Pleuromutilin Antibiotics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pleuromutilin and its derivatives are antibacterial drugs that inhibit
 Additionally, three
Additionally, three
protein synthesis
Protein biosynthesis (or protein synthesis) is a core biological process, occurring inside Cell (biology), cells, homeostasis, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via Proteolysis, degradation or Protein targeting, export) through the product ...
in bacteria by binding to the peptidyl transferase component of the 50S
The 50s decade ran from January 1, 50, to December 31, 59. It was the sixth decade in the Anno Domini/Common Era, if the nine-year period from 1 AD to 9 AD is considered as a "decade".
Significant people
* Claudius, Roman Emperor (AD 41â ...
subunit of ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to ...
s.
This class of antibiotics includes the licensed drugs lefamulin
Lefamulin, sold under the brand name Xenleta, is an antibiotic medication used it to treat adults with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.
Relatively common side effects include diarrhea, ...
(for systemic use in humans), retapamulin
Retapamulin is a topical antibiotic developed by GlaxoSmithKline. It is the first drug in the new class of pleuromutilin antibiotics to be approved for human use. It is marketed as an ointment under the brand names Altabax and Altargo.
Retapamu ...
(approved for topical use in humans), valnemulin and tiamulin (approved for use in animals) and the investigational drug azamulin
Azamulin is a pleuromutilin antibiotic. , it is not marketed in the US or Europe.
In pharmacological studies, the substance is used as an inhibitor of the liver enzymes CYP3A4 and CYP3A5
Cytochrome P450 3A5 is a protein that in humans is enc ...
.
History
Pleuromutilin was discovered as an antibiotic in 1951. It is derived from the fungi '' Omphalina mutila'' (formerly ''Pleurotus mutilus'') and '' Clitopilus passeckerianus'' (formerly ''Pleurotus passeckerianus''), and has also been found in ''Drosophila subatrata
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species ...
'', ''Clitopilus scyphoides
''Clitopilus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Entolomataceae. The genus has a widespread distribution, especially in northern temperate areas. Although a 2008 estimate suggested about 30 species in the genus, a more recent publication (2009) u ...
'', and some other '' Clitopilus'' species.
Total synthesis
The total synthesis of pleuromutilin has been reported.Biosynthesis
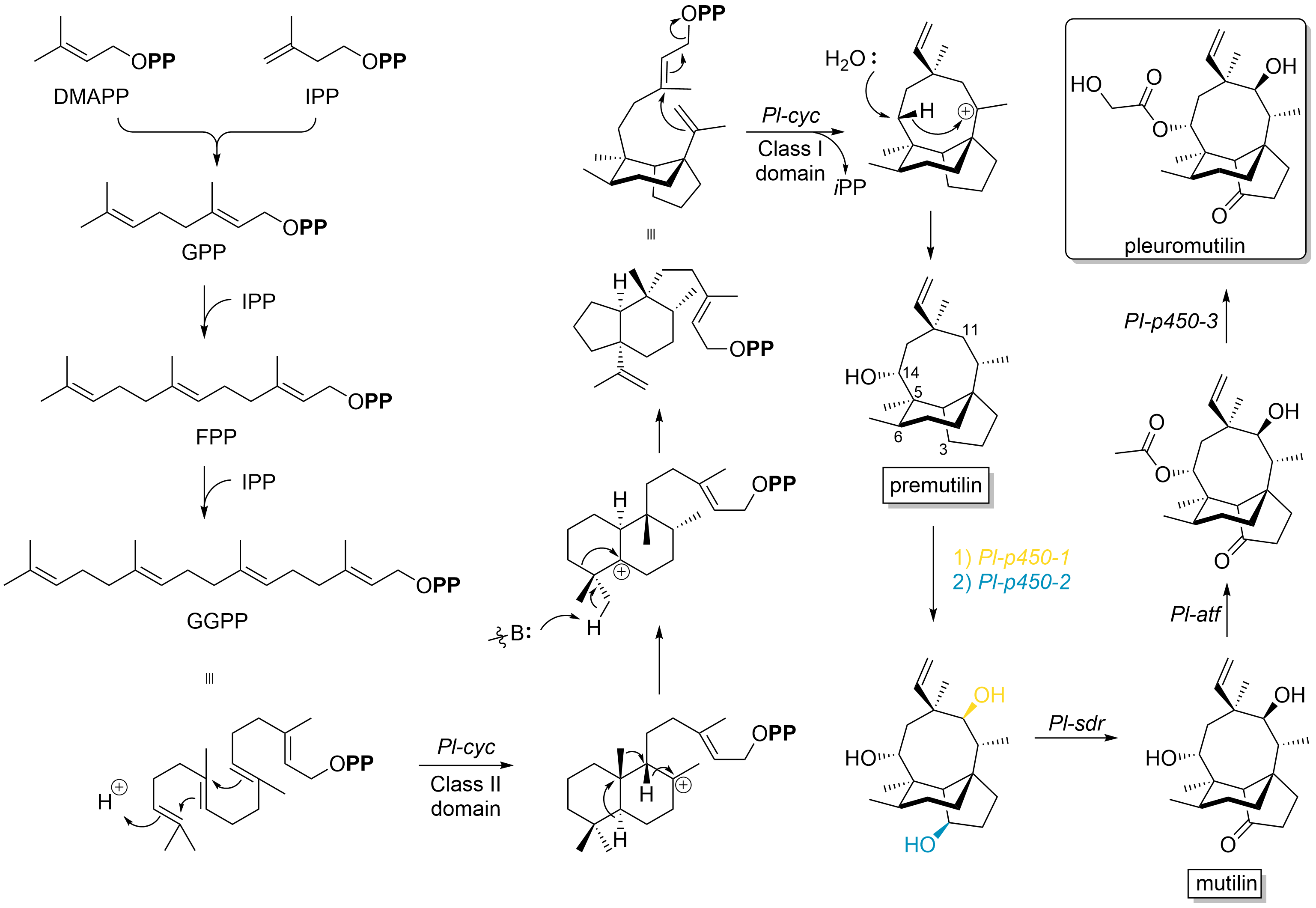
Pleuromutilin belongs to the class of secondary metabolites known as terpenes, which are produced in fungi through the mevalonate pathway (MEP pathway). Its synthetic bottleneck lays on the production of the precursorGGPP
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of diterpenes and di terpenoids. It is also the precursor to carotenoids, gibberellins, tocopherols, and chlorophylls.
It is also a precursor to geranylgeranylated proteins, ...
and the following formation of the tricyclic structure, which is catalyzed by ''Pl-cyc'', a bifunctional diterpene synthase (DTS). This Cyclase shows a new class II DTS activity, catalyzes a ring contraction and the formation of a 5-6-bicyclic ring structure. Specifically, DTS shows two catalytic distinguishable domains: On the one hand it has at the N-terminal region a class II DTS domain, which catalyzes a cascade cyclization, resulting in a decalin core. Subsequently, variable 1,2-proton and methyl shifts occur to translocate the carbocation
A carbocation is an ion with a positively charged carbon atom. Among the simplest examples are the methenium , methanium and vinyl cations. Occasionally, carbocations that bear more than one positively charged carbon atom are also encountere ...
towards one of the two interconnecting C-atoms and this intermediate induces a base-catalyzed ring contraction. Therefore, class II DTS promotes in general a ring contraction during the cyclisation of GGPP
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of diterpenes and di terpenoids. It is also the precursor to carotenoids, gibberellins, tocopherols, and chlorophylls.
It is also a precursor to geranylgeranylated proteins, ...
. On the other hand, at the C-terminal end it has a class I DTS domain, which catalyzes a conjugated dephosphorylation, generating the 8-membered cyclic core, followed by a 1,5-proton shift and a stereospecific hydroxylation to obtain premutilin.
 Additionally, three
Additionally, three cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are ...
s (''Pl-p450-1, Pl-p450-2 and Pl-p450-3'') are involved in the final steps of the pleuromutilin biosynthetic pathway. The P450-1 and P450-2 are essential for hydroxylation of two ring structures regarding the premutilin skeleton, oxidating specifically at position C-11 and C-3, respectively. The short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase
The short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases family (SDR) is a very large family of enzymes, most of which are known to be NAD- or NADP-dependent oxidoreductases. As the first member of this family to be characterised was Drosophila alcohol dehydro ...
enzyme (''Pl-sdr'') has a regiospecific activity and converts the 3-hydroxy group to a ketone, forming the intermediate mutilin
Retapamulin is a topical antibiotic developed by GlaxoSmithKline. It is the first drug in the new class of pleuromutilin antibiotics to be approved for human use. It is marketed as an ointment under the brand names Altabax and Altargo.
Retapam ...
. Acetyltransferase (''Pl-at''f) catalyzes the transfer of acetyl group to 14-OH of mutilin. Finally, ''Pl-p450-3'' hydroxylates the α-methyl group of the acetyl side chain generating pleuromutilin.
References
Further reading
* * {{Protein synthesis inhibitor antibiotics Pleuromutilin antibiotics Cyclopentanes