Prayer In Latter Day Saint Theology And Practice on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Prayer is an
Prayer is an
 Anthropologically, the concept of prayer is closely related to that of
Anthropologically, the concept of prayer is closely related to that of 
 In this approach, the purpose of prayer is to enable the person praying to gain a direct experience of the recipient of the prayer (or as close to direct as a specific theology permits). This approach is very significant in Christianity and widespread in Judaism (although less popular theologically). In
In this approach, the purpose of prayer is to enable the person praying to gain a direct experience of the recipient of the prayer (or as close to direct as a specific theology permits). This approach is very significant in Christianity and widespread in Judaism (although less popular theologically). In
 In the Hebrew Bible prayer is an evolving means of interacting with
In the Hebrew Bible prayer is an evolving means of interacting with
 Observant Jews pray three times a day,
Observant Jews pray three times a day,  There are also many other ritualistic prayers a Jew performs during their day, such as washing before eating bread, washing after one wakes up in the morning, and doing grace after meals.
There are also many other ritualistic prayers a Jew performs during their day, such as washing before eating bread, washing after one wakes up in the morning, and doing grace after meals.
 Christian prayers are quite varied. They can be completely spontaneous, or read entirely from a text, like the Anglican
Christian prayers are quite varied. They can be completely spontaneous, or read entirely from a text, like the Anglican
 The
The
 In the earliest Buddhist tradition, the
In the earliest Buddhist tradition, the
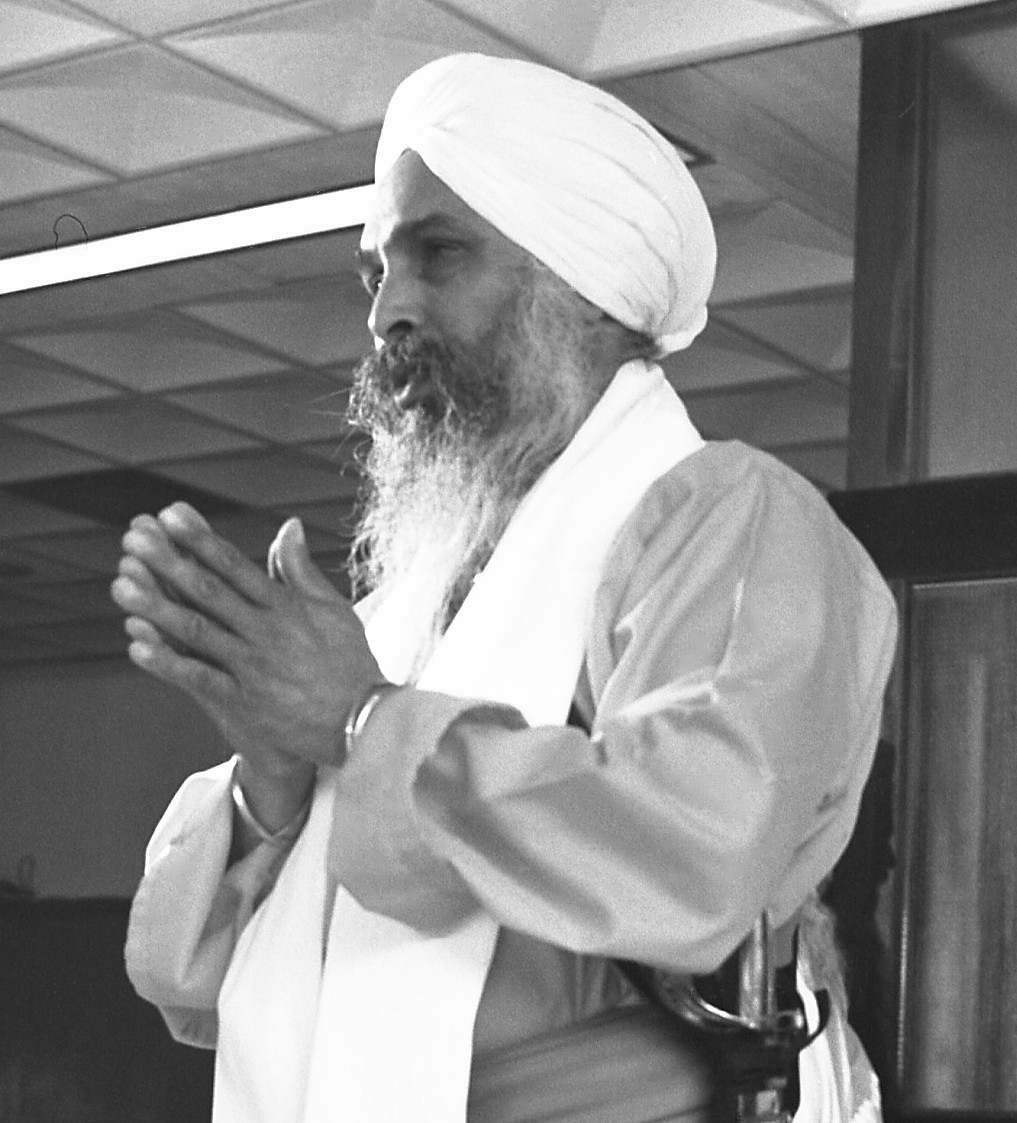
 The ''Ardās'' (Punjabi: ਅਰਦਾਸ) is a Sikh prayer that is done before performing or after undertaking any significant task; after reciting the daily ''Banis'' (prayers); or completion of a service like the ''Paath'' (scripture reading/recitation), ''kirtan'' (hymn-singing) program or any other religious program. In Sikhism, these prayers are also said before and after eating. The prayer is a plea to God to support and help the devotee with whatever he or she is about to undertake or has done.
The ''Ardas'' is usually always done standing up with folded hands. The beginning of the ''Ardas'' is strictly set by the tenth Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh. When it comes to conclusion of this prayer, the devotee uses words like "Waheguru please bless me in the task that I am about to undertake" when starting a new task or "Akal Purakh, having completed the hymn-singing, we ask for your continued blessings so that we can continue with your memory and remember you at all times", etc. The word "Ardās" is derived from Persian word 'Arazdashat', meaning a request, supplication, prayer, petition or an address to a superior authority.
Ardās is a unique prayer based on the fact that it is one of the few well-known prayers in the Sikh religion that was not written in its entirety by the Gurus. The Ardās cannot be found within the pages of the Guru Granth Sahib because it is a continually changing devotional text that has evolved over time in order for it to encompass the feats, accomplishments, and feelings of all generations of Sikhs within its lines. Taking the various derivation of the word Ardās into account, the basic purpose of this prayer is an appeal to Waheguru for his protection and care, as well as being a plea for the welfare and prosperity of all mankind, and a means for the Sikhs to thank Waheguru for all that he has done.
The ''Ardās'' (Punjabi: ਅਰਦਾਸ) is a Sikh prayer that is done before performing or after undertaking any significant task; after reciting the daily ''Banis'' (prayers); or completion of a service like the ''Paath'' (scripture reading/recitation), ''kirtan'' (hymn-singing) program or any other religious program. In Sikhism, these prayers are also said before and after eating. The prayer is a plea to God to support and help the devotee with whatever he or she is about to undertake or has done.
The ''Ardas'' is usually always done standing up with folded hands. The beginning of the ''Ardas'' is strictly set by the tenth Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh. When it comes to conclusion of this prayer, the devotee uses words like "Waheguru please bless me in the task that I am about to undertake" when starting a new task or "Akal Purakh, having completed the hymn-singing, we ask for your continued blessings so that we can continue with your memory and remember you at all times", etc. The word "Ardās" is derived from Persian word 'Arazdashat', meaning a request, supplication, prayer, petition or an address to a superior authority.
Ardās is a unique prayer based on the fact that it is one of the few well-known prayers in the Sikh religion that was not written in its entirety by the Gurus. The Ardās cannot be found within the pages of the Guru Granth Sahib because it is a continually changing devotional text that has evolved over time in order for it to encompass the feats, accomplishments, and feelings of all generations of Sikhs within its lines. Taking the various derivation of the word Ardās into account, the basic purpose of this prayer is an appeal to Waheguru for his protection and care, as well as being a plea for the welfare and prosperity of all mankind, and a means for the Sikhs to thank Waheguru for all that he has done.
 In Thelema (which includes both theist as well as atheist practitioners) adherents share a number of practices that are forms of individual prayer, including basic yoga; (asana and pranayama); various forms of ritual magick (Aleister Crowley), magick; rituals of one's own devising (often based upon a syncretism of religions, or Western Esotericism, such as the Lesser Banishing Ritual of the Pentagram and Star Ruby); and performance of Liber Resh vel Helios (aka Liber 200), which consists of four daily adorations to the sun (often consisting of four hand/body positions and recitation of a memorized song, normally spoken, addressing different godforms identified with the sun).
While no dogma within Thelema expresses the purpose behind any individual aspirant who chooses to perform "Resh", note that the practice of "Resh" is not a simple petition toward the sun, nor a form of "worshiping" the celestial body that we call the Sun, but instead uses the positioning of that source of light, which enables life on our planet, as well as using mythological images of that solar force, so that the individual can perform the prayer, possibly furthering a self-identification with the sun, so "that repeated application of the Liber Resh adorations expands the consciousness of the individual by compelling him to take a different perspective, by inducing him to 'look at things from the point of view of the Sun' [...]".
In Thelema (which includes both theist as well as atheist practitioners) adherents share a number of practices that are forms of individual prayer, including basic yoga; (asana and pranayama); various forms of ritual magick (Aleister Crowley), magick; rituals of one's own devising (often based upon a syncretism of religions, or Western Esotericism, such as the Lesser Banishing Ritual of the Pentagram and Star Ruby); and performance of Liber Resh vel Helios (aka Liber 200), which consists of four daily adorations to the sun (often consisting of four hand/body positions and recitation of a memorized song, normally spoken, addressing different godforms identified with the sun).
While no dogma within Thelema expresses the purpose behind any individual aspirant who chooses to perform "Resh", note that the practice of "Resh" is not a simple petition toward the sun, nor a form of "worshiping" the celestial body that we call the Sun, but instead uses the positioning of that source of light, which enables life on our planet, as well as using mythological images of that solar force, so that the individual can perform the prayer, possibly furthering a self-identification with the sun, so "that repeated application of the Liber Resh adorations expands the consciousness of the individual by compelling him to take a different perspective, by inducing him to 'look at things from the point of view of the Sun' [...]".
Online reprint
by Internet Infidels at Infidels.org. Some attempt to heal by prayer, mental practices, spiritual insights, or other techniques, claiming they can summon divine or supernatural intervention on behalf of the ill. Others advocate that ill people may achieve healing through prayer performed by themselves. According to the varied beliefs of those who practice it, faith healing may be said to afford gradual relief from pain or sickness or to bring about a sudden "miracle cure", and it may be used in place of, or in tandem with, conventional medical techniques for alleviating or curing diseases. Faith healing has been criticized on the grounds that those who use it may delay seeking potentially curative conventional medical care. This is particularly problematic when parents use faith healing techniques on children.
 In 1872, Francis Galton conducted a famous statistics, statistical experiment to determine whether prayer had a physical effect on the external environment. Galton hypothesized that if prayer was effective, members of the British Royal family would live longer, given that thousands prayed for their wellbeing every Sunday. He therefore compared longevity in the British Royal family with that of the general population, and found no difference. While the experiment was probably intended to satirize, and suffered from a number of Confounding variable, confounders, it set the precedent for a number of different studies, the results of which are contradictory.
Two studies claimed that patients who are being prayed for recover more quickly or more frequently although critics have claimed that the methodology of such studies are flawed, and the perceived effect disappears when controls are tightened. One such study, with a double-blind design and about 500 subjects per group, was published in 1988; it suggested that intercessory prayer by born again Christians had a statistically significant positive effect on a coronary care unit population. Critics contend that there were severe methodological problems with this study. Another such study was reported by Harris et al. Critics also claim that the 1988 study was not fully double-blinded, and that in the Harris study, patients actually had a longer hospital stay in the prayer group, if one discounts the patients in both groups who left before prayers began, although the Harris study did demonstrate the prayed for patients on average received lower course scores (indicating better recovery).
One of the largest randomized, blind clinical trials was a remote ''retroactive'' intercessory prayer study conducted in Israel by Leibovici. This study used 3393 patient records from 1990 to 1996, and blindly assigned some of these to an intercessory prayer group. The prayer group had shorter hospital stays and duration of fever.
Several studies of prayer effectiveness have yielded null results. A 2001 double-blind study of the Mayo Clinic found no significant difference in the recovery rates between people who were (unbeknownst to them) assigned to a group that prayed for them and those who were not. Similarly, the MANTRA study conducted by Duke University found no differences in outcome of cardiac procedures as a result of prayer. In another similar study published in the ''American Heart Journal'' in 2006, Christian intercessory prayer when reading a scripted prayer was found to have no effect on the recovery of heart surgery patients; however, the study found patients who had knowledge of receiving prayer had slightly higher instances of complications than those who did not know if they were being prayed for or those who did not receive prayer. Another 2006 study suggested that prayer actually had a significant negative effect on the recovery of cardiac bypass patients, resulting in more frequent deaths and slower recovery time for those patient who received prayers.
Many believe that prayer can aid in recovery, not due to divine influence but due to psychological and physical benefits. It has also been suggested that if a person knows that he or she is being prayed for it can be uplifting and increase morale, thus aiding recovery. (See Subject-expectancy effect.) Many studies have suggested that prayer can reduce physical stress, regardless of the god or gods a person prays to, and this may be true for many worldly reasons. According to a study by Centra State Hospital, "the psychological benefits of prayer may help reduce stress and anxiety, promote a more positive outlook, and strengthen the will to live." Other practices such as yoga, T'ai chi ch'uan, t'ai chi, and meditation may also have a positive impact on physical and psychological health.
"W"
Others feel that the concept of conducting prayer experiments reflects a misunderstanding of the purpose of prayer. The previously mentioned study published in the ''American Heart Journal'' indicated that some of the intercessors who took part in it complained about the scripted nature of the prayers that were imposed to them, saying that this is not the way they usually conduct prayer:
One scientific movement attempts to track the physical effects of prayer through neuroscience. Leaders in this movement include Andrew B. Newberg, Andrew Newberg, an associate professor at the University of Pennsylvania. In Newberg's brain scans, monks, priests, nuns, Nun#Distinction between a nun and a religious sister, sisters and gurus alike have exceptionally focused attention and compassion sites. This is a result of the frontal lobe of the brain's engagement (Newberg, 2009). Newburg believes that anybody can connect to the supernatural with practice. Those without religious affiliations benefit from the connection to the metaphysical as well. Newberg also states that further evidence towards humans' need for metaphysical relationships is that as science had increased spirituality has not decreased. Newburg believes that at the end of the 18th century, when the scientific method began to consume the human mind, religion could have vanished. However, two hundred years later, the perception of spirituality, in many instances, appears to be gaining in strength (2009). Newberg's research also provides the connection between prayer and meditation and health. By understanding how the brain works during religious experiences and practices Newberg's research shows that the brain changes during these practices allowing an understanding of how religion affects psychological and physical health (2009). For example, brain activity during meditation indicates that people who frequently practice prayer or meditation experience lower blood-pressure, lower heart rates, decreased anxiety, and decreased depression.
In 1872, Francis Galton conducted a famous statistics, statistical experiment to determine whether prayer had a physical effect on the external environment. Galton hypothesized that if prayer was effective, members of the British Royal family would live longer, given that thousands prayed for their wellbeing every Sunday. He therefore compared longevity in the British Royal family with that of the general population, and found no difference. While the experiment was probably intended to satirize, and suffered from a number of Confounding variable, confounders, it set the precedent for a number of different studies, the results of which are contradictory.
Two studies claimed that patients who are being prayed for recover more quickly or more frequently although critics have claimed that the methodology of such studies are flawed, and the perceived effect disappears when controls are tightened. One such study, with a double-blind design and about 500 subjects per group, was published in 1988; it suggested that intercessory prayer by born again Christians had a statistically significant positive effect on a coronary care unit population. Critics contend that there were severe methodological problems with this study. Another such study was reported by Harris et al. Critics also claim that the 1988 study was not fully double-blinded, and that in the Harris study, patients actually had a longer hospital stay in the prayer group, if one discounts the patients in both groups who left before prayers began, although the Harris study did demonstrate the prayed for patients on average received lower course scores (indicating better recovery).
One of the largest randomized, blind clinical trials was a remote ''retroactive'' intercessory prayer study conducted in Israel by Leibovici. This study used 3393 patient records from 1990 to 1996, and blindly assigned some of these to an intercessory prayer group. The prayer group had shorter hospital stays and duration of fever.
Several studies of prayer effectiveness have yielded null results. A 2001 double-blind study of the Mayo Clinic found no significant difference in the recovery rates between people who were (unbeknownst to them) assigned to a group that prayed for them and those who were not. Similarly, the MANTRA study conducted by Duke University found no differences in outcome of cardiac procedures as a result of prayer. In another similar study published in the ''American Heart Journal'' in 2006, Christian intercessory prayer when reading a scripted prayer was found to have no effect on the recovery of heart surgery patients; however, the study found patients who had knowledge of receiving prayer had slightly higher instances of complications than those who did not know if they were being prayed for or those who did not receive prayer. Another 2006 study suggested that prayer actually had a significant negative effect on the recovery of cardiac bypass patients, resulting in more frequent deaths and slower recovery time for those patient who received prayers.
Many believe that prayer can aid in recovery, not due to divine influence but due to psychological and physical benefits. It has also been suggested that if a person knows that he or she is being prayed for it can be uplifting and increase morale, thus aiding recovery. (See Subject-expectancy effect.) Many studies have suggested that prayer can reduce physical stress, regardless of the god or gods a person prays to, and this may be true for many worldly reasons. According to a study by Centra State Hospital, "the psychological benefits of prayer may help reduce stress and anxiety, promote a more positive outlook, and strengthen the will to live." Other practices such as yoga, T'ai chi ch'uan, t'ai chi, and meditation may also have a positive impact on physical and psychological health.
"W"
Others feel that the concept of conducting prayer experiments reflects a misunderstanding of the purpose of prayer. The previously mentioned study published in the ''American Heart Journal'' indicated that some of the intercessors who took part in it complained about the scripted nature of the prayers that were imposed to them, saying that this is not the way they usually conduct prayer:
One scientific movement attempts to track the physical effects of prayer through neuroscience. Leaders in this movement include Andrew B. Newberg, Andrew Newberg, an associate professor at the University of Pennsylvania. In Newberg's brain scans, monks, priests, nuns, Nun#Distinction between a nun and a religious sister, sisters and gurus alike have exceptionally focused attention and compassion sites. This is a result of the frontal lobe of the brain's engagement (Newberg, 2009). Newburg believes that anybody can connect to the supernatural with practice. Those without religious affiliations benefit from the connection to the metaphysical as well. Newberg also states that further evidence towards humans' need for metaphysical relationships is that as science had increased spirituality has not decreased. Newburg believes that at the end of the 18th century, when the scientific method began to consume the human mind, religion could have vanished. However, two hundred years later, the perception of spirituality, in many instances, appears to be gaining in strength (2009). Newberg's research also provides the connection between prayer and meditation and health. By understanding how the brain works during religious experiences and practices Newberg's research shows that the brain changes during these practices allowing an understanding of how religion affects psychological and physical health (2009). For example, brain activity during meditation indicates that people who frequently practice prayer or meditation experience lower blood-pressure, lower heart rates, decreased anxiety, and decreased depression.
 Prayer is an
Prayer is an invocation
An invocation (from the Latin verb ''invocare'' "to call on, invoke, to give") may take the form of:
*Supplication, prayer or spell.
*A form of possession.
*Command or conjuration.
*Self-identification with certain spirits.
These forms are ...
or act that seeks to activate a rapport
Rapport () is a close and harmonious relationship in which the people or groups concerned are "in sync" with each other, understand each other's feelings or ideas, and communicate smoothly.
The word stems from the French verb which means liter ...
with an object of worship through deliberate communication
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquir ...
. In the narrow sense, the term refers to an act of supplication
Supplication (also known as petitioning) is a form of prayer, wherein one party humbly or earnestly asks another party to provide something, either for the party who is doing the supplicating (e.g., "Please spare my life.") or on behalf of someon ...
or intercession
Intercession or intercessory prayer is the act of praying to a deity on behalf of others, or Intercession of saints, asking a saint in heaven to pray on behalf of oneself or for others.
The Apostle Paul's exhortation to Saint Timothy, Timothy sp ...
directed towards a deity
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greate ...
or a deified ancestor
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder or a forebear, is a parent or (recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from whom ...
. More generally, prayer can also have the purpose of thanksgiving
Thanksgiving is a national holiday celebrated on various dates in the United States, Canada, Grenada, Saint Lucia, Liberia, and unofficially in countries like Brazil and Philippines. It is also observed in the Netherlander town of Leiden and ...
or praise
Praise as a form of social interaction expresses recognition, reassurance or admiration.
Praise is expressed verbally as well as by body language (facial expression and gestures).
Verbal praise consists of a positive evaluations of another's a ...
, and in comparative religion
Comparative religion is the branch of the study of religions with the systematic comparison of the doctrines and practices, themes and impacts (including migration) of the world's religions. In general the comparative study of religion yie ...
is closely associated with more abstract forms of meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally cal ...
and with charms or spells.
Prayer can take a variety of forms: it can be part of a set liturgy
Liturgy is the customary public ritual of worship performed by a religious group. ''Liturgy'' can also be used to refer specifically to public worship by Christians. As a religious phenomenon, liturgy represents a communal response to and partic ...
or ritual
A ritual is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, actions, or objects, performed according to a set sequence. Rituals may be prescribed by the traditions of a community, including a religious community. Rituals are characterized, b ...
, and it can be performed alone or in groups. Prayer may take the form of a hymn
A hymn is a type of song, and partially synonymous with devotional song, specifically written for the purpose of adoration or prayer, and typically addressed to a deity or deities, or to a prominent figure or personification. The word ''hymn'' ...
, incantation
An incantation, a spell, a charm, an enchantment or a bewitchery, is a magical formula intended to trigger a magical effect on a person or objects. The formula can be spoken, sung or chanted. An incantation can also be performed during ceremo ...
, formal creed
A creed, also known as a confession of faith, a symbol, or a statement of faith, is a statement of the shared beliefs of a community (often a religious community) in a form which is structured by subjects which summarize its core tenets.
The ea ...
al statement, or a spontaneous utterance in the praying person.
The act of prayer is attested in written sources as early as 5000 years ago. Today, most major religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, ...
s involve prayer in one way or another; some ritualize the act, requiring a strict sequence of actions or placing a restriction on who is permitted to pray, while others teach that prayer may be practised spontaneously by anyone at any time.
Scientific studies regarding the use of prayer have mostly concentrated on its effect on the healing of sick or injured people. The efficacy of prayer
The efficacy of prayer has been studied since at least 1872, generally through experiments to determine whether prayer or intercessory prayer has a measurable effect on the health of the person for whom prayer is offered. A study in 2006 indicate ...
in faith healing
Faith healing is the practice of prayer and gestures (such as laying on of hands) that are believed by some to elicit divine intervention in spiritual and physical healing, especially the Christian practice. Believers assert that the healing ...
has been evaluated in numerous studies, with contradictory results.
Etymology
The English term ''prayer'' is from . TheVulgate
The Vulgate (; also called (Bible in common tongue), ) is a late-4th-century Latin translation of the Bible.
The Vulgate is largely the work of Jerome who, in 382, had been commissioned by Pope Damasus I to revise the Gospels u ...
Latin is , which translates Greek προσευχή in turn the Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond th ...
translation of Biblical Hebrew
Biblical Hebrew (, or , ), also called Classical Hebrew, is an archaic form of the Hebrew language, a language in the Canaanite branch of Semitic languages spoken by the Israelites in the area known as the Land of Israel, roughly west of ...
''tĕphillah''.
Act of prayer
Various spiritual traditions offer a wide variety of devotional acts. There are morning and evening prayers, graces said over meals, and reverent physical gestures. Some Christians bow their heads and fold their hands. Some Native Americans regard dancing as a form of prayer. SomeSufis
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spiri ...
whirl
Whirl may refer to:
Spinning
* Whirling, a dance genre
* Whirl (''Transformers''), a character in the ''Transformers'' franchise
* Tilt-A-Whirl, a type of amusement ride
* Atomic whirl, a symbol of atheism
* ''Whirl'' magazine, a luxury lifesty ...
. Hindus chant mantras. Jewish prayer may involve swaying back and forth and bowing. Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
prayer involves bowing, kneeling and prostration
Prostration is the gesture of placing one's body in a reverentially or submissively prone position. Typically prostration is distinguished from the lesser acts of bowing or kneeling by involving a part of the body above the knee, especially t ...
. Quakers keep silent. Some pray according to standardized rituals and liturgies, while others prefer extemporaneous prayers. Still others combine the two.
Friedrich Heiler Friedrich Heiler (January 30, 1892 – April 18, 1967) was a German theologian and historian of religion.
Heiler came from a Roman Catholic family. 1918 he became ''Privatdozent'' in University of Munich, from where he 1920 moved to theological fac ...
is often cited in Christian circles for his systematic ''Typology of Prayer'' which lists six types of prayer: primitive, ritual, Greek cultural, philosophical, mystical, and prophetic. Some forms of prayer require a prior ritualistic form of cleansing or purification such as in ghusl
( ar, غسل ', ) is an Arabic term to the full-body ritual purification mandatory before the performance of various rituals and prayers, for any adult Muslim after sexual intercourse/ejaculation or completion of the menstrual cycle.
The washin ...
and wudhu
Wuḍūʾ ( ar, الوضوء ' ) is the Islamic procedure for cleansing parts of the body, a type of ritual purification, or ablution. The 4 Fardh (Mandatory) acts of ''Wudu'' consists of washing the face, arms, then wiping the head and the feet ...
.
Prayer may be done privately and individually, or it may be done corporately in the presence of fellow believers. Prayer can be incorporated into a daily "thought life", in which one is in constant communication with a god. Some people pray throughout all that is happening during the day and seek guidance as the day progresses. This is actually regarded as a requirement in several Christian denominations, although enforcement is not possible nor desirable. There can be many different answers to prayer, just as there are many ways to interpret an answer to a question, if there in fact comes an answer. Some may experience audible, physical, or mental epiphanies. If indeed an answer comes, the time and place it comes is considered random.
Some outward acts that sometimes accompany prayer are: anointing with oil; ringing a bell; burning incense or paper; lighting a candle or candles; See, for example, facing a specific direction (i.e. towards Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red ...
or the East); making the sign of the cross
Making the sign of the cross ( la, signum crucis), or blessing oneself or crossing oneself, is a ritual blessing made by members of some branches of Christianity. This blessing is made by the tracing of an upright cross or + across the body with ...
. One less noticeable act related to prayer is fasting
Fasting is the abstention from eating and sometimes drinking. From a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (see " Breakfast"), or to the metabolic state achieved after ...
.
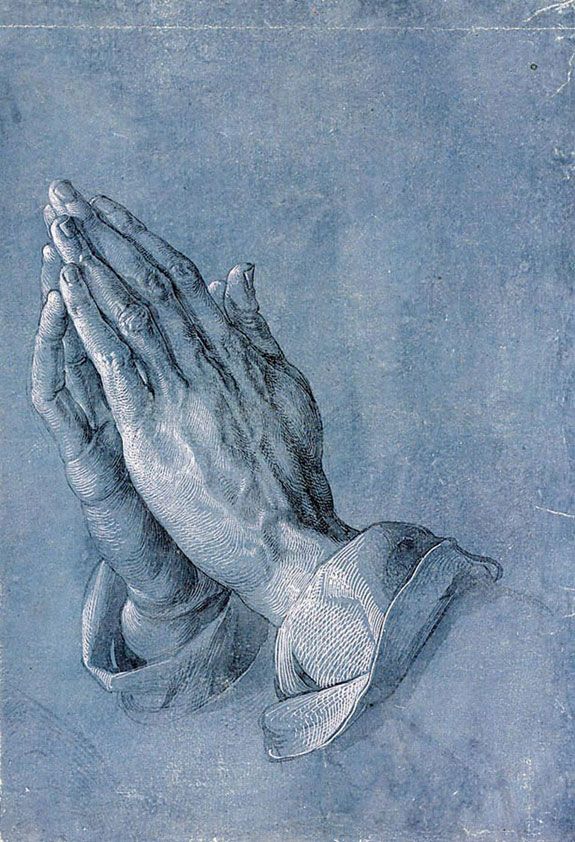
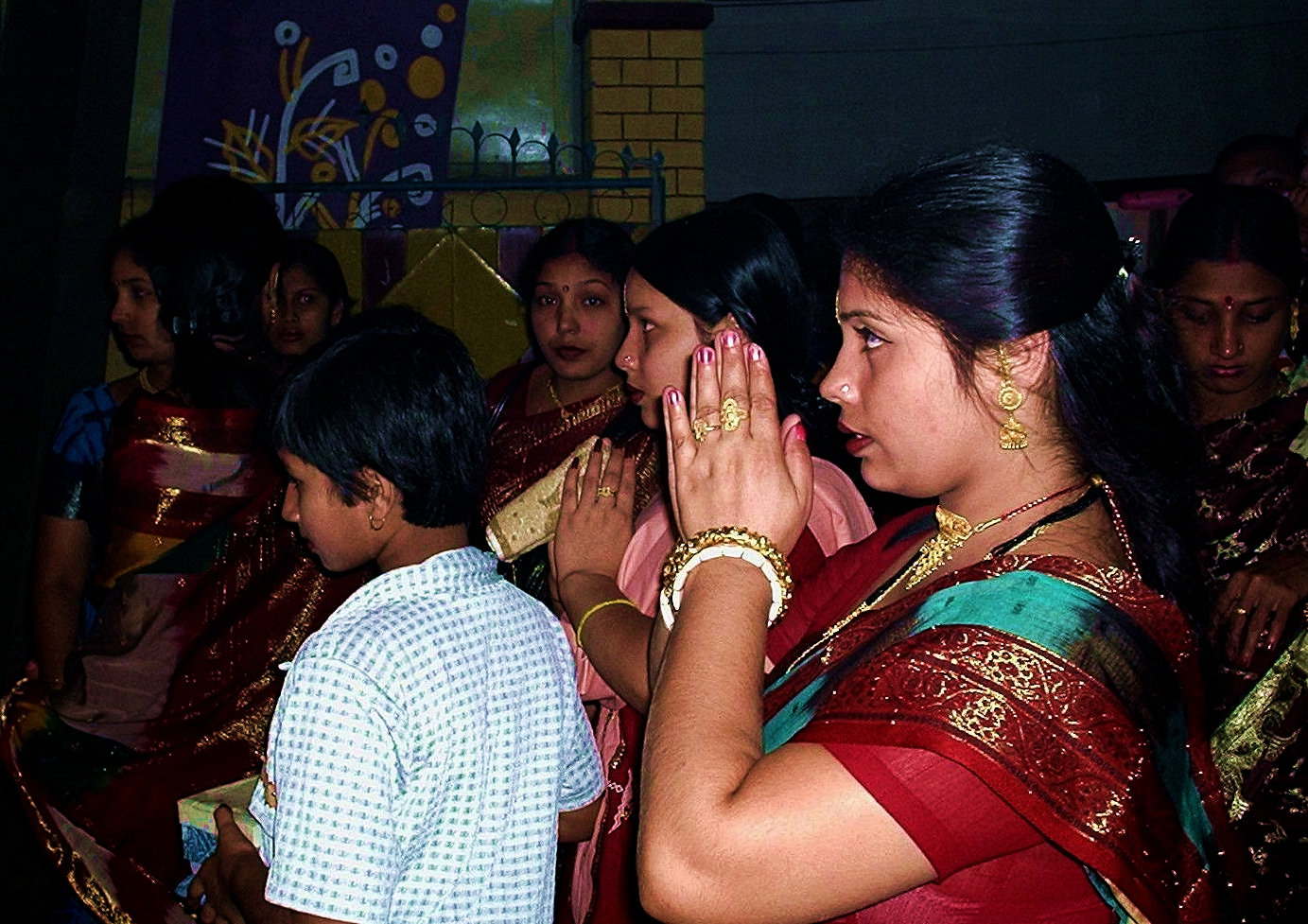
A variety of body postures may be assumed, often with specific meaning (mainly respect or adoration) associated with them: standing; sitting; kneeling; prostrate on the floor; eyes opened; eyes closed; hands folded or clasped; hands upraised; holding hands with others; a laying on of hands and others. Prayers may be recited from memory, read from a book of prayers, or composed spontaneously as they are prayed. They may be said, chanted, or sung. They may be with musical accompaniment or not. There may be a time of outward silence while prayers are offered mentally. Often, there are prayers to fit specific occasions, such as the blessing of a meal, the birth or death of a loved one, other significant events in the life of a believer, or days of the year that have special religious significance. Details corresponding to specific traditions are outlined below.
Origins and early history
 Anthropologically, the concept of prayer is closely related to that of
Anthropologically, the concept of prayer is closely related to that of surrender
Surrender may refer to:
* Surrender (law), the early relinquishment of a tenancy
* Surrender (military), the relinquishment of territory, combatants, facilities, or armaments to another power
Film and television
* ''Surrender'' (1927 film), an ...
and supplication
Supplication (also known as petitioning) is a form of prayer, wherein one party humbly or earnestly asks another party to provide something, either for the party who is doing the supplicating (e.g., "Please spare my life.") or on behalf of someon ...
.
The traditional posture of prayer in medieval Europe is kneeling or supine with clasped hands, in antiquity more typically with raised hands. The early Christian prayer posture was standing, looking up to heaven, with outspread arms and bare head. This is the pre-Christian, pagan prayer posture (except for the bare head, which was prescribed for males in Corinthians 11:4, in Roman paganism, the head had to be covered in prayer). Certain Cretan and Cypriote figures of the Late Bronze Age, with arms raised, have been interpreted as worshippers. Their posture is similar to the "flight" posture, a crouching posture with raised hands, observed in schizophrenic patients and related to the universal "hands up" gesture of surrender. The kneeling posture with clasped hands appears to have been introduced only with the beginning high medieval period, presumably adopted from a gesture of feudal homage.
Although prayer in its literal sense is not used in animism
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning 'breath, Soul, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct Spirituality, spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things—Animal, animals, Plant, plants, Ro ...
, communication with the spirit world is vital to the animist way of life. This is usually accomplished through a shaman
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritu ...
who, through a trance
Trance is a state of semi-consciousness in which a person is not self-aware and is either altogether unresponsive to external stimuli (but nevertheless capable of pursuing and realizing an aim) or is selectively responsive in following the dir ...
, gains access to the spirit world and then shows the spirits' thoughts to the people. Other ways to receive messages from the spirits include using astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of Celestial o ...
or contemplating fortune tellers
Fortune telling is the practice of predicting information about a person's life. Melton, J. Gordon. (2008). ''The Encyclopedia of Religious Phenomena''. Visible Ink Press. pp. 115-116. The scope of fortune telling is in principle identical wi ...
and healers.
Some of the oldest extant literature, such as the Kesh temple hymn (c. 26th century BC) are liturgy addressed to deities and thus technically "prayer". The Egyptian Pyramid Texts
The Pyramid Texts are the oldest ancient Egyptian funerary texts, dating to the late Old Kingdom. They are the earliest known corpus of ancient Egyptian religious texts. Written in Old Egyptian, the pyramid texts were carved onto the subterranea ...
of about the same period similarly contain spells or incantations addressed to the gods. In the loosest sense, in the form of magical thinking
Magical thinking, or superstitious thinking, is the belief that unrelated events are causally connected despite the absence of any plausible causal link between them, particularly as a result of supernatural effects. Examples include the idea that ...
combined with animism
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning 'breath, Soul, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct Spirituality, spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things—Animal, animals, Plant, plants, Ro ...
, prayer has been argued as representing a human cultural universal
A cultural universal (also called an anthropological universal or human universal) is an element, pattern, trait, or institution that is common to all known human cultures worldwide. Taken together, the whole body of cultural universals is known ...
, which would have been present since the emergence of behavioral modernity
Behavioral modernity is a suite of behavioral and cognitive traits that distinguishes current ''Homo sapiens'' from other anatomically modern humans, hominins, and primates. Most scholars agree that modern human behavior can be characterized by ...
, by anthropologists
An anthropologist is a person engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropology is the study of aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms and v ...
such as Sir Edward Burnett Tylor
Sir Edward Burnett Tylor (2 October 18322 January 1917) was an English anthropologist, and professor of anthropology.
Tylor's ideas typify 19th-century cultural evolutionism. In his works '' Primitive Culture'' (1871) and ''Anthropology'' ...
and Sir James George Frazer
Sir James George Frazer (; 1 January 1854 – 7 May 1941) was a Scottish social anthropologist and folklorist influential in the early stages of the modern studies of mythology and comparative religion.
Personal life
He was born on 1 Janua ...
.
Reliable records are available for the polytheistic
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, the ...
religions of the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
, most notably Ancient Greek religion
Religious practices in ancient Greece encompassed a collection of beliefs, rituals, and mythology, in the form of both popular public religion and cult practices. The application of the modern concept of "religion" to ancient cultures has been ...
(which strongly influenced Roman religion
Religion in ancient Rome consisted of varying imperial and provincial religious practices, which were followed both by the people of Rome as well as those who were brought under its rule.
The Romans thought of themselves as highly religious, ...
). These religious traditions were direct developments of the earlier Bronze Age religions.
Ceremonial prayer was highly formulaic and ritual
A ritual is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, actions, or objects, performed according to a set sequence. Rituals may be prescribed by the traditions of a community, including a religious community. Rituals are characterized, b ...
ized.
In ancient polytheism, ancestor worship
The veneration of the dead, including one's ancestors, is based on love and respect for the deceased. In some cultures, it is related to beliefs that the dead have a continued existence, and may possess the ability to influence the fortune of t ...
is indistinguishable from theistic worship (see also Euhemerism
Euhemerism () is an approach to the interpretation of mythology in which mythological accounts are presumed to have originated from real historical events or personages. Euhemerism supposes that historical accounts become myths as they are exagge ...
).
Vestiges of ancestor worship persist, to a greater or lesser extent, in modern religious traditions throughout the world, most notably in Japanese Shinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintois ...
and in Chinese folk religion
Chinese folk religion, also known as Chinese popular religion comprehends a range of traditional religious practices of Han Chinese, including the Chinese diaspora. Vivienne Wee described it as "an empty bowl, which can variously be filled ...
. The practices involved in Shinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintois ...
prayer are heavily influenced by Buddhism; Japanese Buddhism
Buddhism has been practiced in Japan since about the 6th century CE. Japanese Buddhism () created many new Buddhist schools, and some schools are original to Japan and some are derived from Chinese Buddhist schools. Japanese Buddhism has had a ...
has also been strongly influenced by Shinto in turn. Shinto prayers quite frequently consist of wishes or favors asked of the ''kami
are the deities, divinities, spirits, phenomena or "holy powers", that are venerated in the Shinto religion. They can be elements of the landscape, forces of nature, or beings and the qualities that these beings express; they can also be the sp ...
'', rather than lengthy praises or devotions. The practice of votive offering
A votive offering or votive deposit is one or more objects displayed or deposited, without the intention of recovery or use, in a sacred place for religious purposes. Such items are a feature of modern and ancient societies and are generally ...
is also universal, and is attested at least since the Bronze Age. In Shinto, this takes the form of a small wooden tablet, called an '' ema''.
Prayers in Etruscan __NOTOC__
Etruscan may refer to:
Ancient civilization
*The Etruscan language, an extinct language in ancient Italy
*Something derived from or related to the Etruscan civilization
**Etruscan architecture
**Etruscan art
**Etruscan cities
** Etrusca ...
were used in the Roman world by augur
An augur was a priest and official in the classical Roman world. His main role was the practice of augury, the interpretation of the will of the gods by studying the flight of birds. Determinations were based upon whether they were flying i ...
s and other oracle
An oracle is a person or agency considered to provide wise and insightful counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. As such, it is a form of divination.
Description
The word '' ...
s long after Etruscan became a dead language. The Carmen Arvale
The ''Carmen Arvale'' is the preserved chant of the Arval priests or ''Fratres Arvales'' of ancient Rome.
The Arval priests were devoted to the goddess Dia, and offered sacrifices to her to ensure the fertility of ploughed fields (Latin ''ar ...
and the Carmen Saliare
The ''Carmen Saliare'' is a fragment of archaic Latin, which played a part in the rituals performed by the Salii (Salian priests, a.k.a. "leaping priests") of Ancient Rome. There are 35 extant fragments of the ''Carmen Saliare'', which can be r ...
are two specimens of partially preserved prayers that seem to have been unintelligible to their scribes, and whose language is full of archaism
In language, an archaism (from the grc, ἀρχαϊκός, ''archaïkós'', 'old-fashioned, antiquated', ultimately , ''archaîos'', 'from the beginning, ancient') is a word, a sense of a word, or a style of speech or writing that belongs to a hi ...
s and difficult passages.
Roman prayers and sacrifice
Sacrifice is the offering of material possessions or the lives of animals or humans to a deity as an act of propitiation or worship. Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Greeks, and possibly exi ...
s were often envisioned as legal
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
bargains between deity and worshipper. The Roman principle was expressed as ''do ut des
The vocabulary of ancient Roman religion was highly specialized. Its study affords important information about the religion, traditions and beliefs of the ancient Romans. This legacy is conspicuous in European cultural history in its influence o ...
'': "I give, so that you may give." Cato the Elder
Marcus Porcius Cato (; 234–149 BC), also known as Cato the Censor ( la, Censorius), the Elder and the Wise, was a Roman soldier, senator, and historian known for his conservatism and opposition to Hellenization. He was the first to write histo ...
's treatise on agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
contains many examples of preserved traditional prayers; in one, a farmer addresses the unknown deity of a possibly sacred grove, and sacrifices a pig in order to placate the god or goddess of the place and beseech his or her permission to cut down some trees from the grove.

Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
, Germanic and Slavic religions are recorded much later, and much more fragmentarily, than the religions of classical antiquity. They nevertheless show substantial parallels to the better-attested religions of the Iron Age. In the case of Germanic religion, the practice of prayer is reliably attested, but no actual liturgy is recorded from the early (Roman era) period. An Old Norse prayer is on record in the form of a dramatization in skaldic poetry
A skald, or skáld (Old Norse: , later ; , meaning "poet"), is one of the often named poets who composed skaldic poetry, one of the two kinds of Old Norse poetry, the other being Eddic poetry, which is anonymous. Skaldic poems were traditionally ...
. This prayer is recorded in stanzas2 and3 of the poem ''Sigrdrífumál
(also known as ) is the conventional title given to a section of the ''Poetic Edda'' text in .
It follows without interruption, and it relates the meeting of Sigurðr with the valkyrie Brynhildr, here identified as ("driver to victory").
Its ...
'', compiled in the 13th century ''Poetic Edda
The ''Poetic Edda'' is the modern name for an untitled collection of Old Norse anonymous narrative poems, which is distinct from the ''Prose Edda'' written by Snorri Sturluson. Several versions exist, all primarily of text from the Icelandic me ...
'' from earlier traditional sources, where the valkyrie
In Norse mythology, a valkyrie ("chooser of the slain") is one of a host of female figures who guide souls of the dead to the god Odin's hall Valhalla. There, the deceased warriors become (Old Norse "single (or once) fighters"Orchard (1997:36) ...
Sigrdrífa prays to the gods and the earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
after being woken by the hero Sigurd
Sigurd ( non, Sigurðr ) or Siegfried (Middle High German: ''Sîvrit'') is a legendary hero of Germanic heroic legend, who killed a dragon and was later murdered. It is possible he was inspired by one or more figures from the Frankish Meroving ...
.
A prayer to Odin
Odin (; from non, Óðinn, ) is a widely revered Æsir, god in Germanic paganism. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, v ...
is mentioned in chapter2 of the ''Völsunga saga
The ''Völsunga saga'' (often referred to in English as the ''Volsunga Saga'' or ''Saga of the Völsungs'') is a legendary saga, a late 13th-century poetic rendition in Old Norse of the origin and decline of the Völsung clan (including the stor ...
'' where King Rerir
In ''Völsunga saga'', Rerir, the son of Sigi, succeeds his murdered father and avenges his death. He rules in Hunaland and becomes a powerful ruler. Rerir's son is Völsung.
Rerir and his wife were unable to have children until the goddess Frigg ...
prays for a child. In stanza9 of the poem ''Oddrúnargrátr
''Oddrúnargrátr'' (''Oddrún's lament'') or ''Oddrúnarkviða'' (''Oddrún's poem'') is an Eddic poem, found in the Codex Regius manuscript where it follows ''Guðrúnarkviða III'' and precedes ''Atlakviða''.
The main content of the poem is th ...
'', a prayer is made to "kind wights
A wight (Old English: ''wiht'') is a mythical sentient being, often undead.
In its original use the word ''wight'' described a living human being, but has come to be used in fictional works in the fantasy genre to describe certain immortal bei ...
, Frigg and Freyja
In Norse paganism, Freyja (Old Norse "(the) Lady") is a goddess associated with love, beauty, fertility, sex, war, gold, and seiðr (magic for seeing and influencing the future). Freyja is the owner of the necklace Brísingamen, rides a chario ...
, and many gods In chapter 21 of ''Jómsvíkinga saga
The ''Jómsvíkinga saga'' ("''Saga of the Jomsvikings''") is a medieval saga, Icelandic saga composed by an anonymous author. The saga was composed in Iceland during the 13th century. It exists in several manuscripts which vary from each other. T ...
'', wishing to turn the tide of the Battle of Hjörungavágr
The Battle of Hjörungavágr (Norwegian: ''Slaget ved Hjørungavåg'') is a semi-legendary naval battle that took place in the late 10th century between the Jarls of Lade and a Danish invasion fleet led by the fabled Jomsvikings. This battle play ...
, Haakon Sigurdsson
Haakon Sigurdsson ( non, Hákon Sigurðarson , no, Håkon Sigurdsson; 937–995), known as Haakon Jarl (Old Norse: ''Hákon jarl''), was the ''de facto'' ruler of Norway from about 975 to 995. Sometimes he is styled as Haakon the Powerful ( n ...
eventually finds his prayers answered by the goddesses Þorgerðr Hölgabrúðr and Irpa
Þorgerðr Hölgabrúðr (''Thorgerdr Holgabrudr'') and Irpa are divine figures in Norse mythology. They appear together in Jómsvíkinga saga, Njáls saga, and Þorleifs þáttr jarlsskálds. Irpa's name does not appear outside of these four att ...
.Hollander, Lee (trans.) (1955). ''The saga of the Jómsvíkings'', p. 100. University of Texas Press
The University of Texas Press (or UT Press) is a university press that is part of the University of Texas at Austin. Established in 1950, the Press publishes scholarly books and journals in several areas, including Latin American studies, Texan ...
Folk religion
In religious studies and folkloristics, folk religion, popular religion, traditional religion or vernacular religion comprises various forms and expressions of religion that are distinct from the official doctrines and practices of organized re ...
in the medieval period produced syncretism
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various school of thought, schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or religious assimilation, assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in t ...
s between pre-Christian and Christian traditions. An example is the 11th-century Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
charm ''Æcerbot The Æcerbot (; Old English for "Field-Remedy") is an Anglo-Saxon metrical charm recorded in the 11th century, intended to remedy fields that yielded poorly.Grigsby (2005:96f, 246).
Overview
The charm consists of a partially Christianized prayer an ...
'' for the fertility of crops and land, or the medical ''Wið færstice "Wið færstice" is an Old English medical text surviving in the collection known now as ''Lacnunga'' in the British Library. ''Wið fǣrstiċe'' means 'against a sudden/violent stabbing pain'; and according to Felix Grendon, whose collection of An ...
''. The 8th-century Wessobrunn Prayer
The Wessobrunn Prayer (german: Wessobrunner Gebet, also ''Wessobrunner Schöpfungsgedicht'', "Wessobrunn Creation Poem") is among the earliest known poetic works in Old High German, believed to date from the end of the 8th century.
Provenance and ...
has been proposed as a Christianized pagan prayer and compared to the pagan ''Völuspá
''Vǫluspá'' (also ''Völuspá'', ''Vǫlospá'' or ''Vǫluspǫ́''; Old Norse: 'Prophecy of the völva, a seeress'; reconstructed Old Norse: ) is the best known poem of the ''Poetic Edda''. It tells the story of the creation of the world and ...
''Lambdin, Laura C and Robert T. (2000). ''Encyclopedia of Medieval Literature'', p. 227. Greenwood Publishing Group and the Merseburg Incantations
The Merseburg charms or Merseburg incantations (german: die Merseburger Zaubersprüche) are two medieval magic spells, charms or incantations, written in Old High German. They are the only known examples of Germanic pagan belief preserved in the ...
, the latter recorded in the 9th or 10th century but of much older traditional origins.Wells, C.J." (1985). ''German, a Linguistic History to 1945: A Linguistic History to 1945'', p. 51. Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
In Australian Aboriginal mythology
Australian Aboriginal religion and mythology is the sacred spirituality represented in the stories performed by Aboriginal Australians within each of the Aboriginal Australian languages, language groups across Australia in their Aboriginal ce ...
, prayers to the "Great Wit" are performed by the "clever men" and "clever women", or ''kadji''. These Aboriginal shamans use maban
Maban, mabain or mabanba is a material that is held to be magical in Australian Aboriginal mythology. It is the material from which the shamans and elders of indigenous Australia supposedly derive their magical powers.
Among the Ngaanyatjarra
...
or mabain, the material that is believed to give them their purported magical powers. The Pueblo
In the Southwestern United States, Pueblo (capitalized) refers to the Native tribes of Puebloans having fixed-location communities with permanent buildings which also are called pueblos (lowercased). The Spanish explorers of northern New Spain ...
Indians are known to have used prayer stick
A prayer stick is a stick-shaped object used for prayer. Background
In the rituals of the Pueblo contain many prayers; thus the Zuñi have prayers for food, health, and rain. Prayer-sticks, that is sticks with feathers attached as supplicatory of ...
s, that is, sticks with feathers attached as supplicatory offerings. The Hopi
The Hopi are a Native American ethnic group who primarily live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census, there are 19,338 Hopi in the country. The Hopi Tribe is a sovereign nation within the Unite ...
Indians used prayer sticks as well, but they attached to it a small bag of sacred meal.
Approaches to prayer
Direct petitions
There are different forms of prayer. One of them is to directly appeal to a deity to grant one's requests. Some have termed this as the social approach to prayer.Atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
arguments against prayer are mostly directed against petitionary prayer
Supplication (also known as petitioning) is a form of prayer, wherein one party humbly or earnestly asks another party to provide something, either for the party who is doing the supplicating (e.g., "Please spare my life.") or on behalf of someon ...
in particular. Daniel Dennett
Daniel Clement Dennett III (born March 28, 1942) is an American philosopher, writer, and cognitive scientist whose research centers on the philosophy of mind, philosophy of science, and philosophy of biology, particularly as those fields relat ...
argued that petitionary prayer might have the undesirable psychological effect of relieving a person of the need to take active measures.
This potential drawback manifests in extreme forms in such cases as Christian Scientists
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
who rely on prayers instead of seeking medical treatment for family members for easily curable conditions which later result in death.
Christopher Hitchens
Christopher Eric Hitchens (13 April 1949 – 15 December 2011) was a British-American author and journalist who wrote or edited over 30 books (including five essay collections) on culture, politics, and literature. Born and educated in England, ...
(2012) argued that praying to a god which is omnipotent and all-knowing would be presumptuous. For example, he interprets Ambrose Bierce
Ambrose Gwinnett Bierce (June 24, 1842 – ) was an American short story writer, journalist, poet, and American Civil War veteran. His book ''The Devil's Dictionary'' was named as one of "The 100 Greatest Masterpieces of American Literature" by t ...
's definition of prayer by stating that "the man who prays is the one who thinks that god has arranged matters all wrong, but who also thinks that he can instruct god how to put them right."
Educational approach
In this view, prayer is not a conversation. Rather, it is meant to inculcate certain attitudes in the one who prays, but not to influence. Among Jews, this has been the approach of Rabbenu Bachya, RabbiYehuda Halevi
Judah Halevi (also Yehuda Halevi or ha-Levi; he, יהודה הלוי and Judah ben Shmuel Halevi ; ar, يهوذا اللاوي ''Yahuḏa al-Lāwī''; 1075 – 1141) was a Spanish Jewish physician, poet and philosopher. He was born in Spain, ...
, Joseph Albo
Joseph Albo ( he, יוסף אלבו; c. 1380–1444) was a Jewish philosopher and rabbi who lived in Spain during the fifteenth century, known chiefly as the author of ''Sefer ha-Ikkarim'' ("Book of Principles"), the classic work on the fundamenta ...
, Samson Raphael Hirsch
Samson Raphael Hirsch (; June 20, 1808 – December 31, 1888) was a German Orthodox rabbi best known as the intellectual founder of the ''Torah im Derech Eretz'' school of contemporary Orthodox Judaism. Occasionally termed ''neo-Orthodoxy'', his ...
, and Joseph B. Soloveitchik
Joseph Ber Soloveitchik ( he, יוסף דב הלוי סולובייצ׳יק ''Yosef Dov ha-Levi Soloveychik''; February 27, 1903 – April 9, 1993) was a major American Orthodox rabbi, Talmudist, and modern Jewish philosopher. He was a scion ...
. This view is expressed by Rabbi Nosson Scherman
Nosson Scherman ( he, נתן שרמן, born 1935, Newark, New Jersey) is an American Haredi rabbi best known as the general editor of ArtScroll/Mesorah Publications.
Early life
Scherman was born and raised in Newark, New Jersey, where his paren ...
in the overview to the Artscroll
ArtScroll is an imprint of translations, books and commentaries from an Orthodox Jewish perspective published by Mesorah Publications, Ltd., a publishing company based in Rahway, New Jersey. Rabbi Nosson Scherman is the general editor.
ArtScroll' ...
Siddur
A siddur ( he, סִדּוּר ; plural siddurim ) is a Jewish prayer book containing a set order of daily prayers. The word comes from the Hebrew root , meaning 'order.'
Other terms for prayer books are ''tefillot'' () among Sephardi Jews, ' ...
(p. XIII).
Among Christian theologians, E.M. Bounds stated the educational purpose of prayer in every chapter of his book, ''The Necessity of Prayer''. Prayer books such as the Book of Common Prayer
The ''Book of Common Prayer'' (BCP) is the name given to a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion and by other Christian churches historically related to Anglicanism. The original book, published in 1549 in the reign ...
are both a result of this approach and an exhortation to keep it.
Rationalist approach
In this view, the ultimate goal of prayer is to help train a person to focus on divinity through philosophy and intellectual contemplation (meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally cal ...
). This approach was taken by the Jewish scholar and philosopher Maimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, רמב״ם), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah ...
and the other medieval rationalists. It became popular in Jewish, Christian, and Islamic intellectual circles, but never became the most popular understanding of prayer among the laity in any of these faiths. In all three of these faiths today, a significant minority of people still hold to this approach.
Experiential approach
 In this approach, the purpose of prayer is to enable the person praying to gain a direct experience of the recipient of the prayer (or as close to direct as a specific theology permits). This approach is very significant in Christianity and widespread in Judaism (although less popular theologically). In
In this approach, the purpose of prayer is to enable the person praying to gain a direct experience of the recipient of the prayer (or as close to direct as a specific theology permits). This approach is very significant in Christianity and widespread in Judaism (although less popular theologically). In Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first m ...
, this approach is known as hesychasm
Hesychasm (; Greek: Ησυχασμός) is a contemplative monastic tradition in the Eastern Orthodox Church in which stillness (''hēsychia'') is sought through uninterrupted Jesus prayer. While rooted in early Christian monasticism, it took it ...
. It is also widespread in Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ...
Islam, and in some forms of mysticism
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute, but may refer to any kind of ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight in u ...
. It has some similarities with the rationalist approach, since it can also involve contemplation
In a religious context, the practice of contemplation seeks a direct awareness of the divine which transcends the intellect, often in accordance with prayer or meditation.
Etymology
The word ''contemplation'' is derived from the Latin word '' ...
, although the contemplation is not generally viewed as being as rational or intellectual.
Christian and Roman Catholic traditions also include an experiential approach to prayer within the practice of ''lectio divina
In Western Christianity, ''Lectio Divina'' (Latin for "Divine Reading") is a traditional monastic practice of scriptural reading, meditation and prayer intended to promote communion with God and to increase the knowledge of God's word. In the v ...
''. Historically a Benedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG
, caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal
, abbreviation = OSB
, formation =
, motto = (English: 'Pray and Work')
, foun ...
practice, ''lectio divina'' involves the following steps: a short scripture passage is read aloud; the passage is meditated upon using the mind to place the listener within a relationship or dialogue with the text; recitation of a prayer; and concludes with contemplation
In a religious context, the practice of contemplation seeks a direct awareness of the divine which transcends the intellect, often in accordance with prayer or meditation.
Etymology
The word ''contemplation'' is derived from the Latin word '' ...
. The Catechism of the Catholic Church
The ''Catechism of the Catholic Church'' ( la, Catechismus Catholicae Ecclesiae; commonly called the ''Catechism'' or the ''CCC'') is a catechism promulgated for the Catholic Church by Pope John Paul II in 1992. It aims to summarize, in book for ...
describes prayer and meditation as follows: Meditation engages thought, imagination, emotion, and desire. This mobilization of faculties is necessary in order to deepen our convictions of faith, prompt the conversion of our heart, and strengthen our will to follow Christ. Christian prayer tries above all to meditate on the mysteries of Christ, as inThe experience of God withinlectio divina In Western Christianity, ''Lectio Divina'' (Latin for "Divine Reading") is a traditional monastic practice of scriptural reading, meditation and prayer intended to promote communion with God and to increase the knowledge of God's word. In the v ...or therosary The Rosary (; la, , in the sense of "crown of roses" or "garland of roses"), also known as the Dominican Rosary, or simply the Rosary, refers to a set of prayers used primarily in the Catholic Church, and to the physical string of knots or b .... This form of prayerful reflection is of great value, but Christian prayer should go further: to the knowledge of the love of the Lord Jesus, to union with him.
Christian mysticism
Christian mysticism is the tradition of mystical practices and mystical theology within Christianity which "concerns the preparation f the personfor, the consciousness of, and the effect of ..a direct and transformative presence of God" ...
has been contrasted with the concept of experiential religion or mystical experience
Scholarly approaches to mysticism include typology (disambiguation), typologies of mysticism and the explanation of mystical states. Since the 19th century, mystical experience has evolved as a distinctive concept. It is closely related to "mystic ...
because of a long history or authors living and writing about experience with the divine in a manner that identifies God as unknowable and ineffable, the language of such ideas could be characterized paradoxically as "experiential", as well as without the phenomena of experience.
The notion of "religious experience" can be traced back to William James
William James (January 11, 1842 – August 26, 1910) was an American philosopher, historian, and psychologist, and the first educator to offer a psychology course in the United States.
James is considered to be a leading thinker of the lat ...
, who used a term called "religious experience" in his book, ''The Varieties of Religious Experience
''The Varieties of Religious Experience: A Study in Human Nature'' is a book by Harvard University psychologist and philosopher William James. It comprises his edited Gifford Lectures on natural theology, which were delivered at the University of ...
''. The origins of the use of this term can be dated further back.
In the 18th, 19th, and 20th centuries, several historical figures put forth very influential views that religion and its beliefs can be grounded in experience itself. While Kant
Immanuel Kant (, , ; 22 April 1724 – 12 February 1804) was a German Philosophy, philosopher and one of the central Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinkers. Born in Königsberg, Kant's comprehensive and systematic works in epistemolo ...
held that moral experience justified religious belief
Faith, derived from Latin ''fides'' and Old French ''feid'', is confidence or trust in a person, thing, or In the context of religion, one can define faith as "belief in God or in the doctrines or teachings of religion".
Religious people often ...
s, John Wesley
John Wesley (; 2 March 1791) was an English people, English cleric, Christian theology, theologian, and Evangelism, evangelist who was a leader of a Christian revival, revival movement within the Church of England known as Methodism. The soci ...
in addition to stressing individual moral exertion thought that the religious experiences in the Methodist movement
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related Christian denomination, denominations of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John W ...
(paralleling the Romantic Movement
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
) were foundational to religious commitment as a way of life.
Wayne Proudfoot
Wayne Lee Proudfoot (born November 17, 1939) is an American scholar of religion and has written several works in that field, specializing in the philosophy of religion.
Proudfoot earned the degree of Master of Theology from the Harvard Divinity S ...
traces the roots of the notion of "religious experience" to the German theologian Friedrich Schleiermacher
Friedrich Daniel Ernst Schleiermacher (; 21 November 1768 – 12 February 1834) was a German Reformed theologian, philosopher, and biblical scholar known for his attempt to reconcile the criticisms of the Enlightenment with traditional P ...
(1768–1834), who argued that religion is based on a feeling of the infinite. The notion of "religious experience" was used by Schleiermacher and Albert Ritschl to defend religion against the growing scientific and secular critique, and defend the view that human (moral and religious) experience justifies religious belief
Faith, derived from Latin ''fides'' and Old French ''feid'', is confidence or trust in a person, thing, or In the context of religion, one can define faith as "belief in God or in the doctrines or teachings of religion".
Religious people often ...
s.
Such religious empiricism would be later seen as highly problematic and was – during the period in-between world wars – famously rejected by Karl Barth
Karl Barth (; ; – ) was a Swiss Calvinist theologian. Barth is best known for his commentary '' The Epistle to the Romans'', his involvement in the Confessing Church, including his authorship (except for a single phrase) of the Barmen Declara ...
. In the 20th century, religious as well as moral experience as justification for religious beliefs still holds sway. Some influential modern scholars holding this liberal theological view are Charles Raven and the Oxford physicist/theologian Charles Coulson
Charles Alfred Coulson (13 December 1910 – 7 January 1974) was a British applied mathematician and theoretical chemist.
Coulson's major scientific work was as a pioneer of the application of the quantum theory of valency to problems of mol ...
.
The notion of "religious experience" was adopted by many scholars of religion, of whom William James was the most influential.
The notion of "experience" has been criticised. Robert Sharf points out that "experience" is a typical Western term, which has found its way into Asian religiosity via western influences. The notion of "experience" introduces a false notion of duality between "experiencer" and "experienced", whereas the essence of kensho is the realisation of the "non-duality" of observer and observed. "Pure experience" does not exist; all experience is mediated by intellectual and cognitive activity. The specific teachings and practices of a specific tradition may even determine what "experience" someone has, which means that this "experience" is not the ''proof'' of the teaching, but a ''result'' of the teaching. A pure consciousness without concepts, reached by "cleaning the doors of perception", would be an overwhelming chaos of sensory input without coherence.
Abrahamic religions
Hebrew Bible
 In the Hebrew Bible prayer is an evolving means of interacting with
In the Hebrew Bible prayer is an evolving means of interacting with God
In monotheism, monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator deity, creator, and principal object of Faith#Religious views, faith.Richard Swinburne, Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Ted Honderich, Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Ox ...
, most frequently through a spontaneous, individual, unorganized form of petitioning and/or thanking. Standardized prayer such as is done today is non-existent, although beginning in Deuteronomy
Deuteronomy ( grc, Δευτερονόμιον, Deuteronómion, second law) is the fifth and last book of the Torah (in Judaism), where it is called (Hebrew: hbo, , Dəḇārīm, hewords Moses.html"_;"title="f_Moses">f_Moseslabel=none)_and_th ...
, the Bible lays the groundwork for organized prayer, including basic liturgical guidelines, and by the Bible's later books, prayer has evolved to a more standardized form, although still radically different from the form practiced by modern Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
.
Individual prayer is described by the Tanakh two ways. The first of these is when prayer is described as occurring, and a result is achieved, but no further information regarding a person's prayer is given. In these instances, such as with Isaac
Isaac; grc, Ἰσαάκ, Isaák; ar, إسحٰق/إسحاق, Isḥāq; am, ይስሐቅ is one of the three patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He was the ...
, Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
, Samuel
Samuel ''Šəmūʾēl'', Tiberian: ''Šămūʾēl''; ar, شموئيل or صموئيل '; el, Σαμουήλ ''Samouḗl''; la, Samūēl is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the bibl ...
, and Job
Work or labor (or labour in British English) is intentional activity people perform to support the needs and wants of themselves, others, or a wider community. In the context of economics, work can be viewed as the human activity that contr ...
, the act of praying is a method of changing a situation for the better. The second way in which prayer is depicted is through fully fleshed out episodes of prayer, where a person's prayer is related in full. Many famous biblical personalities have such a prayer, including every major character from Hannah to Hezekiah
Hezekiah (; hbo, , Ḥīzqīyyahū), or Ezekias); grc, Ἐζεκίας 'Ezekías; la, Ezechias; also transliterated as or ; meaning "Yahweh, Yah shall strengthen" (born , sole ruler ), was the son of Ahaz and the 13th king of Kingdom of Jud ...
.
New Testament
In the New Testament prayer is presented as a positive command. ThePeople of God
''People of God'' ( he, עם האלהים) is a term used in the Hebrew Bible to refer to the Israelites and used in Christianity to refer to Christians.
In the Bible
Hebrew Bible and Old Testament
In the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament, the Isr ...
are challenged to include Christian prayer
Christian prayer is an important activity in Christianity, and there are several different forms used for this practice.
Christian prayers are diverse: they can be completely spontaneous, or read entirely from a text, such as from a breviary, ...
in their everyday life, even in the busy struggles of marriage as it brings people closer to God
In monotheism, monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator deity, creator, and principal object of Faith#Religious views, faith.Richard Swinburne, Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Ted Honderich, Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Ox ...
.
Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
encouraged his disciples to pray in secret in their private rooms, using the Lord's Prayer
The Lord's Prayer, also called the Our Father or Pater Noster, is a central Christian prayer which Jesus taught as the way to pray. Two versions of this prayer are recorded in the gospels: a longer form within the Sermon on the Mount in the Gosp ...
, as a humble response to the prayer of the Pharisees
The Pharisees (; he, פְּרוּשִׁים, Pərūšīm) were a Jewish social movement and a school of thought in the Levant during the time of Second Temple Judaism. After the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE, Pharisaic beliefs bec ...
, whose practices in prayer were regarded as impious by the New Testament writers.
Throughout the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
, prayer is shown to be God's appointed method by which we obtain what He has to bestow. Further, the Book of James
The Epistle of James). is a general epistle and one of the 21 epistles ( didactic letters) in the New Testament.
James 1:1 identifies the author as "James, a servant of God and of the Lord Jesus Christ" who is writing to "the twelve tribes ...
says that the lack of blessing
In religion, a blessing (also used to refer to bestowing of such) is the impartation of something with grace, holiness, spiritual redemption, or divine will.
Etymology and Germanic paganism
The modern English language term ''bless'' likely ...
s in life results from a failure to pray. Jesus healed through prayer and expected his followers to do so also. The apostle Paul wrote to the churches of Thessalonica to "Pray continually."
Judaism
 Observant Jews pray three times a day,
Observant Jews pray three times a day, Shacharit
''Shacharit'' ( he, שַחֲרִית ''šaḥăriṯ''), or ''Shacharis'' in Ashkenazi Hebrew, is the morning ''tefillah'' (prayer) of Judaism, one of the three daily prayers.
Different traditions identify different primary components of ...
, Mincha
Mincha ( he, מִנחַה, pronounced as ; sometimes spelled ''Minchah'' or ''Minḥa'') is the afternoon prayer service in Judaism.
Etymology
The name ''Mincha'', meaning "present", is derived from the meal offering that accompanied each sacrif ...
, and Ma'ariv
''Maariv'' or ''Maʿariv'' (, ), also known as ''Arvit'' (, ), is a Jewish prayer service held in the evening or night. It consists primarily of the evening ''Shema'' and ''Amidah''.
The service will often begin with two verses from Psalms, ...
with lengthier prayers on special days, such as the Shabbat
Shabbat (, , or ; he, שַׁבָּת, Šabbāṯ, , ) or the Sabbath (), also called Shabbos (, ) by Ashkenazim, is Judaism's day of rest on the seventh day of the week—i.e., Saturday. On this day, religious Jews remember the biblical storie ...
and Jewish holidays
Jewish holidays, also known as Jewish festivals or ''Yamim Tovim'' ( he, ימים טובים, , Good Days, or singular , in transliterated Hebrew []), are holidays observed in Judaism and by JewsThis article focuses on practices of mainstre ...
including Musaf and the reading of the Torah. The siddur is the prayerbook used by Jews all over the world, containing a set order of daily prayers. Jewish prayer is usually described as having two aspects: ''kavanah
Kavanah, kavvanah or kavana (also pronounced /kaˈvonə/ by some Ashkenazi Jews) (כַּוָּנָה; in Biblical Hebrew kawwānā), plural kavanot or kavanos (Ashkenazim), literally means "intention" or "sincere feeling, direction of the heart". ...
'' (intention) and ''keva'' (the ritualistic, structured elements).
The most important Jewish prayers are the Shema Yisrael
''Shema Yisrael'' (''Shema Israel'' or ''Sh'ma Yisrael''; he , שְׁמַע יִשְׂרָאֵל ''Šəmaʿ Yīsrāʾēl'', "Hear, O Israel") is a Jewish prayer (known as the Shema) that serves as a centerpiece of the morning and evening Jewis ...
("Hear O Israel") and the Amidah
The ''Amidah Amuhduh'' ( he, תפילת העמידה, ''Tefilat HaAmidah'', 'The Standing Prayer'), also called the ''Shemoneh Esreh'' ( 'eighteen'), is the central prayer of the Jewish liturgy. Observant Jews recite the ''Amidah'' at each o ...
("the standing prayer").
Communal prayer is preferred over solitary prayer, and a quorum of ten adult males (a ''minyan
In Judaism, a ''minyan'' ( he, מניין \ מִנְיָן ''mīnyān'' , lit. (noun) ''count, number''; pl. ''mīnyānīm'' ) is the quorum of ten Jewish adults required for certain religious obligations. In more traditional streams of Jud ...
'') is considered by Orthodox Judaism
Orthodox Judaism is the collective term for the traditionalist and theologically conservative branches of contemporary Judaism. Theologically, it is chiefly defined by regarding the Torah, both Written and Oral, as revealed by God to Moses on M ...
a prerequisite for several communal prayers.
 There are also many other ritualistic prayers a Jew performs during their day, such as washing before eating bread, washing after one wakes up in the morning, and doing grace after meals.
There are also many other ritualistic prayers a Jew performs during their day, such as washing before eating bread, washing after one wakes up in the morning, and doing grace after meals.
Rationalist approach
In this view, the ultimate goal of prayer is to help train a person to focus on divinity through philosophy and intellectual contemplation. This approach was taken byMaimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, רמב״ם), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah ...
and the other medieval rationalists. One example of this approach to prayer is noted by Rabbi Steven Weil, who was appointed the Orthodox Union's Executive-Vice President in 2009. He notes that the word "prayer" is a derivative of the Latin "precari", which means "to beg". The Hebrew equivalent "tefilah", however, along with its root "pelel" or its reflexive "l'hitpallel", means the act of self-analysis or self-evaluation. This approach is sometimes described as the person praying having a dialogue or conversation with God.
Educational approach
In this view, prayer is not a conversation. Rather, it is meant to inculcate certain attitudes in the one who prays, but not to influence. This has been the approach of Rabbenu Bachya,Yehuda Halevy
Judah Halevi (also Yehuda Halevi or ha-Levi; he, יהודה הלוי and Judah ben Shmuel Halevi ; ar, يهوذا اللاوي ''Yahuḏa al-Lāwī''; 1075 – 1141) was a Spanish Jewish physician, poet and philosopher. He was born in Spain, ...
, Joseph Albo
Joseph Albo ( he, יוסף אלבו; c. 1380–1444) was a Jewish philosopher and rabbi who lived in Spain during the fifteenth century, known chiefly as the author of ''Sefer ha-Ikkarim'' ("Book of Principles"), the classic work on the fundamenta ...
, Samson Raphael Hirsch
Samson Raphael Hirsch (; June 20, 1808 – December 31, 1888) was a German Orthodox rabbi best known as the intellectual founder of the ''Torah im Derech Eretz'' school of contemporary Orthodox Judaism. Occasionally termed ''neo-Orthodoxy'', his ...
, and Joseph Dov Soloveitchik
Joseph Ber Soloveitchik ( he, יוסף דב הלוי סולובייצ׳יק ''Yosef Dov ha-Levi Soloveychik''; February 27, 1903 – April 9, 1993) was a major American Orthodox rabbi, Talmudist, and modern Jewish philosopher. He was a scion ...
. This view is expressed by Rabbi Nosson Scherman
Nosson Scherman ( he, נתן שרמן, born 1935, Newark, New Jersey) is an American Haredi rabbi best known as the general editor of ArtScroll/Mesorah Publications.
Early life
Scherman was born and raised in Newark, New Jersey, where his paren ...
in the overview to the Artscroll
ArtScroll is an imprint of translations, books and commentaries from an Orthodox Jewish perspective published by Mesorah Publications, Ltd., a publishing company based in Rahway, New Jersey. Rabbi Nosson Scherman is the general editor.
ArtScroll' ...
Siddur (p. XIII); note that Scherman goes on to also affirm the Kabbalistic view (see below).
Kabbalistic approach
Kabbalah
Kabbalah ( he, קַבָּלָה ''Qabbālā'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and Jewish theology, school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''Məqūbbāl'' "rece ...
uses a series of ''kavanot
Kavanah, kavvanah or kavana (also pronounced /kaˈvonə/ by some Ashkenazi Jews) (כַּוָּנָה; in Biblical Hebrew kawwānā), plural kavanot or kavanos (Ashkenazim), literally means "intention" or "sincere feeling, direction of the heart". ...
'', directions of intent, to specify the path the prayer ascends in the dialog with God, to increase its chances of being answered favorably. Kabbalists ascribe a higher meaning to the purpose of prayer, which is no less than affecting the very fabric of reality itself, restructuring and repairing the universe in a real fashion. In this view, every word of every prayer, and indeed, even every letter of every word, has a precise meaning and a precise effect. Prayers thus literally affect the mystical forces of the universe, and repair the fabric of creation.
Among Jews, this approach has been taken by the Chassidei Ashkenaz
The Hasidim of Ashkenaz ( he, חסידי אשכנז, trans. ''Khasidei Ashkenaz''; "German Pietists") were a Jewish mystical, ascetic movement in the German Rhineland during the 12th and 13th centuries.
Background
The leaders of the community o ...
(German pietists of the Middle-Ages), the Arizal's Kabbalist tradition, Ramchal
Moshe Chaim Luzzatto ( he, משה חיים לוצאטו, also ''Moses Chaim'', ''Moses Hayyim'', also ''Luzzato'') (1707 – 16 May 1746 (26 ''Iyar'' 5506)), also known by the Hebrew acronym RaMCHaL (or RaMHaL, ), was a prominent Italia ...
, most of Hassidism
Hasidism, sometimes spelled Chassidism, and also known as Hasidic Judaism (Ashkenazi Hebrew: חסידות ''Ḥăsīdus'', ; originally, "piety"), is a Jewish religious group that arose as a spiritual revival movement in the territory of contem ...
, the Vilna Gaon
Elijah ben Solomon Zalman, ( he , ר' אליהו בן שלמה זלמן ''Rabbi Eliyahu ben Shlomo Zalman'') known as the Vilna Gaon (Yiddish: דער װילנער גאון ''Der Vilner Gaon'', pl, Gaon z Wilna, lt, Vilniaus Gaonas) or Elijah of ...
, and Jacob Emden
Jacob Emden, also known as Ya'avetz (June 4, 1697 April 19, 1776), was a leading German rabbi and talmudist who championed Orthodox Judaism in the face of the growing influence of the Sabbatean movement. He was acclaimed in all circles for his ...
.
Christianity
 Christian prayers are quite varied. They can be completely spontaneous, or read entirely from a text, like the Anglican
Christian prayers are quite varied. They can be completely spontaneous, or read entirely from a text, like the Anglican Book of Common Prayer
The ''Book of Common Prayer'' (BCP) is the name given to a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion and by other Christian churches historically related to Anglicanism. The original book, published in 1549 in the reign ...
. The most common prayer among Christians is the Lord's Prayer
The Lord's Prayer, also called the Our Father or Pater Noster, is a central Christian prayer which Jesus taught as the way to pray. Two versions of this prayer are recorded in the gospels: a longer form within the Sermon on the Mount in the Gosp ...
, which according to the gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words an ...
accounts (e.g. Matthew 6:9–13) is how Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
taught his disciples to pray.''Examining Religions: Christianity Foundation Edition'' by Anne Geldart 1999 p. 108 The Lord's Prayer is a model for prayers of adoration, confession and petition in Christianity.
In the second century ''Apostolic Tradition
The ''Apostolic Tradition'' (or ''Egyptian Church Order'') is an early Christian treatise which belongs to the genre of the ancient Church Orders. It has been described to be of "incomparable importance as a source of information about church lif ...
'', Hippolytus instructed Christians to pray at seven fixed prayer times: "on rising, at the lighting of the evening lamp, at bedtime, at midnight" and "the third, sixth and ninth hours of the day, being hours associated with Christ's Passion." Breviaries
A breviary (Latin: ''breviarium'') is a liturgical book used in Christianity for praying the canonical hours, usually recited at seven fixed prayer times.
Historically, different breviaries were used in the various parts of Christendom, such as ...
such as the Shehimo
Shehimo ( syr, , ml, ഷഹീമോ; English language, English: Book of Common Prayer, also spelled Sh'himo) is the West Syriac Rite, West Syriac Christian breviary of the Syriac Orthodox Church and the West Syriac Rite, West Syriac Saint Tho ...
and Agpeya
The ''Agpeya'' (Coptic: Ϯⲁⲅⲡⲓⲁ, ar, أجبية) is the Coptic Christian "Prayer Book of the Hours" or breviary, and is equivalent to the Shehimo in the Indian Orthodox Church (another Oriental Orthodox Christian denomination), as we ...
are used by Oriental Orthodox Christians to pray these seven canonical hours while facing in the eastward direction of prayer.
In medieval England, prayers (particularly the ''paternoster
''Pater Noster'', or the Lord's Prayer, is a prayer in Christianity.
Pater Noster or Paternoster may also refer to:
Places
* Paternoster, Western Cape, a fishing village in South Africa
* Paternosters, uninhabitable rocks in the Bailiwick of Jer ...
'') were frequently used as a measure of time in medical and culinary recipe books.
Christians generally pray to God. Some Christians, such as Catholics, Lutherans, Orthodox, and Methodists pray for the dead
Religions with the belief in a future judgment, a resurrection of the dead or a purgatory often offer prayers on behalf of the dead to God.
Buddhism
For most funerals that follow the tradition of Chinese Buddhism, common practices include chanti ...
; Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
s, will also ask the righteous in heaven and "in Christ," such as the Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother o ...
or other saints to intercede by praying on their behalf (intercession of saints
Intercession of the Saints is a Christian doctrine held by the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Catholic churches. The practice of praying through saints can be found in Christian writings from the 3rd century onward.
The 4th-century Apo ...
). Formulaic closures in many Christian denominations, such as Lutheranism and Catholicism include "through our Lord Jesus Christ, Your Son, who lives and reigns with You, in the unity of the Holy Spirit, God, through all the ages of ages," and "in the name of the Father, and the Son, and the Holy Spirit."
It is customary among Christians to end prayers with "In Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
' name, Amen" or more commonly, with the sign of the cross
Making the sign of the cross ( la, signum crucis), or blessing oneself or crossing oneself, is a ritual blessing made by members of some branches of Christianity. This blessing is made by the tracing of an upright cross or + across the body with ...
while saying the Trinitarian formula
The Trinitarian formula is the phrase "in the name of the Father, and of the Son, and of the Holy Spirit" ( grc-x-koine, εἰς τὸ ὄνομα τοῦ Πατρὸς καὶ τοῦ Υἱοῦ καὶ τοῦ Ἁγίου Πνεύματος, e ...
. The most commonly used closure of prayer in Christianity is "Amen
Amen ( he, אָמֵן, ; grc, ἀμήν, ; syc, ܐܡܝܢ, ; ar, آمين, ) is an Abrahamic declaration of affirmation which is first found in the Hebrew Bible, and subsequently found in the New Testament. It is used in Jews, Jewish, Christia ...
" (from a Hebrew adverb used as a statement of affirmation or agreement, usually translated as ''so be it'').
In the Western or Latin Rite
Latin liturgical rites, or Western liturgical rites, are Catholic rites of public worship employed by the Latin Church, the largest particular church ''sui iuris'' of the Catholic Church, that originated in Europe where the Latin language once ...
of the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, probably the most common is the Rosary
The Rosary (; la, , in the sense of "crown of roses" or "garland of roses"), also known as the Dominican Rosary, or simply the Rosary, refers to a set of prayers used primarily in the Catholic Church, and to the physical string of knots or b ...
; In the Eastern Church (the Eastern rites of the Catholic Church and Orthodox Church), the Jesus Prayer
The Jesus Prayer,; syr, ܨܠܘܬܐ ܕܝܫܘܥ, translit=slotho d-yeshu'; syr, label=Amharic, Geez and Tigrinya, እግዚኦ መሐረነ ክርስቶስ, translit=igizi'o meḥarene kirisitosi. "Note: We are still searching the Fathers for t ...
. The Jesus Prayer is also often repeated as part of the meditative
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally calm ...
hesychasm
Hesychasm (; Greek: Ησυχασμός) is a contemplative monastic tradition in the Eastern Orthodox Church in which stillness (''hēsychia'') is sought through uninterrupted Jesus prayer. While rooted in early Christian monasticism, it took it ...
practice in Eastern Christianity
Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, Asia Minor, the Caucasus, Northeast Africa, the Fertile Crescent and ...
.
Roman Catholic tradition includes specific prayers and devotions as acts of reparation which do not involve a petition for a living or deceased beneficiary, but aim to repair the sins of others, e.g. for the repair of the sin of blasphemy performed by others.
Other forms of prayer among Catholics would be meditative prayer, contemplative prayer and infused prayer discussed at length by Catholic Saints St. John of the Cross
John of the Cross, OCD ( es, link=no, Juan de la Cruz; la, Ioannes a Cruce; born Juan de Yepes y Álvarez; 24 June 1542 – 14 December 1591) was a Spanish Catholic priest, mystic, and a Carmelite friar of converso origin. He is a major fi ...
and St. Theresa of Jesus.
Pentecostalism
InPentecostal
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a Protestant Charismatic Christian movement
congregations, prayer is often accompanied by speaking in an unknown tongue, a practice now known as glossolalia
Speaking in tongues, also known as glossolalia, is a practice in which people utter words or speech-like sounds, often thought by believers to be languages unknown to the speaker. One definition used by linguists is the fluid vocalizing of sp ...
. Practitioners of Pentecostal glossolalia may claim that the languages they speak in prayer are real foreign languages, and that the ability to speak those languages spontaneously is a gift of the Holy Spirit
In Judaism, the Holy Spirit is the divine force, quality, and influence of God over the Universe or over his creatures. In Nicene Christianity, the Holy Spirit or Holy Ghost is the third person of the Trinity. In Islam, the Holy Spirit acts as ...
. Some people outside of the movement, however, have offered dissenting views. George Barton Cutten suggested that glossolalia was a sign of mental illness. Felicitas Goodman
Felicitas D. Goodman (January 30, 1914 in Budapest, Hungary – March 30, 2005 in Columbus, Ohio, Columbus, Ohio, USA) was an American linguistics, linguist and anthropologist. She was a highly regarded expert in linguistics and anthropology an ...
suggested that tongue speakers were under a form of hypnosis. Others suggest that it is a learned behaviour. Some of these views have allegedly been refuted.
Christian Science
Christian Science
Christian Science is a set of beliefs and practices associated with members of the Church of Christ, Scientist. Adherents are commonly known as Christian Scientists or students of Christian Science, and the church is sometimes informally know ...
teaches that prayer is a spiritualization of thought or an understanding of God and of the nature of the underlying spiritual creation. Adherents believe that this can result in healing, by bringing spiritual reality into clearer focus in the human scene. The world as it appears to the senses is regarded as a distorted version of the world of spiritual ideas. Prayer can heal the distortion. Christian Scientists believe that prayer does not change the spiritual creation but gives a clearer view of it, and the result appears in the human scene as healing: the human picture adjusts to coincide more nearly with the divine reality. Christian Scientists do not practice intercessory prayer
Intercession or intercessory prayer is the act of praying to a deity on behalf of others, or asking a saint in heaven to pray on behalf of oneself or for others.
The Apostle Paul's exhortation to Timothy specified that intercession prayers s ...
as it is commonly understood, and they generally avoid combining prayer with medical treatment in the belief that the two practices tend to work against each other. Prayer works through love
Love encompasses a range of strong and positive emotional and mental states, from the most sublime virtue or good habit, the deepest Interpersonal relationship, interpersonal affection, to the simplest pleasure. An example of this range of ...
: the recognition of God's creation as spiritual, intact, and inherently lovable.
Islam
 The
The Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
word for prayer is ''salah
(, plural , romanized: or Old Arabic ͡sˤaˈloːh, ( or Old Arabic ͡sˤaˈloːtʰin construct state) ), also known as ( fa, نماز) and also spelled , are prayers performed by Muslims. Facing the , the direction of the Kaaba wit ...
''. In Islam, five daily obligatory prayers are considered one of the pillars of the religion. The command of ritual prayer repeatedly occurs in the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Classical Arabic, Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation in Islam, revelation from God in Islam, ...
. The person performs the prayer while they are facing the Kaaba
The Kaaba (, ), also spelled Ka'bah or Kabah, sometimes referred to as al-Kaʿbah al-Musharrafah ( ar, ٱلْكَعْبَة ٱلْمُشَرَّفَة, lit=Honored Ka'bah, links=no, translit=al-Kaʿbah al-Musharrafah), is a building at the c ...
in Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red ...
. There is the "call for prayer" ('' the adhan''), where the ''muezzin
The muezzin ( ar, مُؤَذِّن) is the person who proclaims the call to the daily prayer ( ṣalāt) five times a day (Fajr prayer, Zuhr prayer, Asr prayer, Maghrib prayer and Isha prayer) at a mosque. The muezzin plays an important role ...
'' calls for all the followers to stand together for the prayer. The prayer consists of actions such as glorifying and praising God (such as mentioning 'Allāhu Akbar' (God is Great)) while standing, recitation of chapters of the Quran (such as the opening chapter of the book (''Al-Fatiha
Al-Fatiha (alternatively transliterated Al-Fātiḥa or Al-Fātiḥah; ar, ألْفَاتِحَة, ; ), is the first ''surah'' (chapter) of the Quran. It consists of 7 '' ayah'' (verses) which are a prayer for guidance and mercy. Al-Fatiha i ...
'')), bowing down then praising God, prostrating (''sujud
Sujūd ( ar, سُجود, ), or sajdah (, ), is the act of low bowing or prostration to God facing the ''qiblah'' (direction of the Kaaba at Mecca). It is usually done in standardized prayers (salah). The position involves kneeling and bowing t ...
'') then again praising God. It ends with the words: "Peace be with you and God's mercy." During the prayer, a Muslim cannot talk or do anything else besides pray. Once the prayer is complete, one can offer personal prayers or supplications to God for their needs, known as ''dua
In Islam, ( ar, دعاء , plural: ' ) is a prayer of invocation, supplication or request, even asking help or assistance from God.
Role in Islam
Muslims regard this as a profound act of worship. Muhammad is reported to have said ...
''. There are many standard invocations in Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
to be recited at various times (''e.g.'' after the prayer) and for various occasions (''e.g.'' for one's parents) with manners and etiquette such as before eating. Muslims may also say ''dua'' in their own words and languages for any issue they wish to communicate with God in the hope that God will answer their prayers. Certain Shi'a
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam. It holds that the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad designated Ali, ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his S ...
sects pray the five daily prayers divided into three separate parts of the day, providing several Hadith as supporting evidence; although according to Shia Islam
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, m ...
, it is also permissible to pray at five times.
Mandaeism
Daily prayer in Mandaeism
Daily prayer in Mandaeism, called ''brakha'' in Mandaic (cognate with Hebrew ''berakhah'' and Arabic ''barakah'') or occasionally ''birukta'' (''birukhta''), consists of set prayers that are recited three times per day. Mandaeans stand facing n ...
called ''brakha'' consists of a set prayers that are recited three times per day. Mandaeans stand facing north while reciting daily prayers. Unlike in Islam and Coptic Orthodox Christianity, prostration
Prostration is the gesture of placing one's body in a reverentially or submissively prone position. Typically prostration is distinguished from the lesser acts of bowing or kneeling by involving a part of the body above the knee, especially t ...
is not practiced.
Mandaean priest
A Mandaean priest or ''Rabbi'' refers to an ordained religious leader in Mandaeism.
Overview
All priests must undergo lengthy ordination ceremonies, beginning with tarmida initiation. Mandaean religious leaders and copyists of religious texts hol ...
s recite rahma
Rahma most commonly refers to an Arabic name, which may refer to:
*Al-Rahma mosque, on Hatherley Street, Liverpool, England
*''Malak al-Rahma'', a classic 1946 Egyptian film directed and written by Youssef Wahbi
People
*Rahma el-Dennaoui (born 20 ...
prayersLidzbarski, Mark. 1920. ''Mandäische Liturgien''. Abhandlungen der Königlichen Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften zu Göttingen, phil.-hist. Klasse, NF 17.1. Berlin. three times every day, while laypeople also recite the ''Rushma
The rushma ( myz, ࡓࡅࡔࡌࡀ, translit=rušma, lit=sign) is one of the most commonly recited prayers in Mandaeism. It is a "signing" prayer recited during daily ablutions (rishama). The same word can also be used to refer to the ritual signing ...
'' (signing prayer) and ''Asiet Malkia
The ''Asiet Malkia'' ("Salutation of Kings") is one of the most commonly recited prayers in Mandaeism. In the prayer, the reciter wishes health and victory (''asuta u-zakuta'' ) upon dozens of heavenly and ancestral figures. According to E. S. Dr ...
'' ("Healing of Kings") daily.
The three prayer times in Mandaeism
Mandaeism (Classical Mandaic: ࡌࡀࡍࡃࡀࡉࡉࡀ ; Arabic: المندائيّة ), sometimes also known as Nasoraeanism or Sabianism, is a Gnostic, monotheistic and ethnic religion. Its adherents, the Mandaeans, revere Adam, Abel, S ...
are:Drower, Ethel Stefana. 1937. ''The Mandaeans of Iraq and Iran''. Oxford At The Clarendon Press.
*dawn (sunrise)
*noontime (the "seventh hour")
*evening (sunset)
Baháʼí Faith
Bahá'u'lláh, theBáb
The Báb (b. ʿAlí Muḥammad; 20 October 1819 – 9 July 1850), was the messianic founder of Bábism, and one of the central figures of the Baháʼí Faith. He was a merchant from Shiraz in Qajar Iran who, in 1844 at the age of 25, claimed ...
, and `Abdu'l-Bahá wrote many prayers for general use, and some for specific occasions, including for unity, detachment, spiritual upliftment, and healing among others. Followers of the Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the Baháʼí Faith and the unity of religion, essential worth of all religions and Baháʼí Faith and the unity of humanity, the unity of all people. Established by ...
are also required to recite each day one of three obligatory prayers composed by Bahá'u'lláh. The believers have been enjoined to face in the direction of the Qiblih
__NOTOC__
In the Baháʼí Faith the Qiblih ( ar, , "direction") is the location to which Baháʼís face when saying their daily obligatory prayers. The Qiblih is fixed at the Shrine of Baháʼu'lláh, near Acre, in present-day Israel; appr ...
when reciting their Obligatory Prayer. The longest obligatory prayer may be recited at any time during the day; another, of medium length, is recited once in the morning, once at midday, and once in the evening; and the shortest can be recited anytime between noon and sunset. Baháʼís also read from and meditate on the scriptures every morning and evening.
Eastern religions
In bothBuddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
and Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, the repetition of mantra
A mantra (Pali: ''manta'') or mantram (मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words in Sanskrit, Pali and other languages believed by practitioners to have religious, ma ...
s is closely related to the practice of repetitive prayer in Western religion (rosary
The Rosary (; la, , in the sense of "crown of roses" or "garland of roses"), also known as the Dominican Rosary, or simply the Rosary, refers to a set of prayers used primarily in the Catholic Church, and to the physical string of knots or b ...
, Jesus prayer
The Jesus Prayer,; syr, ܨܠܘܬܐ ܕܝܫܘܥ, translit=slotho d-yeshu'; syr, label=Amharic, Geez and Tigrinya, እግዚኦ መሐረነ ክርስቶስ, translit=igizi'o meḥarene kirisitosi. "Note: We are still searching the Fathers for t ...
). Many of the most widespread Hindu and Buddhist mantras are in origin invocations of deities, e.g. Gayatri Mantra
The Gāyatrī Mantra, also known as the Sāvitri Mantra, is a highly revered mantra from the '' Rig Veda'' (Mandala 3.62.10), dedicated to the Vedic deity Savitr. is the name of the Goddess of the Vedic meter in which the verse is composed. It ...
dedicated to Savitr
Savitṛ (Sanskrit: stem ', nominative singular '), also rendered as Savitur, in Vedic scriptures is an Aditya i.e. off-spring of the Vedic primeval mother goddess Aditi. His name in Vedic Sanskrit connotes "impeller, rouser, vivifier."
H ...
, Pavamana Mantra
The Pavamana Mantra (''pavamāna'' meaning "being purified, strained", historically a name of Soma), also known as ''pavamāna abhyāroha'' (''abhyāroha'', lit. "ascending", being an Upanishadic technical term for "prayer")
is an ancient Indian ...
to Soma Pavamana, and many of the Buddhist Dhāraṇī
Dharanis (IAST: ), also known as ''Parittas'', are Buddhist chants, mnemonic codes, incantations, or recitations, usually the mantras consisting of Sanskrit or Pali phrases. Believed to be protective and with powers to generate merit for the Bud ...
originate as recitations of lists of names or attributes of deities. Most of the shorter Buddhist mantras originate as the invocation of the name of a specific deity or ''bodhisattva
In Buddhism, a bodhisattva ( ; sa, 𑀩𑁄𑀥𑀺𑀲𑀢𑁆𑀢𑁆𑀯 (Brahmī), translit=bodhisattva, label=Sanskrit) or bodhisatva is a person who is on the path towards bodhi ('awakening') or Buddhahood.
In the Early Buddhist schools ...
'', such as ''Om mani padme hum
' ( sa, ॐ मणि पद्मे हूँ, ) is the six-syllabled Sanskrit mantra particularly associated with the four-armed Shadakshari form of Avalokiteshvara, the bodhisattva of compassion. It first appeared in the Mahayana ''Kāraṇ ...
'' being in origin the invocation of a ''bodhisattva'' called ''Maṇipadma''. However, from an early time these mantras were interpreted in the context of mystical sound symbolism
In linguistics, sound symbolism is the resemblance between sound and meaning. It is a form of linguistic iconicity. For example, the English word ''ding'' may sound similar to the actual sound of a bell. Linguistic sound may be perceived as simil ...
. The most extreme example of this is the om syllable, which as early as in the Aitareya Brahmana The Aitareya Brahmana ( sa, ऐतरेय ब्राह्मण) is the Brahmana of the Shakala Shakha of the Rigveda, an ancient Indian collection of sacred hymns. This work, according to the tradition, is ascribed to Mahidasa Aitareya.
Auth ...
was claimed as equivalent to the entire Vedas
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the ...
(collection of ritual hymns).
Buddhism
 In the earliest Buddhist tradition, the
In the earliest Buddhist tradition, the Theravada
''Theravāda'' () ( si, ථේරවාදය, my, ထေရဝါဒ, th, เถรวาท, km, ថេរវាទ, lo, ເຖຣະວາດ, pi, , ) is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school' ...
, and in the later Mahayana
''Mahāyāna'' (; "Great Vehicle") is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, texts, philosophies, and practices. Mahāyāna Buddhism developed in India (c. 1st century BCE onwards) and is considered one of the three main existing bra ...
tradition of Zen
Zen ( zh, t=禪, p=Chán; ja, text= 禅, translit=zen; ko, text=선, translit=Seon; vi, text=Thiền) is a school of Mahayana Buddhism that originated in China during the Tang dynasty, known as the Chan School (''Chánzong'' 禪宗), and ...
(or Chán
Chan (; of ), from Sanskrit '' dhyāna'' (meaning "meditation" or "meditative state"), is a Chinese school of Mahāyāna Buddhism. It developed in China from the 6th century CE onwards, becoming especially popular during the Tang and So ...
), prayer plays only an ancillary role. It is largely a ritual expression of wishes for success in the practice and in helping all beings.
The skillful means
Upaya (Sanskrit: उपाय, , ''expedient means'', ''pedagogy'') is a term used in Buddhism to refer to an aspect of guidance along the Buddhist paths to liberation where a conscious, voluntary action "is driven by an incomplete reasoning" a ...
(Sanskrit: ''upāya'') of the transfer of merit (Sanskrit: ''pariṇāmanā
Transfer of merit ( sa, pariṇāmanā, italic=yes, pi, pattidāna, italic=yes or ''pattānumodanā'') is a standard part of Buddhist spiritual discipline where the practitioner's merit, resulting from good deeds, is transferred to deceased r ...
'') is an evocation
Evocation is the act of evoking, calling upon, or summoning a spirit, demon, deity or other supernatural agents, in the Western mystery tradition. Comparable practices exist in many religions and magical traditions and may employ the use of mi ...
and prayer. Moreover, indeterminate buddhas are available for intercession as they reside in awoken-fields (Sanskrit: ''buddha-kshetra'').
The '' nirmānakāya'' of an awoken-field is what is generally known and understood as a mandala
A mandala ( sa, मण्डल, maṇḍala, circle, ) is a geometric configuration of symbols. In various spiritual traditions, mandalas may be employed for focusing attention of practitioners and adepts, as a spiritual guidance tool, for e ...
. The opening and closing of the ring (Sanskrit: ''maṇḍala'') is an active prayer. An active prayer is a mindful activity, an activity in which mindfulness
Mindfulness is the practice of purposely bringing one's attention to the present-moment experience without evaluation, a skill one develops through meditation or other training. Mindfulness derives from ''sati'', a significant element of Hind ...
is not just cultivated but ''is''. A common prayer is "May the merit of my practice, adorn Buddhas' Pure Lands, requite the fourfold kindness from above, and relieve the suffering of the three life-journeys below. Universally wishing sentient beings, Friends, foes, and karmic creditors, all to activate the Bodhi
The English term enlightenment is the Western translation of various Buddhist terms, most notably bodhi and vimutti. The abstract noun ''bodhi'' (; Sanskrit: बोधि; Pali: ''bodhi''), means the knowledge or wisdom, or awakened intellect ...
mind, and all to be reborn in the Pure Land of Ultimate Bliss." (願以此功德 莊嚴佛淨土 上報四重恩 下濟三途苦 普願諸眾生 冤親諸債主 悉發菩提心 同生極樂國)
The Generation Stage
The fundamental practice of Vajrayana and Tibetan tantric practice, Tibetan tantra is deity yoga (''devatayoga''), meditation on a chosen deity or "cherished divinity" (Skt. ''Iṣṭa-devatā,'' Tib. ''yidam''), which involves the recitation o ...
(Sanskrit: ''utpatti-krama'') of Vajrayana involves prayer elements.
The Tibetan Buddhism tradition emphasizes an instructive and devotional relationship to a guru; this may involve devotional practices known as guru yoga which are congruent with prayer. It also appears that Tibetan Buddhism posits the existence of various deities, but the peak view of the tradition is that the deities or ''yidam'' are no more existent or real than the continuity (Sanskrit: ''santana''; refer mindstream) of the practitioner, environment and activity. But how practitioners engage ''yidam'' or tutelary deities will depend upon the level or more appropriately ''yana (Buddhism), yana'' at which they are practicing. At one level, one may pray to a deity for protection or assistance, taking a more subordinate role. At another level, one may invoke the deity, on a more equal footing. And at a higher level one may deliberately cultivate the idea that one has become the deity, whilst remaining aware that its ultimate nature is ''śūnyatā''. The views of the more esoteric ''yana'' are impenetrable for those without direct experience and empowerment.
Pure Land Buddhism emphasizes the recitation by devotees of prayer-like mantra
A mantra (Pali: ''manta'') or mantram (मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words in Sanskrit, Pali and other languages believed by practitioners to have religious, ma ...
s, a practice often called ''Nembutsu''."The Flowering of Faith: Buddhism's Pure Land Tradition" (pp. 185–98) in On one level it is said that reciting these mantras can ensure rebirth into a ''Sambhogakāya'' land (Sanskrit: ''buddha-kshetra'') after bodily dissolution, a sheer ball spontaneously co-emergent to a buddha's enlightened intention. According to Shinran, the founder of the Pure Land Buddhism tradition that is most prevalent in the US, "for the long haul nothing is as efficacious as the Nembutsu." On another, the practice is a form of meditation aimed at achieving realization.
But beyond all these practices the Buddha emphasized the primacy of individual practice and experience. He said that supplication to gods or deities was not necessary. Nevertheless, today many lay people in East Asian countries pray to the Buddha in ways that resemble Western prayer—asking for intervention and offering devotion.
Hinduism

Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
has incorporated many kinds of prayer (Sanskrit: ''prārthanā''), from fire-based yajna, rituals to philosophical musings. While chanting involves 'by dictum' recitation of timeless verses or verses with timings and notations, ''Dhyāna in Hinduism, dhyanam'' involves deep meditation (however short or long) on the preferred deity/God. Again the object to which prayers are offered could be a persons referred as ''devtas'', trinity or incarnation of either ''devtas'' or trinity or simply plain formless meditation as practiced by the ancient sages. These prayers can be directed to fulfilling personal needs or deep spiritual enlightenment, and also for the benefit of others. Ritual invocation
An invocation (from the Latin verb ''invocare'' "to call on, invoke, to give") may take the form of:
*Supplication, prayer or spell.
*A form of possession.
*Command or conjuration.
*Self-identification with certain spirits.
These forms are ...
was part and parcel of the Historical Vedic religion, Vedic religion and as such permeated their sacred texts. Indeed, the highest sacred texts of the Hindus, the Vedas
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the ...
, are a large collection of mantra
A mantra (Pali: ''manta'') or mantram (मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words in Sanskrit, Pali and other languages believed by practitioners to have religious, ma ...
s and prayer rituals. Classical Hinduism came to focus on extolling a single supreme force, Brahman, that is made manifest in several lower forms as the familiar gods of the Hindu pantheon. Hindus in India have numerous devotional movements. Hindus may pray to the highest absolute God Brahman, or more commonly to its three manifestations, a creator god called Brahma (god), Brahma, a preserver god called Vishnu and a destroyer god (so that the creation cycle can start afresh) Shiva, and at the next level to Vishnu's avatars (earthly appearances) Rama and Krishna or to many other male or female deities. Typically, Hindus pray with their hands (the palms) joined in ''pranam''. The hand gesture is similar to the popular Indian greeting ''namaste''.
Sikhism
 The ''Ardās'' (Punjabi: ਅਰਦਾਸ) is a Sikh prayer that is done before performing or after undertaking any significant task; after reciting the daily ''Banis'' (prayers); or completion of a service like the ''Paath'' (scripture reading/recitation), ''kirtan'' (hymn-singing) program or any other religious program. In Sikhism, these prayers are also said before and after eating. The prayer is a plea to God to support and help the devotee with whatever he or she is about to undertake or has done.
The ''Ardas'' is usually always done standing up with folded hands. The beginning of the ''Ardas'' is strictly set by the tenth Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh. When it comes to conclusion of this prayer, the devotee uses words like "Waheguru please bless me in the task that I am about to undertake" when starting a new task or "Akal Purakh, having completed the hymn-singing, we ask for your continued blessings so that we can continue with your memory and remember you at all times", etc. The word "Ardās" is derived from Persian word 'Arazdashat', meaning a request, supplication, prayer, petition or an address to a superior authority.
Ardās is a unique prayer based on the fact that it is one of the few well-known prayers in the Sikh religion that was not written in its entirety by the Gurus. The Ardās cannot be found within the pages of the Guru Granth Sahib because it is a continually changing devotional text that has evolved over time in order for it to encompass the feats, accomplishments, and feelings of all generations of Sikhs within its lines. Taking the various derivation of the word Ardās into account, the basic purpose of this prayer is an appeal to Waheguru for his protection and care, as well as being a plea for the welfare and prosperity of all mankind, and a means for the Sikhs to thank Waheguru for all that he has done.
The ''Ardās'' (Punjabi: ਅਰਦਾਸ) is a Sikh prayer that is done before performing or after undertaking any significant task; after reciting the daily ''Banis'' (prayers); or completion of a service like the ''Paath'' (scripture reading/recitation), ''kirtan'' (hymn-singing) program or any other religious program. In Sikhism, these prayers are also said before and after eating. The prayer is a plea to God to support and help the devotee with whatever he or she is about to undertake or has done.
The ''Ardas'' is usually always done standing up with folded hands. The beginning of the ''Ardas'' is strictly set by the tenth Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh. When it comes to conclusion of this prayer, the devotee uses words like "Waheguru please bless me in the task that I am about to undertake" when starting a new task or "Akal Purakh, having completed the hymn-singing, we ask for your continued blessings so that we can continue with your memory and remember you at all times", etc. The word "Ardās" is derived from Persian word 'Arazdashat', meaning a request, supplication, prayer, petition or an address to a superior authority.
Ardās is a unique prayer based on the fact that it is one of the few well-known prayers in the Sikh religion that was not written in its entirety by the Gurus. The Ardās cannot be found within the pages of the Guru Granth Sahib because it is a continually changing devotional text that has evolved over time in order for it to encompass the feats, accomplishments, and feelings of all generations of Sikhs within its lines. Taking the various derivation of the word Ardās into account, the basic purpose of this prayer is an appeal to Waheguru for his protection and care, as well as being a plea for the welfare and prosperity of all mankind, and a means for the Sikhs to thank Waheguru for all that he has done.
Iranian religions
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism, Zoroastrians are not Fire worship, fire-worshippers, as some Westerners wrongly believe. Zoroastrians believe that the elements are pure and that fire represents Ahura Mazda, God's light or wisdom. Zoroastrian worship practices have evolved from ancient times to the present day.Over time, Zoroastrians developed the concept of worshipping in temples, sometimes called fire temples.New religious movements
Wiccan prayers can include meditation, rituals and incantations. Wiccans see prayers as a form of communication with the God and Goddess. Such communication may include prayers for ''esbat'' and ''sabbat'' celebrations, for dinner, for pre-dawn times or for one's own or others' safety, for healing or for the dead. In Raëlism rites and practises vary from initiation ceremonies to sensual meditation. An initiation ceremony usually involves a Raelian putting water on the forehead of a new member. Such ceremonies take place on certain special days on the Raelian calendar. Sensual meditation techniques include breathing exercises and various forms of erotic meditation. In Eckankar, one of the basic forms of prayer includes singing the word "HU" (pronounced as "hue"), a holy name of God. ECKists may do this with eyes closed or open, aloud or silently. Practitioners may experience the divine ECK or Holy Spirit. Practitioners of Theurgy#Esoteric Christianity, theurgy and Western esotericism may practice a form of ritual which uses both pre-sanctioned prayers and names of God, and prayers "from the heart" that, when combined, allow the participant to ascend spiritually, and in some instances, induce a trance in which God or other spiritual beings may be realized. Very much as in Hermetic Qabalah and orthodox Kabbalah, it is believed that prayer can influence both the physical and non-physical worlds. The use of ritualistic signs and names are believed to be archetypes in which the subconscious may take form as the Inner God, or another spiritual being, and the "prayer from the heart" to be that spiritual force speaking through the participant. In Thelema (which includes both theist as well as atheist practitioners) adherents share a number of practices that are forms of individual prayer, including basic yoga; (asana and pranayama); various forms of ritual magick (Aleister Crowley), magick; rituals of one's own devising (often based upon a syncretism of religions, or Western Esotericism, such as the Lesser Banishing Ritual of the Pentagram and Star Ruby); and performance of Liber Resh vel Helios (aka Liber 200), which consists of four daily adorations to the sun (often consisting of four hand/body positions and recitation of a memorized song, normally spoken, addressing different godforms identified with the sun).
While no dogma within Thelema expresses the purpose behind any individual aspirant who chooses to perform "Resh", note that the practice of "Resh" is not a simple petition toward the sun, nor a form of "worshiping" the celestial body that we call the Sun, but instead uses the positioning of that source of light, which enables life on our planet, as well as using mythological images of that solar force, so that the individual can perform the prayer, possibly furthering a self-identification with the sun, so "that repeated application of the Liber Resh adorations expands the consciousness of the individual by compelling him to take a different perspective, by inducing him to 'look at things from the point of view of the Sun' [...]".
In Thelema (which includes both theist as well as atheist practitioners) adherents share a number of practices that are forms of individual prayer, including basic yoga; (asana and pranayama); various forms of ritual magick (Aleister Crowley), magick; rituals of one's own devising (often based upon a syncretism of religions, or Western Esotericism, such as the Lesser Banishing Ritual of the Pentagram and Star Ruby); and performance of Liber Resh vel Helios (aka Liber 200), which consists of four daily adorations to the sun (often consisting of four hand/body positions and recitation of a memorized song, normally spoken, addressing different godforms identified with the sun).
While no dogma within Thelema expresses the purpose behind any individual aspirant who chooses to perform "Resh", note that the practice of "Resh" is not a simple petition toward the sun, nor a form of "worshiping" the celestial body that we call the Sun, but instead uses the positioning of that source of light, which enables life on our planet, as well as using mythological images of that solar force, so that the individual can perform the prayer, possibly furthering a self-identification with the sun, so "that repeated application of the Liber Resh adorations expands the consciousness of the individual by compelling him to take a different perspective, by inducing him to 'look at things from the point of view of the Sun' [...]".
Prayer healing
Prayer is often used as a means offaith healing
Faith healing is the practice of prayer and gestures (such as laying on of hands) that are believed by some to elicit divine intervention in spiritual and physical healing, especially the Christian practice. Believers assert that the healing ...
in an attempt to use religious or spirituality, spiritual means to prevent illness, cure disease, or improve health.
Scientific studies regarding the use of prayer have mostly concentrated on its effect on the healing of sick or injured people. meta-study, Meta-studies have been performed showing evidence only for no effect or a potentially small effect. For instance, a 2006 meta analysis on 14 studies concluded that there is "no discernable effect" while a 2007 systemic review of studies on intercessory prayer reported inconclusive results, noting that seven of 17 studies had "small, but significant, effect sizes" but the review noted that the most methodologically rigorous studies failed to produce significant findings. Some studies have indicated increased medical complications in groups receiving prayer over those without.
*
The efficacy of petition in prayer for physical healing to a deity has been evaluated in numerous other studies, with contradictory results. As found in There has been some criticism of the way the studies were conducted.Online reprint
by Internet Infidels at Infidels.org. Some attempt to heal by prayer, mental practices, spiritual insights, or other techniques, claiming they can summon divine or supernatural intervention on behalf of the ill. Others advocate that ill people may achieve healing through prayer performed by themselves. According to the varied beliefs of those who practice it, faith healing may be said to afford gradual relief from pain or sickness or to bring about a sudden "miracle cure", and it may be used in place of, or in tandem with, conventional medical techniques for alleviating or curing diseases. Faith healing has been criticized on the grounds that those who use it may delay seeking potentially curative conventional medical care. This is particularly problematic when parents use faith healing techniques on children.
Efficacy of prayer healing
 In 1872, Francis Galton conducted a famous statistics, statistical experiment to determine whether prayer had a physical effect on the external environment. Galton hypothesized that if prayer was effective, members of the British Royal family would live longer, given that thousands prayed for their wellbeing every Sunday. He therefore compared longevity in the British Royal family with that of the general population, and found no difference. While the experiment was probably intended to satirize, and suffered from a number of Confounding variable, confounders, it set the precedent for a number of different studies, the results of which are contradictory.
Two studies claimed that patients who are being prayed for recover more quickly or more frequently although critics have claimed that the methodology of such studies are flawed, and the perceived effect disappears when controls are tightened. One such study, with a double-blind design and about 500 subjects per group, was published in 1988; it suggested that intercessory prayer by born again Christians had a statistically significant positive effect on a coronary care unit population. Critics contend that there were severe methodological problems with this study. Another such study was reported by Harris et al. Critics also claim that the 1988 study was not fully double-blinded, and that in the Harris study, patients actually had a longer hospital stay in the prayer group, if one discounts the patients in both groups who left before prayers began, although the Harris study did demonstrate the prayed for patients on average received lower course scores (indicating better recovery).
One of the largest randomized, blind clinical trials was a remote ''retroactive'' intercessory prayer study conducted in Israel by Leibovici. This study used 3393 patient records from 1990 to 1996, and blindly assigned some of these to an intercessory prayer group. The prayer group had shorter hospital stays and duration of fever.
Several studies of prayer effectiveness have yielded null results. A 2001 double-blind study of the Mayo Clinic found no significant difference in the recovery rates between people who were (unbeknownst to them) assigned to a group that prayed for them and those who were not. Similarly, the MANTRA study conducted by Duke University found no differences in outcome of cardiac procedures as a result of prayer. In another similar study published in the ''American Heart Journal'' in 2006, Christian intercessory prayer when reading a scripted prayer was found to have no effect on the recovery of heart surgery patients; however, the study found patients who had knowledge of receiving prayer had slightly higher instances of complications than those who did not know if they were being prayed for or those who did not receive prayer. Another 2006 study suggested that prayer actually had a significant negative effect on the recovery of cardiac bypass patients, resulting in more frequent deaths and slower recovery time for those patient who received prayers.
Many believe that prayer can aid in recovery, not due to divine influence but due to psychological and physical benefits. It has also been suggested that if a person knows that he or she is being prayed for it can be uplifting and increase morale, thus aiding recovery. (See Subject-expectancy effect.) Many studies have suggested that prayer can reduce physical stress, regardless of the god or gods a person prays to, and this may be true for many worldly reasons. According to a study by Centra State Hospital, "the psychological benefits of prayer may help reduce stress and anxiety, promote a more positive outlook, and strengthen the will to live." Other practices such as yoga, T'ai chi ch'uan, t'ai chi, and meditation may also have a positive impact on physical and psychological health.
"W"
Others feel that the concept of conducting prayer experiments reflects a misunderstanding of the purpose of prayer. The previously mentioned study published in the ''American Heart Journal'' indicated that some of the intercessors who took part in it complained about the scripted nature of the prayers that were imposed to them, saying that this is not the way they usually conduct prayer:
One scientific movement attempts to track the physical effects of prayer through neuroscience. Leaders in this movement include Andrew B. Newberg, Andrew Newberg, an associate professor at the University of Pennsylvania. In Newberg's brain scans, monks, priests, nuns, Nun#Distinction between a nun and a religious sister, sisters and gurus alike have exceptionally focused attention and compassion sites. This is a result of the frontal lobe of the brain's engagement (Newberg, 2009). Newburg believes that anybody can connect to the supernatural with practice. Those without religious affiliations benefit from the connection to the metaphysical as well. Newberg also states that further evidence towards humans' need for metaphysical relationships is that as science had increased spirituality has not decreased. Newburg believes that at the end of the 18th century, when the scientific method began to consume the human mind, religion could have vanished. However, two hundred years later, the perception of spirituality, in many instances, appears to be gaining in strength (2009). Newberg's research also provides the connection between prayer and meditation and health. By understanding how the brain works during religious experiences and practices Newberg's research shows that the brain changes during these practices allowing an understanding of how religion affects psychological and physical health (2009). For example, brain activity during meditation indicates that people who frequently practice prayer or meditation experience lower blood-pressure, lower heart rates, decreased anxiety, and decreased depression.
In 1872, Francis Galton conducted a famous statistics, statistical experiment to determine whether prayer had a physical effect on the external environment. Galton hypothesized that if prayer was effective, members of the British Royal family would live longer, given that thousands prayed for their wellbeing every Sunday. He therefore compared longevity in the British Royal family with that of the general population, and found no difference. While the experiment was probably intended to satirize, and suffered from a number of Confounding variable, confounders, it set the precedent for a number of different studies, the results of which are contradictory.
Two studies claimed that patients who are being prayed for recover more quickly or more frequently although critics have claimed that the methodology of such studies are flawed, and the perceived effect disappears when controls are tightened. One such study, with a double-blind design and about 500 subjects per group, was published in 1988; it suggested that intercessory prayer by born again Christians had a statistically significant positive effect on a coronary care unit population. Critics contend that there were severe methodological problems with this study. Another such study was reported by Harris et al. Critics also claim that the 1988 study was not fully double-blinded, and that in the Harris study, patients actually had a longer hospital stay in the prayer group, if one discounts the patients in both groups who left before prayers began, although the Harris study did demonstrate the prayed for patients on average received lower course scores (indicating better recovery).
One of the largest randomized, blind clinical trials was a remote ''retroactive'' intercessory prayer study conducted in Israel by Leibovici. This study used 3393 patient records from 1990 to 1996, and blindly assigned some of these to an intercessory prayer group. The prayer group had shorter hospital stays and duration of fever.
Several studies of prayer effectiveness have yielded null results. A 2001 double-blind study of the Mayo Clinic found no significant difference in the recovery rates between people who were (unbeknownst to them) assigned to a group that prayed for them and those who were not. Similarly, the MANTRA study conducted by Duke University found no differences in outcome of cardiac procedures as a result of prayer. In another similar study published in the ''American Heart Journal'' in 2006, Christian intercessory prayer when reading a scripted prayer was found to have no effect on the recovery of heart surgery patients; however, the study found patients who had knowledge of receiving prayer had slightly higher instances of complications than those who did not know if they were being prayed for or those who did not receive prayer. Another 2006 study suggested that prayer actually had a significant negative effect on the recovery of cardiac bypass patients, resulting in more frequent deaths and slower recovery time for those patient who received prayers.
Many believe that prayer can aid in recovery, not due to divine influence but due to psychological and physical benefits. It has also been suggested that if a person knows that he or she is being prayed for it can be uplifting and increase morale, thus aiding recovery. (See Subject-expectancy effect.) Many studies have suggested that prayer can reduce physical stress, regardless of the god or gods a person prays to, and this may be true for many worldly reasons. According to a study by Centra State Hospital, "the psychological benefits of prayer may help reduce stress and anxiety, promote a more positive outlook, and strengthen the will to live." Other practices such as yoga, T'ai chi ch'uan, t'ai chi, and meditation may also have a positive impact on physical and psychological health.
"W"
Others feel that the concept of conducting prayer experiments reflects a misunderstanding of the purpose of prayer. The previously mentioned study published in the ''American Heart Journal'' indicated that some of the intercessors who took part in it complained about the scripted nature of the prayers that were imposed to them, saying that this is not the way they usually conduct prayer:
One scientific movement attempts to track the physical effects of prayer through neuroscience. Leaders in this movement include Andrew B. Newberg, Andrew Newberg, an associate professor at the University of Pennsylvania. In Newberg's brain scans, monks, priests, nuns, Nun#Distinction between a nun and a religious sister, sisters and gurus alike have exceptionally focused attention and compassion sites. This is a result of the frontal lobe of the brain's engagement (Newberg, 2009). Newburg believes that anybody can connect to the supernatural with practice. Those without religious affiliations benefit from the connection to the metaphysical as well. Newberg also states that further evidence towards humans' need for metaphysical relationships is that as science had increased spirituality has not decreased. Newburg believes that at the end of the 18th century, when the scientific method began to consume the human mind, religion could have vanished. However, two hundred years later, the perception of spirituality, in many instances, appears to be gaining in strength (2009). Newberg's research also provides the connection between prayer and meditation and health. By understanding how the brain works during religious experiences and practices Newberg's research shows that the brain changes during these practices allowing an understanding of how religion affects psychological and physical health (2009). For example, brain activity during meditation indicates that people who frequently practice prayer or meditation experience lower blood-pressure, lower heart rates, decreased anxiety, and decreased depression.
Efficacy of prayer for fertility
One study found that prayer combined with IVF treatment nearly doubled the number of women who were successfully pregnant, and more than doubled the number of successful implantations. But three years later it was revealed that the results of the study were fake.Prevalence of prayer for health
Some modalities of alternative medicine employ prayer. A survey released in May 2004 by the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine, part of the National Institutes of Health in the United States, found that in 2002, 43% of Americans pray for their own health, 24% pray for others' health, and 10% participate in a prayer group for their own health.See also
* Affirmative prayer * Christian contemplation * Christian devotional literature * Continual prayer * Daily Prayer for Peace * Hoʻoponopono * Interior life (Catholic theology) * List of Jewish prayers and blessings, Jewish prayers and blessings * Jewish prayer * List of prayers * Magical thinking * Mani stone * Moment of silence * National Day of Prayer, National Day of Prayer (US) * Novena * Orans * Prayer beads * Prayer in LDS theology and practice * Prayer in the Catholic Church * Prayer in school * Prayer wheel * Prie-dieu *Rosary
The Rosary (; la, , in the sense of "crown of roses" or "garland of roses"), also known as the Dominican Rosary, or simply the Rosary, refers to a set of prayers used primarily in the Catholic Church, and to the physical string of knots or b ...
* Shuckling
* Tibetan prayer flag
Further reading
* * * * * * *Notes
References
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Prayer Prayer, Religious practices Spirituality Spiritual practice Articles containing video clips