Plasmonic Nanolithography on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Plasmonic nanolithography (also known as plasmonic lithography or plasmonic photolithography) is a nanolithographic process that utilizes surface plasmon excitations such as
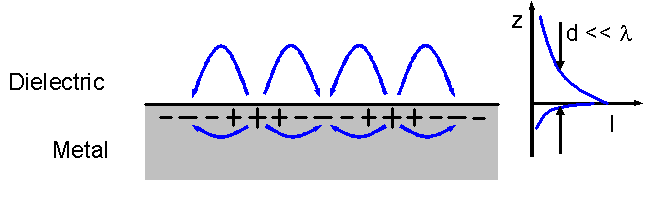 Surface plasmon polaritons are surface
Surface plasmon polaritons are surface
 Plasmonic contact lithography, a modification on the evanescent near-field lithography, uses a metal photomask, on which the SPPs are excited. Similar to common photolithographic processes, photoresist is exposed to SPPs that propagate from the mask. Photomasks with holes enable grating coupling of SPPs; the fields only propagate for nanometers. Srituravanich et al. has demonstrated the lithographic process experimentally with a 2D
Plasmonic contact lithography, a modification on the evanescent near-field lithography, uses a metal photomask, on which the SPPs are excited. Similar to common photolithographic processes, photoresist is exposed to SPPs that propagate from the mask. Photomasks with holes enable grating coupling of SPPs; the fields only propagate for nanometers. Srituravanich et al. has demonstrated the lithographic process experimentally with a 2D
surface plasmon polariton
Surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) are electromagnetic waves that travel along a metal–dielectric or metal–air interface, practically in the infrared or visible-frequency. The term "surface plasmon polariton" explains that the wave involves bot ...
s (SPPs) to fabricate nanoscale structures. SPPs, which are surface waves that propagate in between planar dielectric-metal layers in the optical regime, can bypass the diffraction limit on the optical resolution that acts as a bottleneck for conventional photolithography
In integrated circuit manufacturing, photolithography or optical lithography is a general term used for techniques that use light to produce minutely patterned thin films of suitable materials over a substrate, such as a silicon wafer (electroni ...
.
Theory
 Surface plasmon polaritons are surface
Surface plasmon polaritons are surface electromagnetic wave
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible ...
s that propagate in between two surfaces with sign-changing permittivities
In electromagnetism, the absolute permittivity, often simply called permittivity and denoted by the Greek letter ''ε'' (epsilon), is a measure of the electric polarizability of a dielectric. A material with high permittivity polarizes more in r ...
. They originate from coupling of photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are Massless particle, massless ...
s to plasma oscillations, quantized as plasmon
In physics, a plasmon is a quantum of plasma oscillation. Just as light (an optical oscillation) consists of photons, the plasma oscillation consists of plasmons. The plasmon can be considered as a quasiparticle since it arises from the qua ...
s. SPPs result in evanescent fields that decay perpendicularly to the interface where the propagation occurs. The dispersion relation for SPPs permits the excitation of wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tr ...
s shorter than the free-space wavelength of the inbound light, additionally ensuring subwavelength field confinement. Nevertheless, the excitation of SPPs necessitate momentum mismatch; prism and grating coupling methods are common. For plasmonic nanolithography processes, this is achieved through surface roughness and perforations.
Methods
silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
hole array mask; 90 nm hole arrays were produced at 365 nm wavelength, which is beyond diffraction limit. Zayats and Smolyaninov utilized a multi-layered metal film mask to enhance the subwavelength aperture; such structures can be realized by thin film deposition methods. Bowtie apertures and nanogaps were also suggested as alternative apertures. A version of the method, named as surface plasmon interference nanolithography by Liu et al., uses SPP interference patterns. Despite offering high resolution and throughput, plasmonic contact lithography is regarded as an expensive and complex method; contamination due to contact is also a limiting factor.
Planar lens imaging nanolithography uses plasmonic lenses or negative-index superlenses, which were first proposed by John Pendry. Many superlens designs, such as Pendry's thin silver film or Fang et al.'s superlens, benefit from plasmonic excitations to focus Fourier components of incoming light beyond the diffraction limit. Chaturvedi et al. has demonstrated the imaging of a 30 nm chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and h ...
grating through silver superlens photolithography at 380 nm, while Shi et al. simulated a 20 nm lithography resolution at 193 nm wavelength with an aluminum superlens. Srituravanich et al. has developed a mechanically adjustable, hovering plasmonic lens for maskless near-field nanolithography, whereas another maskless approach by Pan et al. uses a "multi-stage plasmonic lens" for progressive coupling.
Plasmonic direct writing is a maskless form of photolithography that is based on scanning probe lithography; the method uses localized surface plasmon
A localized surface plasmon (LSP) is the result of the confinement of a surface plasmon in a nanoparticle of size comparable to or smaller than the wavelength of light used to excite the plasmon. When a small spherical metallic nanoparticle is ...
(LSP) enhancements from embedded plasmonic scanning probes to expose the photoresist. Wang et al. experimentally demonstrated 100 nm field confinement with this method. Kim et al. has developed a ~50 nm resolution scanning probe with a patterning speed of ~10 mm/s. Gold nanoparticles and other plasmonic nanostructures such as nanogaps have been used as masks for lithography; etching in this case can be achieved through either through photomasking principles or enhanced local heating in the vicinity of the nanostructure due to the LSP resonances. Lin et al. also used localized thermal excitations in gold nanoparticles to fabricate two-dimensional structures such as patterned graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure.
and molybdenum disulfide monolayers in a process termed as "optothermoplasmonic nanolithography." Photochemical effects of LSP resonances were also used as a catalyst in lithographic processes: Saito et al. demonstrated selective etching of silver nanocubes on titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble ...
substrates by the means of plasmon-induced charge separation.
See also
* Electron-beam lithography * Nanoimprint lithography *Nanosphere lithography Nanosphere lithography (NSL) is an economical technique for generating single-layer hexagonally close packed or similar patterns of nanoscale features. Generally, NSL applies planar ordered arrays of nanometer-sized latex or silica spheres as lith ...
* Plasmonic metamaterial A plasmonic metamaterial is a metamaterial that uses surface plasmons to achieve optical properties not seen in nature. Plasmons are produced from the interaction of light with metal-dielectric materials. Under specific conditions, the incident li ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Plasmonic Nanolithography Lithography (microfabrication) Plasmonics