|
Roof Prism
A roof prism, also called a Dachkanten prism or Dach prism (from German: ''Dachkante'', lit. "roof edge"), is a reflective prism containing a section where two faces meet at a 90° angle, resembling the roof of a building and thus the name. Reflection from the two 90° faces returns an image that is flipped laterally across the axis where the faces meet. Characteristic for a roof prism is that the beam is split in half, with one half of the beam hitting first one face then the other face, while it is invert for the other half of the beam. Therefore, a roof prism can be used only with some distance to focal planes, or the "edge" of the roof would introduce slight distortions. Furthermore, the angle between the two faces has to be very close to 90°, or image quality would be degraded. The simplest roof prism is the Amici roof prism, with other common roof prism designs being the Abbe–Koenig prism, the Schmidt–Pechan prism and probably the best known being the roof pentapr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interference (wave Propagation)
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two waves combine by adding their displacement together at every single point in space and time, to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or the same amplitude. Constructive and destructive interference result from the interaction of waves that are correlated or coherent with each other, either because they come from the same source or because they have the same or nearly the same frequency. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves, for example, light, radio, acoustic, surface water waves, gravity waves, or matter waves. Etymology The word ''interference'' is derived from the Latin words ''inter'' which means "between" and ''fere'' which means "hit or strike", and was coined by Thomas Young in 1801. Mechanisms The principle of superposition of waves states that when two or more propagating waves of the same type are incident on the same point, the resultant amplitude at that point is equal to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Incidence (optics)
The angle of incidence, in geometric optics, is the angle between a ray incident on a surface and the line perpendicular (at 90 degree angle) to the surface at the point of incidence, called the normal. The ray can be formed by any waves, such as optical, acoustic, microwave, and X-ray. In the figure below, the line representing a ray makes an angle θ with the normal (dotted line). The angle of incidence at which light is first totally internally reflected is known as the critical angle. The angle of reflection and angle of refraction are other angles related to beams. In computer graphics and geography, the angle of incidence is also known as the illumination angle of a surface with a light source, such as the Earth's surface and the Sun. It can also be equivalently described as the angle between the tangent plane of the surface and another plane at right angles to the light rays. This means that the illumination angle of a certain point on Earth's surface is 0° if the Sun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Zeiss (company)
Carl Zeiss AG (), branded as ZEISS, is a German manufacturer of optical systems and optoelectronics, founded in Jena, Germany in 1846 by optician Carl Zeiss. Together with Ernst Abbe (joined 1866) and Otto Schott (joined 1884) he laid the foundation for today's multi-national company. The current company emerged from a reunification of Carl Zeiss companies in East and West Germany with a consolidation phase in the 1990s. ZEISS is active in four business segments with approximately equal revenue (Industrial Quality and Research, Medical Technology, Consumer Markets and Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology) in almost 50 countries, has 30 production sites and around 25 development sites worldwide. Carl Zeiss AG is the holding of all subsidiaries within Zeiss Group, of which Carl Zeiss Meditec AG is the only one that is traded at the stock market. Carl Zeiss AG is owned by the foundation Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung. The Zeiss Group has its headquarters in southern Germany, in the small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
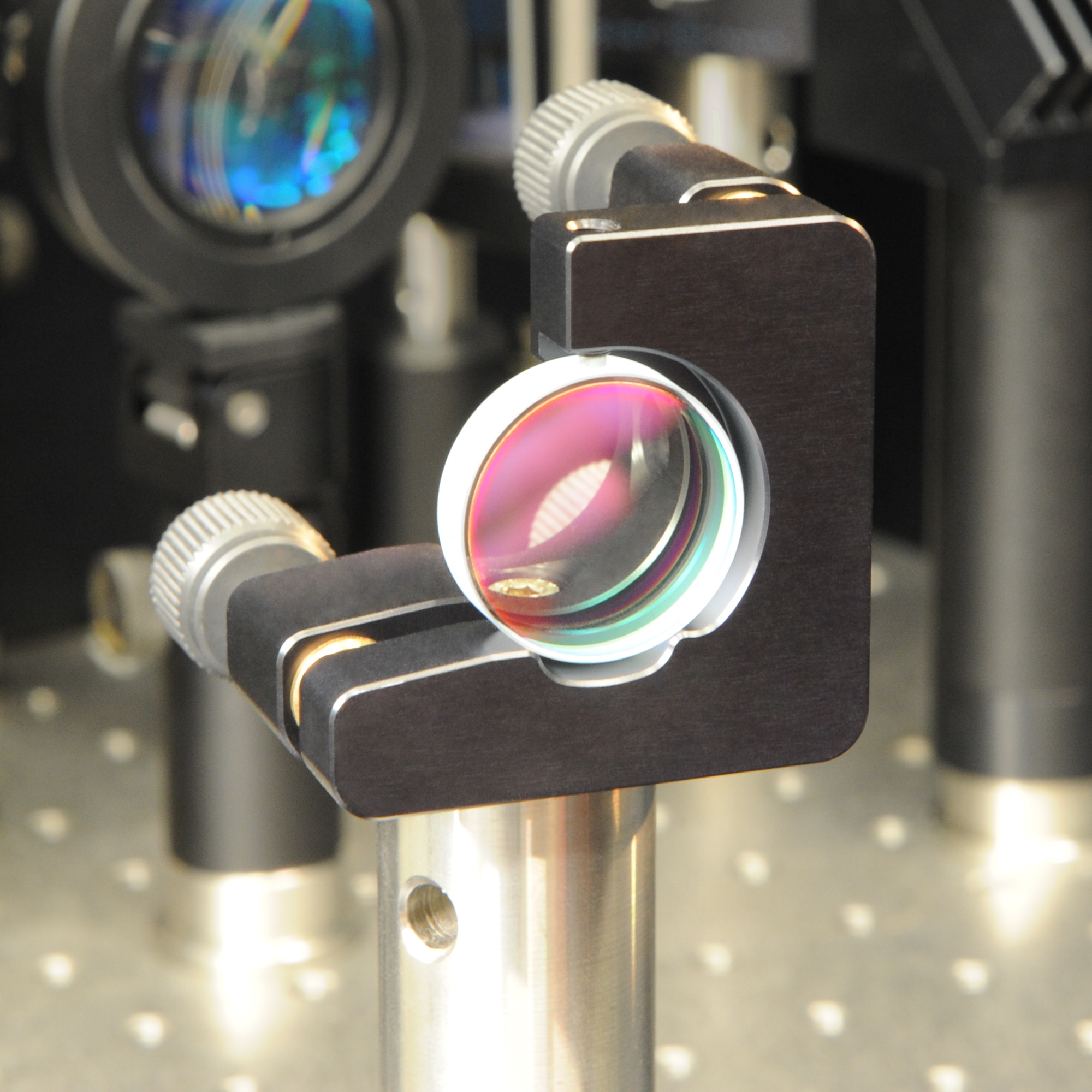
Dielectric Coating
A dielectric mirror, also known as a Bragg mirror, is a type of mirror composed of multiple thin layers of dielectric material, typically deposited on a substrate of glass or some other optical material. By careful choice of the type and thickness of the dielectric layers, one can design an optical coating with specified reflectivity at different wavelengths of light. Dielectric mirrors are also used to produce ultra-high reflectivity mirrors: values of 99.999% or better over a narrow range of wavelengths can be produced using special techniques. Alternatively, they can be made to reflect a broad spectrum of light, such as the entire visible range or the spectrum of the Ti-sapphire laser. Mirrors of this type are very common in optics experiments, due to improved techniques that allow inexpensive manufacture of high-quality mirrors. Examples of their applications include laser cavity end mirrors, hot and cold mirrors, thin-film beamsplitters, high damage threshold mirrors, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Vapor Deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films. In typical CVD, the wafer (substrate) is exposed to one or more volatile precursors, which react and/or decompose on the substrate surface to produce the desired deposit. Frequently, volatile by-products are also produced, which are removed by gas flow through the reaction chamber. Microfabrication processes widely use CVD to deposit materials in various forms, including: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous, and epitaxial. These materials include: silicon ( dioxide, carbide, nitride, oxynitride), carbon (fiber, nanofibers, nanotubes, diamond and graphene), fluorocarbons, filaments, tungsten, titanium nitride and various high-κ dielectrics. The term ''chemical vapour deposition'' was coined 1960 by ''John M. Blocher, Jr.'' who intended to differentiate ''chemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction
Diffraction is defined as the interference or bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the propagating wave. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word ''diffraction'' and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1660. In classical physics, the diffraction phenomenon is described by the Huygens–Fresnel principle that treats each point in a propagating wavefront as a collection of individual spherical wavelets. The characteristic bending pattern is most pronounced when a wave from a coherent source (such as a laser) encounters a slit/aperture that is comparable in size to its wavelength, as shown in the inserted image. This is due to the addition, or interference, of different points on the wavefront (or, equivalently, each wavelet) that travel by paths of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airy Disk
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best- focused spot of light that a perfect lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of light. The Airy disk is of importance in physics, optics, and astronomy. The diffraction pattern resulting from a uniformly illuminated, circular aperture has a bright central region, known as the Airy disk, which together with the series of concentric rings around is called the Airy pattern. Both are named after George Biddell Airy. The disk and rings phenomenon had been known prior to Airy; John Herschel described the appearance of a bright star seen through a telescope under high magnification for an 1828 article on light for the ''Encyclopedia Metropolitana'': Airy wrote the first full theoretical treatment explaining the phenomenon (his 1835 "On the Diffraction of an Object-glass with Circular Aperture"). Mathematically, the diffraction pattern is characterized by the wavelen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Berry (physicist)
Sir Michael Victor Berry, (born 14 March 1941), is a mathematical physicist at the University of Bristol, England. He is known for the Berry phase, a phenomenon observed e.g. in quantum mechanics and optics, as well as Berry connection and curvature. He specialises in semiclassical physics (asymptotic physics, quantum chaos), applied to wave phenomena in quantum mechanics and other areas such as optics. Education and early life Berry was brought up in a Jewish family and was the son of a London taxi driver and a dressmaker. Berry has a BSc in physics from the University of Exeter and a PhD from the University of St. Andrews. Career and research He has spent his whole career at the University of Bristol: research fellow, 1965–67; lecturer, 1967–74; reader, 1974–78; Professor of Physics, 1978–88; Royal Society Research Professor 1988–2006. Since 2006 he is Melville Wills Professor of Physics (Emeritus) at Bristol University. Publications *''Diffraction of Light by Ul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Phase
In classical and quantum mechanics, geometric phase is a phase difference acquired over the course of a cycle, when a system is subjected to cyclic adiabatic processes, which results from the geometrical properties of the parameter space of the Hamiltonian. The phenomenon was independently discovered by S. Pancharatnam (1956), in classical optics and by H. C. Longuet-Higgins (1958)See page 12 in molecular physics; it was generalized by Sir Michael Berry in (1984). It is also known as the Pancharatnam–Berry phase, Pancharatnam phase, or Berry phase. It can be seen in the conical intersection of potential energy surfaces and in the Aharonov–Bohm effect. Geometric phase around the conical intersection involving the ground electronic state of the C6H3F3+ molecular ion is discussed on pages 385–386 of the textbook by Bunker and Jensen. In the case of the Aharonov–Bohm effect, the adiabatic parameter is the magnetic field enclosed by two interference paths, and it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction Spike
Diffraction spikes are lines radiating from bright light sources, causing what is known as the starburst effect or sunstars in photographs and in vision. They are artifacts caused by light diffracting around the support vanes of the secondary mirror in reflecting telescopes, or edges of non-circular camera apertures, and around eyelashes and eyelids in the eye. Diffraction spikes due to support vanes In the vast majority of reflecting telescope designs, the secondary mirror has to be positioned at the central axis of the telescope and so has to be held by struts within the telescopes tube. No matter how fine these support rods are they diffract the incoming light from a subject star and this appears as diffraction spikes which are the Fourier transform of the support struts. The spikes represent a loss of light that could have been used to image the star. Although diffraction spikes can obscure parts of a photograph and are undesired in professional contexts, some amateur a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porro Prism
In optics, a Porro prism, named for its inventor Ignazio Porro, is a type of ''reflection prism'' used in optical instruments to alter the orientation of an image. Description It consists of a block of material shaped like a right geometric prism with right-angled triangular end faces. In operation, light enters the large rectangular face of the prism, undergoes total internal reflection twice from the sloped faces, and exits again through the large rectangular face. When the light enters and therefore exits the glass at normal incidence, the prism is not dispersive. An image travelling through a Porro prism is rotated by 180° and exits in the opposite direction offset from its entry point. While a single Porro prism can be constructed to work as well as a roof prism, it is seldom used as such. Therefore, to reduce the cost of production for a Porro prism, the edge of the roof is usually left out. Sometimes only one small window as an entrance surface and one window as e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)