Perceptual Constancy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Subjective constancy or perceptual constancy is the
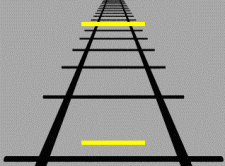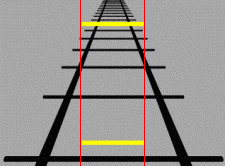 * ''Size constancy'' is one type of visual subjective constancy. Within a certain range, people's perception of one particular object's size will not change, regardless of changes in distance or the video size change on the retina. The perception of image is still based upon the actual size of the perceptual characteristics. According to optical principles, for the same object, the size of the image on the retina changes as the distance from the object to the observer changes. The greater the distance, the smaller the image is sensed by the retina. When someone is observing an object, although the distance of observation is different, the perceptional size is similar to the actual size. However, sensory and perception systems can be tricked by the use of illusions. Size constancy is related to distance, experience, and environment. Some examples of size constancy are
* ''Size constancy'' is one type of visual subjective constancy. Within a certain range, people's perception of one particular object's size will not change, regardless of changes in distance or the video size change on the retina. The perception of image is still based upon the actual size of the perceptual characteristics. According to optical principles, for the same object, the size of the image on the retina changes as the distance from the object to the observer changes. The greater the distance, the smaller the image is sensed by the retina. When someone is observing an object, although the distance of observation is different, the perceptional size is similar to the actual size. However, sensory and perception systems can be tricked by the use of illusions. Size constancy is related to distance, experience, and environment. Some examples of size constancy are  * ''Shape constancy'' is similar to size constancy in that it relies largely on the perception of distance. Regardless of changes to an object's orientation (such as a door opening), the shape of the object is perceived the same. That is the actual shape of the object is sensed as changing but then perceived as the same. According to Kanwisher & associates, the localized part of the brain responsible for this is the extrastriate cortex.
* ''
* ''Shape constancy'' is similar to size constancy in that it relies largely on the perception of distance. Regardless of changes to an object's orientation (such as a door opening), the shape of the object is perceived the same. That is the actual shape of the object is sensed as changing but then perceived as the same. According to Kanwisher & associates, the localized part of the brain responsible for this is the extrastriate cortex.
* ''
perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system ...
of an object or quality as constant even though our sensation
Sensation (psychology) refers to the processing of the senses by the sensory system.
Sensation or sensations may also refer to:
In arts and entertainment In literature
*Sensation (fiction), a fiction writing mode
*Sensation novel, a British ...
of the object changes. While the physical characteristics of an object may not change, in an attempt to deal with the external world, the human perceptual system has mechanisms that adjust to the stimulus.
Visual
There are several types of perceptual constancies invisual perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment through photopic vision (daytime vision), color vision, scotopic vision (night vision), and mesopic vision (twilight vision), using light in the visible spectrum reflecte ...
:
 * ''Size constancy'' is one type of visual subjective constancy. Within a certain range, people's perception of one particular object's size will not change, regardless of changes in distance or the video size change on the retina. The perception of image is still based upon the actual size of the perceptual characteristics. According to optical principles, for the same object, the size of the image on the retina changes as the distance from the object to the observer changes. The greater the distance, the smaller the image is sensed by the retina. When someone is observing an object, although the distance of observation is different, the perceptional size is similar to the actual size. However, sensory and perception systems can be tricked by the use of illusions. Size constancy is related to distance, experience, and environment. Some examples of size constancy are
* ''Size constancy'' is one type of visual subjective constancy. Within a certain range, people's perception of one particular object's size will not change, regardless of changes in distance or the video size change on the retina. The perception of image is still based upon the actual size of the perceptual characteristics. According to optical principles, for the same object, the size of the image on the retina changes as the distance from the object to the observer changes. The greater the distance, the smaller the image is sensed by the retina. When someone is observing an object, although the distance of observation is different, the perceptional size is similar to the actual size. However, sensory and perception systems can be tricked by the use of illusions. Size constancy is related to distance, experience, and environment. Some examples of size constancy are Müller-Lyer illusion
The Müller-Lyer illusion is an optical illusion consisting of three stylized arrows. When viewers are asked to place a mark on the figure at the midpoint, they tend to place it more towards the "tail" end. The illusion was devised by Franz Carl ...
and Ponzo illusion
The Ponzo illusion is a geometrical-optical illusion that was first demonstrated by the Italian psychologist Mario Ponzo (1882–1960) in 1911. He suggested that the human mind judges an object's size based on its background. He showed this by dr ...
. Another illusion experienced every day is the size of the moon – when closer to the horizon, the moon appears larger. See moon illusion. Human perception is largely influenced by the environment; that is, the context in which the object is found. * ''Shape constancy'' is similar to size constancy in that it relies largely on the perception of distance. Regardless of changes to an object's orientation (such as a door opening), the shape of the object is perceived the same. That is the actual shape of the object is sensed as changing but then perceived as the same. According to Kanwisher & associates, the localized part of the brain responsible for this is the extrastriate cortex.
* ''
* ''Shape constancy'' is similar to size constancy in that it relies largely on the perception of distance. Regardless of changes to an object's orientation (such as a door opening), the shape of the object is perceived the same. That is the actual shape of the object is sensed as changing but then perceived as the same. According to Kanwisher & associates, the localized part of the brain responsible for this is the extrastriate cortex.
* ''Color constancy
Color constancy is an example of subjective constancy and a feature of the human color perception system which ensures that the perceived color of objects remains relatively constant under varying illumination conditions. A green apple f ...
'' is a feature of the human color perception
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different wavelengths (i.e., different spectral power distributions) independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of ...
system which ensures that the color of an object remains similar under varying conditions and is the result of a very complicated 'calculation' by an unconsciously
The unconscious mind (or the unconscious) consists of the processes in the mind which occur automatically and are not available to introspection and include thought processes, memories, interests, and motivations.
Even though these processes exist ...
working mechanism within the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
.
:
* ''Lightness constancy'' refers to the constancy of an object's lightness regardless of varying amounts of light cast upon it. We detect, in the context of an object's surroundings, the characteristics of the fixed physical property and, from there, the lightness remains constant despite vast changes. See also Luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls withi ...
.
* ''Distance constancy'' refers to the relationship between apparent distance and physical distance. An illusion example of this would be the moon - when it is near the horizon it is perceived as larger (size constancy) and/or closer to earth than when it is above our heads.
* ''Location constancy'' refers to the relationship between the viewer and the object. A stationary object is perceived as remaining stationary despite the retina sensing the object changing as the viewer moves (due to parallax). Location constancy is largely influenced by the context in which the object is found. An example of this would be looking at a parked car as one walks towards a building; the car is perceived as remaining stationary as one moves forward.
Auditory
*Inmusic
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
, subjective constancy is the identification of a musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who pl ...
as constant under changing timbre
In music, timbre ( ), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound quality of a musical note, sound or musical tone, tone. Timbre distinguishes different types of sound production, such as choir voice ...
or "conditions of changing pitch and loudness, in different environments and with different players."
*In speech perception
Speech perception is the process by which the sounds of language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by wh ...
this means that vowels or consonants are perceived as constant categories even if acoustically, they vary greatly due to phonetic environment (coarticulation Coarticulation in its general sense refers to a situation in which a conceptually isolated speech sound is influenced by, and becomes more like, a preceding or following speech sound. There are two types of coarticulation: ''anticipatory coarticulat ...
), speech tempo, speaker's age and sex, speaker's dialect, etc.
Tactile
Rats’ perceptual reports about the relative location of external objects are hardly affected by strong environmental winds. This perceptual report constancy was shown to be achieved via motor control, whereby the perceptually-relevant sensory variables (the ‘proximal stimulus’) is maintained relatively constant.Saraf-Sinik, I., E. Assa, and E. Ahissar (2015) Motion Makes Sense: An Adaptive Motor-Sensory Strategy Underlies the Perception of Object Location in Rats. The Journal of Neuroscience 35:8777-8789. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4149-14.2015Research
*Comparing perception abilities in schizophrenic patients – A study found that distance constancy, being closely related to size constancy, was poorer in theschizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdra ...
patients than in the control group (labeled "normals"). "The result of poor distance constancy is that visual perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment through photopic vision (daytime vision), color vision, scotopic vision (night vision), and mesopic vision (twilight vision), using light in the visible spectrum reflecte ...
in schizophrenics is lacking in depth and that these patients live in a 'flatter' world."
*Visual auditory distance constancy – Researchers explored the relationship between visual and auditory responses and how they influence distance constancy. A study found that at a certain distance, when a sound is sensed, the eye is stimulated slightly before the ear is.
References
{{Reflist Subjective experience Perception