Proposals for new Australian States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 There have been numerous proposals for the creation or incorporation of new
There have been numerous proposals for the creation or incorporation of new
 Immediately before federation in 1901, the Australian mainland comprised six separate British
Immediately before federation in 1901, the Australian mainland comprised six separate British
 Proposed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the state of Auralia (meaning "land of gold") would have comprised the
Proposed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the state of Auralia (meaning "land of gold") would have comprised the
 Supporters of the
Supporters of the
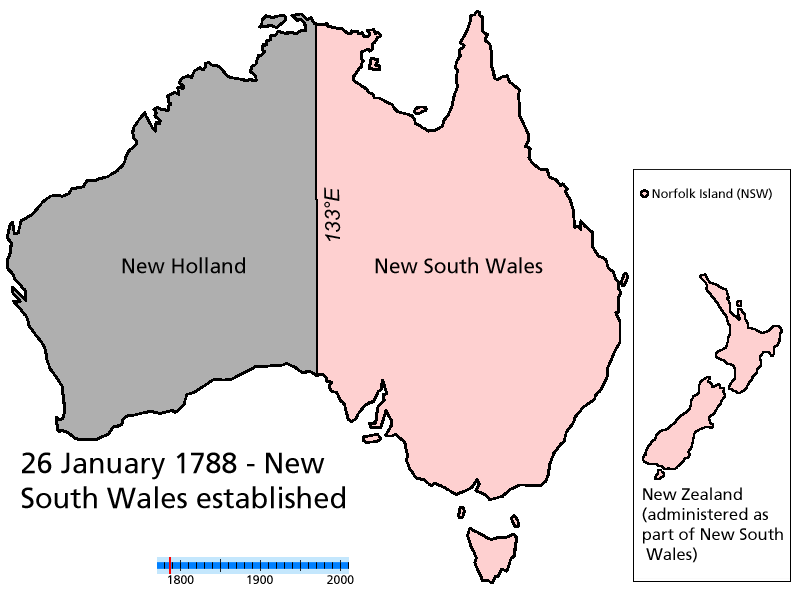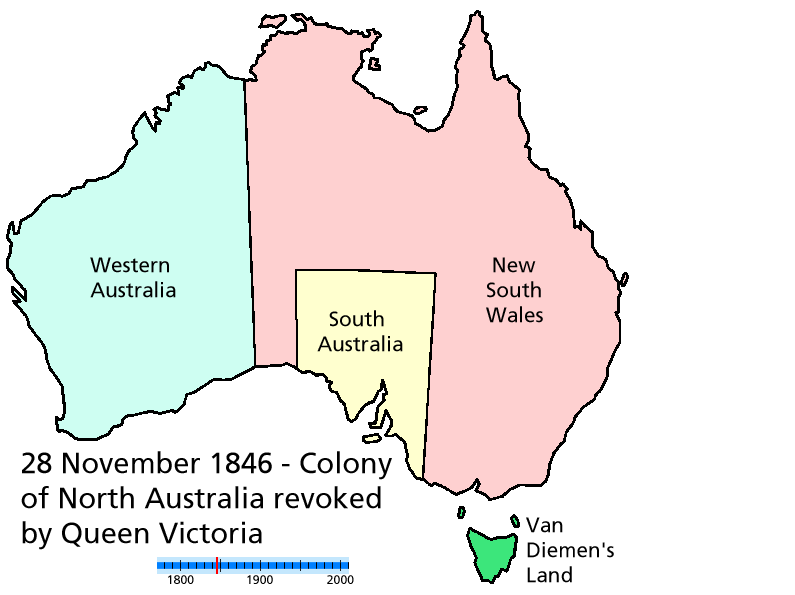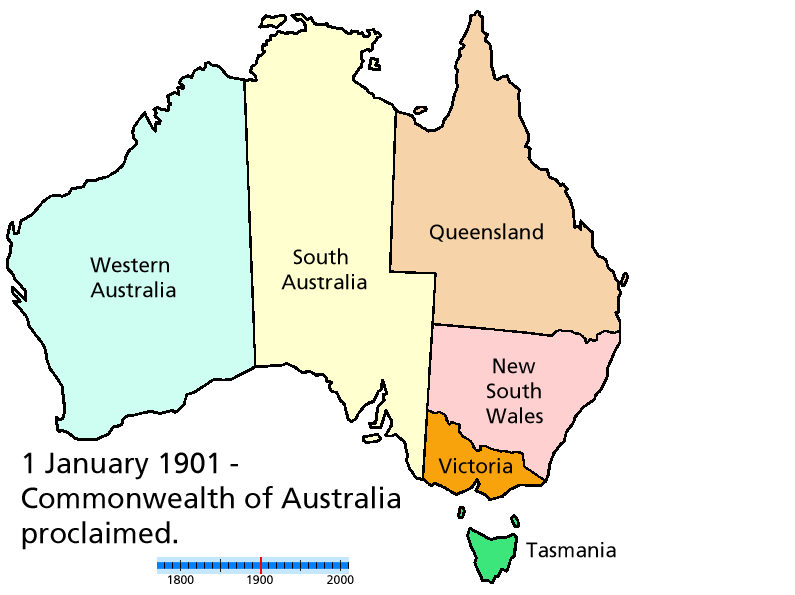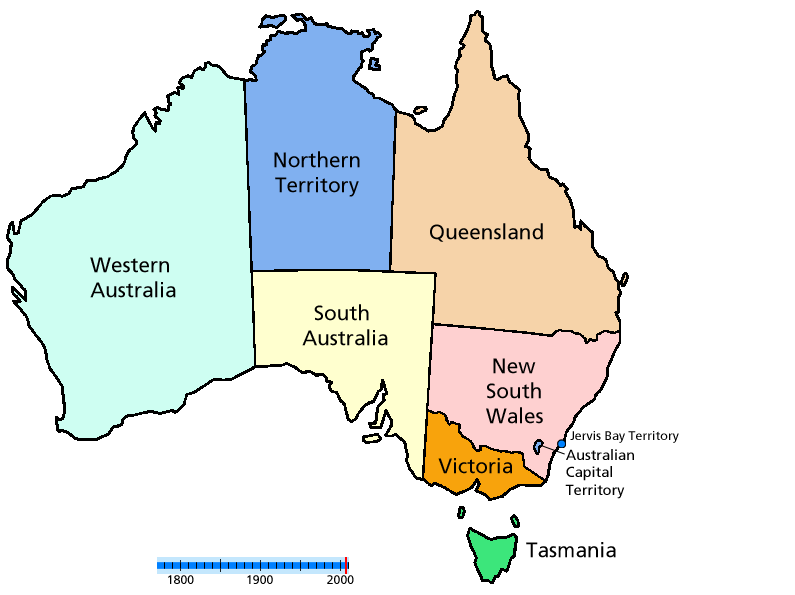
 In 1788,
In 1788,
 The
The
Why New Zealand did not become an Australian State
The Australian Empire
{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Proposed States Of Australia Government of Australia * Australia–Papua New Guinea relations Australia–Fiji relations Australia–New Zealand relations National unifications States, proposed Proposals in Australia
 There have been numerous proposals for the creation or incorporation of new
There have been numerous proposals for the creation or incorporation of new states of Australia
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* '' State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* '' Our ...
, since the late 19th century. These proposals have involved: giving existing territories the official status of states; negotiating the inclusion of other independent countries (or one of their overseas territories), and; forming new states from parts of existing states. However, no new states have been added since the federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-govern ...
of six former British self-governing colonies in 1901, as states of the new Commonwealth of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
.
Unofficial proposals have involved current territories, especially the Northern Territory
The Northern Territory (commonly abbreviated as NT; formally the Northern Territory of Australia) is an Australian territory in the central and central northern regions of Australia. The Northern Territory shares its borders with Western Au ...
(NT) and, to a lesser extent, the Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (commonly abbreviated as ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) until 1938, is a landlocked federal territory of Australia containing the national capital Canberra and some surrounding townships. ...
(ACT). Other, long-standing proposals have included negotiating the addition of: New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
(as either one or two states), Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
, Fiji or East Timor
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-we ...
. More recently, there have been proposals for an Aboriginal
Aborigine, aborigine or aboriginal may refer to:
*Aborigines (mythology), in Roman mythology
* Indigenous peoples, general term for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area
*One of several groups of indigenous peoples, see ...
state, possibly modelled on the Inuit territory of Nunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, ᓄᓇᕗᑦ , ; ) is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the '' Nunavut Act'' and the '' Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act'' ...
in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
.
Procedure
Section 124 of the Constitution of Australia
Section 124 of the Constitution of Australia provides a constitutional provision for creating new Australian States.
See also
* List of proposed states of Australia
There have been numerous proposals for the creation or incorporation of ne ...
provides for the establishment or admission of new States to the Federation. It may also increase, diminish, or otherwise alter the limits of a State, form a new state by separating territory from an existing State, or join multiple States or parts of States, but in each case, it must have the approval of the Parliament(s) of the State(s) in question.
In relation to parliamentary representation, the Joint Select Committee on Electoral Reform in 1985 recommended that territories be entitled to:
* Separate representation from the ACT or NT once they have more than half a quota of population (for a House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
seat);
* A floor of two senators for the ACT and NT each; and
* One extra senator for every two lower house members.
* That new states should not have representation any more favourable than Territories as prescribed in the Commonwealth Electoral Act 1918.
Historical proposals
 Immediately before federation in 1901, the Australian mainland comprised six separate British
Immediately before federation in 1901, the Australian mainland comprised six separate British self-governing colonies
In the British Empire, a self-governing colony was a colony with an elected government in which elected rulers were able to make most decisions without referring to the colonial power with nominal control of the colony. This was in contrast to ...
. Throughout the 19th century, the borders of these colonies changed often, there were numerous proposals for new colonies and, in some instances, new colonies were gazetted
A gazette is an official journal, a newspaper of record, or simply a newspaper.
In English and French speaking countries, newspaper publishers have applied the name ''Gazette'' since the 17th century; today, numerous weekly and daily newspaper ...
, but later dissolved and incorporated (or reincorporated) into other colonies.
In 1838, the ''Journal of the Royal Geographical Society'' published "Considerations on the Political Geography and Geographical Nomenclature of Australia" (1838), in which a major reorganisation of the colonial borders was proposed. The following new colonies were proposed:
* "Dampieria", in north-west Australia;
* "Victoria" (not to be confused with the modern Victoria), in South West Western Australia;
* "Tasmania", (not to be confused with the modern Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
) in western Arnhem Land
Arnhem Land is a historical region of the Northern Territory of Australia, with the term still in use. It is located in the north-eastern corner of the territory and is around from the territory capital, Darwin. In 1623, Dutch East India Company ...
and part of the later Kimberley
Kimberly or Kimberley may refer to:
Places and historical events
Australia
* Kimberley (Western Australia)
** Roman Catholic Diocese of Kimberley
* Kimberley Warm Springs, Tasmania
* Kimberley, Tasmania a small town
* County of Kimberley, a ...
;
* "Nuytsland", covering most of the Nullarbor Plain
The Nullarbor Plain ( ; Latin: feminine of , 'no', and , 'tree') is part of the area of flat, almost treeless, arid or semi-arid country of southern Australia, located on the Great Australian Bight coast with the Great Victoria Desert to i ...
(except for its western edges);
* "Carpentaria", on the shores of the Gulf of Carpentaria
The Gulf of Carpentaria (, ) is a large, shallow sea enclosed on three sides by northern Australia and bounded on the north by the eastern Arafura Sea (the body of water that lies between Australia and New Guinea). The northern boundary ...
;
* "Flindersland", covering most of the area of the future South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
;
* "Torresia" in what would become northern Queensland (including far north Queensland
Far North Queensland (FNQ) is the northernmost part of the Australian state of Queensland. Its largest city is Cairns and it is dominated geographically by Cape York Peninsula, which stretches north to the Torres Strait, and west to the Gulf ...
);
* "Cooksland" centred on Brisbane
Brisbane ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the states and territories of Australia, Australian state of Queensland, and the list of cities in Australia by population, third-most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a populati ...
, and including northern New South Wales, and;
* "Guelphia" – central and southern New South Wales (which at the time included all of the future Victoria).
(Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania used by the British during the European exploration of Australia in the 19th century. A British settlement was established in Van Diemen's Land in 1803 before it became a sep ...
, later known as Tasmania, was to be preserved in its then current form.)
These proposed colonies were geometric divisions of the continent, and did not take into account soil fertility, aridity or population. This meant that central and western Australia were divided into several states, despite their low populations both then and now.
For several months in 1846, a Colony of North Australia technically existed, with its capital at Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone ( ; 29 December 1809 – 19 May 1898) was a British statesman and Liberal politician. In a career lasting over 60 years, he served for 12 years as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, spread over four non-con ...
. The short-lived colony officially included most of the future Queensland (except Brisbane and surrounding areas) and the future Northern Territory. Between the time it was gazetted, in February 1846 and the time it was officially cancelled, that December, the area of the new colony continued to be controlled by the government of New South Wales; at no point did a separate colonial administration of North Australia take control of it.
There was also a proposal in 1857 for the "Seven United Provinces of Eastern Australia" with separate provinces of Flinders Land, Leicharts (sic) Land (taken from the name of Ludwig Leichhardt
Friedrich Wilhelm Ludwig Leichhardt (), known as Ludwig Leichhardt, (23 October 1813 – c. 1848) was a German explorer and naturalist, most famous for his exploration of northern and central Australia.Ken Eastwood,'Cold case: Leichhardt's dis ...
) and Cooks Land in modern day Queensland (also named from James Cook).
Auralia
 Proposed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the state of Auralia (meaning "land of gold") would have comprised the
Proposed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the state of Auralia (meaning "land of gold") would have comprised the Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to ...
n Goldfields, the western portion of the Nullarbor Plain
The Nullarbor Plain ( ; Latin: feminine of , 'no', and , 'tree') is part of the area of flat, almost treeless, arid or semi-arid country of southern Australia, located on the Great Australian Bight coast with the Great Victoria Desert to i ...
and the port town of Esperance. Its capital would have been Kalgoorlie
Kalgoorlie is a city in the Goldfields–Esperance region of Western Australia, located east-northeast of Perth at the end of the Great Eastern Highway. It is sometimes referred to as Kalgoorlie–Boulder, as the surrounding urban area inclu ...
.
However, the population in the modern region of Goldfields-Esperance is currently lower than that of the Northern Territory
The Northern Territory (commonly abbreviated as NT; formally the Northern Territory of Australia) is an Australian territory in the central and central northern regions of Australia. The Northern Territory shares its borders with Western Au ...
, and there is little evidence of recent support, although the idea of a state centred around Kalgoorlie was proposed in 2003.
East Timor
During the process of Portuguese decolonisation inEast Timor
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-we ...
in 1974, a political party was formed called ADITLA ''Associação Democrática para a Integração de Timor Leste na Austrália'' (Democratic Association for the Integration of East Timor into Australia) by local businessman Henrique Pereira. It found some support from the ethnic Chinese community, fearful of independence or integration with Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
but was disbanded when the Australian government rejected the idea in 1975.
Illawarra Province
Also known as theIllawarra
The Illawarra is a coastal region in the Australian state of New South Wales, nestled between the mountains and the sea. It is situated immediately south of Sydney and north of the South Coast region. It encompasses the two cities of Wollongo ...
Territory, this proposed new state would consist of the Illawarra region centred on Wollongong
Wollongong ( ), colloquially referred to as The Gong, is a city located in the Illawarra region of New South Wales, Australia. The name is believed to originate from the Dharawal language, meaning either 'five islands/clouds', 'ground near w ...
on the New South Wales south coast. Originally this idea arose after disagreements between local landowners and migrants from Sydney in the mid-19th century. However the idea has continued in various incarnations ever since with most movements proposing the state's capital be situated in "Illawarra City", or the amalgamation of the Shellharbour
Shellharbour (also known as Shellharbour Village) is a suburb located in the Illawarra region of New South Wales, Australia. It also gives its name to the local government area, City of Shellharbour, and its central business district, Shellhar ...
and Kiama
Kiama () is a coastal town 120 kilometres south of Sydney in the Illawarra. One of the main tourist attractions is the Kiama Blowhole. Kiama features several popular surfing beaches and caravan parks, and numerous alfresco cafes and restaurant ...
local government areas.
North Coast
This proposed state would take in the northern part of New South Wales from Taree to the Queensland Border, mainly in the north east, and excluding most of north west NSW.Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
is physically closest of any country to geographically remote Australia, with some of the Torres Strait Islands
The Torres Strait Islands are a group of at least 274 small islands in the Torres Strait, a waterway separating far northern continental Australia's Cape York Peninsula and the island of New Guinea. They span an area of , but their total land ...
just off the main island of the country. Its Southern part became an Australian colony in 1902, while its Northern part was seized by Australia from Germany in 1914 and administered as a "C" Mandate of the League of Nations
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for administ ...
from 1920. Both territories were amalgamated after Second World War into a single Australian colony. In 1953, the editor of the conservative '' Quadrant'' magazine, Professor James McAuley, wrote that the territory would be "a coconut republic which would do little good for itself", and advocated its "perpetual union" with Australia, with "equal citizenship rights", but this was rejected by the Australian government. Papua New Guinea was granted self-government and full independence in 1975.
Princeland
This proposed colony resulted from a movement in the 1860s to create a new colony that incorporated the isolated western Victoria and south-eastern South Australia regions centred onMount Gambier
Mount Gambier is the second most populated city in South Australia, with an estimated urban population of 33,233 . The city is located on the slopes of Mount Gambier, a volcano in the south east of the state, about south-east of the capital Ad ...
and Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
. A petition was presented to Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previ ...
, but was rejected.
South Coast
There was a small movement in the 1940s to create a new state in south-east New South Wales and north-east Victoria. The proposed state would have reached from Batemans Bay on the coast toKiandra
Kiandra is an abandoned gold mining town and the birthplace of Australian skiing. The town is situated in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia, in the Snowy Monaro Regional Council inside the Kosciuszko National Park. Its na ...
in the Snowy Mountains
The Snowy Mountains, known informally as "The Snowies", is an IBRA subregion in southern New South Wales, Australia, and is the tallest mountain range in mainland Australia, being part of the continent's Great Dividing Range cordillera syst ...
, and as far south as Sale in Victoria. The proposed state capital was Bega. Despite calls from local advocacy groups for a Royal Commission into the idea, it was met with little success.
Current proposals
Since 2000, proposals for reorganisation have continued to be put forward. For instance, in 2003, Bryan Pape suggested a reorganisation into about twenty states, each with Senate representation.Republicanism
Republicanism is a political ideology centered on citizenship in a state organized as a republic. Historically, it emphasises the idea of self-rule and ranges from the rule of a representative minority or oligarchy to popular sovereignty. It ...
, changing mineral wealth and tax distribution have been seen as reasons to revisit federation. Proposals include redivision between the local, state and federal levels of government, either consolidation or fragmentation. It has been argued that new technologies in service delivery are enablers of greater decentralisation or are a reason for greater efficiency in centralisation.
Aboriginal state
There are also supporters of an Aboriginal state, along the lines ofNunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, ᓄᓇᕗᑦ , ; ) is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the '' Nunavut Act'' and the '' Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act'' ...
in Canada. The Aboriginal Provisional Government was established in 1990 for the purpose; Paul Coe sued the Commonwealth for Aboriginal sovereignty (''Coe v Commonwealth'' 979HCA 68) and see Kevin Gilbert 'Treaty 88'. All advocated for an Aboriginal state. Agence France Presse
Agence France-Presse (AFP) is a French international news agency headquartered in Paris, France. Founded in 1835 as Havas, it is the world's oldest news agency.
AFP has regional headquarters in Nicosia, Montevideo, Hong Kong and Washington, D ...
(21 August 1998) claims Australia blocked a United Nations resolution calling for the self-determination of peoples, because it would have bolstered support for an Aboriginal state within Australia. Among those supporting such a state are the Council for Aboriginal Reconciliation
Reconciliation in Australia is a process which officially began in 1991, focused on the improvement of race relations between the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples of Australia and the rest of the population. The Council for Aborigina ...
.
Australian Capital Territory
 Supporters of the
Supporters of the Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (commonly abbreviated as ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) until 1938, is a landlocked federal territory of Australia containing the national capital Canberra and some surrounding townships. ...
(ACT) becoming a state believe the ACT, with a population only 20% lower than that of Tasmania, is underrepresented in the Australian Parliament
The Parliament of Australia (officially the Federal Parliament, also called the Commonwealth Parliament) is the legislative branch of the government of Australia. It consists of three elements: the monarch (represented by the governor-gen ...
.
Despite this, the movement is small and no prominent political figures have given it support as of 2022; further to this, the wording of s.125 of the Australian Constitution implies that the ACT must remain a territory owned by the Commonwealth and cannot become a state.
New England
New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian province ...
is a region of New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
and a proposed state. Some supporters also propose a "River-Eden" state in the south of NSW.
New Zealand
There have been several proposals forNew Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
to become the seventh state of Australia. One proposal, suggested humorously by the Liberal Senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the e ...
Ian Macdonald
Ian MacCormick (known by the pseudonym Ian MacDonald; 3 October 1948 – 20 August 2003) was a British music critic and author, best known for both '' Revolution in the Head'', his critical history of the Beatles which borrowed techniques from ...
, is that New Zealand's North Island
The North Island, also officially named Te Ika-a-Māui, is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but much less populous South Island by the Cook Strait. The island's area is , making it the world's 14th-larges ...
and South Island
The South Island, also officially named , is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasma ...
could become the seventh and eighth states of the Commonwealth. New Zealand was one of the colonies asked to join in the creation of the Commonwealth of Australia, even by the time the '' Commonwealth of Australia Constitution Act'' 1900 (Imp) was enacted, that law still provided for New Zealand to be one of the potential states of Australia. As ties have grown closer, people have made proposals for a customs union
A customs union is generally defined as a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff.GATTArticle 24 s. 8 (a)
Customs unions are established through trade pacts where the participant countries set up ...
, currency union
A currency union (also known as monetary union) is an intergovernmental agreement that involves two or more states sharing the same currency. These states may not necessarily have any further integration (such as an economic and monetary union, ...
and even a joint defence force The phrase Defence Force(s) (or Defense Force(s) in US English - see spelling differences) is in the title of the armed forces of certain countries and territories.
Defence forces
*Ambazonia Defence Forces
* Artsakh Defence Army
*Australian Defenc ...
. New Zealand and Australia enjoy close economic and political relations, mainly by way of the Trans-Tasman Travel Arrangement, Closer Economic Relations
The Australia–New Zealand Closer Economic Relations Trade Agreement, commonly known as Closer Economic Relations (CER), is a free trade agreement between the governments of New Zealand and Australia. It came into force on 1 January 1983, but ...
(CER) free trade agreement signed in 1983 and the Closer Defence Relations agreement signed in 1990. In 1989, former Prime Minister of New Zealand
The prime minister of New Zealand ( mi, Te pirimia o Aotearoa) is the head of government of New Zealand. The prime minister, Jacinda Ardern, leader of the New Zealand Labour Party, took office on 26 October 2017.
The prime minister (inform ...
Sir Geoffrey Palmer said that New Zealand had "gained most of the advantages of being a state of Australia without becoming one". The two countries, along with the USA, are in ANZUS
The Australia, New Zealand, United States Security Treaty (ANZUS or ANZUS Treaty) is a 1951 non-binding collective security agreement between Australia and New Zealand and, separately, Australia and the United States, to co-operate on military ...
, but New Zealand's opposition to nuclear weapons has weakened this treaty.
History
 In 1788,
In 1788, Arthur Phillip
Admiral Arthur Phillip (11 October 1738 – 31 August 1814) was a British Royal Navy officer who served as the first governor of the Colony of New South Wales.
Phillip was educated at Greenwich Hospital School from June 1751 unti ...
assumed the position of Governor of New South Wales
The governor of New South Wales is the viceregal representative of the Australian monarch, King Charles III, in the state of New South Wales. In an analogous way to the governor-general of Australia at the national level, the governors of the ...
, claiming New Zealand as part of New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
. In 1835, a group of Māori chiefs signed the ''Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of ...
'', which established New Zealand as a sovereign nation. A few years later, the Treaty of Waitangi
The Treaty of Waitangi ( mi, Te Tiriti o Waitangi) is a document of central importance to the history, to the political constitution of the state, and to the national mythos of New Zealand. It has played a major role in the treatment of the M ...
re-established British control of New Zealand. The Federal Council of Australasia
The Federal Council of Australasia was a forerunner to the current Commonwealth of Australia, though its structure and members were different.
The final (and successful) push for the Federal Council came at a "Convention" on 28 November 1883, whic ...
was formed with members representing New Zealand, Victoria, Tasmania, South Australia and Fiji. Although it held no official power it was a step into the establishment of the Commonwealth of Australia.
In 1890, there was an informal meeting of members from the Australasian colonies, this was followed by the first National Australasian convention a year later. The New Zealand representatives stated it would be unlikely to join a federation with Australia at its foundation, but it would be interested in doing so at a later date. New Zealand's position was taken into account when the Constitution of Australia was written up. Australia, in an attempt to sway New Zealand to join, gave Māori the right to vote in 1902, while Australian Aboriginal people did not fully gain the right to vote at national elections until 1962. In 1908 and 1912, Australia and New Zealand sent Australasians teams to the Olympic Games. New Zealand and Australian soldiers fought together in 1915 under the name ANZAC
The Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC) was a First World War army corps of the Mediterranean Expeditionary Force. It was formed in Egypt in December 1914, and operated during the Gallipoli campaign. General William Birdwood comm ...
.
Australian academic Bob Catley wrote a book titled ''Waltzing with Matilda: should New Zealand join Australia?'', a book arguing that New Zealand should become one with Australia, which was described by New Zealand political commentator Colin James
Colin James (born Colin James Munn, August 17, 1964) is a Canadian rock and blues singer and songwriter.
Biography Early years
James was born in Regina, Saskatchewan, Canada. His grandpa was Serbian. He got his break opening for Stevie Ray ...
as "a book for Australians". In December 2006, an Australian Federal Parliamentary Committee recommended that Australia and New Zealand pursue a full union, or at least adopt a common ANZ currency and more common markets. The Committee found that "while Australia and New Zealand are of course two sovereign nations, it seems... that the strong ties between the two countries – the economic, cultural, migration, defence, governmental and people-to-people linkages – suggest that an even closer relationship, including the possibility of union, is both desirable and realistic." This was despite the Australian Treasurer
The Treasurer of Australia (or Federal Treasurer) is a high ranking official and senior minister of the Crown in the Government of Australia who is the head of the Ministry of the Treasury which is responsible for government expenditure and ...
Peter Costello and New Zealand Minister of Finance Michael Cullen saying that a common currency was "not on the agenda".
A 2010 UMR research poll asked 1000 people in Australia and New Zealand a series of questions relating to New Zealand's becoming the seventh state of Australia. One quarter of the people thought it was something to look into. Over 40% thought the idea was worth debating. More Australians than New Zealanders would support such a move.
Advantages
A leading factor for the proposal of New Zealand as a state of Australia is the major economic benefits it could bring. However,free trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. It can also be understood as the free market idea applied to international trade. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold ...
and open borders now appear to be the maximum extent of public acceptance of the proposal. There are many family connections between the two nations, with around 500,000 New Zealanders living in Australia and 60,000 Australians living in New Zealand as of 2013. Peter Slipper
Peter Neil Slipper (born 14 February 1950) is a former Australian politician who served in the House of Representatives from 1984 to 1987 and from 1993 to 2013, representing the Division of Fisher in Queensland. He was Speaker of the House ...
, a former Member of Australia's Parliament, once said, "It's about how can we improve the quality of living for people on both sides of the Tasman" when referring to the proposal.
Disadvantages
Concerns have been expressed about the need for a common currency, about changes to theSouth Pacific Nuclear Free Zone Treaty
The Treaty of Rarotonga is the common name for the South Pacific Nuclear Free Zone Treaty, which formalises a nuclear-weapon-free zone in the South Pacific. The treaty bans the use, testing, and possession of nuclear weapons within the borde ...
, and about the retention of the administrative and political recognition of the ancestral rights of the indigenous Maori population under the Treaty of Waitangi
The Treaty of Waitangi ( mi, Te Tiriti o Waitangi) is a document of central importance to the history, to the political constitution of the state, and to the national mythos of New Zealand. It has played a major role in the treatment of the M ...
.
A number of disparities that could lead to conflict including the current constitutions (written in Australia, unwritten in New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
), the status of political rights (constitutionally entrenched in Australia but not in New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
). Some New Zealanders feel they have established a national identity, one which they feel they may lose if they became part of Australia. Others argue New Zealand is too far away from the mainland of Australia.
North Queensland
One proposal is that Queensland should be divided by the 22nd parallel with the boundary running just south of Sarina on the coast to theNorthern Territory
The Northern Territory (commonly abbreviated as NT; formally the Northern Territory of Australia) is an Australian territory in the central and central northern regions of Australia. The Northern Territory shares its borders with Western Au ...
border between Boulia
Boulia () is an outback town and locality in the Shire of Boulia, Queensland, Australia. In the , Boulia had a population of 301 people.
Boulia is the administrative centre of the Boulia Shire, population approximately 600, which covers an area ...
and Mount Isa
Mount Isa ( ) is a city in the Gulf Country region of Queensland, Australia. It came into existence because of the vast mineral deposits found in the area. Mount Isa Mines (MIM) is one of the most productive single mines in world history, b ...
, and the capital would be Sellheim, near Charters Towers
Charters Towers is a rural town in the Charters Towers Region, Queensland, Australia. It is by road south-west from Townsville on the Flinders Highway. During the last quarter of the 19th century, the town boomed as the rich gold deposits unde ...
, to overcome rivalry between Mackay Mackay may refer to:
*Clan Mackay, the Scottish clan from which the surname "MacKay" derives
Mackay may also refer to:
Places Australia
* Mackay Region, a local government area
** Mackay, Queensland, a city in the above region
*** Mackay Airport ...
, Townsville
Townsville is a city on the north-eastern coast of Queensland, Australia. With a population of 180,820 as of June 2018, it is the largest settlement in North Queensland; it is unofficially considered its capital. Estimated resident population, 30 ...
and Cairns. The name Capricornia has been proposed for this state.
According to ''The Courier-Mail
''The Courier-Mail'' is an Australian newspaper published in Brisbane. Owned by News Corp Australia, it is published daily from Monday to Saturday in tabloid format. Its editorial offices are located at Bowen Hills, in Brisbane's inner northe ...
'' in 2010, the majority of North Queensland Mayors were in favour of the separation from Queensland proper. Only two of the hundred delegates at the NQ Local Government Association meeting were against the proposal – the two being Mayor Val Schier (Cairns) and Mayor Ben Callcott (Charters Towers).
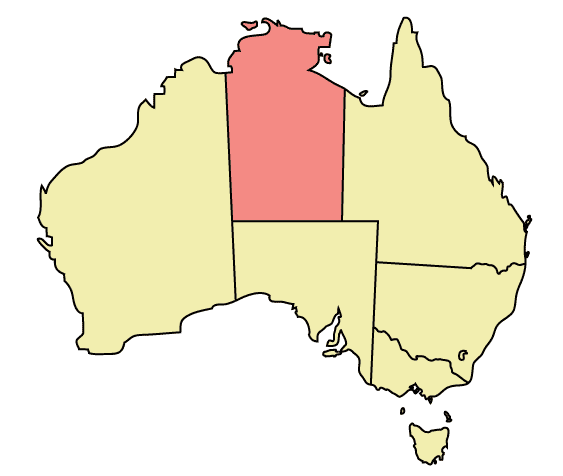
Northern Territory
 The
The Northern Territory
The Northern Territory (commonly abbreviated as NT; formally the Northern Territory of Australia) is an Australian territory in the central and central northern regions of Australia. The Northern Territory shares its borders with Western Au ...
(NT) is the most commonly mentioned potential seventh state.
In a 1998 referendum, the voters of the Northern Territory narrowly rejected a statehood proposal that would have given the territory three senators, rather than the twelve held by the other states, although the name "Northern Territory" would have been retained.
With statehood being rejected, it is likely that the Northern Territory will remain a territory for the near future, though former Chief Minister
A chief minister is an elected or appointed head of government of – in most instances – a sub-national entity, for instance an administrative subdivision or federal constituent entity. Examples include a state (and sometimes a union terri ...
Clare Martin and the majority of Territorians are said to be in favour of statehood.
While statehood would under normal circumstances give the Northern Territory 12 senators, the same number of senators as every other state, its population as of 2021 is only 3% of the largest state, New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
. This means that whilst one NSW senator represents 682,000 people, one NT senator would represent approximately 21,000 people. By comparison, one Tasmanian senator represents 45,000 people, while one South Australian senator (next smallest state by population) represents 148,000 people. If the NT were only given 3 senators as proposed in the 1998 referendum, each would represent around 63,000 people (along with a higher quota for election)
An alternative name for the new state would be North Australia
North Australia can refer to a short-lived former British colony, a former federal territory of the Commonwealth of Australia, or a proposed state which would replace the current Northern Territory.
Colony (1846–1847)
A colony of North Austr ...
, which would be shared by two historic regions. The matter was raised again in July 2015, with a further referendum in 2018 being mooted.
Riverina
Riverina
The Riverina
is an agricultural region of south-western New South Wales, Australia. The Riverina is distinguished from other Australian regions by the combination of flat plains, warm to hot climate and an ample supply of water for irrigation ...
is also a proposed state, in the Murray River
The Murray River (in South Australia: River Murray) ( Ngarrindjeri: ''Millewa'', Yorta Yorta: ''Tongala'') is a river in Southeastern Australia. It is Australia's longest river at extent. Its tributaries include five of the next six longe ...
region, on the border between New South Wales and Victoria. The Division of Riverina is currently a smaller area than traditional Riverina, which would include the Division of Farrer
The Division of Farrer is an Australian electoral division in the state of New South Wales.
Geography
Since 1984, federal electoral division boundaries in Australia have been determined at redistributions by a redistribution committee appointe ...
. Along with the ACT, it is one of the few landlocked proposed states.
In December 2020, there was a proposal by Northern Victoria MP Tim Quilty to form a new state from Northeastern Victoria and Southeastern New South Wales, because people in regional areas feel like they are neglected by their state governments. There was also a proposal to form three new states. They are: A new state comprising Greater Geelong and Metropolitan Melbourne; Regional Northeastern Victoria and Southeastern New South Wales combing, and Greater Sydney to become separate states.
See also
*51st state
51st state in American political discourse refers to areas considered candidates for U.S. statehood, joining the 50 states that have constituted the United States since 1959. The phrase has been applied to external territories as well as parts ...
* Australia–New Zealand relations
Foreign relations between neighbouring countries Australia and New Zealand, also referred to as Trans-Tasman relations, are extremely close. Both countries share a British colonial heritage as antipodean Dominions and settler colonies, and ...
* Australia–Papua New Guinea relations
* Australian regional rivalries
* List of regions in Australia
* New Australia
New Australia was a utopian socialist settlement in Paraguay created by the New Australian Movement. The colony was officially founded on 28 September 1893 as Colonia Nueva Australia and comprised 238 people.
History
The New Australia ...
* Pacific Union
* Proposed provinces and territories of Canada
* Secessionism in Western Australia
References
External links
Why New Zealand did not become an Australian State
The Australian Empire
{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Proposed States Of Australia Government of Australia * Australia–Papua New Guinea relations Australia–Fiji relations Australia–New Zealand relations National unifications States, proposed Proposals in Australia