Pseudo-LRU on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pseudo-LRU or PLRU is a family of
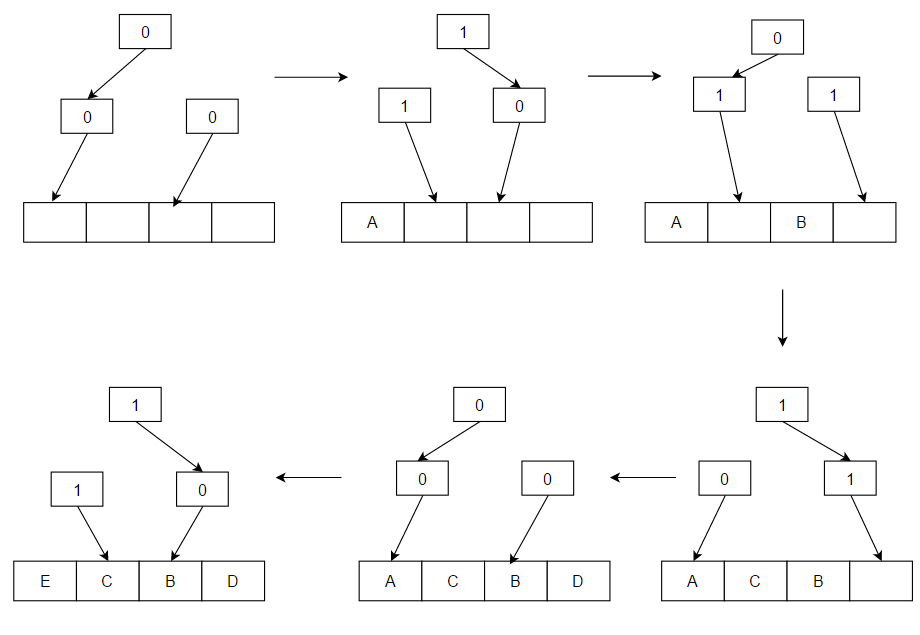 This algorithm can be sub-optimal since it is an approximation. For example, in the above diagram with A, C, B, D cache lines, if the access pattern was: C, B, D, A, on an eviction we would choose B instead of C. This is because both A and C are in the same half and accessing A directs the algorithm to the other half that does not contain cache line C.
This algorithm can be sub-optimal since it is an approximation. For example, in the above diagram with A, C, B, D cache lines, if the access pattern was: C, B, D, A, on an eviction we would choose B instead of C. This is because both A and C are in the same half and accessing A directs the algorithm to the other half that does not contain cache line C.
Automatic Generation of Models of Microarchitectures
/ref>
cache algorithms
In computing, cache algorithms (also frequently called cache replacement algorithms or cache replacement policies) are optimizing instructions, or algorithms, that a computer program or a hardware-maintained structure can utilize in order to ma ...
which improve on the performance of the Least Recently Used
In computing, cache algorithms (also frequently called cache replacement algorithms or cache replacement policies) are optimizing instructions, or algorithms, that a computer program or a hardware-maintained structure can utilize in order to ma ...
(LRU) algorithm by replacing values using approximate measures of age rather than maintaining the exact age of every value in the cache.
PLRU usually refers to two cache replacement algorithms: tree-PLRU and bit-PLRU.
Tree-PLRU
Tree-PLRU is an efficientalgorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specificat ...
to select an item that most likely has not been accessed very recently, given a set of items and a sequence of access events to the items.
This technique is used in the CPU cache
A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to reduce the average cost (time or energy) to access data from the main memory. A cache is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, which ...
of the Intel 486 and in many processors in the PowerPC
PowerPC (with the backronym Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC – Performance Computing, sometimes abbreviated as PPC) is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple Inc., App ...
family, such as Freescale's PowerPC G4 used by Apple Computer
Apple Inc. is an American multinational technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, United States. Apple is the largest technology company by revenue (totaling in 2021) and, as of June 2022, is the world's biggest company b ...
.
The algorithm works as follows: consider a binary search tree for the items in question. Each node of the tree has a one-bit flag denoting "go left to insert a pseudo-LRU element" or "go right to insert a pseudo-LRU element". To find a pseudo-LRU element, traverse the tree according to the values of the flags. To update the tree with an access to an item N, traverse the tree to find N and, during the traversal, set the node flags to denote the direction that is opposite to the direction taken.
 This algorithm can be sub-optimal since it is an approximation. For example, in the above diagram with A, C, B, D cache lines, if the access pattern was: C, B, D, A, on an eviction we would choose B instead of C. This is because both A and C are in the same half and accessing A directs the algorithm to the other half that does not contain cache line C.
This algorithm can be sub-optimal since it is an approximation. For example, in the above diagram with A, C, B, D cache lines, if the access pattern was: C, B, D, A, on an eviction we would choose B instead of C. This is because both A and C are in the same half and accessing A directs the algorithm to the other half that does not contain cache line C.
Bit-PLRU
Bit-PLRU stores one status bit for each cache line. These bits are called MRU-bits. Every access to a line sets its MRU-bit to 1, indicating that the line was recently used. Whenever the last remaining 0 bit of a set's status bits is set to 1, all other bits are reset to 0. At cache misses, the leftmost line whose MRU-bit is 0 is replaced./ref>
See also
*Cache algorithms
In computing, cache algorithms (also frequently called cache replacement algorithms or cache replacement policies) are optimizing instructions, or algorithms, that a computer program or a hardware-maintained structure can utilize in order to ma ...
References
* https://people.cs.clemson.edu/~mark/464/p_lru.txt * http://www.ipdps.org/ipdps2010/ipdps2010-slides/session-22/2010IPDPS.pdf * http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.217.3594&rep=rep1&type=pdf