Psychedelic movement on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Psychedelia refers to the psychedelic subculture of the 1960s and the
Psychedelia refers to the psychedelic subculture of the 1960s and the
 The term was first coined as a noun in 1956 by
The term was first coined as a noun in 1956 by
 Advances in printing and photographic technology in the 1960s saw the traditional
Advances in printing and photographic technology in the 1960s saw the traditional  Blues rock singer Janis Joplin had a psychedelic car, a Porsche 356. The trend also extended to motor vehicles. The earliest, and perhaps most famous of all psychedelic vehicles was the famous " Further" bus, driven by
Blues rock singer Janis Joplin had a psychedelic car, a Porsche 356. The trend also extended to motor vehicles. The earliest, and perhaps most famous of all psychedelic vehicles was the famous " Further" bus, driven by
 A psychedelic festival is a gathering that promotes
A psychedelic festival is a gathering that promotes
"Neotrance and the Psychedelic Festival."
''Dancecult: Journal of Electronic Dance Music Culture,'' 1(1) (2009). These festivals often emphasize the ideals of peace, love, unity, and respect. Notable psychedelic festivals include the biennial Boom Festival in Portugal,
"Psychedelic Science"
'' Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies: MAPS'' Retrieved 2019-09-27. devoted specifically to research of psychedelics in scientific and medical fields, in 2013.
Erowid''Science & Consciousness Review'', The Neurochemistry of Psychedelic Experience
Artists interpretation of psychedelic experiences. Online archive: Religion and Psychoactive Sacraments
*''Magic Mushrooms and Reindeer - Weird Nature''. A short video on the use of ''
{{Hippies Psychedelia, Subcultures Underground culture

 Psychedelia refers to the psychedelic subculture of the 1960s and the
Psychedelia refers to the psychedelic subculture of the 1960s and the psychedelic experience
A psychedelic experience (known colloquially as a trip) is a temporary altered state of consciousness induced by the consumption of a psychedelic substance (most commonly LSD, mescaline, psilocybin mushrooms, or DMT). For example, an acid tr ...
. This includes psychedelic art
Psychedelic art (also known as psychedelia) is art, graphics or visual displays related to or inspired by psychedelic experiences and hallucinations known to follow the ingestion of psychedelic drugs such as LSD, psilocybin, and DMT. The word ...
, psychedelic music
Psychedelic music (sometimes called psychedelia) is a wide range of popular music styles and genres influenced by 1960s psychedelia, a subculture of people who used psychedelic drugs such as LSD, psilocybin mushrooms, mescaline, and cannabis ...
and style of dress during that era. This was primarily generated by people who used psychedelic drug
Psychedelics are a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary states of consciousness (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips").Pollan, Michael (2018). ''How to Change Your Mind: What the New Science ...
s such as LSD, mescaline
Mescaline or mescalin (3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine) is a naturally occurring psychedelic protoalkaloid of the substituted phenethylamine class, known for its hallucinogenic effects comparable to those of LSD and psilocybin.
Biological ...
(found in peyote
The peyote (; ''Lophophora williamsii'' ) is a small, spineless cactus which contains psychoactive alkaloids, particularly mescaline. ''Peyote'' is a Spanish word derived from the Nahuatl (), meaning "caterpillar cocoon", from a root , "to g ...
) and psilocybin
Psilocybin ( , ) is a naturally occurring psychedelic prodrug compound produced by more than 200 species of fungi. The most potent are members of the genus ''Psilocybe'', such as '' P. azurescens'', '' P. semilanceata'', and '' P.&n ...
(found in magic mushrooms
Psilocybin mushrooms, commonly known as magic mushrooms, are a polyphyletic informal group of fungi that contain psilocybin which turns into psilocin upon ingestion. Biological genera containing psilocybin mushrooms include ''Psilocybe'', '' P ...
) and also non-users who were participants and aficionados of this subculture. Psychedelic art and music typically recreate or reflect the experience of altered consciousness. Psychedelic art uses highly distorted, surreal visuals, bright color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are assoc ...
s and full spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of color ...
s and animation (including cartoon
A cartoon is a type of visual art that is typically drawn, frequently animated, in an unrealistic or semi-realistic style. The specific meaning has evolved over time, but the modern usage usually refers to either: an image or series of imag ...
s) to evoke, convey, or enhance the psychedelic experience. Psychedelic music uses distorted electric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar (however combinations of the two - a semi-acoustic guitar and an electric acoustic gu ...
, Indian music
Owing to India's vastness and diversity, Indian music encompasses numerous genres in multiple varieties and forms which include classical music, folk ( Bollywood), rock, and pop. It has a history spanning several millennia and developed ov ...
elements such as the sitar
The sitar ( or ; ) is a plucked stringed instrument, originating from the Indian subcontinent, used in Hindustani classical music. The instrument was invented in medieval India, flourished in the 18th century, and arrived at its present form i ...
, tabla
A tabla, bn, তবলা, prs, طبلا, gu, તબલા, hi, तबला, kn, ತಬಲಾ, ml, തബല, mr, तबला, ne, तबला, or, ତବଲା, ps, طبله, pa, ਤਬਲਾ, ta, தபலா, te, తబల� ...
, electronic effects, sound effect
A sound effect (or audio effect) is an artificially created or enhanced sound, or sound process used to emphasize artistic or other content of films, television shows, live performance, animation, video games, music, or other media. Traditi ...
s and reverb
Reverberation (also known as reverb), in acoustics, is a persistence of sound, after a sound is produced. Reverberation is created when a sound or signal is reflected causing numerous reflections to build up and then decay as the sound is abs ...
, and elaborate studio effects, such as playing tapes backwards or panning the music from one side to another.
A psychedelic experience
A psychedelic experience (known colloquially as a trip) is a temporary altered state of consciousness induced by the consumption of a psychedelic substance (most commonly LSD, mescaline, psilocybin mushrooms, or DMT). For example, an acid tr ...
is characterized by the striking perception of aspects of one's mind previously unknown, or by the creative exuberance of the mind liberated from its ostensibly ordinary fetters. Psychedelic states are an array of experiences including changes of perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system, ...
such as hallucination
A hallucination is a perception in the absence of an external stimulus that has the qualities of a real perception. Hallucinations are vivid, substantial, and are perceived to be located in external objective space. Hallucination is a combinati ...
s, synesthesia
Synesthesia (American English) or synaesthesia (British English) is a perceptual phenomenon in which stimulation of one sensory or cognitive pathway leads to involuntary experiences in a second sensory or cognitive pathway. People who rep ...
, altered states of awareness or focused consciousness, variation in thought patterns, trance
Trance is a state of semi-consciousness in which a person is not self-aware and is either altogether unresponsive to external stimuli (but nevertheless capable of pursuing and realizing an aim) or is selectively responsive in following the dir ...
or hypnotic
Hypnotic (from Greek ''Hypnos'', sleep), or soporific drugs, commonly known as sleeping pills, are a class of (and umbrella term for) psychoactive drugs whose primary function is to induce sleep (or surgical anesthesiaWhen used in anesthesia ...
states, mystical
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute, but may refer to any kind of ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight in u ...
states, and other mind alterations. These processes can lead some people to experience changes in mental operation defining their self-identity (whether in momentary acuity or chronic development) different enough from their previous normal state that it can excite feelings of newly formed understanding such as revelation
In religion and theology, revelation is the revealing or disclosing of some form of truth or knowledge through communication with a deity or other supernatural entity or entities.
Background
Inspiration – such as that bestowed by God on th ...
, enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
, confusion
In medicine, confusion is the quality or state of being bewildered or unclear. The term "acute mental confusion"
, and psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior ...
. Individuals who use psychedelic drugs for spiritual purposes or self-discovery are commonly referred to as ''psychonaut
Psychonautics (from the Ancient Greek ' 'soul, spirit, mind' and ' 'sailor, navigator') refers both to a methodology for describing and explaining the subjective effects of altered states of consciousness, including those induced by meditati ...
s''.
Etymology
 The term was first coined as a noun in 1956 by
The term was first coined as a noun in 1956 by psychiatrist
A psychiatrist is a physician who specializes in psychiatry, the branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, study, and treatment of mental disorders. Psychiatrists are physicians and evaluate patients to determine whether their ...
Humphry Osmond as an alternative descriptor for hallucinogenic drugs in the context of psychedelic psychotherapy
Psychedelic therapy (or psychedelic-assisted therapy) refers to the proposed use of psychedelic drugs, such as psilocybin, MDMA, LSD, and ayahuasca, to treat mental disorders. As of 2021, psychedelic drugs are controlled substances in most cou ...
. It is irregularly derived from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
words ψυχή ''psychḗ'' 'soul, mind' and δηλείν ''dēleín'' 'to manifest', with the meaning "mind manifesting," the implication being that psychedelics can develop unused potentials of the human mind. The term was loathed by American ethnobotanist
Ethnobotany is the study of a region's plants and their practical uses through the traditional knowledge of a local culture and people. An ethnobotanist thus strives to document the local customs involving the practical uses of local flora for m ...
Richard Schultes but championed by American psychologist Timothy Leary
Timothy Francis Leary (October 22, 1920 – May 31, 1996) was an American psychologist and author known for his strong advocacy of psychedelic drugs. Evaluations of Leary are polarized, ranging from bold oracle to publicity hound. He was "a her ...
.
Seeking a name for the experience induced by LSD, Osmond contacted Aldous Huxley
Aldous Leonard Huxley (26 July 1894 – 22 November 1963) was an English writer and philosopher. He wrote nearly 50 books, both novels and non-fiction works, as well as wide-ranging essays, narratives, and poems.
Born into the prominent Huxle ...
, a personal acquaintance and advocate for the therapeutic use of the substance. Huxley coined the term "phanerothyme," from the Greek terms for "manifest" (φανερός) and "spirit" (θύμος). In a letter to Osmond, he wrote:
To which Osmond responded:
It was on this term that Osmond eventually settled, because it was "clear, euphonious and uncontaminated by other associations." This mongrel spelling of the word 'psychedelic' was loathed by American ethnobotanist
Ethnobotany is the study of a region's plants and their practical uses through the traditional knowledge of a local culture and people. An ethnobotanist thus strives to document the local customs involving the practical uses of local flora for m ...
Richard Evans Schultes
Richard Evans Schultes (''SHULL-tees'';Jonathan Kandell ''The New York Times'', April 13, 2001, Accessed April 26, 2020. January 12, 1915 – April 10, 2001) was an American biologist. He may be considered the father of modern ethnobotany. He is ...
, but championed by Timothy Leary, who thought it sounded better. Due to the expanded use of the term "psychedelic" in pop culture and a perceived incorrect verbal formulation, Carl A.P. Ruck, Jeremy Bigwood, Danny Staples
(Blaise) Daniel "Danny" Staples (13 July 1948 – December 2005Obituary ''Boston G ...
, Jonathan Ott
Jonathan Ott (born 1949 in Hartford, Connecticut) is an ethnobotanist, writer, translator, publisher, natural products chemist and botanical researcher in the area of entheogens and their cultural and historical uses, and helped coin the term "' ...
, and R. Gordon Wasson proposed the term "entheogen
Entheogens are psychoactive substances that induce alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, or behavior for the purposes of engendering spiritual development or otherwiseRätsch, Christian, ''The Encyclopedia of Psychoact ...
" to describe the religious or spiritual experience produced by such substances.
History
From the second half of the 1950s,Beat Generation
The Beat Generation was a literary subculture movement started by a group of authors whose work explored and influenced American culture and politics in the post-war era. The bulk of their work was published and popularized by Silent Generat ...
writers like William Burroughs
William Seward Burroughs II (; February 5, 1914 – August 2, 1997) was an American writer and visual artist, widely considered a primary figure of the Beat Generation and a major postmodern author who influenced popular cultur ...
, Jack Kerouac
Jean-Louis Lebris de Kérouac (; March 12, 1922 – October 21, 1969), known as Jack Kerouac, was an American novelist and poet who, alongside William S. Burroughs and Allen Ginsberg, was a pioneer of the Beat Generation.
Of French-Canadian anc ...
and Allen Ginsberg
Irwin Allen Ginsberg (; June 3, 1926 – April 5, 1997) was an American poet and writer. As a student at Columbia University in the 1940s, he began friendships with William S. Burroughs and Jack Kerouac, forming the core of the Beat Genera ...
wrote about and took drugs, including cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: '' Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternativel ...
and Benzedrine
Amphetamine (contracted from alpha- methylphenethylamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. It is also commonly used a ...
, raising awareness and helping to popularise their use. In the same period Lysergic acid diethylamide
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), also known colloquially as acid, is a potent psychedelic drug. Effects typically include intensified thoughts, emotions, and sensory perception. At sufficiently high dosages LSD manifests primarily mental, v ...
, better known as LSD, or "acid" (at the time a legal drug), began to be used in the US and UK as an experimental treatment, initially promoted as a potential cure for mental illness. In the early 1960s the use of LSD and other hallucinogens was advocated by proponents of the new "consciousness expansion", such as Timothy Leary
Timothy Francis Leary (October 22, 1920 – May 31, 1996) was an American psychologist and author known for his strong advocacy of psychedelic drugs. Evaluations of Leary are polarized, ranging from bold oracle to publicity hound. He was "a her ...
, Alan Watts
Alan Wilson Watts (6 January 1915 – 16 November 1973) was an English writer, speaker and self-styled "philosophical entertainer", known for interpreting and popularising Japanese, Chinese and Indian traditions of Buddhist, Taoist, and Hindu ...
, Aldous Huxley
Aldous Leonard Huxley (26 July 1894 – 22 November 1963) was an English writer and philosopher. He wrote nearly 50 books, both novels and non-fiction works, as well as wide-ranging essays, narratives, and poems.
Born into the prominent Huxle ...
and Arthur Koestler
Arthur Koestler, (, ; ; hu, Kösztler Artúr; 5 September 1905 – 1 March 1983) was a Hungarian-born author and journalist. Koestler was born in Budapest and, apart from his early school years, was educated in Austria. In 1931, Koestler join ...
, their writings profoundly influenced the thinking of the new generation of youth. There had long been a culture of drug use among jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a majo ...
and blues musicians, and use of drugs (including cannabis, peyote
The peyote (; ''Lophophora williamsii'' ) is a small, spineless cactus which contains psychoactive alkaloids, particularly mescaline. ''Peyote'' is a Spanish word derived from the Nahuatl (), meaning "caterpillar cocoon", from a root , "to g ...
, mescaline
Mescaline or mescalin (3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine) is a naturally occurring psychedelic protoalkaloid of the substituted phenethylamine class, known for its hallucinogenic effects comparable to those of LSD and psilocybin.
Biological ...
and LSD) had begun to grow among folk and rock musicians, who also began to include drug references in their songs.
By the mid-1960s, the psychedelic life-style had already developed in California, and an entire subculture developed. This was particularly true in San Francisco, due in part to the first major underground LSD factory, established there by Owsley Stanley
Augustus Owsley Stanley III (January 19, 1935 – March 12, 2011) was an American-Australian audio engineer and clandestine chemist. He was a key figure in the San Francisco Bay Area hippie movement during the 1960s and played a pivotal role ...
. There was also an emerging music scene of folk clubs, coffee houses and independent radio stations catering to a population of students at nearby Berkeley, and to free thinkers that had gravitated to the city.R. Unterberger, ''Eight Miles High: Folk-Rock's Flight from Haight-Ashbury to Woodstock'' (London: Backbeat Books, 2003), , pp. 11–13. From 1964, the Merry Pranksters
The Merry Pranksters were comrades and followers of American author Ken Kesey in 1964.
Ken Kesey and the Merry Pranksters lived communally at Kesey's homes in California and Oregon, and are noted for the sociological significance of a lengthy roa ...
, a loose group that developed around novelist Ken Kesey
Ken Elton Kesey (September 17, 1935 – November 10, 2001) was an American novelist, essayist and countercultural figure. He considered himself a link between the Beat Generation of the 1950s and the hippies of the 1960s.
Kesey was born ...
, sponsored the Acid Tests, a series of events based around the taking of LSD (supplied by Stanley), accompanied by light shows, film projection and discordant, improvised music known as the ''psychedelic symphony''. The Pranksters helped popularize LSD use through their road trips across America in a psychedelically-decorated school bus, which involved distributing the drug and meeting with major figures of the beat movement, and through publications about their activities such as Tom Wolfe
Thomas Kennerly Wolfe Jr. (March 2, 1930 – May 14, 2018)Some sources say 1931; ''The New York Times'' and Reuters both initially reported 1931 in their obituaries before changing to 1930. See and was an American author and journalist widely ...
's '' The Electric Kool-Aid Acid Test'' (1968).J. Mann, ''Turn on and Tune in: Psychedelics, Narcotics and Euphoriants'' (Royal Society of Chemistry, 2009), , p. 87.
Leary was a well-known proponent of the use of psychedelics, as was Aldous Huxley
Aldous Leonard Huxley (26 July 1894 – 22 November 1963) was an English writer and philosopher. He wrote nearly 50 books, both novels and non-fiction works, as well as wide-ranging essays, narratives, and poems.
Born into the prominent Huxle ...
. However, both advanced widely different opinions on the broad use of psychedelics by state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* '' Our ...
and civil society
Civil society can be understood as the "third sector" of society, distinct from government and business, and including the family and the private sphere.panacea
In Greek mythology, Panacea (Greek ''Πανάκεια'', Panakeia), a goddess of universal remedy, was the daughter of Asclepius and Epione. Panacea and her four sisters each performed a facet of Apollo's art:
* Panacea (the goddess of universa ...
, while Huxley suggested that only the cultural and intellectual elite should partake of entheogens systematically.
In the 1960s
File:1960s montage.png, Clockwise from top left: U.S. soldiers during the Vietnam War; the Beatles led the British Invasion of the U.S. music market; a half-a-million people participate in the 1969 Woodstock Festival; Neil Armstrong and Bu ...
the use of psychedelic drugs became widespread in modern Western culture
image:Da Vinci Vitruve Luc Viatour.jpg, Leonardo da Vinci's ''Vitruvian Man''. Based on the correlations of ideal Body proportions, human proportions with geometry described by the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius in Book III of his treatise '' ...
, particularly in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
and Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
. The movement is credited to Michael Hollingshead
Michael Hollingshead (?–1984?) was a British researcher who studied psychedelic drugs, including psilocybin and LSD, at Harvard University in the mid-20th century. He was the father of comedian Vanessa Hollingshead. He evangelized the use of ...
who arrived in America from London in 1965. He was sent to the U.S. by other members of the psychedelic movement to get their ideas exposure. The Summer of Love
The Summer of Love was a social phenomenon that occurred during the summer of 1967, when as many as 100,000 people, mostly young people sporting hippie fashions of dress and behavior, converged in San Francisco's neighborhood of Haight-Ashbury ...
of 1967 and the resultant popularization of the hippie
A hippie, also spelled hippy, especially in British English, is someone associated with the counterculture of the 1960s, originally a youth movement that began in the United States during the mid-1960s and spread to different countries around ...
culture to the mainstream popularized psychedelia in the minds of popular culture
Popular culture (also called mass culture or pop culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as, popular art or mass art) and objects that are dominant or prevalent in ...
, where it remained dominant through the 1970s.
Modern usage
The impact of psychedelic drugs on western culture in the 1960s led tosemantic drift
Semantic change (also semantic shift, semantic progression, semantic development, or semantic drift) is a form of language change regarding the evolution of word usage—usually to the point that the modern meaning is radically different from t ...
in the use of the word "psychedelic", and it is now frequently used to describe anything with abstract decoration of multiple bright colours, similar to those seen in drug-induced hallucinations. In objection to this new meaning, and to what some consider pejorative
A pejorative or slur is a word or grammatical form expressing a negative or a disrespectful connotation, a low opinion, or a lack of respect toward someone or something. It is also used to express criticism, hostility, or disregard. Sometimes, a ...
meanings of other synonyms such as "hallucinogen
Hallucinogens are a large, diverse class of psychoactive drugs that can produce altered states of consciousness characterized by major alterations in thought, mood, and perception as well as other changes. Most hallucinogens can be categorized ...
" and "psychotomimetic A drug with psychotomimetic (also known as psychotogenic) actions mimics the symptoms of psychosis, including delusions and/or delirium, as opposed to only hallucinations. Psychotomimesis is the onset of psychotic symptoms following the administrati ...
", the term "entheogen" was proposed and is seeing increasing use. However, many consider the term "entheogen" best reserved for religious and spiritual usage, such as certain Native American churches do with the peyote sacrament, and "psychedelic" left to describe those who are using these drugs for recreation, psychotherapy, physical healing, or creative problem solving. In science, hallucinogen
Hallucinogens are a large, diverse class of psychoactive drugs that can produce altered states of consciousness characterized by major alterations in thought, mood, and perception as well as other changes. Most hallucinogens can be categorized ...
remains the standard term.
Visual art
 Advances in printing and photographic technology in the 1960s saw the traditional
Advances in printing and photographic technology in the 1960s saw the traditional lithography
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone ( lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German ...
printing techniques rapidly superseded by the offset printing
Offset printing is a common printing technique in which the inked image is transferred (or "offset") from a plate to a rubber blanket and then to the printing surface. When used in combination with the lithographic process, which is based on ...
system. This and other technical and industrial innovations gave young artists access to exciting new graphic techniques and media, including photographic and mixed media collage, metallic foils, and vivid new fluorescent " DayGlo" inks. This enabled them to explore innovative new illustrative styles including highly distorted visuals, cartoons, and lurid colors and full spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of color ...
s to evoke a sense of altered consciousness; many works also featured idiosyncratic and complex new fonts and lettering styles (most notably in the work of San Francisco-based poster artist Rick Griffin). Many artists in the late 1960s and early 1970s attempted to illustrate the psychedelic experience in paintings
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and ai ...
, drawings
Drawing is a visual art that uses an instrument to mark paper or another two-dimensional surface. The instruments used to make a drawing are pencils, crayons, pens with inks, brushes with paints, or combinations of these, and in more modern times ...
, illustration
An illustration is a decoration, interpretation or visual explanation of a text, concept or process, designed for integration in print and digital published media, such as posters, flyers, magazines, books, teaching materials, animations, vide ...
s, and other forms of graphic design.
The counterculture
A counterculture is a culture whose values and norms of behavior differ substantially from those of mainstream society, sometimes diametrically opposed to mainstream cultural mores.Eric Donald Hirsch. ''The Dictionary of Cultural Literacy''. Ho ...
music scene frequently used psychedelic designs on posters during the Summer of Love
The Summer of Love was a social phenomenon that occurred during the summer of 1967, when as many as 100,000 people, mostly young people sporting hippie fashions of dress and behavior, converged in San Francisco's neighborhood of Haight-Ashbury ...
, leading to a popularization of the style. The most productive and influential centre of psychedelic art in the late 1960s was San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
; a scene driven in large measure by the patronage of the popular local music venues of the day like the Avalon Ballroom
The Avalon Ballroom was a music venue in the Polk Gulch neighborhood of San Francisco, California, at 1244 Sutter Street (or 1268 Sutter, depending on the entrance). The space is known as the location of many concerts of the counterculture move ...
and Bill Graham's Fillmore West
The Fillmore West was a historic rock and roll music venue in San Francisco, California, US which became famous under the direction of concert promoter Bill Graham from 1968 to 1971. Named after The Fillmore at the intersection of Fillmore Str ...
, which regularly commissioned young local artists like Robert Crumb
Robert Dennis Crumb (; born August 30, 1943) is an American cartoonist and musician who often signs his work R. Crumb. His work displays a nostalgia for American folk culture of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and satire of contem ...
, Stanley Mouse, Rick Griffin and others. They produced a wealth of distinctive psychedelic promotional poster
A poster is a large sheet that is placed either on a public space to promote something or on a wall as decoration. Typically, posters include both textual and graphic elements, although a poster may be either wholly graphical or wholly text. ...
s and handbills for concerts that featured emerging psychedelic bands like Big Brother and the Holding Company, The Grateful Dead
The Grateful Dead was an American rock band formed in 1965 in Palo Alto, California. The band is known for its eclectic style, which fused elements of rock, folk, country, jazz, bluegrass, blues, rock and roll, gospel, reggae, world music, an ...
and Jefferson Airplane
Jefferson Airplane was an American rock band based in San Francisco, California, that became one of the pioneering bands of psychedelic rock. Formed in 1965, the group defined the San Francisco Sound and was the first from the Bay Area to ach ...
. Many of these works are now regarded as classics of the poster genre, and original items by these artists command high prices on the collector market today.
Contemporary with the burgeoning San Francisco scene, a smaller but equally creative psychedelic art movement emerged in London, led by expatriate Australian pop artist Martin Sharp
Martin Ritchie Sharp (21 January 1942 – 1 December 2013) was an Australian artist, cartoonist, songwriter and film-maker.
Career
Sharp was born in Bellevue Hill, New South Wales in 1942, and educated at Cranbrook private school, where one ...
, who created many striking psychedelic posters and illustrations for the influential underground publication Oz magazine
''Oz'' was an independently published, alternative/underground magazine associated with the international counterculture of the 1960s. While it was first published in Sydney in 1963, a parallel version of ''Oz'' was published in London from 1967 ...
, as well as the famous album covers for the Cream
Cream is a dairy product composed of the higher-fat layer skimmed from the top of milk before homogenization. In un-homogenized milk, the fat, which is less dense, eventually rises to the top. In the industrial production of cream, this process ...
albums ''Disraeli Gears
''Disraeli Gears'' is the second studio album by the British rock band Cream. It was released in November 1967 and reached No. 5 on the UK Albums Chart. Search "Cream" in ''Name of Artist'', and No. 1 on the Swedish and Finnish charts. The alb ...
'' and '' Wheels of Fire''. Other prominent London practitioners of the style included: design duo Hapshash and the Coloured Coat, whose work included numerous famous posters, as well as psychedelic "makeovers" on a piano for Paul McCartney
Sir James Paul McCartney (born 18 June 1942) is an English singer, songwriter and musician who gained worldwide fame with the Beatles, for whom he played bass guitar and shared primary songwriting and lead vocal duties with John Lennon. On ...
and a car for doomed Guinness
Guinness () is an Irish dry stout that originated in the brewery of Arthur Guinness at St. James's Gate, Dublin, Ireland, in 1759. It is one of the most successful alcohol brands worldwide, brewed in almost 50 countries, and available in ...
heir Tara Browne, and design collective The Fool, who created clothes and album art for several leading UK bands including The Beatles
The Beatles were an English rock band, formed in Liverpool in 1960, that comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are regarded as the most influential band of all time and were integral to the developm ...
, Cream, and The Move
The Move were a British rock band of the late 1960s and the early 1970s. They scored nine top 20 UK singles in five years, but were among the most popular British bands not to find any real success in the United States. For most of their car ...
. The Beatles loved psychedelic designs on their albums, and designer group called The Fool created psychedelic design, art, paint at the short-lived Apple Boutique (1967–1968) in Baker St, London.
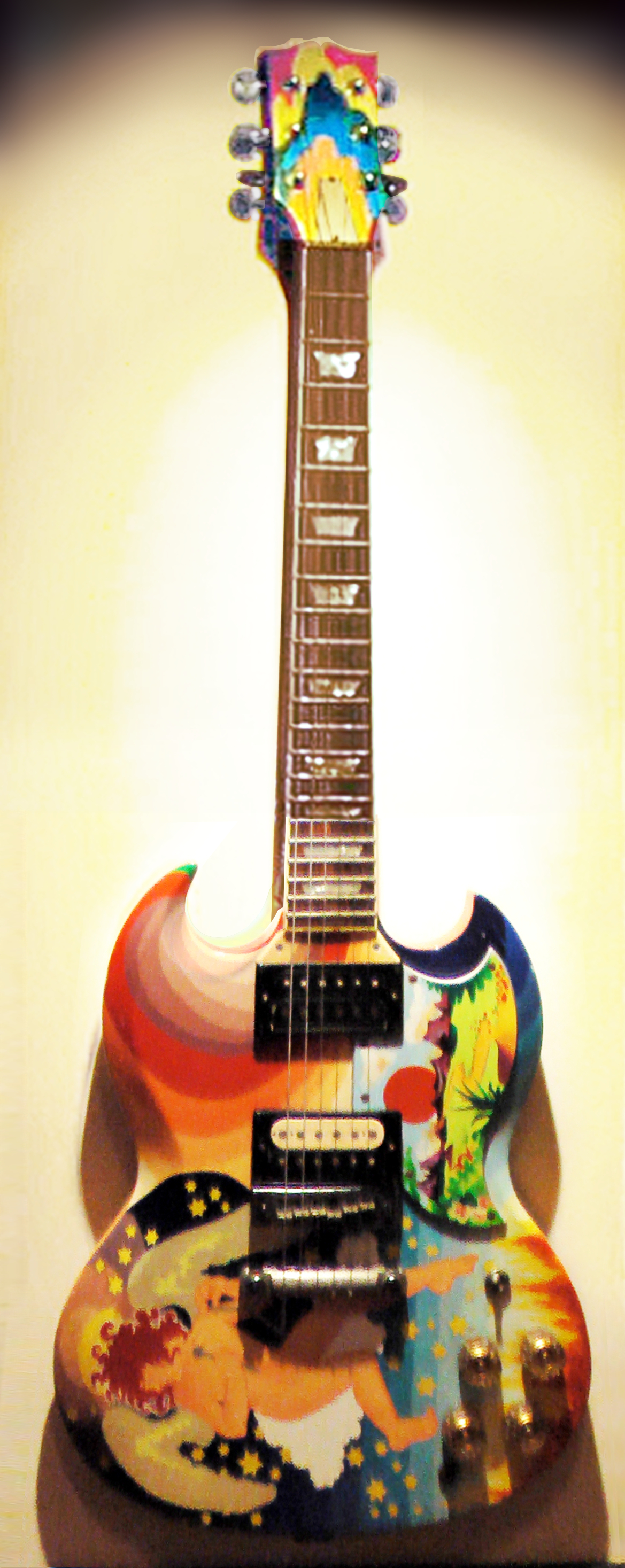
 Blues rock singer Janis Joplin had a psychedelic car, a Porsche 356. The trend also extended to motor vehicles. The earliest, and perhaps most famous of all psychedelic vehicles was the famous " Further" bus, driven by
Blues rock singer Janis Joplin had a psychedelic car, a Porsche 356. The trend also extended to motor vehicles. The earliest, and perhaps most famous of all psychedelic vehicles was the famous " Further" bus, driven by Ken Kesey
Ken Elton Kesey (September 17, 1935 – November 10, 2001) was an American novelist, essayist and countercultural figure. He considered himself a link between the Beat Generation of the 1950s and the hippies of the 1960s.
Kesey was born ...
and The Merry Pranksters, which was painted inside and out in 1964 with bold psychedelic designs (although these were executed in primary colours, since the DayGlo colours that soon became ''de rigueur'' were then not widely available). Another very famous example is the Rolls-Royce owned by John Lennon
John Winston Ono Lennon (born John Winston Lennon; 9 October 19408 December 1980) was an English singer, songwriter, musician and peace activist who achieved worldwide fame as founder, co-songwriter, co-lead vocalist and rhythm guitarist of ...
– originally black, he had it repainted in 1967 in a vivid psychedelic gypsy caravan style, prompting bandmate George Harrison to have his Mini Cooper Mini Cooper may refer to:
*Cars of the original Mini series called the "Mini Cooper", made by the British Motor Corporation and its successors 1961–1971, and 1990–2000
*Cars of the Mini (marque), including a number of different models produced ...
similarly repainted with logos and devices that reflected his burgeoning interest in Indian spirituality.
Music
The fashion for psychedelic drugs gave its name to the style of psychedelia, a term describing a category ofrock music
Rock music is a broad genre of popular music that originated as "rock and roll" in the United States in the late 1940s and early 1950s, developing into a range of different styles in the mid-1960s and later, particularly in the United States and ...
known as psychedelic rock
Psychedelic rock is a rock music Music genre, genre that is inspired, influenced, or representative of psychedelia, psychedelic culture, which is centered on perception-altering hallucinogenic drugs. The music incorporated new electronic sound ...
, as well as visual art
The visual arts are art forms such as painting, drawing, printmaking, sculpture, ceramics, photography, video, filmmaking, design, crafts and architecture. Many artistic disciplines such as performing arts, conceptual art, and textile ar ...
, fashion
Fashion is a form of self-expression and autonomy at a particular period and place and in a specific context, of clothing, footwear, lifestyle, accessories, makeup, hairstyle, and body posture. The term implies a look defined by the fash ...
, and culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these grou ...
that is associated originally with the high 1960s, hippies, and the Haight-Ashbury
Haight-Ashbury () is a district of San Francisco, California, named for the intersection of Haight and Ashbury streets. It is also called The Haight and The Upper Haight. The neighborhood is known as one of the main centers of the counterculture ...
neighborhood of San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the ...
. It often used new recording techniques and effects while drawing on Eastern sources such as the raga
A ''raga'' or ''raag'' (; also ''raaga'' or ''ragam''; ) is a melodic framework for improvisation in Indian classical music akin to a melodic mode. The ''rāga'' is a unique and central feature of the classical Indian music tradition, and as a ...
s and drones
Drone most commonly refers to:
* Drone (bee), a male bee, from an unfertilized egg
* Unmanned aerial vehicle
* Unmanned surface vehicle, watercraft
* Unmanned underwater vehicle or underwater drone
Drone, drones or The Drones may also refer to:
...
of Indian music
Owing to India's vastness and diversity, Indian music encompasses numerous genres in multiple varieties and forms which include classical music, folk ( Bollywood), rock, and pop. It has a history spanning several millennia and developed ov ...
.
One of the first uses of the word in the music scene of this time was in the 1964 recording of "Hesitation Blues
"Hesitation Blues" is a popular song adapted from a traditional tune. One version was published by Billy Smythe, Scott Middleton, and Art Gillham. Another was published by W.C. Handy as "Hesitating Blues". Because the tune is traditional, man ...
" by folk group the Holy Modal Rounders.M. Hicks, ''Sixties Rock: Garage, Psychedelic, and Other Satisfactions'' (Chicago IL: University of Illinois Press
The University of Illinois Press (UIP) is an American university press and is part of the University of Illinois system. Founded in 1918, the press publishes some 120 new books each year, plus 33 scholarly journals, and several electronic projec ...
, 2000), , pp. 59-60. The term was introduced to rock music and popularized by the 13th Floor Elevators
The 13th Floor Elevators was an American rock band from Austin, Texas, United States, formed by guitarist and vocalist Roky Erickson, electric jug player Tommy Hall, and guitarist Stacy Sutherland. The band was together from 1965 to 1969, an ...
1966 album ''The Psychedelic Sounds of the 13th Floor Elevators
''The Psychedelic Sounds of the 13th Floor Elevators'' is the debut studio album by the 13th Floor Elevators. The album's sound, featuring elements of psychedelia, hard rock, garage rock, folk, and blues, is notable for its use of the electri ...
''. Psychedelia truly took off in 1967 with the Summer of Love
The Summer of Love was a social phenomenon that occurred during the summer of 1967, when as many as 100,000 people, mostly young people sporting hippie fashions of dress and behavior, converged in San Francisco's neighborhood of Haight-Ashbury ...
and, although associated with San Francisco, the style soon spread across the US, and worldwide.V. Bogdanov, C. Woodstra and S. T. Erlewine, ''All Music Guide to Rock: the Definitive Guide to Rock, Pop, and Soul'' (Milwaukee, WI: Backbeat Books
In music and music theory, the beat is the basic unit of time, the pulse (music), pulse (regularly repeating event), of the ''mensural level'' (or ''beat level''). The beat is often defined as the rhythm listeners would tap their toes to when li ...
, 3rd edn., 2002), , pp. 1322-3.
The electronic dance music scene is strongly linked to the consumption of psychedelic drugs, particularly MDMA
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), commonly seen in tablet form (ecstasy) and crystal form (molly or mandy), is a potent empathogen–entactogen with stimulant properties primarily used for recreational purposes. The desired ...
. Drug usage in the EDM scene can primarily be traced to British acid house parties and the Second Summer of Love, which marked the beginnings of rave culture; these movements, however, were distinct from and mostly unrelated to 1960s psychedelia.
Festivals
 A psychedelic festival is a gathering that promotes
A psychedelic festival is a gathering that promotes psychedelic music
Psychedelic music (sometimes called psychedelia) is a wide range of popular music styles and genres influenced by 1960s psychedelia, a subculture of people who used psychedelic drugs such as LSD, psilocybin mushrooms, mescaline, and cannabis ...
and art in an effort to unite participants in a communal psychedelic experience
A psychedelic experience (known colloquially as a trip) is a temporary altered state of consciousness induced by the consumption of a psychedelic substance (most commonly LSD, mescaline, psilocybin mushrooms, or DMT). For example, an acid tr ...
. Psychedelic festivals have been described as "temporary communities reproduced via personal and collective acts of transgression ... through the routine expenditure of excess energy, and through self-sacrifice in acts of abandonment involving ecstatic dancing often fuelled by chemical cocktails."St John, Graham"Neotrance and the Psychedelic Festival."
''Dancecult: Journal of Electronic Dance Music Culture,'' 1(1) (2009). These festivals often emphasize the ideals of peace, love, unity, and respect. Notable psychedelic festivals include the biennial Boom Festival in Portugal,
Ozora Festival
The Ozora Festival, stylised as O.Z.O.R.A., is an annual transformational festival and arts festival near the Hungarian village of Ozora.
History and growth
The festival has been held on an estate in Ozora near the small village of Dádpuszta ...
in Hungary, Universo Paralello in Brazil as well as Nevada's Burning Man and California's Symbiosis Gathering in the United States.
Conferences
In recent years there has been a resurgence in interest in psychedelic research and a growing number of conferences now take place across the globe. The psychedelic research charity Breaking Convention have hosted one of the world's largest since 2011. A biennial conference in London, UK, Breaking Convention: a multidisciplinary conference onpsychedelic
Psychedelics are a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary states of consciousness (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips").Pollan, Michael (2018). ''How to Change Your Mind: What the New Science ...
consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scien ...
is a multidisciplinary conference on psychedelic consciousness. In the US MAPS
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes.
Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Althoug ...
held their first Psychedelic Science conference,'' Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies: MAPS'' Retrieved 2019-09-27.
See also
*Counterculture of the 1960s
The counterculture of the 1960s was an anti-establishment cultural phenomenon that developed throughout much of the Western world in the 1960s and has been ongoing to the present day. The aggregate movement gained momentum as the civil rights mo ...
* ''The Doors of Perception
''The Doors of Perception'' is an autobiographical book written by Aldous Huxley. Published in 1954, it elaborates on his psychedelic experience under the influence of mescaline in May 1953. Huxley recalls the insights he experienced, rangi ...
''
* Ego death
Ego death is a "complete loss of subjective self-identity". The term is used in various intertwined contexts, with related meanings. Jungian psychology uses the synonymous term psychic death, referring to a fundamental transformation of the psyc ...
* Erowid
Erowid, also called Erowid Center, is a non-profit educational organization that provides information about psychoactive plants and chemicals.
Erowid documents legal and illegal substances, including their intended and adverse effects. Informat ...
* '' God in a Pill?''
* Psychedelic era
*
* Psychedelic fish
* Psychedelic literature
* Psychedelic plants
* Psychonautics
Psychonautics (from the Ancient Greek ' 'soul, spirit, mind' and ' 'sailor, navigator') refers both to a methodology for describing and explaining the subjective effects of altered states of consciousness, including those induced by meditati ...
* Serotonergic psychedelic
Psychedelics are a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary states of consciousness (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips").Pollan, Michael (2018). ''How to Change Your Mind: What the New Science ...
* Timeline of 1960s counterculture
Notes
References
External links
Erowid
*''Magic Mushrooms and Reindeer - Weird Nature''. A short video on the use of ''
Amanita muscaria
''Amanita muscaria'', commonly known as the fly agaric or fly amanita, is a basidiomycete of the genus ''Amanita''. It is also a muscimol mushroom. Native throughout the temperate and boreal ecosystem, boreal regions of the Northern Hemisphere, ...
'' mushrooms by the Sami people and their reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subsp ...
produced by the BBC{{Hippies Psychedelia, Subcultures Underground culture