receiver which only receives content. It is an audio (sound) transceiver, a transmitter and receiver in one unit, used for bidirection ...
contact with drivers, and vehicle tracking system
A vehicle tracking system combines the use of automatic vehicle location in individual vehicles with software that collects these fleet data for a comprehensive picture of vehicle locations. Modern vehicle tracking systems commonly use GPS or G ...
s.
Urban land-use planning policies are essential for the success of bus transit systems, particularly as mass transit is not feasible in low-density communities. Transportation planners estimate that to support local bus service every thirty minutes, there must be a residential housing density of seven dwelling units per acre.
Fixed infrastructure
Bus services have led to the implementation of various types of infrastructure now common in many urban and suburban settings. The most prevalent example is the ubiquitousbus stop
A bus stop is a place where buses stop for passengers to get on and off the bus. The construction of bus stops tends to reflect the level of usage, where stops at busy locations may have shelters, seating, and possibly electronic passenger ...
. Large interchanges have required the building of bus station
A bus station or a bus interchange is a structure where city or intercity buses stop to pick up and drop off passengers. While the term bus depot can also be used to refer to a bus station, it generally refers to a bus garage. A bus station is l ...
s. In roads and streets, infrastructure for buses has resulted in modifications to the kerb line such as protrusions and indentations, and even special kerb stones. Entire lanes or roads have been reserved for buses in bus lane
A bus lane or bus-only lane is a lane restricted to buses, often on certain days and times, and generally used to speed up public transport that would be otherwise held up by traffic congestion. The related term busway describes a roadway ...
s or busways
Busways is an Australian bus company operating services in Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis ...
. Bus fleets require large storage premises often located in urban areas, and may also make use of central works facilities.
Management
 The level and reliability of bus services are often dependent on the quality of the local road network and levels of
The level and reliability of bus services are often dependent on the quality of the local road network and levels of traffic congestion
Traffic congestion is a condition in transport that is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. Traffic congestion on urban road networks has increased substantially since the 1950s. When traffic de ...
, and the population density. Services may be organised on tightly regulated networks with restrictions on when and where services operate, while other services are operated on an ad hoc
Ad hoc is a Latin phrase meaning literally 'to this'. In English, it typically signifies a solution for a specific purpose, problem, or task rather than a generalized solution adaptable to collateral instances. (Compare with ''a priori''.)
Com ...
basis in the model of share taxi
Share may refer to:
* Share, to make joint use of a resource (such as food, money, or space); see Sharing
* Share (finance), a stock or other financial security (such as a mutual fund)
* Share, Kwara, a town and LGA in Kwara State, Nigeria
Share m ...
s.
Increasingly, technology is being used to improve the information provided to bus users, with vehicle tracking
A vehicle tracking system combines the use of automatic vehicle location in individual vehicles with software that collects these fleet data for a comprehensive picture of vehicle locations. Modern vehicle tracking systems commonly use GPS or G ...
technologies to assist with scheduling, and to achieve real-time integration with passenger information system
A passenger information system, or passenger information display system, is an automated system for supplying users of public transport with information about the nature and the state of a public transport service through visual, voice or other m ...
s that display service information at stops, inside buses, and to waiting passengers through personal mobile device
A mobile device (or handheld computer) is a computer small enough to hold and operate in the hand. Mobile devices typically have a flat LCD or OLED screen, a touchscreen interface, and digital or physical buttons. They may also have a physical ...
s or text messaging
Text messaging, or texting, is the act of composing and sending electronic messages, typically consisting of alphabetic and numeric characters, between two or more users of mobile devices, desktops/laptops, or another type of compatible compute ...
.
Fare models
 Bus drivers may be required to conduct
Bus drivers may be required to conduct fare
A fare is the fee paid by a passenger for use of a public transport system: rail, bus, taxi, etc. In the case of air transport, the term airfare is often used. Fare structure is the system set up to determine how much is to be paid by various pa ...
collection, inspect a travel pass or free travel pass
A free travel pass is the privilege of a certain class of passengers to use a public transport service without paying a fare or presenting a ticket. They may need to present an identification card produced by their employer or other sponsoring org ...
, or oversee stored-value card
A stored-value card (SVC) is a payment card with a monetary value stored on the card itself, not in an external account maintained by a financial institution. This means no network access is required by the payment collection terminals as funds ...
debiting. This may require the fitting of equipment to the bus. Alternatively, this duty and equipment may be delegated to a conductor who rides on the bus. In other areas, public transport buses may operate on a zero-fare
Free public transport, often called fare-free public transit or zero-fare public transport, refers to public transport funded in full by means other than by collecting fares from passengers. It may be funded by national, regional or local gove ...
basis, or ticket validation may be through the use of on-board/off-board proof-of-payment
Proof-of-payment (POP) or proof-of-fare (POF) is an honor-based fare collection system used on many public transportation systems. Instead of checking each passenger as they enter a fare control zone, passengers are required to carry a ticket, p ...
systems, checked by roving ticket controller
Proof-of-payment (POP) or proof-of-fare (POF) is an honor-based fare collection system used on many public transportation systems. Instead of checking each passenger as they enter a fare control zone, passengers are required to carry a ticket, p ...
s who board and alight buses at random.
In some competitive systems, an incumbent
The incumbent is the current holder of an official, office or position, usually in relation to an election. In an election for president, the incumbent is the person holding or acting in the office of president before the election, whether seek ...
operator may introduce a "low-cost unit" paying lower wages, in order to be able to offer lower fares, using older buses cascaded from a main fleet to also reduce costs. In some sectors, operators such as Megabus (both in the UK and in North America) have attempted to emulate the low-cost airlines model in order to attract passengers through low fares, by offering no-frills bus services.
Ownership
Public transport bus operation is differentiated from other bus operation by the fact the owner or driver of a bus is employed by or contracted to an organisation whose main public duty or commercial interest is to provide a public transport service for passengers to turn up and use, rather than fulfilling private contracts between the bus operator and user. Public transport buses are operated as acommon carrier
A common carrier in common law countries (corresponding to a public carrier in some civil law systems,Encyclopædia Britannica CD 2000 "Civil-law public carrier" from "carriage of goods" usually called simply a ''carrier'') is a person or compan ...
under a contract of carriage
A contract of carriage is a contract between a carrier of goods or passengers and the consignor, consignee or passenger. Contracts of carriage typically define the rights, duties and liabilities of parties to the contract, addressing topics such ...
between the passenger and the operator.
The owners of public transport buses may be the municipal
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
authority or transit authority
A transit district or transit authority is a government agency or a public-benefit corporation created for the purpose of providing public transportation within a specific region.
A transit district may operate bus, rail or other types of tra ...
that operates them, or they may be owned by individuals or private companies who operate them on behalf of the authorities on a franchise
Franchise may refer to:
Business and law
* Franchising, a business method that involves licensing of trademarks and methods of doing business to franchisees
* Franchise, a privilege to operate a type of business such as a cable television p ...
or contract
A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties that creates, defines, and governs mutual rights and obligations between them. A contract typically involves the transfer of goods, services, money, or a promise to tran ...
basis. Other buses may be run entirely as private concerns, either on an owner-operator
An owner-operator is a small business or microbusiness owner who also runs the day-to-day operations of the company. Owner-operators are found in many business models and franchising companies in many different industries like restaurant chains, ...
basis, or as multi-national transport groups. Some countries have specifically deregulated their bus services, allowing private operators to provide public bus services. In this case, an authority may make up the shortfall in levels of private service provision by funding or operating ‘socially necessary’ services, such as early or late services, on the weekends, or less busy routes. Ownership/operation of public transport buses can also take the form of a charitable operation or not for profit
A nonprofit organization (NPO) or non-profit organisation, also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, in co ...
social enterprise
A social enterprise is an organization that applies commercial strategies to maximize improvements in financial, social and environmental well-being. This may include maximizing social impact alongside profits for co-owners.
Social enterprises ca ...
s.
Larger operations may have fleets of thousands of vehicles. At its peak in the 1950s, the London Transport Executive
The London Transport Executive was the organisation responsible for public transport in Greater London, England between 1948 and 1962. In common with all London transport authorities from 1933 to 2000, the public name and operational brand of ...
owned a bus fleet of 8,000 buses, the largest in the world. Many small operators have only a few vehicles or a single bus owned by an owner-driver.
Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation
Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (APSRTC) is the state-owned road transport corporation in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. Its headquarters is located at NTR Administrative Block of RTC House in Pandit Nehru bus station of ...
holds the Guinness world record
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a reference book published annually, listing world ...
of having the largest fleet of buses with 22,555 buses.
Regulation
In all cases in thedeveloped world
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
, public transport bus services are usually subject to some form of legal control in terms of vehicle safety standards and method of operation, and possibly the level of fare
A fare is the fee paid by a passenger for use of a public transport system: rail, bus, taxi, etc. In the case of air transport, the term airfare is often used. Fare structure is the system set up to determine how much is to be paid by various pa ...
s charged and routes operated.
Bus services are being made accessible
Accessibility is the design of products, devices, services, vehicles, or environments so as to be usable by people with disabilities. The concept of accessible design and practice of accessible development ensures both "direct access" (i.e ...
, often in response to rules and regulations in disability discrimination laws. This has resulted in the introduction of paratransit
Paratransit is the term used in North America, also known by other names such as community transport ( UK) for transportation services that supplement fixed-route mass transit by providing individualized rides without fixed routes or timetables. ...
services and low-floor bus
A low-floor bus is a bus or trolleybus that has no steps between the ground and the floor of the bus at one or more entrances, and low floor for part or all of the passenger cabin. A bus with a partial low floor may also be referred to as a low- ...
es to support passengers who are elderly, have a disability
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be Cognitive disability, cognitive, Developmental disability, dev ...
, or a medical condition.
Some transit agencies have also started to install bike racks in the front of buses that usually holds two bicycles. Passengers would be able to place their bicycle on the racks when riding to avoid taking up space during rush hour.
Safety
The research conducted inMontreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian ...
(Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
) showed that travelling by bus is safer than travelling by car
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded as ...
, for vehicle occupants but also for pedestrian
A pedestrian is a person traveling on foot, whether walking or running. In modern times, the term usually refers to someone walking on a road or pavement, but this was not the case historically.
The meaning of pedestrian is displayed with ...
s and cyclist
Cycling, also, when on a two-wheeled bicycle, called bicycling or biking, is the use of cycles for transport, recreation, exercise or sport. People engaged in cycling are referred to as "cyclists", "bicyclists", or "bikers". Apart from two ...
s. There were 16 times more injured car occupants than bus occupants. Most pedestrians (95%) and cyclists (96%) were injured by a car. Looking at major injuries only (excluding minor injuries), there were 28 times more injured car occupants than bus occupants. Cars were associated with three cyclist deaths and 42 pedestrian deaths while buses were associated with no cyclist deaths and four pedestrian deaths.
See also
*Straddling bus
The Transit Elevated Bus (TEB) () was a proposed new bus concept where a guided bus straddles above road traffic, giving it the alternative names such as straddling bus, straddle bus, land airbus, or tunnel bus by international media.
A trial was ...
* Trolley bus
A trolleybus (also known as trolley bus, trolley coach, trackless trolley, trackless tramin the 1910s and 1920sJoyce, J.; King, J. S.; and Newman, A. G. (1986). ''British Trolleybus Systems'', pp. 9, 12. London: Ian Allan Publishing. .or troll ...
* Express train
An express train is a type of passenger train that makes a small number of stops between its origin and destination stations, usually major destinations, allowing faster service than Local train, local trains that stop at most or all of the s ...
* Limited stop
In public transit, particularly bus, tram, or train transportation, a limited-stop (or sometimes referred to as semi-fast) service is a trip pattern that stops less frequently than a local service. Many limited-stop or semi-fast services are a com ...
* Destination sign
A destination sign (North American English) or destination indicator/destination blind (British English) is a sign mounted on the front, side or rear of a public transport vehicle, such as a bus, tram/streetcar or light rail vehicle, that dis ...
* Bus rapid transit
Bus rapid transit (BRT), also called a busway or transitway, is a bus-based public transport system designed to have much more capacity, reliability and other quality features than a conventional bus system. Typically, a BRT system includes ...
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Public Transport Bus ServiceBus service
Public transport bus services are generally based on regular operation of transit buses along a route calling at agreed bus stops according to a published public transport timetable.
History of buses Origins
While there are indications ...
Types of bus service