|
Double Layer (plasma)
A double layer is a structure in a plasma consisting of two parallel layers of opposite electrical charge. The sheets of charge, which are not necessarily planar, produce localised excursions of electric potential, resulting in a relatively strong electric field between the layers and weaker but more extensive compensating fields outside, which restore the global potential. Ions and electrons within the double layer are accelerated, decelerated, or deflected by the electric field, depending on their direction of motion. Double layers can be created in discharge tubes, where sustained energy is provided within the layer for electron acceleration by an external power source. Double layers are claimed to have been observed in the aurora and are invoked in astrophysical applications. Similarly, a double layer in the auroral region requires some external driver to produce electron acceleration. Electrostatic double layers are especially common in current-carrying plasmas, and are ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as biological organisms, minerals and chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a network featuring many-to-many links, or a lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built structures are broadly divided by their varying design approaches and standards, into categories including building struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farley–Buneman Instability
The Farley–Buneman instability, or FB instability, is a microscopic plasma instability named after Donald T. Farley and Oscar Buneman. It is similar to the ionospheric Rayleigh-Taylor instability. It occurs in collisional plasma with neutral component, and is driven by drift currents. It can be thought of as a modified two-stream instability arising from the difference in drifts of electrons and ions exceeding the ion acoustic speed. It occurs in collisional plasma with neutrals driven by drift current for two stream instability for unmagnetized plasma it becomes "Buneman instability". It is present in the equatorial and polar ionospheric E-regions. In particular, it occurs in the equatorial electrojet due to the drift of electrons relative to ions, and also in the trails behind ablating meteoroids. Since the FB fluctuations can scatter electromagnetic waves, the instability can be used to diagnose the state of ionosphere by the use of electromagnetic pulses. Condit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charged Particle Beam
A charged particle beam is a spatially localized group of electrically charged particles that have approximately the same position, kinetic energy (resulting in the same velocity), and direction. The kinetic energies of the particles are much larger than the energies of particles at ambient temperature. The high energy and directionality of charged particle beams make them useful for many applications in particle physics (see Particle beam#Applications and Electron-beam technology). Such beams can be split into two main classes: # ''unbunched beams'' (''coasting beams'' or ''DC beams''), which have no longitudinal substructure in the direction of beam motion. # ''bunched beams'', in which the particles are distributed into pulses (bunches) of particles. Bunched beams are most common in modern facilities, since the most modern particle accelerators require bunched beams for acceleration. Assuming a normal distribution of particle positions and impulses, a charged particle bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergalactic Medium
Intergalactic may refer to: * "Intergalactic" (song), a song by the Beastie Boys * ''Intergalactic'' (TV series), a 2021 UK science fiction TV series * Intergalactic space * Intergalactic travel, travel between galaxies in science fiction and speculation * "Intergalactic", a song by the Smashing Pumpkins from '' Atum: A Rock Opera in Three Acts'' * '' Intergalactic: The Heretic Prophet'', an upcoming video game See also * * Interstellar (other) * Interplanetary (other) * Entergalactic (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interplanetary Medium
The interplanetary medium (IPM) or interplanetary space consists of the mass and energy which fills the Solar System, and through which all the larger Solar System bodies, such as planets, dwarf planet A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit around the Sun, massive enough to be hydrostatic equilibrium, gravitationally rounded, but insufficient to achieve clearing the neighbourhood, orbital dominance like the ...s, asteroids, and comets, move. The IPM stops at the Heliopause (astronomy), heliopause, outside of which the interstellar medium begins. Before 1950, interplanetary space was widely considered to either be an empty vacuum, or consisting of "Aether theories, aether". Composition and physical characteristics The interplanetary medium includes Interplanetary dust cloud, interplanetary dust, cosmic rays, and hot Plasma (physics), plasma from the solar wind. The density of the interplanetary medium is very low, decreasing in inverse pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Sheet
A current sheet is an electric current that is confined to a surface, rather than being spread through a volume of space. Current sheets feature in magnetohydrodynamics (MHD), a model of electrically conductive fluids: if there is an electric current through part of the volume of such a fluid, magnetic forces tend to expel it from the fluid, compressing the current into thin layers that pass through the volume. The largest occurring current sheet in the Solar System is the so-called heliospheric current sheet, which is about 10,000 km thick, and extends from the Sun and out beyond the orbit of Pluto. In astrophysical plasmas such as the solar corona, current sheets theoretically might have an aspect ratio (breadth divided by thickness) as high as 100,000:1. By contrast, the pages of most books have an aspect ratio close to 2000:1. Because current sheets are so thin in comparison to their size, they are often treated as if they have zero thickness; this is a result of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction, reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nuclei, nuclei/neutrons, neutron by-products. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of energy. This difference in mass arises as a result of the difference in nuclear binding energy between the atomic nuclei before and after the fusion reaction. Nuclear fusion is the process that powers all active stars, via many Stellar nucleosynthesis, reaction pathways. Fusion processes require an extremely large Lawson criterion, triple product of temperature, density, and confinement time. These conditions occur only in Stellar core, stellar cores, advanced Nuclear weapon design, nuclear weapons, and are approached in List of fusion experiments, fusion power experiments. A nuclear fusion process that produces atomic nuclei lighter than nickel-62 is generally exothermic, due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
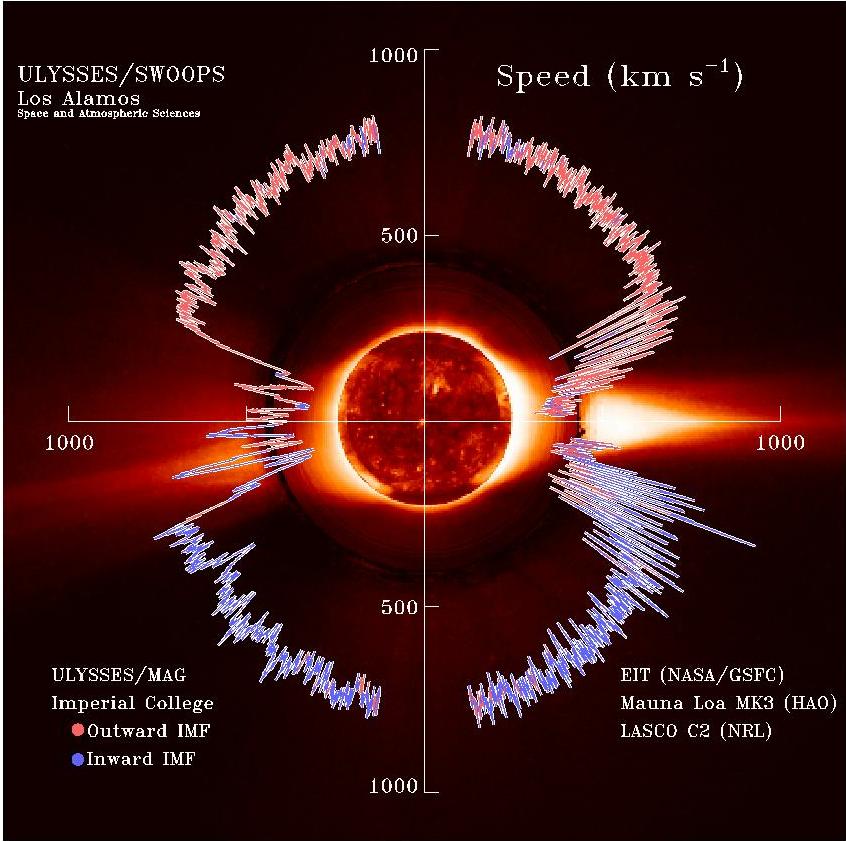
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of particle species found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of Chemical element, elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, and iron. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over Solar coordinate systems#Heliographic, solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. Travel through this layer also impacts GPS signals, resulting in effects such as deflection in their path and delay in the arrival of the signal. History of discovery As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada) usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DL Surface Plot
DL, dL, or dl may stand for: Science and technology Electronics and computing *, an HTML element used for a definition list *Deep learning, a field of machine learning *Description logics, a family of knowledge representation languages * Delete Line (ANSI), an ANSI X3.64 escape sequence *Digital library, a library in which collections are stored in digital formats *Diode logic, a logic family using diodes * DVD-R DL, a DVD Dual Layer engineering method * DL register, the low byte of an X86 16-bit DX register *Dynamic loading, a mechanism for a computer program to load a library Telecommunications *Data link, a computer connection for transmitting data *Distribution list, a function of e-mail clients *Downlink, the link from a satellite to a ground station *Download, a transfer of electronic data Vehicles * Subaru DL, an automobile * Australian National DL class, a class of diesel locomotives built by Clyde Engineering *New Zealand DL class locomotive, a diesel-electric clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device such as a lead-acid battery. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. Conventional current describes the direction in which positive charges move. Electrons, which are the carriers of current in most electrical systems, have a negative electrical charge, so the movement of electrons is ''opposite'' to that of the conventional current flow: this means that electrons flow ''into'' the device's cathode from the external circuit. For example, the end of a household battery marked with a + (plus) is the cathode. The electrode through which conventional current flows the other way, into the device, is termed an anode. Charge flow Conventional current flows from cathode to anode outside the cell or device (with electrons moving in the opposite direction), regardless of the cell or device type and operating mode. Cathode polarity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |