|
Cygnus Loop
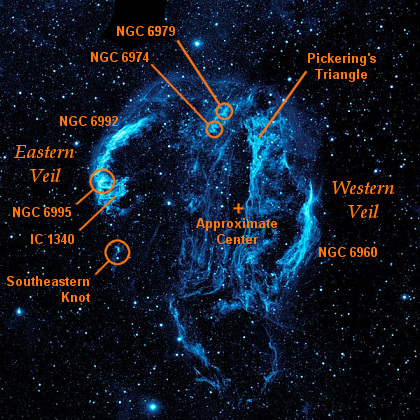
The Cygnus Loop (radio source W78, or Sharpless 103) is a large supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cygnus (constellation), Cygnus, an emission nebula measuring nearly 3° across. Some arcs of the loop, known collectively as the Veil Nebula or Cirrus Nebula, emit in the visible Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic range. Radio, infrared, and X-ray images reveal the complete loop. Visual components: the Veil Nebula The visual portion of the Cygnus Loop is known as the Veil Nebula, also called the Cirrus Nebula or the Filamentary Nebula. Several components have separate names and identifiers, including the "Western Veil" or "Witch's Broom", the "Eastern Veil", and Pickering's Triangle. NGC 6960 NGC 6960, the ''Western Veil'', is the western part of the remnant, also known as the "Witch's Broom", located at J2000 Right ascension, RA Declination, Dec . As the westernmost NGC object in the nebula (first in right ascension), its number is sometimes used as an NG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veil Nebula
The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus. It constitutes the visible portions of the Cygnus Loop, a supernova remnant, many portions of which have acquired their own individual names and catalogue identifiers. The source supernova was a star 20 times more massive than the Sun which exploded between 10,000 and 20,000 years ago. At the time of explosion, the supernova would have appeared brighter than Venus in the sky, and visible in daytime. The remnants have since expanded to cover an area of the sky roughly 3 degrees in diameter (about 6 times the diameter, and 36 times the area, of the full Moon). While previous distance estimates have ranged from 1200 to 5800 light-years, a recent determination of 2400 light-years is based on direct astrometric measurements. (The distance estimates affect also the estimates of size and age.) The Hubble Space Telescope captured several images of the nebul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cygnus Loop Labeled
Cygnus is the Latin word for swan and may refer to: Astronomy * Cygnus (constellation), a northern constellation ** Cygnus A, a radio galaxy within the constellation ** Cygnus X (star complex), a star complex within the constellation ** Cygnus X-1, a binary system within the constellation ** Cygnus X-3, a binary system within the constellation Business & industry * Cygnus 20, a Canadian sailboat design * ''Cygnus'' (spacecraft), a space vehicle developed by Orbital Sciences Corporation and Thales Alenia Space * Cygnus Air or Gestair Cargo, a Spanish cargo airline * Cygnus Business Media, a U.S.-based business-to-business publishing company * Cygnus Solutions, a company that provided commercial support for free software and the original developer of Cygwin Other uses * ''Cygnus'' (genus), the genus of most swans * Cygnus (mythology) or Cycnus, a number of characters in Greek mythology * Cygnus X-1 (song series), a 1977–1978 two-part song series by Rush * Cygnus X (music gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Parsons, 3rd Earl Of Rosse
William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse (17 June 1800 – 31 October 1867), was an Irish astronomer, naturalist, and engineer. He was president of the Royal Society (UK), the most important association of naturalists in the world in the nineteenth century. He built several giant telescopes. His 72-inch telescope, built in 1845 and colloquially known as the "Leviathan of Parsonstown", was the world's largest telescope, in terms of aperture size, until the early 20th century. From April 1807 until February 1841, he was styled as Baron Oxmantown. Life He was born in York, England, the son of Sir Lawrence Parsons, later 2nd Earl of Rosse, and Alice Lloyd. He was educated at Trinity College Dublin and Magdalen College, Oxford, graduating with first-class honours in mathematics in 1822. He inherited an earldom and a large estate in King's County (now County Offaly) in Ireland when his father, Lawrence, 2nd Earl of Rosse, died in February 1841. Lord Rosse married Mary Field, daughter o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einstein Observatory
Einstein Observatory (HEAO-2) was the first fully imaging X-ray telescope put into space and the second of NASA's three High Energy Astrophysical Observatories. Named HEAO B before launch, the observatory's name was changed to honor Albert Einstein upon its successfully attaining orbit. Project conception and design The HEAO Program, High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO) program originated in the late 1960's within the Astronomy Missions Board at NASA, which recommended the launch of a series of satellite observatories dedicated to high-energy astronomy. In 1970, NASA requested proposals for experiments to fly on these observatories, and a team organized by Riccardo Giacconi, Herbert Gursky, George W. Clark, Elihu Boldt, and Robert Novick responded in October 1970 with a proposal for an x-ray telescope. NASA approved four missions in the HEAO program, with the x-ray telescope planned to be the third mission. One of the three missions of the HEAO program was cancelled in F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uhuru (satellite)
Uhuru was the first satellite launched specifically for the purpose of X-ray astronomy. It was also known as the X-ray Explorer Satellite, SAS-A (for Small Astronomy Satellite A, being first of the three-spacecraft SAS series), SAS 1, or Explorer 42. The space observatory, observatory was launched on December 12, 1970 into an initial orbit of about 560 km apogee, 520 km perigee, 3 degrees inclination, with a period of 96 minutes. The mission ended in March 1973. Uhuru was a scanning mission, with a spin period of ~12 minutes. It performed the first comprehensive survey of the entire sky for X-ray sources, with a sensitivity of about 0.001 times the intensity of the Crab nebula. Objectives The main objectives of the mission were: * To survey the sky for cosmic X-ray sources in the 2–20 keV range to a limiting sensitivity of 1.5 × 10−18 joule/(cm2-sec), 5 × 10−4 the flux from the Crab Nebula * To determine discrete source locations with a precision of a few square ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
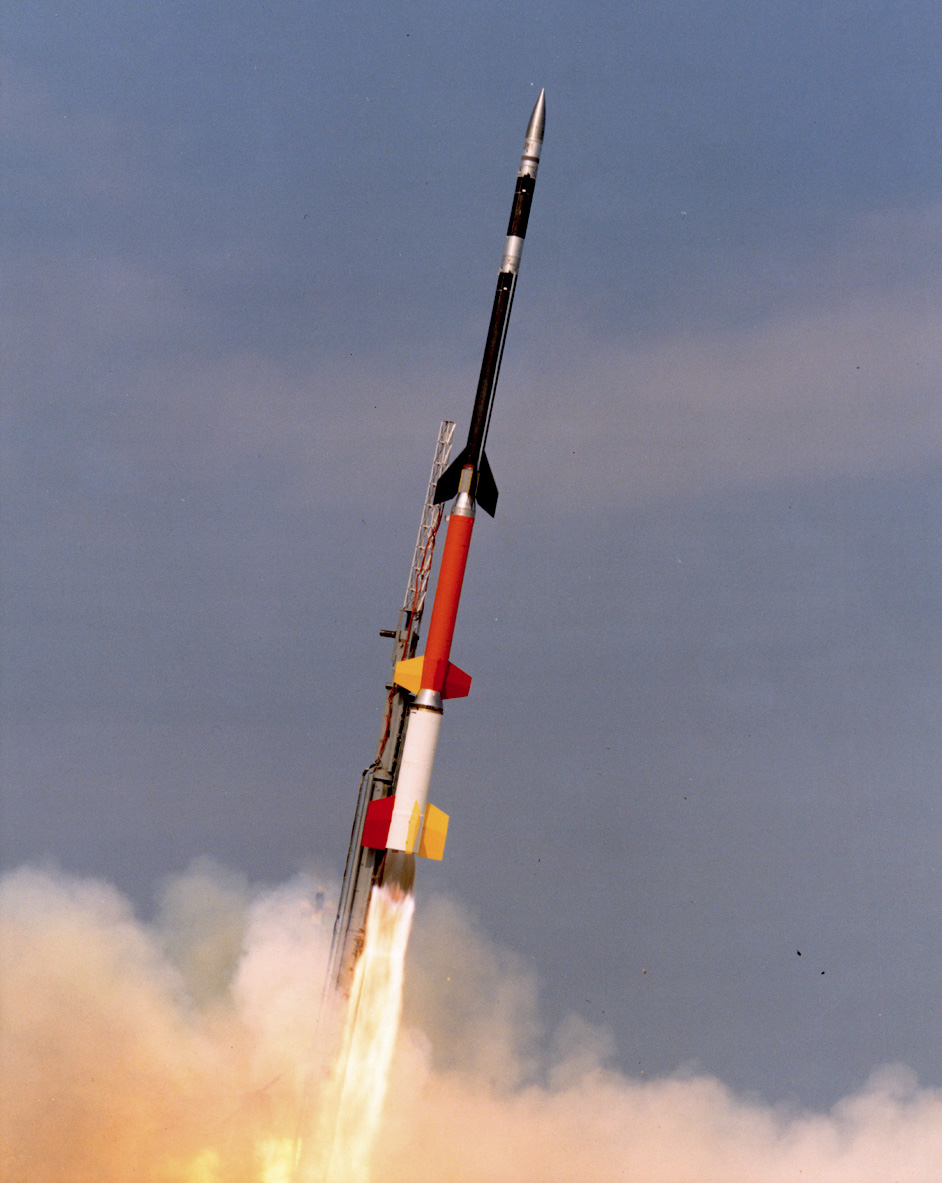
White Sands Missile Range
White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) is a United States Army military testing area and firing range located in the US state of New Mexico. The range was originally established as the White Sands Proving Ground on 9July 1945. White Sands National Park is located within the range. Significant events *The first atomic bomb (code named Trinity) was test detonated at Trinity Site near the northern boundary of the range on 16 July 1945, seven days after the White Sands Proving Ground was established. *After the conclusion of World War II, 100 long-range German V-2 rockets that were captured by U.S. military troops were brought to WSMR. Of these, 67 were test-fired between 1946 and 1951 from the White Sands V-2 Launching Site. (This was followed by the testing of American rockets, which continues to this day, along with testing other technologies.) *NASA's Space Shuttle Columbia landed on the Northrop Strip at WSMR on 30 March 1982 as the conclusion to mission STS-3. This was the only ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Brant (rocket)
The Black Brant is a family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets originally built by Bristol Aerospace, since absorbed by Magellan Aerospace in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Over 800 Black Brants of various versions have been launched since they were first produced in 1961, and the type remains one of the most popular sounding rockets. They have been repeatedly used by the Canadian Space Agency and NASA. History Black Brant was the result of research at Canadian Armament Research and Development Establishment (CARDE) during the 1950s into the nature of the upper part of the atmosphere as part of ongoing research into anti-ballistic missile systems and very-long-range communication. In 1957 CARDE contracted Bristol to produce a simple rocket fuselage, called the Propulsion Test Vehicle, for studies into high-power solid fuels. The resulting design, by Albert Fia, was quite heavy, as it was designed to be able to accommodate a wide variety of engine burning times, propellant loadings and la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to identify atoms and molecules. These "fingerprints" can be compared to the previously collected ones of atoms and molecules, and are thus used to identify the atomic and molecular components of stars and planets, which would otherwise be impossible. Types of line spectra Spectral lines are the result of interaction between a quantum system (usually atoms, but sometimes molecules or atomic nuclei) and a single photon. When a photon has about the right amount of energy (which is connected to its frequency) to allow a change in the energy state of the system (in the case of an atom this is usually an electron changing orbitals), the photon is absorbed. Then the energy will be spontaneously re-emitted, either as one photon at the same frequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionization, ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluorescence, fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet Image Of The Cygnus Loop Nebula Crop
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surfaces with which it comes into contact. For huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaia (spacecraft)
''Gaia'' is a space observatory of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 2013 and expected to operate until 2025. The spacecraft is designed for astrometry: measuring the positions, distances and motions of stars with unprecedented precision. The mission aims to construct by far the largest and most precise 3D space catalog ever made, totalling approximately 1 billion astronomical objects, mainly stars, but also planets, comets, asteroids and quasars, among others. To study the precise position and motion of its target objects, the spacecraft monitored each of them about 70 times over the five years of the nominal mission (2014–2019), and continues to do so during its extension. The spacecraft has enough micro-propulsion fuel to operate until about November 2024. As its detectors are not degrading as fast as initially expected, the mission could therefore be extended. ''Gaia'' targets objects brighter than magnitude 20 in a broad photometric band that covers the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Type
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the Continuum (spectrum), rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |