Plasma Etcher on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Plasma etching is a form of

plasma processing
Plasma processing is a plasma-based material processing technology that aims at modifying the chemical and physical properties of a surface.
Plasma processing techniques include:
* Plasma activation
* Plasma ashing
*Plasma cleaning
* Plasma elec ...
used to fabricate integrated circuits. It involves a high-speed stream of glow discharge ( plasma) of an appropriate gas mixture being shot (in pulses) at a sample. The plasma source, known as etch species, can be either charged (ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
s) or neutral (atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas ...
s and radicals). During the process, the plasma generates volatile etch products at room temperature from the chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and break ...
s between the elements of the material etched and the reactive species generated by the plasma. Eventually the atoms of the shot element embed themselves at or just below the surface of the target, thus modifying the physical properties
A physical property is any property that is measurable, whose value describes a state of a physical system. The changes in the physical properties of a system can be used to describe its changes between momentary states. Physical properties are ...
of the target.
Mechanisms
Plasma generation
A plasma is a high energetic condition in which a lot of processes can occur. These processes happen because of electrons and atoms. To form the plasma electrons have to be accelerated to gain energy. Highly energetic electrons transfer the energy to atoms by collisions. Three different processes can occur because of this collisions: *Excitation
Excitation, excite, exciting, or excitement may refer to:
* Excitation (magnetic), provided with an electrical generator or alternator
* Excite Ballpark, located in San Jose, California
* Excite (web portal), web portal owned by IAC
* Electron ...
* Dissociation
*Ionization
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive Electric charge, charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged a ...
Different species are present in the plasma such as electrons, ions, radicals, and neutral particles. Those species are interacting with each other constantly. Plasma etching can be divided into two main types of interaction:
*generation of chemical species
*interaction with the surrounding surfaces
Without a plasma, all those processes would occur at a higher temperature. There are different ways to change the plasma chemistry and get different kinds of plasma etching or plasma depositions. One of the excitation techniques to form a plasma is by using RF excitation of a power source of 13.56 MHz.
The mode of operation of the plasma system will change if the operating pressure changes. Also, it is different for different structures of the reaction chamber. In the simple case, the electrode structure is symmetrical, and the sample is placed upon the grounded electrode.
Influences on the process
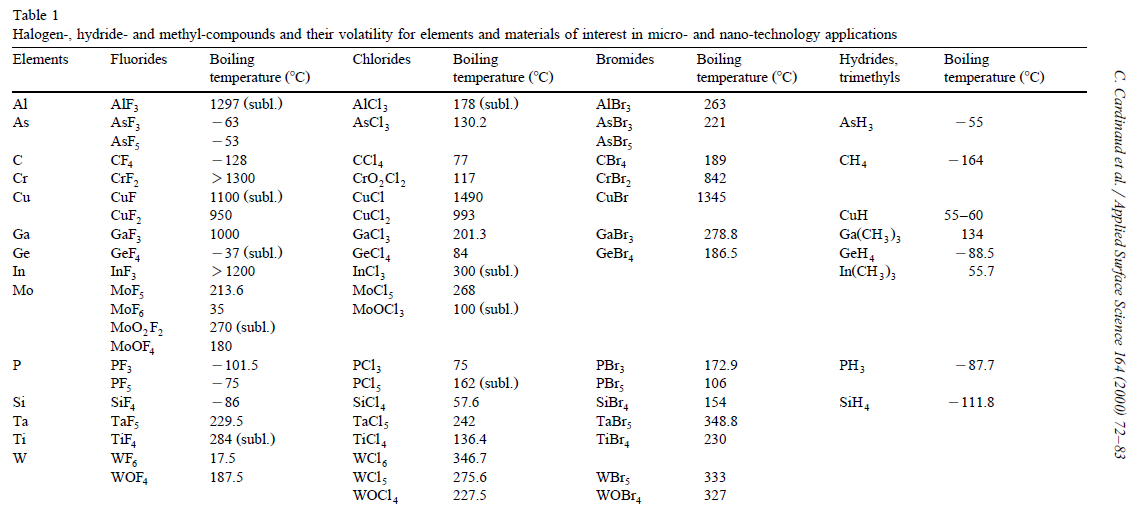
The key to develop successful complex etching processes is to find the appropriate gas etch chemistry that will form volatile products with the material to be etched as shown in Table 1. For some difficult materials (such as magnetic materials), the volatility can only be obtained when the wafer temperature is increased. The main factors that influence the plasma process: *Electron source *Pressure *Gas species *Vacuum
Surface interaction
The reaction of the products depend on the likelihood of dissimilar atoms, photons, or radicals reacting to form chemical compounds. The temperature of the surface also affects the reaction of products. Adsorption happens when a substance is able to gather and reach the surface in a condensed layer, ranging in thickness (usually a thin, oxidized layer.) Volatile products desorb in the plasma phase and help the plasma etching process as the material interacts with the sample's walls. If the products are not volatile, a thin film will form at the surface of the material. Different principles that affect a sample's ability for plasma etching: * Volatility *Adsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which ...
*Chemical Affinity In chemical physics and physical chemistry, chemical affinity is the electronic property by which dissimilar chemical species are capable of forming chemical compounds. Chemical affinity can also refer to the tendency of an atom or compound to comb ...
*Ion-bombarding
*Sputtering
In physics, sputtering is a phenomenon in which microscopic particles of a solid material are ejected from its surface, after the material is itself bombarded by energetic particles of a plasma or gas. It occurs naturally in outer space, and ...
Plasma etching can change the surface contact angles, such as hydrophilic to hydrophobic, or vice versa. Argon plasma etching has reported to enhance contact angle from 52 deg to 68 deg, and, Oxygen plasma etching to reduce contact angle from 52 deg to 19 deg for CFRP composites for bone plate applications. Plasma etching has been reported to reduce the surface roughness from hundreds of nanometers to as much lower as 3 nm for metals.
Types
Pressure influences the plasma etching process. For plasma etching to happen, the chamber has to be under low pressure, less than 100 Pa. In order to generate low-pressure plasma, the gas has to be ionized. The ionization happens by a glow charge. Those excitations happen by an external source, which can deliver up to 30 kW and frequencies from 50 Hz (dc) over 5–10 Hz (pulsed dc) to radio and microwave frequency (MHz-GHz).Microwave plasma etching
Microwave etching happens with an excitation sources in the microwave frequency, so between MHz and GHz. One example of plasma etching is shown here.
Hydrogen plasma etching
One form to use gas as plasma etching is hydrogen plasma etching. Therefore, an experimental apparatus like this can be used:Plasma etcher
A plasma etcher, or etching tool, is a tool used in the production ofsemiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. ...
devices. A plasma etcher produces a plasma from a process gas, typically oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
or a fluorine-bearing gas, using a high frequency electric field, typically 13.56 MHz. A silicon wafer
In electronics, a wafer (also called a slice or substrate) is a thin slice of semiconductor, such as a crystalline silicon (c-Si), used for the fabrication of integrated circuits and, in photovoltaics, to manufacture solar cells. The wafer ser ...
is placed in the plasma etcher, and the air is evacuated from the process chamber using a system of vacuum pumps. Then a process gas is introduced at low pressure, and is excited into a plasma through dielectric breakdown
Electrical breakdown or dielectric breakdown is a process that occurs when an electrical insulating material, subjected to a high enough voltage, suddenly becomes an electrical conductor and electric current flows through it. All insulating mate ...
.
Plasma confinement
Industrial plasma etchers often feature plasma confinement to enable repeatable etch rates and precise spatial distributions in plasmas. One method of confining plasmas is by using the properties of theDebye sheath The Debye sheath (also electrostatic sheath) is a layer in a plasma which has a greater density of positive ions, and hence an overall excess positive charge, that balances an opposite negative charge on the surface of a material with which it is i ...
, a near-surface layer in plasmas similar to the double layer in other fluids. For example, if the Debye sheath length on a slotted quartz part is at least half the width of the slot, the sheath will close off the slot and confine the plasma, while still permitting uncharged particles to pass through the slot.
Applications
Plasma etching is currently used to process semiconducting materials for their use in the fabrication of electronics. Small features can be etched into the surface of the semiconducting material in order to be more efficient or enhance certain properties when used in electronic devices. For example, plasma etching can be used to create deep trenches on the surface of silicon for uses inmicroelectromechanical systems
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), also written as micro-electro-mechanical systems (or microelectronic and microelectromechanical systems) and the related micromechatronics and microsystems constitute the technology of microscopic devices, ...
. This application suggests that plasma etching also has the potential to play a major role in the production of microelectronics. Similarly, research is currently being done on how the process can be adjusted to the nanometer scale.
Hydrogen plasma etching, in particular, has other interesting applications. When used in the process of etching semiconductors, hydrogen plasma etching has been shown to be effective in removing portions of native oxides found on the surface. Hydrogen plasma etching also tends to leave a clean and chemically balanced surface, which is ideal for a number of applications.
Oxygen plasma etching can be used for anisotropic deep-etching of diamond nanostructures by application of high bias in inductively coupled plasma/reactive ion etching (ICP/RIE) reactor. On the other hand, the use of oxygen 0V bias plasmas can be used for isotropic surface termination of C-H terminated diamond surface.
Integrated circuits
Plasma can be used to grow asilicon dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one ...
film on a silicon wafer (using an oxygen plasma), or can be used to remove silicon dioxide by using a fluorine bearing gas. When used in conjunction with photolithography
In integrated circuit manufacturing, photolithography or optical lithography is a general term used for techniques that use light to produce minutely patterned thin films of suitable materials over a substrate, such as a silicon wafer (electroni ...
, silicon dioxide can be selectively applied or removed to trace paths for circuits.
For the formation of integrated circuits it is necessary to structure various layers. This can be done with a plasma etcher. Before etching, a photoresist
A photoresist (also known simply as a resist) is a light-sensitive material used in several processes, such as photolithography and photoengraving, to form a patterned coating on a surface. This process is crucial in the electronic industry.
...
is deposited on the surface, illuminated through a mask, and developed. The dry etch is then performed so that structured etching is achieved. After the process, the remaining photoresist has to be removed. This is also done in a special plasma etcher, called an asher
Asher ( he, אָשֵׁר ''’Āšēr''), in the Book of Genesis, was the last of the two sons of Jacob and Zilpah (Jacob's eighth son) and the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Asher.
Name
The text of the Torah states that the name of ''Asher' ...
.
Dry etching allows a reproducible, uniform etching of all materials used in silicon and III-V semiconductor
Semiconductor materials are nominally small band gap insulators. The defining property of a semiconductor material is that it can be compromised by doping it with impurities that alter its electronic properties in a controllable way.
Because o ...
technology. By using inductively coupled plasma/reactive ion etching (ICP/RIE), even hardest materials like e.g. diamond can be nanostructured.
Plasma etchers are also used for de-layering integrated circuits in failure analysis Failure analysis is the process of collecting and analyzing data to determine the cause of a failure, often with the goal of determining corrective actions or liability.
According to Bloch and Geitner, ”machinery failures reveal a reaction chain o ...
.
See also
*List of plasma (physics) articles
This is a list of plasma physics topics.
A
* Ablation
* Abradable coating
* Abraham–Lorentz force
* Absorption band
* Accretion disk
* Active galactic nucleus
* Adiabatic invariant
* ADITYA (tokamak)
* Aeronomy
* Afterglow plasma
...
*Plasma cleaning
Plasma cleaning is the removal of impurities and contaminants from surfaces through the use of an energetic plasma or dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma created from gaseous species. Gases such as argon and oxygen, as well as mixtures such ...
* Plasma etcher
References
External links
*http://stage.iupac.org/publications/pac/pdf/1990/pdf/6209x1699.pdf{{Dead link, date=May 2020 , bot=InternetArchiveBot , fix-attempted=yes Plasma processing Semiconductor device fabrication