Plagioclase Feldspar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Plagioclase is a series of
Plagioclase is a series of
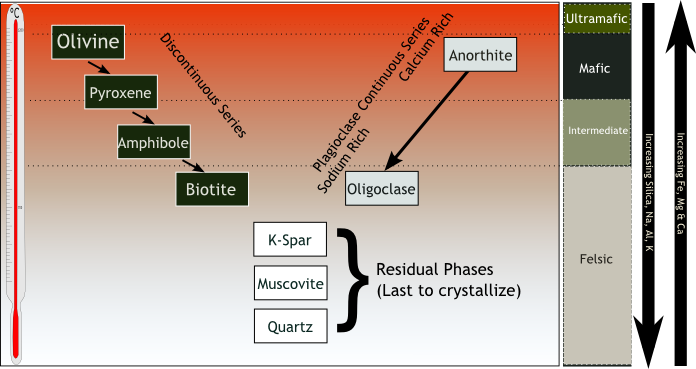
 Plagioclase is the primary aluminium-bearing mineral in
Plagioclase is the primary aluminium-bearing mineral in
 Plagioclase is a series of
Plagioclase is a series of tectosilicate
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust.
In mineralogy, silica (silicon dioxide, ) is usually consi ...
(framework silicate) mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ...
s within the feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feld ...
group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogenous mixture of two different kinds of atoms in solid state and have a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The wor ...
series, more properly known as the plagioclase feldspar series. This was first shown by the German mineralogist Johann Friedrich Christian Hessel (1796–1872) in 1826. The series ranges from albite
Albite is a plagioclase feldspar mineral. It is the sodium endmember of the plagioclase solid solution series. It represents a plagioclase with less than 10% anorthite content. The pure albite endmember has the formula . It is a tectosilica ...
to anorthite
Anorthite is the calcium endmember of the plagioclase feldspar mineral series. The chemical formula of pure anorthite is Ca Al2 Si2O8. Anorthite is found in mafic igneous rocks. Anorthite is rare on the Earth but abundant on the Moon.
Minera ...
endmember
An endmember (also end-member or end member) in mineralogy is a mineral that is at the extreme end of a mineral series in terms of purity of its chemical composition. Minerals often can be described as solid solutions with varying compositions of ...
s (with respective compositions NaAlSi3O8 to CaAl2Si2O8), where sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
and calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
atoms
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas ...
can substitute for each other in the mineral's crystal lattice
In geometry and crystallography, a Bravais lattice, named after , is an infinite array of discrete points generated by a set of discrete translation operations described in three dimensional space by
: \mathbf = n_1 \mathbf_1 + n_2 \mathbf_2 + n ...
structure. Plagioclase in hand samples is often identified by its polysynthetic crystal twinning or 'record-groove' effect.
Plagioclase is a major constituent mineral in the Earth's crust, and is consequently an important diagnostic tool in petrology
Petrology () is the branch of geology that studies rocks and the conditions under which they form. Petrology has three subdivisions: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary petrology. Igneous and metamorphic petrology are commonly taught together ...
for identifying the composition, origin and evolution of igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or l ...
s. Plagioclase is also a major constituent of rock in the highlands of the Moon. Analysis of thermal emission spectra from the surface of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmos ...
suggests that plagioclase is the most abundant mineral in the crust of Mars.
Its name comes from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
( 'oblique') + ( 'fracture'), in reference to its two cleavage angles.
Properties
Plagioclase is the most common and abundantmineral group In geology and mineralogy, a mineral group is a set of mineral species with essentially the same crystal structure and composed of chemically similar elements.Stuart J. Mills, Frédéric Hatert, Ernest H. Nickel, and Giovanni Ferraris (2009): "The s ...
in the Earth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The ...
. Part of the feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feld ...
family of minerals, it is abundant in igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma o ...
and metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, cau ...
, and it is also common as a detrital
Detritus (; adj. ''detrital'' ) is particles of rock derived from pre-existing rock through weathering and erosion.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p G-7 A fragment of detritus is called a clast.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Steph ...
mineral in sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particle ...
. It is not a single mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ...
, but is a solid solution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogenous mixture of two different kinds of atoms in solid state and have a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The wor ...
of two end members, albite
Albite is a plagioclase feldspar mineral. It is the sodium endmember of the plagioclase solid solution series. It represents a plagioclase with less than 10% anorthite content. The pure albite endmember has the formula . It is a tectosilica ...
or sodium feldspar () and anorthite
Anorthite is the calcium endmember of the plagioclase feldspar mineral series. The chemical formula of pure anorthite is Ca Al2 Si2O8. Anorthite is found in mafic igneous rocks. Anorthite is rare on the Earth but abundant on the Moon.
Minera ...
or calcium feldspar (). These can be present in plagioclase in any proportion from pure anorthite to pure albite. The composition of plagioclase can thus be written as where ''x'' ranges from 0 for pure albite to 1 for pure anorthite. This solid solution series is known as the plagioclase series. The composition of a particular sample of plagioclase is customarily expressed as the mol% of anorthite in the sample. For example, plagioclase that is 40 mol% anorthite would be described as An40 plagioclase.
The ability of albite and anorthite to form solid solutions in any proportions at elevated temperature reflects the ease with which calcium and aluminium can substitute for sodium and silicon in the plagioclase crystal structure. Although a calcium ion has a charge of +2, versus +1 for a sodium ion, the two ions have very nearly the same effective radius. The difference in charge is accommodated by the coupled substitution of aluminium (charge +3) for silicon (charge +4), both of which can occupy tetrahedral sites (surrounded by four oxygen ions). This contrasts with potassium, which has the same charge as sodium, but is a significantly larger ion. As a result of the size and charge difference between potassium and calcium, there is a very wide miscibility gap between anorthite and potassium feldspar Potassium feldspar refers to a number of minerals in the feldspar group, and containing potassium:
*Orthoclase
Orthoclase, or orthoclase feldspar ( endmember formula K Al Si3 O8), is an important tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock ...
, (), the third common rock-forming feldspar end member. Potassium feldspar does form a solid solution series with albite
Albite is a plagioclase feldspar mineral. It is the sodium endmember of the plagioclase solid solution series. It represents a plagioclase with less than 10% anorthite content. The pure albite endmember has the formula . It is a tectosilica ...
, due to the identical charges of sodium and potassium ions, which is known as the alkali feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldsp ...
series. Thus, almost all feldspar found on Earth is either plagioclase or alkali feldspar, with the two series overlapping for pure albite. When a plagioclase composition is described by its anorthite mol% (such as An40 in the previous example) it is assumed that the remainder is albite, with only a minor component of potassium feldspar.
Plagioclase of any composition shares many basic physical characteristics, while other characteristics vary smoothly with composition. The Mohs hardness
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness () is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.
The scale was introduced in 1812 by the ...
of all plagioclase species is 6 to 6.5, and cleavage is perfect on 01and good on 10 with the cleavage planes meeting at an angle of 93 to 94 degrees. It is from this slightly oblique cleavage angle that plagioclase gets its name, Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
( 'oblique') + ( 'fracture'). The name was introduced by August Breithaupt in 1847. There is also a poor cleavage on 10rarely seen in hand samples.
The luster is vitreous to pearly and the diaphaneity is transparent to translucent. The tenacity
Tenacity may refer to:
* Tenacity (psychology), having persistence in purpose
* Tenacity (mineralogy) a mineral's resistance to breaking or deformation
* Tenacity (herbicide), a brand name for a selective herbicide
* Tenacity (textile strength)
* ...
is brittle, and the fracture is uneven or conchoidal, but the fracture is rarely observed due to the strong tendency of the mineral to cleave instead. At low temperature, the crystal structure belongs to the triclinic system, space group ''P'' Well-formed crystals are rare and are most commonly sodic in composition. Well-shaped samples are instead typically cleavage fragments. Well-formed crystals are typically bladed or tabular parallel to 10
Plagioclase is usually white to greyish-white in color, with a slight tendency for more calcium-rich samples to be darker. Impurities can infrequently tint the mineral greenish, yellowish, or flesh-red. The specific gravity increases smoothly with calcium content, from 2.62 for pure albite to 2.76 for pure anorthite, and this can provide a useful estimate of composition if measured accurately. The index of refraction likewise varies smoothly from 1.53 to 1.58, and, if measured carefully, this also gives a useful composition estimate.
Plagioclase almost universally shows a characteristic polysynthetic twinning that produces twinning striations on 10 These striations allow plagioclase to be distinguished from alkali feldspar. Plagioclase often also displays Carlsbad, Baveno, and Manebach Law twinning.
Plagioclase series members
The composition of a plagioclase feldspar is typically denoted by its overall fraction ofanorthite
Anorthite is the calcium endmember of the plagioclase feldspar mineral series. The chemical formula of pure anorthite is Ca Al2 Si2O8. Anorthite is found in mafic igneous rocks. Anorthite is rare on the Earth but abundant on the Moon.
Minera ...
(%An) or albite
Albite is a plagioclase feldspar mineral. It is the sodium endmember of the plagioclase solid solution series. It represents a plagioclase with less than 10% anorthite content. The pure albite endmember has the formula . It is a tectosilica ...
(%Ab). There are several named plagioclase feldspars that fall between albite and anorthite in the series. The following table shows their compositions in terms of constituent anorthite and albite percentages.
The distinction between these minerals cannot easily be made in the field. The composition can be roughly determined by specific gravity, but accurate measurement requires chemical or optical tests. The composition in a crushed grain mount
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legumes ...
can be obtained by the Tsuboi method, which yields an accurate measurement of the minimum refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, o ...
that in turn gives an accurate composition. In thin section
In optical mineralogy and petrography, a thin section (or petrographic thin section) is a thin slice of a rock or mineral sample, prepared in a laboratory, for use with a polarizing petrographic microscope, electron microscope and electron m ...
, the composition can be determined by either the Michel Lévy or Carlsbad-albite methods. The former relies on accurate measure of minimum index of refraction, while the latter relies on measuring the '' extinction angle'' under a polarizing microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisibl ...
. The extinction angle is an optical characteristic and varies with the albite fraction (%Ab).
Endmembers
*Anorthite
Anorthite is the calcium endmember of the plagioclase feldspar mineral series. The chemical formula of pure anorthite is Ca Al2 Si2O8. Anorthite is found in mafic igneous rocks. Anorthite is rare on the Earth but abundant on the Moon.
Minera ...
was named by Gustav Rose in 1823 from Greek ('not') + ('straight'), literally 'oblique', referring to its triclinic crystallization. Anorthite is a comparatively rare mineral but occurs in the basic plutonic rocks of some orogenic calc-alkaline
The calc-alkaline magma series is one of two main subdivisions of the subalkaline magma series, the other subalkaline magma series being the tholeiitic series. A magma series is a series of compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic m ...
suites.
*Albite
Albite is a plagioclase feldspar mineral. It is the sodium endmember of the plagioclase solid solution series. It represents a plagioclase with less than 10% anorthite content. The pure albite endmember has the formula . It is a tectosilica ...
is named from the Latin , in reference to its unusually pure white color. The name was first applied by Johan Gottlieb Gahn
Johan Gottlieb Gahn (19 August 1745 – 8 December 1818) was a Swedish chemist and metallurgist who isolated manganese in 1774.
Gahn studied in Uppsala 1762 – 1770 and became acquainted with chemists Torbern Bergman and Carl Wilhelm Scheele. 17 ...
and Jöns Jacob Berzelius
Baron Jöns Jacob Berzelius (; by himself and his contemporaries named only Jacob Berzelius, 20 August 1779 – 7 August 1848) was a Swedish chemist. Berzelius is considered, along with Robert Boyle, John Dalton, and Antoine Lavoisier, to be ...
in 1815. It is a relatively common and important rock-making mineral associated with the more silica-rich rock types, in hydrothermal
Hydrothermal circulation in its most general sense is the circulation of hot water (Ancient Greek ὕδωρ, ''water'',Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with th ...
veins, with greenschist facies
Greenschists are metamorphic rocks that formed under the lowest temperatures and pressures usually produced by regional metamorphism, typically and 2–10 kilobars (). Greenschists commonly have an abundance of green minerals such as chlorite, ...
metamorphic rocks, and in pegmatite
A pegmatite is an igneous rock showing a very coarse texture, with large interlocking crystals usually greater in size than and sometimes greater than . Most pegmatites are composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silicic co ...
dikes, often as the variety ''cleavelandite'' and associated with rarer minerals like tourmaline
Tourmaline ( ) is a crystalline silicate mineral group in which boron is compounded with elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium. Tourmaline is a gemstone and can be found in a wide variety of colors.
...
and beryl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2Si6O18. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and aquamarine. Naturally occurring, hexagonal crystals of beryl can be up to several ...
.
Intermediate members
The intermediate members of the plagioclase group are very similar to each other and normally cannot be distinguished except by their optical properties. The specific gravity in each member (albite 2.62) increases 0.02 per 10% increase in anorthite (2.75). *Bytownite
Bytownite is a calcium rich member of the plagioclase solid solution series of feldspar minerals with composition between anorthite and labradorite. It is usually defined as having between 70 and 90% An (formula: (Ca0.7-0.9,Na0.3-0.1) l(Al,Si)Si2O ...
, named after the former name for Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core ...
, Ontario, Canada—Bytown— is a rare mineral occasionally found in more basic rocks.
*Labradorite
Labradorite (( Ca, Na)( Al, Si)4 O8) is a calcium-enriched feldspar mineral first identified in Labrador, Canada, which can display an iridescent effect (schiller).
Labradorite is an intermediate to calcic member of the plagioclase series. It ...
is the characteristic feldspar of the more basic rock types such as gabbro or basalt. Labradorite frequently shows an iridescent
Iridescence (also known as goniochromism) is the phenomenon of certain surfaces that appear to gradually change color as the angle of view or the angle of illumination changes. Examples of iridescence include soap bubbles, feathers, butterfl ...
display of colors due to light refracting within the lamellae of the crystal. It is named after Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
, where it is a constituent of the intrusive igneous rock anorthosite
Anorthosite () is a phaneritic, intrusive igneous rock characterized by its composition: mostly plagioclase feldspar (90–100%), with a minimal mafic component (0–10%). Pyroxene, ilmenite, magnetite, and olivine are the mafic minerals most ...
which is composed almost entirely of plagioclase. A variety of labradorite known as spectrolite is found in Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bo ...
.Michael O'Donoghue, ''Gems'', Butterworth-Heinemann, 6th ed., 2006, pp. 238-267, Walter Schumann, ''Gemstones of the World,'' Sterling, 3rd ed., 2007, pp. 52 - 53, 182
* Andesine is a characteristic mineral of rocks such as diorite which contain a moderate amount of silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is o ...
and related volcanics
Volcanic rock (often shortened to volcanics in scientific contexts) is a rock formed from lava erupted from a volcano. In other words, it differs from other igneous rock by being of volcanic origin. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic r ...
such as andesite
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predomina ...
.
*Oligoclase
Oligoclase is a rock-forming mineral belonging to the plagioclase feldspars. In chemical composition and in its crystallographic and physical characters it is intermediate between albite ( Na Al Si3 O8) and anorthite ( CaAl2Si2O8). The albite:an ...
is common in granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies und ...
and monzonite. The name ''oligoclase'' is derived from the Greek ('small, slight') + ('fracture'), in reference to the fact that its cleavage angle differs significantly from 90°. The term was first used by Breithaupt in 1826. Sunstone is mainly oligoclase (sometimes albite) with flakes of hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of ...
.
Petrogenesis

mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks includ ...
rocks formed at low pressure. It is normally the first and most abundant feldspar to crystallize from a cooling primitive magma
In geology, igneous differentiation, or magmatic differentiation, is an umbrella term for the various processes by which magmas undergo bulk chemical change during the partial melting process, cooling, emplacement, or eruption. The sequence of (u ...
. Anorthite has a much higher melting point than albite, and, as a result, calcium-rich plagioclase is the first to crystallize. The plagioclase becomes more enriched in sodium as the temperature drops, forming Bowen's continuous reaction series. However, the composition with which plagioclase crystallizes also depends on the other components of the melt, so it is not by itself a reliable thermometer.
The liquidus
The liquidus temperature, TL or Tliq, specifies the temperature above which a material is completely liquid, and the maximum temperature at which crystals can co-exist with the melt in thermodynamic equilibrium. It is mostly used for impure subst ...
of plagioclase (the temperature at which the plagioclase first begins to crystallize) is about for olivine basalt, with a composition of 50.5 wt% silica; in andesite
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predomina ...
with a silica content of 60.7 wt%; and in dacite
Dacite () is a volcanic rock formed by rapid solidification of lava that is high in silica and low in alkali metal oxides. It has a fine-grained ( aphanitic) to porphyritic texture and is intermediate in composition between andesite and rhy ...
with a silica content of 69.9 wt%. These values are for dry magma. The liquidus is greatly lowered by the addition of water, and much more for plagioclase than for mafic minerals. The eutectic (minimum melting mixture) for a mixture of anorthite and diopside
Diopside is a monoclinic pyroxene mineral with composition . It forms complete solid solution series with hedenbergite () and augite, and partial solid solutions with orthopyroxene and pigeonite. It forms variably colored, but typically dul ...
shifts from 40 wt% anorthite to 78 wt% anorthite as the water vapor pressure goes from 1 bar to 10 kbar. The presence of water also shifts the composition of the crystallizing plagioclase towards anorthite. The eutectic for this wet mixture drops to about .
Crystallizing plagioclase is always richer in anorthite than the melt from which it crystallizes. This ''plagioclase effect'' causes the residual melt to be enriched in sodium and silicon and depleted in aluminium and calcium. However, the simultaneous crystallization of mafic minerals not containing aluminium can partially offset the depletion in aluminium. In volcanic rock, the crystallized plagioclase incorporates most of the potassium in the melt as a trace element.
New plagioclase crystals nucleate only with difficulty, and diffusion is very slow within the solid crystals. As a result, as a magma cools, increasingly sodium-rich plagioclase is usually crystallized onto the rims of existing plagioclase crystals, which retain their more calcium-rich cores. This results in compositional zoning of plagioclase in igneous rocks. In rare cases, plagioclase shows reverse zoning, with a more calcium-rich rim on a more sodium-rich core. Plagioclase also sometimes shows oscillatory zoning, with the zones fluctuating between sodium-rich and calcium-rich compositions, though this is usually superimposed on an overall normal zoning trend.
Classification of igneous rocks
Plagioclase is very important for the classification of crystalline igneous rocks. Generally, the more silica is present in the rock, the fewer the mafic minerals, and the more sodium-rich the plagioclase. Alkali feldspar appears as the silica content becomes high. Under the QAPF classification, plagioclase is one of the three key minerals, along with quartz and alkali feldspar, used to make the initial classification of the rock type. Low-silica igneous rocks are further divided into dioritic rocks having sodium-rich plagioclase (An<50) andgabbro
Gabbro () is a phaneritic (coarse-grained), mafic intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling of magnesium-rich and iron-rich magma into a holocrystalline mass deep beneath the Earth's surface. Slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro is ...
ic rocks having calcium-rich plagioclase (An>50). Anorthosite
Anorthosite () is a phaneritic, intrusive igneous rock characterized by its composition: mostly plagioclase feldspar (90–100%), with a minimal mafic component (0–10%). Pyroxene, ilmenite, magnetite, and olivine are the mafic minerals most ...
is an intrusive rock
Intrusive rock is formed when magma penetrates existing rock, crystallizes, and solidifies underground to form '' intrusions'', such as batholiths, dikes, sills, laccoliths, and volcanic necks.Intrusive RocksIntrusive rocks accessdate: Marc ...
composed of at least 90% plagioclase.
Albite is an end member of both the alkali and plagioclase series. However, it is included in the alkali feldspar fraction of the rock in the QAPF classification.
In metamorphic rocks
Plagioclase is also common in metamorphic rock. Plagioclase tends to be albite in low-grade metamorphic rock, while oligoclase to andesine are more common in medium- to high-grade metamorphic rock. Metacarbonate rock sometimes contains fairly pure anorthite.In sedimentary rocks
Feldspar makes up between 10 and 20 percent of the framework grains in typicalsandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
s. Alkali feldspar is usually more abundant than plagioclase in sandstone because Alkali feldspars are more resistant to chemical weathering and more stable, but sandstone derived from volcanic rock contains more plagioclase. Plagioclase weathers relatively rapidly to clay minerals
Clay minerals are hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates (e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4), sometimes with variable amounts of iron, magnesium, alkali metals, alkaline earths, and other cations found on or near some planetary surfaces.
Clay mineral ...
such as smectite.
At the Mohorovičić discontinuity
TheMohorovičić discontinuity
The Mohorovičić discontinuity ( , ), usually referred to as the Moho discontinuity or the Moho, is the boundary between the Earth's crust and the mantle. It is defined by the distinct change in velocity of seismic waves as they pass through ch ...
, which defines the boundary between the Earth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The ...
and the upper mantle, is thought to be the depth where feldspar disappears from the rock. While plagioclase is the most important aluminium-bearing mineral in the crust, it breaks down at the high pressure of the upper mantle, with the aluminium tending to be incorporated into clinopyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe II) ...
as ''Tschermak's molecule'' () or in jadeite
Jadeite is a pyroxene mineral with composition Na Al Si2 O6. It is hard (Mohs hardness of about 6.5 to 7.0), very tough, and dense, with a specific gravity of about 3.4. It is found in a wide range of colors, but is most often found in shades ...
. At still higher pressure, the aluminium is incorporated into garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different ...
.
Exsolution
At very high temperatures, plagioclase forms a solid solution with potassium feldspar, but this becomes highly unstable on cooling. The plagioclase separates from the potassium feldspar, a process called ''exsolution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogenous mixture of two different kinds of atoms in solid state and have a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The word ...
''. The resulting rock, in which fine streaks of plagioclase (''lamellae'') are present in potassium feldspar, is called perthite.
The solid solution between anorthite and albite remains stable to lower temperatures, but ultimately becomes unstable as the rock approaches ambient surface temperatures. The resulting exsolution results in very fine lamellar and other intergrowths, normally detected only by sophisticated means. However, exsolution in the andesite to labradorite compositional range sometimes produces lamellae with thicknesses comparable to the wavelength of visible light. This acts like a diffraction grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure that diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions (i.e., different diffraction angles). The emerging coloration is a form of structural ...
, causing the labradorite to show the beautiful play of colors known as ''chatoyance
In gemology, chatoyancy ( ), or chatoyance or cat's eye effect, is an optical reflectance effect seen in certain gemstones, woods, and carbon fibre. Coined from the French "œil de chat", meaning "cat's eye", chatoyancy arises either from the ...
''.
Uses
In addition to its importance to geologists in classifying igneous rocks, plagioclase finds practical use asconstruction aggregate
Construction aggregate, or simply aggregate, is a broad category of coarse- to medium-grained particulate material used in construction, including sand, gravel, crushed stone, slag, recycled concrete and geosynthetic aggregates. Aggregate ...
, as dimension stone
Dimension stone is natural stone or rock that has been selected and finished (e.g., trimmed, cut, drilled, ground, or other) to specific sizes or shapes. Color, texture and pattern, and surface finish of the stone are also normal requirements. ...
, and in powdered form as a filler in paint, plastics, and rubber. Sodium-rich plagioclase finds use in the manufacture of glass and ceramics.
Anorthosite could someday be important as a source of aluminium.
See also
*Hypersolvus
In hypersolvus granites, as used by Tuttle and Bowen in 1958,TUTTLE O.F. & BOWEN N.L. (1958): Origin of granite in the light of experimental studies in the system NaAlSi3O8-KAlSi3O8-SiO2-H2O, ''Geological Society of America Memoirs'', 74, 153 p cry ...
*List of minerals
This is a list of minerals for which there are articles on Wikipedia.
Minerals are distinguished by various chemical and physical properties. Differences in chemical composition and crystal structure distinguish the various ''species''. Within a m ...
*Subsolvus
In subsolvus or ''two feldspar'' granites crystallisation occurs at high water pressures resulting in the formation of two types of feldspar as opposed to hypersolvus granites in which crystallization at relatively low water pressures results in t ...
*Planetary differentiation
In planetary science, planetary differentiation is the process by which the chemical elements of a planetary body accumulate in different areas of that body, due to their physical or chemical behavior (e.g. density and chemical affinities). The p ...
References
External links
{{Authority control Sodium minerals Aluminium minerals Calcium minerals Tectosilicates Feldspar Triclinic minerals Minerals in space group 2 de:Feldspat#Plagioklase