Pirogue 2650 Carnavalet 2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
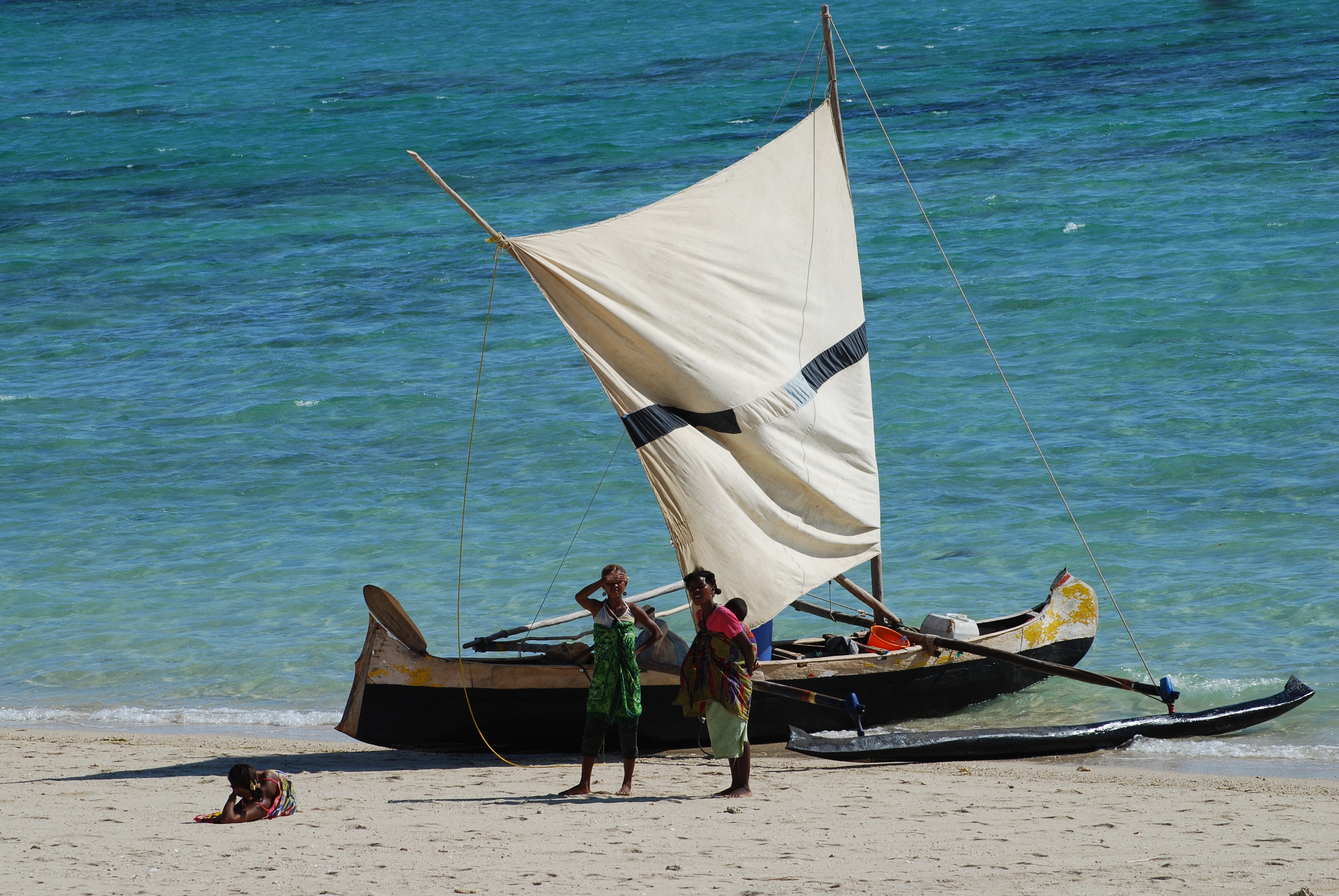


 A pirogue ( or ), also called a piragua or piraga, is any of various small
A pirogue ( or ), also called a piragua or piraga, is any of various small
 In 626, when the Avars were besieging
In 626, when the Avars were besieging "Pirogues"
''Discovering Lewis & Clark'', The Lewis and Clark Fort Mandan Foundation, 2009
Pirogues: time-tested craft for hunters and fishermen
{{Use dmy dates, date=March 2017 Types of fishing vessels Cajun West Africa Symbols of Illinois
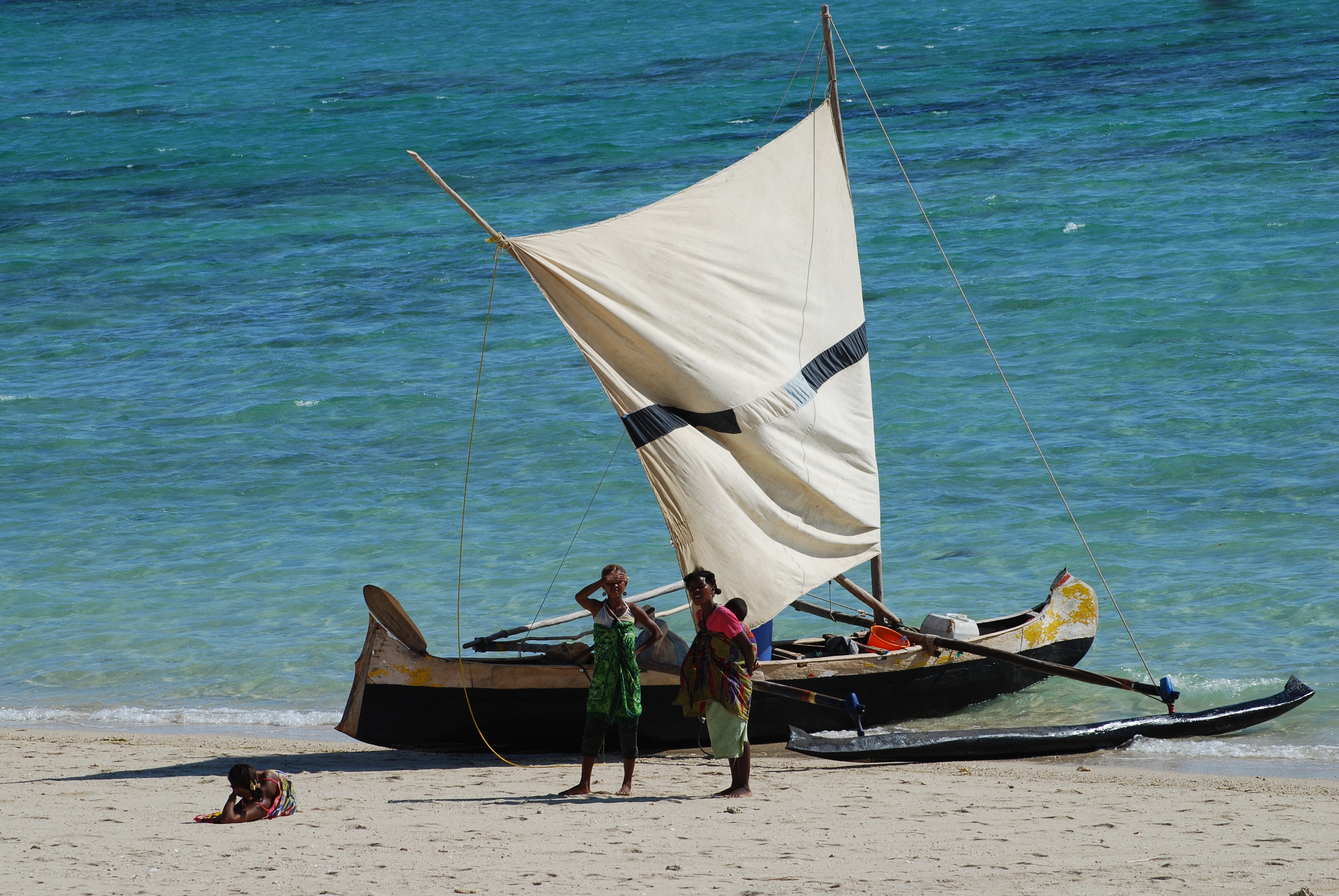


 A pirogue ( or ), also called a piragua or piraga, is any of various small
A pirogue ( or ), also called a piragua or piraga, is any of various small boat
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size, shape, cargo or passenger capacity, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically found on inl ...
s, particularly dugouts
Dugout may refer to:
* Dugout (shelter), an underground shelter
* Dugout (boat), a logboat
* Dugout (smoking), a marijuana container
Sports
* In bat-and-ball sports, a dugout is one of two areas where players of the home or opposing teams sit whe ...
and native canoe
A canoe is a lightweight narrow water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using a single-bladed paddle.
In British English, the term ...
s. The word is French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and is derived from Spanish , which comes from the Carib '.Description
The term 'pirogue' does not refer to a specific kind of boat, but is a generic term for small native boats in regions once colonized byFrance
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, particularly dugouts made from a single log. In French West Africa
French West Africa (french: Afrique-Occidentale française, ) was a federation of eight French colonial territories in West Africa: Mauritania, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guinea (now Guinea), Ivory Coast, Upper Volta (now Burki ...
, the term refers to handcrafted banana-shaped boats used by traditional fishermen. In Madagascar, it also includes the more elaborate Austronesian '' lakana'' outrigger canoe.
Pirogues are usually propelled by paddles
A paddle is a handheld tool with an elongated handle and a flat, widened distal end (i.e. the ''blade''), used as a lever to apply force onto the bladed end. It most commonly describes a completely handheld tool used to propel a human-powered wa ...
that have one blade (as opposed to a kayak paddle, which has two). It can also be punted with a push pole in shallow water. Small sails are built by local fishermen, and they can also be employed. There are two types of sails with differences in their shapes: the square one is used mainly for fishing near the coast and is only useful for Tailwind, while the triangular-shaped ones are used to transfer goods from one place to another by maintaining a bowline direction. Outboard motors are increasingly being used in many regions.
Uses in military and piracy contexts
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, the Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
crossed the Golden Horn in their pirogues and landed on the shore of the Lower Blachernae
Blachernae ( gkm, Βλαχέρναι) was a suburb in the northwestern section of Constantinople, the capital city of the Byzantine Empire. It is the site of a water source and a number of prominent churches were built there, most notably the great ...
, and in spite of all defensive measures that were taken, looted churches.
There are accounts of 17th and 18th century Caribbean pirates
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
using pirogues to attack and take by force much larger vessels including sloop
A sloop is a sailboat with a single mast typically having only one headsail in front of the mast and one mainsail aft of (behind) the mast. Such an arrangement is called a fore-and-aft rig, and can be rigged as a Bermuda rig with triangular sa ...
s and even barca-longa
A barca-longa (1600s, also barqua-; 1600s–1700s barco-longo) was a two- or three-masted lugger used near the coasts of Spain and Portugal, and more widely in the Mediterranean Sea. Barca-longas were used in Spain and Portugal for fishing, and we ...
s. Pirogues were used extensively by pirates and buccaneer
Buccaneers were a kind of privateers or free sailors particular to the Caribbean Sea during the 17th and 18th centuries. First established on northern Hispaniola as early as 1625, their heyday was from Stuart Restoration, the Restoration in 16 ...
s throughout the Caribbean, the now-Mexican and Gulf Coasts and the East Coast of what is now the United States. For the most part, though, such vessels were used for scouting or as tenders.
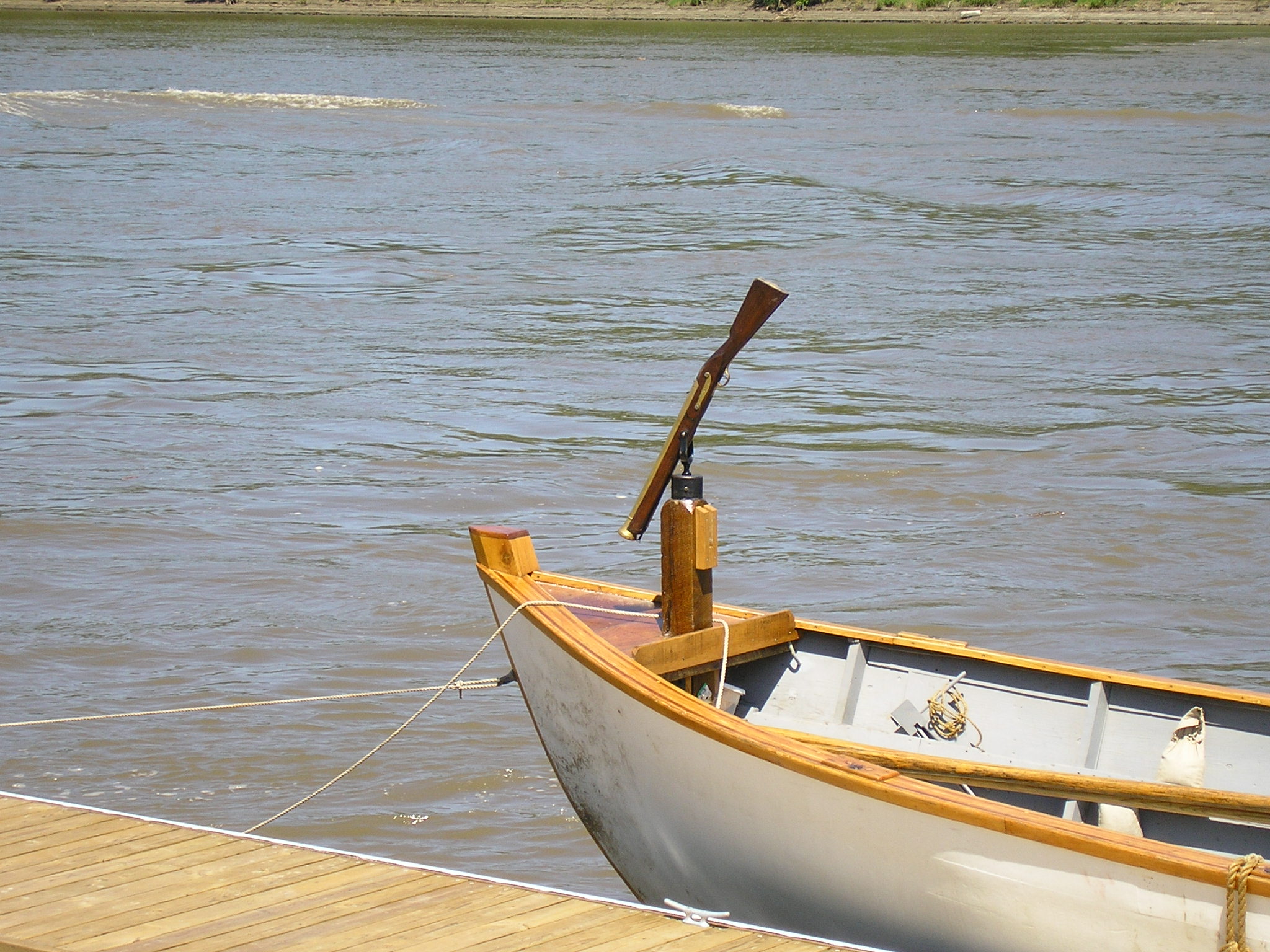
Pirogues were used by Lewis and Clark on the Missouri River and westward from 1804–1806, in addition to bateaux, larger flat-bottomed boats that could only be used in large rivers. Their pirogues were medium-sized boats of the company carrying eight rowers and a pilot, capable of carrying eight tons of cargo.''Discovering Lewis & Clark'', The Lewis and Clark Fort Mandan Foundation, 2009
Henry D. Thoreau
Henry David Thoreau (July 12, 1817May 6, 1862) was an American naturalist, essayist, poet, and philosopher. A leading transcendentalist, he is best known for his book ''Walden'', a reflection upon simple living in natural surroundings, and ...
writes of using heavy pirogues in his book ''The Maine Woods''.
Louisiana
Pirogues in theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
are associated particularly with the Cajuns of the Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
marsh. The early Creole pirogues were cypress dugouts but today they are usually flat-bottomed boats. Pirogues are not usually intended for overnight travel but are light and small enough to be easily taken onto land. The design also allows the pirogue to move through the very shallow water of marshes and be easily turned over to drain any water that may get into the boat. A pirogue has "hard chines" which means that instead of a smooth curve from the gunwales to the keel, there is often a flat bottom which meets the plane of the side.
In his 1952 classic song "Jambalaya
Jambalaya ( , ) is an American Creole and Cajun rice dish of French (especially Provençal cuisine), African, and Spanish influence, consisting mainly of meat and vegetables mixed with rice.
Ingredients
Traditionally, the meat includes sau ...
", Hank Williams
Hank Williams (born Hiram Williams; September 17, 1923 – January 1, 1953) was an American singer, songwriter, and musician. Regarded as one of the most significant and influential American singers and songwriters of the 20th century, he reco ...
refers to the pirogue in the line "me gotta go pole the pirogue down the bayou". Johnny Horton
John LaGale Horton (April 30, 1925 – November 5, 1960) was an American singer-songwriter and musician. Initially performing traditional country, Horton later performed rockabilly songs. He is best known for a series of history-inspired narrat ...
, an avid Louisiana fisherman who celebrated Cajun customs and culture, also mentions pirogues in his 1956 song "I Got a Hole in My Pirogue". Hank Williams, Jr.
Randall Hank Williams (born May 26, 1949), known professionally as Hank Williams Jr. or Bocephus, is an American singer-songwriter and musician. His musical style is often considered a blend of southern rock, blues, and country. He is the son of ...
(son of the aforementioned Hank Williams) had a hit song in 1969 "Cajun Baby", which refers to the pirogue in the line "ride around in my old pirogue".
Doug Kershaw
Douglas James Kershaw (born January 24, 1936) is an American fiddle player, singer and songwriter from Louisiana. Active since 1948, he began his career as part of the duo Rusty and Doug, along with his brother, Rusty Kershaw. He had an extens ...
's 1961 hit "Louisiana Man" includes the line "he jumps in his pirogue headed down the bayou". Many online lyrics sites misunderstand this line, saying 'hero' or sometimes 'biro' instead.
See also
* Periagua, a cognate which became applied to a different kind of sailing vessel in the 18th century *Perahu
Proas are various types of multi-hull outrigger sailboats of the Austronesian peoples. The terms were used for native Austronesian ships in European records during the Colonial era indiscriminately, and thus can confusingly refer to the do ...
* Mackinaw boat
The Mackinaw boat is a loose, non-standardized term for a light, open sailboat used in the interior of North America during the fur trading era. Within this term two different ''Mackinaw boats'' evolved: one for use on the upper Great Lakes, and t ...
References
External links
Pirogues: time-tested craft for hunters and fishermen
{{Use dmy dates, date=March 2017 Types of fishing vessels Cajun West Africa Symbols of Illinois