Planned New Art Museums And Galleries on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Planning is the
Planning is the
 Planning is one of the
Planning is one of the
 There are a variety of neuropsychological tests which can be used to measure variance of planning ability between the subject and controls.
* Tower of Hanoi (TOH-R), a puzzle invented in 1883 by the French mathematician Édouard Lucas. There are different variations of the puzzle, the classic version consists of three rods and usually seven to nine discs of subsequently smaller size. Planning is a key component of the problem solving skills necessary to achieve the objective, which is to move the entire stack to another rod, obeying the following rules:
** Only one disk may be moved at a time.
** Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the rods and sliding it onto another rod, on top of the other disks that may already be present on that rod.
** No disk may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
There are a variety of neuropsychological tests which can be used to measure variance of planning ability between the subject and controls.
* Tower of Hanoi (TOH-R), a puzzle invented in 1883 by the French mathematician Édouard Lucas. There are different variations of the puzzle, the classic version consists of three rods and usually seven to nine discs of subsequently smaller size. Planning is a key component of the problem solving skills necessary to achieve the objective, which is to move the entire stack to another rod, obeying the following rules:
** Only one disk may be moved at a time.
** Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the rods and sliding it onto another rod, on top of the other disks that may already be present on that rod.
** No disk may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
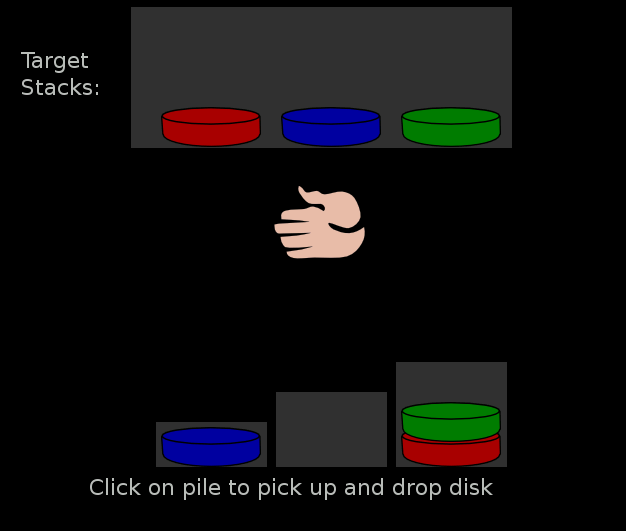 * Tower of London (TOL) is another test that was developed in 1992 (Shallice 1992) specifically to detect deficits in planning as may occur with damage to the frontal lobe. Test participants with damage to the left anterior frontal lobe demonstrated planning deficits (i.e., greater number of moves required for solution).
Test participants with damage to the right anterior, and left or right posterior areas of the frontal lobes showed no impairment. The results implicating the left anterior frontal lobes involvement in solving the TOL were supported in concomitant neuroimaging studies which also showed a reduction in regional cerebral blood flow to the left pre-frontal lobe. For the number of moves, a significant negative correlation was observed for the left prefrontal area: i.e. subjects that took more time planning their moves showed greater activation in the left prefrontal area.
* Tower of London (TOL) is another test that was developed in 1992 (Shallice 1992) specifically to detect deficits in planning as may occur with damage to the frontal lobe. Test participants with damage to the left anterior frontal lobe demonstrated planning deficits (i.e., greater number of moves required for solution).
Test participants with damage to the right anterior, and left or right posterior areas of the frontal lobes showed no impairment. The results implicating the left anterior frontal lobes involvement in solving the TOL were supported in concomitant neuroimaging studies which also showed a reduction in regional cerebral blood flow to the left pre-frontal lobe. For the number of moves, a significant negative correlation was observed for the left prefrontal area: i.e. subjects that took more time planning their moves showed greater activation in the left prefrontal area.
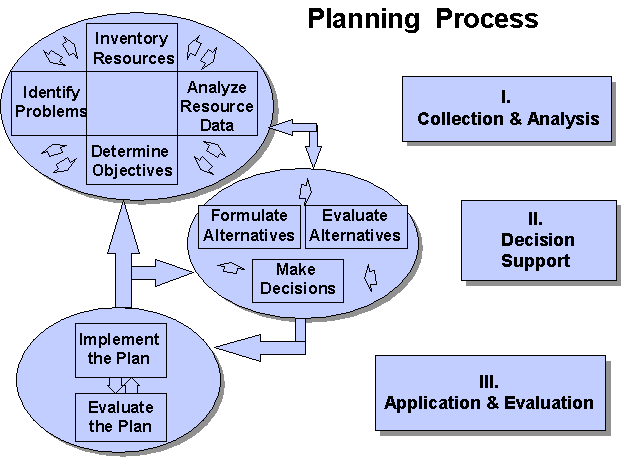 Patrick Montana and Bruce Charnov outline a three-step result-oriented process for planning:
# Choosing a destination
# Evaluating alternative routes
# Deciding the specific course of the plan
In organizations, planning can become a management process, concerned with defining goals for a future direction and determining on the missions and resources to achieve those targets. To meet the goals, managers may develop plans such as a business plan or a marketing plan. Planning always has a purpose. The purpose may involve the achievement of certain goals or targets: efficient use of resources, reducing risk, expanding the organisation and its assets etc.
Patrick Montana and Bruce Charnov outline a three-step result-oriented process for planning:
# Choosing a destination
# Evaluating alternative routes
# Deciding the specific course of the plan
In organizations, planning can become a management process, concerned with defining goals for a future direction and determining on the missions and resources to achieve those targets. To meet the goals, managers may develop plans such as a business plan or a marketing plan. Planning always has a purpose. The purpose may involve the achievement of certain goals or targets: efficient use of resources, reducing risk, expanding the organisation and its assets etc.
Bazin, A. (2012). Bilateral and multilateral planning: Best practices and lessons learned. Strategos.
* Das, J P, Binod C Kar, Rauno K Parrila. Cognitive Planning: The Psychological Basis of Intelligent Behaviour. Sage Publications Pvt. Ltd; illustrated edition. English * * * * * Yiftachel, Oren, 1995, "The Dark Side of Modernism: Planning as Control of an Ethnic Minority," in Sophie Watson and Katherine Gibson, eds., Postmodern Cities and Spaces (Oxford and Cambridge, MA: Blackwell), pp. 216–240. * * {{Authority control Neuropsychological assessment Systems engineering
 Planning is the
Planning is the process
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
*Business process, activities that produce a specific se ...
of thinking
In their most common sense, the terms thought and thinking refer to conscious cognitive processes that can happen independently of sensory stimulation. Their most paradigmatic forms are judging, reasoning, concept formation, problem solving, an ...
regarding the activities required to achieve a desired goal
A goal is an idea of the future or desired result that a person or a group of people envision, plan and commit to achieve. People endeavour to reach goals within a finite time by setting deadlines.
A goal is roughly similar to a purpose or ai ...
. Planning is based on foresight, the fundamental capacity for mental time travel
In psychology, mental time travel is the capacity to mentally reconstruct personal events from the past (episodic memory) as well as to imagine possible scenarios in the future (episodic foresight / episodic future thinking). The term was coine ...
. The evolution of forethought, the capacity to think ahead, is considered to have been a prime mover in human evolution
Human evolution is the evolutionary process within the history of primates that led to the emergence of ''Homo sapiens'' as a distinct species of the hominid family, which includes the great apes. This process involved the gradual development of ...
. Planning is a fundamental property of intelligent behavior. It involves the use of logic and imagination to visualise not only a desired end result, but the steps necessary to achieve that result.
An important aspect of planning is its relationship to forecasting. Forecasting aims to predict what the future will look like, while planning imagines what the future could look like.
Planning according to established principles is a core part of many professional occupations, particularly in fields such as management
Management (or managing) is the administration of an organization, whether it is a business, a nonprofit organization, or a government body. It is the art and science of managing resources of the business.
Management includes the activities o ...
and business
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for pr ...
. Once a plan has been developed it is possible to measure and assess progress
Progress is the movement towards a refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. In the context of progressivism, it refers to the proposition that advancements in technology, science, and social organization have resulted, and by extension wi ...
, efficiency
Efficiency is the often measurable ability to avoid wasting materials, energy, efforts, money, and time in doing something or in producing a desired result. In a more general sense, it is the ability to do things well, successfully, and without ...
and effectiveness
Effectiveness is the capability of producing a desired result or the ability to produce desired output. When something is deemed effective, it means it has an intended or expected outcome, or produces a deep, vivid impression.
Etymology
The ori ...
. As circumstances change, plans may need to be modified or even abandoned.
Psychology
 Planning is one of the
Planning is one of the executive function
In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions (collectively referred to as executive function and cognitive control) are a set of cognitive processes that are necessary for the cognitive control of behavior: selecting and succe ...
s of the brain, encompassing the neurological
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal ...
processes involved in the formulation, evaluation and selection of a sequence of thoughts and actions to achieve a desired goal. Various studies utilizing a combination of neuropsychological
Neuropsychology is a branch of psychology concerned with how a person's cognition and behavior are related to the brain and the rest of the nervous system. Professionals in this branch of psychology often focus on how injuries or illnesses of ...
, neuropharmacological and functional neuroimaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Incre ...
approaches have suggested there is a positive relationship between impaired planning ability and damage to the frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove betwe ...
.
A specific area within the mid-dorsolateral frontal cortex located in the frontal lobe has been implicated as playing an intrinsic role in both cognitive planning
Cognitive planning is one of the executive functions. It encompasses the neurological processes involved in the formulation, evaluation and selection of a sequence of thoughts and actions to achieve a desired goal. Various studies utilizing a combi ...
and associated executive traits such as working memory
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term memory, ...
.
Disruption of the neural pathway
In neuroanatomy, a neural pathway is the connection formed by axons that project from neurons to make synapses onto neurons in another location, to enable neurotransmission (the sending of a signal from one region of the nervous system to ano ...
s, via various mechanisms such as traumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity (ranging from mild traumatic brain injury TBI/concussionto severe traumatic b ...
, or the effects of neurodegenerative diseases between this area of the frontal cortex and the basal ganglia, specifically the striatum
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamate ...
(cortico-striatal pathway), may disrupt the processes required for normal planning function.
Individuals who were born Very Low Birth Weight (<1500 grams) and Extremely Low BirthWeight (ELBW) are at greater risk for various cognitive deficits including planning ability.№Neuropsychological tests
 There are a variety of neuropsychological tests which can be used to measure variance of planning ability between the subject and controls.
* Tower of Hanoi (TOH-R), a puzzle invented in 1883 by the French mathematician Édouard Lucas. There are different variations of the puzzle, the classic version consists of three rods and usually seven to nine discs of subsequently smaller size. Planning is a key component of the problem solving skills necessary to achieve the objective, which is to move the entire stack to another rod, obeying the following rules:
** Only one disk may be moved at a time.
** Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the rods and sliding it onto another rod, on top of the other disks that may already be present on that rod.
** No disk may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
There are a variety of neuropsychological tests which can be used to measure variance of planning ability between the subject and controls.
* Tower of Hanoi (TOH-R), a puzzle invented in 1883 by the French mathematician Édouard Lucas. There are different variations of the puzzle, the classic version consists of three rods and usually seven to nine discs of subsequently smaller size. Planning is a key component of the problem solving skills necessary to achieve the objective, which is to move the entire stack to another rod, obeying the following rules:
** Only one disk may be moved at a time.
** Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the rods and sliding it onto another rod, on top of the other disks that may already be present on that rod.
** No disk may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
 * Tower of London (TOL) is another test that was developed in 1992 (Shallice 1992) specifically to detect deficits in planning as may occur with damage to the frontal lobe. Test participants with damage to the left anterior frontal lobe demonstrated planning deficits (i.e., greater number of moves required for solution).
Test participants with damage to the right anterior, and left or right posterior areas of the frontal lobes showed no impairment. The results implicating the left anterior frontal lobes involvement in solving the TOL were supported in concomitant neuroimaging studies which also showed a reduction in regional cerebral blood flow to the left pre-frontal lobe. For the number of moves, a significant negative correlation was observed for the left prefrontal area: i.e. subjects that took more time planning their moves showed greater activation in the left prefrontal area.
* Tower of London (TOL) is another test that was developed in 1992 (Shallice 1992) specifically to detect deficits in planning as may occur with damage to the frontal lobe. Test participants with damage to the left anterior frontal lobe demonstrated planning deficits (i.e., greater number of moves required for solution).
Test participants with damage to the right anterior, and left or right posterior areas of the frontal lobes showed no impairment. The results implicating the left anterior frontal lobes involvement in solving the TOL were supported in concomitant neuroimaging studies which also showed a reduction in regional cerebral blood flow to the left pre-frontal lobe. For the number of moves, a significant negative correlation was observed for the left prefrontal area: i.e. subjects that took more time planning their moves showed greater activation in the left prefrontal area.Planning theories
Business
 Patrick Montana and Bruce Charnov outline a three-step result-oriented process for planning:
# Choosing a destination
# Evaluating alternative routes
# Deciding the specific course of the plan
In organizations, planning can become a management process, concerned with defining goals for a future direction and determining on the missions and resources to achieve those targets. To meet the goals, managers may develop plans such as a business plan or a marketing plan. Planning always has a purpose. The purpose may involve the achievement of certain goals or targets: efficient use of resources, reducing risk, expanding the organisation and its assets etc.
Patrick Montana and Bruce Charnov outline a three-step result-oriented process for planning:
# Choosing a destination
# Evaluating alternative routes
# Deciding the specific course of the plan
In organizations, planning can become a management process, concerned with defining goals for a future direction and determining on the missions and resources to achieve those targets. To meet the goals, managers may develop plans such as a business plan or a marketing plan. Planning always has a purpose. The purpose may involve the achievement of certain goals or targets: efficient use of resources, reducing risk, expanding the organisation and its assets etc.
Public policy
Public policies include laws, rules, decisions, and decrees. Public policy can be defined as efforts to tackle social issues via policy-making. A policy is crafted with a specific goal in mind in order to address a societal problem that has been prioritized by the government. Public policy planning includes environmental, land use, regional, urban and spatial planning. In many countries, the operation of a town and country planning system is often referred to as "planning" and the professionals which operate the system are known as " planners". It is a conscious as well as sub-conscious activity. It is "an anticipatory decision making process" that helps in coping with complexities. It is deciding future course of action from amongst alternatives. It is a process that involves making and evaluating each set of interrelated decisions. It is selection of missions, objectives and "translation of knowledge into action." A planned performance brings better results compared to an unplanned one. A manager's job is planning, monitoring and controlling. Planning and goal setting are important traits of an organization. It is done at all levels of the organization. Planning includes the plan, the thought process, action, and implementation. Planning gives more power over the future. Planning is deciding in advance what to do, how to do it, when to do it, and who should do it. This bridges the gap from where the organization is to where it wants to be. The planning function involves establishing goals and arranging them in logical order. An organization that plans well achieves faster goals than one that does not plan before implementation.Personal
Planning is not just a professional activity: it is a feature of everyday life, whether for career advancement, organising an event or even just getting through a busy day.Alternatives to planning
Opportunism can supplement or replace planning.Types of planning
*Automated planning and scheduling
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines ...
* Business plan
* Central planning
* Collaborative planning, forecasting, and replenishment
* Comprehensive planning
* Contingency planning
* Economic planning
Economic planning is a resource allocation mechanism based on a computational procedure for solving a constrained maximization problem with an iterative process for obtaining its solution. Planning is a mechanism for the allocation of resources b ...
* Enterprise architecture planning
* Environmental planning
Environmental planning is the process of facilitating decision making to carry out land development with the consideration given to the natural environment, social, political, economic and governance factors and provides a holistic framework to ...
* Event planning
* Family planning
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marita ...
* Financial planning
* Land use planning
* Landscape planning
* Lesson planning
* Marketing plan
* Network resource planning
* Operational planning
* Planning Domain Definition Language
* Regional planning
* Site planning
* Spatial planning
* Strategic planning
Strategic planning is an organization's process of defining its strategy or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to attain strategic goals.
It may also extend to control mechanisms for guiding the implementation of the st ...
* Succession planning
* Time management
* Urban planning
See also
* Futures studies * Learning theory (education) * Planning fallacy * Project management * Time managementReferences
Further reading
*Bazin, A. (2012). Bilateral and multilateral planning: Best practices and lessons learned. Strategos.
* Das, J P, Binod C Kar, Rauno K Parrila. Cognitive Planning: The Psychological Basis of Intelligent Behaviour. Sage Publications Pvt. Ltd; illustrated edition. English * * * * * Yiftachel, Oren, 1995, "The Dark Side of Modernism: Planning as Control of an Ethnic Minority," in Sophie Watson and Katherine Gibson, eds., Postmodern Cities and Spaces (Oxford and Cambridge, MA: Blackwell), pp. 216–240. * * {{Authority control Neuropsychological assessment Systems engineering