Pickering's Triangle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
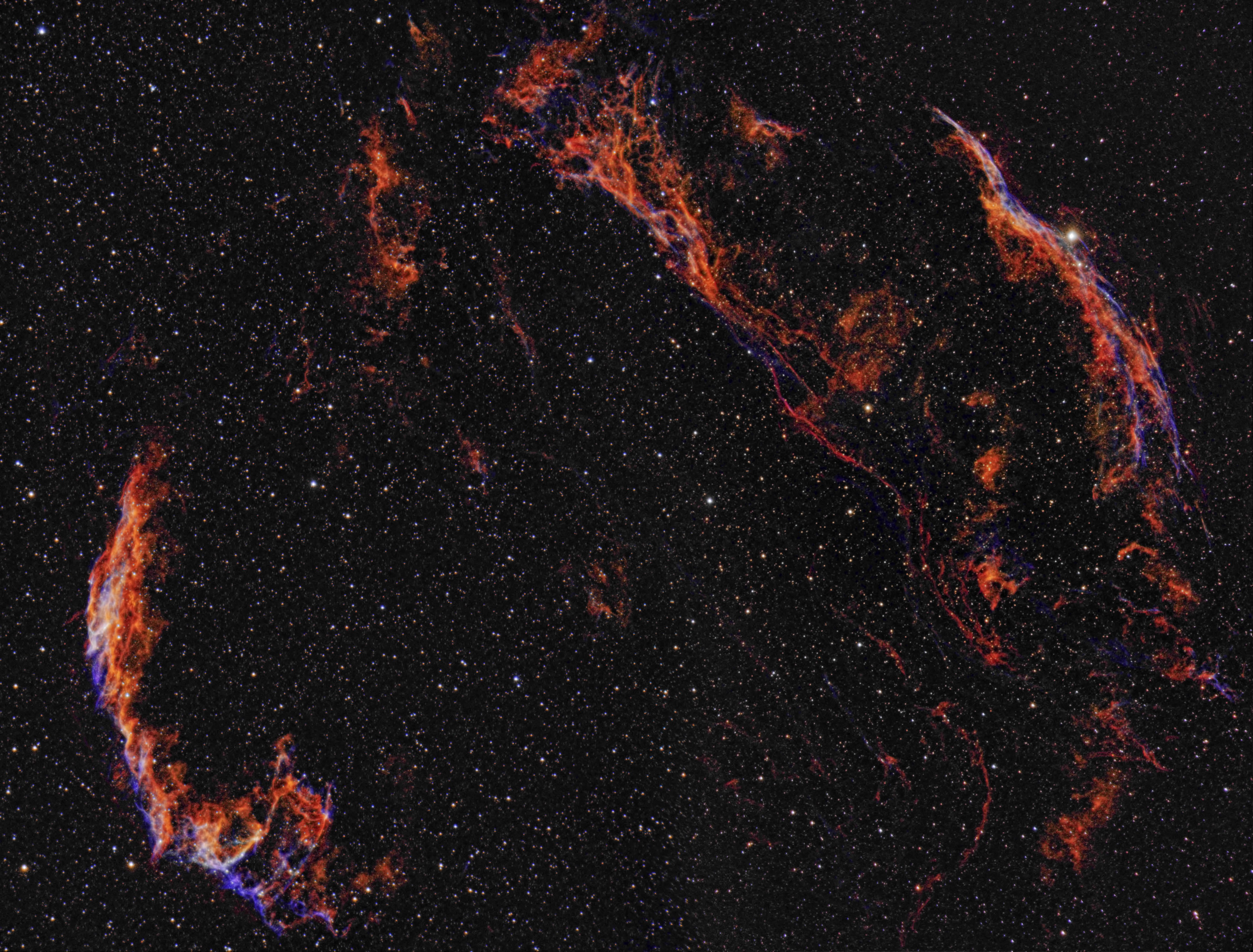 The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and and dust in the constellation Cygnus.
It constitutes the visible portions of the
The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and and dust in the constellation Cygnus.
It constitutes the visible portions of the
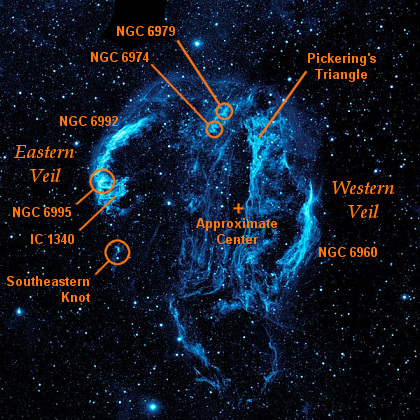 In modern usage, the names ''Veil Nebula'', ''Cirrus Nebula'', and ''Filamentary Nebula'' generally refer to all the visible structure of the remnant, or even to the entire loop itself. The structure is so large that several NGC numbers were assigned to various arcs of the nebula.
There are three main visual components:
* The Western Veil (also known as Caldwell 34), consisting of NGC 6960 (the "Witch's Broom",
Lacework Nebula,
"Filamentary Nebula") near the foreground star
In modern usage, the names ''Veil Nebula'', ''Cirrus Nebula'', and ''Filamentary Nebula'' generally refer to all the visible structure of the remnant, or even to the entire loop itself. The structure is so large that several NGC numbers were assigned to various arcs of the nebula.
There are three main visual components:
* The Western Veil (also known as Caldwell 34), consisting of NGC 6960 (the "Witch's Broom",
Lacework Nebula,
"Filamentary Nebula") near the foreground star
 Even though the nebula has a relatively bright integrated magnitude of 7, it is spread over so large an area that the surface brightness is quite low, so the nebula is notorious among astronomers as being difficult to see. However, an observer can see the nebula clearly in a telescope using an O-III astronomical filter (isolating the wavelength of light from doubly ionized oxygen), as almost all light from this nebula is emitted at this wavelength. An telescope equipped with an O-III filter shows the delicate lacework apparent in photographs. Smaller telescopes with an O-III filter can show the nebula as well, and some argue that it can be seen without any optical aid except an O-III filter held up to the eye.
The brighter segments of the nebula have the
Even though the nebula has a relatively bright integrated magnitude of 7, it is spread over so large an area that the surface brightness is quite low, so the nebula is notorious among astronomers as being difficult to see. However, an observer can see the nebula clearly in a telescope using an O-III astronomical filter (isolating the wavelength of light from doubly ionized oxygen), as almost all light from this nebula is emitted at this wavelength. An telescope equipped with an O-III filter shows the delicate lacework apparent in photographs. Smaller telescopes with an O-III filter can show the nebula as well, and some argue that it can be seen without any optical aid except an O-III filter held up to the eye.
The brighter segments of the nebula have the
File:Eastern Veil.jpg, ''Eastern Veil, wide view, amateur equipment ''(NGC6992)
File:EasternveilBicolorHunterWilson.jpg, ''Eastern Veil'' (NGC 6992/95)
File:Veil Nebula 800x600.jpg, ''Eastern Veil Detail'' (NGC6992)
File:PickeringHunterWilson.jpg, ''Pickering's (Fleming's) Triangular Wisp''
File:Veil Nebula - NGC6960.jpg, ''Western Veil'' (NGC 6960)
File:Close-up Veil Nebula.jpg, Detail of the Veil Nebula.
File:Veil Nebula by Hubble 2007, segment 2.jpg, Portion photographed by Hubble Space Telescope
File:Revisiting the Veil Nebula.jpg, Veil Nebula observed by Hubble Space Telescope.
File:Ultraviolet image of the Cygnus Loop Nebula crop.jpg, A broad view of Cygnus loop/Veil nebula in ultraviolet
File:Pickering's Triangle in Veil nebula.jpg, alt=, Pickering's Triangle in Veil nebula
IC 1340, photograph
– by David Malin, Australian Astronomical Observatory
– spacetelescope.com, with several Hubble Space Telescope photos
– Nebulae in the Northern Cross, showing Veil Nebula to scale in Cygnus
– Photo of the entire Veil Nebula
– NGC 6992: Filaments of the Veil Nebula
– Filaments in the Cygnus Loop
– Shockwaves in the Cygnus Loop (an
underlying HST photo
– Bill Blair (Johns Hopkins University)
– Bill Blair (Johns Hopkins University)
Bill Blair
(Johns Hopkins University) – Overview photo of Cygnus Loop and Veil Nebula *
Veil Nebula
at Constellation Guide {{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System 17840905 033b Cygnus (constellation) NGC objects Supernova remnants
 The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and and dust in the constellation Cygnus.
It constitutes the visible portions of the
The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and and dust in the constellation Cygnus.
It constitutes the visible portions of the Cygnus Loop
The Cygnus Loop (radio source W78, or Sharpless 103) is a large supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cygnus (constellation), Cygnus, an emission nebula measuring nearly 3° across. Some arcs of the loop, known collectively as the Veil Nebul ...
,
a supernova remnant, many portions of which have acquired their own individual names and catalogue identifiers. The source supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when ...
was a star 20 times more massive than the Sun which exploded between 10,000 and 20,000 years ago. At the time of explosion, the supernova would have appeared brighter than Venus in the sky, and visible in daytime. The remnants have since expanded to cover an area of the sky roughly 3 degrees in diameter (about 6 times the diameter, and 36 times the area, of the full Moon). While previous distance estimates have ranged from 1200 to 5800 light-years, a recent determination of 2400 light-years is based on direct astrometric measurements. (The distance estimates affect also the estimates of size and age.)
The Hubble Space Telescope captured several images of the nebula
A nebula ('cloud' or 'fog' in Latin; pl. nebulae, nebulæ or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regio ...
. The analysis of the emissions
Emission may refer to:
Chemical products
* Emission of air pollutants, notably:
**Flue gas, gas exiting to the atmosphere via a flue
** Exhaust gas, flue gas generated by fuel combustion
** Emission of greenhouse gases, which absorb and emit rad ...
from the nebula indicates the presence of oxygen, sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
, and hydrogen. The Cygnus Loop is also a strong emitter of radio wave
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz (GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (short ...
s and x-rays.
On 24 September 2015 new images and videos of the Veil Nebula were released by the Space Telescope Science Institute, with an explanation of the images.
Components
 In modern usage, the names ''Veil Nebula'', ''Cirrus Nebula'', and ''Filamentary Nebula'' generally refer to all the visible structure of the remnant, or even to the entire loop itself. The structure is so large that several NGC numbers were assigned to various arcs of the nebula.
There are three main visual components:
* The Western Veil (also known as Caldwell 34), consisting of NGC 6960 (the "Witch's Broom",
Lacework Nebula,
"Filamentary Nebula") near the foreground star
In modern usage, the names ''Veil Nebula'', ''Cirrus Nebula'', and ''Filamentary Nebula'' generally refer to all the visible structure of the remnant, or even to the entire loop itself. The structure is so large that several NGC numbers were assigned to various arcs of the nebula.
There are three main visual components:
* The Western Veil (also known as Caldwell 34), consisting of NGC 6960 (the "Witch's Broom",
Lacework Nebula,
"Filamentary Nebula") near the foreground star 52 Cygni
52 Cygni is a giant star in the northern constellation of Cygnus with an apparent magnitude of 4.22. Based on its Hipparcos parallax, it is about away.
52 Cygni is a probable horizontal branch (red clump) star, fusing helium in its c ...
;
* The Eastern Veil (also known as Caldwell 33), whose brightest area is NGC 6992, trailing off farther south into NGC 6995 (together with NGC 6992 also known as "Network Nebula") and IC 1340; and
* Pickering's Triangle (or Pickering's Triangular Wisp), brightest at the north central edge of the loop, but visible in photographs continuing toward the central area of the loop.
NGC 6974 and NGC 6979 are luminous knots in a fainter patch of nebulosity on the northern rim between NGC 6992 and Pickering's Triangle.
Observation
The nebula was discovered on 5 September 1784 by William Herschel. He described the western end of the nebula as "Extended; passes thro' 52 Cygni... near 2 degree in length", and described the eastern end as "Branching nebulosity ... The following part divides into several streams uniting again towards the south." When finely resolved, some parts of the nebula appear to be rope-like filaments. The standard explanation is that the shock waves are so thin, less than one part in 50,000 of the radius, that the shell is visible only when viewed exactly edge-on, giving the shell the appearance of a filament. At the estimated distance of 2400 light-years, the nebula has a radius of 65 light-years (a diameter of 130 light-years). The thickness of each filament is th of the radius, or about 4 billion miles, roughly the distance from Earth to Pluto. Undulations in the surface of the shell lead to multiple filamentary images, which appear to be intertwined. Even though the nebula has a relatively bright integrated magnitude of 7, it is spread over so large an area that the surface brightness is quite low, so the nebula is notorious among astronomers as being difficult to see. However, an observer can see the nebula clearly in a telescope using an O-III astronomical filter (isolating the wavelength of light from doubly ionized oxygen), as almost all light from this nebula is emitted at this wavelength. An telescope equipped with an O-III filter shows the delicate lacework apparent in photographs. Smaller telescopes with an O-III filter can show the nebula as well, and some argue that it can be seen without any optical aid except an O-III filter held up to the eye.
The brighter segments of the nebula have the
Even though the nebula has a relatively bright integrated magnitude of 7, it is spread over so large an area that the surface brightness is quite low, so the nebula is notorious among astronomers as being difficult to see. However, an observer can see the nebula clearly in a telescope using an O-III astronomical filter (isolating the wavelength of light from doubly ionized oxygen), as almost all light from this nebula is emitted at this wavelength. An telescope equipped with an O-III filter shows the delicate lacework apparent in photographs. Smaller telescopes with an O-III filter can show the nebula as well, and some argue that it can be seen without any optical aid except an O-III filter held up to the eye.
The brighter segments of the nebula have the New General Catalogue
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and ...
designations NGC 6960, 6974, 6979, 6992, and 6995. The easiest segment to find is 6960, which runs behind 52 Cygni
52 Cygni is a giant star in the northern constellation of Cygnus with an apparent magnitude of 4.22. Based on its Hipparcos parallax, it is about away.
52 Cygni is a probable horizontal branch (red clump) star, fusing helium in its c ...
, a star that can be seen with the naked eye. NGC 6992 & 6995 are objects on the eastern side of the loop which are also relatively easy to see. NGC 6974 and NGC 6979 are visible as knots in an area of nebulosity along the northern rim. Pickering's Triangle is much fainter, and has no NGC number (though 6979 is occasionally used to refer to it). It was discovered photographically in 1904 by Williamina Fleming
(15 May 1857 – 21 May 1911) was a Scottish-American astronomer. She was a single mother, hired by the director of the Harvard College Observatory to help in the photographic classification of stellar spectra. She helped develop a common d ...
(after the ''New General Catalogue
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and ...
'' was published), but credit went to Edward Charles Pickering, the director of her observatory, as was the custom of the day.
The Veil Nebula is expanding at a velocity of about 1.5 million kilometers per hour. Using images taken by the Hubble Space Telescope between 1997 and 2015, the expansion of the Veil Nebula has been directly observed.
Gallery
See also
* List of supernova remnantsReferences
External links
IC 1340, photograph
– by David Malin, Australian Astronomical Observatory
– spacetelescope.com, with several Hubble Space Telescope photos
– Nebulae in the Northern Cross, showing Veil Nebula to scale in Cygnus
– Photo of the entire Veil Nebula
– NGC 6992: Filaments of the Veil Nebula
– Filaments in the Cygnus Loop
– Shockwaves in the Cygnus Loop (an
underlying HST photo
– Bill Blair (Johns Hopkins University)
– Bill Blair (Johns Hopkins University)
Bill Blair
(Johns Hopkins University) – Overview photo of Cygnus Loop and Veil Nebula *
Veil Nebula
at Constellation Guide {{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System 17840905 033b Cygnus (constellation) NGC objects Supernova remnants