|
Exsolution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogeneous mixture of two compounds in solid state and having a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The word "solution" is used to describe the intimate mixing of components at the atomic level and distinguishes these homogeneous materials from physical mixtures of components. Two terms are mainly associated with solid solutions – ''solvents'' and ''solutes,'' depending on the relative abundance of the atomic species. In general if two compounds are isostructural then a solid solution will exist between the end members (also known as parents). For example sodium chloride and potassium chloride have the same cubic crystal structure so it is possible to make a pure compound with any ratio of sodium to potassium (Na1-xKx)Cl by dissolving that ratio of NaCl and KCl in water and then evaporating the solution. A member of this family is sold under the brand na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Solution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogeneous mixture of two compounds in solid state and having a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The word "solution" is used to describe the intimate mixing of components at the atomic level and distinguishes these homogeneous materials from physical mixtures of components. Two terms are mainly associated with solid solutions – ''solvents'' and ''solutes,'' depending on the relative abundance of the atomic species. In general if two compounds are isostructural then a solid solution will exist between the end members (also known as parents). For example sodium chloride and potassium chloride have the same cubic crystal structure so it is possible to make a pure compound with any ratio of sodium to potassium (Na1-xKx)Cl by dissolving that ratio of NaCl and KCl in water and then evaporating the solution. A member of this family is sold under the bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is the foundation of all quantum physics, which includes quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Quantum mechanics can describe many systems that classical physics cannot. Classical physics can describe many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic and Microscopic scale, (optical) microscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at very small submicroscopic (atomic and subatomic) scales. Classical mechanics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation that is valid at ordinary scales. Quantum systems have Bound state, bound states that are Quantization (physics), quantized to Discrete mathematics, discrete values of energy, momentum, angular momentum, and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallography
Crystallography is the branch of science devoted to the study of molecular and crystalline structure and properties. The word ''crystallography'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (; "clear ice, rock-crystal"), and (; "to write"). In July 2012, the United Nations recognised the importance of the science of crystallography by proclaiming 2014 the International Year of Crystallography.UN announcement "International Year of Crystallography" iycr2014.org. 12 July 2012 Crystallography is a broad topic, and many of its subareas, such as X-ray crystallography, are themselves important scientific topics. Crystallography ranges from the fundamentals of crystal structure to the mathematics of Crystal system, crystal geometry, including those that are Aperiodic crystal, not periodic or quasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during chemical reaction, reactions with other chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegard's Law
In crystallography, materials science and metallurgy, Vegard's law is an empirical finding (heuristic approach) resembling the rule of mixtures. In 1921, Lars Vegard discovered that the lattice parameter of a solid solution of two constituents is approximately a weighted mean of the two constituents' lattice parameters at the same temperature: :a_ = (1-x)\ a_\mathrm + x\ a_\mathrm ''e.g.'', in the case of a mixed oxide of uranium and plutonium as used in the fabrication of MOX nuclear fuel: :a_\mathrm = 0.93\ a_\mathrm + 0.07\ a_\mathrm Vegard's law assumes that both components A and B in their pure form (''i.e.'', before mixing) have the same crystal structure. Here, is the lattice parameter of the solid solution, and are the lattice parameters of the pure constituents, and is the molar fraction of B in the solid solution. Vegard's law is seldom perfectly obeyed; often deviations from the linear behavior are observed. A detailed study of such deviations was conducted by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
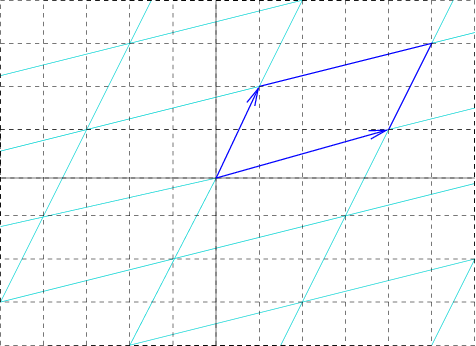
Unit Cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector In mathematics, a unit vector in a normed vector space is a Vector (mathematics and physics), vector (often a vector (geometry), spatial vector) of Norm (mathematics), length 1. A unit vector is often denoted by a lowercase letter with a circumfle ..., for example) does not necessarily have unit size, or even a particular size at all. Rather, the primitive cell is the closest analogy to a unit vector, since it has a determined size for a given lattice and is the basic building block from which larger cells are constructed. The concept is used particularly in describing crystal structure in two and three dimensions, though it makes sense in all dimensions. A lattice can be characterized by the geometry of its unit cell, which is a section of the tiling (a parallelogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstitial Defect
In materials science, an interstitial defect is a type of point crystallographic defect where an atom of the same or of a different type, occupies an interstitial site in the crystal structure. When the atom is of the same type as those already present they are known as a self-interstitial defect. Alternatively, small atoms in some crystals may occupy interstitial sites, such as hydrogen in palladium. Interstitials can be produced by bombarding a crystal with elementary particles having energy above the displacement threshold for that crystal, but they may also exist in small concentrations in thermodynamic equilibrium. The presence of interstitial defects can modify the physical and chemical properties of a material. History The idea of interstitial compounds was started in the late 1930s and they are often called Hagg phases after Hägg. Transition metals generally crystallise in either the hexagonal close packed or face centered cubic structures, both of which can be conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallographic Defect
A crystallographic defect is an interruption of the regular patterns of arrangement of atoms or molecules in Crystal, crystalline solids. The positions and orientations of particles, which are repeating at fixed distances determined by the Crystal structure#unit cell, unit cell parameters in crystals, exhibit a periodic crystal structure, but this is usually imperfect.Ehrhart, P. (1991Properties and interactions of atomic defects in metals and alloys, volume 25 of Landolt-Börnstein, New Series III, chapter 2, p. 88, Springer, Berlin Several types of defects are often characterized: point defects, line defects, planar defects, bulk defects. Topological homotopy establishes a mathematical method of characterization. Point defects Point defects are defects that occur only at or around a single lattice point. They are not extended in space in any dimension. Strict limits for how small a point defect is are generally not defined explicitly. However, these defects typically involve at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Lattice
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystal, crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of Three-dimensional space (mathematics), three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in a material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive Translation (geometry), translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of principal axes/edges, of the unit cell and angles between them are lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of a crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
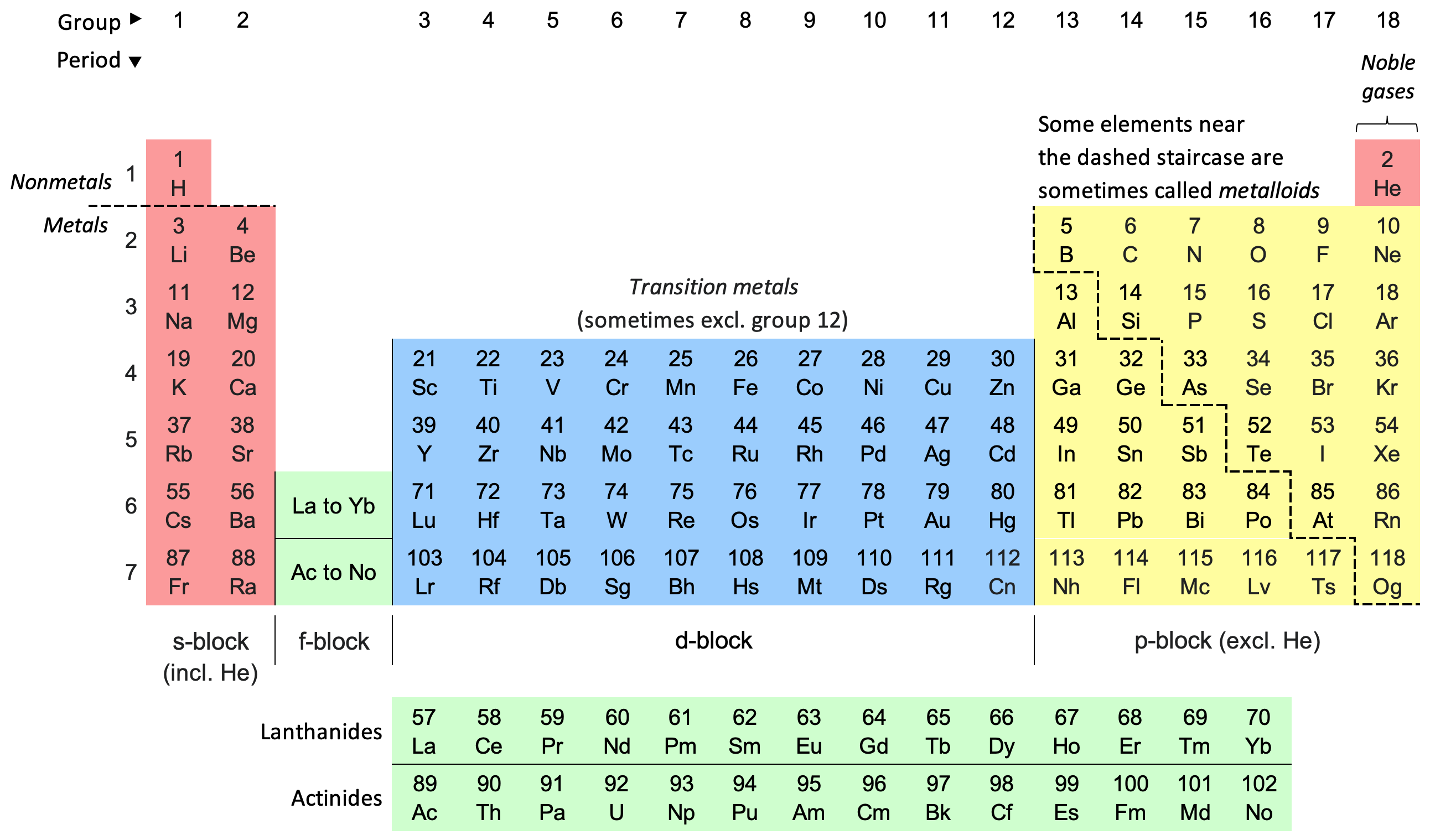
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics. Vertical, horizontal and diagonal trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and from right to left across a period. Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top right. The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869; he formulated the periodic law as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against nonmetallic materials which do not. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into a wire) and malleable (can be shaped via hammering or pressing). A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polythiazyl, polymeric sulfur nitride. The general science of metals is called metallurgy, a subtopic of materials science; aspects of the electronic and thermal properties are also within the scope of condensed matter physics and solid-state chemistry, it is a multidisciplinary topic. In colloquial use materials such as steel alloys are referred to as metals, while others such as polymers, wood or ceramics are nonmetallic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |