Petrochemical Engineering on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Petrochemicals (sometimes abbreviated as petchems) are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other
Petrochemicals (sometimes abbreviated as petchems) are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other
/ref>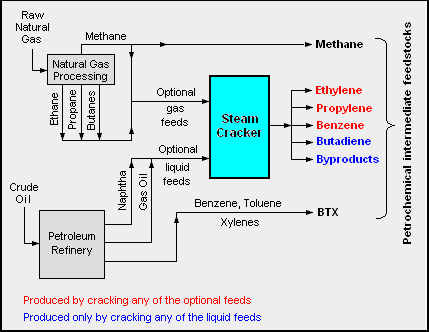 Like commodity chemicals, petrochemicals are made on a very large scale. Petrochemical manufacturing units differ from commodity chemical plants in that they often produce a number of related products. Compare this with specialty chemical and fine chemical manufacture where products are made in discrete batch processes.
Petrochemicals are predominantly made in a few manufacturing locations around the world, for example in Jubail & Yanbu Industrial Cities in Saudi Arabia, Texas & Louisiana in the US, in Teesside in the
Like commodity chemicals, petrochemicals are made on a very large scale. Petrochemical manufacturing units differ from commodity chemical plants in that they often produce a number of related products. Compare this with specialty chemical and fine chemical manufacture where products are made in discrete batch processes.
Petrochemicals are predominantly made in a few manufacturing locations around the world, for example in Jubail & Yanbu Industrial Cities in Saudi Arabia, Texas & Louisiana in the US, in Teesside in the
 *
*  * propylene – used as a monomer and a chemical feedstock
** isopropyl alcohol – 2-propanol; often used as a solvent or rubbing alcohol
** acrylonitrile – useful as a monomer in forming Orlon, ABS
** polypropylene – polymerized propylene
** propylene oxide
***polyether polyol – used in the production of polyurethanes
*** propylene glycol – used in engine coolant and aircraft deicer fluid
*** glycol ethers – from the condensation of glycols
**
* propylene – used as a monomer and a chemical feedstock
** isopropyl alcohol – 2-propanol; often used as a solvent or rubbing alcohol
** acrylonitrile – useful as a monomer in forming Orlon, ABS
** polypropylene – polymerized propylene
** propylene oxide
***polyether polyol – used in the production of polyurethanes
*** propylene glycol – used in engine coolant and aircraft deicer fluid
*** glycol ethers – from the condensation of glycols
**
 * benzene – the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon
** ethylbenzene – made from benzene and ethylene
*** styrene – made by dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene; used as a monomer
****
* benzene – the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon
** ethylbenzene – made from benzene and ethylene
*** styrene – made by dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene; used as a monomer
****  * toluene – methylbenzene; can be a solvent or precursor for other chemicals
** benzene
** toluene diisocyanate (TDI) – used as co-monomers with polyether polyols to form polyurethanes or with di- or poly amines to form polyureas polyurethanes
** benzoic acid – carboxybenzene
*** caprolactam
* toluene – methylbenzene; can be a solvent or precursor for other chemicals
** benzene
** toluene diisocyanate (TDI) – used as co-monomers with polyether polyols to form polyurethanes or with di- or poly amines to form polyureas polyurethanes
** benzoic acid – carboxybenzene
*** caprolactam
 * mixed xylenes – any of three dimethylbenzene isomers, could be a solvent but more often precursor chemicals
** ''ortho''-xylene – both methyl groups can be oxidized to form (''ortho-'')phthalic acid
*** phthalic anhydride
** ''para''-xylene – both methyl groups can be oxidized to form terephthalic acid
*** dimethyl terephthalate – can be copolymerized to form certain polyesters
****
* mixed xylenes – any of three dimethylbenzene isomers, could be a solvent but more often precursor chemicals
** ''ortho''-xylene – both methyl groups can be oxidized to form (''ortho-'')phthalic acid
*** phthalic anhydride
** ''para''-xylene – both methyl groups can be oxidized to form terephthalic acid
*** dimethyl terephthalate – can be copolymerized to form certain polyesters
****
 Petrochemicals (sometimes abbreviated as petchems) are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other
Petrochemicals (sometimes abbreviated as petchems) are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels m ...
s, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as maize, palm fruit or sugar cane.
The two most common petrochemical classes are olefins
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, an ...
(including ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene i ...
and propylene) and aromatics (including benzene, toluene and xylene isomers).
Oil refineries produce olefins and aromatics by fluid catalytic cracking
Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) is the conversion process used in petroleum refineries to convert the high-boiling point, high-molecular weight hydrocarbon fractions of petroleum (crude oils) into gasoline, olefinic gases, and other petroleum prod ...
of petroleum fractions. Chemical plant
A chemical plant is an industrial process plant that manufactures (or otherwise processes) chemicals, usually on a large scale. The general objective of a chemical plant is to create new material wealth via the chemical or biological transform ...
s produce olefins by steam cracking
Steam cracking is a petrochemical process in which saturated hydrocarbons are broken down into smaller, often unsaturated, hydrocarbons. It is the principal industrial method for producing the lighter alkenes (or commonly olefins), including ethe ...
of natural gas liquids like ethane and propane
Propane () is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula . It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used a ...
. Aromatics are produced by catalytic reforming of naphtha. Olefins and aromatics are the building-blocks for a wide range of materials such as solvents, detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. There are a large variety of detergents, a common family being the alkylbenzene sulfonates, which are soap-like compounds that are more ...
s, and adhesive
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
The use of adhesives offers certain advant ...
s. Olefins are the basis for polymers and oligomer
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relativ ...
s used in plastics, resins, fibers, elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic p ...
s, lubricant
A lubricant (sometimes shortened to lube) is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, t ...
s, and gels.
Global ethylene production was 190 million tonnes and propylene was 120 million tonnes in 2019. Aromatics production is approximately 70 million tonnes. The largest petrochemical industries are located in the USA and Western Europe; however, major growth in new production capacity is in the Middle East and Asia. There is substantial inter-regional petrochemical trade.
Primary petrochemicals are divided into three groups depending on their chemical structure:
* Olefins
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, an ...
includes ethene, propene, butenes and butadiene. Ethylene and propylene are important sources of industrial chemicals and plastics
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their Plasticity (physics), plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be Injection moulding, moulded, Extrusion, e ...
products. Butadiene is used in making synthetic rubber
A synthetic rubber is an artificial elastomer. They are polymers synthesized from petroleum byproducts. About 32-million metric tons of rubbers are produced annually in the United States, and of that amount two thirds are synthetic. Synthetic rubbe ...
.
* Aromatics includes benzene, toluene and xylenes, as a whole referred to as BTX and primarily obtained from petroleum refineries by extraction from the reformate produced in catalytic reformers using naphtha obtained from petroleum refineries. Alternatively, BTX can be produced by aromatization of alkanes. Benzene is a raw material for dyes
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and ...
and synthetic detergents, and benzene and toluene for isocyanates MDI and TDI
TDI (Turbocharged Direct Injection) is Volkswagen Group's term for its current common rail direct injection turbodiesel engine range that have an intercooler in addition to the turbo compressor.
TDI engines are used in motor vehicles sold by ...
used in making polyurethanes. Manufacturers use xylenes to produce plastics and synthetic fibers.
* Synthesis gas is a mixture
In chemistry, a mixture is a material made up of two or more different chemical substances which are not chemically bonded. A mixture is the physical combination of two or more substances in which the identities are retained and are mixed in the ...
of carbon monoxide and hydrogen used to produce methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a ...
and other chemicals. Steam crackers are not to be confused with steam reforming plants used to produce hydrogen for ammonia production. Ammonia is used to make the fertilizer urea and methanol is used as a solvent and chemical intermediate.
* Methane, ethane, propane
Propane () is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula . It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used a ...
and butane
Butane () or ''n''-butane is an alkane with the formula C4H10. Butane is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. Butane is a highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gas that quickly vaporizes at room temperature. The name but ...
s obtained primarily from natural gas processing plants.
* Methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a ...
and formaldehyde.
In 2007, the amounts of ethylene and propylene produced in steam crackers were about 115 M t (megatonnes) and 70 Mt, respectively. The output ethylene capacity of large steam crackers ranged up to as much as 1.0 – 1.5 Mt per year.
The adjacent diagram schematically depicts the major hydrocarbon sources and processes used in producing petrochemicals.SBS Polymer Supply Outlook/ref>
 Like commodity chemicals, petrochemicals are made on a very large scale. Petrochemical manufacturing units differ from commodity chemical plants in that they often produce a number of related products. Compare this with specialty chemical and fine chemical manufacture where products are made in discrete batch processes.
Petrochemicals are predominantly made in a few manufacturing locations around the world, for example in Jubail & Yanbu Industrial Cities in Saudi Arabia, Texas & Louisiana in the US, in Teesside in the
Like commodity chemicals, petrochemicals are made on a very large scale. Petrochemical manufacturing units differ from commodity chemical plants in that they often produce a number of related products. Compare this with specialty chemical and fine chemical manufacture where products are made in discrete batch processes.
Petrochemicals are predominantly made in a few manufacturing locations around the world, for example in Jubail & Yanbu Industrial Cities in Saudi Arabia, Texas & Louisiana in the US, in Teesside in the Northeast of England
North East England is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. The region has three current administrative levels below the region level in the region; combined authority, unitary authority ...
in the United Kingdom, in Rotterdam in the Netherlands, in Jamnagar
Jamnagar () is a city located on the western coast of India in the state of Gujarat of Saurashtra (region), Saurashtra region. It is the administrative headquarters of the Jamnagar district and the fifth largest city in Gujarat. The city lies ...
, Dahej in Gujarat, India and in Singapore. Not all of the petrochemical or commodity chemical materials produced by the chemical industry are made in one single location but groups of related materials are often made in adjacent manufacturing plants to induce industrial symbiosis as well as material and utility efficiency and other economies of scale. This is known in chemical engineering terminology as integrated manufacturing. Specialty and fine chemical companies are sometimes found in similar manufacturing locations as petrochemicals but, in most cases, they do not need the same level of large-scale infrastructure (e.g., pipelines, storage, ports, and power, etc.) and therefore can be found in multi-sector business parks.
The large scale petrochemical manufacturing locations have clusters of manufacturing units that share utilities and large scale infrastructures such as power stations, storage tanks, port facilities, road and rail terminals. In the United Kingdom, for example, there are 4 main locations for such manufacturing: near the River Mersey in North West England, on the Humber on the East coast of Yorkshire, in Grangemouth near the Firth of Forth in Scotland, and in Teesside as part of the Northeast of England Process Industry Cluster (NEPIC). To demonstrate the clustering and integration, some 50% of the United Kingdom's petrochemical and commodity chemicals are produced by the NEPIC industry cluster companies in Teesside.
History
In 1835, Henri Victor Regnault, a French chemist left vinyl chloride in the sun and found white solid at the bottom of the flask which was polyvinyl chloride. In 1839, Eduard Simon discovered polystyrene by accident by distilling storax. In 1856, William Henry Perkin discovered the first synthetic dye, Mauveine. In 1888,Friedrich Reinitzer
Friedrich Richard Reinitzer (25 February 1857 in Prague – 16 February 1927 in Graz) was an Austrian botanist and chemist. In late 1880s, experimenting with cholesteryl benzoate, he discovered properties of liquid crystals (named later by Otto ...
, an Austrian plant scientist observed cholesteryl benzoate had two different melting points. In 1909, Leo Hendrik Baekeland
Leo Hendrik Baekeland (November 14, 1863 – February 23, 1944) was a Belgian chemist. He is best known for the inventions of Velox photographic paper in 1893, and Bakelite in 1907. He has been called "The Father of the Plastics Industr ...
invented bakelite
Polyoxybenzylmethylenglycolanhydride, better known as Bakelite ( ), is a thermosetting phenol formaldehyde resin, formed from a condensation reaction of phenol with formaldehyde. The first plastic made from synthetic components, it was developed ...
made from phenol and formaldehyde. In 1928, synthetic fuels were invented using Fischer-Tropsch process. In 1929, Walter Bock invented synthetic rubber Buna-S
Styrene-butadiene or styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) describe families of synthetic rubbers derived from styrene and butadiene (the version developed by Goodyear is called Neolite). These materials have good abrasion resistance and good aging s ...
which is made up of styrene and butadiene and used to make car tires. In 1933, Otto Röhm
Otto Karl Julius Röhm (; 14 March 1876, Öhringen, Germany – 17 September 1939, Berlin) was one of the founders and a longtime president of the ''Röhm und Haas'' chemical company which became later in the USA the Rohm and Haas (today ''D ...
polymerized the first acrylic glass methyl methacrylate
Methyl methacrylate (MMA) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)COOCH3. This colorless liquid, the methyl ester of methacrylic acid (MAA), is a monomer produced on a large scale for the production of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA ...
. In 1935, Michael Perrin
Sir Michael Willcox Perrin, CBE, FRSC (13 September 1905 – 18 August 1988) was a scientist who created the first practical polythene, directed the first British atomic bomb programme, and participated in the Allied intelligence of the Nazi a ...
invented polyethylene. In 1937, Wallace Hume Carothers invented nylon. In 1938, Otto Bayer invented polyurethane. In 1941, Roy Plunkett
Roy J. Plunkett (June 26, 1910 – May 12, 1994) was an American chemist. He discovered polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), better known as Teflon, in 1938.
Personal life and education
Plunkett was born in New Carlisle, Ohio and attended Newton Hig ...
invented Teflon. In 1946, he invented Polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natural ...
. Polyethylene terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods ...
(PET) bottles are made from ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene i ...
and paraxylene. In 1949, Fritz Stastny turned polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
into foam. After World War II, polypropylene was discovered in the early 1950s. In 1965, Stephanie Kwolek
Stephanie Louise Kwolek (; July 31, 1923 – June 18, 2014) was a Polish-American chemist who is known for inventing Kevlar. Her career at the DuPont company spanned more than 40 years. She discovered the first of a family of synthetic fibers of ...
invented Kevlar.
Olefins
The following is a partial list of major commercial petrochemicals and their derivatives: *
* ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene i ...
– the simplest olefin; used as a chemical feedstock and ripening stimulant
** polyethylene – polymerized ethylene; LDPE, HDPE, LLDPE
** ethanol – via ethylene hydration Hydration may refer to:
* Hydrate, a substance that contains water
* Hydration enthalpy, energy released through hydrating a substance
* Hydration reaction, a chemical addition reaction where a hydroxyl group and proton are added to a compound
* ...
( chemical reaction adding water) of ethylene
** ethylene oxide – via ethylene oxidation
*** ethylene glycol – via ethylene oxide hydration
**** engine coolant – ethylene glycol, water and inhibitor mixture
**** polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natural ...
s – any of several polymers with ester linkages in the main chain
*** glycol ethers – via glycol condescension
*** ethoxylates
** vinyl acetate
** 1,2-dichloroethane
The chemical compound 1,2-dichloroethane, commonly known as ethylene dichloride (EDC), is a chlorinated hydrocarbon. It is a colourless liquid with a chloroform-like odour. The most common use of 1,2-dichloroethane is in the production of vinyl ...
*** trichloroethylene
*** tetrachloroethylene – also called perchloroethylene; used as a dry cleaning solvent and degreaser
*** vinyl chloride – monomer for polyvinyl chloride
**** polyvinyl chloride (PVC) – a type of plastic used for piping, tubing, other things
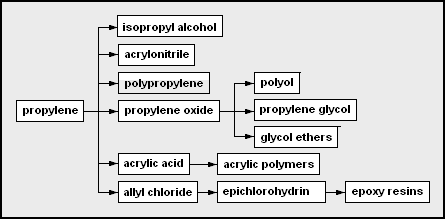
 * propylene – used as a monomer and a chemical feedstock
** isopropyl alcohol – 2-propanol; often used as a solvent or rubbing alcohol
** acrylonitrile – useful as a monomer in forming Orlon, ABS
** polypropylene – polymerized propylene
** propylene oxide
***polyether polyol – used in the production of polyurethanes
*** propylene glycol – used in engine coolant and aircraft deicer fluid
*** glycol ethers – from the condensation of glycols
**
* propylene – used as a monomer and a chemical feedstock
** isopropyl alcohol – 2-propanol; often used as a solvent or rubbing alcohol
** acrylonitrile – useful as a monomer in forming Orlon, ABS
** polypropylene – polymerized propylene
** propylene oxide
***polyether polyol – used in the production of polyurethanes
*** propylene glycol – used in engine coolant and aircraft deicer fluid
*** glycol ethers – from the condensation of glycols
** acrylic acid
Acrylic acid (IUPAC: propenoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCOOH. It is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid, consisting of a vinyl group connected directly to a carboxylic acid terminus. This colorless liquid has a ...
***acrylic polymer
An acrylate polymer (also known as acrylic or polyacrylate) is any of a group of polymers prepared from acrylate monomers. These plastics are noted for their transparency, resistance to breakage, and elasticity.
Acrylate polymer is commonly used ...
s
** allyl chloride
*** epichlorohydrin
Epichlorohydrin (abbreviated ECH) is an organochlorine compound and an epoxide. Despite its name, it is not a halohydrin. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, garlic-like odor, moderately soluble in water, but miscible with most polar organi ...
– chloro-oxirane; used in epoxy resin formation
**** epoxy resin
Epoxy is the family of basic components or cured end products of epoxy resins. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. The epoxide functional group is also coll ...
s – a type of polymerizing glue from bisphenol A, epichlorohydrin, and some amine
* butene
** isomers of butylene – useful as monomers or co-monomers
*** isobutylene – feed for making methyl ''tert''-butyl ether (MTBE) or monomer for copolymerization with a low percentage of isoprene
Isoprene, or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common volatile organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)−CH=CH2. In its pure form it is a colorless volatile liquid. Isoprene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. It is produced by many plants and animals ...
to make butyl rubber
** 1,3-butadiene
1,3-Butadiene () is the organic compound with the formula (CH2=CH)2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two viny ...
(or buta-1,3-diene) – a diene often used as a monomer or co-monomer for polymerization to elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic p ...
s such as polybutadiene
Polybutadiene utadiene rubber BRis a synthetic rubber. Polybutadiene rubber is a polymer formed from the polymerization of the monomer 1,3-butadiene. Polybutadiene has a high resistance to wear and is used especially in the manufacture of tir ...
, styrene-butadiene rubber
Styrene-butadiene or styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) describe families of synthetic rubbers derived from styrene and butadiene (the version developed by Goodyear is called Neolite). These materials have good abrasion resistance and good aging s ...
, or a plastic such as acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (chemical formula (C8H8)''x''·(C4H6)''y''·(C3H3N)''z'' is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately . ABS is Amorphous solid, amorphous and therefore has no true m ...
(ABS)
*** synthetic rubber
A synthetic rubber is an artificial elastomer. They are polymers synthesized from petroleum byproducts. About 32-million metric tons of rubbers are produced annually in the United States, and of that amount two thirds are synthetic. Synthetic rubbe ...
s – synthetic elastomers made of any one or more of several petrochemical (usually) monomers such as 1,3- butadiene, styrene, isobutylene, isoprene
Isoprene, or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common volatile organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)−CH=CH2. In its pure form it is a colorless volatile liquid. Isoprene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. It is produced by many plants and animals ...
, chloroprene; elastomeric polymers are often made with a high percentage of conjugated diene monomers such as 1,3-butadiene, isoprene, or chloroprene
* higher olefins
**polyolefin
A polyolefin is a type of polymer with the general formula (CH2CHR)n where R is an alkyl group. They are usually derived from a small set of simple olefins (alkenes). Dominant in a commercial sense are polyethylene and polypropylene. More speciali ...
s – such poly-alpha-olefins, which are used as lubricants
** alpha-olefins – used as monomers, co-monomers, and other chemical precursors. For example, a small amount of 1-hexene can be copolymerized with ethylene into a more flexible form of polyethylene.
** other higher olefins
** detergent alcohols
Aromatics
 * benzene – the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon
** ethylbenzene – made from benzene and ethylene
*** styrene – made by dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene; used as a monomer
****
* benzene – the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon
** ethylbenzene – made from benzene and ethylene
*** styrene – made by dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene; used as a monomer
**** polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
s – polymers with styrene as a monomer
** cumene – isopropylbenzene; a feedstock in the cumene process
*** phenol – hydroxybenzene; often made by the cumene process
*** acetone – dimethyl ketone; also often made by the cumene process
*** bisphenol A
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical compound primarily used in the manufacturing of various plastics. It is a colourless solid which is soluble in most common organic solvents, but has very poor solubility in water. BPA is produced on an industrial s ...
– a type of "double" phenol used in polymerization in epoxy resins and making a common type of polycarbonate
**** epoxy resin
Epoxy is the family of basic components or cured end products of epoxy resins. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. The epoxide functional group is also coll ...
s – a type of polymerizing glue from bisphenol A, epichlorohydrin, and some amine
**** polycarbonate
Polycarbonates (PC) are a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate groups in their chemical structures. Polycarbonates used in engineering are strong, tough materials, and some grades are optically transparent. They are easily work ...
– a plastic polymer made from bisphenol A and phosgene
Phosgene is the organic chemical compound with the formula COCl2. It is a toxic, colorless gas; in low concentrations, its musty odor resembles that of freshly cut hay or grass. Phosgene is a valued and important industrial building block, espe ...
(carbonyl dichloride)
*** solvents
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for p ...
– liquids used for dissolving materials; examples often made from petrochemicals include ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, acetone, benzene, toluene, xylenes
** cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula . Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohexan ...
– a 6-carbon aliphatic cyclic hydrocarbon sometimes used as a non-polar solvent
*** adipic acid – a 6-carbon dicarboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
, which can be a precursor used as a co-monomer together with a di amine to form an alternating copolymer form of nylon.
**** nylons – types of polyamides, some are alternating copolymers formed from copolymerizing dicarboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl groups (). The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as , where R can be aliphatic or aromatic. In general, dicarboxylic acids show ...
or derivatives with diamines
*** caprolactam – a 6-carbon cyclic amide
**** nylons – types of polyamides, some are from polymerizing caprolactam
** nitrobenzene
Nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5 NO2. It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odor. It freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor t ...
– can be made by single nitration of benzene
*** aniline – aminobenzene
**** methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) – used as a co-monomer with diol
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups ( groups). An aliphatic diol is also called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified.
The most common industrial diol is e ...
s or polyols to form polyurethanes or with di- or poly amines to form polyureas
** alkylbenzene – a general type of aromatic hydrocarbon, which can be used as a precursor for a sulfonate surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming ...
(detergent)
***detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. There are a large variety of detergents, a common family being the alkylbenzene sulfonates, which are soap-like compounds that are more ...
s – often include surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming ...
s types such as alkylbenzene sulfonates and nonylphenol ethoxylates
** chlorobenzene
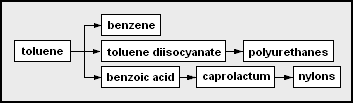
 * toluene – methylbenzene; can be a solvent or precursor for other chemicals
** benzene
** toluene diisocyanate (TDI) – used as co-monomers with polyether polyols to form polyurethanes or with di- or poly amines to form polyureas polyurethanes
** benzoic acid – carboxybenzene
*** caprolactam
* toluene – methylbenzene; can be a solvent or precursor for other chemicals
** benzene
** toluene diisocyanate (TDI) – used as co-monomers with polyether polyols to form polyurethanes or with di- or poly amines to form polyureas polyurethanes
** benzoic acid – carboxybenzene
*** caprolactam
 * mixed xylenes – any of three dimethylbenzene isomers, could be a solvent but more often precursor chemicals
** ''ortho''-xylene – both methyl groups can be oxidized to form (''ortho-'')phthalic acid
*** phthalic anhydride
** ''para''-xylene – both methyl groups can be oxidized to form terephthalic acid
*** dimethyl terephthalate – can be copolymerized to form certain polyesters
****
* mixed xylenes – any of three dimethylbenzene isomers, could be a solvent but more often precursor chemicals
** ''ortho''-xylene – both methyl groups can be oxidized to form (''ortho-'')phthalic acid
*** phthalic anhydride
** ''para''-xylene – both methyl groups can be oxidized to form terephthalic acid
*** dimethyl terephthalate – can be copolymerized to form certain polyesters
**** polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natural ...
s – although there can be many types, polyethylene terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods ...
is made from petrochemical products and is very widely used in petrol stations
*** purified terephthalic acid
Terephthalic acid is an organic compound with formula C6H4(CO2H)2. This white solid is a commodity chemical, used principally as a precursor to the polyester PET, used to make clothing and plastic bottles. Several million tonnes are produced annua ...
– often copolymerized to form polyethylene terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods ...
**** polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natural ...
s
** ''meta''-xylene
*** isophthalic acid
**** alkyd resins
**** polyamide resins
**** unsaturated polyesters
List of petrochemicals
See also
* Petroleum *Petroleum product
Petroleum products are materials derived from crude oil (petroleum) as it is processed in oil refineries. Unlike petrochemicals, which are a collection of well-defined usually pure organic compounds, petroleum products are complex mixtures. The m ...
s
* Instrumentation in petrochemical industries
* Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries
* Asia Petrochemical Industry Conference (APIC)
* Northeast of England Process Industry Cluster (NEPIC)
References
External links
{{Authority control __FORCETOC__