Poverty In The United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In the United States,
In the United States,
Incarceration and social inequality.
Daedalus, 139(3), 8-19 The majority of adults living in poverty are employed and have at least a high school education. Although the US is a relatively wealthy country by international standards, it has a persistently high poverty rate compared to other developed countries due in part to a less generous welfare system. Efforts to alleviate poverty include
Washington Post November 8, 2013
 Orshansky based her thresholds on work she had done with the
Orshansky based her thresholds on work she had done with the
 The issue of understating poverty is especially pressing in states with both a
The issue of understating poverty is especially pressing in states with both a

 The highest poverty rates in the United States are in the U.S. territories ( American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico and the
The highest poverty rates in the United States are in the U.S. territories ( American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico and the
Below 100% of Poverty – All Races
.'' This number varied by race and ethnicity as follows: * 5.4% of all white persons (which includes white Hispanics),U.S. Census Bureau. Current Population Survey. ''People in Families by Family Structure, Age, and Sex, Iterated by Income-to-Poverty Ratio and Race: 2007
Below 100% of Poverty – White Alone
.'' * 10.7% of all black persons (which includes black Hispanics), * 14.9% of all Hispanic persons (of any race) living in poverty. Among single-parent (male or female) families: 26.6% lived in poverty. This number varied by race and ethnicity as follows: * 22.5% of all white persons (which includes white Hispanics), * 44.0% of all black persons (which includes black Hispanics), * 33.4% of all Hispanic persons (of any race) living in poverty. Among individuals living alone: 19.1% lived in poverty. This number varied by race and ethnicity as follows: * 18% of white persons (which includes white Hispanics), * 28.9% of black persons (which includes black Hispanics) * 27% of Hispanic persons (of any race) are living in poverty.
 The US Census declared that in 2014, 14.8% of the general population lived in poverty:Income and Poverty in the United States: 2014
The US Census declared that in 2014, 14.8% of the general population lived in poverty:Income and Poverty in the United States: 2014
. U.S. Census Bureau As of 2010 about half of those living in poverty are non-Hispanic white (19.6 million). Non-Hispanic white children comprised 57% of all poor rural children. In FY 2009, African American families comprised 33.3% of TANF families, non-Hispanic white families comprised 31.2%, and 28.8% were Hispanic.
 As of 2010, the US Census declared that 15.1% of the general population of the United States lived in poverty:
* 22% of all people under the age of 18
* 13.7% of those between the ages of 19-21
* 9% of all people either 65 or older
The
As of 2010, the US Census declared that 15.1% of the general population of the United States lived in poverty:
* 22% of all people under the age of 18
* 13.7% of those between the ages of 19-21
* 9% of all people either 65 or older
The 
 There are numerous factors related to poverty in the United States.
*Income has a high correlation with educational levels. In 2007, the median earnings of household headed by individuals with less than a 9th grade education was $20,805 while households headed by high school graduates earned $40,456, households headed by holders of bachelor's degrees earned $77,605, and families headed by individuals with professional degrees earned $100,000. Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen stated in 2014: "Public funding of education is another way that governments can help offset the advantages some households have in resources available for children. One of the most consequential examples is early childhood education. Research shows that children from lower-income households who get good-quality pre-Kindergarten education are more likely to graduate from high school and attend college as well as hold a job and have higher earnings, and they are less likely to be incarcerated or receive public assistance."
*In many cases, poverty is caused by job loss. In 2007, the poverty rate was 21.5% for individuals who were unemployed, but only 2.5% for individuals who were employed full-time.
*
There are numerous factors related to poverty in the United States.
*Income has a high correlation with educational levels. In 2007, the median earnings of household headed by individuals with less than a 9th grade education was $20,805 while households headed by high school graduates earned $40,456, households headed by holders of bachelor's degrees earned $77,605, and families headed by individuals with professional degrees earned $100,000. Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen stated in 2014: "Public funding of education is another way that governments can help offset the advantages some households have in resources available for children. One of the most consequential examples is early childhood education. Research shows that children from lower-income households who get good-quality pre-Kindergarten education are more likely to graduate from high school and attend college as well as hold a job and have higher earnings, and they are less likely to be incarcerated or receive public assistance."
*In many cases, poverty is caused by job loss. In 2007, the poverty rate was 21.5% for individuals who were unemployed, but only 2.5% for individuals who were employed full-time.
* *The poor in the United States are
*The poor in the United States are
27 percent of households – nearly double the percentage that are income poor – are living in "asset poverty." These families do not have the savings or other assets to cover basic expenses (equivalent to what could be purchased with a poverty level income) for three months if a layoff or other emergency leads to loss of income. Since 2009, the number of asset poor families has increased by 21 percent from about one in five families to one in four families. In order to provide assistance to such asset poor families, Congress appropriated $24 million to administer the Assets for Independence Program under the supervision of the US Department for Health and Human Services. The program enables community-based nonprofits and government agencies to implement Individual Development Account or IDA programs, which are an asset-based development initiative. Every dollar accumulated in IDA savings is matched by federal and non-federal funds to enable households to add to their assets portfolio by buying their first home, acquiring a post-secondary education, or starting or expanding a small business. Additionally, th
Earned Income Tax Credit
(EITC or EIC) is a credit for people who earn low-to-moderate incomes. This credit allows them to get money from the government if their total tax outlay is less than the total credit earned, meaning it is not just a reduction in total tax paid but can also bring new income to the household. The Earned Income Tax Credit is viewed as the largest poverty reduction program in the United States. There is an ongoing debate in the U.S. about what the most effective way to fight poverty is, through the tax code with the EITC, or through the minimum wage laws. Government safety-net programs put in place since the War on Poverty have helped reduce the poverty rate from 26% in 1967 to 16% in 2012, according to a Supplemental Poverty Model (SPM) created by Columbia University, while the official U.S. Poverty Rate has not changed, as the economy by itself has done little to reduce poverty. According to the 2013 Columbia University study which created the (SPM) method of measuring poverty, without such programs the poverty rate would be 29% today. An analysis of the study by Kevin Drum suggests the American welfare state effectively reduces poverty among the elderly but provides relatively little assistance to the working-age poor. A 2014 study by
The Land of Too Much: American Abundance and the Paradox of Poverty
'' ( Harvard University Press, 2012),
Report of the Special Rapporteur on extreme poverty and human rights on his mission to the United States of America
OHCHR. * Berkowitz, Edward, and Kim McQuaid. (1992) ''Creating the Welfare State: The Political Economy of Twentieth-Century Reform'' (UP of Kansas, 1992) * * Cray, Robert E., Jr. ''Paupers and Poor Relief in New York City and Its Rural Environs, 1700–1830'' (Temple University Press, 1988
online
* * DeParle, Jason, "How to Fix Child Poverty" (review of
The Routledge Handbook of Poverty in the United States
'' Routledge, 2015. . * Howe, Louise Kapp, ed. (1970). ''The White Majority: between Poverty and Affluence'', in series, ''Vintage Book '' New York: New York: Random House. xii, 303 p. SBN 394-71666-3 * Katz, Michael B (2013). ''The Undeserving Poor: America's Enduring Confrontation with Poverty: Fully Updated and Revised.'' Oxford University Press; 2 edition. * Lyon-Callo, Vincent (2004). ''Inequality, Poverty, and Neoliberal Governance: Activist Ethnography in the Homeless Sheltering Industry.'' University of Toronto Press. * Mink, Gwendolyn, and Alice O'Connor, eds. ''Poverty in the United States: An Encyclopedia of History, Politics, and Policy'' (ABC-CLIO 2004). * Patterson, James T. (2000) ''America's Struggle against Poverty in the Twentieth Century'' (Harvard UP, 2000
online
* Prasad, Monica (2012). ''The Land of Too Much: American Abundance and the Paradox of Poverty.'' Harvard University Press. * * Sciandra, M., Sanbonmatsu, L., Duncan, G. J., Gennetian, L. A., Katz, L. F., Kessler, R. C., et al. (2013). Long-term effects of the Moving to Opportunity residential mobility experiment on crime and delinquency. Journal of Exp Criminol 9, 451–489. * Shipler, David K (2004). ''The Working Poor: Invisible in America, '' Knopf. * Wacquant, Loïc (2009). ''Prisons of Poverty.'' University of Minnesota Press. * ——— (2009).
Punishing the Poor: The Neoliberal Government of Social Insecurity
'. Duke University Press. ; Videos: * // Accompanied article: *
Poverty Definition
*U.S. Census Burea
��''
The American Way of Poverty: As Inequality Hits Record High, Sasha Abramsky on the Forgotten Poor
'' DemocracyNow!'' September 12, 2013.
America's Shameful Poverty Stats
Sasha Abramsky. '' The Nation,'' September 18, 2013.
How Much Money to End Poverty in America?
'' Truthdig.'' September 26, 2013.
Poverty in the United States: 2012
Congressional Research Service
It Is Expensive to Be Poor
'' The Atlantic.'' January 13, 2014.
Here's The Painful Truth About What It Means To Be 'Working Poor' In America
'' The Huffington Post,'' May 19, 2014.
10 Poverty Myths, Busted
'' Mother Jones,'' March/April 2014 issue.
FPL Calculator
A mobile app for calculating federal poverty level.
The Poor Get Prison
Institute for Policy Studies, 2015.
Measuring the impact of poverty in education, EducationDive, August 8, 2016
''
Economic policies sacrifice poor Americans
Reuters. June 2, 2023. {{Social class
 In the United States,
In the United States, poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
has both social and political implications. In 2020, there were 37.2 million people in poverty. Some of the many causes include income inequality, inflation, unemployment, debt traps and poor education.Western, B. & Pettit, B., (2010)Incarceration and social inequality.
Daedalus, 139(3), 8-19 The majority of adults living in poverty are employed and have at least a high school education. Although the US is a relatively wealthy country by international standards, it has a persistently high poverty rate compared to other developed countries due in part to a less generous welfare system. Efforts to alleviate poverty include
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Cons ...
-era legislation during the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
, to the national war on poverty in the 1960s and poverty alleviation efforts during the 2008 Great Recession. The federal government has two departments which measure poverty. Under the Department of Commerce
The United States Department of Commerce is an executive department of the U.S. federal government concerned with creating the conditions for economic growth and opportunity. Among its tasks are gathering economic and demographic data for bu ...
, the Census Bureau has been reporting the Official Poverty Measure (OPM) since the 1960's, while the Department of Health and Human Services defines income levels for which people are eligible for governmental anti-poverty assistance. The OPM includes cash assistance from programs like Supplemental Security Income
Supplemental Security Income (SSI) is a means-tested program that provides cash payments to disabled children, disabled adults, and individuals aged 65 or older who are citizens or nationals of the United States. SSI was created by the Social Se ...
and Temporary Assistance to Needy Families (Welfare) as part of someone's income when reporting on how many people are in poverty. Since 2011 the Census Bureau has also been reporting a newer Supplemental Poverty Measure (SPM), which includes non-cash anti-poverty government assistance like Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program
In the United States, the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), formerly known as the Food Stamp Program, is a federal program that provides food-purchasing assistance for low- and no-income people. It is a federal aid program, ad ...
(Food stamps) and Medicaid (health care for the poor), and also accounts for regional differences in the cost of living. The SPM is considered a more comprehensive estimate of poverty.
For 2021, the percentage of Americans in poverty per the SPM was 7.8%, and per the OPM was 11.6%. By the OPM, the poverty threshold for 2021 for a single person was $13,800, and for a family of four was $27,700. In 2020, the World Bank reported that 0.25% of Americans lived below the international definition of extreme poverty
Extreme poverty, deep poverty, abject poverty, absolute poverty, destitution, or penury, is the most severe type of poverty, defined by the United Nations (UN) as "a condition characterized by severe deprivation of basic human needs, includi ...
, which is living on less than $2.15 per day in 2017 Purchasing Power Parity
Purchasing power parity (PPP) is the measurement of prices in different countries that uses the prices of specific goods to compare the absolute purchasing power of the countries' currency, currencies. PPP is effectively the ratio of the price of ...
dollars. The SPM increased by 4.6% in 2022 to 12.4%, due to the ending of pandemic stimulus payments and tax credits, with around 15.3 million Americans falling into poverty over this time period according to the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
The 2020 assessment by the U.S. Census Bureau showed the percentage of Americans living in poverty for 2019 (before the COVID-19 pandemic) had fallen to some of the lowest levels ever recorded due to the record-long period of economic growth. However, between May and October 2020, some eight million people were put into poverty due to the economic effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and the ending of funds from the CARES Act.
History
Progressive era 1890s-1920s
Catalyzed by Henry George's 1873 book '' Progress and Poverty,'' public interest in how poverty could arise even in a time of economic progress arose in the 19th century with the rise of the Progressive movement. The Progressive American social survey began with the publication of ''Hull House Maps and Papers'' in 1895. This study included essays and maps collected by Florence Kelley and her colleagues working at Hull House and staff of the United States Bureau of Labor. It focused on studying the conditions of the slums in Chicago, including four maps color-coded by nationality and income level, which were based on Charles Booth's earlier pioneering work, '' Life and Labour of the People in London.'' Another social reformer, Jacob Riis, documented the living conditions of New York tenements and slums in his 1890 work '' How the Other Half Lives''.Great Depression
A group especially vulnerable to poverty consisted of poor sharecroppers and tenant farmers in the South. These farmers consisted of around a fourth of the South's population, and over a third of these people were African Americans. Historian James T. Patterson refers to these people as the "old poverty," as opposed to the "new poverty" that emerged after the onset of theGreat Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
.
During the Depression, the government did not provide any unemployment insurance, so people who lost jobs easily became impoverished. People who lost their jobs or homes lived in shantytowns or Hoovervilles. Many New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Cons ...
programs were designed to increase employment and reduce poverty. The Federal Emergency Relief Administration
The Federal Emergency Relief Administration (FERA) was a program established by President Franklin Roosevelt in 1933, building on the Hoover administration's Emergency Relief and Construction Act. It was replaced in 1935 by the Works Progress Adm ...
specifically focused on creating jobs for alleviating poverty. Jobs were more expensive than direct cash payments (called "the dole"), but were psychologically more beneficial to the unemployed, who wanted any sort of job for morale. Other New Deal initiatives that aimed at job creation and wellbeing included the Civilian Conservation Corps and Public Works Administration
The Public Works Administration (PWA), part of the New Deal of 1933, was a large-scale public works construction agency in the United States headed by Secretary of the Interior Harold L. Ickes. It was created by the National Industrial Recove ...
. Additionally, the institution of Social Security was one of the largest factors that helped to reduce poverty.Poverty in 13 states is worse than we thoughtWashington Post November 8, 2013
War on Poverty
A number of factors helped start the national War on Poverty in the 1960s. In 1962, Michael Harrington's book '' The Other America'' helped increase public debate and awareness of the poverty issue. The War on Poverty embraced expanding the federal government's roles in education and health care as poverty reduction strategies, and many of its programs were administered by the newly established Office of Economic Opportunity. The War on Poverty coincided with more methodological and precise statistical versions of studying poverty; the "official" U.S. statistical measure of poverty was only adopted in 1969.21st century
In the 21st century, the Great Recession helped to raise the poverty levels again. , the number of people who were in poverty was approaching 1960s levels that led to the national War on Poverty. The 2010 census data shows that half the population qualifies as poor or low income, with one in fivemillennials
Millennials, also known as Generation Y or Gen Y, are the Western demographic cohort following Generation X and preceding Generation Z. Researchers and popular media use the early 1980s as starting birth years and the mid-1990s to early 2000 ...
living in poverty. Academic contributors to ''The Routledge Handbook of Poverty in the United States'' postulate that new and extreme forms of poverty have emerged in the U.S. as a result of neoliberal
Neoliberalism (also neo-liberalism) is a term used to signify the late 20th century political reappearance of 19th-century ideas associated with free-market capitalism after it fell into decline following the Second World War. A prominent fa ...
structural adjustment policies and globalization, which have rendered economically marginalized communities as destitute "surplus populations" in need of control and punishment.
Many international bodies have emphasized the issues of poverty that the United States faces. A 2013 UNICEF report ranked the U.S. as having the second-highest relative child poverty rates in the developed world. , the IMF
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster globa ...
warned the United States that its high poverty rate needs to be tackled urgently by raising the minimum wage and offering paid maternity leave to women to encourage them to enter the labor force. In December 2017, the United Nations special rapporteur on extreme poverty
Extreme poverty, deep poverty, abject poverty, absolute poverty, destitution, or penury, is the most severe type of poverty, defined by the United Nations (UN) as "a condition characterized by severe deprivation of basic human needs, includi ...
and human rights, Philip Alston, undertook a two-week investigation on the effects of systemic poverty in the United States, and sharply condemned "private wealth and public squalor," declaring the state of Alabama to have the "worst poverty in the developed world." Alston's report was issued in May 2018 and highlights that 40 million people live in poverty and over five million live "in ' Third World' conditions."
According to a 2020 assessment by the U.S. Census Bureau, the percentage of Americans living in poverty for 2019 (before the COVID-19 pandemic) had fallen to some of lowest levels ever recorded due to the record-long economic growth period and stood at 11.1% (adjusted for smaller response during the pandemic). However, between May and October 2020, the economic effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the exhaustion of the funding provided by the CARES Act, dragged some eight million people into poverty.
According to OECD, nearly 23 percent of American workers work in low-wage jobs, compared with 17 percent in Britain, 11 percent in Japan and 5 percent in Italy. In January 2021, according to the U.S. Census Bureau, 11.6 percent of the US population, or 37.9 million people, were living in poverty(using as an example a family of three earning less than $21,559). In his 2023 book '' Poverty, by America'', sociologist Matthew Desmond writes that the poverty rate in the United States has not improved in half a century, with 11% of the population living in poverty in 2019, compared to 12% in 1970.
Social scientist Mark Robert Rank
Mark Robert Rank is a social scientist and Herbert S. Hadley Professor of Social Welfare at George Warren Brown School of Social Work at Washington University in St. Louis, known for his work on "poverty, social welfare, economic inequality and s ...
writes in 2023 that the last four decades has seen a retrenchment of the social safety net, with a reduction in eligibility and amount of benefits transferred. This, along with the failure of the US to provide universal child care, medical insurance and other social benefits as done in peer countries, has resulted in the US having much higher poverty rates by comparison.
Measuring poverty
There are several measures used by the U.S. federal government to measure poverty. The Census Bureau issues the poverty thresholds, which are generally used for statistical purposes—for example, to estimate the number of people in poverty nationwide each year and classify them by type of residence, race, and other social, economic, and demographic characteristics. The Department of Health and Human Services issues the poverty guidelines for administrative purposes—for instance, to determine whether a person or family is eligible for assistance through various federal programs. Both the poverty thresholds and poverty guidelines are updated yearly. More recently, the Census Bureau has begun using the Supplemental Poverty Measure as an additional statistic to measure poverty and supplement the existing measures.Poverty income thresholds
The poverty income thresholds originate from work done byMollie Orshansky
Mollie Orshansky (January 9, 1915 – December 18, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who, in 1963–65, developed the ''Orshansky Poverty Thresholds'', which are used in the United States as a measure of the income that a household ...
, an American economist working for the Social Security Administration. Orshansky introduced the poverty thresholds in a 1963 ''Social Security Bulletin'' article, "Children of the Poor."
 Orshansky based her thresholds on work she had done with the
Orshansky based her thresholds on work she had done with the economy food plan
The Thrifty Food Plan (TFP) is one of four USDA-designed food plans specifying categories and amounts of foods to provide adequate nutrition. The other plans are known as the Low-Cost, Moderate-Cost, and Liberal food plans. Each plan specifies a ...
while at the USDA. According to the USDA's 1955 Household Food Consumption Survey, families of three or more people spent one-third of their after-tax income on food. For these families, poverty thresholds were set at three times the cost of the economy food plan. Different procedures were used for calculating poverty thresholds for two-person households and persons living alone.
Her work appeared at an opportune moment, as President Johnson declared the War on Poverty just six months later—and Orshansky's work offered a numerical way to measure progress in this effort. The newly formed Office of Economic Opportunity (OEO) adopted the Orshansky poverty thresholds for statistical, planning, and budgetary purposes in May 1965. Officials at the OEO were enthusiastic; as research director Joseph Kershaw remarked, "Mollie Orshansky says that when you have more people in the family, you need more money. Isn't that sensible?"
Officials at the Social Security Administration began to plan on how to adjust poverty thresholds for changes in the standard of living. The Bureau of the Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). OMB's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, but it also examines agency programs, poli ...
resisted these changes, but formed an interagency committee that, in 1969, decided that poverty thresholds would be adjusted for inflation by being tied to the Consumer Price Index
A consumer price index (CPI) is a price index, the price of a weighted average market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households. Changes in measured CPI track changes in prices over time.
Overview
A CPI is a statistica ...
, rather than changes in the standard of living. In August 1969, the Bureau of the Budget designated these revised thresholds as the federal government's official definition of poverty.
Apart from minor changes in 1981 that changed the number of thresholds from 124 to 48, poverty thresholds have remained static for the past fifty years despite criticism that the thresholds may not be completely accurate. Although the poverty thresholds assumes that the average household of three spends one-third of its budget on food, more recent surveys have shown that that number has decreased to one-fifth in the 1980s and one-sixth by the 1990s. If the poverty thresholds were recalculated based on the share of household budgets taken by food costs as of 2008, the economy food budget multiplier would have been 7.8 rather than 3, greatly increasing the thresholds.
Poverty income guidelines
The poverty guidelines are a version of the poverty thresholds used by federal agencies for administrative purposes, such as determining eligibility for federal assistance programs. They are useful because poverty thresholds for one calendar year are not published until the summer of the next calendar year; poverty guidelines, on the other hand, allow agencies to work with more timely data. Poverty guidelines were issued by the OEO starting in December 1965. After the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1981, responsibility for issuing the guidelines was transferred to the Department of Health and Human Services. Poverty guidelines are also referred to as the "federal poverty level" (FPL), but the HHS discourages that term as ambiguous.Supplemental Poverty Measure
In 1990, a Congressional committee requested the National Research Council (NRC) to conduct a study on revising the poverty measure. The NRC convened a panel, which published a 1995 report ''Measuring Poverty: A New Approach'' that concluded that the official poverty measure in the United States is flawed. The panel noted that the thresholds are the same irrespective of geography and stated that due to "rising living standards in the United States, most approaches for developing poverty thresholds (including the original one) would produce higher thresholds today than the current ones." Additionally, the report suggested an alternative measure of poverty, which uses actual expenditure data to develop a threshold value for a family of four—and then update this threshold every year and according to geographic location. This alternative measure of poverty would also change the income calculation for a family, including certain non-cash benefits that satisfied "basic needs" such as food stamps and public housing while excluding "non-basic needs" such as medical costs and child care. The work of the panel led to the development of the Supplemental Poverty Measure (SPM), which was intended to address some of the weaknesses of the existing poverty guidelines. In October 2014, the Census Bureau released a report describing the SPM and stated its intention to publish SPM measures every year. However, SPM is intended to "supplement" the existing poverty thresholds, not "replace" them, as poverty thresholds will remain the "official" Census Bureau measure and poverty guidelines will be derived only from the "official" poverty measures. Unlike the poverty thresholds, and in line with the NRC recommendations, the SPM both includes certain non-cash benefits in a family's income and adjusts thresholds for differences in housing costs by geographic area. Additionally, the SPM thresholds are based on how much a "reference" family with two children spends on food, clothing, shelter, and utilities (FCSU).Criticism
Understating poverty
Many sociologists and government officials have argued that poverty in the United States is understated, meaning that there are more households living in actual poverty than there are households below the poverty threshold. A study taken in 2012 estimated that roughly 38% of Americans live "paycheck to paycheck." In 1969, the Bureau of Labor Statistics put forward suggested budgets for adequate family living. 60% of working-class Americans lived below the "intermediate" budget, which allowed for the following:It assumes, for example, that the family will own: ... A toaster that will last for 33 years. ... A vacuum cleaner that will last 14 years. The budget assumes that a family will buy a two-year-old car and keep it for four years... Finally, the budget allows nothing whatever for savings.Given that the "intermediate" budget was fairly modest, observers questioned whether poverty levels were really capturing the full extent of prosperity, challenging the long-established view that most Americans had attained an affluent standard of living in the two decades following the end of the Second World War. There have also been criticism of the methodology used to develop the U.S. poverty thresholds in the first place. The poverty thresholds used by the US government were originally developed during the Johnson administration's War on Poverty initiative in the early 1960s. The thresholds were based on the cost of a food basket at the time, multiplied by three, under the assumption that the average family spent one-third of its income on food. However, the poverty line only takes into account food purchases that were common more than 50 years ago. It assumes that Americans spend one third of their income on food; in fact, Americans typically spent less than one tenth of their after-tax income on food in 2000. For many families, the costs of housing,
health insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among ma ...
and medical care, transportation, and access to basic telecommunications take a much larger bite out of the family's income than a half century ago, yet none of these costs are considered in determining the official poverty thresholds.
According to John Schwarz, a political scientist at the University of Arizona:The official poverty line today is essentially what it takes in today's dollars, adjusted for inflation, to purchase the same poverty-line level of living that was appropriate to a half century ago, in 1955 .... Updated thereafter only for inflation, the poverty line lost all connection over time with current consumption patterns of the average family. Quite a few families then didn't have their own private telephone, or a car, or even a mixer in their kitchen... The official poverty line has thus been allowed to fall substantially below a socially decent minimum, even though its intention was to measure such a minimum.
high cost of living
High may refer to:
Science and technology
* Height
* High (atmospheric), a high-pressure area
* High (computability), a quality of a Turing degree, in computability theory
* High (tectonics), in geology an area where relative tectonic uplift to ...
and a high poverty rate such as California where the median home price
Real estate appraisal, property valuation or land valuation is the process of developing an opinion of value for real property (usually market value). Real estate transactions often require appraisals because they occur infrequently and every prop ...
in 2006 was $564,430. In the Monterey area, where the low-pay industry of agriculture is the largest sector in the economy and the majority of the population lacks a college education, the median home price was $723,790, requiring an upper middle class income only earned by roughly 20% of all households in the county. Such fluctuations in local markets are, however, not considered in the federal poverty threshold and may leave many who live in poverty-like conditions out of the total number of households classified as poor.
The Supplemental Poverty Measure, introduced in 2011, aims at providing a more accurate picture of the true extent of poverty in the United States by taking account of non-cash benefits and geographic variations. According to this new measure, 16% of Americans lived in poverty in 2011, compared with the official figure of 15.2%. With the new measure, one study estimated that nearly half of all Americans lived within 200% of the federal poverty line.
According to American economist Sandy Darity, Jr., "There is no exact way of measuring poverty. The measures are contingent on how we conceive of and define poverty. Efforts to develop more refined measures have been dominated by researchers who intentionally want to provide estimates that reduce the magnitude of poverty."
Matthew Desmond writes that the "overwhelming majority" of prisoners and former prisoners of the US prison system are extremely poor, and this group is largely omitted from poverty statistics and national surveys, "which means there are millions more poor Americans than official statistics let on."
Overstating poverty
Some critics assert that the official U.S. poverty definition is inconsistent with how it is defined by its own citizens and the rest of the world, because the U.S. government considers many citizens statistically impoverished despite their ability to sufficiently meet their basic needs. According to '' Vox'', there is a "near-unanimous consensus among poverty researchers that the official poverty measure (OPM) in the United States is a disaster" primarily because of its failure to include all anti-poverty government benefits as income when calculating whether or not an individual is poor. The OPM includes governmental anti-poverty cash aid likeSupplemental Security Income
Supplemental Security Income (SSI) is a means-tested program that provides cash payments to disabled children, disabled adults, and individuals aged 65 or older who are citizens or nationals of the United States. SSI was created by the Social Se ...
and Welfare but does not include non-cash aid like Food stamps
In the United States, the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), formerly known as the Food Stamp Program, is a federal program that provides food-purchasing assistance for low- and no-income people. It is a federal aid program, ad ...
, housing assistance, and Medicaid (health care for the poor). Since 2011, the Census Bureau has started publishing the Supplemental Poverty Measure (SPM), which factors these non-cash benefits into the calculation, along with regional differences in cost of living, and is widely seen as a more comprehensive measure.
Burkhauser et al. find that accounting for cash income, taxes, and major in-kind transfers and updating poverty thresholds for inflation show that a Full-income Poverty Rate based on President Johnson's standards fell from 19.5 percent to 2.3 percent over the 1963–2017 period.
Geography
Poverty in U.S. territories

 The highest poverty rates in the United States are in the U.S. territories ( American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico and the
The highest poverty rates in the United States are in the U.S. territories ( American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands
The United States Virgin Islands,. Also called the ''American Virgin Islands'' and the ''U.S. Virgin Islands''. officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory ...
).http://www.gao.gov/new.items/d10240r.pdf ''Poverty Determination In U.S. Insular Areas.'' Retrieved August 30, 2019. American Samoa has the lowest per capita income in the United States — it has a per capita income comparable to that of Botswana. In 2010, American Samoa had a per capita income of $6,311. The county or county-equivalent with the lowest per capita income in the United States is the Manu'a District in American Samoa (per capita income of $5,441). In 2018, Puerto Rico had the lowest median household income of any state/territory in the United States ($20,166).https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/PR/ U.S. Census Bureau. QuickFacts - Puerto Rico. Retrieved July 4, 2020. Also in 2018, Comerío, Puerto Rico had a median household income of $12,812 — the lowest median household income of any county or county-equivalent in the United States.
In the 2010 U.S. Census, Guam had a poverty rate of 22.9%, the Northern Mariana Islands had a poverty rate of 52.3%, and the U.S. Virgin Islands
The United States Virgin Islands,. Also called the ''American Virgin Islands'' and the ''U.S. Virgin Islands''. officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory ...
had a poverty rate of 22.4% (all higher than any U.S. state). In 2018, Puerto Rico had a poverty rate of 43.1%. In 2017, American Samoa had a poverty rate of 65% — the highest poverty rate of any state or territory in the United States.
Poverty in U.S. states
As of 2018, the state with the lowest poverty rate was New Hampshire (7.6% poverty rate). Other states with low poverty rates in 2018 include Hawaii (8.8% poverty rate), Maryland (9.0% poverty rate), and Minnesota (9.6% poverty rate). Among U.S. states, Mississippi had the highest poverty rate in 2018 (19.7% poverty rate), followed by Louisiana (18.65%), New Mexico (18.55%) and West Virginia (17.10%).Poverty and demographics
Poverty and family status
Among married couple families: 5.8% lived in poverty.U.S. Census Bureau. Current Population Survey. ''Persons in Families by Family Structure, Age, and Sex, Iterated by Income-to-Poverty Ratio and Race: 2007Below 100% of Poverty – All Races
.'' This number varied by race and ethnicity as follows: * 5.4% of all white persons (which includes white Hispanics),U.S. Census Bureau. Current Population Survey. ''People in Families by Family Structure, Age, and Sex, Iterated by Income-to-Poverty Ratio and Race: 2007
Below 100% of Poverty – White Alone
.'' * 10.7% of all black persons (which includes black Hispanics), * 14.9% of all Hispanic persons (of any race) living in poverty. Among single-parent (male or female) families: 26.6% lived in poverty. This number varied by race and ethnicity as follows: * 22.5% of all white persons (which includes white Hispanics), * 44.0% of all black persons (which includes black Hispanics), * 33.4% of all Hispanic persons (of any race) living in poverty. Among individuals living alone: 19.1% lived in poverty. This number varied by race and ethnicity as follows: * 18% of white persons (which includes white Hispanics), * 28.9% of black persons (which includes black Hispanics) * 27% of Hispanic persons (of any race) are living in poverty.
Poverty and race/ethnicity
 The US Census declared that in 2014, 14.8% of the general population lived in poverty:Income and Poverty in the United States: 2014
The US Census declared that in 2014, 14.8% of the general population lived in poverty:Income and Poverty in the United States: 2014. U.S. Census Bureau As of 2010 about half of those living in poverty are non-Hispanic white (19.6 million). Non-Hispanic white children comprised 57% of all poor rural children. In FY 2009, African American families comprised 33.3% of TANF families, non-Hispanic white families comprised 31.2%, and 28.8% were Hispanic.
Poverty among Native Americans
Poverty is also notoriously high on Native American reservations (see Reservation poverty). 7 of the 11 poorest counties in per capita income (in the 50 states), including the 2 poorest in the 50 states, encompass Lakota Sioux reservations in South Dakota. This fact has been cited by some critics as a mechanism that enables the "kidnapping" of Lakota children by the state of South Dakota's Department of Social Services. The Lakota People's Law Project, among other critics, allege that South Dakota "inappropriately equates economic poverty with neglect ... South Dakota's rate of identifying "neglect" is 18% higher than the national average... In 2010, the national average of state discernment of neglect, as a percent of total maltreatment of foster children prior to their being taken into custody by the state, was 78.3%. In South Dakota the rate was 95.8%." Poverty in thePine Ridge Reservation
The Pine Ridge Indian Reservation ( lkt, Wazí Aháŋhaŋ Oyáŋke), also called Pine Ridge Agency, is an Oglala Lakota Indian reservation located entirely within the U.S. state of South Dakota. Originally included within the territory of the Grea ...
in particular has had unprecedented effects on its residents' longevity. "Recent reports state the average life expectancy is 45 years old while others state that it is 48 years old for men and 52 years old for women. With either set of figures, that's the shortest life expectancy for any community in the Western Hemisphere outside Haiti, according to The Wall Street Journal."
In the 2013—2017 American Community Survey
The American Community Survey (ACS) is a demographics survey program conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. It regularly gathers information previously contained only in the long form of the decennial census, such as ancestry, citizenship, educati ...
, Wounded Knee, South Dakota (located in the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation) had the 7th-lowest median household income out of all places in the 50 states/D.C./Puerto Rico.https://factfinder.census.gov/faces/tableservices/jsf/pages/productview.xhtml?pid=ACS_17_5YR_S1901&prodType=table U.S. Census Bureau. American FactFinder. Income in the past 12 months (in 2017 inflation-adjusted dollars). 2013-2017 American Community Survey 5-year estimates. Geography" set to "All Places within United States and Puerto Rico".Retrieved August 30, 2019.
Poverty and LGBTQ+ status
With data collected from 35 states from 2014-2017, the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) survey shows that 21.6% of the LGBTQ+ population is living in poverty. The number varies depending on identity: * 12.1% of cis-gay men * 17.9% of cis-lesbian women * 19.5% of cis-bisexual men * 29.4% of cis-bisexual women * 33.7% of transgender men * 29.6% of transgender women, and * 23.8% of gender nonconforming people. For comparison, 13.4% of cis-straight men and 17.8% of cis-straight women are living in poverty.Transgender poverty
The rate of poverty for the transgender community is larger than any other LGBTQ+ population. The 2015 U.S. Transgender Survey shows that this percentage varies depending on racial and ethnic identity: * 41% Native American or American Indian * 32% Asian * 38% Black or African American * 43% Hispanic or Latino * 34% Middle Eastern * 40% Multiracial For comparison, 24% of White transgender people are living in poverty. The percentage of those living in poverty also increases for transgender people with HIV (51%) and disabilities (45%).Poverty and age
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries ...
(OECD) uses a different measure for poverty and declared in 2008 that child poverty in the US is 20% and poverty among the elderly is 23%. 
Child poverty
In May 2009, the non-profit advocacy group Feeding America released a study based on 2005–2007 data from the U.S. Census Bureau and the Agriculture Department, which claims that 3.5 million children under the age of 5 are at risk of hunger in the United States. The study claims that in 11 states, Louisiana, which has the highest rate, followed by North Carolina, Ohio, Kentucky, Texas, New Mexico, Kansas, South Carolina, Tennessee, Idaho and Arkansas, more than 20 percent of children under 5 are allegedly at risk of going hungry. (receiving fewer than 1,800 calories per day). In 2012, 16.1 million American children were living in poverty. Outside of the 49 million Americans living in food-insecure homes, 15.9 million of them were children. In 2013, child poverty reached record high levels in the U.S., with 16.7 million children living in food insecure households. Many of the neighborhoods these children live in lack basic produce and nutritious food. 47 million Americans depend on food banks, more than 30% above 2007 levels. Households headed bysingle mother
A single parent is a person who has a child or children but does not have a spouse or live-in partner to assist in the upbringing or support of the child. Reasons for becoming a single parent include divorce, break-up, abandonment, becoming wid ...
s are most likely to be affected. 30 percent of low-income single mothers cannot afford diapers. Inability to afford this necessity can cause a chain reaction, including mental, health, and behavioral problems. Some women are forced to make use of one or two diapers, using them more than once. This causes rashes and sanitation problems as well as health problems. Without diapers, children are unable to enter into daycare. The lack of childcare can be detrimental to single mothers, hindering their ability to obtain employment. Worst affected are Oregon, Arizona, New Mexico, Florida, and the District of Columbia, while North Dakota, New Hampshire, Virginia, Minnesota and Massachusetts are the least affected. 31 million low-income children received free or reduced-price meals daily through the National School lunch program during the 2012 federal fiscal year. Nearly 14 million children are estimated to be served by Feeding America with over 3 million being of the ages of 5 and under.
A 2014 report by the National Center on Family Homelessness states the number of homeless children in the U.S. has reached record levels, calculating that 2.5 million children, or one child in every 30, experienced homelessness in 2013. High levels of poverty, lack of affordable housing and domestic violence were cited as the primary causes. A 2017 peer-reviewed study published in '' Health Affairs'' found that the U.S. has the highest levels of child mortality among 20 OECD countries.
Racial inequality is also visible when it comes to discerning poverty among children in America. In 2021, Children's Defense Fund estimated that 71% of children living in poverty are children of color.
Poverty is also associated with expanded adverse childhood experiences, such as witnessing violence, feeling discrimination, and experiencing bullying. According to a 2016 study by the Urban Institute, teenagers in low income communities are often forced to join gangs, save school lunches, sell drugs or exchange sexual favors because they cannot afford food.
According to the Save the Children fund, food insecurity among families with children as increased by two-thirds since March 2020. The fund further states that "the U.S. continues to lag behind most peer countries in meeting the needs of children and families during the pandemic".
Children living in poverty may also experience many health and developmental problems due to food insecurity and malnutrition. Children in low socioeconomic statuses are shown to have more gray matter which affects educational and life outcomes. They may have a lower immune systems due to malnutrition, and they are more likely to have chronic disease like asthma.
Child poverty more than doubled from 5.2% in 2021 to 12.4% in 2022 largely as the result of pandemic aid running out, in particular the expansion of the child tax credit.
Effects of poverty
Education
Poverty affects individual access to quality education. TheU.S. education system
Education in the United States is provided in State school#United States, public and private school, private schools and by individuals through Homeschooling in the United States, homeschooling. U.S. state, State governments set overall educa ...
is often funded by local communities; therefore the quality of materials and teachers can reflect the affluence of community. That said, many communities address this by supplementing these areas with funds from other districts. Low income communities are often not able to afford the quality education that high-income communities do which results in a cycle of poverty.
Health disparities
Factors in poverty
 There are numerous factors related to poverty in the United States.
*Income has a high correlation with educational levels. In 2007, the median earnings of household headed by individuals with less than a 9th grade education was $20,805 while households headed by high school graduates earned $40,456, households headed by holders of bachelor's degrees earned $77,605, and families headed by individuals with professional degrees earned $100,000. Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen stated in 2014: "Public funding of education is another way that governments can help offset the advantages some households have in resources available for children. One of the most consequential examples is early childhood education. Research shows that children from lower-income households who get good-quality pre-Kindergarten education are more likely to graduate from high school and attend college as well as hold a job and have higher earnings, and they are less likely to be incarcerated or receive public assistance."
*In many cases, poverty is caused by job loss. In 2007, the poverty rate was 21.5% for individuals who were unemployed, but only 2.5% for individuals who were employed full-time.
*
There are numerous factors related to poverty in the United States.
*Income has a high correlation with educational levels. In 2007, the median earnings of household headed by individuals with less than a 9th grade education was $20,805 while households headed by high school graduates earned $40,456, households headed by holders of bachelor's degrees earned $77,605, and families headed by individuals with professional degrees earned $100,000. Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen stated in 2014: "Public funding of education is another way that governments can help offset the advantages some households have in resources available for children. One of the most consequential examples is early childhood education. Research shows that children from lower-income households who get good-quality pre-Kindergarten education are more likely to graduate from high school and attend college as well as hold a job and have higher earnings, and they are less likely to be incarcerated or receive public assistance."
*In many cases, poverty is caused by job loss. In 2007, the poverty rate was 21.5% for individuals who were unemployed, but only 2.5% for individuals who were employed full-time.
*Children
A child ( : children) is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. The legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person younger ...
growing up in female-headed families with no spouse present have a poverty rate over four times that of children in married-couple families.
*Income levels vary with age. For example, the median 2009 income for households headed by individuals age 15–24 was only $30,750, but increased to $50,188 for household headed by individuals age 25–34 and $61,083 for household headed by individuals 35–44. Work experience and additional education may be factors.
* Income levels vary along racial/ethnic lines: 21% of all children in the United States live in poverty, about 46% of black children and 40% of Latino children. The poverty rate is 9.9% for black married couples, and only 30% of black children are born to married couples (see Marriage below). The poverty rate for native born and naturalized whites is identical (9.6%). On the other hand, the poverty rate for naturalized blacks is 11.8% compared to 25.1% for native born blacks, suggesting race alone does not explain income disparity. Not all minorities have low incomes. Asian families have higher incomes than all other ethnic groups. For example, the 2005 median income of Asian families was $68,957 compared to the median income of white families of $59,124. Asians, however, report discrimination occurrences more frequently than blacks. Specifically, 31% of Asians reported employment discrimination compared to 26% of blacks in 2005.
*Policies that address income and wealth inequality (i.e., policies that transfer money from higher-income and more wealthy families to less wealthy families) bear significantly on poverty. Economist Jared Bernstein and Elise Gould of the Economic Policy Institute suggest that poverty could have decreased significantly if inequality had not increased over the last few decades. Economist Larry Summers estimated that at 1979 levels of income inequality, the bottom 80% of families would have an average of $11,000 more per year in income in 2014.
*According to Mark Robert Rank
Mark Robert Rank is a social scientist and Herbert S. Hadley Professor of Social Welfare at George Warren Brown School of Social Work at Washington University in St. Louis, known for his work on "poverty, social welfare, economic inequality and s ...
, the high rates of poverty in the U.S. cannot be explained as simply the result of personal and behavioral failures of individuals, but rather structural failures at the economic and political levels. The free market economy of the U.S. mostly produces jobs that are inadequate in supporting families, and the very nature of capitalism itself is to make certain that a "modest level" of unemployment always exists. Both of these, combined with failings at the policy level to support the economically vulnerable, have ensured that "there are not nearly enough opportunities and resources to support the entire population." Matthew Desmond writes that the U.S. "offers some of the lowest wages in the industrialized world," which has "swelled the ranks of the working poor, most of whom are thirty-five or older."
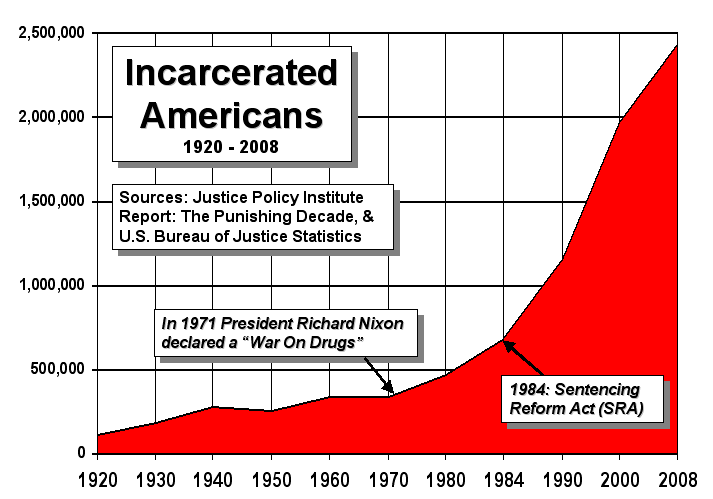
*The relationship between tax rates and poverty is disputed. A study comparing high tax Scandinavian countries with the U. S. suggests high tax rates are inversely correlated with poverty rates. The poverty rate, however, is low in some low tax countries like Switzerland. A comparison of poverty rates between states reveals that some low tax states have low poverty rates. For example, New Hampshire has the lowest poverty rate of any state in the U. S., and has very low taxes (46th among all states). It is true however that both Switzerland and New Hampshire have a very high household income and other measures offsetting the lack of taxation. For example, Switzerland has Universal Healthcare and a free system of education for children as young as four years old. New Hampshire has no state income tax or sales tax, but does have the nation's highest property taxes. *The poor in the United States are
*The poor in the United States are incarcerated
A prison, also known as a jail, gaol (dated, standard English, Australian, and historically in Canada), penitentiary (American English and Canadian English), detention center (or detention centre outside the US), correction center, correcti ...
at a much higher rate than their counterparts in other developed nations, with penal confinement being, according to sociologist Bruce Western
Bruce Prichart Western (born July 1, 1964) is an Australian-born American sociologist and a professor of sociology at Columbia University.
Early life and education
Western was born in Australia, to a white native Australian father who taught at ...
, "commonplace for poor men of working age." Scholars assert that the transformation of the already anemic U.S. welfare state to a post-welfare punitive state, along with neoliberal structural adjustment policies, the globalization of the U.S. economy and the dominance of global financial institutions, have created more extreme forms of "destitute poverty" in the U.S. which must be contained by expanding the criminal justice system and the carceral state into every aspect of the lives of the poor, which, according to Reuben Jonathan Miller and Emily Shayman, has resulted in "transforming what it means to be poor in America."
* Matthew Desmond writes that in 2020 around 18 million people, including more than 5 million children, lived in "deep poverty" (the poverty line cut in half), which amounted to an annual income below $6,380 for individuals and $13,100 for family of four.
*A 2012 study by the Urban Institute found that 75% of adults in "deep poverty" had not worked in the previous year.
*According to a 2017 academic study by MIT economist Peter Temin, Americans trapped in poverty live in conditions rivaling the developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
, and are forced to contend with substandard education, dilapidated housing, and few stable employment opportunities. A 2017 study published in ''The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene
The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH) is an Arlington, Virginia-based non-profit organization of scientists, clinicians, students and program professionals whose longstanding mission is to promote global health through the ...
'' found that hookworm
Hookworms are intestinal, blood-feeding, parasitic roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with poor access to adequate water, sanitation, an ...
, a parasite that thrives on extreme poverty, is flourishing in the Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the war ...
. A report on the study in ''The Guardian'' stated:
*Some 12 million Americans live with diseases associated with extreme poverty.
*Poverty may be fueling the Obesity epidemic, with the poorest states, counties and neighborhoods having the highest death rates from heart disease, stroke, diabetes and other diseases related to obesity. For every $10,000 poorer a neighborhood is, the death rate of heart disease increases by 10%
* In poor and disadvantaged neighborhoods, landlords extract higher profits from tenants than from their counterparts in affluent communities, which Matthew Desmond and Nathan Wilmers describe in a 2019 article published in the ''American Journal of Sociology
The ''American Journal of Sociology'' is a peer-reviewed bi-monthly academic journal that publishes original research and book reviews in the field of sociology and related social sciences. It was founded in 1895 as the first journal in its disci ...
'' as tenant exploitation ("overcharging renters relative to the market value of their home"). Landlords perceive operating in poorer neighborhoods as a greater risk, even though losses are rare, and therefore raise rents on all tenants, which "contributes to their economic scarcity and hardship and is a source of residential insecurity, eviction, and homelessness." The authors argue that the higher profit margins implies that the lack of affordable housing in these areas is driven in part by "the market dynamics of landlords" in addition to "supply levels or regulatory barriers."
Fighting poverty
There have been governmental and nongovernmental efforts to reduce poverty and their effects. These range in scope from neighborhood efforts to campaigns with a national focus. They target specific groups affected by poverty such as children, people who are autistic, immigrants, or people who are homeless. Efforts to alleviate poverty use a disparate set of methods, such as advocacy, education, social work, legislation, direct service or charity, andcommunity organizing
Community organizing is a process where people who live in proximity to each other or share some common problem come together into an organization that acts in their shared self-interest.
Unlike those who promote more-consensual community bui ...
.
Recent debates have centered on the need for policies that focus on both "income poverty" and "asset poverty." Advocates for the approach argue that traditional governmental poverty policies focus solely on supplementing the income of the poor through programs such as Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF, formerly Aid to Families with Dependent Children, AFDC) and Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program
In the United States, the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), formerly known as the Food Stamp Program, is a federal program that provides food-purchasing assistance for low- and no-income people. It is a federal aid program, ad ...
(SNAP, formerly the Food Stamp Program). According to the CFEDbr>2012 Assets & Opportunity Scorecard27 percent of households – nearly double the percentage that are income poor – are living in "asset poverty." These families do not have the savings or other assets to cover basic expenses (equivalent to what could be purchased with a poverty level income) for three months if a layoff or other emergency leads to loss of income. Since 2009, the number of asset poor families has increased by 21 percent from about one in five families to one in four families. In order to provide assistance to such asset poor families, Congress appropriated $24 million to administer the Assets for Independence Program under the supervision of the US Department for Health and Human Services. The program enables community-based nonprofits and government agencies to implement Individual Development Account or IDA programs, which are an asset-based development initiative. Every dollar accumulated in IDA savings is matched by federal and non-federal funds to enable households to add to their assets portfolio by buying their first home, acquiring a post-secondary education, or starting or expanding a small business. Additionally, th
Earned Income Tax Credit
(EITC or EIC) is a credit for people who earn low-to-moderate incomes. This credit allows them to get money from the government if their total tax outlay is less than the total credit earned, meaning it is not just a reduction in total tax paid but can also bring new income to the household. The Earned Income Tax Credit is viewed as the largest poverty reduction program in the United States. There is an ongoing debate in the U.S. about what the most effective way to fight poverty is, through the tax code with the EITC, or through the minimum wage laws. Government safety-net programs put in place since the War on Poverty have helped reduce the poverty rate from 26% in 1967 to 16% in 2012, according to a Supplemental Poverty Model (SPM) created by Columbia University, while the official U.S. Poverty Rate has not changed, as the economy by itself has done little to reduce poverty. According to the 2013 Columbia University study which created the (SPM) method of measuring poverty, without such programs the poverty rate would be 29% today. An analysis of the study by Kevin Drum suggests the American welfare state effectively reduces poverty among the elderly but provides relatively little assistance to the working-age poor. A 2014 study by
Pew Charitable Trusts
The Pew Charitable Trusts is an independent non-profit, non-governmental organization
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent ...
shows that without social programs like food stamps
In the United States, the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), formerly known as the Food Stamp Program, is a federal program that provides food-purchasing assistance for low- and no-income people. It is a federal aid program, ad ...
, social security and the federal EITC, the poverty rate in the U.S. would be much higher. Nevertheless, the U.S. has the weakest social safety net of all developed nations. Sociologist Monica Prasad of Northwestern University argues that this developed because of government intervention rather than lack of it, which pushed consumer credit for meeting citizens' needs rather than applying social welfare policies as in Europe.Monica Prasad, The Land of Too Much: American Abundance and the Paradox of Poverty
'' ( Harvard University Press, 2012),
See also
*Causes of poverty in the United States
Theories on the causes of poverty are the foundation upon which poverty reduction strategies are based.
While in developed nations poverty is often seen as either a personal or a structural defect, in developing nations the issue of poverty is mor ...
* Eviction in the United States
* Income in the United States
* Income inequality in the United States
Income inequality in the United States is the extent to which income is distributed in differing amounts among the American population. It has fluctuated considerably since measurements began around 1915, moving in an arc between peaks in t ...
* Income deficit
* List of U.S. states and territories by poverty rate
* List of lowest-income places in the United States
* Lowest-income counties in the United States
* Homelessness in the United States
* Hunger in the United States
* Poor person
* Social programs in the United States
* Pathways out of Poverty Pathways Out of Poverty (POP) is an American workforce development program that was established on August 14, 2009 by the Obama administration and funded by the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA) of 2009. The Department of Labor's Employ ...
(POP)
Other
* Human Poverty Index * Mississippi Teacher Corps * Basic Income * Negative Income Tax * Tipping Point Community * Redistributive change *De-industrialization crisis
Deindustrialization is a process of social and economic change caused by the removal or reduction of industrial capacity or activity in a country or region, especially of heavy industry or manufacturing industry.
There are different interpre ...
* '' The Other America''
* '' Two Americas''
* Kids Against Hunger
* '' Can you hear their voices?'' (1931 play)
* Feminization of poverty
* Unintended pregnancy
* Social determinants of health in poverty
International
* Poverty by country *International Ranking of Household Income
Household income is a measure of the combined incomes of all people sharing a particular household or place of residence. It includes every form of income, e.g., salaries and wages, retirement income, near cash government transfers like food stamp ...
* List of Average Wages per Country
Notes
References
Bibliography and further reading
* * Alston, Philip. (2018Report of the Special Rapporteur on extreme poverty and human rights on his mission to the United States of America
OHCHR. * Berkowitz, Edward, and Kim McQuaid. (1992) ''Creating the Welfare State: The Political Economy of Twentieth-Century Reform'' (UP of Kansas, 1992) * * Cray, Robert E., Jr. ''Paupers and Poor Relief in New York City and Its Rural Environs, 1700–1830'' (Temple University Press, 1988
online
* * DeParle, Jason, "How to Fix Child Poverty" (review of
Jeff Madrick
Jeffrey G. Madrick is a journalist, economic policy consultant and analyst. He is editor of '' Challenge: The Magazine of Economic Affairs,'' visiting professor of humanities at The Cooper Union, and director of policy research at the Schwartz Cen ...
, ''Invisible Americans: The Tragic Cost of Child Poverty'', Knopf, 2020, , 231 pp.; and ''A Roadmap to Reducing Child Poverty: a report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, edited by Greg Duncan and Suzanne Le Menestrel, National Academies Press, 596 pp., free PDF available at nap.edu/25246), '' The New York Review of Books'', vol. LXVII, no. 12 (23 July 2020), pp. 33–35.
* Desmond, Matthew (2016). '' Evicted: Poverty and Profit in the American City.'' Crown Publishing Group.
*
* Edin, Kathryn and Lein, Laura (1997). ''Making Ends Meet: How Single Mothers Survive Welfare and Low-Wage Work.'' Russell Sage Foundation
The Russell Sage Foundation is an American non-profit organisation established by Margaret Olivia Sage in 1907 for “the improvement of social and living conditions in the United States.” It was named after her recently deceased husband, rail ...
.
* Edin, Kathryn and H. Luke Shaefer (2016). ''$2.00 a Day: Living on Almost Nothing in America.'' Mariner Books.
* Ehrenreich, Barbara (2001). '' Nickel and Dimed: On (Not) Getting By in America''. Metropolitan Books.
*
*
* Haymes, Stephen, Maria Vidal de Haymes and Reuben Miller (eds). The Routledge Handbook of Poverty in the United States
'' Routledge, 2015. . * Howe, Louise Kapp, ed. (1970). ''The White Majority: between Poverty and Affluence'', in series, ''Vintage Book '' New York: New York: Random House. xii, 303 p. SBN 394-71666-3 * Katz, Michael B (2013). ''The Undeserving Poor: America's Enduring Confrontation with Poverty: Fully Updated and Revised.'' Oxford University Press; 2 edition. * Lyon-Callo, Vincent (2004). ''Inequality, Poverty, and Neoliberal Governance: Activist Ethnography in the Homeless Sheltering Industry.'' University of Toronto Press. * Mink, Gwendolyn, and Alice O'Connor, eds. ''Poverty in the United States: An Encyclopedia of History, Politics, and Policy'' (ABC-CLIO 2004). * Patterson, James T. (2000) ''America's Struggle against Poverty in the Twentieth Century'' (Harvard UP, 2000
online
* Prasad, Monica (2012). ''The Land of Too Much: American Abundance and the Paradox of Poverty.'' Harvard University Press. * * Sciandra, M., Sanbonmatsu, L., Duncan, G. J., Gennetian, L. A., Katz, L. F., Kessler, R. C., et al. (2013). Long-term effects of the Moving to Opportunity residential mobility experiment on crime and delinquency. Journal of Exp Criminol 9, 451–489. * Shipler, David K (2004). ''The Working Poor: Invisible in America, '' Knopf. * Wacquant, Loïc (2009). ''Prisons of Poverty.'' University of Minnesota Press. * ——— (2009).
Punishing the Poor: The Neoliberal Government of Social Insecurity
'. Duke University Press. ; Videos: * // Accompanied article: *
External links
*U.S. Census BureaPoverty Definition
*U.S. Census Burea
��''
Huffington Post
''HuffPost'' (formerly ''The Huffington Post'' until 2017 and sometimes abbreviated ''HuffPo'') is an American progressive news website, with localized and international editions. The site offers news, satire, blogs, and original content, and ...
'', July 28, 2013The American Way of Poverty: As Inequality Hits Record High, Sasha Abramsky on the Forgotten Poor
'' DemocracyNow!'' September 12, 2013.
America's Shameful Poverty Stats
Sasha Abramsky. '' The Nation,'' September 18, 2013.
How Much Money to End Poverty in America?
'' Truthdig.'' September 26, 2013.
Poverty in the United States: 2012
Congressional Research Service
It Is Expensive to Be Poor
'' The Atlantic.'' January 13, 2014.
Here's The Painful Truth About What It Means To Be 'Working Poor' In America
'' The Huffington Post,'' May 19, 2014.
10 Poverty Myths, Busted
'' Mother Jones,'' March/April 2014 issue.
FPL Calculator
A mobile app for calculating federal poverty level.
The Poor Get Prison
Institute for Policy Studies, 2015.
Measuring the impact of poverty in education, EducationDive, August 8, 2016
''
New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
''. January 5, 2018.Economic policies sacrifice poor Americans
Reuters. June 2, 2023. {{Social class