Plesiosaurus2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Plesiosaurus'' (Greek: ' ('), near to + ' ('), lizard) is a genus of extinct, large marine sauropterygian
 The first complete skeleton of ''Plesiosaurus'' was discovered by early paleontologist and fossil hunter Mary Anning in Sinemurian ( Early Jurassic)-age rocks of the lower Lias Group in December 1823.Storrs 1997 pp. 146 Additional fossils of ''Plesiosaurus'' were found in rocks of the Lias Group of Dorset for many years, "until the cessation of quarrying activities in the Lias Group, early in this
The first complete skeleton of ''Plesiosaurus'' was discovered by early paleontologist and fossil hunter Mary Anning in Sinemurian ( Early Jurassic)-age rocks of the lower Lias Group in December 1823.Storrs 1997 pp. 146 Additional fossils of ''Plesiosaurus'' were found in rocks of the Lias Group of Dorset for many years, "until the cessation of quarrying activities in the Lias Group, early in this
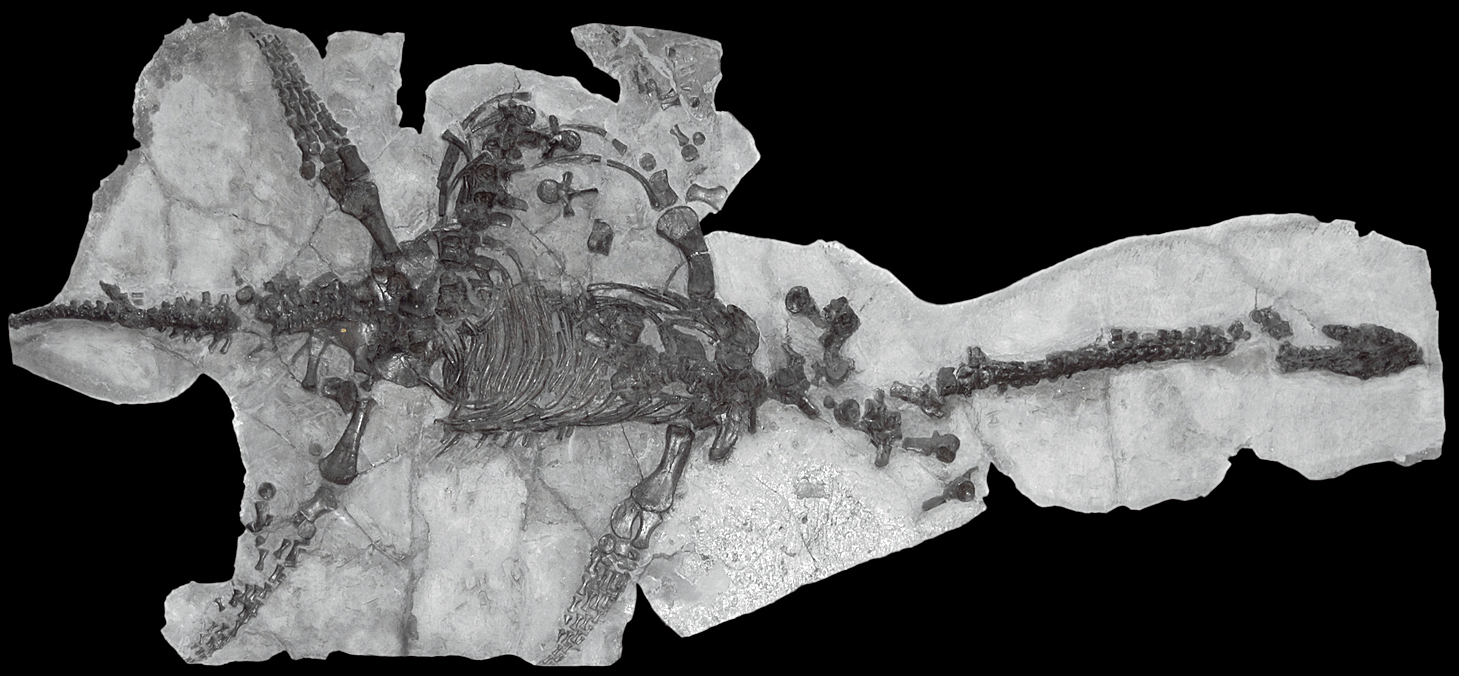
 Compared to other plesiosaur genera, ''Plesiosaurus'' has a small head. The skull is much narrower than long,Storrs 1997 pp. 166 reaching its greatest width just behind the eyes (the postorbital bar).Storrs 1997 pp. 165 The
Compared to other plesiosaur genera, ''Plesiosaurus'' has a small head. The skull is much narrower than long,Storrs 1997 pp. 166 reaching its greatest width just behind the eyes (the postorbital bar).Storrs 1997 pp. 165 The  The two rami of the lower jaw make a "V" shape with an angle of about 45°. The specialized region where they meet, the symphysis, is robust. The two rami are fused at the symphysis, making a pointed, shallow scoop-like shape.Storrs 1997 pp. 169.
The teeth of ''Plesiosaurus'' are "simple, needle-like cones" that are "slightly curved and circular in transverse section". They are sharply pointed with fine striations running from tip to base, and point forward (procumbent). This procumbency becomes more pronounced near the leading end of the skull, where they may be only 10–15° above horizontal. There are 20 to 25 teeth per upper jaw tooth row, and 24 per low jaw tooth row. Up to four teeth of a lower jaw's tooth row are found in the symphyseal region.
The two rami of the lower jaw make a "V" shape with an angle of about 45°. The specialized region where they meet, the symphysis, is robust. The two rami are fused at the symphysis, making a pointed, shallow scoop-like shape.Storrs 1997 pp. 169.
The teeth of ''Plesiosaurus'' are "simple, needle-like cones" that are "slightly curved and circular in transverse section". They are sharply pointed with fine striations running from tip to base, and point forward (procumbent). This procumbency becomes more pronounced near the leading end of the skull, where they may be only 10–15° above horizontal. There are 20 to 25 teeth per upper jaw tooth row, and 24 per low jaw tooth row. Up to four teeth of a lower jaw's tooth row are found in the symphyseal region.
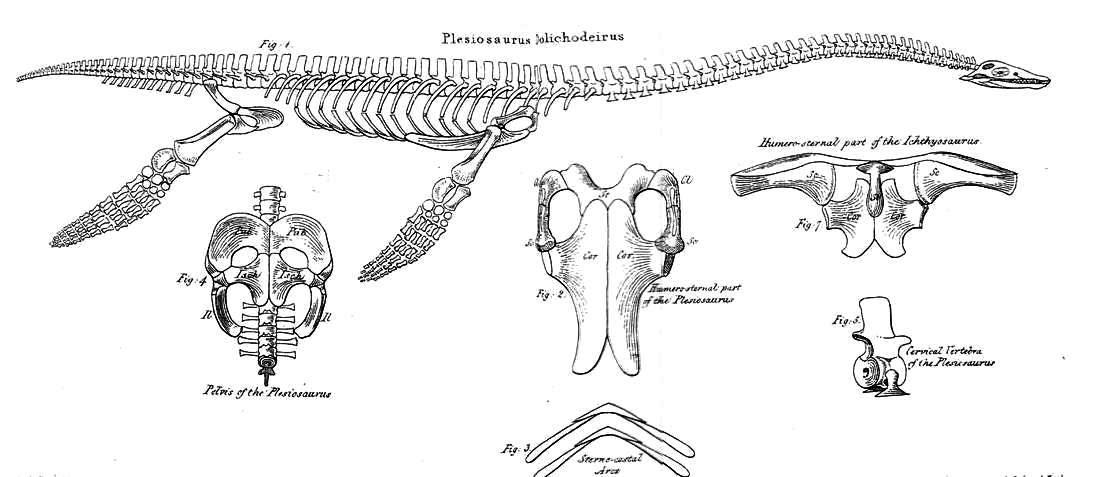 ''Plesiosaurus'' was a moderately sized plesiosaur that grew to in length and in body mass.Storrs 1997 pp. 149 There are approximately 40
''Plesiosaurus'' was a moderately sized plesiosaur that grew to in length and in body mass.Storrs 1997 pp. 149 There are approximately 40
 The shoulder girdle is only partly known but appears to be typical for plesiosaurs. It includes fused clavicles at the anterior end, scapulae (shoulder blades), and large coracoids. The scapulae and coracoids both contribute to the glenoids (arm sockets). A pair of oval holes called pectoral fenestrae are found midway along the scapular/coracoid contacts. The forelimbs are elongate and relatively narrow compared to those of most plesiosaurs. The
The shoulder girdle is only partly known but appears to be typical for plesiosaurs. It includes fused clavicles at the anterior end, scapulae (shoulder blades), and large coracoids. The scapulae and coracoids both contribute to the glenoids (arm sockets). A pair of oval holes called pectoral fenestrae are found midway along the scapular/coracoid contacts. The forelimbs are elongate and relatively narrow compared to those of most plesiosaurs. The
 Unequivocal specimens of ''Plesiosaurus dolichodeirus'' are limited to the Lyme Regis area of Dorset. It appears to be the most common species of plesiosaur in the Lias Group of England. ''Plesiosaurus'' is best represented from the "upper part of the Blue Lias, the 'Shales with Beef,' and the lower Black Ven Marls" the latter of which form part of the Charmouth Mudstone; using the Lias Group
Unequivocal specimens of ''Plesiosaurus dolichodeirus'' are limited to the Lyme Regis area of Dorset. It appears to be the most common species of plesiosaur in the Lias Group of England. ''Plesiosaurus'' is best represented from the "upper part of the Blue Lias, the 'Shales with Beef,' and the lower Black Ven Marls" the latter of which form part of the Charmouth Mudstone; using the Lias Group
Genus Plesiosaurus
– The Plesiosaur Directory
– Palaeos
– Mikko's Phylogeny Archive {{Taxonbar, from=Q857081 Early Jurassic plesiosaurs of Europe Plesiosauroids Fossil taxa described in 1821 Taxa named by William Conybeare Sauropterygian genera Taxa named by Henry De la Beche
reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
that lived during the Early Jurassic. It is known by nearly complete skeletons from the Lias of England. It is distinguishable by its small head, long and slender neck, broad turtle-like body, a short tail, and two pairs of large, elongated paddles. It lends its name to the order Plesiosauria, of which it is an early, but fairly typical member. It contains only one species, the type
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* Ty ...
, ''Plesiosaurus dolichodeirus''. Other species once assigned to this genus, including ''P. brachypterygius'', ''P. guilielmiimperatoris'', and ''P. tournemirensis'' have been reassigned to new genera, such as ''Hydrorion
''Hydrorion'' (meaning 'water hunter') is a genus of plesiosaur from the Toarcian Age of the Lower Jurassic. It is only known from multiple specimens, all discovered in the Posidonia Shale of southwestern Germany. The only species of ''Hyd ...
'', ''Seeleyosaurus
''Seeleyosaurus'' is an extinct genus of plesiosaur that was initially placed within the genus '' Plesiosaurus'' in 1895Dames, H. W. (1895). Die Plesiosaurier der süddeutschen Liasformation. ''Abhandlungen der Königlichen Akademie der Wissens ...
'' and ''Occitanosaurus
''Microcleidus'' is an extinct genus of sauropterygian reptile belonging to the Plesiosauroidea. The species has 40 neck vertebrae and a short tail of 28 vertebrae. Fossils of the genus have been found in France, the Posidonia Shale
The Posid ...
''.
Discovery
 The first complete skeleton of ''Plesiosaurus'' was discovered by early paleontologist and fossil hunter Mary Anning in Sinemurian ( Early Jurassic)-age rocks of the lower Lias Group in December 1823.Storrs 1997 pp. 146 Additional fossils of ''Plesiosaurus'' were found in rocks of the Lias Group of Dorset for many years, "until the cessation of quarrying activities in the Lias Group, early in this
The first complete skeleton of ''Plesiosaurus'' was discovered by early paleontologist and fossil hunter Mary Anning in Sinemurian ( Early Jurassic)-age rocks of the lower Lias Group in December 1823.Storrs 1997 pp. 146 Additional fossils of ''Plesiosaurus'' were found in rocks of the Lias Group of Dorset for many years, "until the cessation of quarrying activities in the Lias Group, early in this 0th
0th or zeroth may refer to:
Mathematics, science and technology
* 0th or zeroth, an ordinal for the number zero
* 0th dimension, a topological space
* 0th element, of a data structure in computer science
* Zeroth (software), deep learning softwar ...
century." although less complete remains were used by Henry De la Beche and William Conybeare to name the species two years earlier in 1821,De la Beche, H. T. & W. D. Conybeare. (1821). Notice of the discovery of a new fossil animal, forming a link between the '' Ichthyosaurus'' and crocodile
Crocodiles (family (biology), family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to inclu ...
, together with general remarks on the osteology of the ''Ichthyosaurus''. ''Transactions of the Geological Society of London'' 5: 559–594 and despite being discovered first, Conybeare's remains were not the holotype; Anning's were.
''Plesiosaurus'' was one of the first of the " antediluvian reptiles" to be discovered and excited great interest in 19th-century England. It was so-named ("near lizard") by William Conybeare and Henry De la Beche, to indicate that it was more like a normal reptile than '' Ichthyosaurus'', which had been found in the same rock strata just a few years earlier. ''Plesiosaurus'' is the archetypical genus of Plesiosauria and the first to be described, hence lending its name to the order. Conybeare and De la Beche coined the name for scattered finds from the Bristol region, Dorset, and Lyme Regis in 1821. The type species of ''Plesiosaurus'', ''P. dolichodeirus'', was named and described by Conybeare in 1824 on the basis of Anning's original finds.
Description
Skull and dentition

 Compared to other plesiosaur genera, ''Plesiosaurus'' has a small head. The skull is much narrower than long,Storrs 1997 pp. 166 reaching its greatest width just behind the eyes (the postorbital bar).Storrs 1997 pp. 165 The
Compared to other plesiosaur genera, ''Plesiosaurus'' has a small head. The skull is much narrower than long,Storrs 1997 pp. 166 reaching its greatest width just behind the eyes (the postorbital bar).Storrs 1997 pp. 165 The anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
portion is "bluntly triangular". In lateral view, the skull reaches its highest point at the rear of the skull table
The skull roof, or the roofing bones of the skull, are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes and all land-living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone and are part of the dermatocranium.
In comparati ...
.Storrs 1997 pp. 167 "The external nostrils overlie the internal nares". They are not positioned at the tip of the snout, but farther back, nearer the eyes than the tip of the skull. Unlike the nostrils of '' Rhomaleosaurus'', they do not appear to be adapted for underwater olfaction. The orbits (eye sockets) are roughly circular and are positioned about halfway along the length of the skull. They face up and to the sides. Just posterior to the orbits are the supratemporal fenestra
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
e, which are about the same size as the orbits and also roughly circular. Between the four openings is the pineal foramen, and between the temporal fenestrae is a narrow sagittal ridge. As in other plesiosaurs, the pterygoids of the palate are fused to the basioccipital of the braincase
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skul ...
, although the union is not as robust as in the pliosaurs ''Rhomaleosaurus'' and '' Pliosaurus''. "The palatal bones are thin, but there is no suborbital fenestra."
Vertebral column
 ''Plesiosaurus'' was a moderately sized plesiosaur that grew to in length and in body mass.Storrs 1997 pp. 149 There are approximately 40
''Plesiosaurus'' was a moderately sized plesiosaur that grew to in length and in body mass.Storrs 1997 pp. 149 There are approximately 40 cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In ...
(neck vertebrae), with different specimens preserving 38 to 42 cervical vertebrae.Storrs 1997 pp. 170 Of the rest of the vertebral column, there are a handful (four or five in the holotype specimen) of "pectoral" vertebrae from the neck-torso transition, approximately 21 dorsal or back vertebrae, three or more sacral vertebrae
The sacrum (plural: ''sacra'' or ''sacrums''), in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part ...
, and at least 28 caudal vertebrae.Storrs 1997 pp. 171 Generally, the centra of the cervical vertebrae are relatively elongated, being slightly longer than tall. The width, however, is usually greater than or equal to the length. The articular surfaces of the cervical centra are "slightly concave and kidney-shaped, with rounded, slightly rugose edges." Small holes called foramina subcentralia are found on the ventral surface of the centra. Some of the dorsals have rugose articular edges, like the cervicals; this feature is typically absent from the caudals.
Ribs are found from the neck to the tail. Cervical ribs are hatchet-shaped and have two articular heads. Dorsal ribs are thick and have only one head. Sacral ribs are "short, robust, and blunt or knob-like on both ends." Caudal ribs have different morphologies depending on their location along the tail, with anterior examples being pointed and more distal examples being "broad and blunt."Storrs 1997 pp. 170 ''Plesiosaurus'' also has gastralia, also known as "belly ribs." Nine or more sets of gastralia are present between the shoulder and pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
. Each set is composed of seven elements: a bone on the midline flanked by three lateral elements.
Limbs
 The shoulder girdle is only partly known but appears to be typical for plesiosaurs. It includes fused clavicles at the anterior end, scapulae (shoulder blades), and large coracoids. The scapulae and coracoids both contribute to the glenoids (arm sockets). A pair of oval holes called pectoral fenestrae are found midway along the scapular/coracoid contacts. The forelimbs are elongate and relatively narrow compared to those of most plesiosaurs. The
The shoulder girdle is only partly known but appears to be typical for plesiosaurs. It includes fused clavicles at the anterior end, scapulae (shoulder blades), and large coracoids. The scapulae and coracoids both contribute to the glenoids (arm sockets). A pair of oval holes called pectoral fenestrae are found midway along the scapular/coracoid contacts. The forelimbs are elongate and relatively narrow compared to those of most plesiosaurs. The humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a roun ...
(upper arm bone) has distinctive curvature, which appears to be a retained primitive feature among sauropterygians. Mature ''Plesiosaurus'' also have a distinctive groove along the ventral surface of the humerus. The forearm includes a flat, broad, crescent-shaped ulna and a "robust and pillar-like" radius. The wrist includes six bones.Storrs 1997 pp. 173 The hand paddle has five digits; the phalangeal formula is uncertain, but the count for one large individual, from "thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb ...
" to fifth "finger", is 4-8-9-8-6.Storrs 1997 pp. 176
The pelvis includes equant pubic bones, ischia, and blade-shaped ilia connecting the pelvis to the vertebral column.Storrs 1997 pp. 178 The acetabulum
The acetabulum (), also called the cotyloid cavity, is a concave surface of the pelvis. The head of the femur meets with the pelvis at the acetabulum, forming the hip joint.
Structure
There are three bones of the ''os coxae'' (hip bone) that c ...
is formed by surfaces on the pubic bones and ischia. Similar to the pectoral girdle, there is a pair of holes between the ischia and pubic bones. The hindlimbs are long and narrow, and in adults, they are much smaller than the forelimbs. The thigh bones are straight. The lower hindlimb includes two roughly equal-sized bones, the robust tibia and the semilunate-shaped fibula. There are six bones in the ankle. The foot paddle includes five digits. Like the hand, the phalangeal formula is uncertain, but is at least 3-7-9-8-7 from innermost to outer "toe".
Classifications
''Plesiosaurus'' has historically been a wastebasket taxon. This is due in part to few anatomical or taxonomic studies of the relevant fossils. Uncritical taxonomic work resulted in hundreds of species representing most of the world and most of the Mesozoic being assigned to ''Plesiosaurus.'' None of the younger Jurassic or Cretaceous species belong to ''Plesiosaurus''. Review of the Early Jurassic species indicates that the only English species properly assigned to ''Plesiosaurus'' is ''P. dolichodeirus''. Several other European Early Jurassic species have been assigned to new genera. ''P. brachypterygius'', ''P. guilielmiimperatoris'' and ''P. tournemirensis'', for example, were assigned to the new genera ''Hydrorion
''Hydrorion'' (meaning 'water hunter') is a genus of plesiosaur from the Toarcian Age of the Lower Jurassic. It is only known from multiple specimens, all discovered in the Posidonia Shale of southwestern Germany. The only species of ''Hyd ...
'', ''Seeleyosaurus
''Seeleyosaurus'' is an extinct genus of plesiosaur that was initially placed within the genus '' Plesiosaurus'' in 1895Dames, H. W. (1895). Die Plesiosaurier der süddeutschen Liasformation. ''Abhandlungen der Königlichen Akademie der Wissens ...
'' and ''Occitanosaurus
''Microcleidus'' is an extinct genus of sauropterygian reptile belonging to the Plesiosauroidea. The species has 40 neck vertebrae and a short tail of 28 vertebrae. Fossils of the genus have been found in France, the Posidonia Shale
The Posid ...
''.
The following cladogram follows an analysis by Benson ''et al.'', 2012, and shows the placement of ''Plesiosaurus'' within Plesiosauria.
Stratigraphy
 Unequivocal specimens of ''Plesiosaurus dolichodeirus'' are limited to the Lyme Regis area of Dorset. It appears to be the most common species of plesiosaur in the Lias Group of England. ''Plesiosaurus'' is best represented from the "upper part of the Blue Lias, the 'Shales with Beef,' and the lower Black Ven Marls" the latter of which form part of the Charmouth Mudstone; using the Lias Group
Unequivocal specimens of ''Plesiosaurus dolichodeirus'' are limited to the Lyme Regis area of Dorset. It appears to be the most common species of plesiosaur in the Lias Group of England. ''Plesiosaurus'' is best represented from the "upper part of the Blue Lias, the 'Shales with Beef,' and the lower Black Ven Marls" the latter of which form part of the Charmouth Mudstone; using the Lias Group ammonite
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish) ...
fossil zones, these rocks date to the early Sinemurian stage. Some other ''Plesiosaurus'' fossils are from later Sinemurian rocks. The oldest specimen may be a skull thought to come from late Rhaetian
The Rhaetian is the latest age of the Triassic Period (in geochronology) or the uppermost stage of the Triassic System (in chronostratigraphy). It was preceded by the Norian and succeeded by the Hettangian (the lowermost stage or earliest age ...
or early Hettangian
The Hettangian is the earliest age and lowest stage of the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (My ...
rocks.Storrs 1997 pp.180
Paleoecology
''Plesiosaurus'' fed mainly on clams and snails, and is thought to have eaten belemnites, fish and other prey as well. Its U-shaped jaw and sharp teeth would have been like a fish trap. It propelled itself by the paddles, the tail being too short to be of much use. Its neck could have been used as a rudder when navigating during a chase. ''Plesiosaurus'' gave live birth to live young in the water like sea snakes. The young might have lived in estuaries before moving out into the open ocean. It has been postulated that the long neck of ''Plesiosaurus'' would have been a hindrance when trying to speed up, any bend in the neck creating turbulences. If that is the case then ''Plesiosaurus'' would have had to keep its neck straight to achieve good acceleration, something that would make hunting difficult. For this reason it may be possible that these animals would actually lie in wait for prey to come close instead of trying to pursue them.See also
* Timeline of plesiosaur research * List of plesiosaur genera * Loch Ness MonsterReferences
Notes
Sources
* Andrews, C. W. 1896. "On the structure of the plesiosaurian skull". ''Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society'', London, 52, 246–253. * Brown, D. S. 1981. "The English Upper Jurassic Plesiosauroidea (Reptilia) and a review of the phylogeny and classification of the Plesiosauria". ''Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History): Geology'', 35, (4), 253–347. * Cruickshank, A. R. I.; Small, P. G.; and Taylor, M. A. 1991. "Dorsal nostrils and hydrodynamically driven underwater olfaction in plesiosaurs". ''Nature'', 352, 62–64. *Lydekker, R. 1889. Catalogue of the fossil Reptilia and Amphibia in the British Museum (Natural History), Part II. Containing the Orders Ichthyopterygia and Sauropterygia. British Museum (Natural History) *Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and paleontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkable gift for interpreting fossils.
Owe ...
, Fossil Reptili of the Liassic Formations, pt iii. (Monogr. Palaeont. Soc., 1865)
* Persson, P. O. 1963. A revision of the classification of the Plesiosauria with a synopsis of the stratigraphical and geographical distribution of the group. Lunds Universitets Årsskrift, N. F. Avd. 2. 59, 1–59.
* Storrs, G. W. 1991. "Anatomy and relationships of ''Corosaurus alcovensis'' (Diapsida: Sauropterygia) and the Triassic Alcova Limestone of Wyoming". ''Bulletin of the Peabody Museum of Natural History'', 44, 1–151.
* Storrs, G. W. and Taylor, M. A. 1996. "Cranial anatomy of a new plesiosaur genus from the lowermost Lias (Rhaetian/Hettangian) of Street, Somerset, England". ''Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology'', 16, (3), 403–420.
* Storrs, G. W. 1997. "Morphological and taxonomic clarification of the genus ''Plesiosaurus''". 145–190. In Callaway, J. M and Nicholls, E. L. (eds.). ''Ancient Marine Reptiles''. Academic press. London.
*Taylor, M. A. and Cruickshank, A. R. I. 1993. Cranial anatomy and functional morphology of Pliosaurus brachyspondylus (Reptilia: Plesiosauria) from the Upper Jurassuc of Westbury, Wiltshire. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B, 341, 399–418.
* Torrens, Hugh 1995. "Mary Anning (1799–1847) of Lyme; 'The Greatest Fossilist the World Ever Knew'". ''The British Journal for the History of Science'', 25 (3): 257–284
External links
Genus Plesiosaurus
– The Plesiosaur Directory
– Palaeos
– Mikko's Phylogeny Archive {{Taxonbar, from=Q857081 Early Jurassic plesiosaurs of Europe Plesiosauroids Fossil taxa described in 1821 Taxa named by William Conybeare Sauropterygian genera Taxa named by Henry De la Beche