Perimeter College At Georgia State University Faculty on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A perimeter is a closed
A perimeter is a closed
 The perimeter is the distance around a shape. Perimeters for more general shapes can be calculated, as any path, with , where is the length of the path and is an infinitesimal line element. Both of these must be replaced by algebraic forms in order to be practically calculated. If the perimeter is given as a closed piecewise smooth plane curve with
:
then its length can be computed as follows:
:
A generalized notion of perimeter, which includes
The perimeter is the distance around a shape. Perimeters for more general shapes can be calculated, as any path, with , where is the length of the path and is an infinitesimal line element. Both of these must be replaced by algebraic forms in order to be practically calculated. If the perimeter is given as a closed piecewise smooth plane curve with
:
then its length can be computed as follows:
:
A generalized notion of perimeter, which includes

 The perimeter of a
The perimeter of a
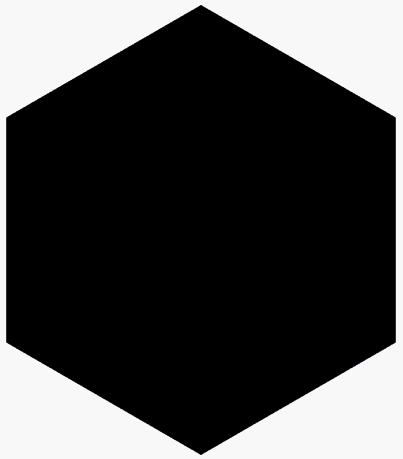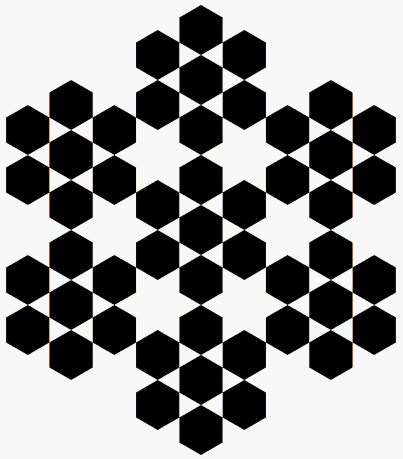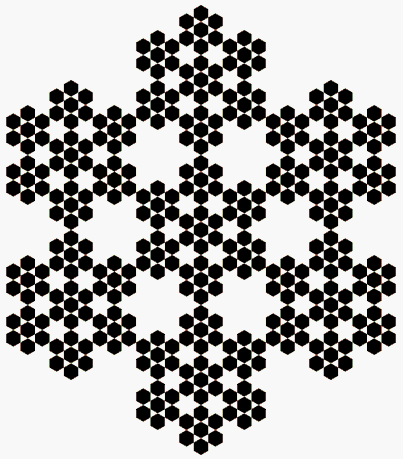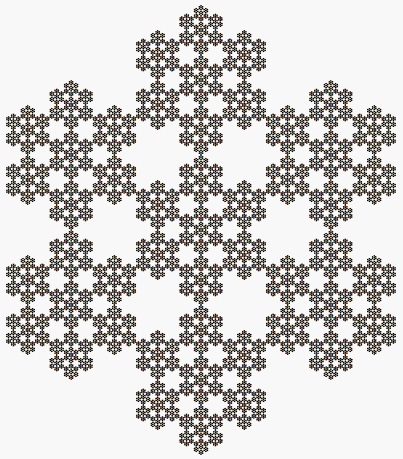
 The perimeter and the
The perimeter and the
path
A path is a route for physical travel – see Trail.
Path or PATH may also refer to:
Physical paths of different types
* Bicycle path
* Bridle path, used by people on horseback
* Course (navigation), the intended path of a vehicle
* Desire p ...
that encompasses, surrounds, or outlines either a two dimensional
In mathematics, a plane is a Euclidean (flat), two-dimensional surface that extends indefinitely. A plane is the two-dimensional analogue of a point (zero dimensions), a line (one dimension) and three-dimensional space. Planes can arise as s ...
shape
A shape or figure is a graphics, graphical representation of an object or its external boundary, outline, or external Surface (mathematics), surface, as opposed to other properties such as color, Surface texture, texture, or material type.
A pl ...
or a one-dimensional
In physics and mathematics, a sequence of ''n'' numbers can specify a location in ''n''-dimensional space. When , the set of all such locations is called a one-dimensional space. An example of a one-dimensional space is the number line, where the ...
length
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a base unit for length is chosen, from which all other units are derived. In the Interna ...
. The perimeter of a circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is const ...
or an ellipse
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focus (geometry), focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special ty ...
is called its circumference
In geometry, the circumference (from Latin ''circumferens'', meaning "carrying around") is the perimeter of a circle or ellipse. That is, the circumference would be the arc length of the circle, as if it were opened up and straightened out to ...
.
Calculating the perimeter has several practical applications. A calculated perimeter is the length of fence required to surround a yard or garden. The perimeter of a wheel/circle (its circumference) describes how far it will roll in one revolution
In political science, a revolution (Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due ...
. Similarly, the amount of string wound around a spool is related to the spool's perimeter; if the length of the string was exact, it would equal the perimeter.
Formulas
hypersurface
In geometry, a hypersurface is a generalization of the concepts of hyperplane, plane curve, and surface. A hypersurface is a manifold or an algebraic variety of dimension , which is embedded in an ambient space of dimension , generally a Euclidean ...
s bounding volumes in -dimensional
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coordi ...
Euclidean space
Euclidean space is the fundamental space of geometry, intended to represent physical space. Originally, that is, in Euclid's Elements, Euclid's ''Elements'', it was the three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, but in modern mathematics ther ...
s, is described by the theory of Caccioppoli set
In mathematics, a Caccioppoli set is a set whose boundary is measurable and has (at least locally) a ''finite measure''. A synonym is set of (locally) finite perimeter. Basically, a set is a Caccioppoli set if its characteristic function is a func ...
s.
Polygons
Polygon
In geometry, a polygon () is a plane figure that is described by a finite number of straight line segments connected to form a closed ''polygonal chain'' (or ''polygonal circuit''). The bounded plane region, the bounding circuit, or the two toge ...
s are fundamental to determining perimeters, not only because they are the simplest shapes but also because the perimeters of many shapes are calculated by approximating them with sequences
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is called t ...
of polygons tending to these shapes. The first mathematician known to have used this kind of reasoning is Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists ...
, who approximated the perimeter of a circle by surrounding it with regular polygon
In Euclidean geometry, a regular polygon is a polygon that is Equiangular polygon, direct equiangular (all angles are equal in measure) and Equilateral polygon, equilateral (all sides have the same length). Regular polygons may be either convex p ...
s.
The perimeter of a polygon equals the sum of the lengths of its sides (edges). In particular, the perimeter of a rectangle
In Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as: an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal (360°/4 = 90°); or a parallelogram containi ...
of width and length equals
An equilateral polygon
In geometry, an equilateral polygon is a polygon which has all sides of the same length. Except in the triangle case, an equilateral polygon does not need to also be equiangular (have all angles equal), but if it does then it is a regular polygon ...
is a polygon which has all sides of the same length (for example, a rhombus
In plane Euclidean geometry, a rhombus (plural rhombi or rhombuses) is a quadrilateral whose four sides all have the same length. Another name is equilateral quadrilateral, since equilateral means that all of its sides are equal in length. The ...
is a 4-sided equilateral polygon). To calculate the perimeter of an equilateral polygon, one must multiply the common length of the sides by the number of sides.
A regular polygon
In Euclidean geometry, a regular polygon is a polygon that is Equiangular polygon, direct equiangular (all angles are equal in measure) and Equilateral polygon, equilateral (all sides have the same length). Regular polygons may be either convex p ...
may be characterized by the number of its sides and by its circumradius
In geometry, the circumscribed circle or circumcircle of a polygon is a circle that passes through all the vertices of the polygon. The center of this circle is called the circumcenter and its radius is called the circumradius.
Not every polyg ...
, that is to say, the constant distance between its centre
Center or centre may refer to:
Mathematics
*Center (geometry), the middle of an object
* Center (algebra), used in various contexts
** Center (group theory)
** Center (ring theory)
* Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentricity ...
and each of its vertices. The length of its sides can be calculated using trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. T ...
. If is a regular polygon's radius and is the number of its sides, then its perimeter is
:
A splitter of a triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three Edge (geometry), edges and three Vertex (geometry), vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC.
In Euclidean geometry, an ...
is a cevian
In geometry, a cevian is a line that intersects both a triangle's vertex, and also the side that is opposite to that vertex. Medians and angle bisectors are special cases of cevians. The name "cevian" comes from the Italian mathematician Giovann ...
(a segment from a vertex to the opposite side) that divides the perimeter into two equal lengths, this common length being called the semiperimeter
In geometry, the semiperimeter of a polygon is half its perimeter. Although it has such a simple derivation from the perimeter, the semiperimeter appears frequently enough in formulas for triangles and other figures that it is given a separate name ...
of the triangle. The three splitters of a triangle all intersect each other at the Nagel point
In geometry, the Nagel point (named for Christian Heinrich von Nagel) is a triangle center, one of the points associated with a given triangle whose definition does not depend on the placement or scale of the triangle. It is the point of concur ...
of the triangle.
A cleaver
A cleaver is a large knife that varies in its shape but usually resembles a rectangular-bladed hatchet. It is largely used as a kitchen or butcher knife and is mostly intended for splitting up large pieces of soft bones and slashing through ...
of a triangle is a segment from the midpoint of a side of a triangle to the opposite side such that the perimeter is divided into two equal lengths. The three cleavers of a triangle all intersect each other at the triangle's Spieker center
In geometry, the Spieker center is a special point associated with a plane triangle. It is defined as the center of mass of the perimeter of the triangle. The Spieker center of a triangle is the center of gravity of a homogeneous wire frame in t ...
.
Circumference of a circle
 The perimeter of a
The perimeter of a circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is const ...
, often called the circumference, is proportional to its diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid for ...
and its radius
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the ...
. That is to say, there exists a constant number pi, (the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''p'' for perimeter), such that if is the circle's perimeter and its diameter then,
:
In terms of the radius of the circle, this formula becomes,
:
To calculate a circle's perimeter, knowledge of its radius or diameter and the number suffices. The problem is that is not rational
Rationality is the quality of being guided by or based on reasons. In this regard, a person acts rationally if they have a good reason for what they do or a belief is rational if it is based on strong evidence. This quality can apply to an abili ...
(it cannot be expressed as the quotient
In arithmetic, a quotient (from lat, quotiens 'how many times', pronounced ) is a quantity produced by the division of two numbers. The quotient has widespread use throughout mathematics, and is commonly referred to as the integer part of a ...
of two integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign (−1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the language ...
s), nor is it algebraic (it is not a root of a polynomial equation with rational coefficients). So, obtaining an accurate approximation of is important in the calculation. The computation of the digits of is relevant to many fields, such as mathematical analysis
Analysis is the branch of mathematics dealing with continuous functions, limit (mathematics), limits, and related theories, such as Derivative, differentiation, Integral, integration, measure (mathematics), measure, infinite sequences, series (m ...
, algorithmics
Algorithmics is the systematic study of the design and analysis of algorithms. It is fundamental and one of the oldest fields of computer science. It includes algorithm design, the art of building a procedure which can solve efficiently a specific ...
and computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, information theory, and automation) to Applied science, practical discipli ...
.
Perception of perimeter

 The perimeter and the
The perimeter and the area
Area is the quantity that expresses the extent of a region on the plane or on a curved surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape
A shape or figure is a graphics, graphical representation of an obje ...
are two main measures of geometric figures. Confusing them is a common error, as well as believing that the greater one of them is, the greater the other must be. Indeed, a commonplace observation is that an enlargement (or a reduction) of a shape make its area grow (or decrease) as well as its perimeter. For example, if a field is drawn on a 1/ scale map, the actual field perimeter can be calculated multiplying the drawing perimeter by . The real area is times the area of the shape on the map. Nevertheless, there is no relation between the area and the perimeter of an ordinary shape. For example, the perimeter of a rectangle of width 0.001 and length 1000 is slightly above 2000, while the perimeter of a rectangle of width 0.5 and length 2 is 5. Both areas are equal to 1.
Proclus
Proclus Lycius (; 8 February 412 – 17 April 485), called Proclus the Successor ( grc-gre, Πρόκλος ὁ Διάδοχος, ''Próklos ho Diádokhos''), was a Greek Neoplatonist philosopher, one of the last major classical philosophers ...
(5th century) reported that Greek peasants "fairly" parted fields relying on their perimeters. However, a field's production is proportional to its area, not to its perimeter, so many naive peasants may have gotten fields with long perimeters but small areas (thus, few crops).
If one removes a piece from a figure, its area decreases but its perimeter may not. In the case of very irregular shapes, confusion between the perimeter and the convex hull
In geometry, the convex hull or convex envelope or convex closure of a shape is the smallest convex set that contains it. The convex hull may be defined either as the intersection of all convex sets containing a given subset of a Euclidean space ...
may arise. The convex hull of a figure may be visualized as the shape formed by a rubber band stretched around it. In the animated picture on the left, all the figures have the same convex hull; the big, first hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Ancient Greek, Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple polygon, simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexa ...
.
Isoperimetry
The isoperimetric problem is to determine a figure with the largest area, amongst those having a given perimeter. The solution is intuitive; it is thecircle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is const ...
. In particular, this can be used to explain why drops of fat on a broth
Broth, also known as bouillon (), is a savory liquid made of water in which meat, fish or vegetables have been simmered for a short period of time. It can be eaten alone, but it is most commonly used to prepare other dishes, such as soups, ...
surface are circular.
This problem may seem simple, but its mathematical proof requires some sophisticated theorems. The isoperimetric problem is sometimes simplified by restricting the type of figures to be used. In particular, to find the quadrilateral
In geometry a quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon, having four edges (sides) and four corners (vertices). The word is derived from the Latin words ''quadri'', a variant of four, and ''latus'', meaning "side". It is also called a tetragon, ...
, or the triangle, or another particular figure, with the largest area amongst those with the same shape having a given perimeter. The solution to the quadrilateral isoperimetric problem is the square
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90-degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length adj ...
, and the solution to the triangle problem is the equilateral triangle
In geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length. In the familiar Euclidean geometry, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each othe ...
. In general, the polygon with sides having the largest area and a given perimeter is the regular polygon
In Euclidean geometry, a regular polygon is a polygon that is Equiangular polygon, direct equiangular (all angles are equal in measure) and Equilateral polygon, equilateral (all sides have the same length). Regular polygons may be either convex p ...
, which is closer to being a circle than is any irregular polygon with the same number of sides.
Etymology
The word comes from theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
περίμετρος ''perimetros'', from περί ''peri'' "around" and μέτρον ''metron'' "measure".
See also
* Arclength *Area
Area is the quantity that expresses the extent of a region on the plane or on a curved surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape
A shape or figure is a graphics, graphical representation of an obje ...
* Coastline paradox
The coastline paradox is the counterintuitive observation that the coastline of a landmass does not have a well-defined length. This results from the fractal curve-like properties of coastlines; i.e., the fact that a coastline typically has a fr ...
* Girth (geometry)
In three-dimensional geometry, the girth of a geometric object, in a certain direction, is the perimeter of its parallel projection in that direction... For instance, the girth of a unit cube in a direction parallel to one of the three coordinate a ...
* Pythagorean theorem
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite t ...
* Surface area
The surface area of a solid object is a measure of the total area that the surface of the object occupies. The mathematical definition of surface area in the presence of curved surfaces is considerably more involved than the definition of arc ...
* Volume
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). The de ...
* Wetted perimeter
The wetted perimeter is the perimeter of the cross sectional area that is "wet". The length of line of the intersection of channel wetted surface with a cross sectional plane normal to the flow direction. The term wetted perimeter is common in ci ...
References
External links
* * {{Authority control Elementary geometry Length