Phanerozoic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Phanerozoic Eon is the current
 The Silurian spans from 444 million to 419 million years ago, which saw a warming from an icehouse Earth. This period saw the mass evolution of fish, as jawless fish became more numerous, and early jawed and freshwater fish appeared in the fossil record. Arthropods remained abundant, and some groups, such as eurypterids, became apex predators. Fully terrestrial life established itself on land, including early
The Silurian spans from 444 million to 419 million years ago, which saw a warming from an icehouse Earth. This period saw the mass evolution of fish, as jawless fish became more numerous, and early jawed and freshwater fish appeared in the fossil record. Arthropods remained abundant, and some groups, such as eurypterids, became apex predators. Fully terrestrial life established itself on land, including early
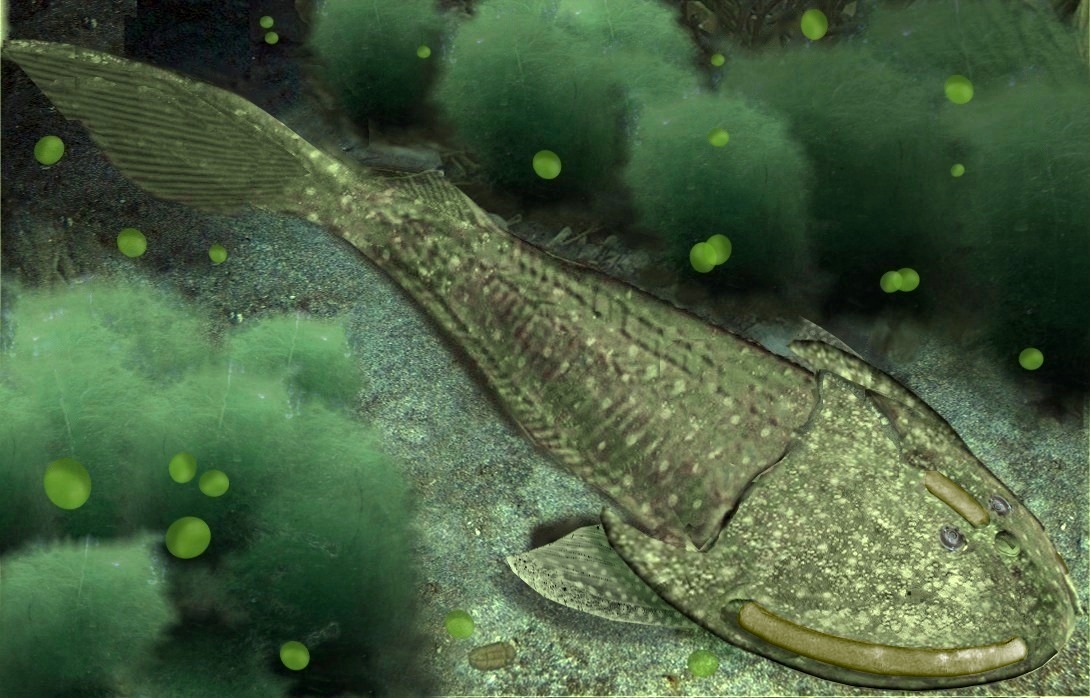 The Devonian spans from 419 million to 359 million years ago. Also informally known as the "Age of the Fish", the Devonian features a huge diversification in fish. Armored fish included jawless "agnathans", as well as jawed placoderms such as '' Dunkleosteus.'' The Devonian also saw a diversification of modern fish groups such as chondricthyans (sharks and kin), osteichthyans (ray-finned fish), and sarcopterygians (lobe-finned fish). One lineage of sarcopterygians evolved into the first four-limbed vertebrates, which would eventually become
The Devonian spans from 419 million to 359 million years ago. Also informally known as the "Age of the Fish", the Devonian features a huge diversification in fish. Armored fish included jawless "agnathans", as well as jawed placoderms such as '' Dunkleosteus.'' The Devonian also saw a diversification of modern fish groups such as chondricthyans (sharks and kin), osteichthyans (ray-finned fish), and sarcopterygians (lobe-finned fish). One lineage of sarcopterygians evolved into the first four-limbed vertebrates, which would eventually become
 The Carboniferous spans from 359 million to 299 million years ago. Tropical swamps dominated the Earth, and the large amounts of trees created much of the carbon that became coal deposits (hence the name Carboniferous). About 90% of all coal beds were deposited in the Carboniferous and Permian periods, which represent just 2% of the Earth's geologic history. The high
The Carboniferous spans from 359 million to 299 million years ago. Tropical swamps dominated the Earth, and the large amounts of trees created much of the carbon that became coal deposits (hence the name Carboniferous). About 90% of all coal beds were deposited in the Carboniferous and Permian periods, which represent just 2% of the Earth's geologic history. The high
 The Permian spans from 298 million to 251 million years ago and was the last period of the Paleozoic era. At its beginning, all continents came together to form the super-continent
The Permian spans from 298 million to 251 million years ago and was the last period of the Paleozoic era. At its beginning, all continents came together to form the super-continent
 The Middle Triassic spans from 247 million to 237 million years ago. The Middle Triassic featured the beginnings of the break-up of
The Middle Triassic spans from 247 million to 237 million years ago. The Middle Triassic featured the beginnings of the break-up of
 The Jurassic ranges from 201 million to 145 million years ago, and features three major epochs:
The Jurassic ranges from 201 million to 145 million years ago, and features three major epochs: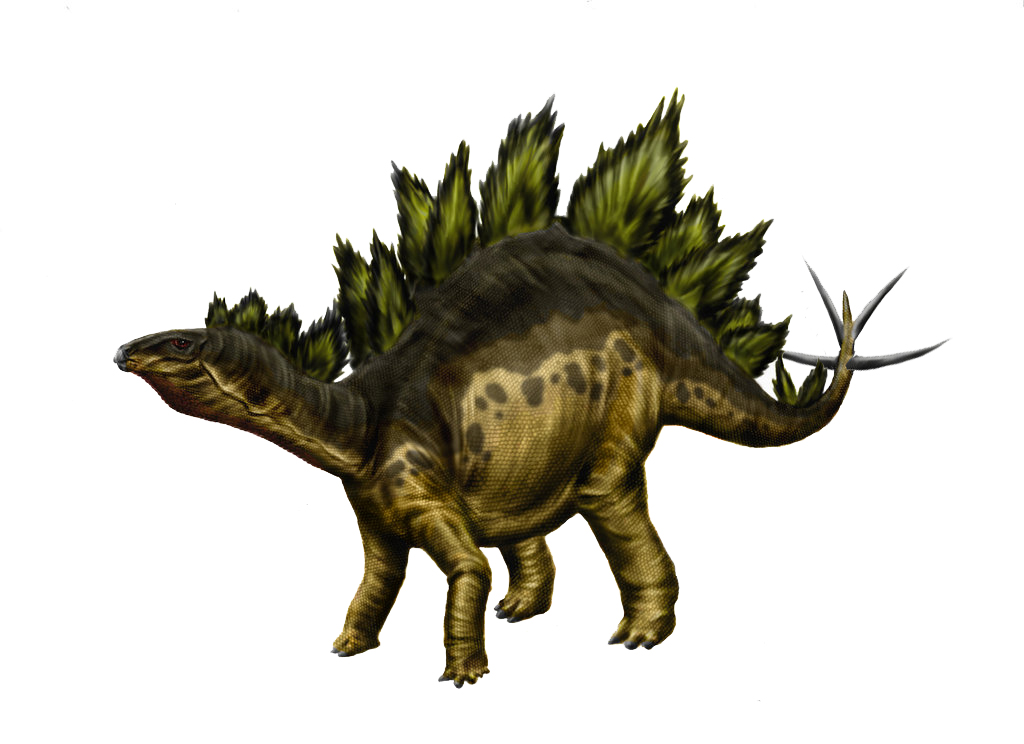  The Middle and Late Jurassic Epochs span from 174 million to 145 million years ago. Conifer savannahs made up a large portion of the world's forests. In the oceans, plesiosaurs were quite common, and ichthyosaurs were flourishing. The Late Jurassic Epoch spans from 163 million to 145 million years ago. The Late Jurassic featured a severe extinction of sauropods in northern continents, alongside many ichthyosaurs. However, the Jurassic-Cretaceous boundary did not strongly impact most forms of life.
The Middle and Late Jurassic Epochs span from 174 million to 145 million years ago. Conifer savannahs made up a large portion of the world's forests. In the oceans, plesiosaurs were quite common, and ichthyosaurs were flourishing. The Late Jurassic Epoch spans from 163 million to 145 million years ago. The Late Jurassic featured a severe extinction of sauropods in northern continents, alongside many ichthyosaurs. However, the Jurassic-Cretaceous boundary did not strongly impact most forms of life.
 The Early Cretaceous Epoch spans from 145 million to 100 million years ago. Dinosaurs continued to be abundant, with groups such as
The Early Cretaceous Epoch spans from 145 million to 100 million years ago. Dinosaurs continued to be abundant, with groups such as
 The Paleocene Epoch began with the K–Pg extinction event, and the early part of the Paleocene saw the recovery of the Earth from that event. The continents began to take their modern shapes, but most continents (and India) remained separated from each other:
The Paleocene Epoch began with the K–Pg extinction event, and the early part of the Paleocene saw the recovery of the Earth from that event. The continents began to take their modern shapes, but most continents (and India) remained separated from each other:
 The Quaternary spans from 2.58 million years ago to present day, and is the shortest geological period in the Phanerozoic Eon. It features modern animals, and dramatic changes in the climate. It is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene and the Holocene.
The Pleistocene lasted from 2.58 million to 11,700 years ago. This epoch was marked by a series of glacial periods (ice ages) as a result of the cooling trend that started in the Mid-Eocene. There were numerous separate glaciation periods marked by the advance of ice caps as far south as 40 degrees N latitude in mountainous areas. Meanwhile, Africa experienced a trend of desiccation which resulted in the creation of the Sahara, Namib, and Kalahari deserts. Mammoths, giant ground sloths, dire wolves, sabre-toothed cats, and humans were common and widespread during the Pleistocene. As the Pleistocene drew to a close, a major extinction wiped out much of the world's megafauna, including non-''Homo sapiens'' human species such as '' Homo neanderthalensis''. All the continents were affected, but Africa was impacted to a lesser extent. That continent retained many large animals, such as elephants, rhinos, and hippos. The extent to which ''Homo Sapiens'' were involved in this extinction is debated.
The Holocene began 11,700 years ago and lasts until the present day. All recorded history and "
The Quaternary spans from 2.58 million years ago to present day, and is the shortest geological period in the Phanerozoic Eon. It features modern animals, and dramatic changes in the climate. It is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene and the Holocene.
The Pleistocene lasted from 2.58 million to 11,700 years ago. This epoch was marked by a series of glacial periods (ice ages) as a result of the cooling trend that started in the Mid-Eocene. There were numerous separate glaciation periods marked by the advance of ice caps as far south as 40 degrees N latitude in mountainous areas. Meanwhile, Africa experienced a trend of desiccation which resulted in the creation of the Sahara, Namib, and Kalahari deserts. Mammoths, giant ground sloths, dire wolves, sabre-toothed cats, and humans were common and widespread during the Pleistocene. As the Pleistocene drew to a close, a major extinction wiped out much of the world's megafauna, including non-''Homo sapiens'' human species such as '' Homo neanderthalensis''. All the continents were affected, but Africa was impacted to a lesser extent. That continent retained many large animals, such as elephants, rhinos, and hippos. The extent to which ''Homo Sapiens'' were involved in this extinction is debated.
The Holocene began 11,700 years ago and lasts until the present day. All recorded history and "
 It has been demonstrated that changes in biodiversity through the Phanerozoic correlate much better with the hyperbolic model (widely used in
It has been demonstrated that changes in biodiversity through the Phanerozoic correlate much better with the hyperbolic model (widely used in
 *
*
Phanerozoic (chronostratigraphy scale)
{{Authority control
geologic eon
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronol ...
in the geologic time scale
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geoch ...
, and the one during which abundant animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
and plant
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for Cell growth, growth, reaction to Stimu ...
has existed. It covers 538.8 million years to the present, and it began with the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ag ...
Period, when animals first developed hard shells preserved in the fossil record. The time before the Phanerozoic, called the ''Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of th ...
'', is now divided into the Hadean, Archaean and Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
eons.
The time span of the Phanerozoic starts with the sudden appearance of fossilised evidence of a number of animal phyla Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phyl ...
; the evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
of those phyla into diverse forms; the emergence and development of complex plants; the evolution of fish
The evolution of fish began about 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion. It was during this time that the early chordates developed the skull and the vertebral column, leading to the first craniates and vertebrates. The first fi ...
; the emergence of insects and tetrapods
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant taxon, extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (p ...
; and the development of modern fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as ''biota''. Zoo ...
. Plant
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
life on land appeared in the early Phanerozoic eon. During this time span, tectonic forces which move the continents had collected them into a single landmass known as Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 millio ...
(the most recent supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which lea ...
), which then separated into the current continental landmasses.
Etymology
The term ''Phanerozoic'' derives from theAncient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
words (), meaning ''visible'', and (), meaning ''life''; since it was once believed that life began in the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ag ...
, the first period of this eon. The term "Phanerozoic" was coined in 1930 by the American geologist George Halcott Chadwick (1876–1953).
Proterozoic-Phanerozoic boundary
TheProterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
-Phanerozoic boundary is at 538.8 million years ago. In the 19th century, the boundary was set at time of appearance of the first abundant animal (metazoa
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage ...
n) fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s but several hundred groups (taxa
In biology, a taxon ( back-formation from '' taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular n ...
) of metazoa of the preceding Proterozoic eon have been identified since the systematic study of those forms started in the 1950s.
Eras of the Phanerozoic
The Phanerozoic is divided into three eras: thePaleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
, Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Creta ...
, and Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configu ...
, which are further subdivided into 12 periods. The Paleozoic features the evolution of fish, amphibians and reptiles. The Mesozoic features the evolution of lizards, crocodiles, snakes, turtles, mammals, and dinosaurs (including birds). The Cenozoic begins with the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs, and features evolution of great diversity in birds and mammals. Humans appeared and evolved during the most recent part of the Cenozoic.
Paleozoic Era
The Paleozoic is a time in Earth's history when complex life forms evolved, took their first breath ofoxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
on dry land, and when the forerunners of all multicelular life on Earth began to diversify. There are six periods in the Paleozoic era: Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ag ...
, Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. ...
, Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoi ...
, Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, w ...
, Carboniferous and Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Pale ...
.
Cambrian Period
The Cambrian is the first period of the Paleozoic Era and ran from 539 million to 485 million years ago. The Cambrian sparked a rapid expansion in the diversity of animals, in an event known as the Cambrian explosion, during which the greatest number of animal body plans evolved in a single period in the history of Earth. Complex algae evolved, and the fauna was dominated by armoured arthropods, such astrilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the ...
s. Almost all phyla Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phyl ...
of marine animals evolved in this period. During this time, the super-continent Pannotia began to break up, most of which later recombined into the super-continent Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final st ...
.
Ordovician Period
The Ordovician spans from 485 million to 444 million years ago. The Ordovician was a time in Earth's history in which many groups still prevalent today evolved or diversified, such as primitivecephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda ( Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, ...
s, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% ...
, and corals
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secre ...
. This process is known as the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event, or GOBE. Trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the ...
s began to be replaced by articulate brachiopods, and crinoid
Crinoids are marine animals that make up the Class (biology), class Crinoidea. Crinoids that are attached to the sea bottom by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms are called feather stars or coma ...
s also became an increasingly important part of the fauna. The first arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arth ...
s crept ashore to colonise Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final st ...
, a continent empty of animal life. By the end of the Ordovician, Gondwana had moved from the equator to the South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole, Terrestrial South Pole or 90th Parallel South, is one of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on Earth and lies antipod ...
, and Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
had collided with Baltica, closing the Iapetus Ocean. The glaciation of Gondwana resulted in a major drop in sea level, killing off all life that had established along its coast. Glaciation caused an icehouse Earth, leading to the Ordovician–Silurian extinction, during which 60% of marine invertebrates and 25% of families became extinct. Though one of the deadliest mass extinctions in earth's history, the O–S extinction did not cause profound ecological changes between the periods.
Silurian Period
 The Silurian spans from 444 million to 419 million years ago, which saw a warming from an icehouse Earth. This period saw the mass evolution of fish, as jawless fish became more numerous, and early jawed and freshwater fish appeared in the fossil record. Arthropods remained abundant, and some groups, such as eurypterids, became apex predators. Fully terrestrial life established itself on land, including early
The Silurian spans from 444 million to 419 million years ago, which saw a warming from an icehouse Earth. This period saw the mass evolution of fish, as jawless fish became more numerous, and early jawed and freshwater fish appeared in the fossil record. Arthropods remained abundant, and some groups, such as eurypterids, became apex predators. Fully terrestrial life established itself on land, including early arachnid
Arachnida () is a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals ( arthropods), in the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, harvestmen, camel spiders, whip spiders and ...
s, fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
, and myriapods (many-legged arthropods). The evolution of vascular plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They ...
s such as '' Cooksonia'' allowed plants to gain a foothold on land as well. These early terrestrial plants are the forerunners of all plant life on land. During this time, there were four continents: Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final st ...
(Africa, South America, Australia, Antarctica, India), Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
(North America with parts of Europe), Baltica (the rest of Europe), and Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
(Northern Asia).
Devonian Period
 The Devonian spans from 419 million to 359 million years ago. Also informally known as the "Age of the Fish", the Devonian features a huge diversification in fish. Armored fish included jawless "agnathans", as well as jawed placoderms such as '' Dunkleosteus.'' The Devonian also saw a diversification of modern fish groups such as chondricthyans (sharks and kin), osteichthyans (ray-finned fish), and sarcopterygians (lobe-finned fish). One lineage of sarcopterygians evolved into the first four-limbed vertebrates, which would eventually become
The Devonian spans from 419 million to 359 million years ago. Also informally known as the "Age of the Fish", the Devonian features a huge diversification in fish. Armored fish included jawless "agnathans", as well as jawed placoderms such as '' Dunkleosteus.'' The Devonian also saw a diversification of modern fish groups such as chondricthyans (sharks and kin), osteichthyans (ray-finned fish), and sarcopterygians (lobe-finned fish). One lineage of sarcopterygians evolved into the first four-limbed vertebrates, which would eventually become tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant taxon, extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (p ...
s. On land, plant groups diversified; the first trees and seeds evolved during this period. By the Middle Devonian, shrub-like forests of early plants existed: lycophytes
The lycophytes, when broadly circumscribed, are a vascular plant (tracheophyte) subgroup of the kingdom Plantae. They are sometimes placed in a division Lycopodiophyta or Lycophyta or in a subdivision Lycopodiophytina. They are one of the oldest ...
, horsetails, fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except ...
s, and progymnosperm. This event also allowed the diversification of arthropod life as they took advantage of the new habitat. Near the end of the Devonian, 70% of all species became extinct in a sequence of mass extinction events, collectively known as the Late Devonian extinction.
Carboniferous Period
 The Carboniferous spans from 359 million to 299 million years ago. Tropical swamps dominated the Earth, and the large amounts of trees created much of the carbon that became coal deposits (hence the name Carboniferous). About 90% of all coal beds were deposited in the Carboniferous and Permian periods, which represent just 2% of the Earth's geologic history. The high
The Carboniferous spans from 359 million to 299 million years ago. Tropical swamps dominated the Earth, and the large amounts of trees created much of the carbon that became coal deposits (hence the name Carboniferous). About 90% of all coal beds were deposited in the Carboniferous and Permian periods, which represent just 2% of the Earth's geologic history. The high oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
levels caused by these swamps allowed massive arthropods, normally limited in size by their respiratory systems, to proliferate. Tetrapods diversified during the Carboniferous, and one lineage acquired an amniotic egg which could survive outside of the water. These tetrapods, the amniotes, included the first reptiles and synapsid
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes rep ...
s (mammal relatives). Throughout the Carboniferous, there was a cooling pattern, which eventually led to the glaciation of Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final st ...
as much of it was situated around the south pole. This event was known as the Permo-Carboniferous Glaciation
The Permo-Carboniferous refers to the time period including the latter parts of the Carboniferous and early part of the Permian period. Permo-Carboniferous rocks are in places not differentiated because of the presence of transitional fossils, an ...
and resulted in a major loss of area for coal forests, the Carboniferous rainforest collapse.
Permian Period
 The Permian spans from 298 million to 251 million years ago and was the last period of the Paleozoic era. At its beginning, all continents came together to form the super-continent
The Permian spans from 298 million to 251 million years ago and was the last period of the Paleozoic era. At its beginning, all continents came together to form the super-continent Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 millio ...
, surrounded by one ocean called Panthalassa. The Earth was relatively dry compared to the Carboniferous, with harsh seasons, as the climate of the interior of Pangaea was not moderated by large bodies of water. Amniotes flourished and diversified in the new dry climate, particularly synapsid
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes rep ...
s such as ''Dimetrodon
''Dimetrodon'' ( or ,) meaning "two measures of teeth,” is an extinct genus of non- mammalian synapsid that lived during the Cisuralian (Early Permian), around 295–272 million years ago (Mya). It is a member of the family Sphenacodo ...
,'' '' Edaphosaurus,'' and the ancestors of modern mammals. The first conifers evolved during this period, then dominated the terrestrial landscape. The Permian ended with at least one mass extinction, the Permian-Triassic mass extinction, an event sometimes known as " the Great Dying". This extinction was the largest in earth's history and led to the loss of 95% of all species of life.
Mesozoic Era
The Mesozoic ranges from 252 million to 66 million years ago. Also referred to as the Age of Reptiles or Age of Conifers, the Mesozoic featured the appearance of many modern tetrapods, as reptiles ascended to ecological dominance over synapsids. The Mesozoic is subdivided into three periods: the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous.Triassic Period
The Triassic ranges from 252 million to 201 million years ago. The Triassic is a transitional time in Earth's history between the Permian Extinction and the lush Jurassic Period. It has three major epochs:Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a ...
, Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between Ma ...
. and Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch ...
.
The Early Triassic lasted between 252 million to 247 million years ago, and was a hot and arid epoch in the aftermath of the Permian Extinction. Many tetrapods during this epoch represented a disaster fauna, a group of animals with low diversity and cosmopolitanism (wide geographic ranges). Temnospondyli
Temnospondyli (from Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carb ...
recovered and rediversified into large aquatic predators during the Triassic. Reptiles also diversified rapidly, with aquatic reptiles such as ichthyosaurs and sauropterygians proliferating in the seas. On land, the first true archosaur
Archosauria () is a clade of diapsids, with birds and crocodilians as the only living representatives. Archosaurs are broadly classified as reptiles, in the cladistic sense of the term which includes birds. Extinct archosaurs include non-avi ...
s appeared, including pseudosuchians (crocodile relatives) and avemetatarsalians (bird/dinosaur relatives).  The Middle Triassic spans from 247 million to 237 million years ago. The Middle Triassic featured the beginnings of the break-up of
The Middle Triassic spans from 247 million to 237 million years ago. The Middle Triassic featured the beginnings of the break-up of Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 millio ...
as rifting commenced in north Pangaea. The northern part of the Tethys Ocean, the Paleotethys Ocean, had become a passive basin, but a spreading center was active in the southern part of the Tethys Ocean, the Neotethys Ocean. Phytoplankton, coral, crustaceans, and many other invertebrates recovered from the Permian extinction by the end of the Middle Triassic. Meanwhile, on land, reptiles continued to diversify, conifer forests flourished, as well as the first flies.
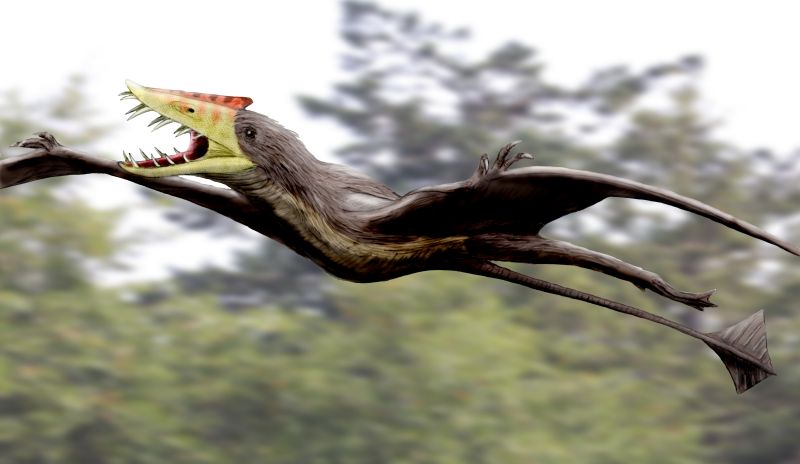
The Late Triassic spans from 237 million to 201 million years ago. Following the bloom of the Middle Triassic, the Late Triassic was warm and arid, with a strong monsoon climate and with most precipitation limited to coastal regions and high latitudes. The first true dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s appeared early in the Late Triassic, and pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the Order (biology), order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cre ...
s evolved a bit later. Other large reptilian competitors to the dinosaurs were wiped out by the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, in which most archosaurs (excluding crocodylomorphs, pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the Order (biology), order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cre ...
s, and dinosaurs), many synapsids, and almost all large amphibians became extinct, as well as 34% of marine life in the fourth mass extinction event. The cause of the extinction is debated, but likely resulted from eruptions of the CAMP large igneous province.
Jurassic Period
 The Jurassic ranges from 201 million to 145 million years ago, and features three major epochs:
The Jurassic ranges from 201 million to 145 million years ago, and features three major epochs: Early Jurassic
The Early Jurassic Epoch (in chronostratigraphy corresponding to the Lower Jurassic Series) is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event, 201.3 Ma ...
, Middle Jurassic
The Middle Jurassic is the second epoch of the Jurassic Period. It lasted from about 174.1 to 163.5 million years ago. Fossils of land-dwelling animals, such as dinosaurs, from the Middle Jurassic are relatively rare, but geological formations ...
, and Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time from 163.5 ± 1.0 to 145.0 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic strata.Owen 1987.
In European lithostratigraphy, the ...
.
The Early Jurassic Epoch spans from 201 million to 174 million years ago. The climate was much more humid than during the Triassic, and as a result, the world was warm and partially tropical, though possibly with short colder intervals. Plesiosaurs, ichthyosaurs and ammonite
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttle ...
s dominated the seas, while dinosaurs and other reptiles dominated the land, with species such as '' Dilophosaurus'' at the apex. Crocodylomorphs evolved into aquatic forms, pushing the large amphibians to near extinction. True mammals were present during the Jurassic but remained small, with average body masses of less than until the end of the Cretaceous.
 The Middle and Late Jurassic Epochs span from 174 million to 145 million years ago. Conifer savannahs made up a large portion of the world's forests. In the oceans, plesiosaurs were quite common, and ichthyosaurs were flourishing. The Late Jurassic Epoch spans from 163 million to 145 million years ago. The Late Jurassic featured a severe extinction of sauropods in northern continents, alongside many ichthyosaurs. However, the Jurassic-Cretaceous boundary did not strongly impact most forms of life.
The Middle and Late Jurassic Epochs span from 174 million to 145 million years ago. Conifer savannahs made up a large portion of the world's forests. In the oceans, plesiosaurs were quite common, and ichthyosaurs were flourishing. The Late Jurassic Epoch spans from 163 million to 145 million years ago. The Late Jurassic featured a severe extinction of sauropods in northern continents, alongside many ichthyosaurs. However, the Jurassic-Cretaceous boundary did not strongly impact most forms of life.
Cretaceous Period
The Cretaceous is the Phanerozoic's longest period, and the last period of the Mesozoic. It spans from 145 million to 66 million years ago, and is divided into two epochs:Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous ( chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pr ...
, and Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
.
 The Early Cretaceous Epoch spans from 145 million to 100 million years ago. Dinosaurs continued to be abundant, with groups such as
The Early Cretaceous Epoch spans from 145 million to 100 million years ago. Dinosaurs continued to be abundant, with groups such as tyrannosauroids
Tyrannosauroidea (meaning 'tyrant lizard forms') is a superfamily (or clade) of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that includes the family Tyrannosauridae as well as more basal relatives. Tyrannosauroids lived on the Laurasian supercontinent be ...
, avialans (birds), marginocephalians, and ornithopods seeing early glimpses of later success. Other tetrapods, such as stegosaurs and ichthyosaurs, declined significantly, and sauropods were restricted to southern continents.
The Late Cretaceous Epoch spans from 100 million to 66 million years ago. The Late Cretaceous featured a cooling trend that would continue into the Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configu ...
Era. Eventually, the tropical climate was restricted to the equator and areas beyond the tropic lines featured more seasonal climates. Dinosaurs still thrived as new species such as ''Tyrannosaurus
''Tyrannosaurus'' is a genus of large theropod dinosaur. The species ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' (''rex'' meaning "king" in Latin), often called ''T. rex'' or colloquially ''T-Rex'', is one of the best represented theropods. ''Tyrannosaurus'' live ...
'', '' Ankylosaurus'', ''Triceratops
''Triceratops'' ( ; ) is a genus of herbivorous chasmosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur that first appeared during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous period, about 68 million years ago in what is now North America. It is ...
'' and hadrosaurs dominated the food web. Whether or not pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the Order (biology), order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cre ...
s went into a decline as birds radiated is debated; however, many families survived until the end of the Cretaceous, alongside new forms such as the gigantic '' Quetzalcoatlus''. Mammals diversified despite their small sizes, with metatheria
Metatheria is a mammalian clade that includes all mammals more closely related to marsupials than to placentals. First proposed by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1880, it is a more inclusive group than the marsupials; it contains all marsupials as we ...
ns (marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a ...
s and kin) and eutherians ( placentals and kin) coming into their own. In the oceans, mosasaurs diversified to fill the role of the now-extinct ichthyosaurs, alongside huge plesiosaurs such as '' Elasmosaurus''. Also, the first flowering plants evolved. At the end of the Cretaceous, the Deccan Traps and other volcanic eruptions were poisoning the atmosphere. As this was continued, it is thought that a large meteor smashed into Earth, creating the Chicxulub Crater
The Chicxulub crater () is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Its center is offshore near the community of Chicxulub, after which it is named. It was formed slightly over 66 million years ago when a large ast ...
and the event known as the K–Pg extinction, the fifth and most recent mass extinction event, during which 75% of life on Earth became extinct, including all non-avian dinosaurs. Every living thing with a body mass over 10 kilograms became extinct, and the age of the dinosaurs came to an end.
Cenozoic Era
The Cenozoic featured the rise of mammals as the dominant class of animals, as the end of the age of the dinosaurs left significant open niches. There are three divisions of the Cenozoic: Paleogene, Neogene and Quaternary.Paleogene Period
The Paleogene spans from the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs, some 66 million years ago, to the dawn of the Neogene 23 million years ago. It features three epochs:Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pal ...
, Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " ...
and Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but ...
.
 The Paleocene Epoch began with the K–Pg extinction event, and the early part of the Paleocene saw the recovery of the Earth from that event. The continents began to take their modern shapes, but most continents (and India) remained separated from each other:
The Paleocene Epoch began with the K–Pg extinction event, and the early part of the Paleocene saw the recovery of the Earth from that event. The continents began to take their modern shapes, but most continents (and India) remained separated from each other: Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
were separated by the Tethys Sea, and the Americas were separated by the strait of Panama, as the Isthmus of Panama had not yet formed. This epoch featured a general warming trend, and the earliest modern jungle
A jungle is land covered with dense forest and tangled vegetation, usually in tropical climates. Application of the term has varied greatly during the past recent century.
Etymology
The word ''jungle'' originates from the Sanskrit word ''ja� ...
s expanded, eventually reaching the poles. The oceans were dominated by sharks, as the large reptiles that had once ruled had become extinct. Mammals diversified rapidly, but most remained small. The largest tetrapod carnivores during the Paleocene were reptiles, including crocodyliforms, choristodera
Choristodera (from the Greek χωριστός ''chōristos'' + δέρη ''dérē'', 'separated neck') is an extinct order of semiaquatic diapsid reptiles that ranged from the Middle Jurassic, or possibly Triassic, to the late Miocene (168 to 1 ...
ns, and snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s. '' Titanoboa,'' the largest known snake, lived in South America during the Paleocene.
The Eocene Epoch ranged from 56 million to 34 million years ago. In the early Eocene, most land mammals were small and living in cramped jungles, much like the Paleocene. Among them were early primates, whales and horses along with many other early forms of mammals. The climate was warm and humid, with little temperature gradient from pole to pole. In the Middle Eocene Epoch, the circum-Antarctic current between Australia and Antarctica formed, disrupting ocean currents worldwide, resulting in global cooling, and causing the jungles to shrink. More modern forms of mammals continued to diversify with the cooling climate even as more archaic forms died out. By the end of the Eocene, whales such as '' Basilosaurus'' had become fully aquatic. The late Eocene Epoch saw the rebirth of seasons, which caused the expansion of savanna-like areas with the earliest substantial grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur natur ...
s. At the transition between the Eocene and Oligocene epochs there was a significant extinction event, the cause of which is debated.
The Oligocene Epoch spans from 34 million to 23 million years ago. The Oligocene was an important transitional period between the tropical world of the Eocene and more modern ecosystems. This period featured a global expansion of grass which led to many new species taking advantage, including the first elephants, cats, dogs, marsupials and many other species still prevalent today. Many other species of plants evolved during this epoch also, such as the evergreen trees. The long term cooling continued and seasonal rain patterns established. Mammals continued to grow larger. '' Paraceratherium'', one of the largest land mammals to ever live, evolved during this epoch, along with many other perissodactyls.
Neogene Period
The Neogene spans from 23.03 million to 2.58 million years ago. It features two epochs: the Miocene and the Pliocene. The Miocene spans from 23.03 million to 5.333 million years ago and is a period in which grass spread further across, effectively dominating a large portion of the world, diminishing forests in the process. Kelp forests evolved, leading to the evolution of new species, such as sea otters. During this time, perissodactyls thrived, and evolved into many different varieties. Alongside them were the apes, which evolved into 30 species. Overall, arid and mountainous land dominated most of the world, as did grazers. The Tethys Sea finally closed with the creation of the Arabian Peninsula and in its wake left the Black, Red, Mediterranean and Caspian Seas. This only increased aridity. Many new plants evolved, and 95% of modern seed plants evolved in the mid-Miocene. The Pliocene lasted from 5.333 million to 2.58 million years ago. The Pliocene featured dramatic climatic changes, which ultimately led to modern species and plants. The Mediterranean Sea dried up for hundreds of thousand years in theMessinian salinity crisis
The Messinian salinity crisis (MSC), also referred to as the Messinian event, and in its latest stage as the Lago Mare event, was a geological event during which the Mediterranean Sea went into a cycle of partial or nearly complete desiccation (dr ...
. Along with these major geological events, Africa saw the appearance of ''Australopithecus
''Australopithecus'' (, ; ) is a genus of early hominins that existed in Africa during the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. The genus ''Homo'' (which includes modern humans) emerged within ''Australopithecus'', as sister to e.g. ''Austral ...
,'' the ancestor of ''Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus '' Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely relat ...
''. The isthmus of Panama formed, and animals migrated between North and South America, wreaking havoc on the local ecology. Climatic changes brought savannas that are still continuing to spread across the world, Indian monsoons, deserts in East Asia, and the beginnings of the Sahara desert. The Earth's continents and seas moved into their present shapes. The world map has not changed much since, save for changes brought about by the glaciations of the Quaternary, such as the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five la ...
.
Quaternary Period
 The Quaternary spans from 2.58 million years ago to present day, and is the shortest geological period in the Phanerozoic Eon. It features modern animals, and dramatic changes in the climate. It is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene and the Holocene.
The Pleistocene lasted from 2.58 million to 11,700 years ago. This epoch was marked by a series of glacial periods (ice ages) as a result of the cooling trend that started in the Mid-Eocene. There were numerous separate glaciation periods marked by the advance of ice caps as far south as 40 degrees N latitude in mountainous areas. Meanwhile, Africa experienced a trend of desiccation which resulted in the creation of the Sahara, Namib, and Kalahari deserts. Mammoths, giant ground sloths, dire wolves, sabre-toothed cats, and humans were common and widespread during the Pleistocene. As the Pleistocene drew to a close, a major extinction wiped out much of the world's megafauna, including non-''Homo sapiens'' human species such as '' Homo neanderthalensis''. All the continents were affected, but Africa was impacted to a lesser extent. That continent retained many large animals, such as elephants, rhinos, and hippos. The extent to which ''Homo Sapiens'' were involved in this extinction is debated.
The Holocene began 11,700 years ago and lasts until the present day. All recorded history and "
The Quaternary spans from 2.58 million years ago to present day, and is the shortest geological period in the Phanerozoic Eon. It features modern animals, and dramatic changes in the climate. It is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene and the Holocene.
The Pleistocene lasted from 2.58 million to 11,700 years ago. This epoch was marked by a series of glacial periods (ice ages) as a result of the cooling trend that started in the Mid-Eocene. There were numerous separate glaciation periods marked by the advance of ice caps as far south as 40 degrees N latitude in mountainous areas. Meanwhile, Africa experienced a trend of desiccation which resulted in the creation of the Sahara, Namib, and Kalahari deserts. Mammoths, giant ground sloths, dire wolves, sabre-toothed cats, and humans were common and widespread during the Pleistocene. As the Pleistocene drew to a close, a major extinction wiped out much of the world's megafauna, including non-''Homo sapiens'' human species such as '' Homo neanderthalensis''. All the continents were affected, but Africa was impacted to a lesser extent. That continent retained many large animals, such as elephants, rhinos, and hippos. The extent to which ''Homo Sapiens'' were involved in this extinction is debated.
The Holocene began 11,700 years ago and lasts until the present day. All recorded history and "Human history
Human history, also called world history, is the narrative of humanity's past. It is understood and studied through anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and linguistics. Since the invention of writing, human history has been studied t ...
" lies within the boundaries of the Holocene epoch. Human activity is blamed for an ongoing mass extinction that began roughly 10,000 years ago, though the species becoming extinct have only been recorded since the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
. This is sometimes referred to as the " Sixth Extinction". Hundreds of species have become extinct due to human activity since the Industrial Revolution.
Biodiversity
demography
Demography () is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups defined by criteria such as ed ...
and macrosociology) than with exponential and logistic models (traditionally used in population biology
The term population biology has been used with different meanings.
In 1971 Edward O. Wilson ''et al''. used the term in the sense of applying mathematical models to population genetics, community ecology, and population dynamics. Alan Hastings us ...
and extensively applied to fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
biodiversity as well). The latter models imply that changes in diversity are guided by a first-order positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in th ...
(more ancestors, more descendants) or a negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by othe ...
that arises from resource limitation, or both. The hyperbolic model implies a second-order positive feedback. The hyperbolic pattern of the human population
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture ...
growth arises from quadratic positive feedback, caused by the interaction of the population size and the rate of technological growth.See, e. g., The character of biodiversity growth in the Phanerozoic Eon can be similarly accounted for by a feedback between the diversity and community structure complexity. It has been suggested that the similarity between the curves of biodiversity and human population probably comes from the fact that both are derived from the superposition on the hyperbolic trend of cyclical and random dynamics.
See also

 *
*
Citations
General references
* *External links
Phanerozoic (chronostratigraphy scale)
{{Authority control