Phosphonium Compounds on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In polyatomic cations with the chemical formula (where R is a hydrogen or an alkyl, aryl, or
In polyatomic cations with the chemical formula (where R is a hydrogen or an alkyl, aryl, or
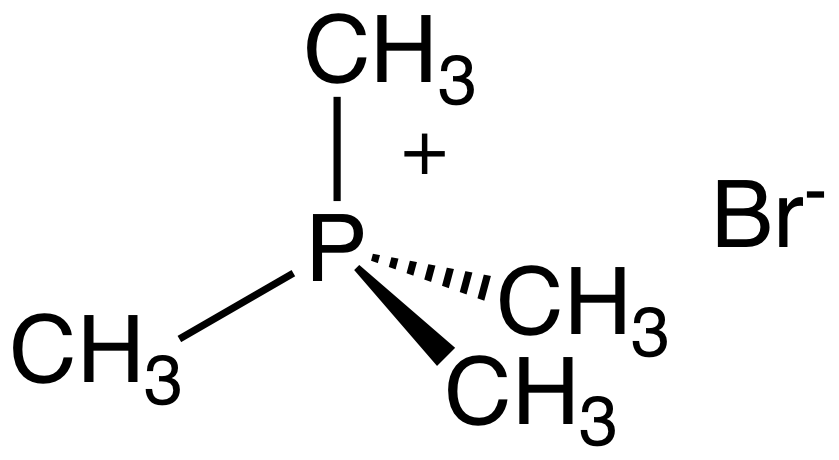
 Quaternary phosphonium cations () are produced by alkylation of organophosphines. For example, the reaction of triphenylphosphine with
Quaternary phosphonium cations () are produced by alkylation of organophosphines. For example, the reaction of triphenylphosphine with
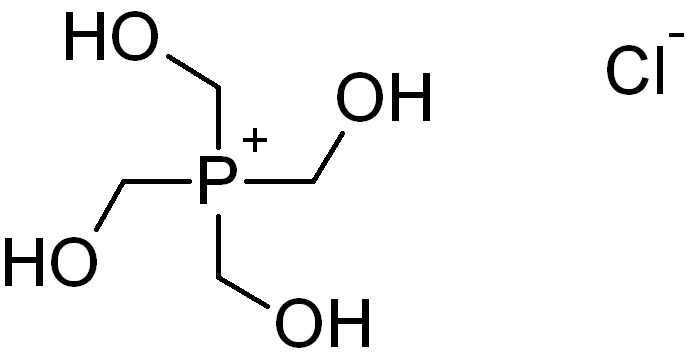 Tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride has industrial importance in the production of crease-resistant and
Tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride has industrial importance in the production of crease-resistant and
Nitrogen reduction to ammonia at high efficiency and rates based on a phosphonium proton shuttle
/ref>
 In polyatomic cations with the chemical formula (where R is a hydrogen or an alkyl, aryl, or
In polyatomic cations with the chemical formula (where R is a hydrogen or an alkyl, aryl, or halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fluor ...
group). These cations have tetrahedral structures. The salts are generally colorless or take the color of the anions.
Types of phosphonium cations
Protonated phosphines
The parent phosphonium is as found in the iodide salt, phosphonium iodide. Salts of the parent are rarely encountered, but this ion is an intermediate in the preparation of the industrially useful tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride: :PH3 + HCl + 4 CH2O → Many organophosphonium salts are produced by protonation of primary, secondary, and tertiary phosphines: :PR3 + H+ → The basicity of phosphines follows the usual trends, with R = alkyl being more basic than R = aryl.Tetraorganophosphonium cations
The most common phosphonium compounds have four organic substituents attached to phosphorus. Thequaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
phosphonium cations include tetraphenylphosphonium, (C6H5)4P+ and tetramethylphosphonium .

 Quaternary phosphonium cations () are produced by alkylation of organophosphines. For example, the reaction of triphenylphosphine with
Quaternary phosphonium cations () are produced by alkylation of organophosphines. For example, the reaction of triphenylphosphine with methyl bromide
Bromomethane, commonly known as methyl bromide, is an organobromine compound with formula C H3 Br. This colorless, odorless, nonflammable gas is produced both industrially and biologically. It has a tetrahedral shape and it is a recognized ozon ...
gives methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide:
:PPh3 + CH3Br → H3PPh3sup>+Br−
The methyl group in such phosphonium salts is mildly acidic, with a p''K''a estimated to be near 15:
: H3PPh3sup>+ + base → CH2=PPh3 + basesup>+
This deprotonation reaction gives Wittig reagents.
Phosphorus pentachloride and related compounds
Solid phosphorus pentachloride is anionic compound
In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound composed of ions held together by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonding. The compound is neutral overall, but consists of positively charged ions called cations and negatively charged i ...
, formulated , that is, a salt containing the tetrachlorophosphonium cation. Dilute solutions dissociate according to the following equilibrium:
:PCl5 + Cl−
Triphenylphosphine dichloride (Ph3PCl2) exists both as the pentacoordinate phosphorane and as the chlorotriphenylphosphonium chloride, depending on the medium. The situation is similar to that of PCl5. It is an ionic compound (PPh3Cl)+Cl− in polar solution
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end.
Polar molecules must contain one or more polar ...
s and a molecular species with trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry in apolar solution.
Alkoxyphosphonium salts: Arbuzov reaction
The Michaelis–Arbuzov reaction is the chemical reaction of a trivalent phosphorus ester with an alkyl halide to form apentavalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules.
Description
The combining capacity, or affinity of a ...
phosphorus species and another alkyl halide. Commonly, the phosphorus substrate is a phosphite ester (P(OR)3) and the alkylating agent is an alkyl iodide.
center, 600px, The mechanism of the Michaelis–Arbuzov reaction
Uses
Textile finishes
 Tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride has industrial importance in the production of crease-resistant and
Tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride has industrial importance in the production of crease-resistant and flame-retardant
The term flame retardants subsumes a diverse group of chemicals that are added to manufactured materials, such as plastics and textiles, and surface finishes and coatings. Flame retardants are activated by the presence of an ignition source and ...
finishes on cotton textiles and other cellulosic fabrics.Svara, Jürgen; Weferling, Norbert ; Hofmann, Thomas. Phosphorus Compounds, Organic. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2008 A flame-retardant finish can be prepared from THPC by the Proban Process, in which THPC is treated with urea. The urea condenses with the hydroxymethyl groups on THPC. The phosphonium structure is converted to phosphine oxide
Phosphine oxides are phosphorus compounds with the formula OPX3. When X = alkyl or aryl, these are organophosphine oxides. Triphenylphosphine oxide is an example. An inorganic phosphine oxide is phosphoryl chloride (POCl3).
Structure and bonding ...
as the result of this reaction.
Phase-transfer catalysts and precipitating agents
Organic phosphonium cations are lipophilic and can be useful inphase transfer catalysis
In chemistry, a phase-transfer catalyst or PTC is a catalyst that facilitates the transition of a reactant from one phase into another phase where reaction occurs. Phase-transfer catalysis is a special form of heterogeneous catalysis. Ionic reac ...
, much like quaternary ammonium salts. Salts or inorganic anions and tetraphenylphosphonium () are soluble in polar organic solvents. One example is the perrhenate The perrhenate ion is the anion with the formula , or a compound containing this ion. The perrhenate anion is tetrahedral, being similar in size and shape to perchlorate and the valence isoelectronicity, isoelectronic permanganate. The perrhenate a ...
(PPh4 eO4.
Reagents for organic synthesis
Wittig reagents are used inorganic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
. They are derived from phosphonium salts. A strong base such as butyllithium or sodium amide is required for the deprotonation:
: h3P+CH2R− + C4H9Li → Ph3P=CHR + LiX + C4H10
One of the simplest ylides is methylenetriphenylphosphorane (Ph3P=CH2).. Describes Ph3P=CH2.
The compounds Ph3PX2 (X = Cl, Br) are used in the Kirsanov reaction.
The Kinnear–Perren reaction is used to prepare alkylphosphonyl dichlorides (RP(O)Cl2) and esters (RP(O)(OR′)2). A key intermediate are alkyltrichlorophosphonium salts, obtained by the alkylation of phosphorus trichloride
Phosphorus trichloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PCl3. A colorless liquid when pure, it is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of phosphites and other organophosphorus compounds. It is toxic a ...
:
:RCl + PCl3 + AlCl3 → PCl3sup>+
Ammonia production for "green hydrogen"
The main industrial procedure for the production of ammonia today is the thermal Haber-Bosch process, which generally uses fossil gas as a source of hydrogen, which is then combined with nitrogen to produce ammonia. In 2021, Professor Doug MacFarlane and collaborators Alexandr Simonov and Bryan Suryanto of Monash University devised a method of producing green ammonia that has the potential to make Haber-Bosch plants obsolete. Their process is similar to the electrolysis approach for producing hydrogen. While working with local company Verdant, which wanted to make bleach from saltwater by electrolysis, Suryanto discovered that a tetraalkyl phosphonium salt allowed the efficient production of ammonia at room temperature./ref>
See also
*Ammonium
The ammonium cation is a positively-charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary a ...
()
* Hydronium (H3O+)
* Onium compounds
* Organophosphorus chemistry
References
{{Reflist Cations Functional groups Phosphonium compounds