Popcorn Grown In Garden on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Popcorn (also called popped corn, popcorns or pop-corn) is a variety of
 Popcorn's accessibility increased rapidly in the 1890s with
Popcorn's accessibility increased rapidly in the 1890s with  During the Great Depression, popcorn was fairly inexpensive at 5–10 cents a bag and became popular. Thus, while other businesses failed, the popcorn business thrived and became a source of income for many struggling farmers, including the Redenbacher family, namesake of the famous popcorn brand. During
During the Great Depression, popcorn was fairly inexpensive at 5–10 cents a bag and became popular. Thus, while other businesses failed, the popcorn business thrived and became a source of income for many struggling farmers, including the Redenbacher family, namesake of the famous popcorn brand. During  In 1970,
In 1970,
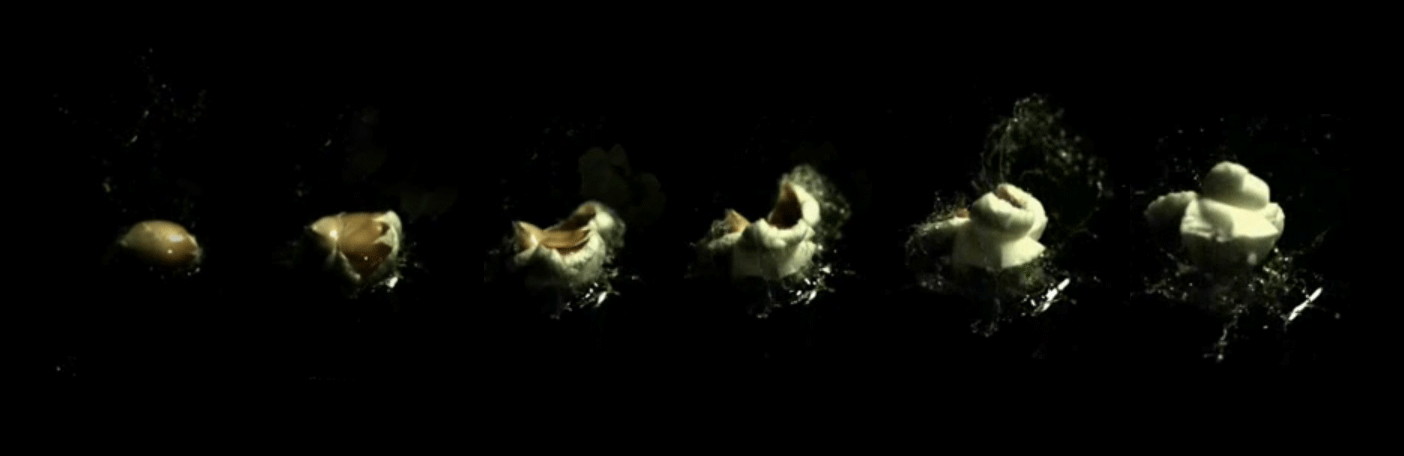 Each kernel of popcorn contains moisture and oil. Unlike most other grains, the outer hull of the popcorn kernel is strong and impervious to moisture, and the starch inside consists almost entirely of a hard type.Lusas & Rooney, p. 388.
As the oil and water in the kernel are heated, they turn into steam. Under these conditions, the starch inside the kernel gelatinizes and softens. The steam pressure increases until the breaking point of the hull is reached; a pressure of approximately and a temperature of . The hull ruptures, causing a sudden drop in pressure inside the kernel and a corresponding rapid expansion of the steam, which expands the starch and
Each kernel of popcorn contains moisture and oil. Unlike most other grains, the outer hull of the popcorn kernel is strong and impervious to moisture, and the starch inside consists almost entirely of a hard type.Lusas & Rooney, p. 388.
As the oil and water in the kernel are heated, they turn into steam. Under these conditions, the starch inside the kernel gelatinizes and softens. The steam pressure increases until the breaking point of the hull is reached; a pressure of approximately and a temperature of . The hull ruptures, causing a sudden drop in pressure inside the kernel and a corresponding rapid expansion of the steam, which expands the starch and
 Popcorn can be cooked with butter or oil. Although small quantities can be popped in a stove-top
Popcorn can be cooked with butter or oil. Although small quantities can be popped in a stove-top
 In the popcorn industry, a popped kernel of corn is known as a "flake". Two shapes of flakes are commercially important. "Butterfly" (or "snowflake") flakes are irregular in shape and have a number of protruding "wings". "Mushroom" flakes are largely ball-shaped, with few wings. Butterfly flakes are regarded as having better
In the popcorn industry, a popped kernel of corn is known as a "flake". Two shapes of flakes are commercially important. "Butterfly" (or "snowflake") flakes are irregular in shape and have a number of protruding "wings". "Mushroom" flakes are largely ball-shaped, with few wings. Butterfly flakes are regarded as having better


 Popcorn is a popular
Popcorn is a popular
corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn ( North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. ...
kernel
Kernel may refer to:
Computing
* Kernel (operating system), the central component of most operating systems
* Kernel (image processing), a matrix used for image convolution
* Compute kernel, in GPGPU programming
* Kernel method, in machine lea ...
which expands and puffs up when heated; the same names also refer to the foodstuff produced by the expansion.
A popcorn kernel's strong hull contains the seed's hard, starchy shell endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the embryo an ...
with 14–20% moisture, which turns to steam as the kernel is heated. Pressure from the steam continues to build until the hull ruptures, allowing the kernel to forcefully expand, to 20 to 50 times its original size, and then cool.
Some strains of corn ( taxonomized as ''Zea mays'') are cultivated specifically as popping corns. The ''Zea mays'' variety ''everta'', a special kind of flint corn
Flint corn (''Zea mays'' var. ''indurata''; also known as Indian corn or sometimes calico corn) is a variant of maize, the same species as common corn. Because each kernel has a hard outer layer to protect the soft endosperm, it is likened to bei ...
, is the most common of these.
Popcorn is one of six major types of corn, which includes dent corn
Dent corn, also known as grain corn, is a type of field corn with a high soft starch content. It received its name because of the small indentation, or "dent", at the crown of each kernel on a ripe ear of corn. Reid's Yellow Dent is a variety d ...
, flint corn
Flint corn (''Zea mays'' var. ''indurata''; also known as Indian corn or sometimes calico corn) is a variant of maize, the same species as common corn. Because each kernel has a hard outer layer to protect the soft endosperm, it is likened to bei ...
, pod corn
Pod corn or wild maize is a variety of maize. It is not a wild ancestor of maize but rather a mutant that forms leaves around each kernel.
Pod corn (''tunicata'' Sturt) is not grown commercially, but it is preserved in some localities.
Pod corn ...
, flour corn
Flour corn (''Zea mays'' var. ''amylacea'') is a variety of corn with a soft starchy endosperm and a thin pericarp. It is primarily used to make corn flour.
This type, frequently found in Aztec and Inca graves, is widely grown in the drier par ...
, and sweet corn
Sweet corn (''Zea mays'' convar. ''saccharata'' var. ''rugosa''), also called sugar corn and pole corn, is a variety of maize grown for human consumption with a high sugar content. Sweet corn is the result of a naturally occurring recessive m ...
.
History
Corn was domesticated about 10,000 years ago, in what is nowMexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
. Archaeologists discovered that people have known about popcorn for thousands of years. Fossil evidence from Peru suggests that corn was popped as early as 4,700 BC.
Through the 19th century, popping of the kernels was achieved by hand, on stove tops. Kernels were sold on the East Coast of the United States
The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the coastline along which the Eastern United States meets the North Atlantic Ocean. The eastern seaboard contains the ...
under names such as ''Pearls'' or ''Nonpareil''. The term ''popped corn'' first appeared in John Russell Bartlett
John Russell Bartlett (October 23, 1805 – May 28, 1886) was an American historian and linguist.
Biography
Bartlett was born in Providence, Rhode Island, on October 23, 1805. In 1819 he was a student at the Lowville Academy in Lowville, New ...
's 1848 ''Dictionary of Americanisms''. Popcorn is an ingredient in Cracker Jack
Cracker Jack is an American brand of snack food that consists of molasses-flavored, caramel-coated popcorn, and peanuts, well known for being packaged with a prize of trivial value inside. The Cracker Jack name and slogan, "The More You Eat The ...
and, in the early years of the product, it was popped by hand.
 Popcorn's accessibility increased rapidly in the 1890s with
Popcorn's accessibility increased rapidly in the 1890s with Charles Cretors
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was ...
' invention of the popcorn maker. Cretors, a Chicago candy store owner, had created a number of steam-powered machines for roasting nuts and applied the technology to the corn kernels.
By the turn of the century, Cretors had created and deployed street carts equipped with steam-powered popcorn makers. During the Great Depression, popcorn was fairly inexpensive at 5–10 cents a bag and became popular. Thus, while other businesses failed, the popcorn business thrived and became a source of income for many struggling farmers, including the Redenbacher family, namesake of the famous popcorn brand. During
During the Great Depression, popcorn was fairly inexpensive at 5–10 cents a bag and became popular. Thus, while other businesses failed, the popcorn business thrived and became a source of income for many struggling farmers, including the Redenbacher family, namesake of the famous popcorn brand. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, sugar rations
Rationing is the controlled distribution of scarce resources, goods, services, or an artificial restriction of demand. Rationing controls the size of the ration, which is one's allowed portion of the resources being distributed on a particular ...
diminished candy
Candy, also called sweets (British English) or lollies ( Australian English, New Zealand English), is a confection that features sugar as a principal ingredient. The category, called '' sugar confectionery'', encompasses any sweet confection, ...
production, and Americans compensated by eating three times as much popcorn as they had before. The snack was popular at theaters, much to the initial displeasure of many of the theater owners, who thought it distracted from the films. Their minds eventually changed, however, and in 1938 a Midwestern theater owner named Glen W. Dickinson Sr. installed popcorn machines in the lobbies of his Dickinson theaters. Popcorn was more profitable than theater tickets, and at the suggestion of his production consultant, R. Ray Aden, Dickinson purchased popcorn farms and was able to keep ticket prices down. The venture was a success, and popcorn soon spread. The rise of television in the 1940s brought lower popcorn consumption as theater attendance fell. The Popcorn Institute (a trade association of popcorn processors) promoted popcorn consumption at home, bringing it back to previous levels.
 In 1970,
In 1970, Orville Redenbacher
Orville Clarence Redenbacher (July 16, 1907 – September 19, 1995) was an American food scientist and businessman most often associated with the brand of popcorn that bears his name which is now owned by ConAgra. ''The New York Times'' descri ...
's namesake brand of popcorn was launched. In 1981, General Mills
General Mills, Inc., is an American multinational manufacturer and marketer of branded processed consumer foods sold through retail stores. Founded on the banks of the Mississippi River at Saint Anthony Falls in Minneapolis, the company ori ...
received the first patent for a microwave oven
A microwave oven (commonly referred to as a microwave) is an electric oven that heats and cooks food by exposing it to electromagnetic radiation in the microwave frequency range. This induces polar molecules in the food to rotate and produce ...
popcorn bag; popcorn consumption saw a sharp increase then, by tens of thousands of pounds.
At least six localities (all in the Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
) claim to be the "Popcorn Capital of the World;": Ridgway, Illinois
Ridgway is a village in Gallatin County, Illinois, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 851. As of 2018, Rebecca Mitchell was the town mayor.
History
Ridgway was established in 1866 as a construction camp along what would b ...
; Valparaiso, Indiana
Valparaiso ( ), colloquially Valpo, is a city and the county seat of Porter County, Indiana, United States. The population was 34,151 at the 2020 census.
History
The site of present-day Valparaiso was included in the purchase of land from the ...
; Van Buren, Indiana
Van Buren is a town in Van Buren Township, Grant County, Indiana, United States. The population was 864 at the 2010 census.
History
Joseph Boxell platted Van Buren Township in 1837. Martin Van Buren was the United States president at the time. I ...
; Schaller, Iowa
Schaller is a city in Sac County, Iowa, United States. The population was 729 at the time of the 2020 census.
History
The city of Schaller, named after Phillip Schaller, was incorporated in 1882. The city had been founded in August 1879 as ...
; Marion, Ohio
Marion is a city in and the county seat of Marion County, Ohio, United States. The municipality is located in north-central Ohio, approximately north of Columbus.
The population was 35,999 at the 2020 census, slightly down from 36,837 at the 2 ...
; and North Loup, Nebraska
North Loup is a village in North Loup Township, Valley County, Nebraska, United States. The population was 297 at the 2010 census.
History
In 1871, a party of Seventh Day Baptists from Wisconsin explored Valley County for settlement sites. In ...
. According to the USDA
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of com ...
, specific corn for popcorn is grown, mostly in Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the so ...
and Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th ...
; increasingly in Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
. As the result of an elementary school
A primary school (in Ireland, the United Kingdom, Australia, Trinidad and Tobago, Jamaica, and South Africa), junior school (in Australia), elementary school or grade school (in North America and the Philippines) is a school for primary ed ...
project, popcorn became the official state snack food of Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Roc ...
.
Popping mechanism
 Each kernel of popcorn contains moisture and oil. Unlike most other grains, the outer hull of the popcorn kernel is strong and impervious to moisture, and the starch inside consists almost entirely of a hard type.Lusas & Rooney, p. 388.
As the oil and water in the kernel are heated, they turn into steam. Under these conditions, the starch inside the kernel gelatinizes and softens. The steam pressure increases until the breaking point of the hull is reached; a pressure of approximately and a temperature of . The hull ruptures, causing a sudden drop in pressure inside the kernel and a corresponding rapid expansion of the steam, which expands the starch and
Each kernel of popcorn contains moisture and oil. Unlike most other grains, the outer hull of the popcorn kernel is strong and impervious to moisture, and the starch inside consists almost entirely of a hard type.Lusas & Rooney, p. 388.
As the oil and water in the kernel are heated, they turn into steam. Under these conditions, the starch inside the kernel gelatinizes and softens. The steam pressure increases until the breaking point of the hull is reached; a pressure of approximately and a temperature of . The hull ruptures, causing a sudden drop in pressure inside the kernel and a corresponding rapid expansion of the steam, which expands the starch and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s of the endosperm into airy foam
Foams are materials formed by trapping pockets of gas in a liquid or solid.
A bath sponge and the head on a glass of beer are examples of foams. In most foams, the volume of gas is large, with thin films of liquid or solid separating the ...
. As the foam rapidly cools, the starch and protein polymer
A polymer (; Greek ''poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and ...
s set into the familiar crispy puff. Special varieties are grown to improve popping yield. Though the kernels of some other types will pop, the cultivated strain for popcorn is ''Zea mays everta,'' which is a variety of flint corn
Flint corn (''Zea mays'' var. ''indurata''; also known as Indian corn or sometimes calico corn) is a variant of maize, the same species as common corn. Because each kernel has a hard outer layer to protect the soft endosperm, it is likened to bei ...
.
Cooking methods
 Popcorn can be cooked with butter or oil. Although small quantities can be popped in a stove-top
Popcorn can be cooked with butter or oil. Although small quantities can be popped in a stove-top kettle
A kettle, sometimes called a tea kettle or teakettle, is a type of pot specialized for boiling water, commonly with a ''lid'', ''spout'', and ''handle'', or a small electric kitchen appliance of similar shape that functions in a self-contained ...
or pot in a home kitchen, commercial sale employs specially designed popcorn machines, which were invented in Chicago, Illinois
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
, by Charles Cretors
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was ...
in 1885. Cretors introduced his invention at the Columbian Exposition
The World's Columbian Exposition (also known as the Chicago World's Fair) was a world's fair held in Chicago in 1893 to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1492. The centerpiece of the Fair, hel ...
in 1893. At that fair, F. W. Rueckheim introduced a molasses
Molasses () is a viscous substance resulting from refining sugarcane or sugar beets into sugar. Molasses varies in the amount of sugar, method of extraction and age of the plant. Sugarcane molasses is primarily used to sweeten and flavour foods ...
-flavored "Candied Popcorn", the first caramel corn
Caramel corn or caramel popcorn (toffee popcorn in the UK) is a confection made of popcorn coated with a sugar or molasses based caramel candy shell that is normally less than 1mm thick. Typically a sugar solution or syrup is made and heated unti ...
; his brother, Louis Ruekheim, slightly altered the recipe and introduced it as Cracker Jack
Cracker Jack is an American brand of snack food that consists of molasses-flavored, caramel-coated popcorn, and peanuts, well known for being packaged with a prize of trivial value inside. The Cracker Jack name and slogan, "The More You Eat The ...
in 1896.
Cretors's invention was the first patented steam-driven machine that popped corn in oil. Previously, vendors popped corn by holding a wire basket over an open flame. At best, the result was hot, dry, and unevenly cooked. Cretors's machine popped corn in a mixture of one-third clarified butter
Clarified butter is milk fat rendered from butter to separate the milk solids and water from the butterfat. Typically, it is produced by melting butter and allowing the components to separate by density. The water evaporates, some solids (i ...
, two-thirds lard
Lard is a semi-solid white fat product obtained by rendering the fatty tissue of a pig.Lard
entry in the ...
, and entry in the ...
salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quanti ...
. This mixture can withstand the temperature needed to pop corn and produces little smoke. A fire under a boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, centr ...
created steam that drove a small engine to drive gears, shaft, and the agitator that stirred the corn, and also powered a small puppet, "The Toasty Roasty Man", an attention-getting amusement to attract business. A wire connected to the top of the cooking pan allowed the operator to disengage the drive mechanism, lift the cover, and dump popped corn into the storage bin beneath. Exhaust from the steam engine was piped to a pan below the corn storage bin and kept freshly popped corn warm. Excess steam was also used to operate a small, shrill whistle to attract attention.
A different method of popcorn-making involves the "popcorn hammer
Puffed grains are grains that have been expanded ("puffed") through processing. They have been made for centuries with the simplest methods like popping popcorn. Modern puffed grains are often created using high temperature, pressure, or extrusi ...
", a large cast-iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuriti ...
canister that is sealed with a heavy lid and slowly turned over a fire in rotisserie
Rotisserie, also known as spit-roasting, is a style of roasting where meat is skewered on a spit – a long solid rod used to hold food while it is being cooked over a fire in a fireplace or over a campfire, or roasted in an oven. This metho ...
fashion.
Expansion and yield
Popping results are sensitive to the rate at which the kernels are heated. If heated too quickly, the steam in the outer layers of the kernel can reach high pressures and rupture the hull before the starch in the center of the kernel can fully gelatinize, leading to partially popped kernels with hard centers. Heating too slowly leads to entirely unpopped kernels: the tip of the kernel, where it attached to the cob, is not entirely moisture-proof, and when heated slowly, the steam can leak out of the tip fast enough to keep the pressure from rising sufficiently to break the hull and cause the pop.Lusas & Rooney, pp. 388–389. Producers and sellers of popcorn consider two major factors in evaluating the quality of popcorn: what percentage of the kernels will pop, and how much each popped kernel expands. Expansion is an important factor to both the consumer and vendor. For the consumer, larger pieces of popcorn tend to be more tender and are associated with higher quality. For the grower, distributor and vendor, expansion is closely correlated with profit: vendors such as theaters buy popcorn by weight and sell it by volume. For these reasons, higher-expansion popcorn fetches a higher profit per unit weight. Popcorn will pop when freshly harvested, but not well; its high moisture content leads to poor expansion and chewy pieces of popcorn. Kernels with a high moisture content are also susceptible to mold when stored. For these reasons, popcorn growers and distributors dry the kernels until they reach the moisture level at which they expand the most. This differs by variety and conditions, but is generally in the range of 14–15% moisture by weight. If the kernels are over-dried, the expansion rate will suffer and the percentage of kernels that pop will decline. Old popcorn tends to dry out, lowering the yield. When the popcorn has finished popping, sometimes unpopped kernels remain. Known in the popcorn industry as "old maids", these kernels fail to pop because they do not have enough moisture to create enough steam for an explosion. Re-hydrating prior to popping usually results in eliminating the unpopped kernels. Popcorn varieties are broadly categorized by the shape of the kernels, the color of the kernels, or the shape of the popped corn. While the kernels may come in a variety of colors, the popped corn is always off-yellow or white as it is only the hull (or pericarp) that is colored. "Rice" type popcorn have a long kernel pointed at both ends; "pearl" type kernels are rounded at the top. Commercial popcorn production has moved mostly to pearl types.Hallauer, p. 213. Historically, pearl popcorn were usually yellow and rice popcorn usually white. Today both shapes are available in both colors, as well as others including black, red,mauve
Mauve (, ; , ) is a pale purple color named after the mallow flower (French: ''mauve''). The first use of the word ''mauve'' as a color was in 1796–98 according to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', but its use seems to have been rare befo ...
, purple, and variegated
Variegation is the appearance of differently coloured zones in the leaves and sometimes the stems and fruit of plants. Species with variegated individuals are sometimes found in the understory of tropical rainforests, and this habitat is the s ...
. Mauve and purple popcorn usually have smaller and nutty kernels. Commercial production is dominated by white and yellow.Hallauer, p. 214.
Terminology
 In the popcorn industry, a popped kernel of corn is known as a "flake". Two shapes of flakes are commercially important. "Butterfly" (or "snowflake") flakes are irregular in shape and have a number of protruding "wings". "Mushroom" flakes are largely ball-shaped, with few wings. Butterfly flakes are regarded as having better
In the popcorn industry, a popped kernel of corn is known as a "flake". Two shapes of flakes are commercially important. "Butterfly" (or "snowflake") flakes are irregular in shape and have a number of protruding "wings". "Mushroom" flakes are largely ball-shaped, with few wings. Butterfly flakes are regarded as having better mouthfeel
Mouthfeel refers to the physical sensations in the mouth caused by food or drink, making it distinct from taste. It is a fundamental sensory attribute which, along with taste and smell, determines the overall flavor of a food item. Mouthfeel i ...
, with greater tenderness and less noticeable hulls. Mushroom flakes are less fragile than butterfly flakes and are therefore often used for packaged popcorn or confectionery, such as caramel corn
Caramel corn or caramel popcorn (toffee popcorn in the UK) is a confection made of popcorn coated with a sugar or molasses based caramel candy shell that is normally less than 1mm thick. Typically a sugar solution or syrup is made and heated unti ...
. The kernels from a single cob of popcorn may form both butterfly and mushroom flakes; hybrids that produce 100% butterfly flakes or 100% mushroom flakes exist, the latter developed only as recently as 1998. Growing conditions and popping environment can also affect the butterfly-to-mushroom ratio.
When referring to multiple pieces of popcorn collectively, it is acceptable to use the term "popcorn". When referring to a singular piece of popcorn, the accepted term is "kernel".
Consumption


 Popcorn is a popular
Popcorn is a popular snack food
A snack is a small portion of food generally eaten between meals. Snacks come in a variety of forms including packaged snack foods and other processed foods, as well as items made from fresh ingredients at home.
Traditionally, snacks are ...
at sporting events and in movie theater
A movie theater (American English), cinema (British English), or cinema hall (Indian English), also known as a movie house, picture house, the movies, the pictures, picture theater, the silver screen, the big screen, or simply theater is a ...
s, where it has been served since the 1930s. Cinemas have come under fire due to their high markup
Markup or mark-up can refer to:
* Markup language, a standardized set of notations used to annotate a plain-text document's content to give information regarding the structure of the text or instructions for how it is to be displayed
** Lightweigh ...
on popcorn; Stuart Hanson, a film historian at De Montfort University in Leicester, once said, "One of the great jokes in the industry is that popcorn is second only to cocaine or heroin in terms of profit."
Traditions differ as to whether popcorn is consumed as a hearty snack food with salt (predominating in the United States) or as a sweet snack food with caramelized sugar (predominating in Germany).
Popcorn smell has an unusually attractive quality for human beings. This is largely because it contains high levels of the chemicals 6-acetyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine
6-Acetyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine is an aroma compound and flavor that gives baked goods such as white bread, popcorn, and tortillas their typical smell, together with its structural homolog 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline.
6-Acetyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropy ...
and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline
2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline (2AP) is an aroma compound and flavor that gives freshly baked bread, jasmine rice and basmati rice, the spice ''pandan'' ('' Pandanus amaryllifolius''), and ''bread flowers'' ('' Vallaris'' ''glabra'') their customary sm ...
, very powerful aroma compound
An aroma compound, also known as an odorant, aroma, fragrance or flavoring, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor. For an individual chemical or class of chemical compounds to impart a smell or fragrance, it must be sufficiently vo ...
s that are also used by food and other industries either to make products that smell like popcorn, bread, or other foods containing the compound in nature, or for other purposes.
Popcorn as a breakfast cereal
Cereal, formally termed breakfast cereal (and further categorized as cold cereal or warm cereal), is a traditional breakfast food made from processed cereal grains. It is traditionally eaten as part of breakfast, or a snack food, primarily in ...
was consumed by Americans in the 1800s and generally consisted of popcorn with milk and a sweetener.
Popcorn balls (popped kernels stuck together with a sugary "glue") were hugely popular around the turn of the 20th century, but their popularity has since waned. Popcorn balls are still served in some places as a traditional Halloween
Halloween or Hallowe'en (less commonly known as Allhalloween, All Hallows' Eve, or All Saints' Eve) is a celebration geography of Halloween, observed in many countries on 31 October, the eve of the Western Christian feast of All Saints' Day. ...
treat. Cracker Jack
Cracker Jack is an American brand of snack food that consists of molasses-flavored, caramel-coated popcorn, and peanuts, well known for being packaged with a prize of trivial value inside. The Cracker Jack name and slogan, "The More You Eat The ...
is a popular, commercially produced candy that consists of peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible Seed, seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small ...
s mixed in with caramel
Caramel ( or ) is an orange-brown confectionery product made by heating a range of sugars. It can be used as a flavoring in puddings and desserts, as a filling in bonbons, or as a topping for ice cream and custard.
The process of caramelizat ...
-covered popcorn. Kettle corn
Kettle corn is a sweet variety of popcorn that is typically mixed or seasoned with a light-colored refined sugar, salt, and oil. It was traditionally made in cast iron kettles, hence the name, but in modern times other types of pots and pans a ...
is a variation of normal popcorn, cooked with white sugar and salt, traditionally in a large copper kettle. Once reserved for specialty shops and county fairs, kettle corn has recently become popular, especially in the microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different fre ...
popcorn market. The popcorn maker
A popcorn maker (also called a popcorn popper) is a machine used to pop popcorn. Since ancient times, popcorn has been a popular snack food, produced through the explosive expansion of kernels of heated corn (maize). Commercial large-scale popc ...
is a relatively new home appliance
A home appliance, also referred to as a domestic appliance, an electric appliance or a household appliance, is a machine which assists in household functions such as cooking, cleaning and food preservation.
Appliances are divided into three t ...
, and its popularity is increasing because it offers the opportunity to add flavors of the consumer's own choice and to choose healthy-eating popcorn styles.
Popped sorghum
''Sorghum'' () is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family ( Poaceae). Some of these species are grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species is grown for grain, while many ot ...
is popular as a snack in India. The popped sorghum is similar to popcorn, but the puffs are smaller. Recipes for popping sorghum by microwave, in a pot, etc, are readily available online.
Nutritional value
Air-popped popcorn (no salt or other additives) is 4% water, 78%carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ...
s (including 15% dietary fiber
Dietary fiber (in British English fibre) or roughage is the portion of plant-derived food that cannot be completely broken down by human digestive enzymes. Dietary fibers are diverse in chemical composition, and can be grouped generally by th ...
), 12% protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
, and 4% fat
In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specifically to triglycerides (triple es ...
(table). In a 100 gram reference amount, popcorn provides 382 calorie
The calorie is a unit of energy. For historical reasons, two main definitions of "calorie" are in wide use. The large calorie, food calorie, or kilogram calorie was originally defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of ...
s and is a rich source (20% or more of the Daily Value
The Reference Daily Intake (RDI) used in nutrition labeling on food and dietary supplement products in the U.S. and Canada is the daily intake level of a nutrient that is considered to be sufficient to meet the requirements of 97–98% of health ...
, DV) of riboflavin
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, is a vitamin found in food and sold as a dietary supplement. It is essential to the formation of two major coenzymes, flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide. These coenzymes are involved in e ...
(25% DV) and several dietary minerals
In the context of nutrition, a mineral is a chemical element required as an essential nutrient by organisms to perform functions necessary for life. However, the four major structural elements in the human body by weight (oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, ...
, particularly manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy u ...
, phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ea ...
, and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic t ...
(36-45% DV). B vitamins
B vitamins are a class of water-soluble vitamins that play important roles in cell metabolism and synthesis of red blood cells. Though these vitamins share similar names (B1, B2, B3, etc.), they are chemically distinct compounds that often coexis ...
and other minerals are in appreciable amounts (table).
Saturated fat
Movie theaters commonly usecoconut oil
frameless , right , alt = A cracked coconut and a bottle of coconut oil
Coconut oil (or coconut butter) is an edible oil derived from the wick, meat, and milk of the coconut palm fruit. Coconut oil is a white solid fat; in warmer climates duri ...
to pop the corn, and then top it with butter
Butter is a dairy product made from the fat and protein components of churned cream. It is a semi-solid emulsion at room temperature, consisting of approximately 80% butterfat. It is used at room temperature as a spread (food), spread, melted a ...
or margarine
Margarine (, also , ) is a spread used for flavoring, baking, and cooking. It is most often used as a substitute for butter. Although originally made from animal fats, most margarine consumed today is made from vegetable oil. The spread was orig ...
. Movie theater popcorn contains large amounts of saturated fats and sodium due to its method of preparation.
Phytochemicals
Sorghum
''Sorghum'' () is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family ( Poaceae). Some of these species are grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species is grown for grain, while many ot ...
grains can be popped to form popcorn. All sorghums contain phenolic acid
Phenolic acids or phenolcarboxylic acids are types of aromatic acid compounds. Included in that class are substances containing a phenolic ring and an organic carboxylic acid function (C6-C1 skeleton). Two important naturally occurring types of ph ...
s, and most contain flavonoid
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.
Chemically, flavonoids ...
s. Sorghum grains are one of the highest food sources of the flavonoid, proanthocyanidin
Proanthocyanidins are a class of polyphenols found in many plants, such as cranberry, blueberry, and grape seeds. Chemically, they are oligomeric flavonoids. Many are oligomers of catechin and epicatechin and their gallic acid esters. More compl ...
.
Health risks
Popcorn is included on the list of foods that theAmerican Academy of Pediatrics
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) is an American professional association of pediatricians, headquartered in Itasca, Illinois. It maintains its Department of Federal Affairs office in Washington, D.C.
Background
The Academy was found ...
recommends not serving to children under four, because of the risk of choking
Choking, also known as foreign body airway obstruction (FBAO), is a phenomenon that occurs when breathing is impeded by a blockage inside of the respiratory tract. An obstruction that prevents oxygen from entering the lungs results in oxygen depr ...
.
Microwaveable popcorn represents a special case, since it is designed to be cooked along with its various flavoring agents. One of these formerly common artificial-butter flavorants, diacetyl
Diacetyl (IUPAC systematic name: butanedione or butane-2,3-dione) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH3CO)2. It is a yellow liquid with an intensely buttery flavor. It is a vicinal diketone (two C=O groups, side-by-side). Diace ...
, has been implicated in causing respiratory illnesses in microwave popcorn factory workers, also known as "popcorn lung
Bronchiolitis obliterans (BO), also known as obliterative bronchiolitis, constrictive bronchiolitis and popcorn lung, is a disease that results in obstruction of the smallest airways of the lungs (bronchioles) due to inflammation. Symptoms include ...
". Major manufacturers in the United States have stopped using this chemical, including Orville Redenbacher's
Orville Redenbacher's is an American brand of popcorn made originally by Chester Inc. which was owned by Charles F. Bowman and Orville Redenbacher (who starred in nearly all the commercials until his death in 1995). The product was launched to t ...
, Act II Act II or Act Two or Act 2 may refer to:
Brands
* Act II (popcorn), a brand of popcorn in North America
Music
* ''Act Two'' (Collabro album), 2014
* ''Act Two'' (The Seldom Scene album), 1973
* ''Act II'' (Tokio album), 2005
* '' Act II: The F ...
, Pop Secret
Pop Secret is an American brand of popcorn, owned and marketed by Snyder's-Lance – a subsidiary of Campbell Soup Company since 2017. Snyder's-Lance had acquired the Pop Secret brand from Diamond Foods in early 2016.
''Pop Secret'' popcorns w ...
and Jolly Time
The American Pop Corn Company is a family owned popcorn producer. Founded in 1914, it is the oldest popcorn company in the United States. Its only brand, Jolly Time, is sold globally and in every state in America. It employs 185 people, and its ...
.
Other uses
Popcorn, threaded onto a string, is used as a wall or Christmas tree decoration in some parts of North America, as well as on theBalkan peninsula
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whol ...
.
Some shipping companies have experimented with using popcorn as a biodegradable
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradati ...
replacement for expanded polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
packing material. However, popcorn has numerous undesirable properties as a packing material, including attractiveness to pests
PESTS was an anonymous American activist group formed in 1986 to critique racism, tokenism, and exclusion in the art world. PESTS produced newsletters, posters, and other print material highlighting examples of discrimination in gallery represent ...
, flammability
A combustible material is something that can burn (i.e., ''combust'') in air. A combustible material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort and a flammable mat ...
, and a higher cost and greater density than expanded polystyrene. A more processed form of expanded corn foam has been developed to overcome some of these limitations, forming starch-based foam peanuts.
See also
*Butter salt
Butter salt is a seasoning developed in the late twentieth century for the purpose of combining the flavours found in salt and butter. It is a fine, golden powder, originally salt, enriched with butter flavouring. It is often used as a seasoning ...
* List of dried foods
This is a list of dried foods. Food drying is a method of food preservation that works by removing water from the food, which inhibits the growth of bacteria and has been practiced worldwide since ancient times to preserve food. Where or when d ...
* List of maize dishes
This is a list of maize dishes, in which maize (corn) is used as a primary ingredient. Additionally, some foods and beverages that are prepared with maize are listed.
Ingredients
Corn can be processed into an intermediate form to be cooked furt ...
* List of popcorn brands
This is a list of notable popcorn brands. Popcorn, also known as popping corn, is a type of corn (maize, ''Zea mays var. everta'') that expands from the kernel and puffs up when heated. Popcorn is able to pop because its kernels have a hard moist ...
* Popcorn maker
A popcorn maker (also called a popcorn popper) is a machine used to pop popcorn. Since ancient times, popcorn has been a popular snack food, produced through the explosive expansion of kernels of heated corn (maize). Commercial large-scale popc ...
* Popcorn seasoning
Popcorn seasoning is any ingredient used to add flavor to popcorn. In the United States, popcorn seasoning is mass-produced by several companies for commercial and consumer use. Popcorn seasonings may be used to enhance the flavor of popcorn, and ...
* Puffed grain
Puffed grains are grains that have been expanded ("puffed") through processing. They have been made for centuries with the simplest methods like popping popcorn. Modern puffed grains are often created using high temperature, pressure, or extrusi ...
* Wyandot Popcorn Museum
Wyandot may refer to:
Native American ethnography
* Wyandot people, also known as the Huron
* Wyandot language
* Wyandot religion
Places
* Wyandot, Ohio, an unincorporated community
* Wyandot County, Ohio
* Camp Wyandot, a Camp Fire Boys and ...
References
Further reading
* * * {{Authority control Cuisine of the Midwestern United States Maize products Crops originating from the Americas Native American cuisine Plants used in Native American cuisine Snack foods Dried foods Symbols of Illinois