Perilipin 5 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Perilipin 5, also known as Oxpatperilipin 5 or PLIN5, is a

Uniprot-PLIN5
Genecards
3D interactive model
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
that belongs to perilipin
Perilipin, also known as lipid droplet-associated protein, Perilipin 1, or PLIN, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''PLIN'' gene. The perilipins are a family of proteins that associate with the surface of lipid droplets. Phosphoryla ...
family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
. This protein group has been shown to be responsible for lipid droplet
Lipid droplets, also referred to as lipid bodies, oil bodies or adiposomes, are lipid-rich cellular organelles that regulate the storage and hydrolysis of neutral lipids and are found largely in the adipose tissue. They also serve as a reservoi ...
's biogenesis, structure and degradation. In particular, Perilipin 5 is a lipid droplet-associated protein whose function is to keep the balance between lipolysis
Lipolysis is the metabolic pathway through which lipid triglycerides are hydrolyzed into a glycerol and free fatty acids. It is used to mobilize stored energy during fasting or exercise, and usually occurs in fat adipocytes. The most important ...
and lipogenesis
In biochemistry, lipogenesis is the conversion of fatty acids and glycerol into fats, or a metabolic process through which acetyl-CoA is converted to triglyceride for storage in fat. Lipogenesis encompasses both fatty acid and triglyceride syn ...
, as well as maintaining lipid droplet homeostasis. For example, in oxidative tissues, muscular tissue
Muscle tissue (or muscular tissue) is soft tissue that makes up the different types of muscles in most animals, and give the ability of muscles to contract. Muscle tissue is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. M ...
s and cardiac tissues, PLIN5 promotes association between lipid droplets and mitochondria.
Inside the cell, PLIN5 can be found in multiple intracellular structures including lipid droplets, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and the cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
. The wrong expression of this protein has been proven to be related with diseases such as skeletal muscle diseases, liver disease
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Signs and symptoms
Some of the si ...
s or carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abno ...
.
Perilipin Protein Family
PLIN5 is the fifth of the 5 perilipins which can be found onhuman
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s. All of them (PLIN1
Perilipin, also known as lipid droplet-associated protein, Perilipin 1, or PLIN, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''PLIN'' gene. The perilipins are a family of proteins that associate with the surface of lipid droplets. Phosphoryla ...
, ADRP, TIP47
Mannose-6-phosphate receptor binding protein 1 (M6PRBP1) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''M6PRBP1'' gene. Its gene product, as well as the gene itself, is commonly known as TIP47.
Function
Mannose 6-phosphate receptors (MPRs) ...
, S3-12 and PLIN5) have similar functionality, relating to lipid droplets. They have a 1,252% similarity with 76 identical positions. On the other hand, PLIN5 has its most similarity with PLINS 2 and 3, with over 150 similar positions and 18,644% similarity.
Structure
Perilipin 5 is a relatively large protein. It is composed of 463amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha a ...
s, weighing an average of 50.8 kDa. It contains four basic regions:
* from amino acid 1 to 173: key region for lipid droplet targeting.
* from amino acid 1 to 108: interaction with LIPE, a gene that encodes the formation of hormone-sensitive lipase
Hormone-sensitive lipase (, HSL), also previously known as cholesteryl ester hydrolase (CEH), sometimes referred to as triacylglycerol lipase, is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the ''LIPE'' gene, and catalyzes the following reaction:
...
, also known as HSL, whose main function is to mobilize the previously stored fats.
* from amino acid 185 to 463: interactions with PNPLA2 and ABHD5.
* from amino acid 444 to 463: targets mitochondria for lipid droplet-mitochondria association.
PLIN5 is expressed in 183 organs, having its highest expression level on the stomach fundus
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach ...
.
Protein Kinase A (PKA) phosphorylate
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, ...
s residues 2, 148 and 322. Phosphorylation by PKA enables lipolysis probably by promoting the release of ABHD5
1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase ABHD5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ABHD5'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to a large family of proteins defined by an alpha/beta hydrolase fold, and conta ...
from the perilipin scaffold.
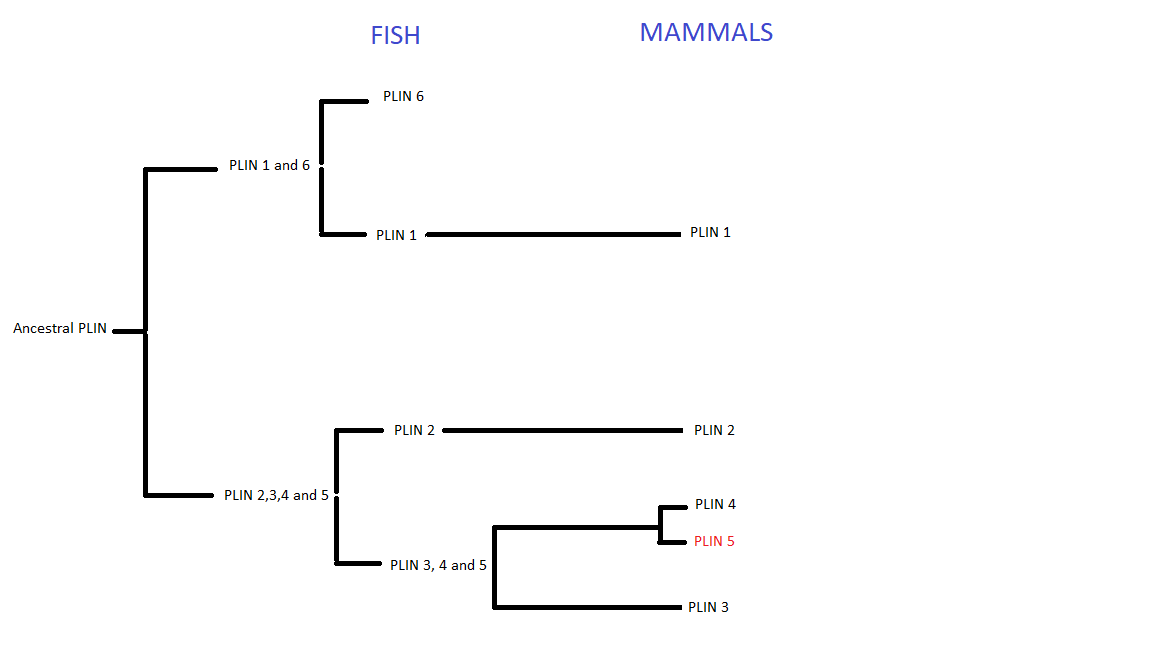
Evolution
Perilipins are considered to have evolved from a common ancestral gene. This family began to split during thefirst
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and second vertebrate genome duplication, giving birth to six types of PLIN genes, expressed throughout the animal kingdom. However, not all types are present in all animals. In fish, PLIN 1 to 6 can be found, whereas in mammals only PLIN1 to 5.

Function
Perilipin 5 is aprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
often found in the adipose tissue
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular ...
, especially in those with high oxidative stress, including the heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
, liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
, skeletal muscle and brown adipose tissue
Brown adipose tissue (BAT) or brown fat makes up the adipose organ together with white adipose tissue (or white fat). Brown adipose tissue is found in almost all mammals.
Classification of brown fat refers to two distinct cell populations with si ...
(BAT). The perilipin family contributes to the creation of lipid droplets and it also plays a pivotal role in determining what the lipid droplet
Lipid droplets, also referred to as lipid bodies, oil bodies or adiposomes, are lipid-rich cellular organelles that regulate the storage and hydrolysis of neutral lipids and are found largely in the adipose tissue. They also serve as a reservoi ...
's function is within the cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
. In addition, perilipin 5 regulates the activation of hepatic stellate cell
Hepatic stellate cells (HSC), also known as perisinusoidal cells or Ito cells (earlier ''lipocytes'' or ''fat-storing cells''), are pericytes found in the perisinusoidal space of the liver, also known as the space of Disse (a small area between th ...
, implicated in fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of perma ...
, which is the creation of new tissue to repair the one damaged.

Beta oxidation
PLIN5, as well as the other members of thisprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
family, is involved in lipid storage and also has energetic functions. Perilipin 5 coats the lipid droplet acting as a barrier to triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''wikt:tri-#Prefix, tri-'' and ''glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other ...
, thus increasing its storage. Under basal condition, PLIN5 decreases lipolysis
Lipolysis is the metabolic pathway through which lipid triglycerides are hydrolyzed into a glycerol and free fatty acids. It is used to mobilize stored energy during fasting or exercise, and usually occurs in fat adipocytes. The most important ...
to prevent energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of hea ...
waste. If energy is needed, perilipin facilitates lipid droplets with lipases
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually tr ...
and promotes enzymatic activity
Enzyme assays are laboratory methods for measuring enzymatic activity. They are vital for the study of enzyme kinetics and enzyme inhibition.
Enzyme units
The quantity or concentration of an enzyme can be expressed in molar amounts, as with an ...
, regulating energy consumption.
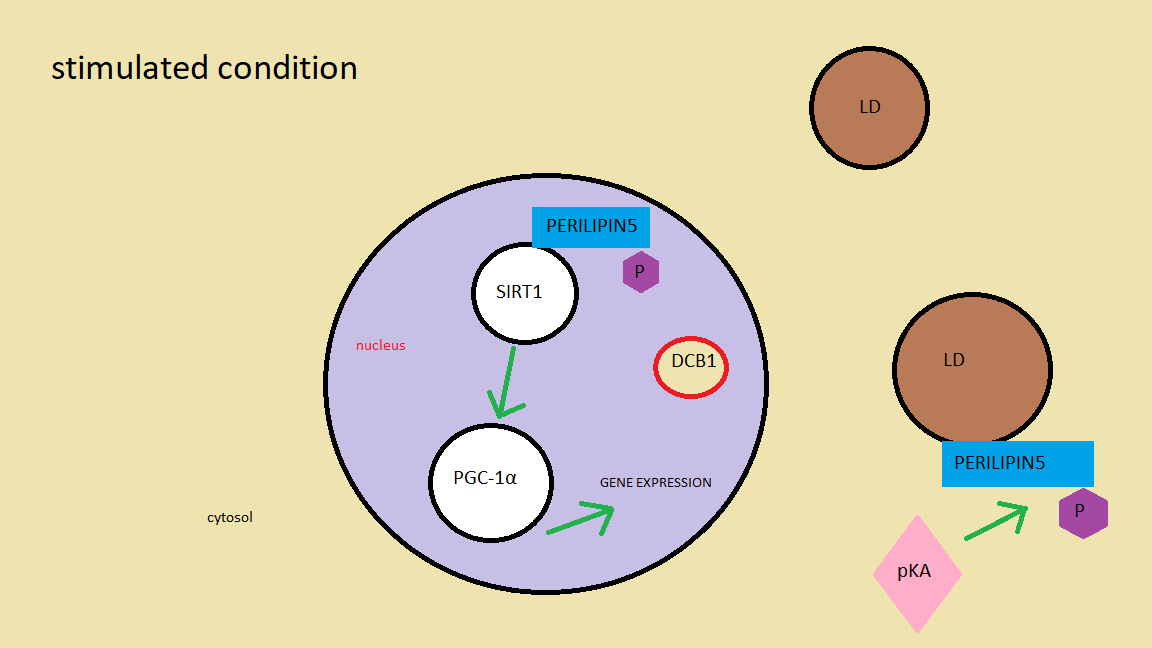
Perilipin 5-Nucleus interactions
The mechanism by which OXPAT5 balances energy remain to be fully clarified. It interacts mainly with LDs, though recent data suggest that this protein also targets thenucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
. When needed, perilipin 5 is phosphorylated
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ...
by protein kinase A
In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of enzymes whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase (). PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulatio ...
, which allows it to access the nucleus and enter the complex SIRT1
Sirtuin 1, also known as NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIRT1 gene.
SIRT1 stands for sirtuin (silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog) 1 ('' S. cerevisiae''), referring to the fact ...
/ PGC-1α, involved in fatty acid oxidation. PLIN5 removes SIRT1 inhibitor DBC1, therefore increasing its activity. As a consequence, PGC-1α boost activity levels activating certain types of genes that enhances mitochondrial function.

Mitochondria and Perilipin 5
Higher levels of perilipin 5 are closely related to the association between lipid droplet and mitochondria. This is useful in case of starvation (energy shortage). When energy is needed and no glucose is available, the cell uses lipids to feed itself. In order to do that, lipid droplets move towards the mitochondria to transfer the stored fatty acids. The perilipin family opens the channel, giving way to lipids to access the mitochondria. On the other hand, this association may occur with the aim of protecting the mitochondria against toxic levels offatty acids
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an B ...
in the cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
.
Mean Corpuscular Volume
PLIN5 is an enhancer of theerythrocytes
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
count in blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
, as well as hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyt ...
concentration.
Lipid Droplet Formation
Mammalian Plin's are not necessary for Lipid Droplet biogenesis, but as they are the primary regulators of lipolysis, they control cellular TAG/CE levels, long-chains whose functions is to provide enough metabolic precursors as polar lipids, which will then create Lipid Droplets.Clinical importance
PLIN5 is an important regulator of cardiac and liver LDs. Both overexpression and deficiency result in serious consequences. Nevertheless, insights into PLIN5 function may contribute to therapeutic strategies that seek to exploit thermogenic adipose tissue; for example, promoting PLIN5 expression in mouse brown adipose tissue is associated with healthy remodeling of subcutaneous white adipose tissue as well as improvements in systemic glucose tolerance.Overexpression
Perilipin 5 overexpression causes LD enlargement, accumulation oftriglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''wikt:tri-#Prefix, tri-'' and ''glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other ...
s (TAG) and mitochondria dysfunction, causing severe health issues.
Cardiac steatosis
An increase in PLIN5 expression leads to the accumulation of triglyceride content and to the enlargement of LDs and a reduction in its number. This results in cardiacsteatosis
Steatosis, also called fatty change, is abnormal retention of fat (lipids) within a cell or organ. Steatosis most often affects the liver – the primary organ of lipid metabolism – where the condition is commonly referred to as fatty liver disea ...
, an abnormal retention of lipids within a cell. Despite massive steatosis, overexpression of cardiac PLIN5 is compatible with normal heart function and lifespan. Overexpression of PLIN5 also results in concentric hypertrophia on the left ventricle.
Change in mitochondrial morphology
Overexpression of PLIN5 causes a change in mitochondrial function as it leads to the "recruitment" of mitochondria to the LD and changes its morphology. Such LD-mitochondria assemblies typically move in unison due to their tight association. This mitochondrial phenotype was only observed in close proximity to LDs.Fatty liver disease
PLIN5 plays an important role in regulating lipid accumulation and its breakdown in the liver. It appears that statins, a class of lipid-lowering medication, were effective in treating fatty liver diseases in non-alcoholic patients, as it decreased the hepatic expression of PLIN5, thus decreasing lipid accumulation.Deficiency
When LDs are lost due to a deficiency in PLIN5, FAs are not sequestered as TAG in LD and therefore larger amounts of FAs are oxidized in the mitochondria leading to an excess generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Medium and high concentrations of ROS can induce apoptosis and eventually cause necrosis through oxidative stress. PLIN deficiency also reduces superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. Furthermore, deficiency in PLIN5 initiates excessive phosforilation of PI3K/Akt which contributes to ischemia-reperfusion injury aggravation. PLIN5-knockout diabetic mice might avoid excess accumulation of lipotoxic molecules such as DAG and ceramide, a common problem among diabetic patients. The built up of DAG and ceramide disrupts several signaling pathways, including PKC pathway. However, in humans, the association is not clear and the packaging of TAG into lipid droplets may be of critical importance in determining whether the accumulation of excess lipids exert a toxic effect on the myocardium. It was found that a deficiency in Plin5 reduces mitochondrial oxidative capacity in mouses. Mitochondria from hearts suffering from a Plin5 deficiency had a membrana whose fatty acyl composition was altered, and its depolarization was compromised. It was also discovered in mice that, if a whole body deficiency of Plin5 was to happen, cardiac lipid droplet formation ability would be reduced, increasing fatty acid oxidations and promoting cardiac dysfunction. This, however, could be prevented by anti-oxidative therapy.Atherosclerosis
Deficiency in PLIN5 increases monocytes which are critical participants in the inflammation process. Because inflammation is essential to atherosclerosis, a deficiency in PLIN5 increases atherosclerosis risk.See also
*Lipid droplet
Lipid droplets, also referred to as lipid bodies, oil bodies or adiposomes, are lipid-rich cellular organelles that regulate the storage and hydrolysis of neutral lipids and are found largely in the adipose tissue. They also serve as a reservoi ...
* Cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
* Mitochondria
* Fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, ...
* Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
* Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
* Protein Kinase A
In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of enzymes whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase (). PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulatio ...
* lipid catabolism
* Nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
* Cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
* Protein domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of ...
* Alpha helix
* Beta strand
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a g ...
External links
Uniprot-PLIN5
Genecards
3D interactive model
References
{{reflist