Perger prism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
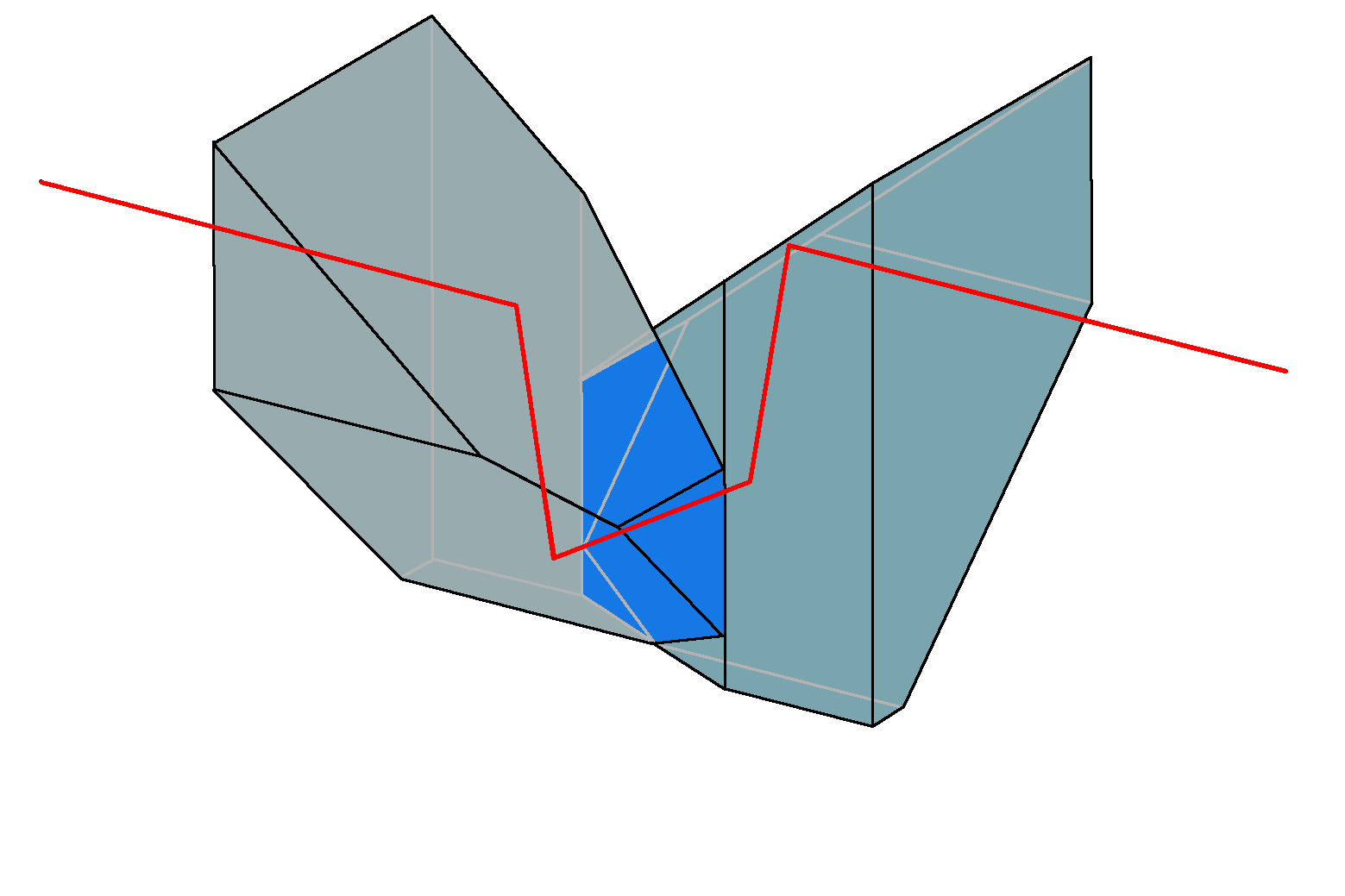
 A Perger prism or Perger–Porro prism system is a
A Perger prism or Perger–Porro prism system is a
EP2463692B1 European Patent Office
/ref>

 A Perger prism or Perger–Porro prism system is a
A Perger prism or Perger–Porro prism system is a prism
Prism usually refers to:
* Prism (optics), a transparent optical component with flat surfaces that refract light
* Prism (geometry), a kind of polyhedron
Prism may also refer to:
Science and mathematics
* Prism (geology), a type of sedimentary ...
, that is used to invert (rotate by 180°) an image. The special feature of this prism is that, like a traditional double Porro prism
In optics, a Porro prism, named for its inventor Ignazio Porro, is a type of ''reflection prism'' used in optical instruments to alter the orientation of an image.
Description
It consists of a block of material shaped like a right geometric ...
system, it manages this with only four beam deflections and has neither a roof edge with the accompanying phase correction problems, a mirrored surface or an air gap. However, in contrast to the traditional double Porro prism, it leads to a significantly reduced eyepiece/objective axis offset. The reduced beam offset allows for slimmer, more straight binocular housings usually found in roof prism
A roof prism, also called a Dachkanten prism or Dach prism (from German: ''Dachkante'', lit. "roof edge"), is a reflective prism containing a section where two faces meet at a 90° angle, resembling the roof of a building and thus the name. R ...
binoculars
Binoculars or field glasses are two refracting telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes (binocular vision) when viewing distant objects. Most binoculars are sized to be held ...
. Complicating production requirements make high-quality roof prism binoculars relatively costly to produce compared to in optical quality equivalent Porro prism or "Perger–Porro prism system" binoculars.
Dr. Andreas Perger patented the inversion system in 2011, and it was initially used in the Geovid HD laser rangefinding binoculars (2013 third generation) from the manufacturer Leica. This manufacturer uses the "Perger–Porro prism system" designation for this binoculars line, which features curved (banana shaped) binocular barrels.
Structure and functionality
The Perger prism consists of two glass prisms of different shapes that can be cemented together. The two prisms variant of the Porro Prisma of the second type (Porro–Abbe prism
A Porro–Abbe prism (sometimes called a Abbe–Porro prism), named for Ignazio Porro and Ernst Abbe, is a type of reflection prism used in some optical instruments to alter the orientation of an image. It is a variant of the more common doub ...
) served as a template for its design. In the next development steps, the cemented surface was first inclined in relation to the beam path. Then the first and last reflecting surfaces were tilted so that the beam has an angle of incidence that exceeds the 45° that is usual in a Porro prism. In this way, the axis offset could be reduced to about 70% of that in the Porro prism of the 2nd type, i.e., be reduced to about half of the value present in the Porro prism.
Since the partial prisms are cemented, and the beam deflection is based entirely on the total reflection
Total internal reflection (TIR) is the optical phenomenon in which waves arriving at the interface (boundary) from one medium to another (e.g., from water to air) are not refracted into the second ("external") medium, but completely reflected b ...
principle, there are no reflection losses within this reversal system. The roof prisms, which are widely used in binocular construction, lead to a loss of image quality due to diffraction effects at the roof edge and also require a phase correction coating
Binoculars or field glasses are two refracting telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes (binocular vision) when viewing distant objects. Most binoculars are sized to be held ...
. These complications are avoided in the Perger prism.
The prism is not dispersive since light enters and exits the prism only at normal incidence. Since the light is reflected an even number of times by the Perger–Porro prism system, the image's handedness
In human biology, handedness is an individual's preferential use of one hand, known as the dominant hand, due to it being stronger, faster or more Fine motor skill, dextrous. The other hand, comparatively often the weaker, less dextrous or sim ...
is not changed.
According to the patent, the Perger–Porro optical system does not lead to any significant impairment compared to the traditional double Porro system, but only to a slight reduction in brightness to the edge of the field of view (vignetting
In photography and optics, vignetting is a reduction of an image's brightness or saturation toward the periphery compared to the image center. The word ''vignette'', from the same root as ''vine'', originally referred to a decorative border ...
).
The manufacturer who commercially offers this optical system in binoculars claims good brightness and a light transmission of over 90 percent in its 2020 models.
Another advantage of the Perger prism is that the inclined position of the cemented surface to the optical axis can be used to couple in a measuring beam or a display, which enables the use of this type of prism in binoculars with integrated range finders. For this purpose, the cemented surface is provided with an dichroic coating that is matched to the wavelengths of the measuring beam and the display in such a way that just the color of the display will reflect back into the eye of the user.
Commercial market share in binoculars
Since its invention, the patented Perger prism optical design found commercial application on a small scale in some Leica binoculars. The anticipated expiration of thepatent term The term of a patent is the maximum time during which it can be maintained in force. It is usually expressed in a number of years either starting from the filing date of the patent application or from the date of grant of the patent. In most patent ...
is in 2031./ref>
References